Classification of Raw Stingless Bee Honeys by Bee Species Origins Using the NMR- and LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Species Identification
2.2. Collection of Honey Samples
2.3. 1H-NMR Spectroscopy
2.3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3.2. Sample Preparation
2.3.3. Data Acquisition
2.3.4. Data Pre-processing
2.3.5. Data Analysis
2.3.6. Characterization of Discriminant Metabolites
2.4. UHPLC-QTOF Mass Spectrometry
2.4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.4.2. Sample Preparation
2.4.3. Data Acquisition
2.4.4. Data Processing
2.4.5. Data Analysis
2.4.6. Characterization of Diagnostic Ions
3. Results
3.1. An Overview by PCA
3.1.1. PCA of 1H-NMR Spectral Data
3.1.2. PCA of UHPLC-QTOF Mass Spectrometric Data
3.2. Classification Models of MVDA
3.2.1. OPLS-DA (1H-NMR Spectral Data)
3.2.2. PLS-DA (UHPLC-QTOF Mass Spectrometric Data)
3.3. Metabolite Identification
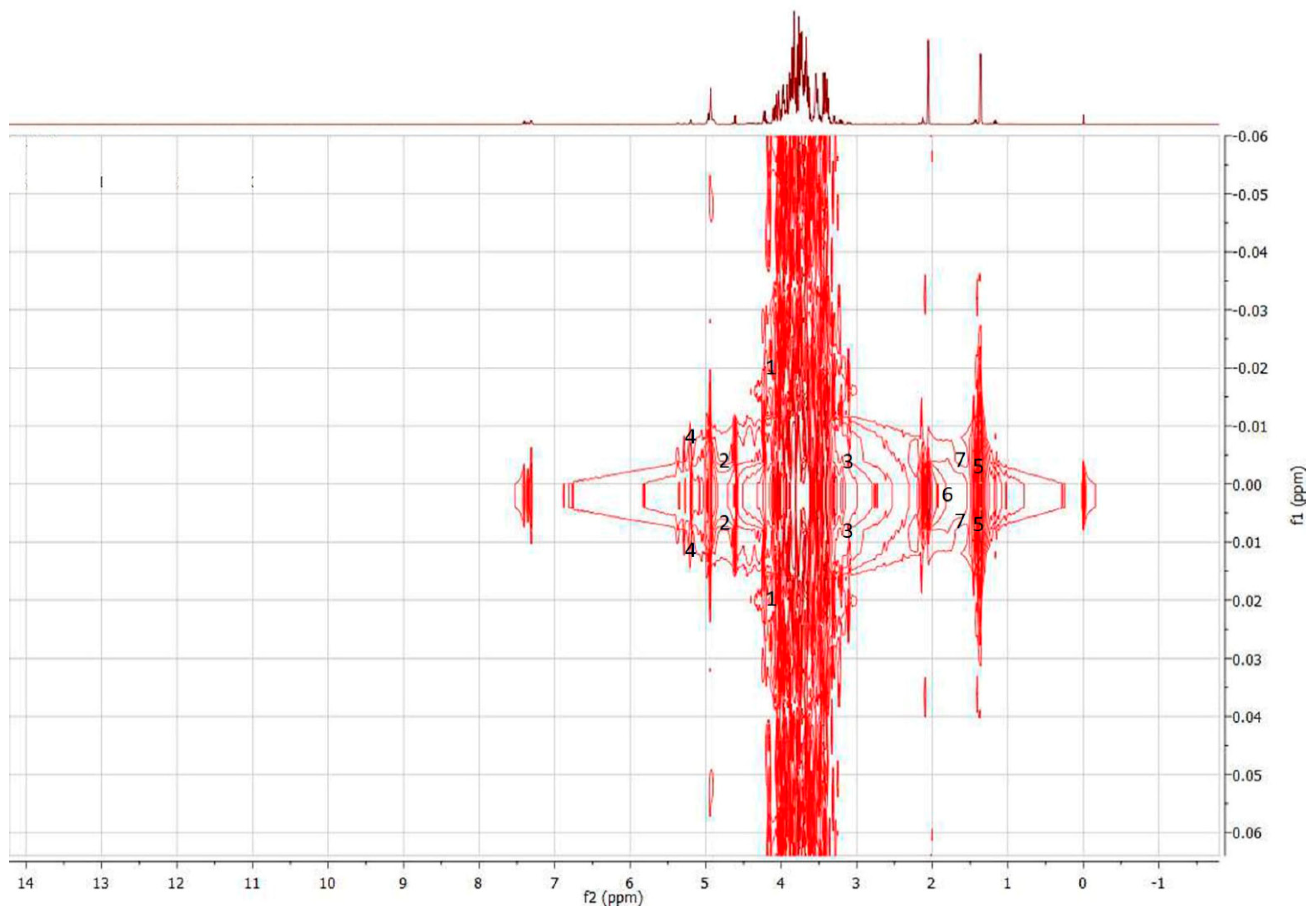
3.3.1. Characterization of Discriminant Metabolites (1H-NMR Spectral Data)
3.3.2. Characterization of Diagnostic Ions (UHPLC-QTOF Mass Spectrometric Data)
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. Standard for Honey Codex Stan 12-1981, 12Codex Stan 1–8. 2001. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/en/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCODEX%2BSTAN%2B12-1981%252Fcxs_012e.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2018).
