Utilizing a Spiro Core with Acridine- and Phenothiazine-Based New Hole Transporting Materials for Highly Efficient Green Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
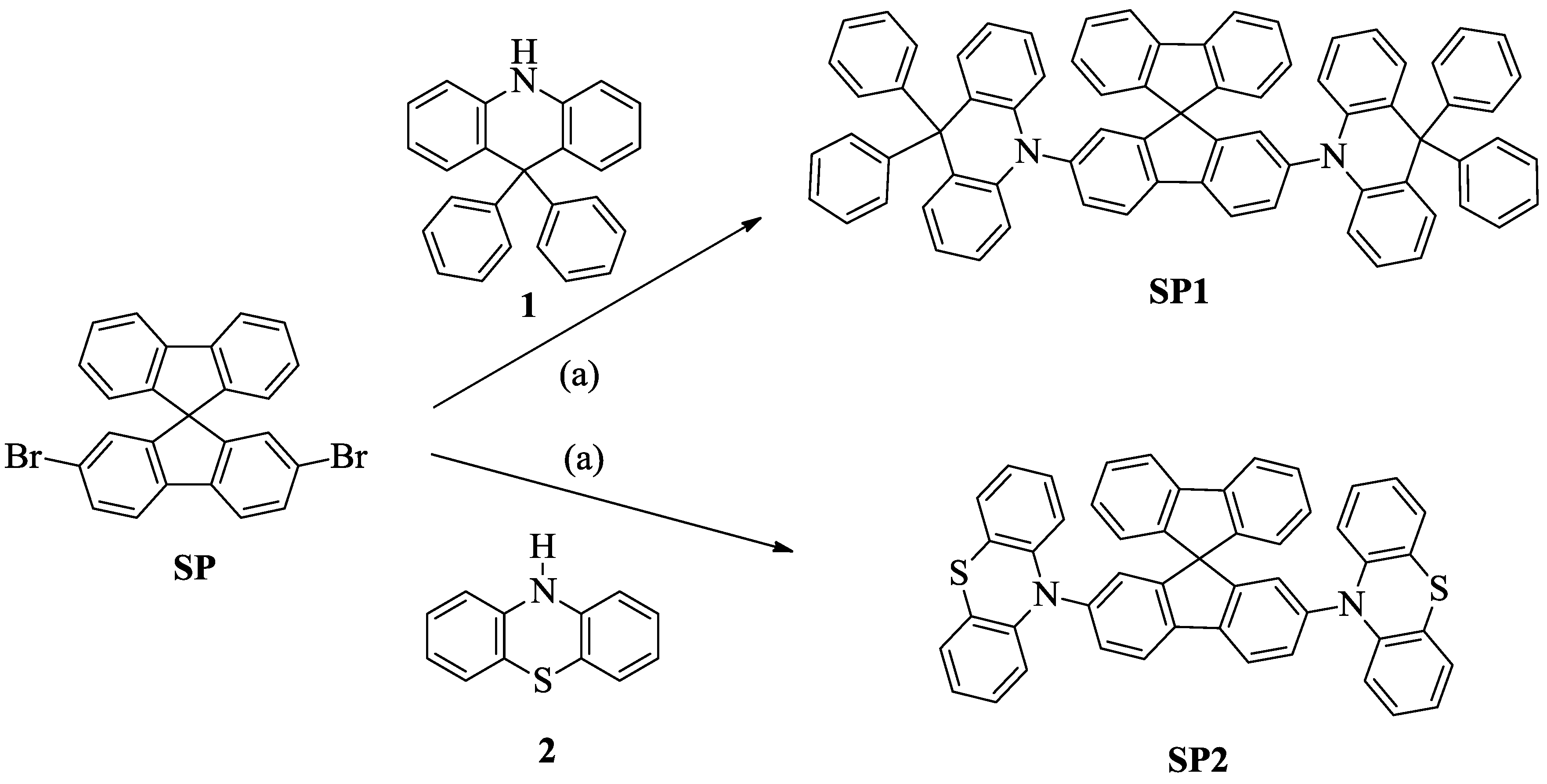
2.1. Synthesis
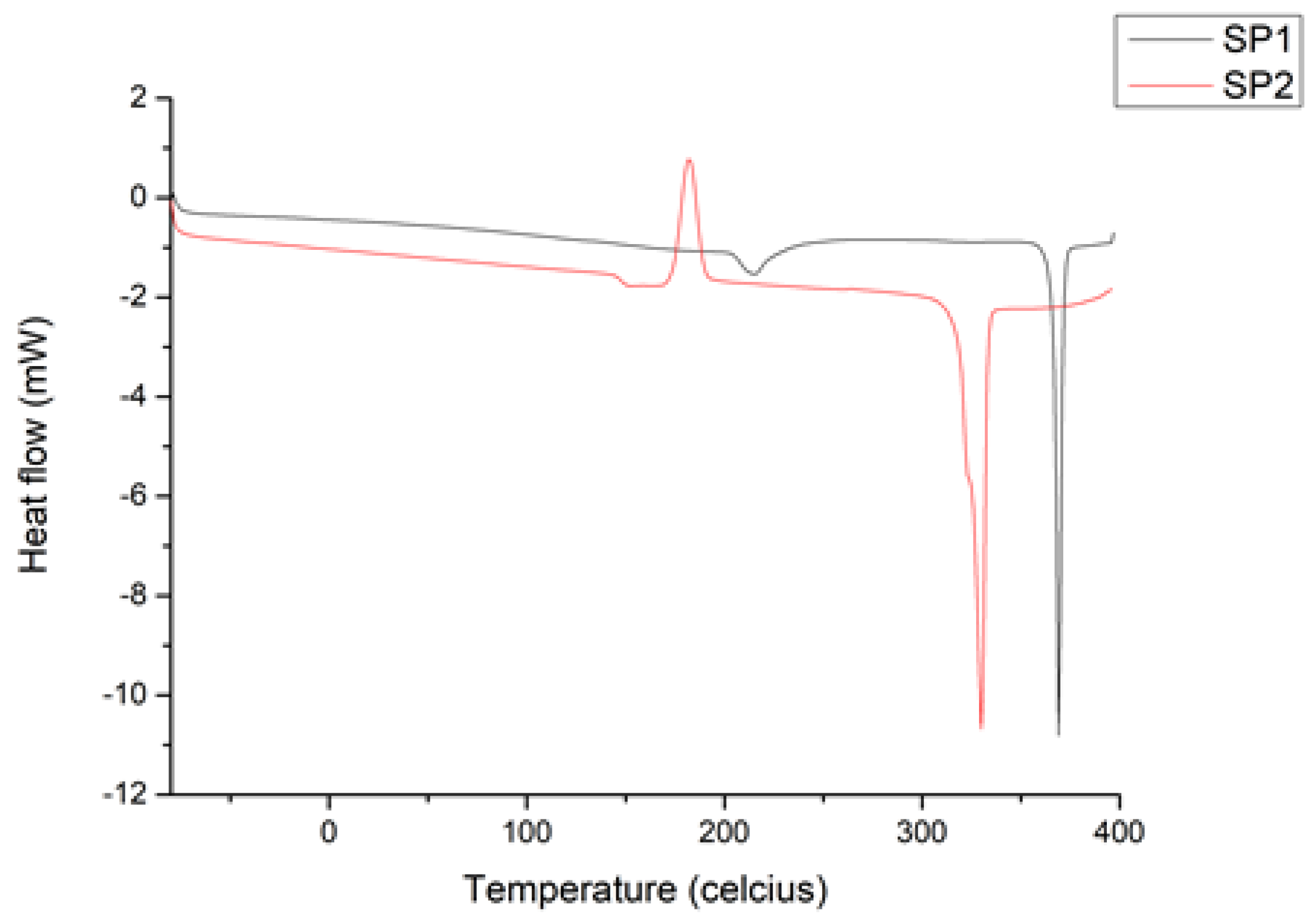
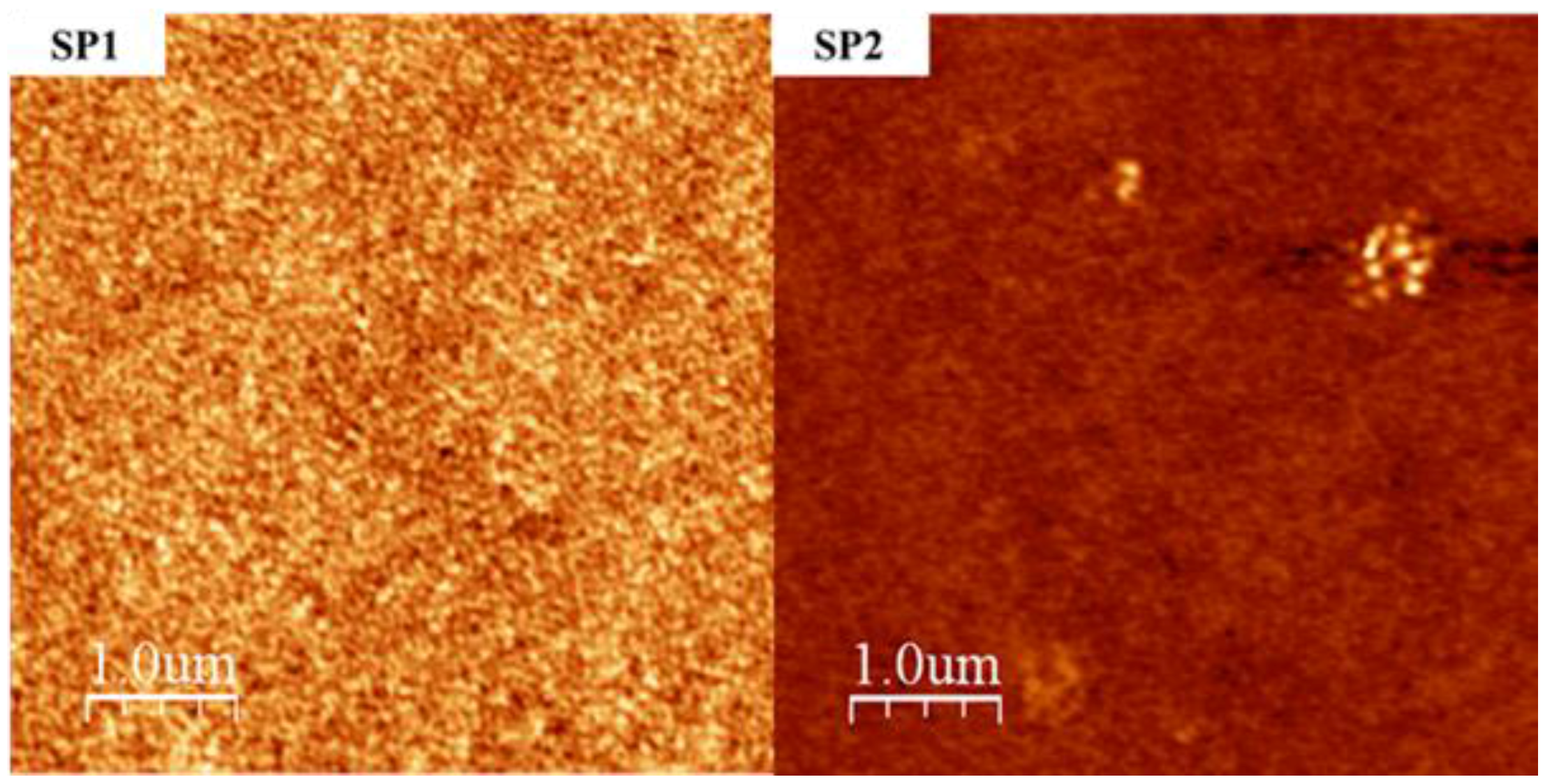
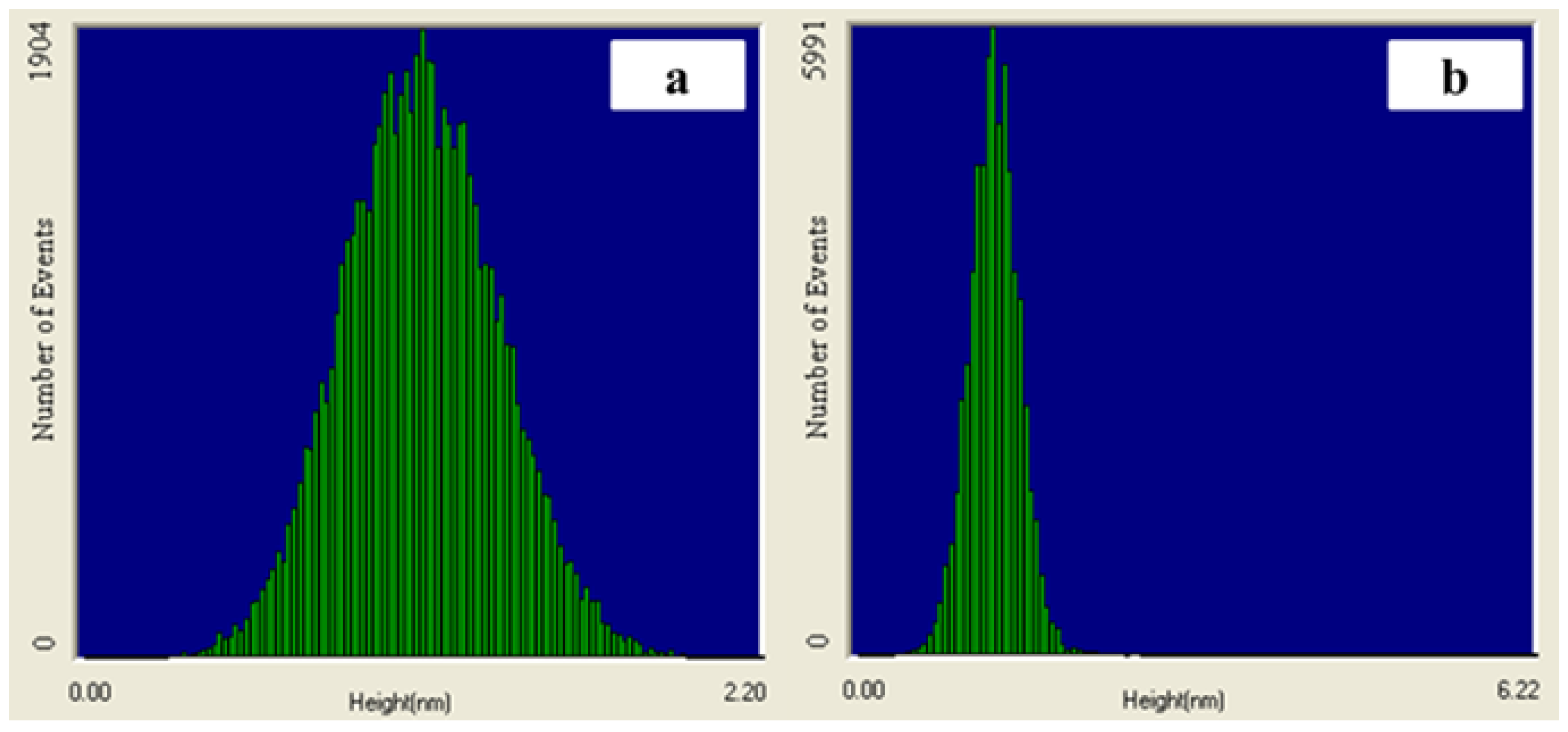
2.2. Thermal and Morphological Properties
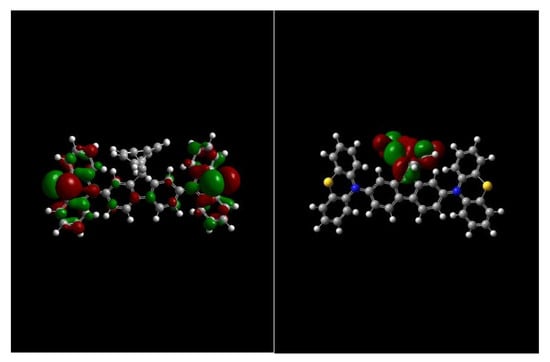
2.3. Photophysical and Electrochemical Properties
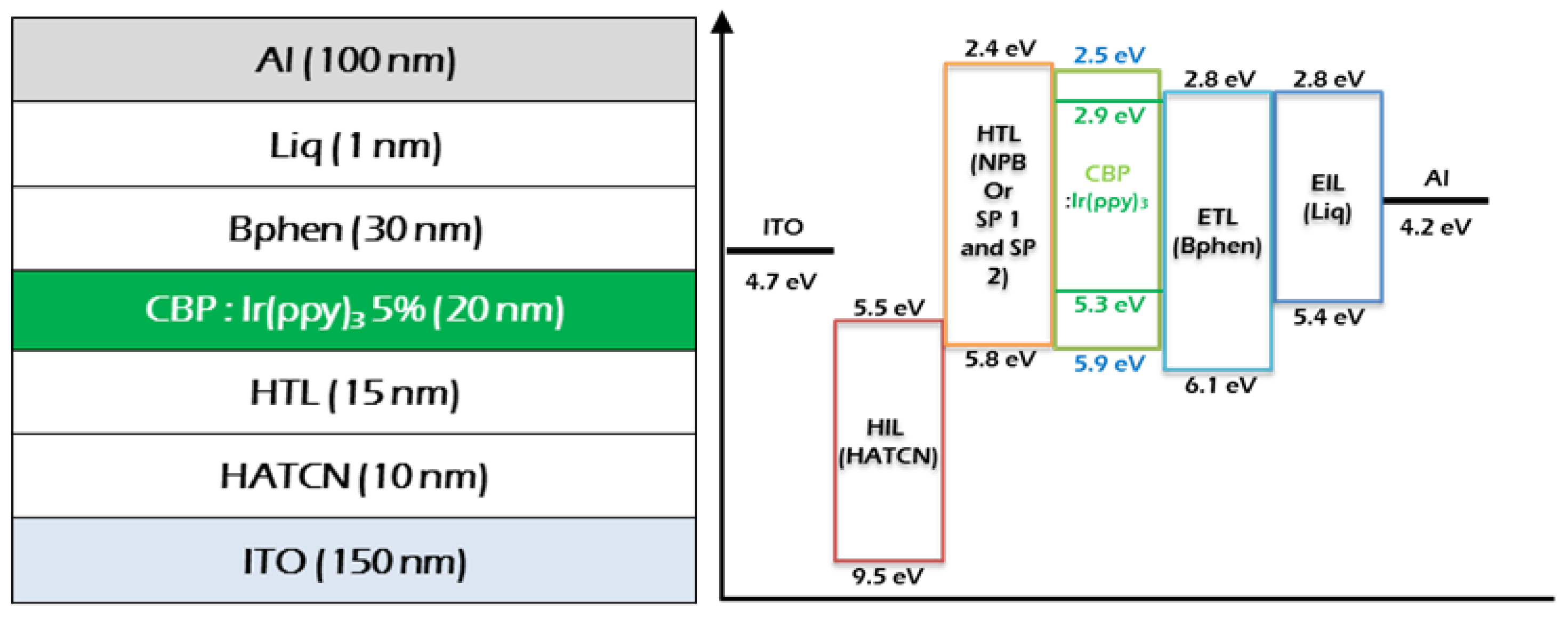
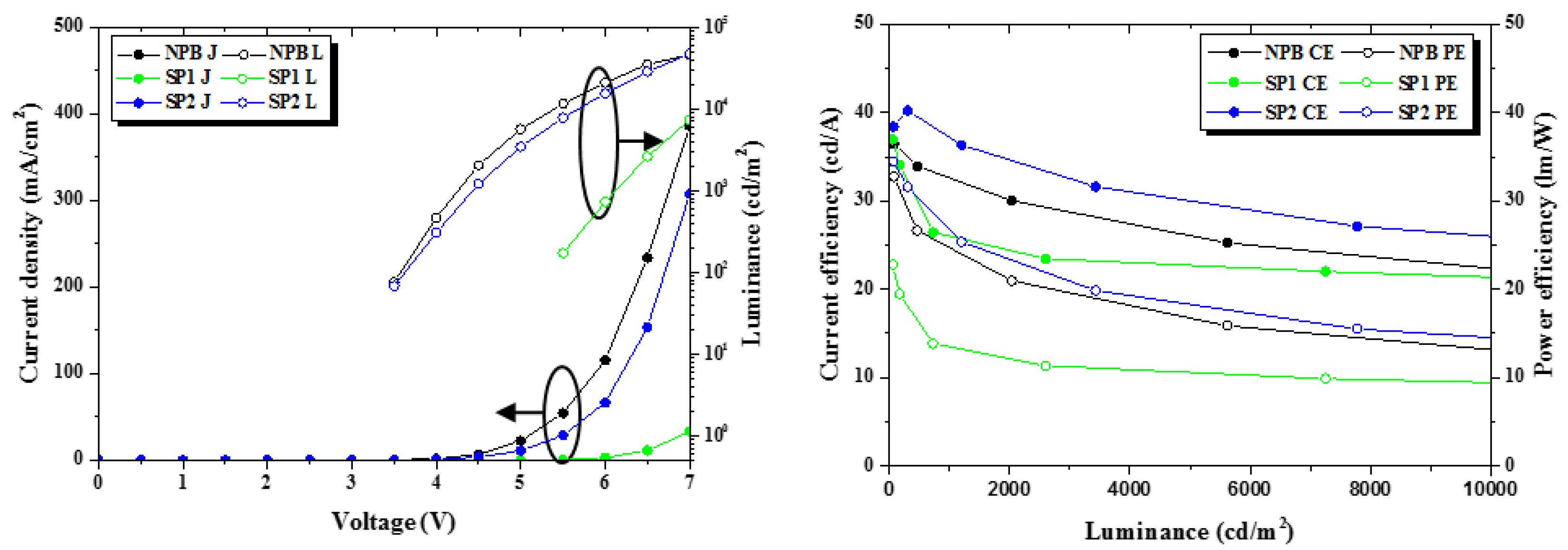
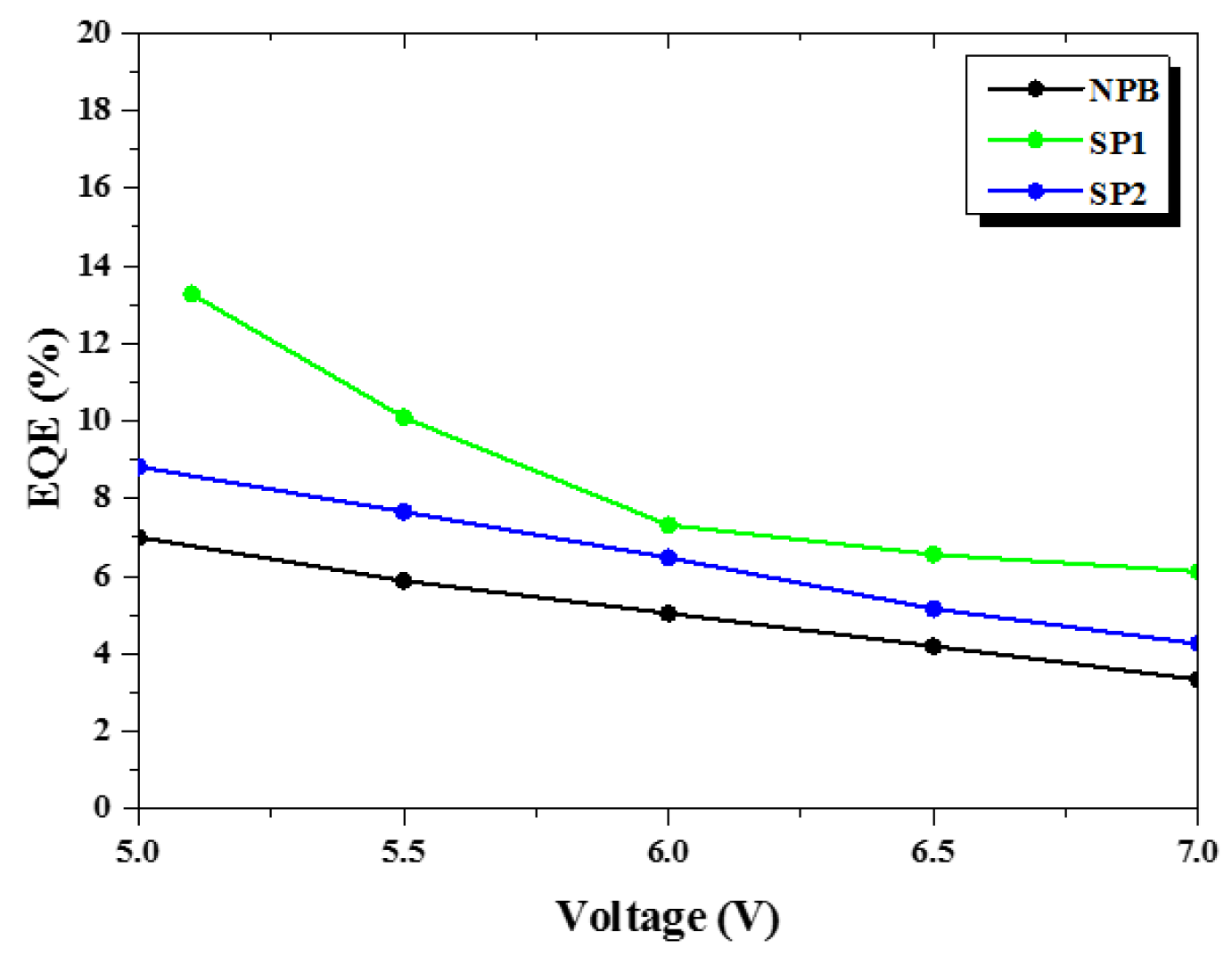
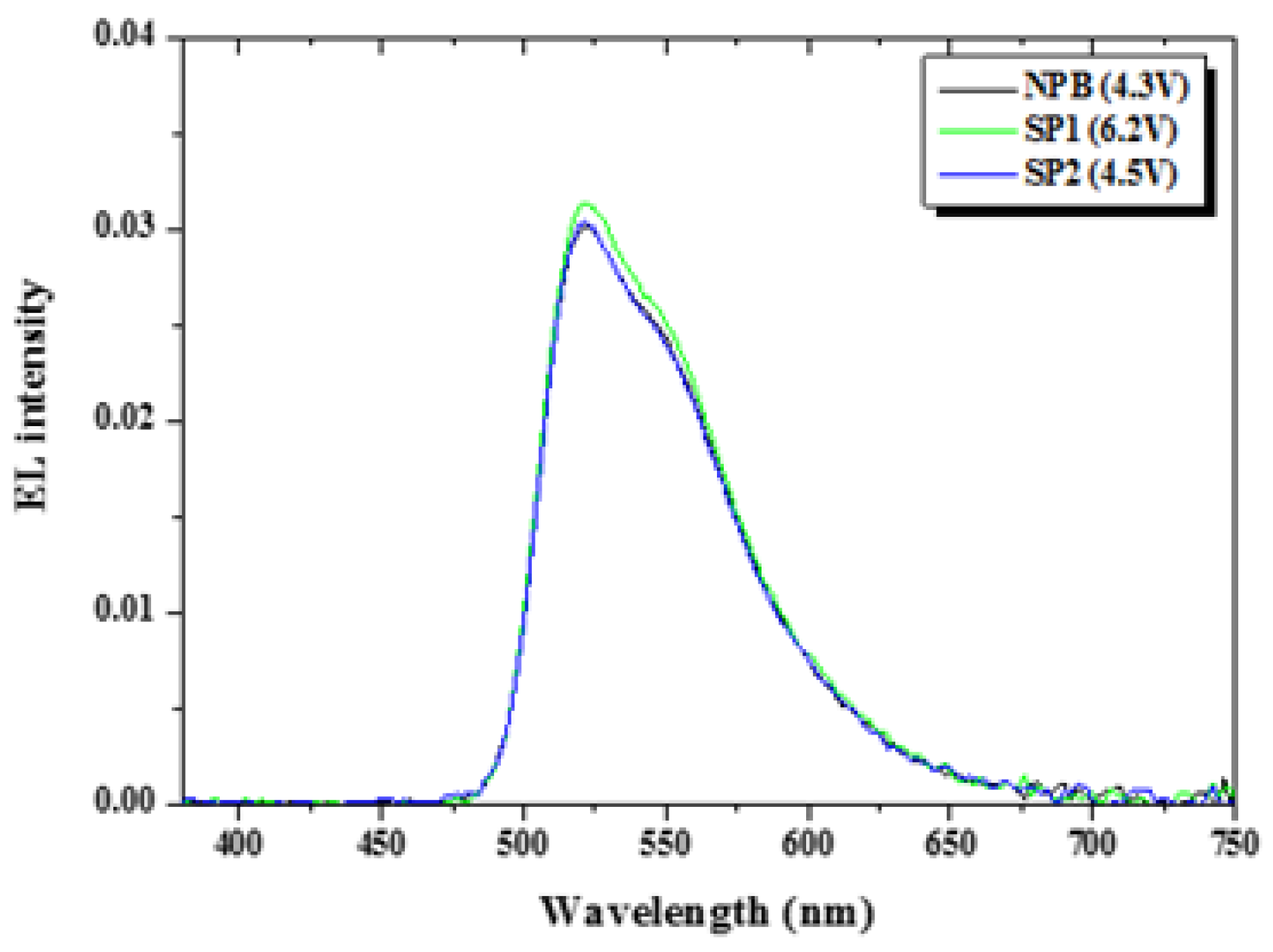
2.4. Device Characteristics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Synthetic Procedures
3.2.1. 2,7-bis(9,9-Diphenylacridin-10(9H)-yl)-9,9′-spirobi[fluorene] (SP1)
3.2.2. 2,7-di(10H-Phenothiazin-10-yl)-9,9′-spirobi[fluorene] (SP2)
3.3. OLED Fabrication and Characterization
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, L.; Zhang, M.; Xu, S.; Zhou, X.; Gao, X.; Shang, Y.; Wei, B. Cyclic arylamines functioning as advanced hole-transporting and emitting materials. Synth. Met. 2012, 162, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.W.; VanSlyke, S.A. Organic electroluminescent diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1987, 51, 913–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, S.R. The