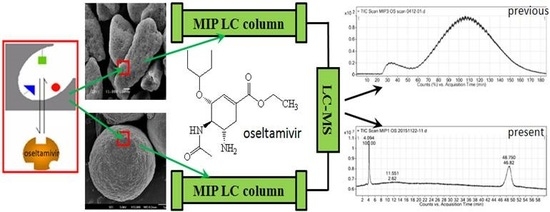
Preparation and Evaluation of Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Silica Gel as Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
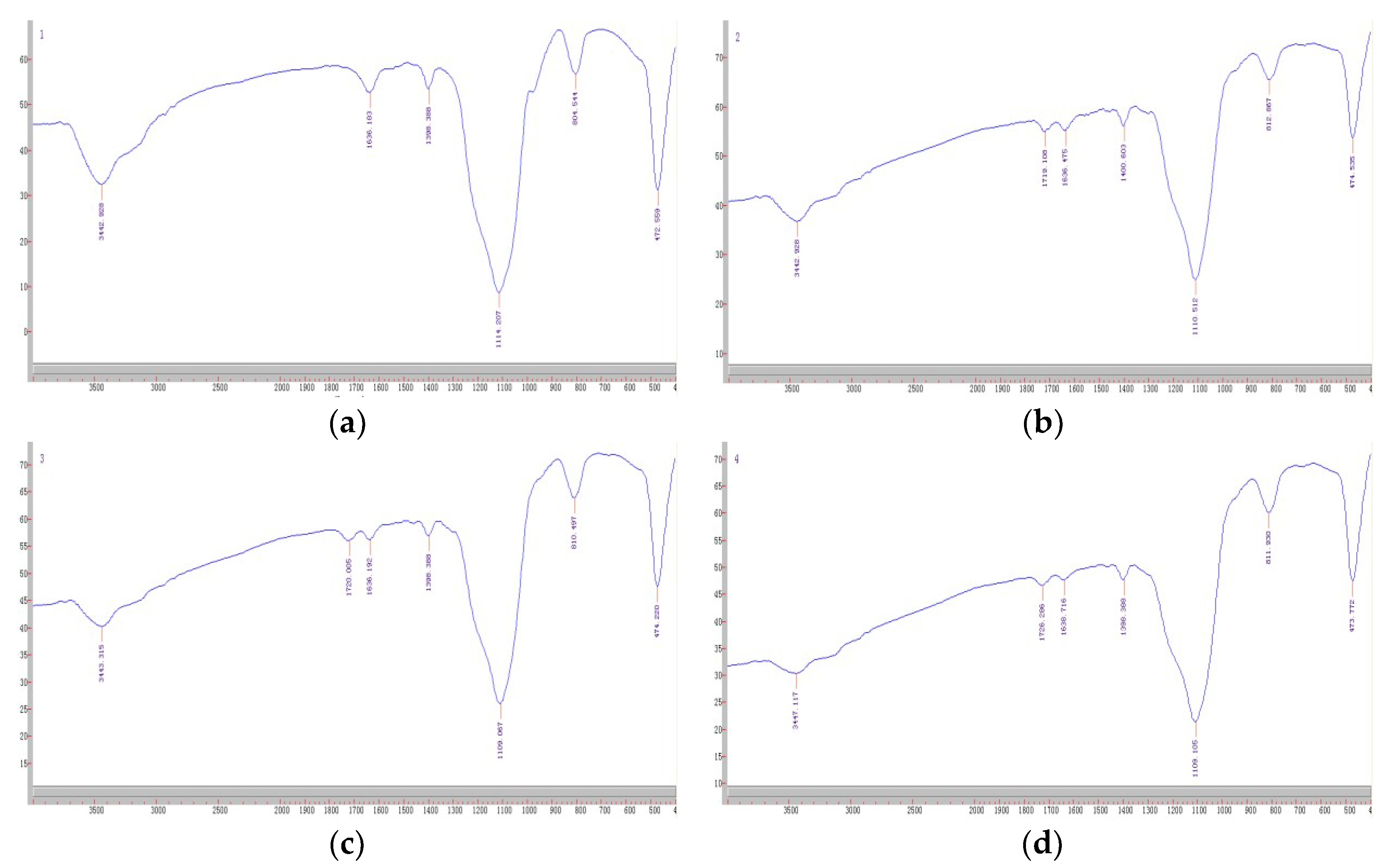
2.1. Derivatization, Polymer Synthesis and Characterization
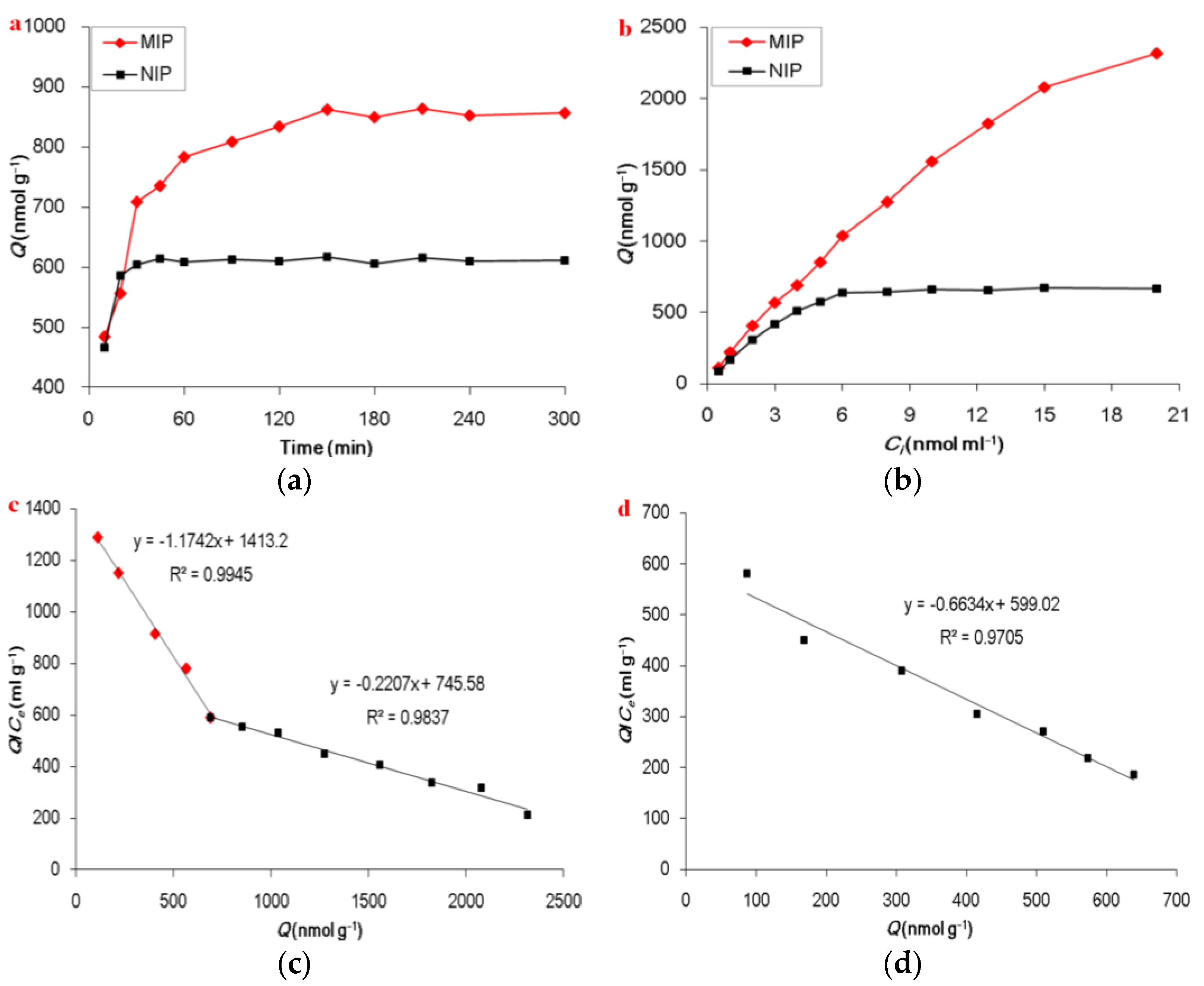
2.2. Adsorption Experiments
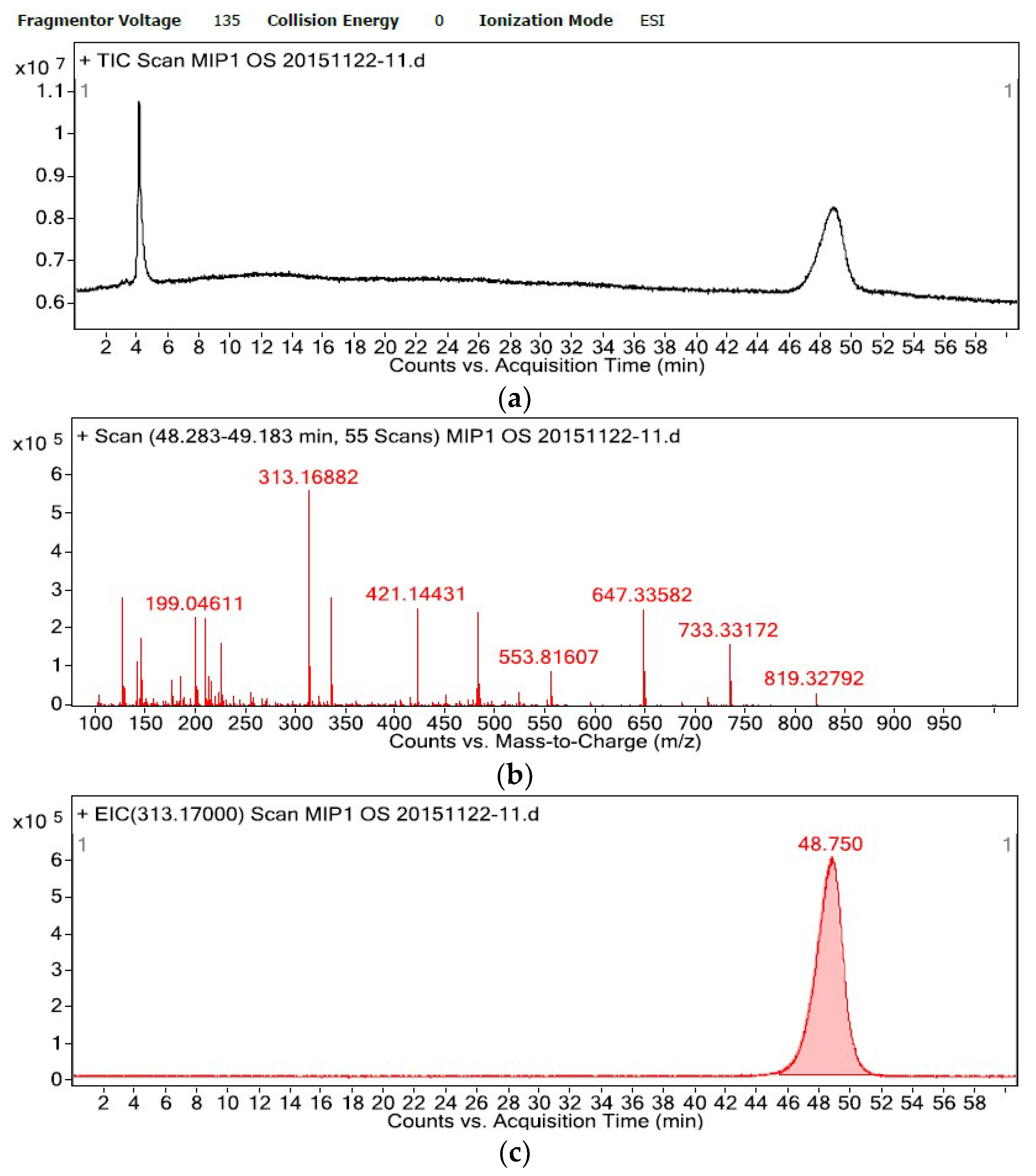
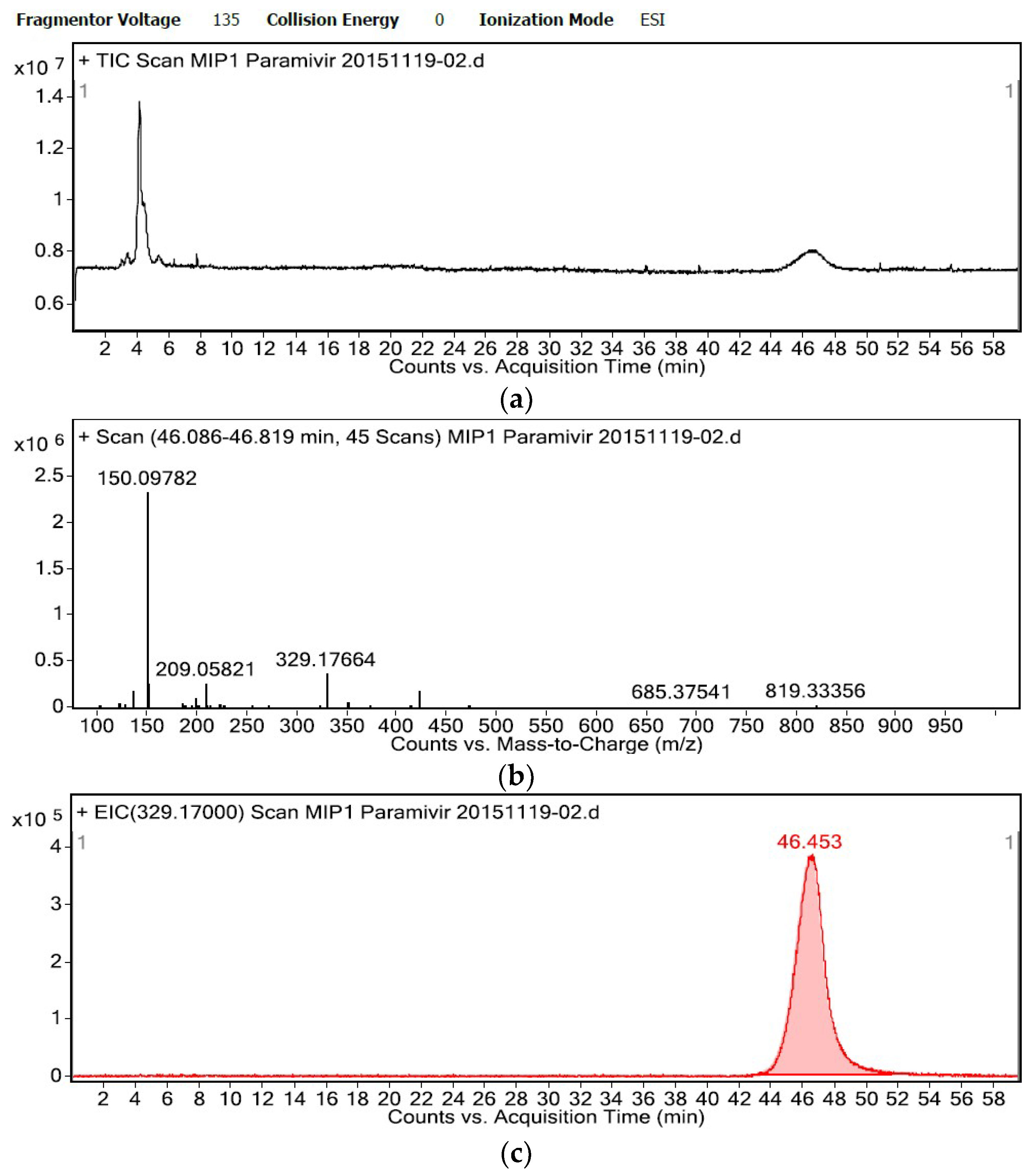
2.3. Specific Affinity of the OSMIP@silica Gel LC Column
3. Experimental
3.1. Reagents and Solvents
3.2. Standard Solutions
3.3. Equipment
3.4. Preparation of MIP
3.4.1. KH570@silica Gel [19]
3.4.2. OSMIP@silica Gel
3.5. Characterization
3.6. Adsorption Experiments
3.7. Specific Affinity of the OSMIP@silica Gel LC Column
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rathbone, D.L. Molecularly imprinted polymers in the drug discovery process. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1854–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nostrum, C.F. Molecular imprinting: A new tool for drug innovation. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2005, 2, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X. New concepts and approaches for drug discovery based on traditional Chinese medicine. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2006, 3, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers as antibody and receptor mimics for assays, sensors and drug discovery. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Pang, W.