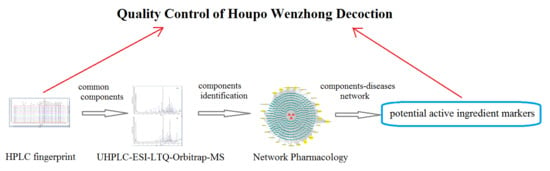
Study on the Material Basis of Houpo Wenzhong Decoction by HPLC Fingerprint, UHPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS, and Network Pharmacology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Optimization of Extraction Conditions for Samples of Fingerprint Analysis and UHPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS Analysis
2.2. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions for Fingerprint Analysis
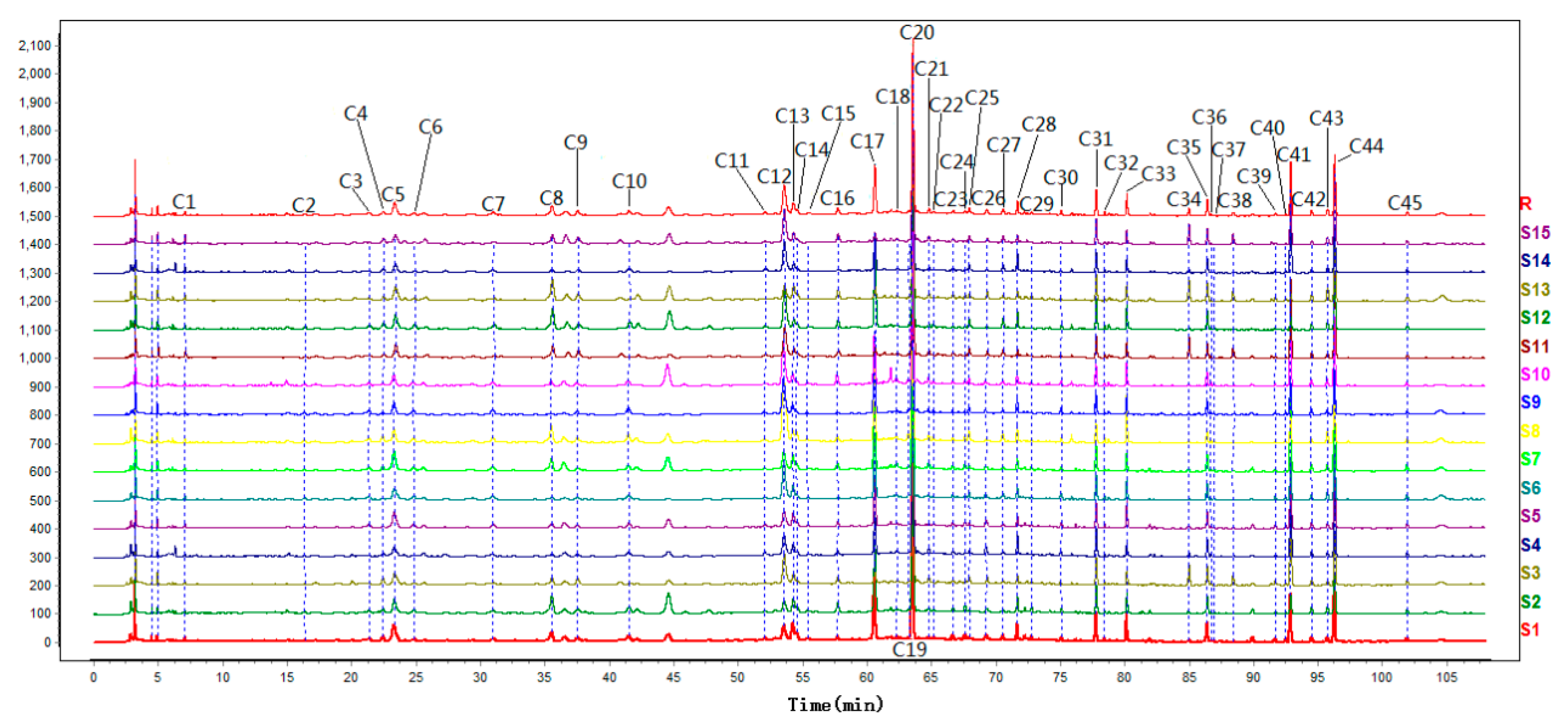
2.3. Validation of the Fingerprint Method
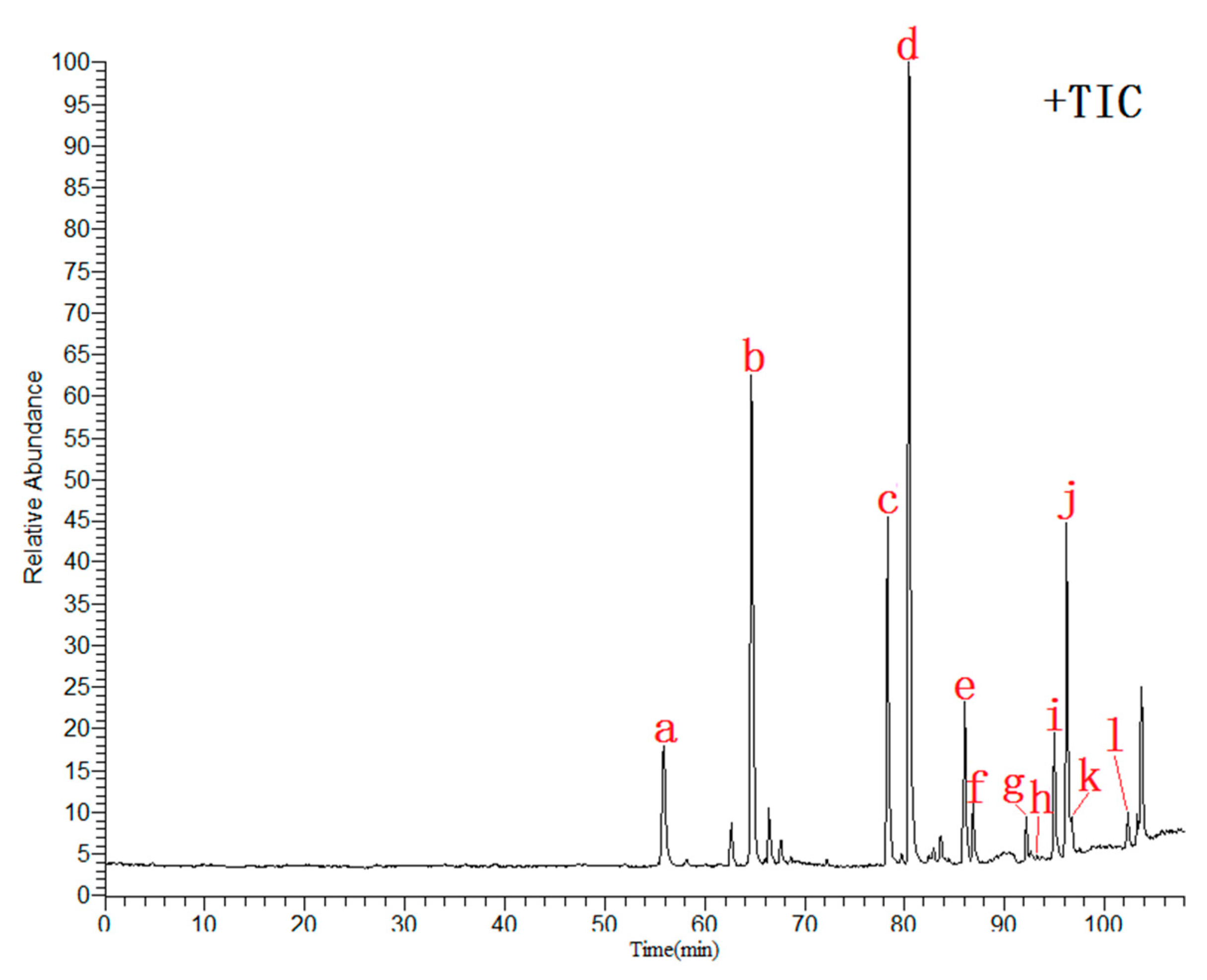
2.4. Similarity Analysis
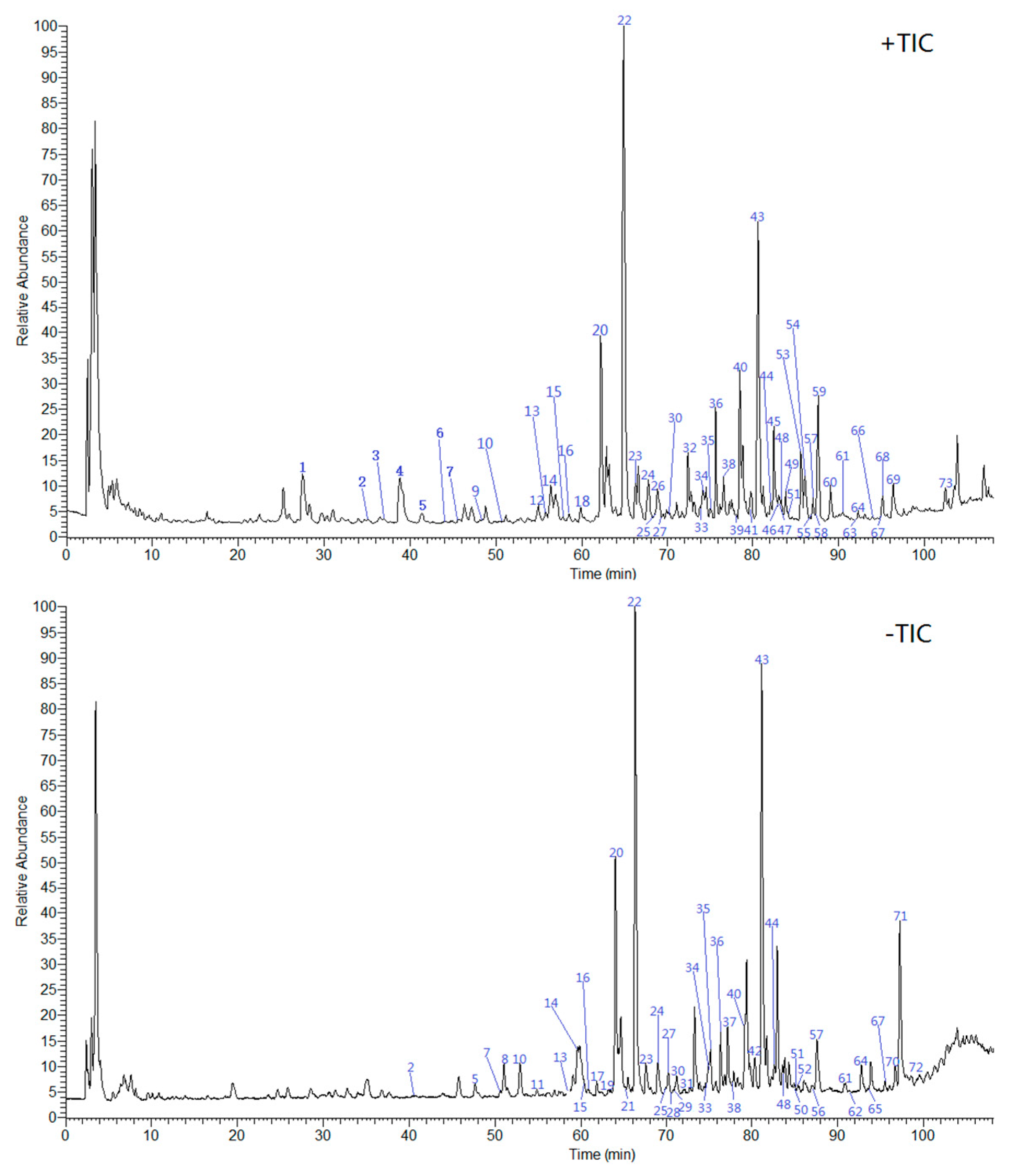
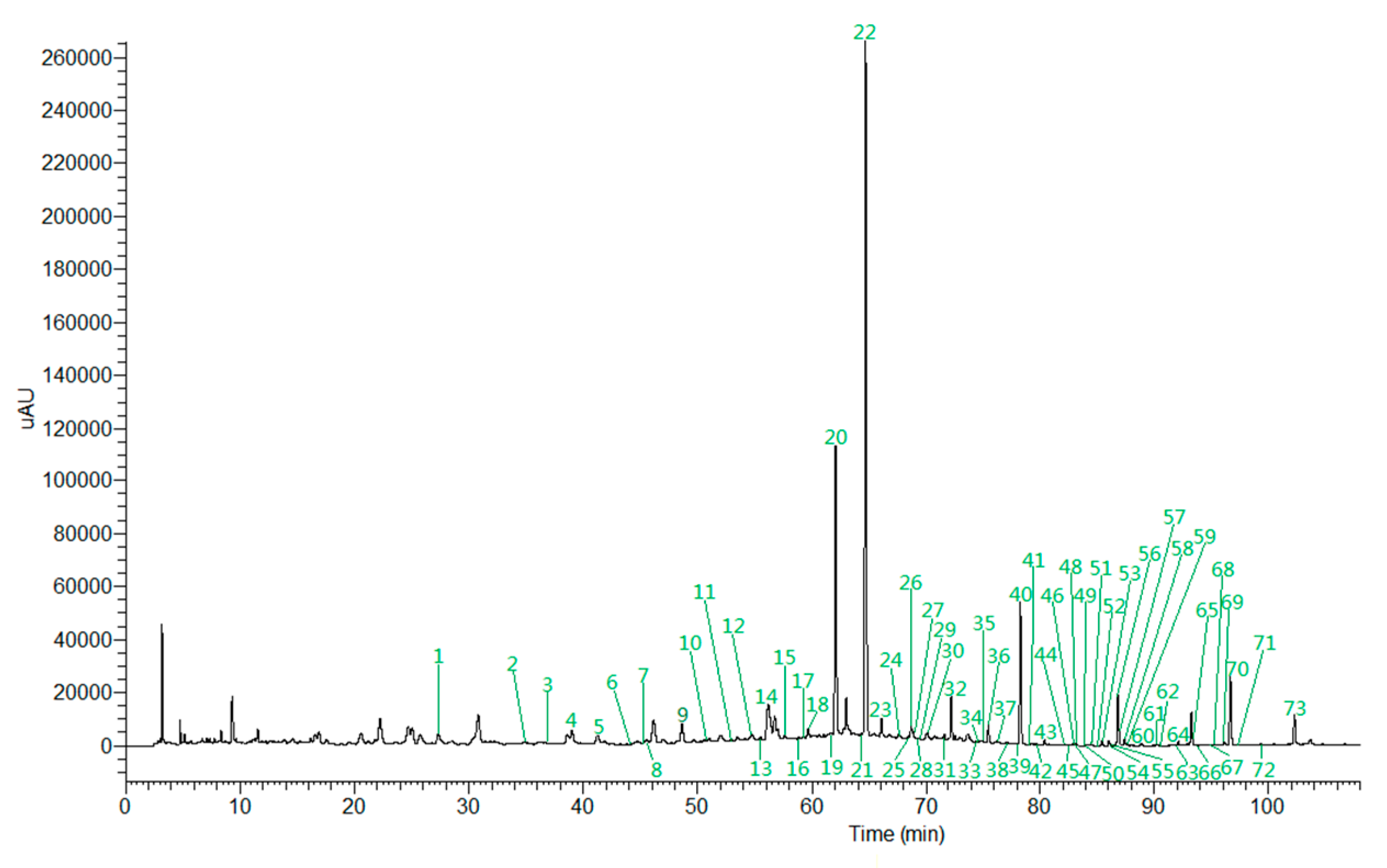
2.5. Chemical Profiling by UHPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS
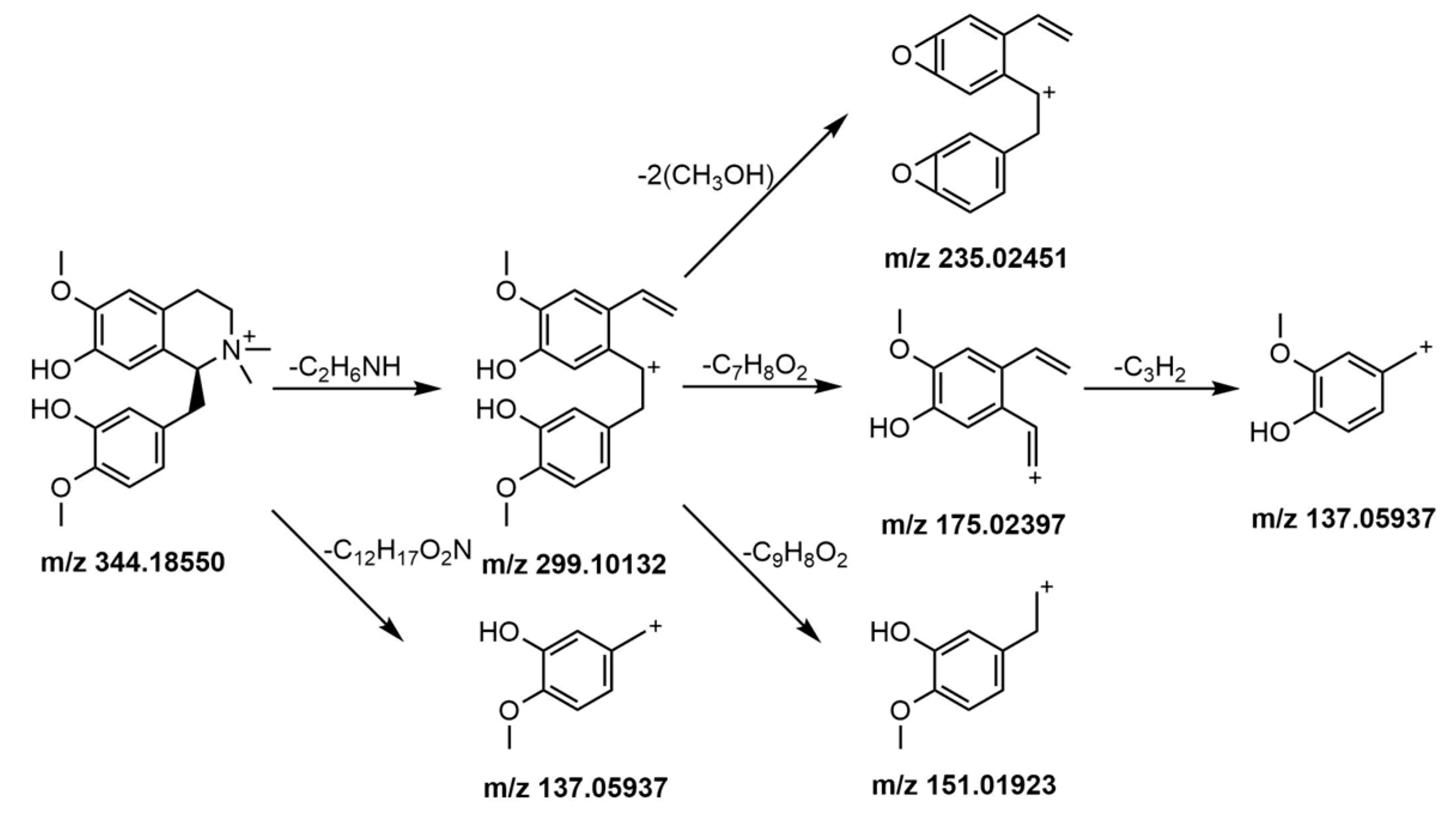
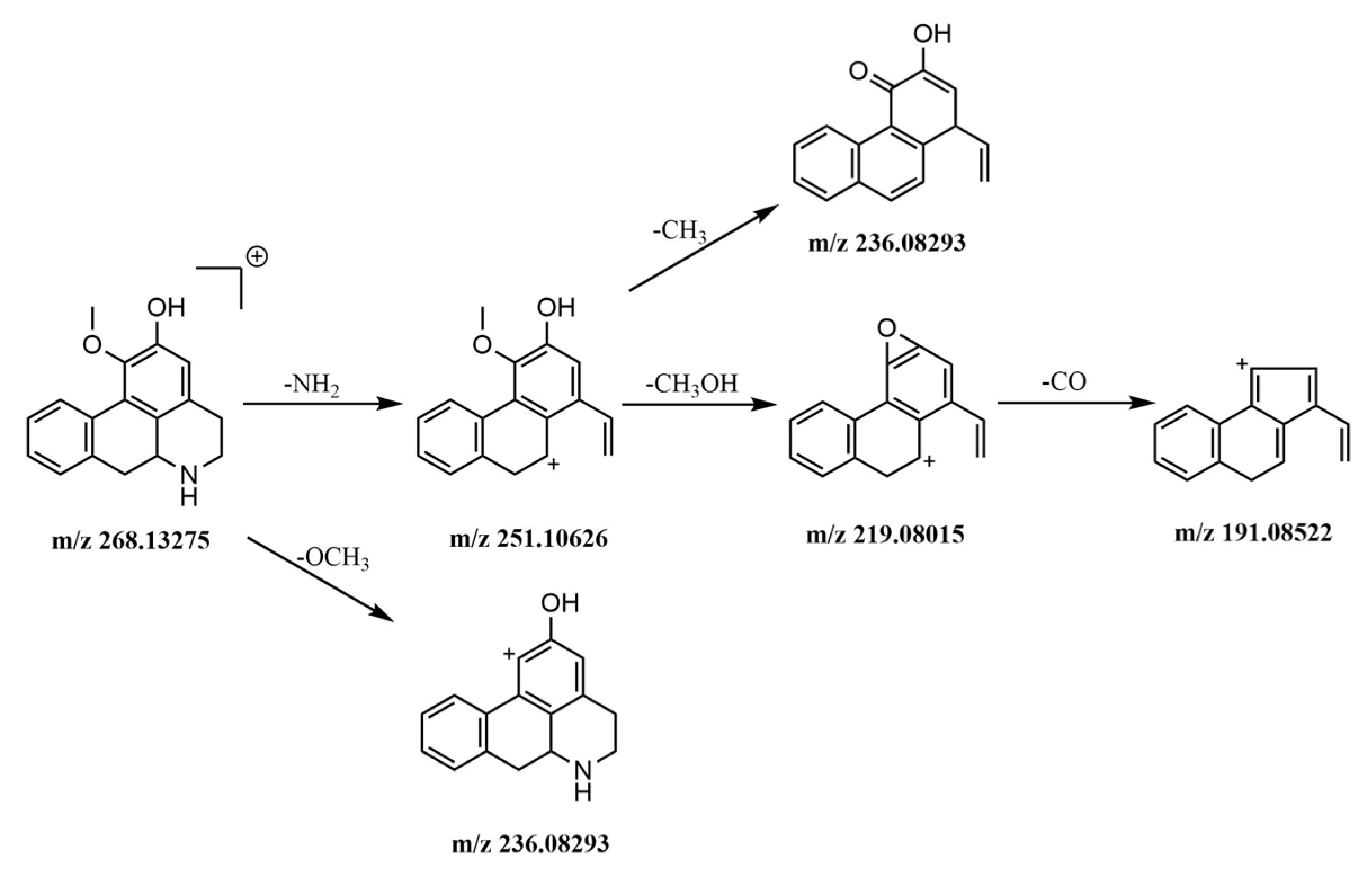
2.5.1. Identification of Alkaloids
2.5.2. Identification of Phenylpropanoids
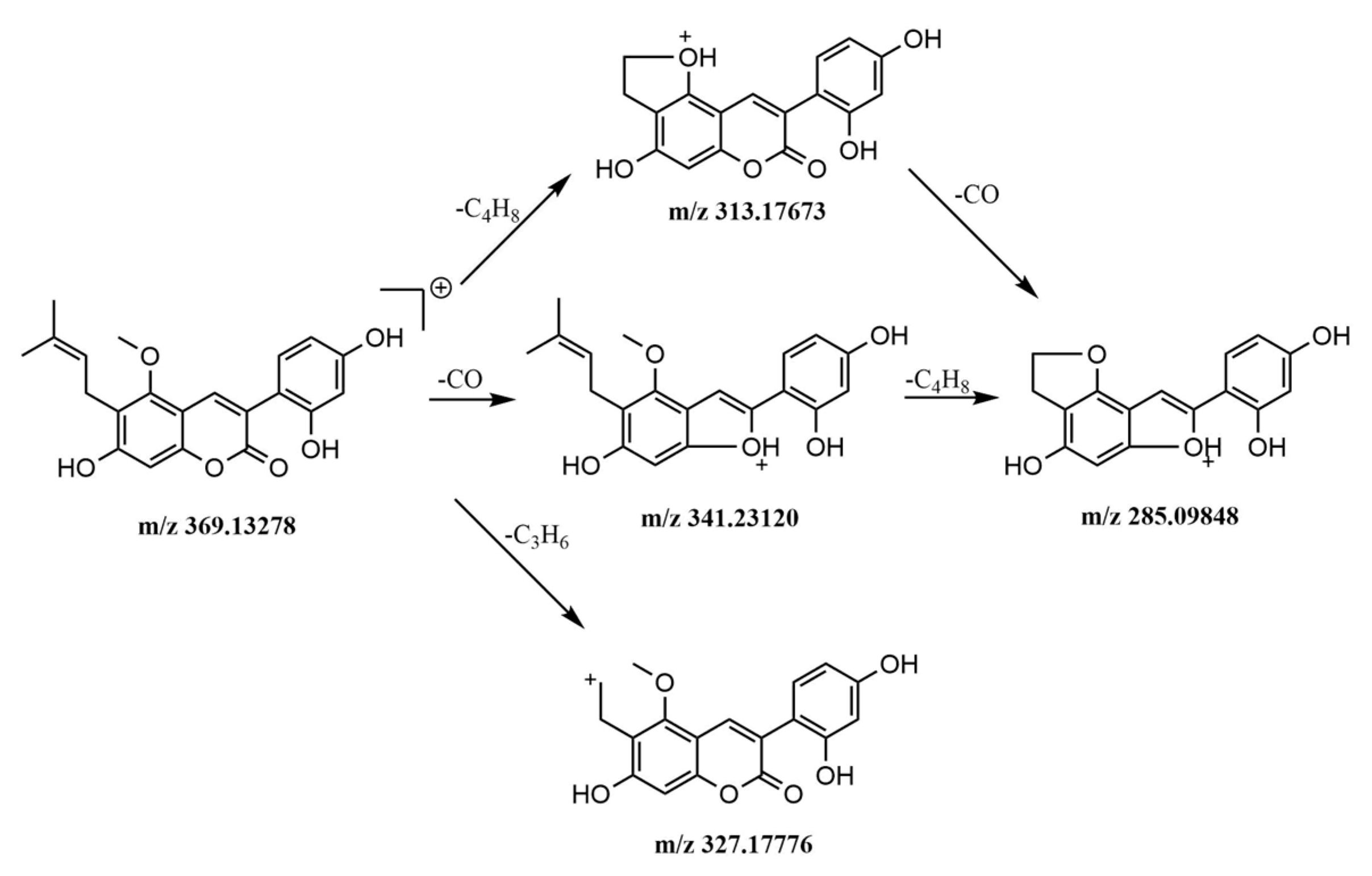
2.5.3. Identification of Flavonoids
2.5.4. Identification of Other Compounds
2.6. Identification of Twelve Chemical Ingredients by Comparison with Reference Substances
2.7. Network Pharmacology
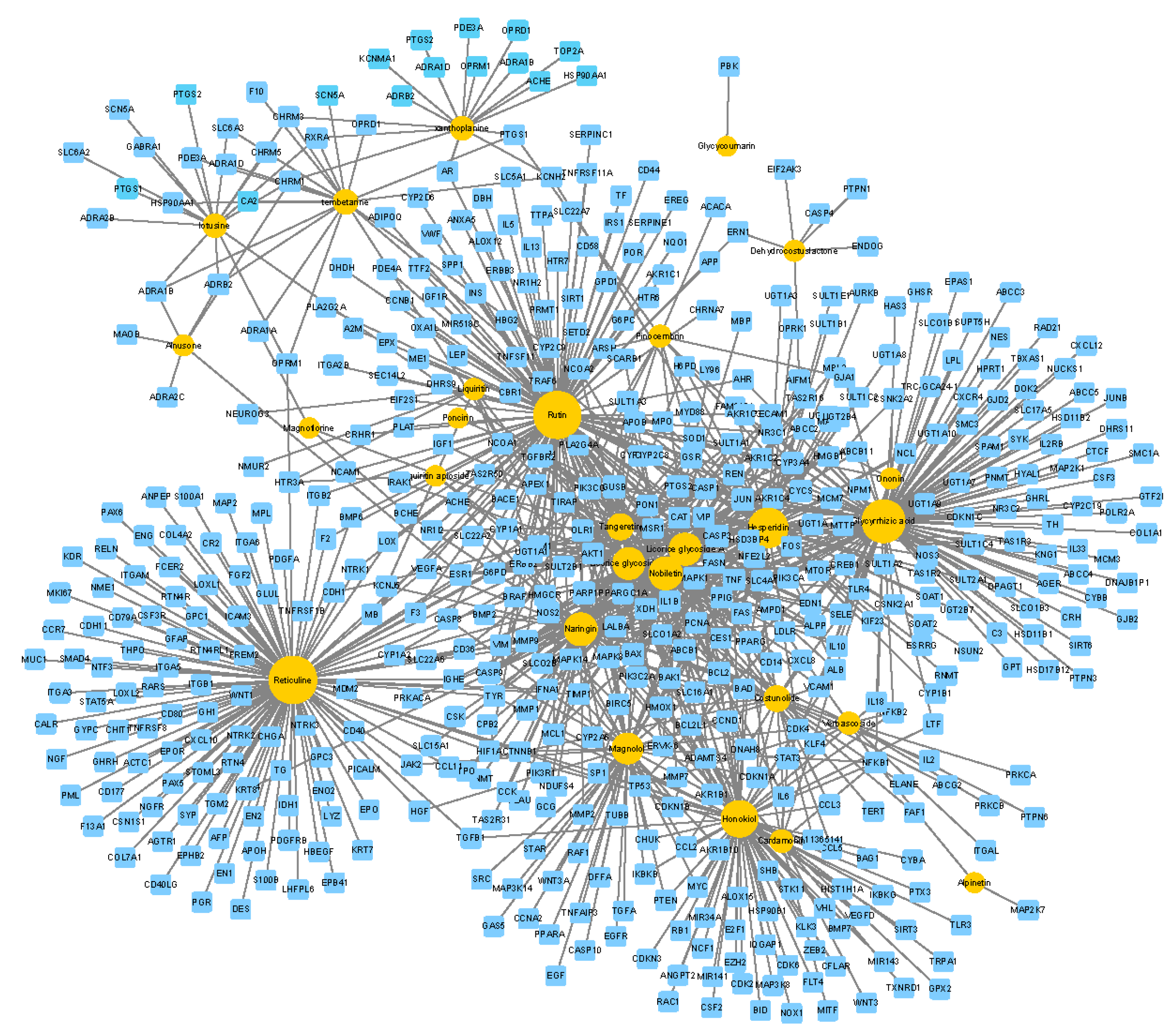
2.7.1. cCCs-cT Network
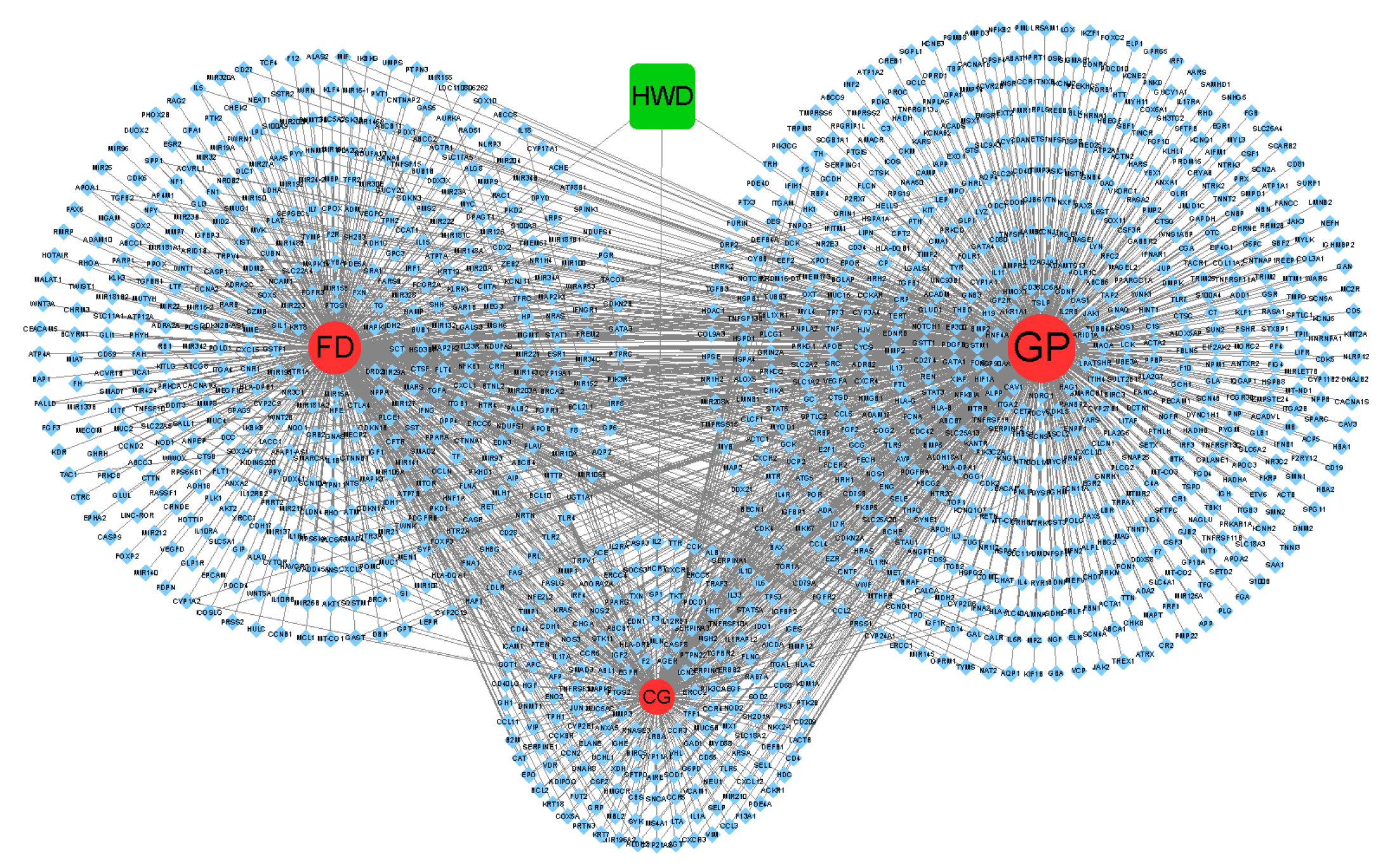
2.7.2. GP/FD/CG-cT Network
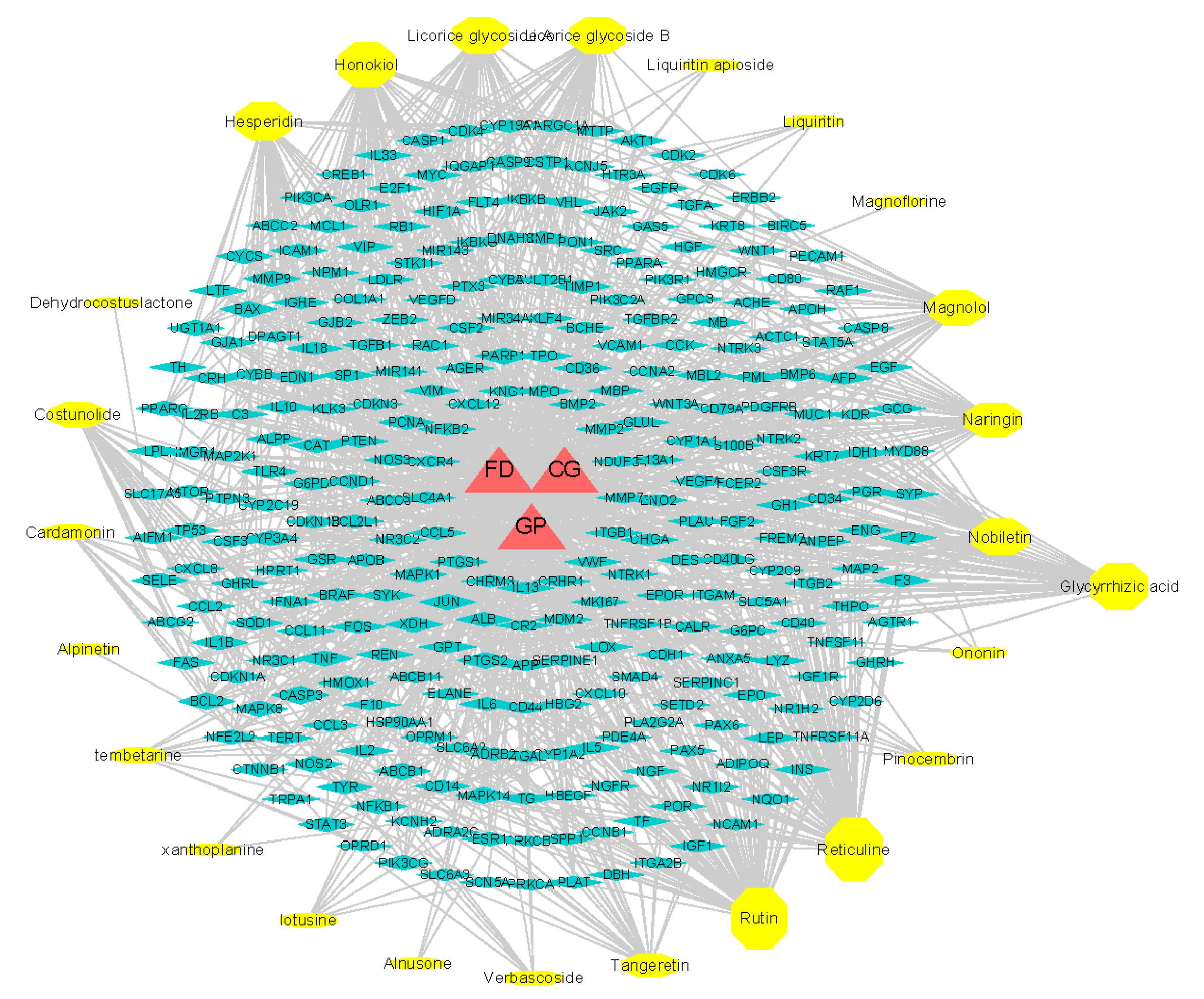
2.7.3. pCCs-pT-GP/FD/CG Network
2.8. Establishment of the Method of Quantitative Determination by HPLC
2.8.1. Linearity Range, Limit of Detection (LOD), and Limit of Quantitation (LOQ)
2.8.2. Precision, Reproducibility, Stability, and Recovery
2.9. Quantitative Determination of Four Potential Active Ingredient Markers in 15 Batches of HWD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Materials
4.2. Preparation of Lyophilized Powder of HWD
4.3. Preparation of Sample Solutions for Fingerprint Analysis and UHPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS Analysis
4.4. Preparation of Standard Solutions
4.5. Instrumentation and Chromatographic Conditions
4.5.1. HPLC Conditions for Fingerprint Analysis
4.5.2. Conditions for UHPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS Analysis
4.6. Similarity Analysis (SA)
4.7. Network Pharmacology (NP)
- (1)
- the ‘candidate CCs-candidate target (cCCs-cT) network’ was established by linking candidate CCs with all of their candidate targets;
