The Plastid Genome of Deschampsia cespitosa (Poaceae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequencing
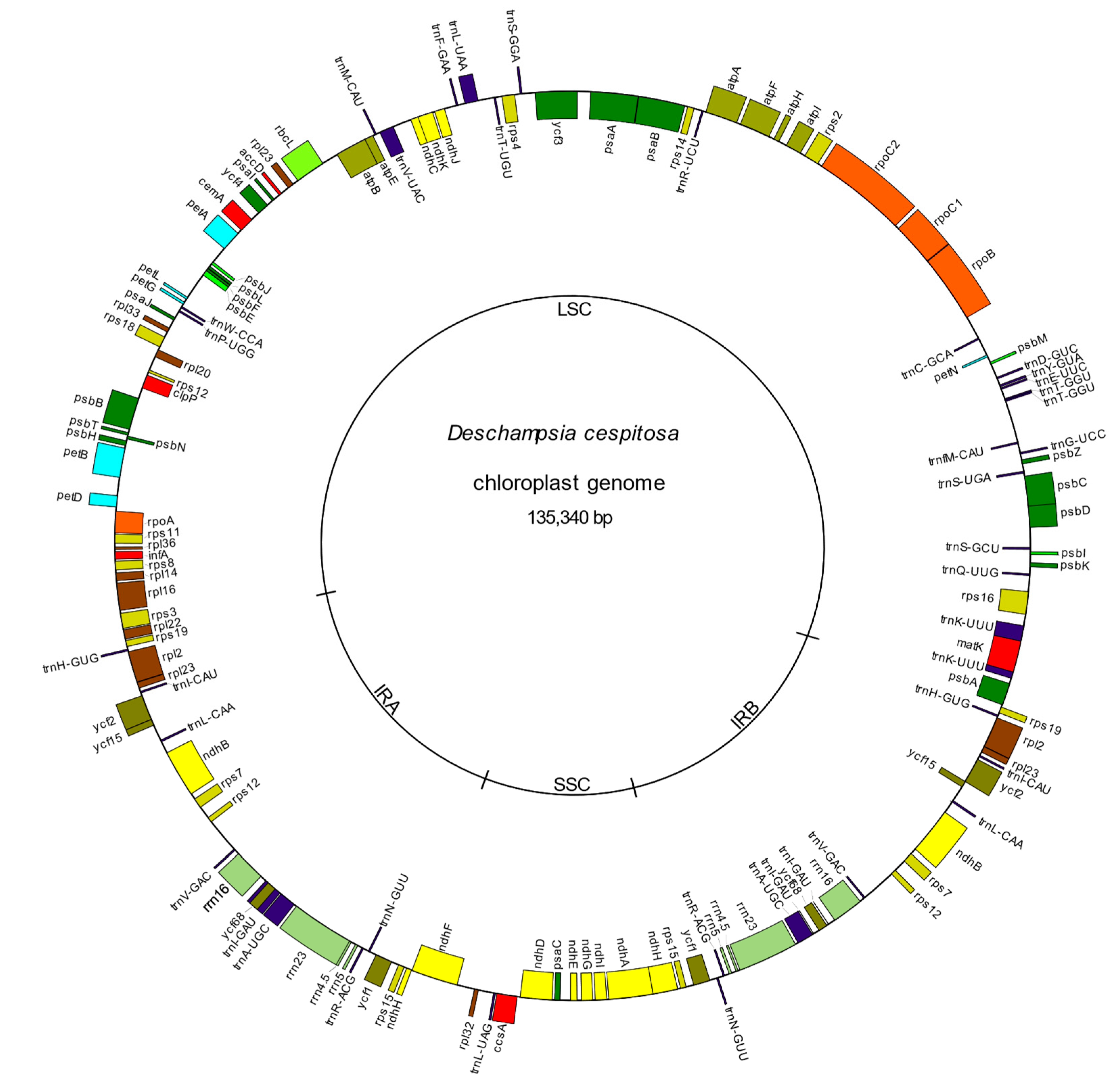
2.2. Genome Assembly and Characteristics
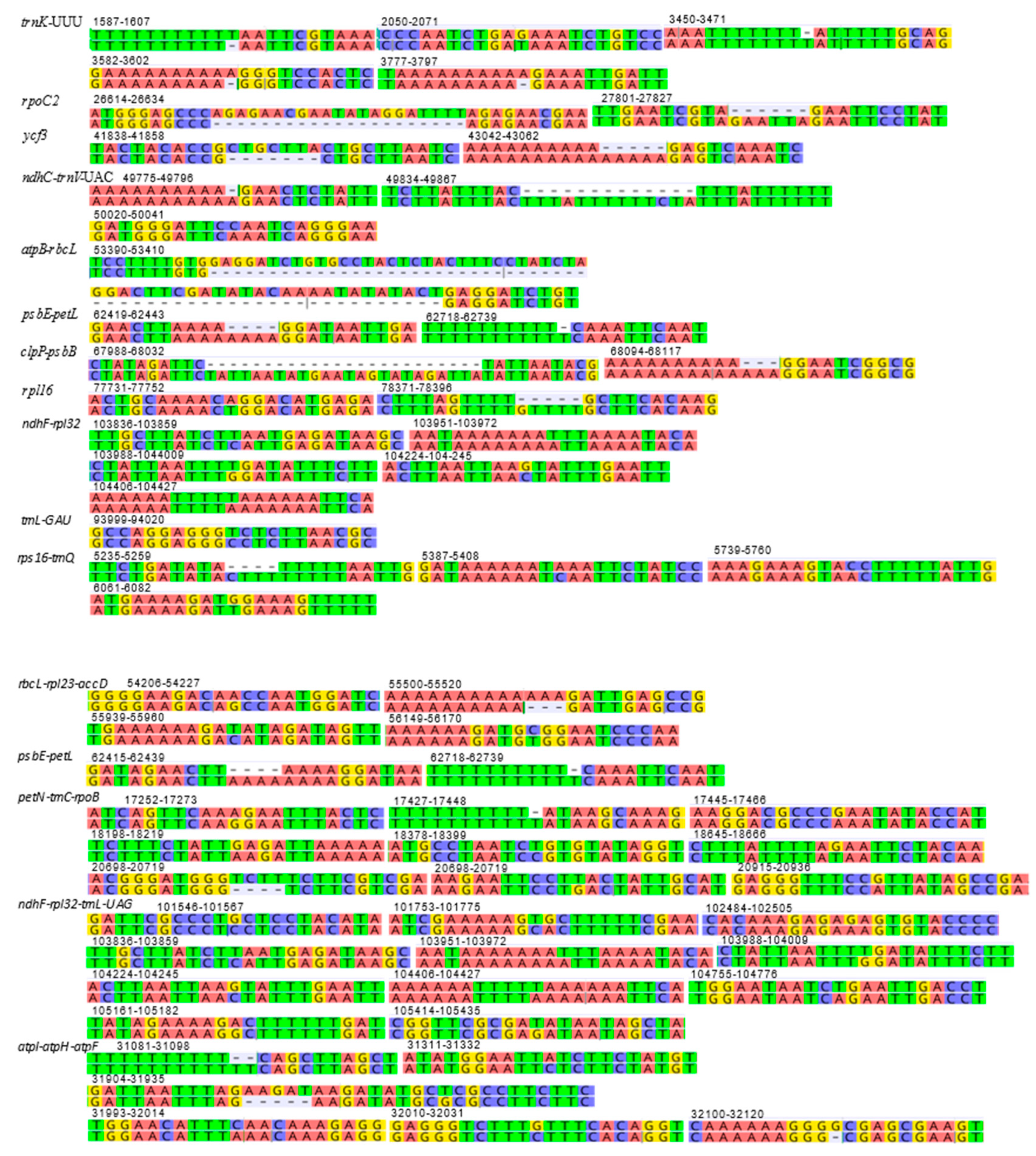
2.3. Repetitive Sequences
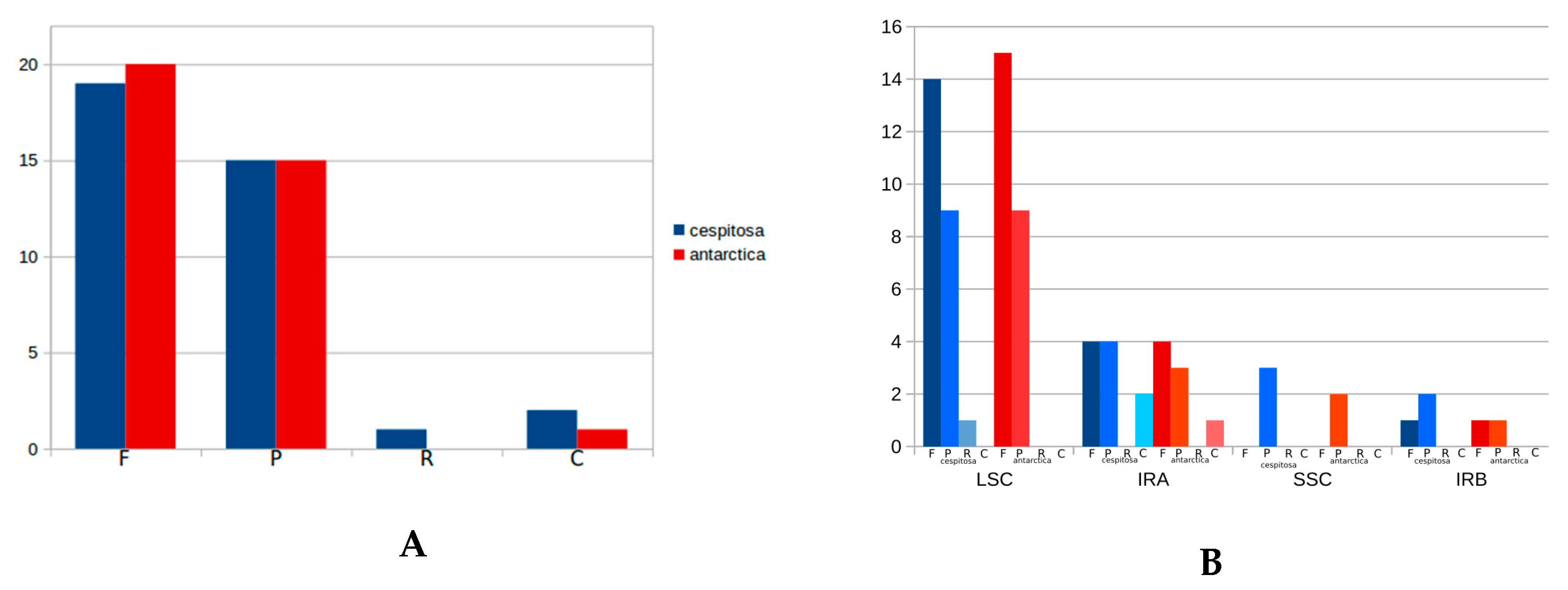
2.4. RNA Editing Sites
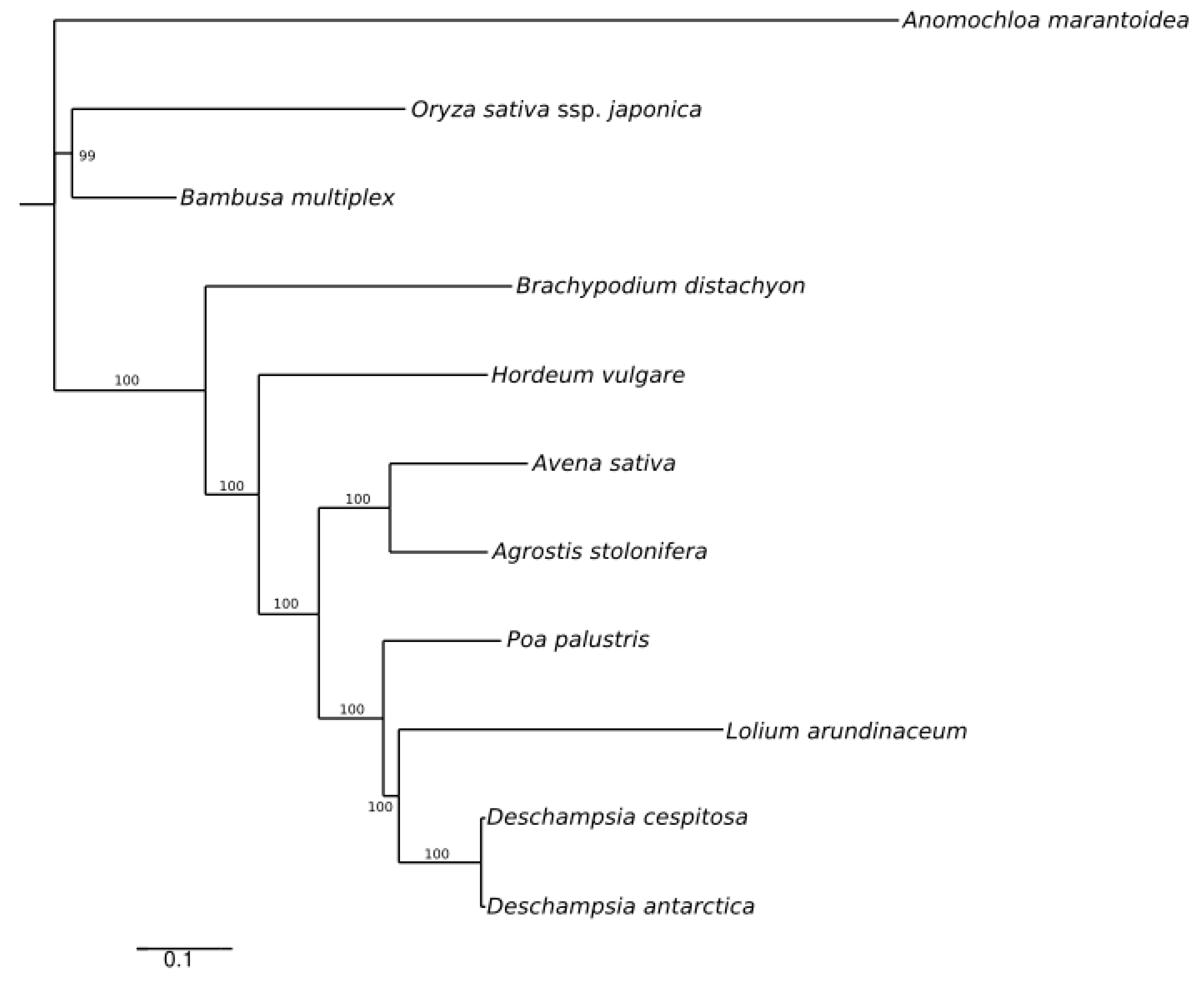
2.5. Phylogenomic Comparison
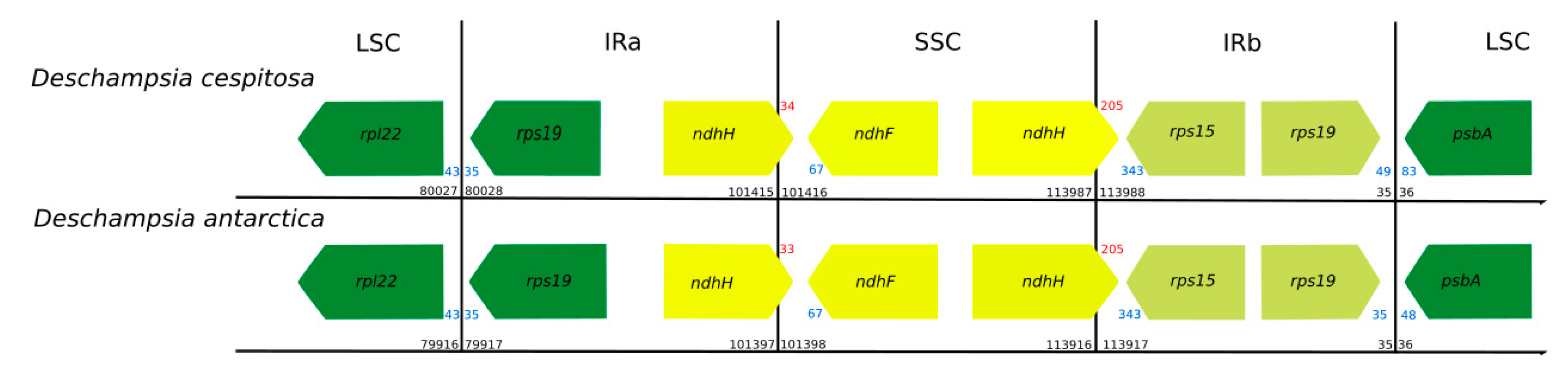
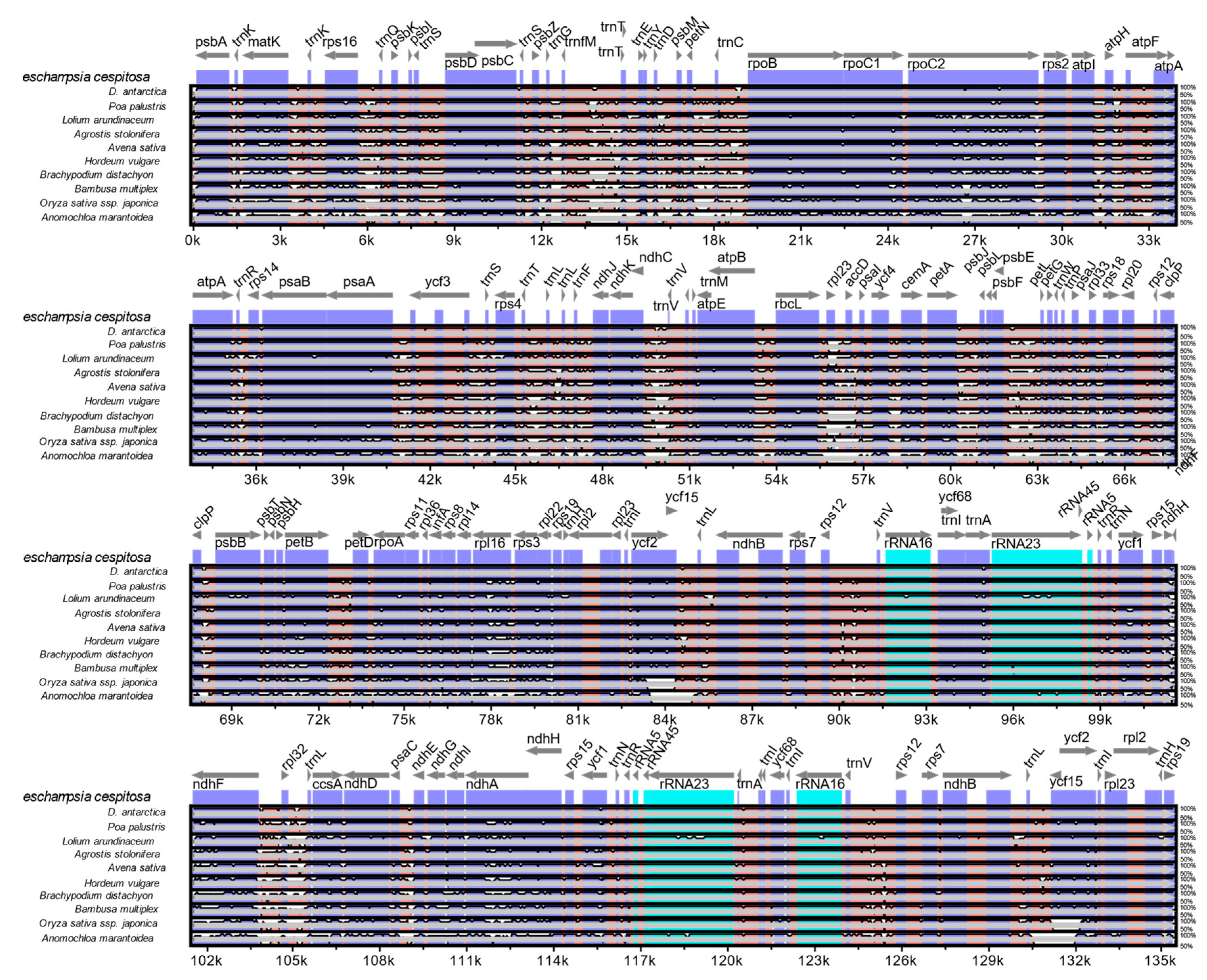
2.6. Genomic Comparison of Deschampsia cespitosa with D. antarctica and other Poaceae
2.7. Microsatellites
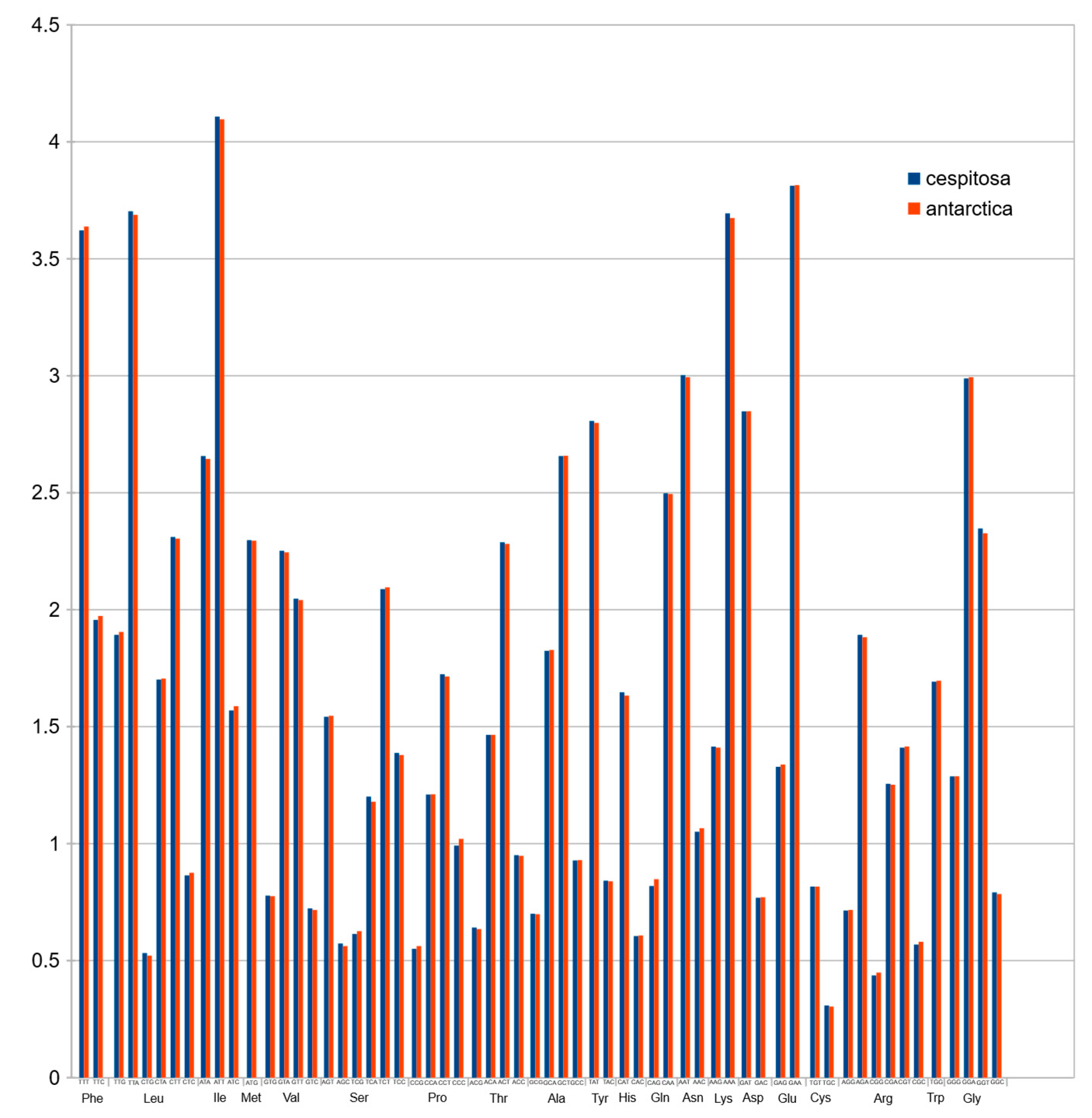
2.8. Codon Usage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Material, DNA Extraction and Sequencing
4.2. Genome Assembly and Annotation
4.3. Repeats Structure
4.4. RNA Editing Sites
4.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.6. Comparative Analyses
4.7. Microsatellite Search
4.8. Codon Usage
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wysocki, W.P.; Clark, L.G.; Kelchner, S.A.; Burke, S.V.; Pires, J.C.; Edger, P.P.; Mayfield, D.R.; Triplett, J.K.; Columbus, J.T.; Ingram, A.L.; et al. A multi-step comparison of short-read full plastome sequence assembly methods in grasses. Taxon 2014, 63, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Ma, P.F.; Li, D.Z. High-throughput sequencing of six bamboo chloroplast genomes: Phylogenetic implications for temperate woody bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, A.P.; Resende-Moreira, L.C.; Buzatti, R.S.; Nazareno, A.G.; Carlsen, M.; Lobo, F.P.; Kalapothakis, E.; Lovato, M.B. Chloroplast genomes of Byrsonima species (Malpighiaceae): Comparative analysis and screening of high divergence sequences. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.-S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.-J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnoliophyta plastid genomes. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/browse#!/organelles/Magnoliophyta (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- Lee, J.; Kang, Y.; Shin, S.C.; Park, H.; Lee, H. Combined analysis of the chloroplast genome and transcriptome of the Antarctic vascular plant Deschampsia antarctica Desv. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Ge, S. The phylogeny of the BEP clade in grasses revisited: Evidence from the whole-genome sequences of chloroplasts. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 62, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.; Lickey, E.B.; Schilling, E.E.; Small, R.L. Comparison of whole chloroplast genome sequences to choose noncoding regions for phylogenetic studies in angiosperms: The tortoise and the hare III. Am. J. Bot. 2007, 94, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D. Plastid chromosomes: Structure and evolution. In The Molecular Biology of Plastids: Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of Plants; Hermann, R.G., Ed.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1991; Volume 7A, pp. 5–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; Müller, K.F.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xia, H.; Cao, M.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, W.; Hu, S.; Tong, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; et al. A comparison of rice chloroplast genomes. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saski, C.; Lee, S.B.; Fjellheim, S.; Guda, C.; Jansen, R.K.; Luo, H.; Tomkins, J.; Rognli, O.A.; Daniell, H.; Clarke, J.L. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Hordeum vulgare, Sorghum bicolor and Agrostis stolonifera, and comparative analyses with other grass genomes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberdi, M.; Bravo, L.A.; Gutiérrez, A.; Gidekel, M.; Corcuera, L.J. Ecophysiology of Antarctic vascular plants. Physiol. Plant. 2002, 115, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, M.A.; Casanova, A.N.; Iturra, G.R.; Reyes, A.U.; Montenegro, G.L.; Alberdi, M.I. Leaf anatomy of Deschampsia antarctica (Poaceae) from the Maritime Antarctic and its plastic response to changes in the growth conditions. Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 1999, 72, 411–425. [Google Scholar]
- Holderegger, R.; Stehlik, I.; Lewis Smith, R.I.; Abbott, R.J. Populations of Antarctic hairgrass (Deschampsia antarctica) show low genetic diversity. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2003, 35, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasanella, M.; Premoli, A.C.; Urdampilleta, J.D.; González, M.L.; Chiapella, J. How did a grass reach Antarctica? The Patagonian connection of Deschampsia antarctica (Poaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 185, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, M.; Kim, I.C.; Yim, J.H.; Lee, H.K. Reference genes validation for qPCR normalization in Deschampsia antarctica during abiotic stresses. Antarct. Sci. 2010, 22, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, M.Y.; Lee, J.; Cui, L.H.; Kang, Y.; Oh, T.K.; Park, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, W.T. Constitutive expression of DaCBF7, an Antarctic vascular plant Deschampsia antarctica CBF homolog, resulted in improved cold tolerance in transgenic rice plants. Plant Sci. 2015, 236, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, H.; Contreras, R.A.; Pizarro, M.; Cortés-Antíquera, R.; Zúñiga, G.E. Antioxidant Responses Induced by UVB Radiation in Deschampsia antarctica Desv. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvicini, M.; Gutierrez-Moraga, A.; Rodriguez, M.M.; Gomez-Bustillo, S.; Salazar, L.; Sunkel, C.; Nozal, L.; Salgado, A.; Hidalgo, M.; Lopez-Casas, P.P.; et al. A tricin derivative from Deschampsia antarctica Desv. inhibits colorectal carcinoma growth and liver metastasis through the induction of a specific immune response. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiapella, J. A molecular phylogenetic study of Deschampsia (Poaceae: Aveneae) inferred from nuclear ITS and plastid trnL sequence data: Support for the recognition of Avenella and Vahlodea. Taxon 2007, 56, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chiapella, J.; Zuloaga, F.O. A Revision of Deschampsia, Avenella, and Vahlodea (Poaceae, Poeae, Airinae) in South America. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2010, 97, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.L.; Urdampilleta, J.D.; Fasanella, M.; Premoli, A.C.; Chiapella, J. Distribution of rDNA and polyploidy in Deschampsia antarctica E. Desv. in Antarctic and Patagonic populations. Polar Biol. 2016, 39, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sablok, G.; Nayak, K.C.; Vazquez, F.; Tatarinova, T.V. Synonymous codon usage, GC 3, and evolutionary patterns across plastomes of three pooid model species: Emerging grass genome models for monocots. Mol. Biotechnol. 2011, 49, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, R.K.; Sigmund, R.; Börner, A.; Korzun, V.; Stein, N.; Sorrells, M.E.; Langridge, P.; Graner, A. Interspecific transferability and comparative mapping of barley EST-SSR markers in wheat, rye and rice. Plant Sci. 2005, 168, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKain, M.R.; Wilson, M. Fast-Plast: Rapid de novo Assembly and Finishing for Whole Chloroplast Genomes. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/mrmckain/Fast-Plast (accessed on 20 November 2018).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nature Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, S.K.; Jansen, R.K.; Boore, J.L. Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3252–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, G.C.; Wolfe, K.H. GenomeVx: Simple web-based creation of editable circular chromosome maps. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinson, G.; Gutman, G.A. Slipped-strand mispairing: A major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauvergeat, V.; Barre, P.; Bonnet, M.; Ghesquiere, M. Sixty simple sequence repeat markers for use in the Festuca–Lolium complex of grasses. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mower, J.P. The PREP Suite: Predictive RNA editors for plant mitochondrial genes, chloroplast genes and user-defined alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soreng, R.J.; Peterson, P.M.; Romaschenko, K.; Davidse, G.; Zuloaga, F.O.; Judziewicz, E.J.; Filgueiras, T.S.; Davis, J.I.; Morrone, O. A worldwide phylogenetic classification of the Poaceae (Gramineae). J. Syst. Evol. 2015, 53, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.M.; Duvall, M.R. The chloroplast genome of Anomochloa marantoidea (Anomochlooideae; Poaceae) comprises a mixture of grass-like and unique features. Am. J. Bot. 2010, 97, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarela, J.M.; Wysocki, W.P.; Barrett, C.F.; Soreng, R.J.; Davis, J.I.; Clark, L.G.; Kelchner, S.A.; Pires, J.C.; Edger, P.P.; Mayfield, D.R.; et al. Plastid phylogenomics of the cool-season grass subfamily: Clarification of relationships among early-diverging tribes. AoB Plants 2015, 