path to ubiquitous and low-cost organic electronic appliances on plastic. Nature 2004, 428, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Ye, T.; Ma, D.; Qin, J.; Yang, C. Star-shaped hexakis (9,9-dihexyl-9H-fluoren-2-yl) benzene end-capped with carbazole and diphenylamine units: solution-processable, high Tg hole-transporting materials for organic light-emitting devices. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23485–23491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hide, F.; DÍaz-GarcÍa, M.A.; Schwartz, B.J.; Heeger, A.J. New developments in the photonic applications of conjugated polymers. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 30, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.; Lyu, Y.Y.; Noh, S.; Lee, H.; Park, M.; Choi, B.; Lee, C. Hole transport materials with high glass transition temperatures for highly stable organic light-emitting diodes. Thin Solid Films. 2012, 520, 7157–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, C.; Nagai, K.; Tamoto, N. Molecular design of hole transport materials for obtaining high durability in organic electroluminescent diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 66, 2679–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koene, B.E.; Loy, D.E.; Thompson, M.E. Asymmetric triaryldiamines as thermally stable hole transporting layers for organic light-emitting devices. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 2235–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, D.F.; Burrows, P.E.; Forrest, S.R.; Koene, B.E.; Loy, D.E.; Thompson, M.E. Hole transporting materials with high glass transition temperatures for use in organic light-emitting devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 1998, 10, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaengthong, A.M.; Saengsuwan, S.; Jungsuttiwong, S.; Keawin, T.; Sudyoadsuk, T.; Promarak, V. Synthesis and characterization of high Tg carbazole-based amorphous hole-transporting materials for organic light-emitting devices. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 4749–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.; Popovic, Z.D.; Hu, N.X.; Hor, A.M.; Xu, G. Degradation mechanism of small molecule-based organic light-emitting devices. Science 1999, 283, 1900–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Fu, W.; Wang, D.; Liu, P.; Jiao, B.; Hao, Y. Stable amorphous bis(diarylamino) biphenyl derivatives as hole-transporting materials in OLEDs. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2013, 9, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Ye, T.; Yang, C.; Yang, D.; Zhu, M.; Zhong, C.; Ma, D. Star-Shaped Oligotriarylamines with Planarized Triphenylamine Core: Solution-Processable, High-Tg Hole-Injecting and Hole-Transporting Materials for Organic Light-Emitting Devices. Chem. Mater. 