- (2)
- the ‘GP, FD, CG-candidate target (GP/FD/CG-cT) network’ was established by inking GP, FD, and CG with all of their candidate targets;
- (3)
- the ‘potential CCs-potential target-GP, FD, CG (pCCs-pT-GP/FD/CG) network’ was constructed by connecting potential CCs and GP, FD, and CG with their potential targets, which were used to screen out potential active ingredient markers.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, Z.Q. Effect of acupoint application of Chinese herbs combined with Houpu Wenzhong Decoction in the treatment of spleen deficiency type stomach. Nei Mongol. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 37, 87–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.S. Effect of acupoint application of Chinese herbs combined with Houpu Wenzhong Decoction in the treatment of spleen deficiency type stomach. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnophar. 2017, 26, 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Shi, P.F. Modified Houpu Wenzhong Decoction for 60 cases of gastric pain due to deficiency of spleen and stomach and cold. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 34, 2425. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Shang, R. Effect of modified Houpu Wenzhong Decoction on plasma gastrointestinal hormones in patients with functional dyspepsia. Mod. J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2017, 26, 2468–2470. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.W.; Li, D.K.; Tang, L.; Guo, J.L. Impact of Houpu Wenzhong Decoction combined with domperidone on plasma gastrointestinal hormone and treatment effect for functional dyspepsia. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form. 2015, 21, 174–177. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.Y.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhou, F. Observation on therapeutic effect of Houpu Wenzhong Decoction on functional dyspepsia. J. Pract. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2010, 26, 677. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.D. 36 Cases of functional dyspepsia treated by modified Houpu Wenzhong Decoction. Acta Chin. Med. 2009, 24, 56–57. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, S.F.; Liu, C.X. Treatment of chronic gastritis of insufficiency-cold in spleen and stomach by modified Matgnoliae Officinalis decoction, analysis of 43 cases. West. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2016, 29, 98–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.M. Treating 60 cases of chronic gastritis with the Houpu Wenzhong decoction. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 7, 107–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F. Curative effect of Houpu Wenzhong Decoction combined with western medicine on chronic gastritis. Contemp. Med. Forum. 2014, 12, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.R.; Zhao, L. Treating 53 cases of chronic gastritis with the Houpu Wenzhong decoction plus catgut implantation at acupoint. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 6, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.J. Clinical observation of modified Houpu Wenzhong Decoction in the treatment of chronic mesenteric lymphadenitis in children. Pract. Clin. J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2015, 15, 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Zou, Z.; Li, Y.Y.; Wu, C.R.; Li, S. Antidiarrheal and in vitro antibacterial effects of Jiawei Houpu Wenzhong Decoction. Herald Med. 2010, 29, 152–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, M.Y. Observation on 30 cases of functional recurrent abdominal pain treated with modified Houpu Wenzhong Decoction. J. Pract. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2009, 25, 722. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Yu, X.; Yu, S.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, B.; Liao, C.; You, J. Effects of tree ages and geographic area on quality of bark of Magnolia officinalis and M. officinalis var. biloba. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2009, 34, 2431–2437. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, C.Z.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wan, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Ruan, C.C.; Yuan, C.S. Dynamic changes in neutral and acidic ginsenosides with different cultivation ages and harvest seasons, identification of chemical characteristics for panax ginseng quality control. Molecules. 