TRPA1 Modulating C14 Polyacetylenes from the Iranian Endemic Plant Echinophora platyloba
Abstract
:1. Introduction
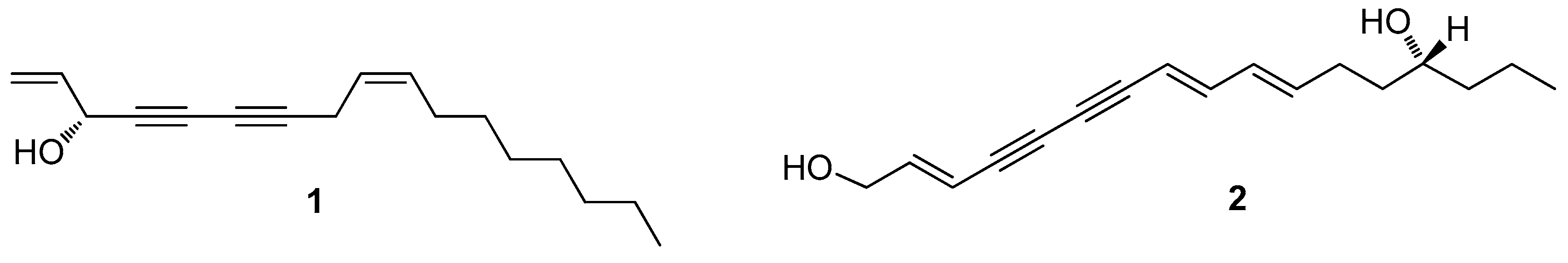
2. Results and Discussion
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
4.4. Echinophorin D (3)
4.5. Thermo-TRPs (TRPV1, TRPV2, TRPV3, TRPV4, TRPM8, TRPA1) Receptor Assays
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hosseini, Z.; Lorigooini, Z.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Shirmardi, H.A.; Solati, K. A review of botany and pharmacological effect and chemical composition of Echinophora species growing in Iran. Pharmacogn. Res. 2017, 9, 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Mirghazanfari, S.M.; Hosseinzadeh, L.; Shokoohinia, Y.; Aslany, M.; Kamali-Nejad, M. Acute and subchronic toxicological evaluation of Echinophora platyloba DC (Apiaceae) total extract in Wistar rats. Clinics 2012, 67, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokbulut, I.; Bilenler, T.; Karabulut, I. Determination of chemical composition, total phenolic, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities of Echinophora tenuifolia essential oil. Int. J. Food Prop. 2013, 16, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, M.; Taheri, P.; Pirbalouti, A.G.; Mehdizadeh, L. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of essential oil from the seed of Echinophora platyloba DC. Against phytopathogens fungi by two different screening methods. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri, Z.; Javadian, F.; Khammari, D.; Hassanshahian, M. Antifungal effects of the aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of Echinophora platyloba and Rosmarinus officinalis. Curr. Med. Mycol. 2016, 2, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahneh, F.Z.; Baradaran, B.; Majidi, J.; Babaloo, Z. Echinophora platyloba DC (Apiaceae) crude extract induces apoptosis in human prostate adenocarcinoma cells (PC 3). Biomed. J. 2014, 37, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shokoohinia, Y.; Rashidi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, L.; Jelodarian, Z. Quercetin-3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside, a dietary flavonoid, protects PC12 cells from H2O2-induced cytotoxicity through inhibition of reactive oxygen species. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazai, V.; Piri, K.H.; Nazeri, S.; Karamian, R.; Zamani, N. Free radical scavenging activity and phenolic and flavonoid contents of Echinophora platyloba DC. Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res. 2011, 1, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, D.W.; Polichuk, D.R.; Buist, P.H.; Ambrose, S.J.; Sasata, R.J.; Savile, C.K.; Ross, A.R.; Covello, P.S. Mechanistic study of an improbable reaction: Alkene dehydrogenation by the delta12 acetylenase of Crepis alpina. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10635–10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, R. Polyacetylenes from terrestrial plants and fungi: Recent phytochemical and biological advances. Fitoterapia 2015, 106, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawid, C.; Dunemann, F.; Schwab, W.; Nothnagel, T.; Hofmann, T. Bioactive C17-polyacetylenes in carrots (Daucus carota L.): Current knowledge and future perspectives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9211–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appendino, G.; Pollastro, F.; Verotta, L.; Ballero, M.; Romano, A.; Wyrembek, P.; Szczuraszek, K.; Mozrzymas, J.W.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Polyacetylenes from Sardinian Oenanthe fistulosa: A molecular clue to risus sardonicus. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurimoto, S.I.; Okasaka, M.; Kashiwada, Y.; Kodzhimatov, O.K.; Takaishi, Y. A C14-polyacetylenic lucoside with an α-pyrone moiety and four C10-polyacetylenic glucosides from Mediasia macrophylla. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelodarian, Z.; Shokoohinia, Y.; Rashidi, M.; Ghiasvand, N.; Hosseinzadeh, L.; Iranshahi, M. New polyacetylenes from Echinophora cinerea (Boiss.) Hedge et Lamond. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2256–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokoohinia, Y.; Chianese, G.; Appendino, G.; Di Marzo, V.; De Petrocellis, L.; Ghannadi, A.; Taghvayi, R.; Fattahian, K.; Soltani, R.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Some like it pungent and vile. TRPA1 as a molecular target for the malodorous vinyl disulfides from asafoetida. Fitoterapia 2013, 90, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, M.K.; Shokoohinia, Y.; Chianese, G.; Zolfaghari, B.; Appendino, G.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Prasad, R.; Di Pietro, A. Jatrophanes from Euphorbia squamosa as potent inhibitors of Candida albicans multidrug transporters. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2700–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valizadeh, H.; Mahmoodi, K.F.; Alizadeh, Z.; Bahadori, M.B. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Secondary Metabolites from Echinophora platyloba DC from Iran. J. Med. Plants 2014, 13, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Appendino, G.; Minassi, A.; Pagani, A.; Ech-Chahad, A. The role of natural products in the ligand deorphanization of TRP Channels. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babudri, F.; Fiandanese, V.; Marchese, G.; Punzi, A. Novel synthetic approach to (S)-coriolic acid. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montell, C.; Birnbaumer, L.; Flockerzi, V. The TRP channels, a remarkably functional family. Cell 2002, 108, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, P.G.; Preti, D.; Materazzi, S.; Geppetti, P. Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) channel as emerging target for novel analgesics and anti-inflammatory agents. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5085–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, I.; Lewis, R.J. Natural product ligands of TRP channels. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 704, 41–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Autelitano, A.; Minassi, A.; Pagani, A.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Appendino, G. The reaction of cinnamaldehyde and cinnam(o)yl derivatives with thiols. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, D.M.; Siemens, J.; Glazer, J.M.; Tsuruda, P.R.; Basbaum, A.I.; Stucky, C.L.; Jordt, S.E.; Julius, D. The menthol receptor TRPM8 is the principal detector of environmental cold. Nature 2007, 448, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avonto, C.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Pollastro, F.; Minassi, A.; Di Marzo, V.; De Petrocellis, L.; Appendino, G. An NMR spectroscopic method to identify and classify thiol-trapping agents: Revival of Michael acceptors for drug discovery? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, G.; Fattorusso, E.; Putra, M.Y.; Calcinai, B.; Bavestrello, G.; Schiano Moriello, A.; De Petrocellis, L.; Di Marzo, V.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Leucettamols, Bifunctionalized Marine Sphingoids, Act as Modulators of TRPA1 and TRPM8 Channels. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2435–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Sakuma, S.; Komatsu, S.; Sato, D.; Nishida, H.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Baba, K.; Fujita, T. Inhibition of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase activity in rabbit gastric antral mucosa by panaxynol isolated from oriental medicines. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1998, 50, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 3–5 are available from the authors. |