- Vit, P.; Oddo, L.P.; Marano, M.L.; Mejias, E.S. Venezuelan stingless bee honeys characterized by multivariate analysis of physicochemical properties. Apidologie 1998, 29, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vit, P.; Medina, M.; Enríquez, M.E. Quality standards for medicinal uses of Meliponinae honey in Guatemala, Mexico, and Venezuela. Bee World 2004, 85, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandrić, Z.; Haughey, S.A.; Frew, R.D.; McComb, K.; Galvin-King, P.; Elliott, C.T.; Cannavan, A. Discrimination of honey of different floral origins by a combination of various chemical parameters. Food Chem. 2015, 189, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeder, J. Honey Laundering: The Sour Side of Nature’s Golden Sweetener. Available online: https://www.theglobeandmail.com/technology/science/honey-laundering-the-sour-side-of-natures-golden-sweetener/article562759/ (accessed on 5 January 2011).
- Bogdanov, S.; Vit, P.; Kilchenmann, V. Sugar profiles and conductivity of stingless bee honeys from Venezuela. Apidologie 1996, 27, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, R.; Bosch-Reig, F. Sugar profiles of Spanish unifloral honeys. Food Chem. 1997, 60, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vit, P.; Sancho, T.; Pascual, A.; Deliza, R. Sensory perception of tropical pot honeys by Spanish consumers, using free choice profile. J. ApiProd. ApiMed. Sci. 2011, 3, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboud, F.; De Pasquale, C.; Sinacori, A.; Massi, S.; Conte, P.; Alonzo, G. Palynological, physico-chemical and aroma characterization of Sicilian honeys. J. ApiProd. ApiMed. Sci. 2011, 3, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Muradian, L.B.; Matsuda, A.H. Physicochemical parameters of Amazon Melipona Honey. Quim. Nova 2007, 30, 707–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Chalhoub, C.; Gotsiou, P.; Lydakis-Simantiris, N.; Kefalas, P. Novel quality control methods in conjunction with chemometrics (multivariate analysis) for detecting honey authenticity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabagias, I.K.; Badeka, A.V.; Kontakos, S.; Karabournioti, S.; Kontominas, M.G. Botanical discrimination of Greek unifloral honeys with physico-chemical and chemometric analyses. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucciarelli, A.B.; Schapovaloff, M.E.; Kummritz, S.; Señuk, I.A.; Brumovsky, L.A.; Dallagnol, A.M. Microbiological and physicochemical analysis of yateí (Tetragonisca angustula) honey for assessing quality standards and commercialization. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2014, 46, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, S.; Villarejo, M.; Espejo, R.; Jodral, M. Chemical and physical parameters of Andalusian honey: Classification of Citrus and Eucalyptus honeys by discriminant analysis. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.M.S.; Dos Santos, F.P.; Evangelista-Rodrigues, A.; Da Silva, E.M.S.; Da Silva, G.S.; De Novais, J.S.; Camara, C.A. Phenolic compounds, melissopalynological, physicochemical analysis and antioxidant activity of jandaíra (Melipona subnitida) honey. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 29, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida-Muradian, L.B.; Stramm, K.M.; Estevinho, L.M. Efficiency of the FT-IR ATR spectrometry for the prediction of the physicochemical characteristics of Melipona subnitida honey and study of the temperature’s effect on those properties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, A.; Bruni, R.; Maietti, S.; Poli, F.; Rossi, D.; Paganetto, G.; Sacchetti, G. Ecuadorian stingless bee (Meliponinae) honey: A chemical and functional profile of an ancient health product. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anklam, E. A review of the analytical methods to determine the geographical and botanical origin of honey. Food Chem. 1998, 63, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.D. Plant metabolomics: From holistic hope, to hype, to hot topic. New Phytol. 2006, 169, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuballa, T.; Brunner, T.S.; Thongpanchang, T.; Walch, S.G.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Application of NMR for authentication of honey, beer and spices. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 19, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, G.; Caneva, E.; Regazzoni, L.; Bakhtyari, N.G.; Maffei Facino, R. A solid-phase extraction procedure coupled to 1H-NMR, with chemometric analysis, to seek reliable markers of the botanical origin of honey. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 62, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzold, E.; Lichtenberg-Kraag, B. Determination of the botanical origin of honey by Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy: An approach for routine analysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandrić, Z.; Frew, R.D.; Fernandez-Cedi, L.N.; Cannavan, A. An investigative study on discrimination of honey of various floral and geographical origins using UPLC-QToF MS and multivariate data analysis. Food Control 2017, 72, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, M.; Bertelli, D.; Plessi, M.; Sabatini, A.G.; Restani, C. Classification of Italian honeys by 2D HR-NMR. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmenhaeuser, M.; Monakhova, Y.B.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Qualitative and quantitative control of honeys using NMR spectroscopy and chemometrics. ISRN Anal. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievano, E.; Peggion, E.; Mammi, S. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of chloroform extracts of honey for chemometric determination of its botanical origin. J. Agric Food Chem. 2019, 58, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yao, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, L.; Zhao, J. Floral classification of honey using liquid chromatography-diode array detection-tandem mass spectrometry and chemometric analysis. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consonni, R.; Cagliani, L.R. Geographical Characterization of Polyfloral and Chemometrics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6873–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donarski, J.A.; Jones, S.A.; Charlton, A.J. Application of cryoprobe 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and multivariate analysis for the verification of Corsican honey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5451–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vit, P.; Fernandez-Maeso, M.C.; Ortiz-Valbuena, A. Potential use of the three frequently occurring sugars in honey to predict stingless bee entomological origin. J. Appl. Entomol. 1998, 122, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón-Sierra, J.M.; Ruiz-Ruiz, J.C.; De La Luz Ortiz-Vázquez, E. Electrophoresis characterisation of protein as a method to establish the entomological origin of stingless bee honeys. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kek, S.P.; Chin, N.L.; Tan, S.W.; Yusof, Y.A.; Chua, L.S. Classification of Honey from Its Bee Origin via Chemical Profiles and Mineral Content. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 10, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vit, P.; Soler, C.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. Profiles of phenolic compounds of Apis mellifera and Melipona spp. honeys from Venezuela. Zeitschrift Fur Lebensmittel -Untersuchung Und -Forschung 1997, 204, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of plants. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katajamaa, M.; Miettinen, J.; Orešič, M. MZmine: Toolbox for processing and visualization of mass spectrometry based molecular profile data. Bioinformatic 2006, 22, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, A.C.H.F.; da Silva Cunha, I.B.; Marcucci, M.C.; Aidar, D.S.; Silva, E.C.A.; Carvalho, C.A.L.; Eberlin, M.N. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry fingerprinting of propolis of native Brazilian stingless bees. Apidologie 2007, 38, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.; Johansson, E.; Kettaneh-Wold, N.; Trygg, J.; Wikstrom, C.; Wold, S. Multi- and Megavariate Data Analysis: Part I: Basic Principles and Applications; Umetrics AB: Umea, Sweden, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jalil, A.H.; Shuib, I. Beescape for Meliponines: Conservation of Indo-Malayan Stingless Bees; Partridge: Singapore, 2014; pp. 13–212. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanov, S.; Lullmann, C.; Mossel, B.L.; D’Arcy, B.R.; Russmann, H.; Vorwohl, G.; Oddo, L.; Sabatini, A.G.; Marcazzan, G.L.; Piro, R.; et al. Honey quality, methods of analysis and international regulatory standards: review of the work of the international honey commission. Mitt. Lebensm. Hyg. 1999, 90, 108–125. [Google Scholar]