2017, 22, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Bai, M.; Ye, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H. Variations in volatile oil yield and composition of “Xin-yi” (magnolia biondii pamp. flower buds) at different growth stages. J. Oleo Sci. 2018, 67, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C.; Yan, R.; Yang, B.; Liao, C.; You, J. Effects of primary processing on quality of cortex Magnolia officinalis. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2010, 35, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, C.M.; Samuelsson, J.; Fornstedt, T.; Dennis, G.R.; Shalliker, R.A. Visualisation of axial temperature gradients and heat transfer process of different solvent compositions in ultra high performance liquid chromatography using thermography. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, C.; Sanwald, C.; Schlotterbeck, J.; Drotleff, B.; Lämmerhofer, M. Comparison of simple monophasic versus classical biphasic extraction protocols for comprehensive UHPLC-MS/MS lipidomic analysis of Hela cells. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1048, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, R.; Chen, M.; Ma, T.; Wu, G.; Xue, N.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Fang, K.; Zhang, W. Novel neuroprotective lead compound ligustrazine derivative mass spectrometry fragmentation rule and metabolites in rats by LC/LTQ-Orbitrap MS. Molecules 2018, 23, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.F.; Wu, W.J.; Huang, M.W.; Long, F.; Liu, X.H.; Zhu, Y.Z. Application of high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with linear ion trap quadrupole orbitrap mass spectrometry for qualitative and quantitative assessment of Shejin-Liyan granule supplements. Molecules 2018, 23, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasot, G.; Martinez-Huelamo, M.; Vallverdu-Queralt, A.; Mercader-Martí, M.; Estruch, R.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Identification of phenolic metabolites in human urine after the intake of a functional food made from grape extract by a high resolution LTQ-Orbitrap-MS approach. Food Res Int. 2017, 100, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, B.; Goli, S.A.H.; Maghsoudlou, Y. Antioxidant activity and chemical composition of the methanolic extract and related fractions of dracocephalum kotschyi leaves using liquid chromatography–Tandem mass spectrometry. Ind Crop Prod. 2017, 104, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ding, J.F.; Maxwell, P.; McCooeye, M.; Windust, A.; Ouerdane, L.; Bakirdere, S.; Willie, S.; Mester, Z. Determination of arsenobetaine in fish tissue by species specific isotope dilution LC-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS and standard addition LC-ICPMS. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3371–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, D.X.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, B.; Xie, S.H.; Wang, Q.; Xu, K.X.; Lin, R. Analysis of chemical constituents in Wuzi-Yanzong-Wan by UPLC-ESI-LTQ-orbitrap-MS. Molecules 2015, 20, 21373–21404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, P.; Huang, J.; Bai, J.Q.; Huang, Z.H.; Liu, X.S.; Qiu, X.H. Chemical analysis and multi-component determination in Chinese medicine preparation bupi yishen formula using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with linear ion trap-orbitrap mass spectrometry and triple-quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Guan, H.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Shi, Y. Simultaneous determination of 14 active constituents of Shengjiang Xiexin decoction using ultrafast liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.Y.; Nie, Y.; Cheng, B.F.; Tao, J.; Ma, X.Y.; Jiang, M.; Gao, J.; Bai, G. Qingfei Xiaoyan Wan, a traditional Chinese medicine formula, ameliorates pseudomonas aeruginosa–induced acute lung inflammation by regulation of PI3K/AKT and Ras/MAPK pathways. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; Cheung, F.; Tan, H.Y.; Hong, M.; Wang, N.; Yang, J.; Feng, Y.B.; Zheng, Q.S. Identification of the active compounds and significant pathways of yinchenhao decoction based on network pharmacology. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4583–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, W.Y.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, C.S.; Han, J.Y.; Yao, X.S.; Zhou, H. Discovery of the mechanisms and major bioactive compounds responsible for the protective effects of Gualou Xiebai Decoction on coronary heart disease by network pharmacology analysis. Phytomedicine 2019, 56, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.T.; Yang, R.N.; Guan, Z.; Chen, A.L.; Li, W. Ultra-performance LC separation and quadrupole time-of-flight MS identification of major alkaloids in Plumula Nelumbinis. Phytochem. Anal. 2014, 25, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.M.; Wang, H.H.; Han, X.F.; Chen, S.W.; Zhu, S.; Dai, J. Fingerprint analysis of polysaccharides from different Ganoderma by HPLC combined with chemometrics methods. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 114, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.N.; Wang, Y.Z.; Sun, X.G.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, W.H.; Long, Z.; Ma, B.P. Chromatographic fingerprint analysis of Toosendan Fructus by HPLC-CAD coupled with chemometrics methods. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 52, 456–461. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wang, B.; Xu, J.Y.; Sun, J.B.; Yan, Q.; Ji, B.; Zhao, Y.L.; Yu, Z.G. Detection and chemical profiling of Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan decoction by ultra performance liquid chromatography-hybrid linear ion trap-orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 53, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.T.; Yang, K.L.; Ge, J.W. Uncovering the pharmacological mechanism of astragalus salvia compound on pregnancy-induced hypertension syndrome by a network pharmacology approach. Sci. Rep-UK. 2017, 7, 16849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.W.; Wang, M.Y.; Olounfeh, K.M.; Zhao, N.; Wang, S.; Meng, F.H. Network pharmacology-based identifcation of potential targets of the flower of Trollius chinensis Bunge acting on anti-inflammatory effectss. Sci. Rep-UK. 2019, 9, 8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, B.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbal Radix Curcumae formula for application to cardiovascular disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Tang, Q.F.; Tian, Y.F.; Fan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Tan, X.M. Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Mahuang Fuzi Xixin decoction for application to allergic rhinitis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 176, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, F. Advance in latest studies on pharmacological effects of magnolol. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 3, 3526–3530. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Q.; Jiang, R.G.; Chen, H.F. Advances in pharmacological effects of magnolol and honokiol. Chin. Tradit. Herbal Drugs. 