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Hu, J. A target analogue imprinted polymer for the recognition of antiplatelet active ingredients in Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae by LC/MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 58, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, X. Application of a molecularly imprinted polymer for the effective recognition of different anti-epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6381–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, N.A.; Paisner, D.A.; Huryn, D.; Shea, K.J. Screening of 5-HT(1A) Receptor Antagonists using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Cai, X. Optimization of polymerization parameters for the sorption of oseltamivir onto molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 3665–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, B. A Non-Biological Method for Screening Active Components against Influenza Virus from Traditional Chinese Medicine by Coupling a LC Column with Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. PLoS ONE 2013, 12, e84458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoravi, S.; Olsson, G.D.; Karlsson, B.C.G.; Bexborn, F.; Abghoui, Y.; Hussain, J.; Wiklander, J.G.; Nicholls, I.A. In silico screening of molecular imprinting prepolymerization systems: Oseltamivir selective polymers through full-system molecular dynamics-based studies. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 4210–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, P.; Zhao, J.; Peng, Y.; Du, S.; Zhang, Z. Molecularly imprinted layer-coated monodisperse spherical silica microparticles toward affinity-enrichment of isoflavonoid glycosides from Radix puerariae. Analyst 2012, 137, 2891–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Luo, L.; Yao, S. Preparation of l-phenylalanine imprinted polymer based on monodisperse hybrid silica microsphere and its application on chiral separation of phenylalanine racemates as HPLC stationary phase. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 87, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordel, S.; Chapuis-Hugon, F.; Eudes, V.; Pichon, V. Selective extraction of nitroaromatic explosives by using molecularly imprinted silica sorbents. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordel-Madeleine, S.; Eudes, V.; Pichon, V. Identification of the nitroaromatic explosives in post-blast samples by online solid phase extraction using molecularly imprinted silica sorbent coupled with reversed-phase chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5237–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhong, H.; Peng, A.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z. Rapid detection of malachite green in fish based on CdTe quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted silica. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Peter, A.G.C.; Mosbach, K. Molecular imprinting on microgel spheres. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 435, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, L.H.; Deng, Q.Y. Preparation of Imprinted Polymer with Theophylline on Silica Surface and Its Characteristics. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2005, 44, 49–53. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chrzanowska, A.M.; Poliwoda, A.; Wieczorek, P.P. Surface molecularly imprinted silica for selective solid-phase extraction of biochanin A, daidzein and genistein from urine samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1392, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kang, Y.F.; Wu, W.H.; Duan, W.P.; Kang, J.X.; Xie, J. Preparation of imprinted polymer with Cu2+ ions on silica surface and its characteristics. Chem. Res. Appl. 2012, 24, 873–878. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Xie, C.; Guan, G.; Wang, D. A surface functional monomer-directing strategy for highly dense imprinting of TNT at surface of silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7859–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.R.; Datta, P.K.; Sarkar, M. Sorption recovery of metal ions using silica gel modified with salicylaldoxime. Talanta 1996, 43, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, Y. Preparation of magnetic indole-3-acetic acid imprinted polymer beads with 4-vinylpyridine and β-cyclodextrin as binary monomer via microwave heating initiated polymerization and their application to trace analysis of auxins in plant tissues. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7337–7344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yuan, L.; Ding, M.; Wang, S.; Ren, F.; Zhang, J.; Du, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. The study of core–shell molecularly imprinted polymers of 17β-estradiol on the surface of silica nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2791–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, A.; Findlay, P.; Renner, T.; Sellergren, B.; Swletlow, A. Analysis of nicotine and its oxidation products in nicotine chewing gum by a molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 3304–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.W.; Choi, S.H.; Huh, J.W.; Lim, C.M.; Koh, Y.; Hong, S.B. Peramivir is as effective as oral oseltamivir in the treatment of severe seasonal influenza. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, M.M.; Skoglund, E.W.; Ison, M.G. Peramivir: An intravenous neuraminidase inhibitor. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Climente, R.; Gomez-Caballero, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Garcia-Mutio, D.; Unceta, N.; Goicolea, M.A.; Barrio, R.J. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles grafted to porous silica as chiral selectors in liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1508, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Shin, Y.; Barnes, C.; Toth, L. Enhancement of uranyl adsorption capacity and selectivity on silica sol-gel glasses via molecular imprinting. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 2521–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds oseltamivir, peramivir trihydrate and quinocetone are available from the authors. |
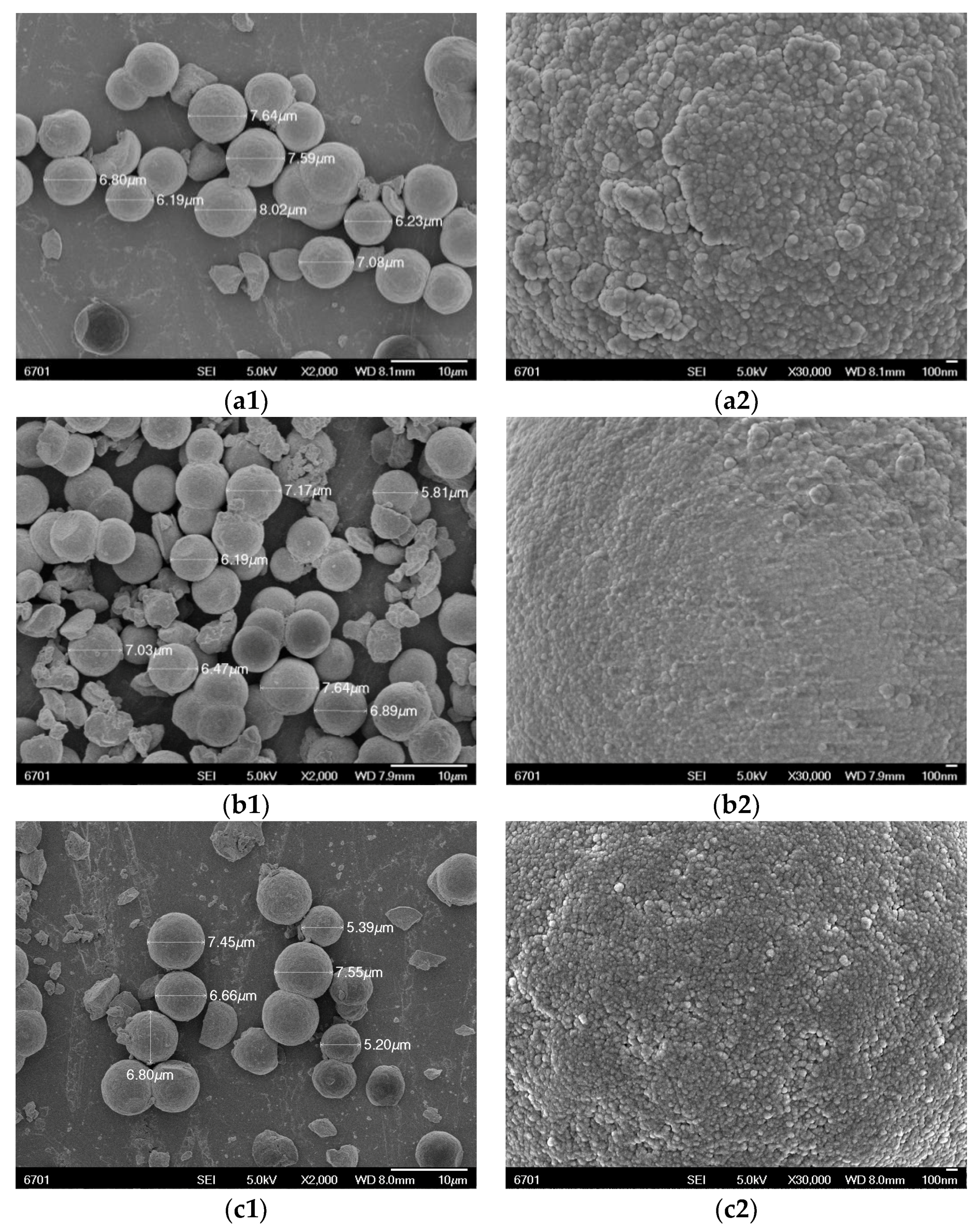