- Vit, P.; Pedro, S.R.M.; Roubik, D.W. Pot-Honey A legacy of Stingless Bees. Pot-Honey: A Legacy of Stingless Bees; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3–654. [Google Scholar]
- Boffo, E.F.; Tavares, L.A.; Tobias, A.C.T.; Ferreira, M.M.C.; Ferreira, A.G. Identification of components of Brazilian honey by 1H-NMR and classification of its botanical origin by chemometric methods. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.-J.; Schultz, A.W.; Wang, J.; Johnson, C.H.; Yannone, S.M.; Patti, G.J.; Siuzdak, G. Liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry characterization of metabolites guided by the Metlin database. Nat. Protocol. 2013, 8, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, H.F. The Indo-Malayan Species of Trigona. Bulletin of The American Museum of Natural History, LXXVI(Art. III); The American Museum of Natural History: New York, NY, USA, 1939; pp. 83–141. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C. Catalog of the Indo-Malayan/Australasian Stingless Bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Meliponini). In Zootaxa; Magnolia Press: Auckland, New Zealand, 2008; pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
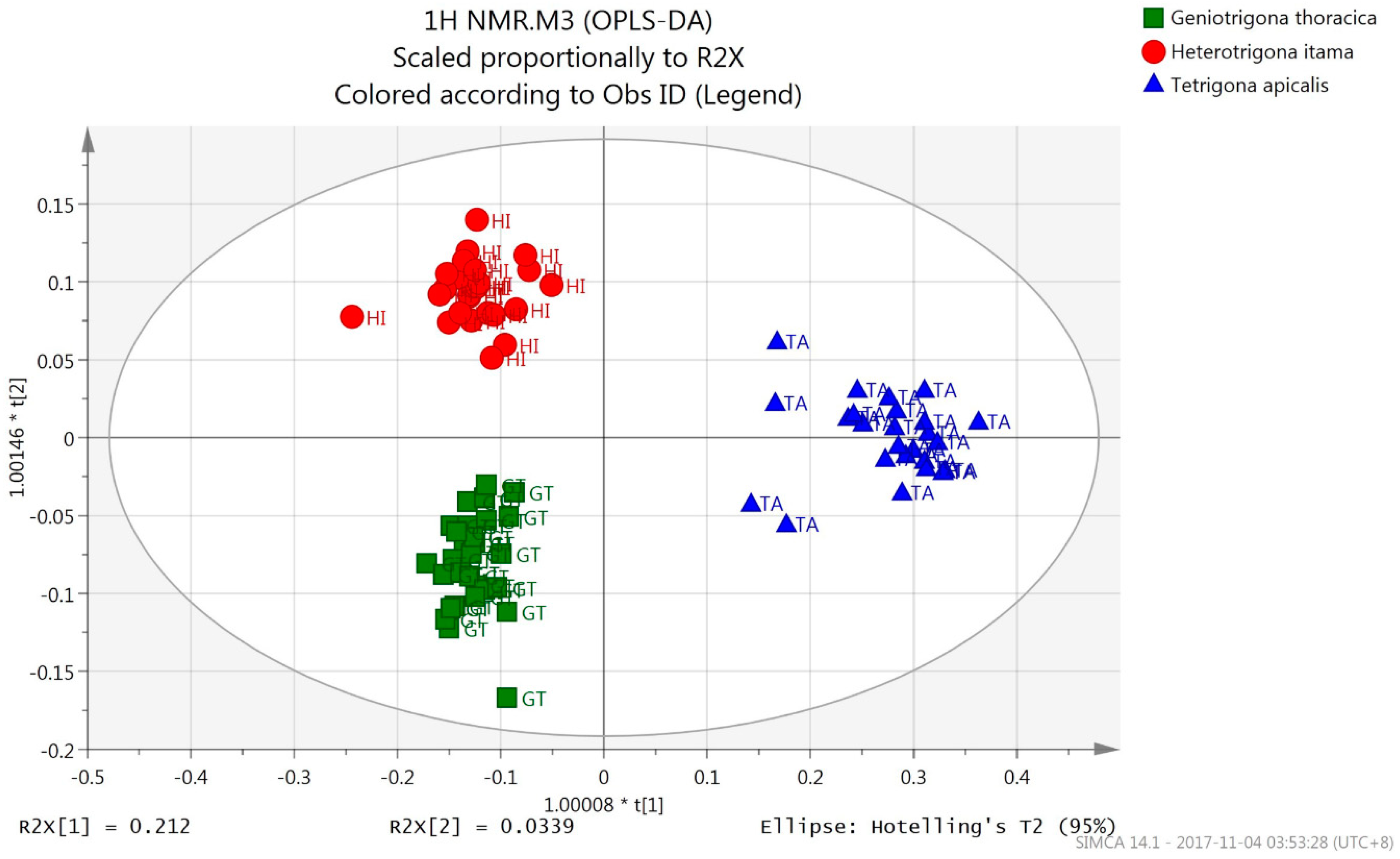
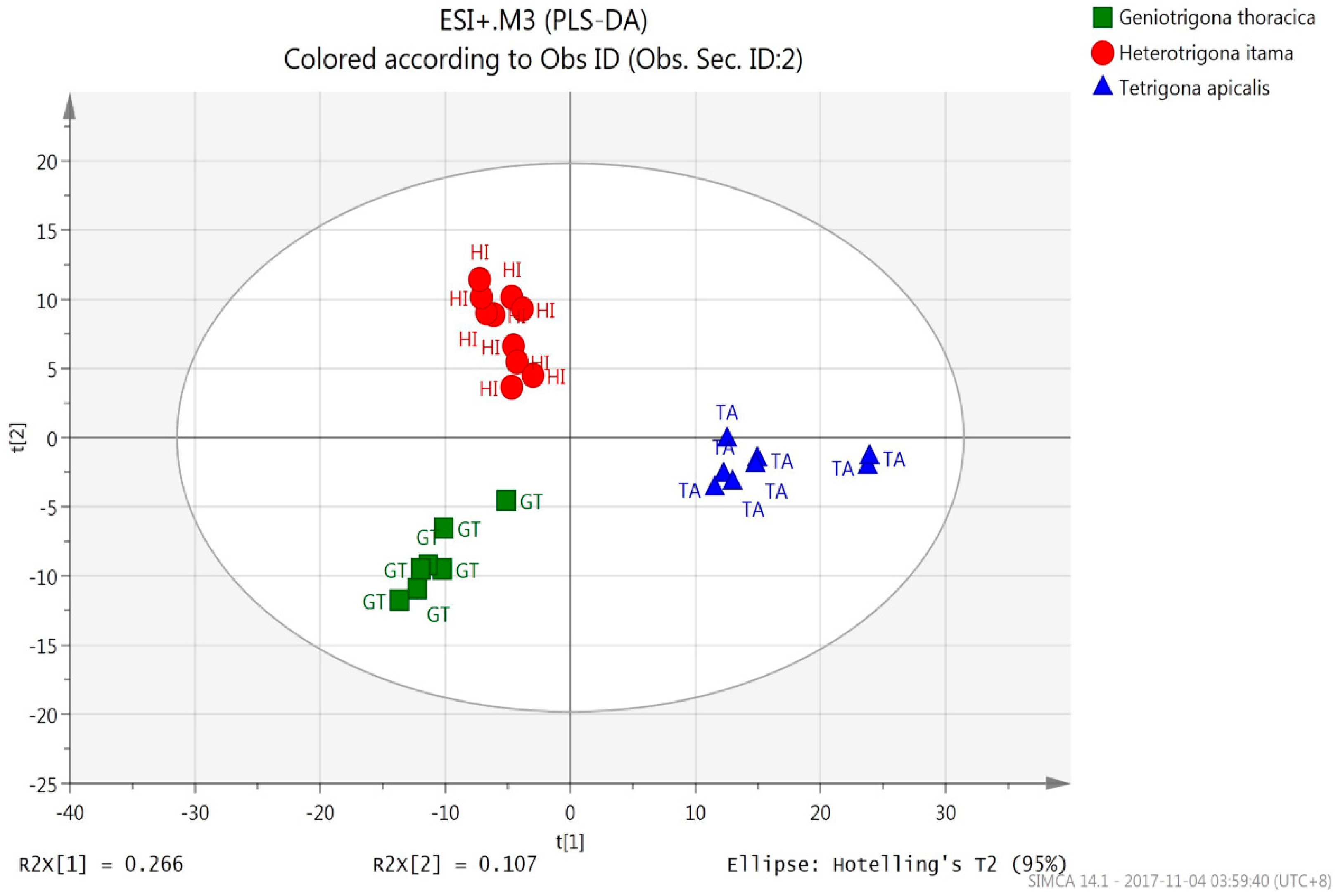
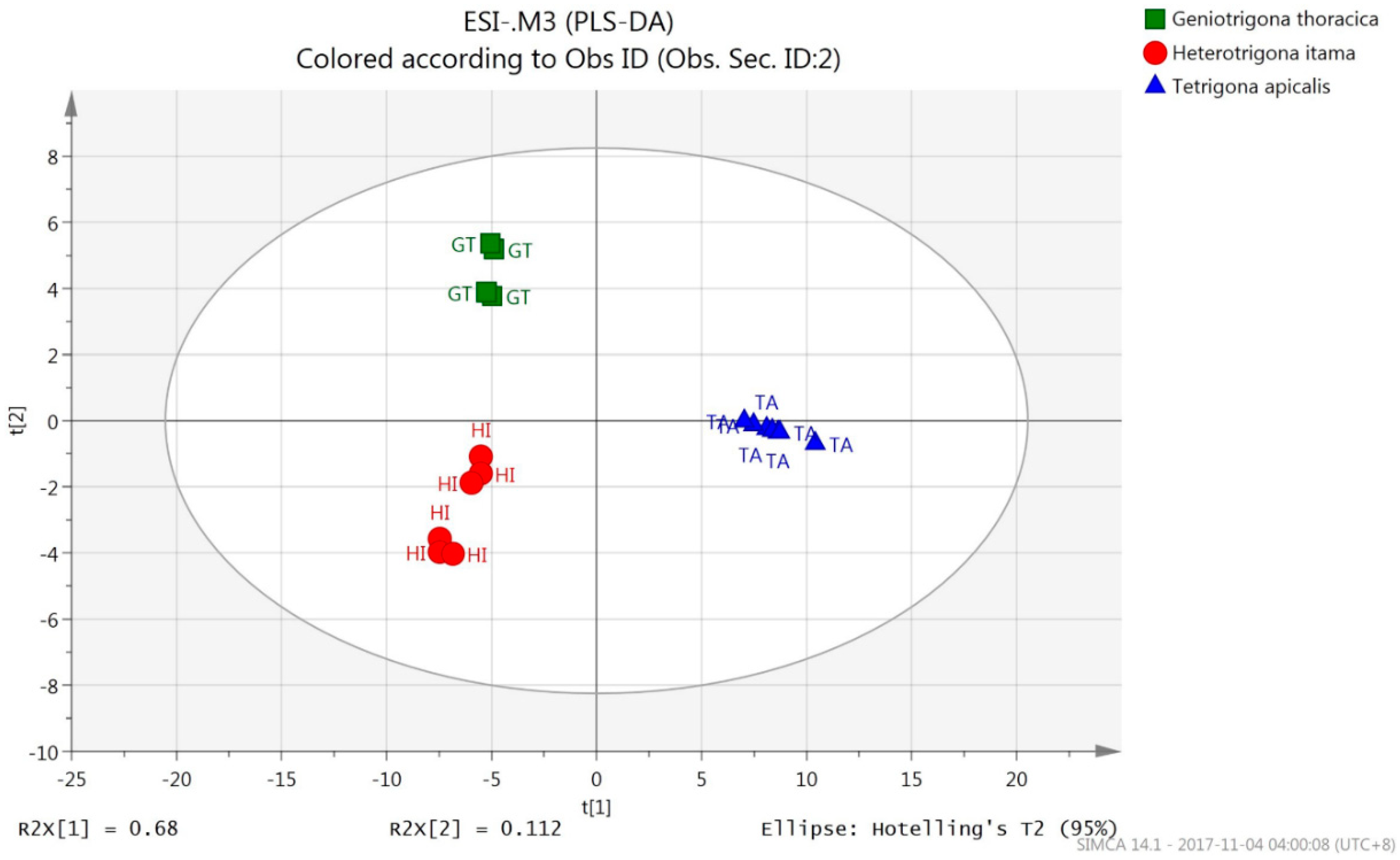
| Species Origin | % Correct | Classes of Honey (OPLS-DA) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. itama | G. thoracica | T. apicalis | ||
| H. itama | 100 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| G. thoracica | 100 | 0 | 29 | 0 |
| T. apicalis | 100 | 0 | 0 | 25 |
| Total | 25 | 29 | 25 | |
| Average | 100 | |||
| Species Origin | % Correct | Classes of Honey (ESI+) | Classes of Honey (ESI-) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. itama | G. thoracica | T. apicalis | H. itama | G. thoracica | T. apicalis | ||
| H. itama | 100 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| G. thoracica | 100 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| T. apicalis | 100 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Total | 10 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 7 | |
| Average | 100 | ||||||
| VIP > 1 | Binned Region | 1H-NMR Characteristics Signals | Online HMDB (1H-NMR) | J-Resolved | HSQC (1H-13C) Characteristics Signals | Online HMDB (HSQC, 1H-13C) | Tentative Discriminant Metabolites | Honey Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.45 | 3.68 | 3.68 (m) | d-Fructofuranose | H. itama | ||||
| 3.56 | 3.52 | 3.52 (m) | ||||||
| 3.32 | 4.00 | 4.00 (m) | ||||||
| 3.13 | 4.08 | 4.10 (d, 8.5) | 4.118 (m) | d | 4.1 (79.747) | 4.1055 (78.2044) | ||
| 2.62 | 3.76 | 3.76 (m) | ||||||
| 2.09 | 3.96 | 3.96 (m) | ||||||
| 2.19 | 4.60 | 4.61 (d, 7.9) | 4.634 (d, 7.957) | d | 4.61 (94.048) | 4.6333 (98.7123) | β-d-Glucose | G. thoracica |
| 1.77 | 3.20 | 3.21 (dd, 9.4, 8.71) | 3.21 (dd, 9.33) | 3.21 (dd, 7.90) | d | 3.2140 (76.4140) | 3.2144 (76.9117) | d-Xylose |
| 1.44 | 5.20 | 5.20 (d, 3.7) | 5.223 (d, 3.677) | d | 5.2 (93.293) | 5.2241 (94.9364) | α-d-Glucose | |