2010, 23, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Dong, Q.; Gou, L.; Su, J.H.; Huang, J. Novel hole transport materials based on N,N′-disubstituted-dihydrophenazine derivatives for electroluminescent diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 9858–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieliauskas, A.; Getautis, V.; Martynaitis, V.; Jankauskas, V.; Kamarauskas, E.; Krikštolaitytė, S.; Šačkus, A. Synthesis of electroactive hydrazones derived from carbazolyl-based 2-propenals for optoelectronics. Synth. Met. 2013, 179, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y. Thermally stable aromatic amine derivative with symmetrically substituted double spirobifluorene core as a hole transport material for green phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes. Thin Solid Films. 2012, 522, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhong, C.; Qin, J.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y. Multifunctional Fluorene-Based Oligomers with Novel Spiro-Annulated Triarylamine: Efficient, Stable Deep-Blue Electroluminescence, Good Hole Injection, and Transporting Materials with Very High Tg. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3987–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragi, T.P.; Fuhrmann-Lieker, T.; Salbeck, J. Comparison of charge-carrier transport in thin films of spiro-linked compounds and their corresponding parent compounds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragi, T.P.; Spehr, T.; Siebert, A.; Fuhrmann-Lieker, T.; Salbeck, J. Spiro compounds for organic optoelectronics. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 1011–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.L.; Hung, W.Y.; Hou, T.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Wong, K.T. Hole mobilities of 2,7-and 2,2′-disubstituted 9,9′-spirobifluorene-based triaryldiamines and their application as hole transport materials in OLEDs. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 6350–6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.J.; Dodda, R.; Wu, C.C.; Wu, F.I.; Liu, T.H.; Chen, H.H.; Shu, C.F. Spirobifluorene-linked bisanthracene: An efficient blue emitter with pronounced thermal stability. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.L.; Peng, Z.K.; Zhang, X.H.; Wang, P.F.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, S.T. Highly Efficient Non-Doped Blue Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Based on Fluorene Derivatives with High Thermal Stability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, F.; Wu, H.; Lv, Z.; Zou, D. Synthesis