7, plv046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, K.; Gao, L.Z. complete chloroplast genome sequence of Bambusa multiplex (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2014, 27, 980–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, R.; Cantalapiedra, C.P.; López Alvarez, D.; Gordon, S.P.; Vogel, J.P.; Catalán, P.; Contreras Moreira, B. Comparative plastome genomics and phylogenomics of Brachypodium: Flowering time signatures, introgression and recombination in recently diverged ecotypes. New Phytol. 2017, 218, 1631–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoon, A.B.; Sharpe, R.M.; Mysayphonh, C.; Thompson, E.J.; Ward, A.D.; Lin, A. The complete chloroplast genome of tall fescue (Lolium arundinaceum; Poaceae) and comparison of whole plastomes from the family Poaceae. Am. J. Bot. 2010, 97, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 9, bbx108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Free open-source vector graphics editor Version 0.92.3. Available online: https://gitlab.com/inkscape/inkscape (accessed on 20 November 2018).
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, G.; Gáspári, Z.; Jurka, J. Microsatellites in different eukaryotic genomes: Survey and analysis. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegren, H. Microsatellites: Simple sequences with complex evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudunuri, S.B.; Nagarajaram, H.A. IMEx: Imperfect microsatellite extractor. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P. The Sequence Manipulation Suite: JavaScript programs for analyzing and formatting protein and DNA sequences. Biotechniques 2000, 28, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples are available from the authors. |
| Feature | Deschampsia cespitosa | Deschampsia antarctica |
|---|---|---|
| Size (bp) | 135,340 | 135,362 |
| LSC (bp) | 79,992 | 79,881 |
| SSC (bp) | 12,572 | 12,519 |
| IR (bp) | 21,388 | 21,481 |
| GC content total (%) | 38.28 | 38.30 |
| GC content LSC (%) | 36.23 | 36.30 |
| GC content SSC (%) | 32.42 | 32.40 |
| GC content IR (%) | 43.81 | 43.85 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiapella, J.O.; Barfuss, M.H.J.; Xue, Z.-Q.; Greimler, J. The Plastid Genome of Deschampsia cespitosa (Poaceae). Molecules 2019, 24, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020216
Chiapella JO, Barfuss MHJ, Xue Z-Q, Greimler J. The Plastid Genome of Deschampsia cespitosa (Poaceae). Molecules. 2019; 24(2):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020216
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiapella, Jorge O., Michael H. J. Barfuss, Zhi-Qing Xue, and Josef Greimler. 2019. "The Plastid Genome of Deschampsia cespitosa (Poaceae)" Molecules 24, no. 2: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020216
APA StyleChiapella, J. O., Barfuss, M. H. J., Xue, Z.-Q., & Greimler, J. (2019). The Plastid Genome of Deschampsia cespitosa (Poaceae). Molecules, 24(2), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020216





