Synthesis, Biological and In Silico Evaluation of Pure Nucleobase-Containing Spiro (Indane-Isoxazolidine) Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of MDM2–p53 Interaction
Abstract
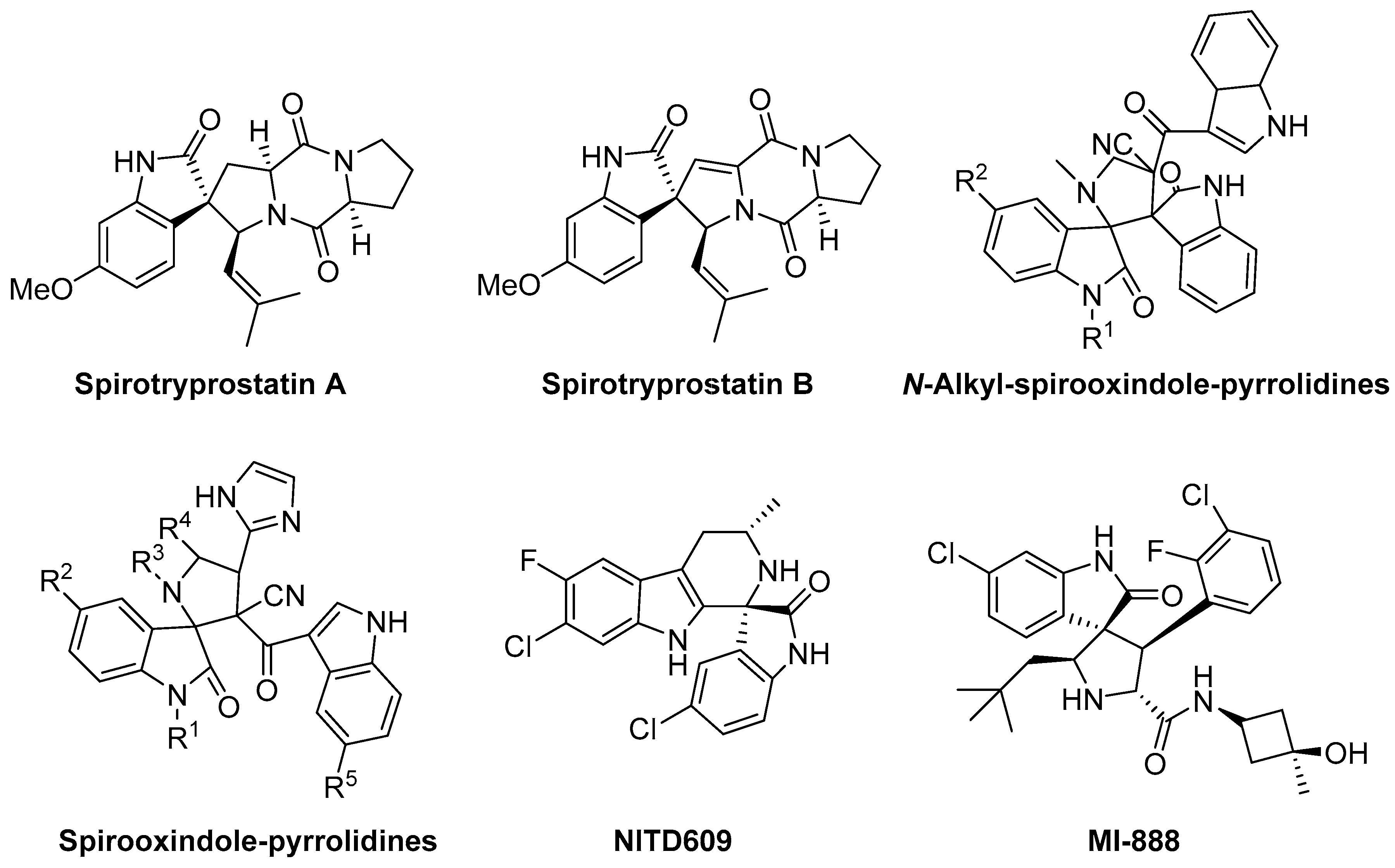
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
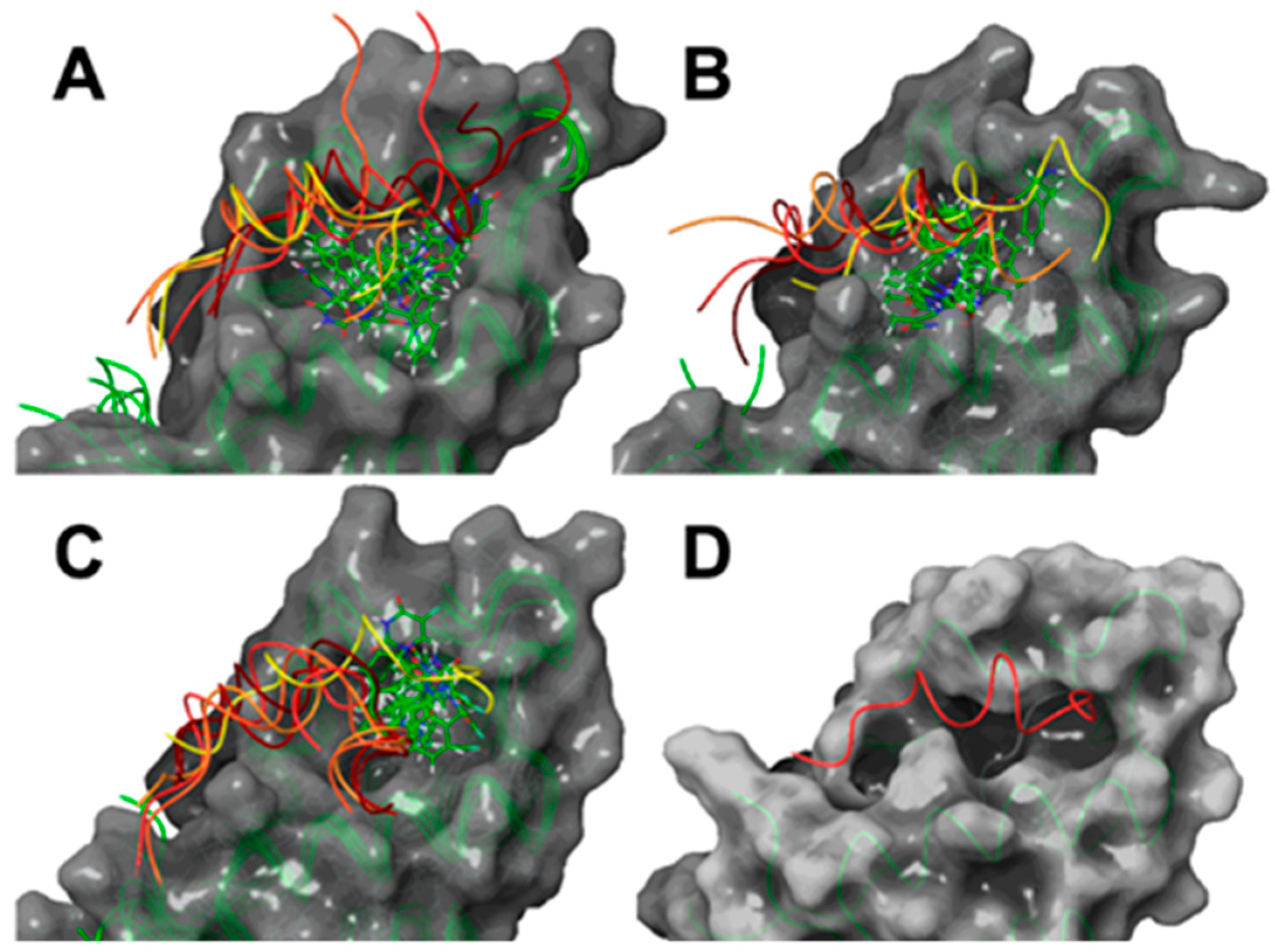
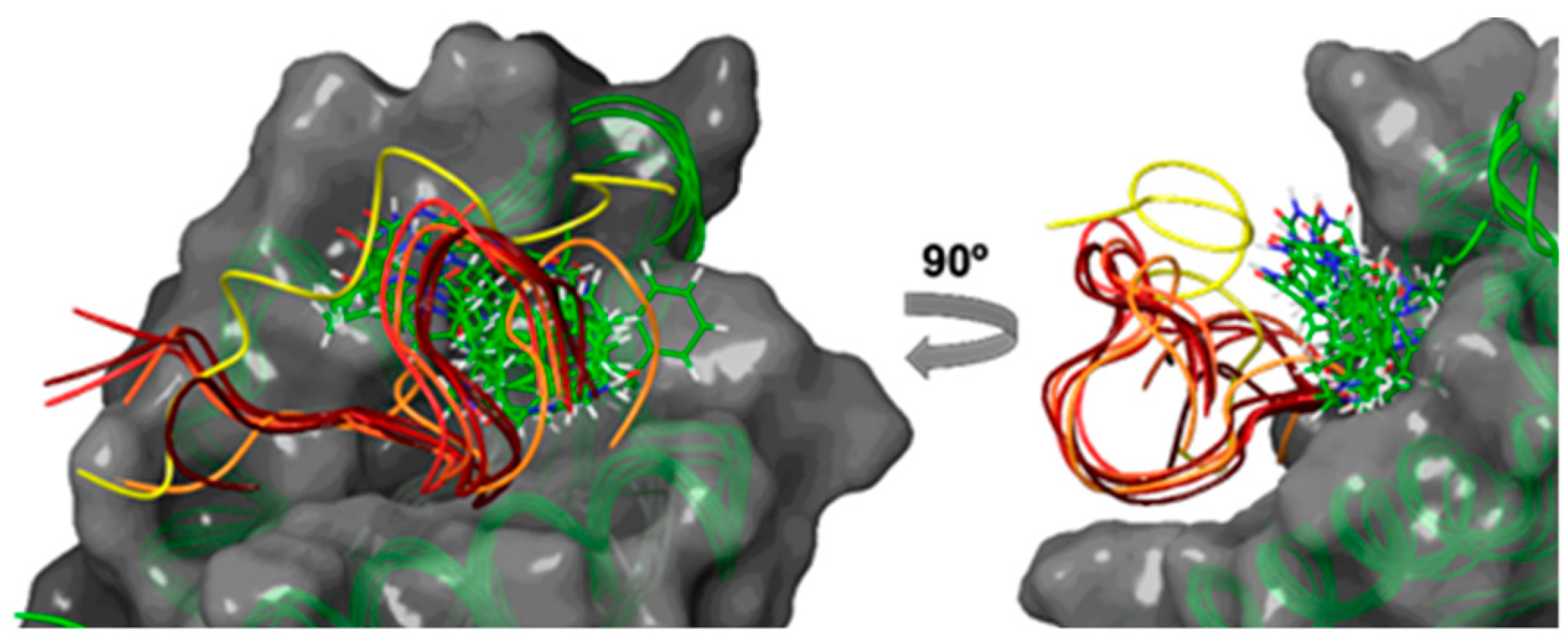
2.2. Computational Studies
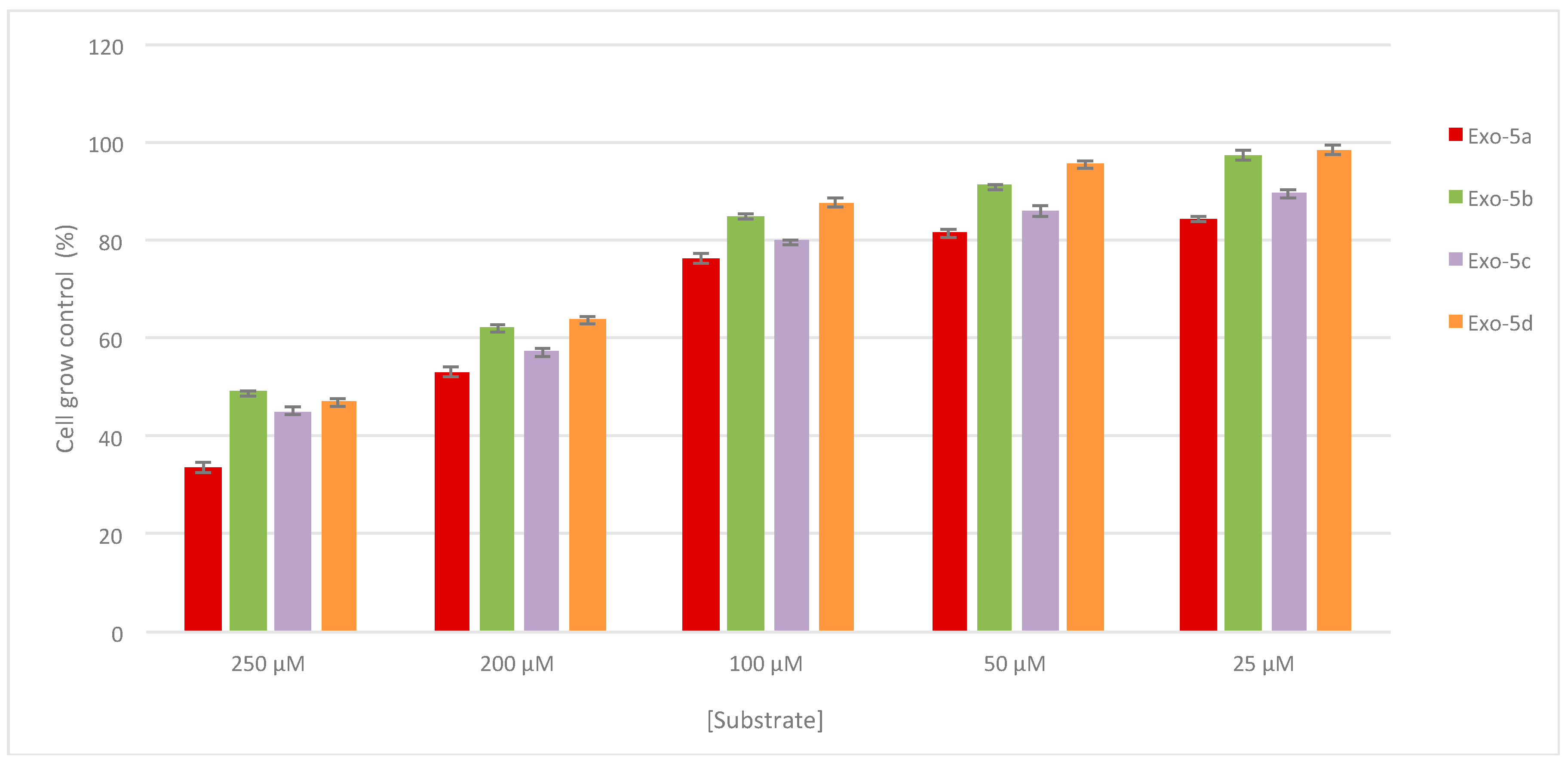
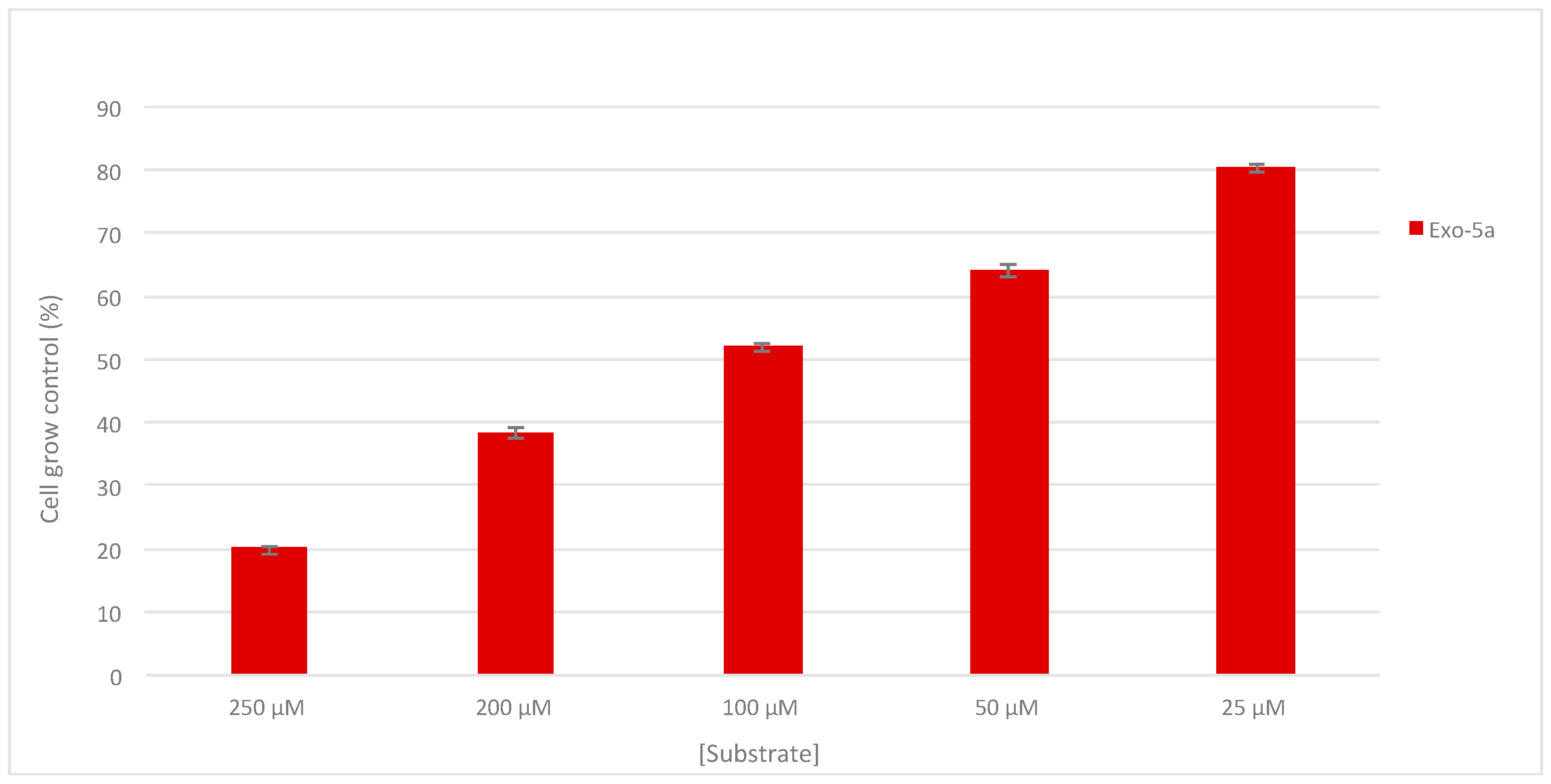
2.3. Antiproliferative Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. General Procedure for Synthesis of 5a–d
3.3. Computational Study
3.3.1. Protein–LIGAND Docking Calculations
3.3.2. Molecular Dynamic Simulations
3.4. Biological Evaluation
3.4.1. Cell Culture
3.4.2. Sulforhodamine B assay
3.4.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhaskar, G.; Arun, Y.; Balachandran, C.; Salikumar, C.; Perumal, P.T. Synthesis of novel spirooxindole derivatives by one pot multicomponent reaction and their antimicrobial activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 51, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-T.; Zhu, J.-F.; Liao, G.; Xu, H.-J.; Yu, B. The Development of Biologically Important Spirooxindoles as New Antimicrobial Agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 2233–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, Y.; Bhaskar, G.; Balachandran, C.; Ignachimuthu, S.; Perumal, P.T. Facile one-pot synthesis of novel dispirooxindole-pyrrolidine derivatives and their antimicrobial and anticancer activity against A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cancer cell line. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Girgis, A.S. Regioselective synthesis of dispiro [1H-indene-2,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,3″-[3H] indole] -1,2″(1″H)-diones of potential anti-tumor properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaranendar, E.; Ramakrishna, K.; Govardhan Reddy, K.; Nagaraju, D.; Reddy, N.Y. A facile synthesis, anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of isoxazolyl-2,3-dihydrospiro [benzo [f] isoindole-1,3′-indoline]-2′,4,9-triones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3954–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molvi, K.I.; Haque, N.; Awen, B.Z.S.; Zameeruddin, M. Synthesis of spiro compounds as medicinal agents; new opportunities for drug design and discovery. World J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 536–563. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Tice, C.M.; Singh, S.B. The use of spirocyclic scaffolds in drug discovery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 4, 3673–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galliford, C.V.; Scheidt, K.A. Pyrrolidinyl-spirooxindole natural products as inspirations for the development of potential therapeutic agents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8748–8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Chen, H.; Wold, E.A.; Shi, P.-Y.; Zhou, J. Therapeutic Potential of Spirooxindoles as Antiviral Agents. ACS Infect. Dis. 2016, 2, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Synthesis of Spirooxindole-O-Naphthoquinone-Tetrazolo [1,5-a] Pyrimidine Hybrids as Potential Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2018, 23, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yu, D.-Q.; Liu, H.-M. Spirooxindoles: Promising scaffolds for anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 673–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball-Jones, N.R.; Badilloa, J.J.; Franz, A.K. Strategies for the enantioselective synthesis of spirooxindoles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 5165–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-F.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Qi, Z.-H.; Li, N.-K.; Geng, Z.-C.; Li, K.; Wang, X.-W. Organocatalytic enantioselective construction of multi-functionalized spiro oxindole dienes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 4372–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, Y.; Saranraj, K.; Balachandran, C.; Perumal, P.T. Novel spirooxindole-pyrrolidine compounds: Synthesis, anticancer and molecular docking studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottmann, M.; McNamara, C.; Yeung, B.K.S.; Lee, M.C.S.; Zou, B.; Russell, B.; Seitz, P.; Plouffe, D.M.; Dharia, N.V.; Tan, J.; et al. Spiroindolones, a potent compound class for the treatment of malaria. Science 2010, 329, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, S.; Sun, W.; Liu, L.; Lu, J.; McEachern, D.; Shargary, S.; Bernard, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, T.; et al. A Potent Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the MDM2–p53 Interaction (MI-888) Achieved Complete and Durable Tumor Regression in Mice. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5553–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, L.J.; Prives, C. p53: Puzzle and paradigm. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1054–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J. p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelstein, B.; Lane, D.; Levine, A.J. Surfing the p53 network. Nature 2000, 408, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, G.; de Oca Luna, M.R. MDM2 function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1377, M55-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momand, J.; Wu, H.H.; Dasgupta, G. MDM2--master regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Gene 2000, 242, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Sebolt, J.T.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y. Efficacy of MDM2 Inhibitor MI-219 against Lung Cancer Cells Alone or in Combination with MDM2 Knockdown, a XIAP Inhibitor or Etoposide. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 3321–3332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chene, P. Inhibiting the p53-MDM2 interaction: An important target for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilev, L.T. p53 Activation by Small Molecules: Application in Oncology. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilev, L.T.; Vu, B.T.; Graves, B.; Carvajal, D.; Podlaski, F.; Filipovic, Z.; Kong, N.; Kammlott, U.; Lukacs, C.; Klein, C.; et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 2004, 303, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, K.; Lu, Y.; Nikolovska-Koleska, Z.; Qiu, S.; Ding, Y.; Gao, W.; Stuckey, J.; Roller, P.P.; Tomita, Y.; Deschamps, J.R.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Potent Non-Peptide MDM2 Inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10130–10131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Lu, Y.; Nikolovska-Coleska, Z.; Wang, G.; Qiu, S.; Shangary, S.; Gao, W.; Qin, D.; Stuckey, J.; Krajewski, K.