| Diameter of Particles (μm) | BET Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Average Pore Diameter (Å) | Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica gel | 5 | 400 | 70 | 0.70 |
| OSMIP@silica gel | 6~8 | 244.13 ± 47.94 | 47.69 ± 5.57 | 0.29 ± 0.04 |
| NIP@silica gel | 6~8 | 276.29 ± 55.29 | 46.22 ± 4.67 | 0.31 ± 0.03 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.-J.; Liu, X.-W.; Kong, X.-J.; Qin, Z.; Jiao, Z.-H.; Li, S.-H.; Li, J.-Y. Preparation and Evaluation of Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Silica Gel as Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase. Molecules 2018, 23, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081881
Yang Y-J, Liu X-W, Kong X-J, Qin Z, Jiao Z-H, Li S-H, Li J-Y. Preparation and Evaluation of Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Silica Gel as Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081881
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ya-Jun, Xi-Wang Liu, Xiao-Jun Kong, Zhe Qin, Zeng-Hua Jiao, Shi-Hong Li, and Jian-Yong Li. 2018. "Preparation and Evaluation of Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Silica Gel as Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase" Molecules 23, no. 8: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081881
APA StyleYang, Y.-J., Liu, X.-W., Kong, X.-J., Qin, Z., Jiao, Z.-H., Li, S.-H., & Li, J.-Y. (2018). Preparation and Evaluation of Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Silica Gel as Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase. Molecules, 23(8), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081881