2005, 36, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.Z.; Sui, H.J.; Zhang, L.L.; Jin, Y. Effects of hesperidin on functional dyspepsia gastrointestinal motility of rats and the expression of Ghrelin. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater. Clin. Med. 2014, 30, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.X.; Luo, G.X.; Tan, D.Q. Protective effect of glycyrrhizic acid, an effective component of Banxia Xiexin Decoction, on gastric mucosa of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis and its effect on TNF-alpha. J. New Chin. Med. 2013, 45, 144–146. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |



| Analyte | Linear Range (μg/mL) | Calibration Curve | r2 | LOD (μg/mL) | LOQ (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnolol | 10.485–262.13 | y = 0.7850x + 0.9241 | 0.9999 | 1.02 | 3.78 |
| Honokiol | 3.626–259.00 | y = 0.5289x + 0.5954 | 0.9999 | 0.738 | 2.61 |
| Hesperidin | 10.752–530.18 | y = 0.3495x − 0.4054 | 0.9999 | 0.582 | 1.23 |
| Glycyrrhizic acid | 14.473–347.68 | y = 0.0609x − 0.8267 | 0.9997 | 1.15 | 3.14 |
| Analyte | Precision | Reproducibility (n = 6) | Stability (n = 10) | Recovery (n= 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-day (n = 6) | Inter-day (n = 3) | |||||
| RSD (%) | RSD (%) | RSD (%) | RSD (%) | Mean | RSD (%) | |
| Magnolol | 0.94 | 1.2 | 1.95 | 1.06 | 101.93 | 1.95 |
| Honokiol | 1.12 | 1.34 | 2.03 | 1.26 | 100.75 | 0.46 |
| Hesperidin | 0.89 | 1.03 | 1.47 | 1.15 | 100.33 | 0.79 |
| Glycyrrhizic acid | 0.57 | 0.89 | 2.42 | 0.97 | 102.49 | 0.55 |
| Sample | Hesperidin | Glycyrrhizic Acid | Honokiol | Magnolol | Similarity Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 278.2418 ± 0.0182 | 205.9195 ± 0.0212 | 43.6655 ± 0.0214 | 33.9597 ± 0.0340 | 0.978 |
| S2 | 268.8197 ± 0.0049 | 162.8062 ± 0.0022 | 16.5347 ± 0.0130 | 24.3066 ± 0.0187 | 0.946 |
| S3 | 292.2355 ± 0.0006 | 127.5041 ± 0.0025 | 84.8151 ± 0.0005 | 32.8499 ± 0.0057 | 0.962 |
| S4 | 309.1562 ± 0.0013 | 109.7176 ± 0.0062 | 71.0671 ± 0.0092 | 40.5120 ± 0.0107 | 0.980 |
| S5 | 231.4275 ± 0.0275 | 189.0328 ± 0.0267 | 63.9387 ± 0.0106 | 36.3183 ± 0.0174 | 0.976 |
| S6 | 210.6112 ± 0.0229 | 138.1133 ± 0.0379 | 36.3562 ± 0.0018 | 33.0920 ± 0.0041 | 0.970 |