| 1.25 | 2.00 | 2.05 (s) | - | - | - | - | Unassigned (2.05) | |
| 3.81 | 1.32 | 1.36 (d, 6.90) | 1.32 (d, 6.96) | d | 1.387 (21.841) | 1.3142 (22.9033) | l-Lactic acid | T. apicalis |
| 2.88 | 1.92 | 1.92 (s) | 1.91 (s) | s | 1.943 (26.751) | 1.9059 (26.0899) | Acetic acid | |
| 1.47 | 5.28 | 5.28 (t, 3.6) | - | - | - | - | Unassigned (5.28) | |
| 1.22 | 1.44 | 1.43 (d, 7.00) | 1.46 (d, 7.14) | d | 1.450 (19.702) | 1.4903 (19.0295) | l-Alanine |
| (a) | |||||
| VIP > 1 | Var ID (Primary) | Ion | RT (min) | Experimental Precursor Ions (m/z) | Experimental MS-MS Fragment Ions (m/z) |
| 1.66 | 492 | [M + H]+ | 1.44 | 193.087 | 165.092, 162.068, 147.044, 135.044, 133.065, 105.071 |
| 1.62 | 493 | [M + H]+ | 1.50 | 151.076 | |
| 1.91 | 428 | [M + H]+ | 1.55 | 446.203 | |
| 1.66 | 399 | [M + H]+ | 1.55 | 105.070 | |
| 1.83 | 359 | [M + H]+ | 1.56 | 122.096 | 106.073, 105.070, 103.054 |
| 1.79 | 396 | [M + H]+ | 1.57 | 266.139 | |
| 1.78 | 397 | [M + H]+ | 1.57 | 284.150 | 268.145, 267.143, 266.139, 249.132, 248.129, 164.107, 134.097, 105.070 |
| 1.77 | 451 | [M + H]+ | 1.57 | 267.142 | |
| 1.72 | 431 | [M + H]+ | 1.80 | 392.133 | |
| 1.71 | 401 | [M + H]+ | 1.80 | 225.110 | 181.084, 165.055, 139.076, 121.065 |
| 1.15 | 490 | [M + H]+ | 1.80 | 234.150 | 191.105, 189.091, 122.032, 121.029, 114.128 |
| 1.08 | 276 | [M + H]+ | 3.03 | 362.327 | |
| 1.07 | 120 | [M + H]+ | 4.94 | 310.311 | |
| 1.03 | 188 | [M + H]+ | 4.95 | 695.361 | |
| 1.08 | 226 | [M + H]+ | 5.04 | 637.307 | |
| 1.03 | 216 | [M + H]+ | 5.04 | 695.360 | 659.294, 581.245, 359.032, 330.992, 289.006, 135.004 |
| 1.47 | 416 | [M + H]+ | 5.13 | 358.309 | 178.945, 177.013, 136.006, 135.003, 132.987, 123.117, 120.987, 105.068, 104.992 |
| 1.22 | 418 | [M + H]+ | 5.13 | 336.327 | |
| 1.05 | 470 | [M + H]+ | 5.27 | 371.102 | |
| 1.57 | 19 | [M + H]+ | 5.54 | 360.324 | 358.365, 135.004 |
| 1.56 | 124 | [M + H]+ | 5.54 | 321.316 | |
| 1.55 | 8 | [M + H]+ | 5.54 | 338.343 | |
| 1.52 | 107 | [M + H]+ | 5.54 | 675.678 | 338.343, 321.316, 303.305, 149.133, 135.117, 111.117, 97.102 |
| 1.05 | 444 | [M + H]+ | 6.07 | 679.366 | |
| 1.45 | 410 | [M + H]+ | 6.09 | 366.374 | |
| 1.15 | 78 | [M − H]- | 1.00 | 668.224 | |
| 1.17 | 50 | [M − H]- | 1.69 | 495.183 | |
| 1.63 | 60 | [M − H]- | 1.73 | 493.168 | |
| 1.57 | 39 | [M − H]- | 1.82 | 119.114 | |
| 1.66 | 42 | [M − H]- | 1.83 | 353.112 | 227.051, 211.030, 190.984, 166.013, 165.009, 147.014, 120.048, 119.046 |
| 1.27 | 31 | [M − H]- | 1.83 | 147.098 | |
| 1.16 | 29 | [M − H]- | 1.83 | 165.102 | |
| 1.41 | 46 | [M − H]- | 1.86 | 206.118 | |
| 1.15 | 45 | [M − H]- | 2.37 | 201.075 | |
| (b) | |||||
| VIP > 1 | Var ID (Primary) | Ion | RT (min) | Experimental Precursor Ions (m/z) | Experimental MS-MS Fragment Ions (m/z) |
| 1.62 | 126 | [M + H]+ | 1.03 | 365.106 | |
| 1.32 | 475 | [M + H]+ | 1.13 | 174.149 | |
| 1.32 | 283 | [M + H]+ | 1.30 | 365.106 | |
| 1.44 | 301 | [M + H]+ | 1.41 | 203.053 | |
| 1.33 | 348 | [M + H]+ | 1.69 | 365.106 | |
| 1.44 | 521 | [M + H]+ | 1.81 | 351.142 | |