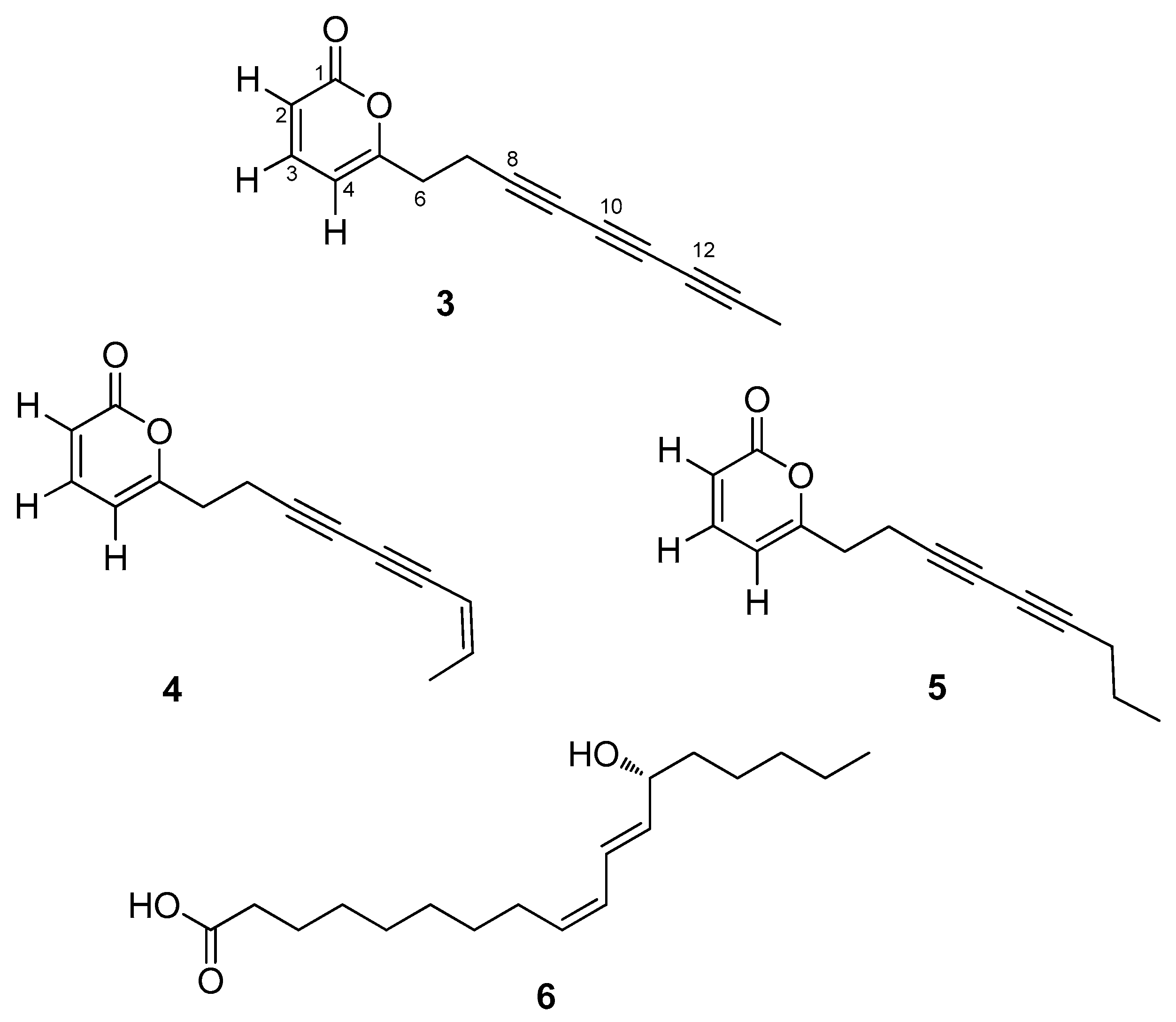
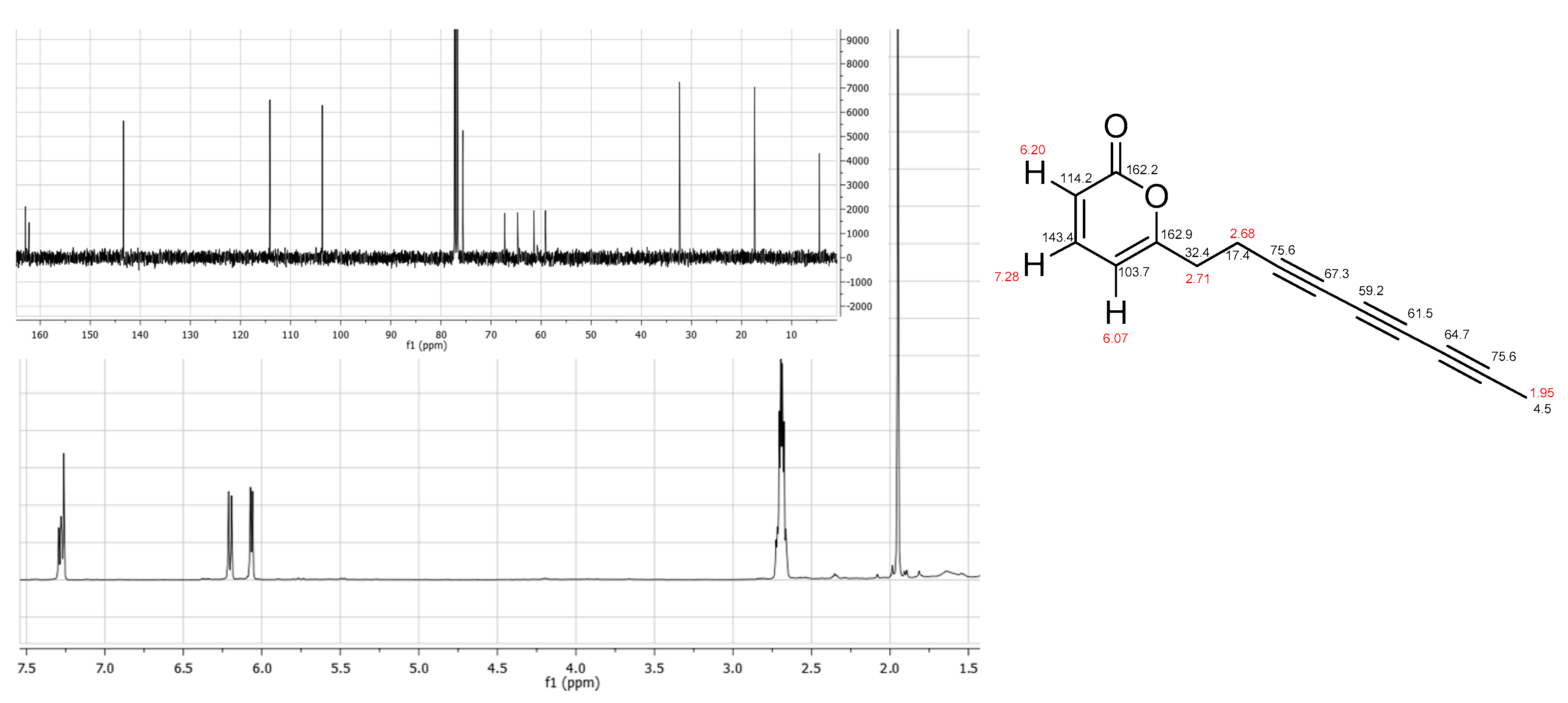
| Pos. | δH, Mult., J in Hz | δH, Mult. |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 162.2, C | |
| 2 | 6.20, d, 9.2 | 114.2, CH |
| 3 | 7.28, dd, 9.2, 6.8 | 143.4, CH |
| 4 | 6.07, d, 6.8 | 103.7, CH |
| 5 | 162.9, C | |
| 6 | 2.71, m | 32.4, CH2 |
| 7 | 2.68, m | 17.4, CH2 |
| 8 | 75.6, C | |
| 9 | 67.3, C | |
| 10 | 59.2, C | |
| 11 | 61.5, C | |
| 12 | 64.7, C | |
| 13 | 75.6, C | |
| 14 | 1.95, s | 4.5, CH3 |
| Compounds | Efficacy a | Potency EC50 μM | IC50 inh TRPA1 μM (AITC 100 μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Echinophorin D (3) | 51.7 ± 1.3 | 30.9 ± 2.8 | 87.0 ± 1.5 |
| Echinophorin B (4) | 82.0 ± 2.8 | 25.0 ± 3.0 | 37.2 ± 0.8 |
| Echinophorin A (5) | 81.0 ± 3.3 | 20.3 ± 3.2 | 45.7 ± 3.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chianese, G.; Sirignano, C.; Shokoohinia, Y.; Mohammadi, Z.; Bazvandi, L.; Jafari, F.; Jalilian, F.; Schiano Moriello, A.; De Petrocellis, L.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; et al. TRPA1 Modulating C14 Polyacetylenes from the Iranian Endemic Plant Echinophora platyloba. Molecules 2018, 23, 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071750
Chianese G, Sirignano C, Shokoohinia Y, Mohammadi Z, Bazvandi L, Jafari F, Jalilian F, Schiano Moriello A, De Petrocellis L, Taglialatela-Scafati O, et al. TRPA1 Modulating C14 Polyacetylenes from the Iranian Endemic Plant Echinophora platyloba. Molecules. 2018; 23(7):1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071750
Chicago/Turabian StyleChianese, Giuseppina, Carmina Sirignano, Yalda Shokoohinia, Zeynab Mohammadi, Leili Bazvandi, Fataneh Jafari, Fereshteh Jalilian, Aniello Schiano Moriello, Luciano De Petrocellis, Orazio Taglialatela-Scafati, and et al. 2018. "TRPA1 Modulating C14 Polyacetylenes from the Iranian Endemic Plant Echinophora platyloba" Molecules 23, no. 7: 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071750
APA StyleChianese, G., Sirignano, C., Shokoohinia, Y., Mohammadi, Z., Bazvandi, L., Jafari, F., Jalilian, F., Schiano Moriello, A., De Petrocellis, L., Taglialatela-Scafati, O., & Rigano, D. (2018). TRPA1 Modulating C14 Polyacetylenes from the Iranian Endemic Plant Echinophora platyloba. Molecules, 23(7), 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071750