of spiro [fluorene-9,9′-xanthene] derivatives and their application as hole-transporting materials for organic light-emitting devices. Synth. Met. 2012, 162, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, C.H.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.; Cui, L.S.; Ji, S.J.; Liao, L.S. Spiro-annulated hole-transport material outperforms NPB with higher mobility and stability in organic light-emitting diodes. Dyes Pigment. 2014, 107, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usluer, O.; Demic, S.; Egbe, D.A.; Birckner, E.; Tozlu, C.; Pivrikas, A.; Sariciftci, N.S. Fluorene-Carbazole Dendrimers: Synthesis, Thermal, Photophysical and Electroluminescent Device Properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 4152–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usluer, Ö. New spirobifluorene-based hole-transporting semiconductors for electroluminescent devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 8098–8104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braveenth, R.; Bae, H.W.; Nguyen, Q.P.B.; Ko, H.M.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, H.J.; Chai, K.Y. Spirobifluorene core-based novel hole transporting materials for red phosphorescence OLEDs. Molecules 2017, 22, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.; Park, S.Y. Highly efficient and stable deep-blue emitting anthracene-derived molecular glass for versatile types of non-doped OLED applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufi, D.; Hosseinpanahi, F. The effect of film thickness on surface morphology of ITO thin films. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2013, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |



| HTMs | Tga (°C) | UV-VIS b (nm) | PL Max (nm) | HOMO (eV) | LUMO (eV) | Egc (eV) | ETd (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP1 | 215 | 395 | 438 | 5.86 | 2.72 | 3.14 | 2.83 |
| SP2 | 150 | 422 | 593 | 5.57 | 2.63 | 2.94 | 2.09 |
| Device Properties | NPB | SP1 | SP2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Turn-on voltage (V) | 3.4 a | 5.1 a | 3.5 a |
| Driving voltage (V) | 4.3 b | 6.2 b | 4.5 b |
| Current (mA) | 0.16 b | 0.20 b | 0.13 b |
| Current efficiency (cd/A) | 32.83 29.52 b | 36.98 24.88 b | 38.41 36.33 b |
| Power efficiency (lm/W) | 30.33 | 22.78 | 34.47 |
| EQE | 11.45% 8.19% b | 13.27% 6.87% b | 13.43% 10.27% b |
| CIE (x,y) | (0.33, 0.62) | (0.33, 0.63) | (0.33, 0.62) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braveenth, R.; Bae, I.-J.; Han, J.-H.; Qiong, W.; Seon, G.; Raagulan, K.; Yang, K.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, M.; Chai, K.Y. Utilizing a Spiro Core with Acridine- and Phenothiazine-Based New Hole Transporting Materials for Highly Efficient Green Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Molecules 2018, 23, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040713
Braveenth R, Bae I-J, Han J-H, Qiong W, Seon G, Raagulan K, Yang K, Park YH, Kim M, Chai KY. Utilizing a Spiro Core with Acridine- and Phenothiazine-Based New Hole Transporting Materials for Highly Efficient Green Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Molecules. 2018; 23(4):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040713
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraveenth, Ramanaskanda, Il-Ji Bae, Ji-Hun Han, Wu Qiong, Guk Seon, Kanthasamy Raagulan, Kihun Yang, Young Hee Park, Miyoung Kim, and Kyu Yun Chai. 2018. "Utilizing a Spiro Core with Acridine- and Phenothiazine-Based New Hole Transporting Materials for Highly Efficient Green Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes" Molecules 23, no. 4: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040713
APA StyleBraveenth, R., Bae, I.-J., Han, J.-H., Qiong, W., Seon, G., Raagulan, K., Yang, K., Park, Y. H., Kim, M., & Chai, K. Y. (2018). Utilizing a Spiro Core with Acridine- and Phenothiazine-Based New Hole Transporting Materials for Highly Efficient Green Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Molecules, 23(4), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040713