| 1.46 | 502 | [M + H]+ | 1.82 | 317.114 | |
| 1.46 | 502 | [M + H]+ | 1.82 | 317.114 | |
| 1.33 | 501 | [M + H]+ | 1.97 | 227.083 | 210.074, 209.071, 199.087, 181.076, 154.065 |
| 1.36 | 517 | [M + H]+ | 1.99 | 521.272 | 519.256, 518.236, 517.228, 366.109, 365.106, 285.887, 218.941, 203.050, 185.042, 140.070, 135.004, 132.985 |
| 1.46 | 528 | [M + H]+ | 2.01 | 301.118 | |
| 1.46 | 528 | [M + H]+ | 2.01 | 301.118 | |
| 1.46 | 528 | [M + H]+ | 2.01 | 301.118 | |
| 1.46 | 528 | [M + H]+ | 2.01 | 301.118 | |
| 1.27 | 479 | [M + H]+ | 2.05 | 321.131 | 319.210, 319.161, 281.016, 279.020, 187.060, 142.948 |
| 1.30 | 388 | [M + H]+ | 2.08 | 183.091 | 182.154, 155.047, 127.016, 98.984 |
| 1.35 | 516 | [M + H]+ | 2.11 | 551.283 | |
| 1.41 | 483 | [M + H]+ | 4.91 | 439.375 | |
| 1.43 | 421 | [M + H]+ | 5.27 | 367.319 | |
| 1.51 | 503 | [M + H]+ | 5.35 | 393.334 | |
| 1.80 | 478 | [M + H]+ | 5.49 | 467.408 | |
| 1.25 | 520 | [M + H]+ | 5.73 | 481.387 | |
| 1.00 | 486 | [M + H]+ | 5.78 | 637.469 | |
| 1.46 | 519 | [M + H]+ | 5.87 | 391.320 | |
| 1.68 | 87 | [M − H]- | 4.86 | 345.255 | |
| 1.80 | 86 | [M − H]- | 5.42 | 373.283 | |
| 1.83 | 88 | [M − H]- | 5.93 | 401.311 | |
| (c) | |||||
| VIP > 1 | Var ID (Primary) | Ion | RT (min) | Experimental Precursor Ions (m/z) | Experimental MS-MS Fragment Ions (m/z) |
| 1.07 | 364 | [M + H]+ | 1.45 | 492.207 | 408.165, 332.243, 292.119, 264.124, 244.097, 166.086, 121.084, 120.081 |
| 1.13 | 183 | [M + H]+ | 1.61 | 158.082 | |
| 1.12 | 245 | [M + H]+ | 1.62 | 178.086 | |
| 1.22 | 110 | [M + H]+ | 1.64 | 389.178 | |
| 1.23 | 171 | [M + H]+ | 1.67 | 515.173 | |
| 1.26 | 250 | [M + H]+ | 1.68 | 238.108 | |
| 1.11 | 208 | [M + H]+ | 1.68 | 535.236 | |
| 1.27 | 362 | [M + H]+ | 1.69 | 311.113 | |
| 1.27 | 111 | [M + H]+ | 1.69 | 227.126 | |
| 1.30 | 140 | [M + H]+ | 1.70 | 353.121 | |
| 1.19 | 146 | [M + H]+ | 1.71 | 373.183 | |
| 1.21 | 119 | [M + H]+ | 1.73 | 211.131 | |
| 1.14 | 137 | [M + H]+ | 1.83 | 260.090 | |
| 1.04 | 191 | [M + H]+ | 1.83 | 401.171 | |
| 1.02 | 373 | [M + H]+ | 1.78 | 107.085 | |
| 1.00 | 365 | [M + H]+ | 1.80 | 180.102 | |
| 1.07 | 369 | [M + H]+ | 1.81 | 151.112 | |
| 1.19 | 85 | [M + H]+ | 1.84 | 120.081 | |
| 1.15 | 142 | [M + H]+ | 1.85 | 649.269 | |
| 1.30 | 141 | [M + H]+ | 1.86 | 192.103 | |
| 1.02 | 195 | [M + H]+ | 1.86 | 230.080 | |
| 1.17 | 215 | [M + H]+ | 1.93 | 162.091 | |
| 1.09 | 381 | [M + H]+ | 1.95 | 644.313 | |
| 1.17 | 382 | [M + H]+ | 1.96 | 283.152 | |
| 1.17 | 382 | [M + H]+ | 1.96 | 283.152 | |
| 1.15 | 246 | [M + H]+ | 1.96 | 153.127 | |
| 1.15 | 246 | [M + H]+ | 1.96 | 153.127 | |
| 1.28 | 17 | [M + H]+ | 2.00 | 487.215 | |
| 1.26 | 69 | [M + H]+ | 2.00 | 482.260 | 355.174, 335.095, 154.131, 153.128, 135.117, 115.039, 97.028 |
| 1.08 | 249 | [M + H]+ | 2.00 | 171.138 | |
| 1.13 | 112 | [M + H]+ | 2.02 | 153.127 | |
| 1.04 | 42 | [M + H]+ | 2.04 | 355.173 | |
| 1.01 | 368 | [M + H]+ | 2.14 | 253.142 | |
| 1.39 | 175 | [M + H]+ | 2.23 | 293.173 | |