| S7 | 236.1765 ± 0.0315 | 145.0608 ± 0.0420 | 73.6863 ± 0.0087 | 58.3732 ± 0.0061 | 0.960 |
| S8 | 246.5579 ± 0.0050 | 336.2496 ± 0.0006 | 23.8629 ± 0.0106 | 38.3361 ± 0.0123 | 0.930 |
| S9 | 247.4581 ± 0.0060 | 127.2972 ± 0.0073 | 32.3751 ± 0.0038 | 27.9307 ± 0.0007 | 0.968 |
| S10 | 248.4521 ± 0.0095 | 150.5337 ± 0.0084 | 64.5708 ± 0.0209 | 44.1939 ± 0.0295 | 0.964 |
| S11 | 293.0197 ± 0.0328 | 131.7915 ± 0.0474 | 72.2159 ± 0.0289 | 55.7920 ± 0.0409 | 0.956 |
| S12 | 273.9662 ± 0.0052 | 181.4631 ± 0.0109 | 10.4443 ± 0.0249 | 31.1806 ± 0.0333 | 0.946 |
| S13 | 281.9760 ± 0.0164 | 138.7783 ± 0.0275 | 6.0745 ± 0.0061 | 43.7450 ± 0.0046 | 0.922 |
| S14 | 284.3605 ± 0.0151 | 113.6962 ± 0.0188 | 78.9074 ± 0.0251 | 29.3832 ± 0.0385 | 0.973 |
| S15 | 282.6103 ± 0.0034 | 108.1412 ± 0.0037 | 51.4084 ± 0.0162 | 48.8744 ± 0.0273 | 0.957 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Chen, G.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Q.; Hu, H.; Li, P.; Bai, J.; Du, S.; Lu, Y.; et al. Study on the Material Basis of Houpo Wenzhong Decoction by HPLC Fingerprint, UHPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS, and Network Pharmacology. Molecules 2019, 24, 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142561
Luo J, Chen G, Liu D, Wang Y, Qi Q, Hu H, Li P, Bai J, Du S, Lu Y, et al. Study on the Material Basis of Houpo Wenzhong Decoction by HPLC Fingerprint, UHPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS, and Network Pharmacology. Molecules. 2019; 24(14):2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142561
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Juyuan, Gongsen Chen, Donghan Liu, Yan Wang, Qi Qi, Haiyan Hu, Pengyue Li, Jie Bai, Shouying Du, Yang Lu, and et al. 2019. "Study on the Material Basis of Houpo Wenzhong Decoction by HPLC Fingerprint, UHPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS, and Network Pharmacology" Molecules 24, no. 14: 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142561
APA StyleLuo, J., Chen, G., Liu, D., Wang, Y., Qi, Q., Hu, H., Li, P., Bai, J., Du, S., Lu, Y., Wang, Y., & Liu, C. (2019). Study on the Material Basis of Houpo Wenzhong Decoction by HPLC Fingerprint, UHPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS, and Network Pharmacology. Molecules, 24(14), 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142561