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Spiro-oxindoles as Potent, Specific Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the MDM2−p53 Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3432–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraswat, P.; Jeyabalan, G.; Hassan, M.Z.; Rahman, M.U.; Nyola, N.K. Review of synthesis and various biological activities of spiro heterocyclic compounds comprising oxindole and pyrrolidine moieties. Synth. Commun. 2016, 46, 1643–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Bernard, D.; Aguilar, A.; Kumar, S. Targeting the MDM2–p53 protein-protein interaction for new cancer therapeutics. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 8, 57–80. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukano, C.; Takemoto, Y. Synthetic Approaches to Spiro-oxindoles and Iminoindolines Based on Formation of C2–C3 Bond. Heterocycles 2014, 89, 2271–2302. [Google Scholar]
- Sebahar, P.R.; Williams, R.M. The Asymmetric Total Synthesis of (+) and (−) Spirotryprostatin B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 5666–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazir, J.; Singh, P.P.; Reddy, M.; Hyder, I.; Shafi, S.; Sawant, S.D.; Chashoo, G.; Mahajan, A.; Alam, M.S.; Saxena, A.K.; et al. Synthesis and anticancer activity of novel spiro-isoxazoline and spiro-isoxazolidine derivatives of α-santonin. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, S.D.; Danishefsky, S.J. The Total Synthesis of Spirotryprostatin A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Henugouven, W.G.B.; Fieselerm, R.M.; Rutjes, F.P.J.T.; Hiemstra, H. First Total Synthesis of ent-Gelsedine via a Novel Iodide-Promoted Allene N-Acyliminium Ion Cyclization. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 8317–8325. [Google Scholar]
- Von Nussbaum, F.; Danishefsky, S.J. A Rapid Total Synthesis of Spirotryprostatin B: Proof of Its Relative and Absolute Stereochemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 2175–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alper, P.B.; Meyers, C.; Lerchner, A.; Siegel, D.R.; Carreira, E.M. Facile, Novel Methodology for the Synthesis of Spiro. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3186–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, L.; Bortolini, O.; De Nino, A.; Russo, B.; Gavioli, R.; Sforza, F. Modified N, O-Nucleosides: Design, Synthesis, and Anti-tumour Activity. Aust. J. Chem. 2014, 67, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, L.; De Nino, A.; Merino, P.; Russo, B.; Stabile, G.; Nardi, M.; D’Agostino, N.; Bernardi, T. Rapid, efficient and solvent free microwave mediated synthesis of aldo- and ketonitrones. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, O.; Mulani, I.; De Nino, A.; Maiuolo, L.; Melicchio, A.; Russo, B.; Granchi, D. Synthesis of a Novel Class of gem-Phosphonate-Phosphates by Reductive Cleavage of the Isoxazolidine Ring. Curr. Org. Synth. 2014, 11, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, L.; Feriotto, G.; Algieri, V.; Nardi, M.; Russo, B.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Furia, E.; Tallarida, M.A.; Mischiati, C.; De Nino, A. Antiproliferative activity of novel isatinyl/indanyl nitrones (INs) as potential spin trapping agents of free radical intermediates. Med. Chem. Commun. 2018, 9, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, A.; Alcaro, S.; De Nino, A.; Maiuolo, L.; Ortuso, F.; Sindona, G. New conformationally locked bicyclic N, O-nucleoside analogues of antiviral drugs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiuolo, L.; Merino, P.; Algieri, V.; Nardi, M.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Russo, B.; Delso, I.; Tallarida, M.A.; De Nino, A. Nitrones and nucleobase-containing spiro-isoxazolidines derived from isatin and indanone: Solvent-free microwave-assisted stereoselective synthesis and theoretical calculations. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 48980–48988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafei, A.K.; Ahmed, E.A.; Abd El-Raheem, E.M.M. Synthesis of Some New Fused and Spiro Heterocyclic Compounds under Phase Transfer Catalysis (PTC) Conditions. Egypt. J. Chem. 2015, 58, 485–494. [Google Scholar]
- Turek, M.; Szczesna, D.; Koprowski, M.; Balczewski, P. Synthesis of 1-indanones with a broad range of biological activity. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 451–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, I.H.; Wong, O.T.; Chi, L.K.; Chen, S.Y. Cytotoxicity and mode of action of substituted indan-1, 3-diones in murine and human tissue cultured cells. Anticancer Res. 1994, 14, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dalpozzo, R.; De Nino, A.; Maiuolo, L.; Procopio, A.; Romeo, R.; Sindona, G. A Convenient Method for the Synthesis of N-Vinyl Derivatives of Nucleobases. Synthesis 2002, 2, 172–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella, A.R.; Smith, D.; Pickard, M. Resistance to chemotherapeutic antimetabolites: A function of salvage pathway involvement and cellular response to DNA damage. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 75, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Gong, S.; Monks, A.; Zaharevitz, D.; Moscow, J.A. Correlation of nucleoside and nucleobase transporter gene expression with antimetabolite drug cytotoxicity. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2002, 2, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsesmetzis, N.; Paulin, C.B.J.; Rudd, S.G.; Herold, N. Nucleobase and Nucleoside Analogues: Resistance and Re-Sensitisation at the Level of Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Metabolism. Cancers 2018, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandra, P.; Longo, A.; Turco Liveri, V. Preparation and Characterisation of Na2S and ZnSO4 Nanoparticles in Water/AOT/n-Heptane Microemulsions. Coll. Pol. Sci. 2001, 279, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandra, P.; Longo, A.; Marciano, V.; Turco Liveri, V. Physicochemical Investigation of Lightfast AgCl and AgBr Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Novel Solid-Solid Reaction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 6724–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandra, P.; Longo, A.; Turco Liveri, V. Synthesis of ultra-small ZnS nanoparticles by solid-solid reaction in the confined space of AOT reversed micelles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaev, A.A.; Bezzubov, S.I.; Desyatkin, V.G.; Vorobyeva, N.S.; Majouga, A.G.; Melnikov, M.Y.; Budynina, E.M. Stereocontrolled [3 + 2] Cycloaddition of Donor−Acceptor Cyclopropanes to Iminooxindoles: Access to Spiro [oxindole-3,2′-pyrrolidines]. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 3340–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollner, A.; Weinstabl, H.; Fuchs, J.E.; Rudolph, D.; Garavel, G.; Hofbauer, K.S.; Karolyi-Oezguer, J.; Gmaschitz, G.; Hela, W.; Kerres, N.; et al. Targeted Synthesis of Complex Spiro [3H-indole-3,2′-pyrrolidin]-2(1H)-ones by Intramolecular Cyclization of Azomethine Ylides: Highly Potent MDM2–p53 Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moll, M.; Petrenko, O. The MDM2–p53 Interaction. Mol. Cancer Res. 2003, 1, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joerger, A.C.; Fersht, A.R. The tumor suppressor p53: From structures to drug discovery. Cold Spring Herb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kussie, P.H.; Gorina, S.; Marechal, V.; Elenbaas, B.; Moreau, J.; Levine, A.J.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure of the MDM2 Oncoprotein Bound to the p53 Tumor Suppressor Transactivation Domain. Science 1996, 274, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, J.; Goffin, S.A.; Gandhi, D.; Searcey, M.; Howell, L.A. Unveiling the “Three-Finger Pharmacophore” Required for p53–MDM2 Inhibition by Saturation-Transfer Difference (STD) NMR Initial Growth-Rates Approach. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 5858–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Bharadwaj, M.; Kumar, A.; Mehrotra, R. Spiro-oxindoles as a Promising Class of Small Molecule Inhibitors of p53–MDM2 Interaction Useful in Targeted Cancer Therapy. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Liang, Z.; Wang, W.; Yi, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q. Insight into binding modes of p53 and inhibitors to MDM2 based on molecular dynamic simulations and principal component analysis. Mol. Phys. 2015, 114, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Cai, L.; Chen, C.; Xie, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, H.; Han, B.; Peng, C. Computational analysis of spiro-oxindoles inhibitors of MDM2–p53 interaction:Insights and selection of novel inhibitors. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, E.B. Fluorine substituent effects (on bioactivity). J. Fluor. Chem. 2001, 109, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, E.; Wu, W.-M.; Shek, E.; Bodor, N. Improved delivery through biological membranes. 38. Brain-specific chemical delivery systems for. beta.-lactam antibiotics. Synthesis and properties of some dihydropyridine and dihydroisoquinoline derivatives of benzylpenicillin. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Babin, V.; Berryman, J.T.; Betz, R.M.; Cai, Q.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E.; Darden, T.A., III; Duke, R.E.; Gohlke, H.; et al. AMBER 14; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 5a–d are available from the authors. |