| 1.14 | 394 | [M + H]+ | 2.26 | 307.152 | |
| 1.00 | 372 | [M + H]+ | 2.26 | 267.158 | |
| 1.34 | 392 | [M + H]+ | 2.30 | 195.138 | |
| 1.34 | 392 | [M + H]+ | 2.30 | 195.138 | |
| 1.37 | 383 | [M + H]+ | 2.33 | 249.146 | |
| 1.32 | 391 | [M + H]+ | 2.38 | 253.179 | |
| 1.27 | 237 | [M + H]+ | 2.38 | 291.157 | |
| 1.38 | 200 | [M + H]+ | 2.41 | 439.230 | |
| 1.30 | 377 | [M + H]+ | 2.42 | 221.154 | |
| 1.44 | 393 | [M + H]+ | 2.44 | 217.159 | |
| 1.34 | 189 | [M + H]+ | 2.45 | 235.170 | |
| 1.37 | 193 | [M + H]+ | 2.47 | 423.235 | |
| 1.06 | 253 | [M + H]+ | 2.47 | 251.165 | |
| 1.36 | 201 | [M + H]+ | 2.48 | 275.162 | |
| 1.02 | 260 | [M + H]+ | 2.49 | 233.154 | |
| 1.00 | 232 | [M + H]+ | 2.52 | 421.219 | |
| 1.45 | 65 | [M + H]+ | 2.61 | 277.178 | |
| 1.11 | 154 | [M + H]+ | 2.63 | 223.169 | |
| 1.42 | 95 | [M + H]+ | 2.73 | 219.175 | |
| 1.06 | 248 | [M + H]+ | 2.76 | 237.185 | |
| 1.09 | 255 | [M + H]+ | 2.77 | 261.183 | |
| 1.40 | 92 | [M + H]+ | 2.89 | 511.340 | |
| 1.11 | 330 | [M + H]+ | 3.05 | 272.259 | |
| 1.17 | 412 | [M + H]+ | 3.67 | 359.030 | |
| 1.26 | 93 | [M + H]+ | 3.73 | 359.030 | |
| 1.09 | 75 | [M + H]+ | 4.06 | 711.131 | |
| 1.00 | 367 | [M + H]+ | 4.95 | 359.030 | 358.368, 358.309, 342.310, 341.307, 285.279, 267.271, 136.007, 135.003, 123.117, 109.102 |
| 1.07 | 194 | [M + H]+ | 5.00 | 359.030 | |
| 1.04 | 61 | [M + H]+ | 5.45 | 983.202 | |
| - | - | [M − H]- | - | - | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Razali, M.T.A.; Zainal, Z.A.; Maulidiani, M.; Shaari, K.; Zamri, Z.; Mohd Idrus, M.Z.; Khatib, A.; Abas, F.; Ling, Y.S.; Rui, L.L.; et al. Classification of Raw Stingless Bee Honeys by Bee Species Origins Using the NMR- and LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Approach. Molecules 2018, 23, 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092160
Razali MTA, Zainal ZA, Maulidiani M, Shaari K, Zamri Z, Mohd Idrus MZ, Khatib A, Abas F, Ling YS, Rui LL, et al. Classification of Raw Stingless Bee Honeys by Bee Species Origins Using the NMR- and LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Approach. Molecules. 2018; 23(9):2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092160
Chicago/Turabian StyleRazali, Muhammad Taufiq Atsifa, Zaim Akmal Zainal, M. Maulidiani, Khozirah Shaari, Zulkifli Zamri, Mohd Zainuri Mohd Idrus, Alfi Khatib, Faridah Abas, Yee Soon Ling, Lim Leong Rui, and et al. 2018. "Classification of Raw Stingless Bee Honeys by Bee Species Origins Using the NMR- and LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Approach" Molecules 23, no. 9: 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092160
APA StyleRazali, M. T. A., Zainal, Z. A., Maulidiani, M., Shaari, K., Zamri, Z., Mohd Idrus, M. Z., Khatib, A., Abas, F., Ling, Y. S., Rui, L. L., & Ismail, I. S. (2018). Classification of Raw Stingless Bee Honeys by Bee Species Origins Using the NMR- and LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Approach. Molecules, 23(9), 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092160





