High Expression Achievement of Active and Robust Anti-β2 microglobulin Nanobodies via E.coli Hosts Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression of the Anti-β2MG VHHs in Four E. coli Hosts
2.2. Affinity of VHHs
2.3. Secondary Structure Analysis for the VHHs
2.4. Resistance to Trypsin Digestion
2.5. Thermal Stability
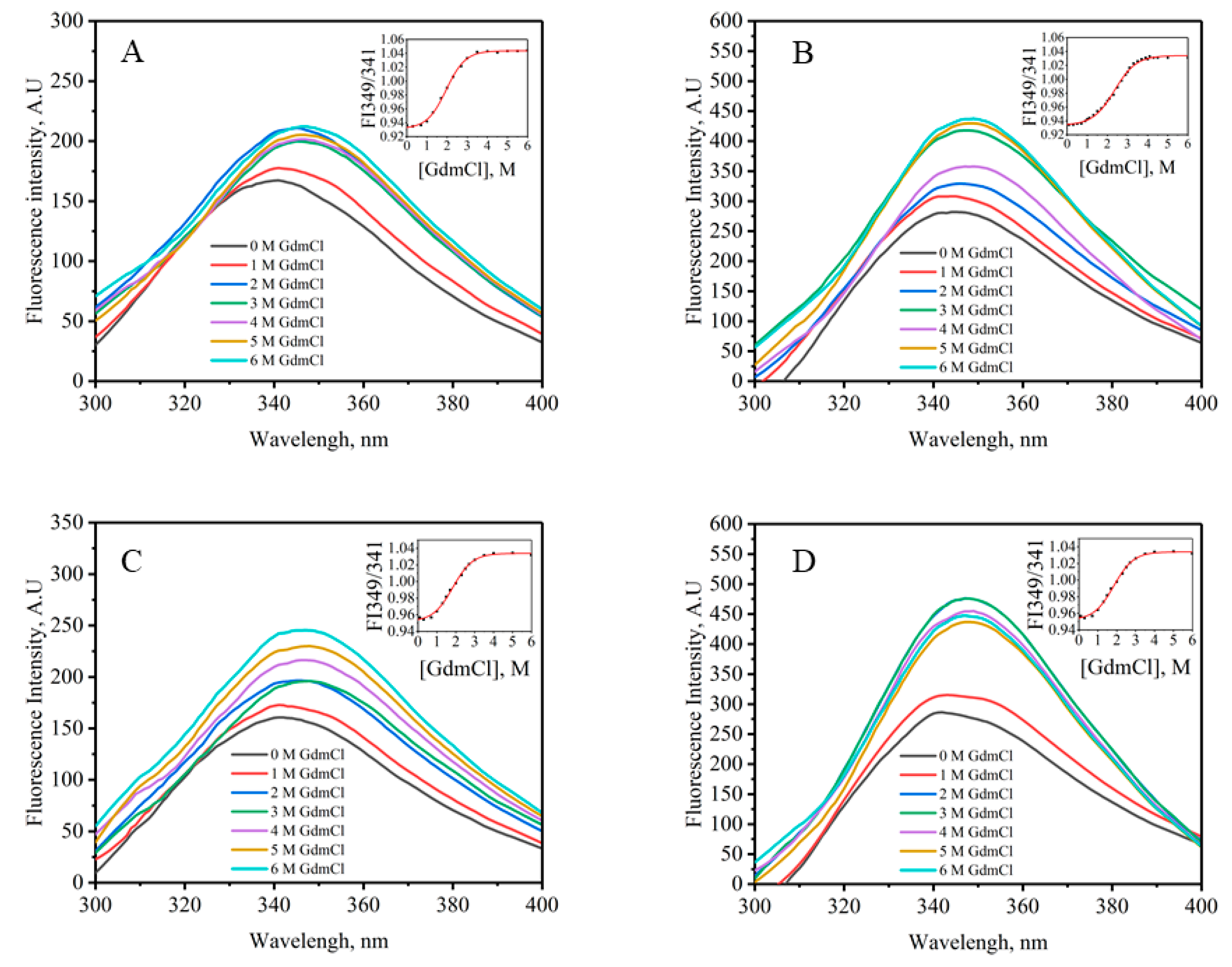
2.6. Chemical Stability
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Expression of the Anti-β2MG VHHs
4.2. Purification of the Recombinant Anti-β2MG VHHs
4.3. The Anti-β2MG VHHs Affinity Analysis
4.4. Circular Dichroism
4.5. Trypsin Treatment
4.6. Equilibrium Denaturation Experiments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamers-Casterman, C.; Atarhouch, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Robinson, G.; Hammers, C.; Songa, E.B.; Bendahman, N.; Hammers, R. Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 1993, 363, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domanska, K.; Vanderhaegen, S.; Srinivasan, V.; Pardon, E.; Dupeux, F.; Marquez, J.A.; Giorgetti, S.; Stoppini, M.; Wyns, L.; Bellotti, V.; et al. Atomic structure of a nanobody-trapped domain-swapped dimer of an amyloidogenic beta 2-microglobulin variant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzadeh-Ghassabeh, G.; Devoogdt, N.; De Pauw, P.; Vincke, C.; Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies and their potential applications. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitriev, O.Y.; Lutsenko, S.; Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies as Probes for Protein Dynamics in Vitro and in Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 3767–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helma, J.; Cardoso, M.C.; Muyldermans, S.; Leonhardt, H. Nanobodies and recombinant binders in cell biology. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 209, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-Miralles, N.; Domingo-Espín, J.; Corchero, J.L.; Vázquez, E.; Villaverde, A. Microbial factories for recombinant pharmaceuticals. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyer, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Depicker, A. Nanobody-based products as research and diagnostic tools. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckers, N.; Saerens, D.; Kanobana, K.; Conrath, K.; Victor, B.; Wernery, U.; Vercruysse, J.; Muyldermans, S.; Dorny, P. Nanobodies, a promising tool for species-specific diagnosis of Taenia solium cysticercosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, I.; Smolarek, D.; Hattab, C.; Grodecka, M.; Hassanzadeh-Ghassabeh, G.; Muyldermans, S.; Sagan, S.; Gutiérrez, C.; Laperche, S.; Le-Van-Kim, C.; et al. VHH (nanobody) directed against human glycophorin A: A tool for autologous red cell agglutination assays. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 438, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Broisat, A.; Hernot, S.; Toczek, J.; De Vos, J.; Riou, L.M.; Martin, S.; Ahmadi, M.; Thielens, N.; Wernery, U.; Caveliers, V.; et al. Nanobodies Targeting Mouse/Human VCAM1 for the Nuclear Imaging of Atherosclerotic Lesions. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, E.J.; Sonneson, G.J.; DeLegge, T.J.; Hofstetter, H.; Horn, J.R.; Hofstetter, O. Production and characterization of a genetically engineered anti-caffeine camelid antibody and its use in immunoaffinity chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussack, G.; Hirama, T.; Ding, W.; Mackenzie, R.; Tanha, J. Engineered Single-Domain Antibodies with High Protease Resistance and Thermal Stability. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies: Natural Single-Domain Antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, K.R.; Smith, C.A.; Hofstetter, H.; Horn, J.R.; Hofstetter, O. Site-directed immobilization of a genetically engineered anti-methotrexate antibody via an enzymatically introduced biotin label significantly increases the binding capacity of immunoaffinity columns. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1021, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimizadeh, W.; Mousavi Gargari, S.L.; Javidan, Z.; Rajabibazl, M. Production of Novel VHH Nanobody Inhibiting Angiogenesis by Targeting Binding Site of VEGF. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1985–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaugh, M.L.; Fanning, S.W.; Sharma, T.M.; Terry, A.M.; Horn, J.R. A Combinatorial Histidine Scanning Library Approach to Engineer Highly pH-Dependent Protein Switches. Protein Sci. 2011, 20, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, C.; Tremblay, J.M.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Mantis, N.J. Mechanisms of Ricin Toxin Neutralization Revealed through Engineered Homodimeric and Heterodimeric Camelid Antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 27880–27889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumada, Y.; Kang, B.; Yamakawa, K.; Kishimoto, M.; Horiuchi, J. Efficient Preparation and Site-Directed Immobilization of VHH Antibodies by Genetic Fusion of Poly(Methylmethacrylate)-Binding Peptide (PMMA-Tag). Biotechnol. Prog. 2015, 31, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarviluoma, A.; Strandin, T.; Lülf, S.; Bouchet, J.; Mäkelä, A.R.; Geyer, M.; Benichou, S.; Saksela, K. High-Affinity Target Binding Engineered via Fusion of a Single-Domain Antibody Fragment with a Ligand-Tailored SH3 Domain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.J.; Wehrle, S.; Weiss, E.; Cavallari, M.; Weber, W. A Two-Step Approach for the Design and Generation of Nanobodies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhoi, S.K.; Rahbarizadeh, F.; Ahmadvand, D.; Moghimi, S.M. Multivalent targeting and killing of HER2 overexpressing breast carcinoma cells with methotrexate-encapsulated tetra-specific non-overlapping variable domain heavy chain anti-HER2 antibody-PEG-liposomes: In vitro proof-of-concept. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 122, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarpour, H.; Banadkoki, S.B.; Keshavarzi, Z.; Morowvat, M.H.; Soleimanpour, M.; Pourmolaei, S.; Shirazi, F.H. Expression analysis and ATR-FTIR characterization of the secondary structure of recombinant human TNF-α from Escherichia coli SHuffle(®) T7 Express and BL21 (DE3) cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gejyo, F.; Yamada, T.; Odani, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Arakawa, M.; Kunitomo, T.; Kataoka, H.; Suzuki, M.; Hirasawa, Y.; Shirahama, T.; et al. A new form of amyloid protein associated with chronic-hemodialysis was identified as beta-2-microglobulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 129, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, B.; Ren, J.; Li, D.; Huang, C.; Ma, H.; Peng, Q.; Ji, F.; Han, L.; Jia, L. Freezing-assisted synthesis of covalent C-C inked bivalent and bispecific nanobodies. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.B.; Xu, L.; Lu, X.; Jia, L. Optimization of dilution refolding conditions for a camelid single domain antibody against human beta-2-microglobulin. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 117, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Jung, J.; Gronenborn, A.M. Structural and biochemical characterization of the childhood cataract-associated R76S mutant of human γD-crystallin. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 2588–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa-Ogawa, Y.; Uegaki, K.; Hagihara, Y. The role of intra-domain disulfide bonds in heat-induced irreversible denaturation of camelid single domain VHH antibodies. J. Biochem. 2016, 159, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novagen. pET System Manual, 10th ed.; Merck KGaA: Armstadt, Germany, 2003; Available online: http://lifeserv.bgu.ac.il/wb/zarivach/media/protocols/Novagen%20pET%20system%20manual.