Shape Effects of Peptide Amphiphile Micelles for Targeting Monocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
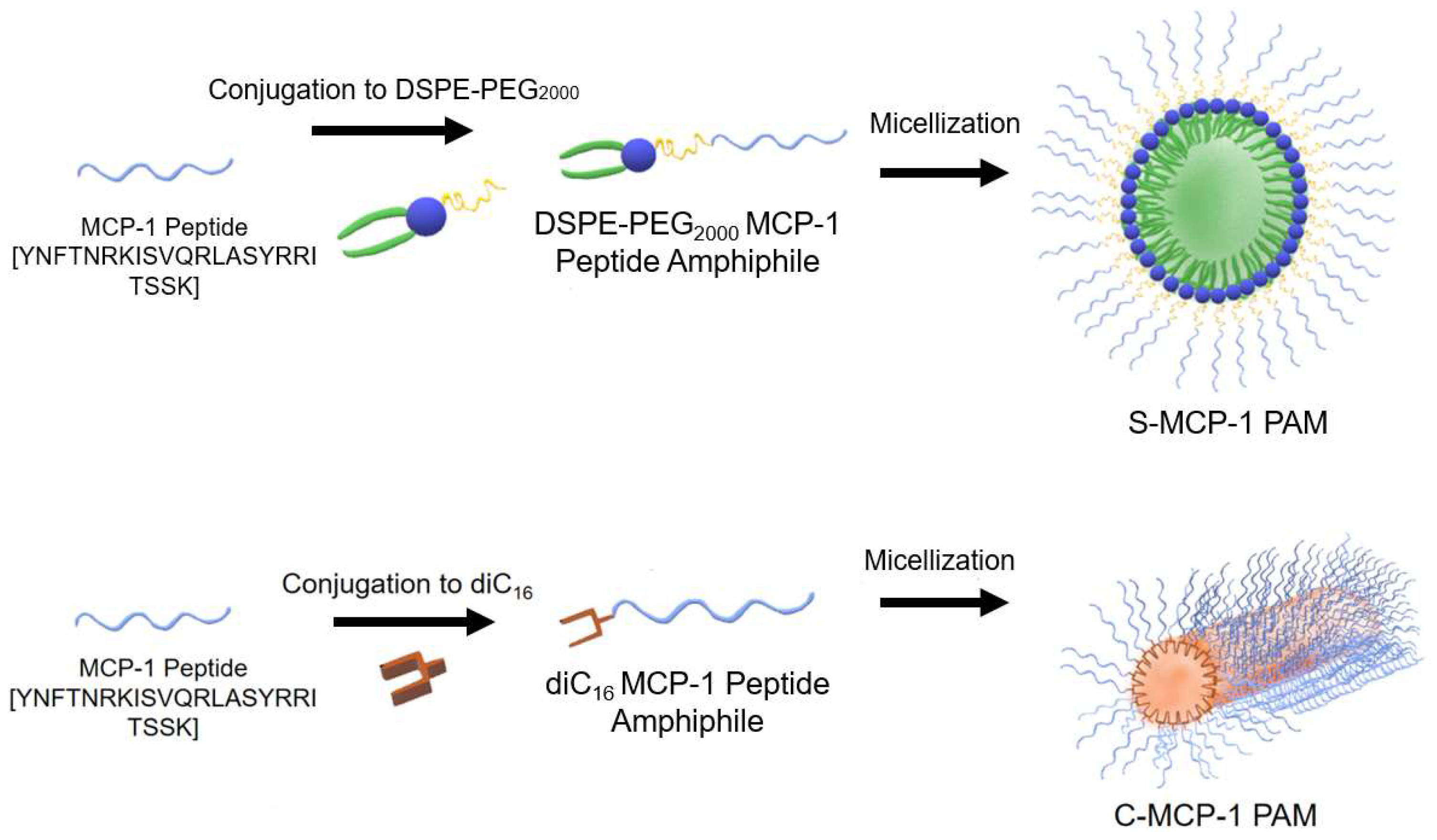
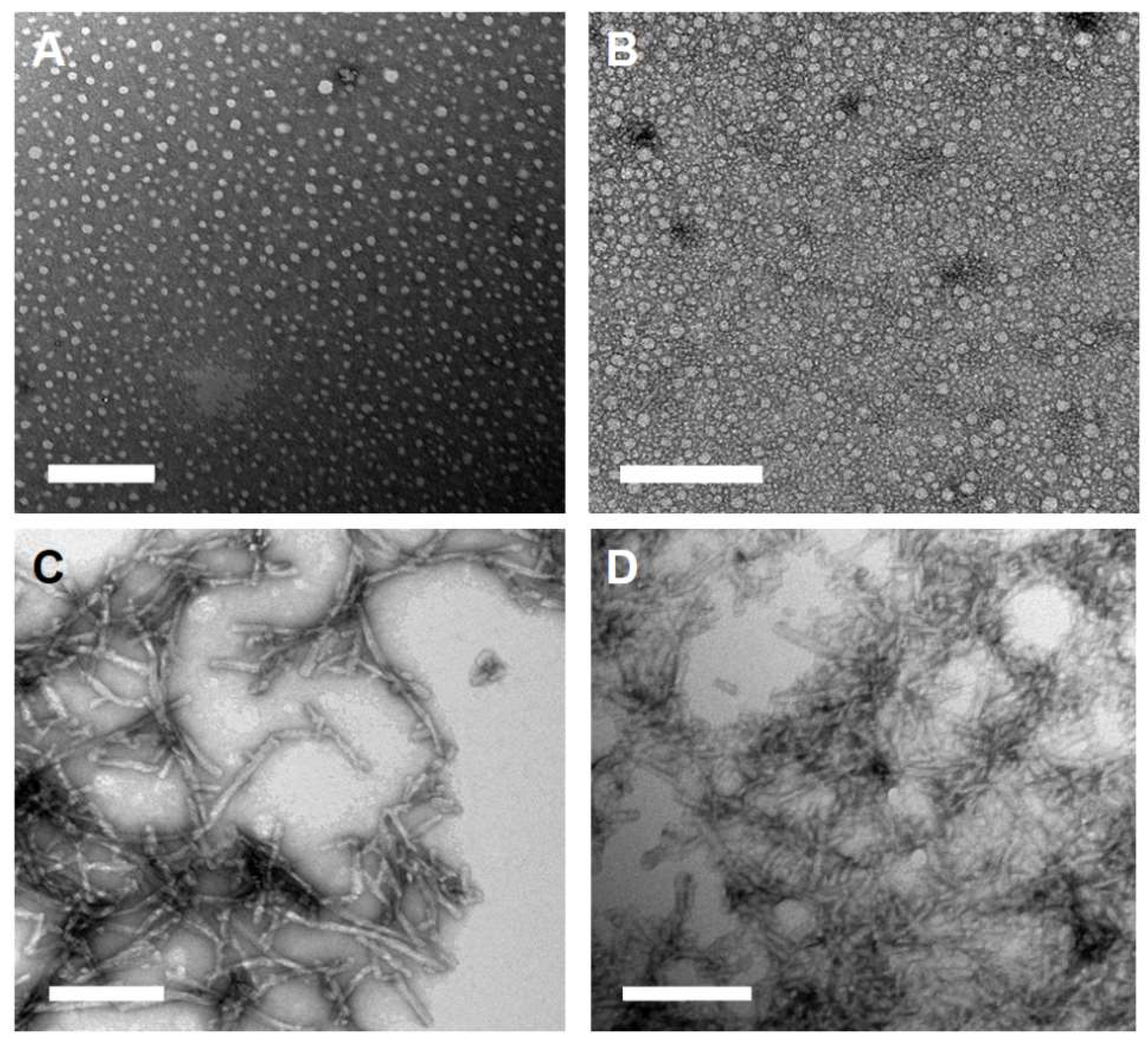