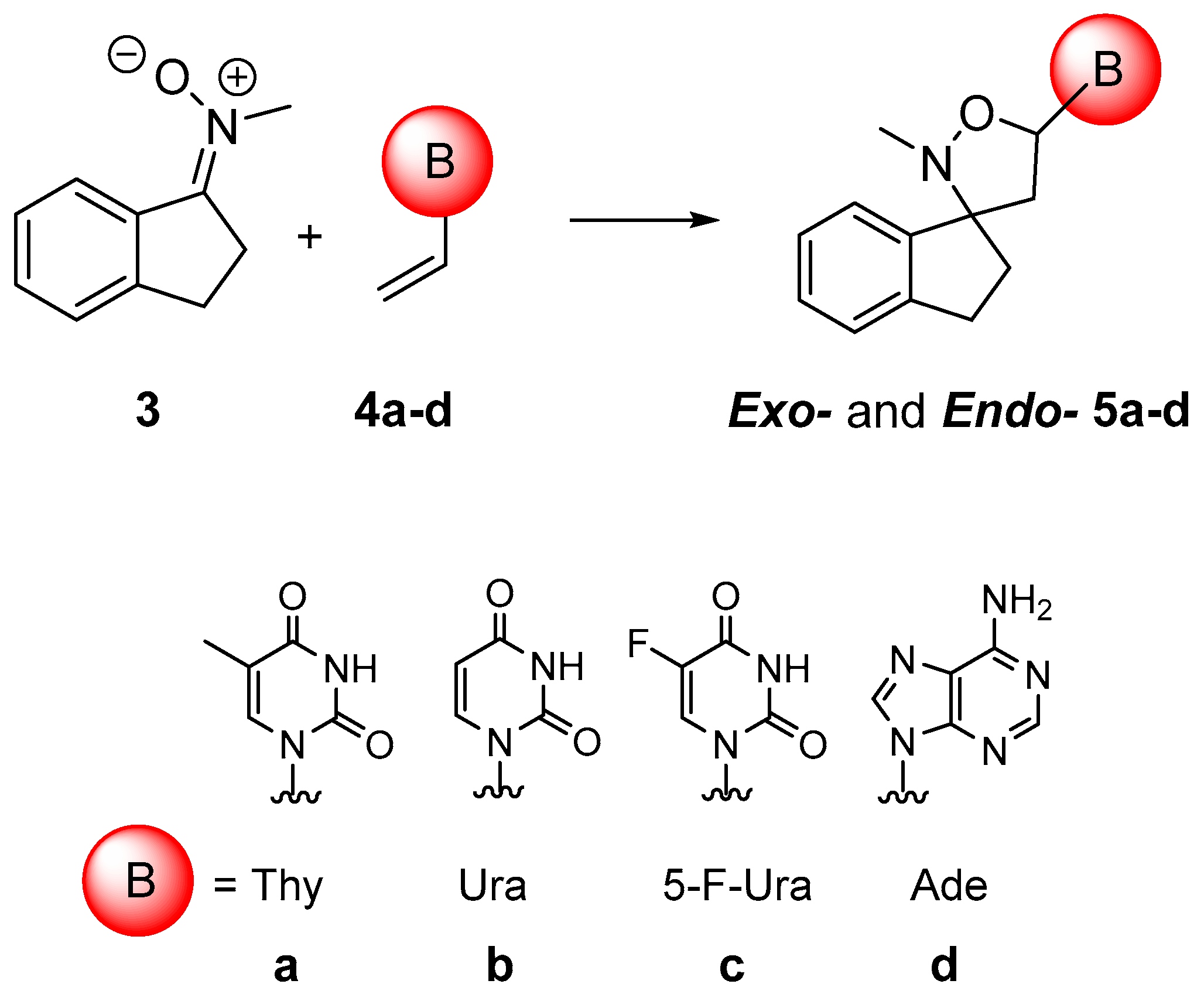
| Entry a | Time (min) | Product | Yield (%) | Exo/endo Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 5a | 77 | 75:25 |
| 2 | 40 | 5b | 76 | 78:22 |
| 3 | 45 | 5c | 89 | 77:23 |
| 4 | 45 | 5d | 86 | 75:25 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maiuolo, L.; Algieri, V.; Russo, B.; Tallarida, M.A.; Nardi, M.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Merchant, Z.; Merino, P.; Delso, I.; De Nino, A. Synthesis, Biological and In Silico Evaluation of Pure Nucleobase-Containing Spiro (Indane-Isoxazolidine) Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of MDM2–p53 Interaction. Molecules 2019, 24, 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162909
Maiuolo L, Algieri V, Russo B, Tallarida MA, Nardi M, Di Gioia ML, Merchant Z, Merino P, Delso I, De Nino A. Synthesis, Biological and In Silico Evaluation of Pure Nucleobase-Containing Spiro (Indane-Isoxazolidine) Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of MDM2–p53 Interaction. Molecules. 2019; 24(16):2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162909
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaiuolo, Loredana, Vincenzo Algieri, Beatrice Russo, Matteo Antonio Tallarida, Monica Nardi, Maria Luisa Di Gioia, Zahra Merchant, Pedro Merino, Ignacio Delso, and Antonio De Nino. 2019. "Synthesis, Biological and In Silico Evaluation of Pure Nucleobase-Containing Spiro (Indane-Isoxazolidine) Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of MDM2–p53 Interaction" Molecules 24, no. 16: 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162909
APA StyleMaiuolo, L., Algieri, V., Russo, B., Tallarida, M. A., Nardi, M., Di Gioia, M. L., Merchant, Z., Merino, P., Delso, I., & De Nino, A. (2019). Synthesis, Biological and In Silico Evaluation of Pure Nucleobase-Containing Spiro (Indane-Isoxazolidine) Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of MDM2–p53 Interaction. Molecules, 24(16), 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162909