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Lobstein, J.; Emrich, C.A.; Jeans, C.; Faulkner, M.; Riggs, P.; Berkmen, M. SHuffle, a novel Escherichia coli protein expression strain capable of correctly folding disulfide bonded proteins in its cytoplasm. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, C.N. Determination and analysis of urea and guanidine hydrochloride denaturation curves. Methods Enzymol. 1986, 131, 266–280. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.M.; Bolen, D.W. Unfolding Free-Energy Changes Determined by the Linear Extrapolation Method. 1. Unfolding of Phenylmethanesulfonyl Alpha-Chymotrypsin Using Different Denaturants. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 8063–8068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |
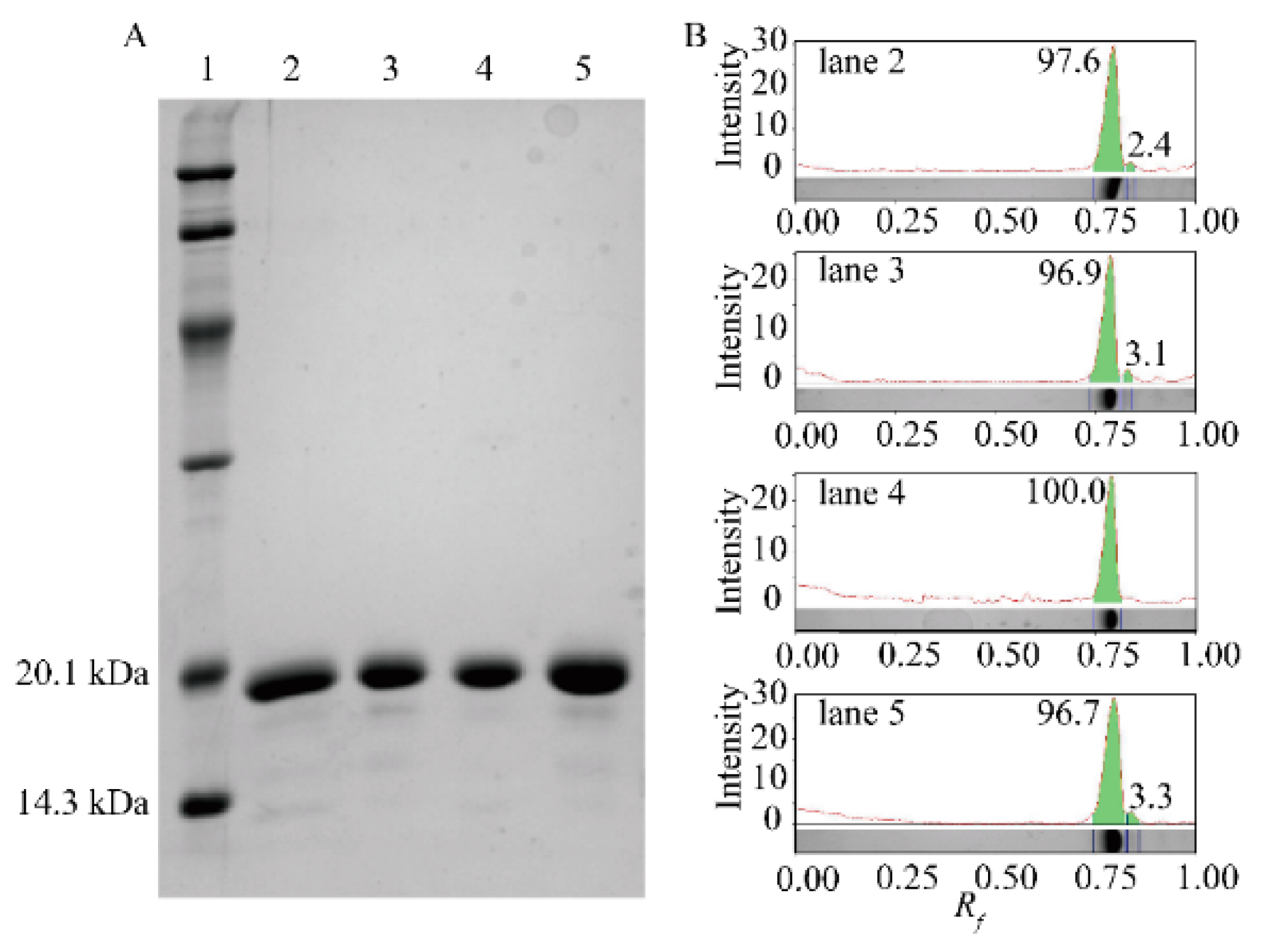




| E. coli Strain | ka (105 /Ms) | kd (10−2/s) | KD (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BL21 (DE3) | 1.21 ± 0.51 | 1.26 ± 0.72 | 100.09 ± 17.77 |
| SHuffle T7 Express | 3.02 ± 0.16 | 2.00 ± 0.78 | 69.83 ± 1.10 |
| Origami 2 (DE3) | 2.52 ± 0.12 | 1.65 ± 0.73 | 67.02 ± 4.79 |
| Rosetta-gami B (DE3) pLysS | 4.35 ± 0.70 | 2.00 ± 0.45 | 45.97± 6.01 |
| E. coli Strain | ΔGD0, (kcal·mol−1) | m, (kcal·mol−1·M−1) | Cm (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BL21 (DE3) | 2.90 ± 0.55 | 1.42 ± 0.18 | 2.25 ± 0.05 |
| SHuffle T7 Express | 5.61 ± 0.07 | 2.21 ± 0.10 | 2.54 ± 0.06 |
| Origami 2 (DE3) | 5.29 ± 0.17 | 2.20 ± 0.10 | 2.41 ± 0.04 |
| Rosetta-gami B (DE3) pLysS | 5.70 ± 0.05 | 2.22 ± 0.04 | 2.57 ± 0.02 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Ji, F.; Huang, C.; Jia, L. High Expression Achievement of Active and Robust Anti-β2 microglobulin Nanobodies via E.coli Hosts Selection. Molecules 2019, 24, 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162860
Li D, Ji F, Huang C, Jia L. High Expression Achievement of Active and Robust Anti-β2 microglobulin Nanobodies via E.coli Hosts Selection. Molecules. 2019; 24(16):2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162860
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Da, Fangling Ji, Chundong Huang, and Lingyun Jia. 2019. "High Expression Achievement of Active and Robust Anti-β2 microglobulin Nanobodies via E.coli Hosts Selection" Molecules 24, no. 16: 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162860
APA StyleLi, D., Ji, F., Huang, C., & Jia, L. (2019). High Expression Achievement of Active and Robust Anti-β2 microglobulin Nanobodies via E.coli Hosts Selection. Molecules, 24(16), 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162860