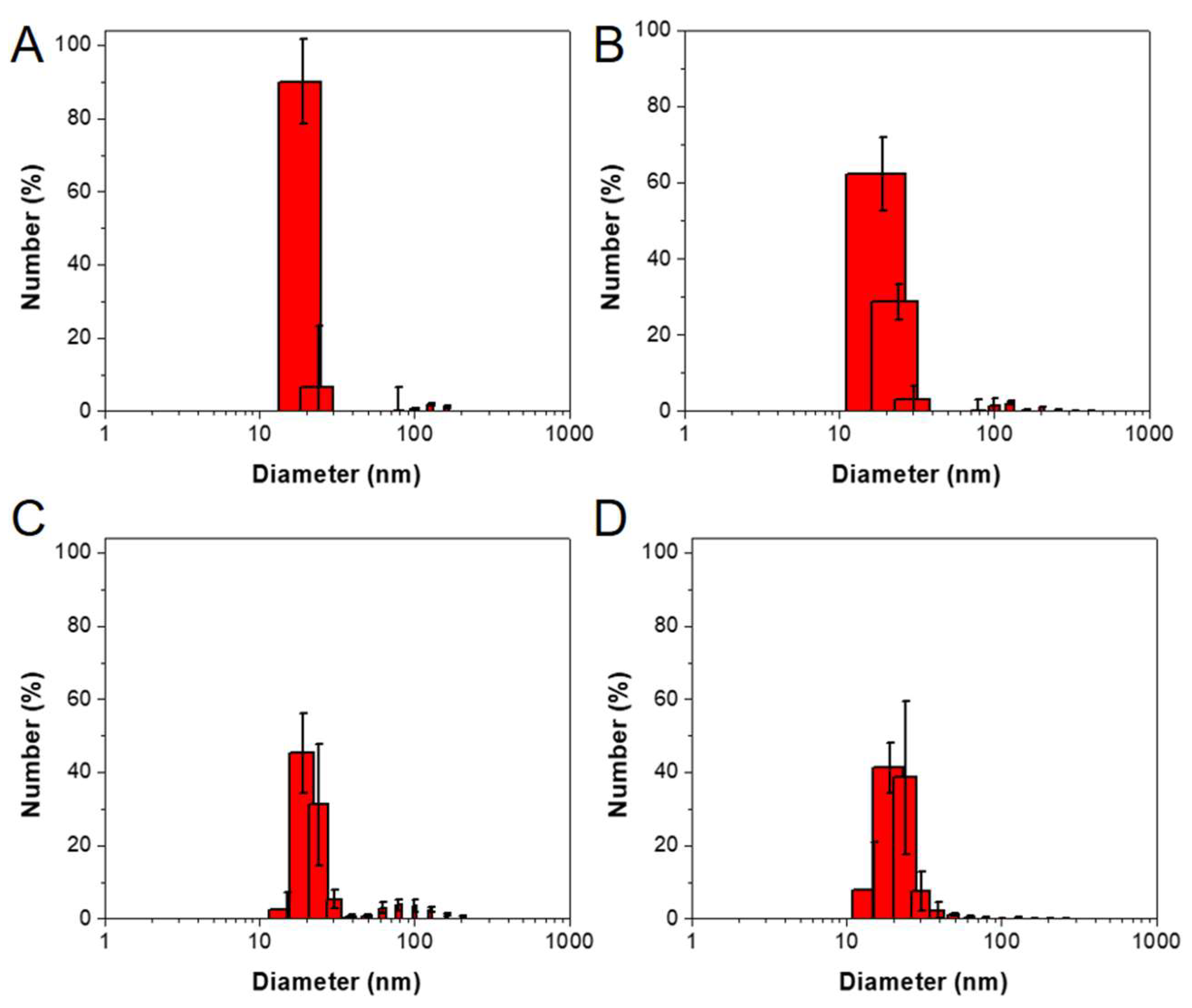
2.1. Peptide Amphiphile Micelle (PAM) Synthesis and Characterization
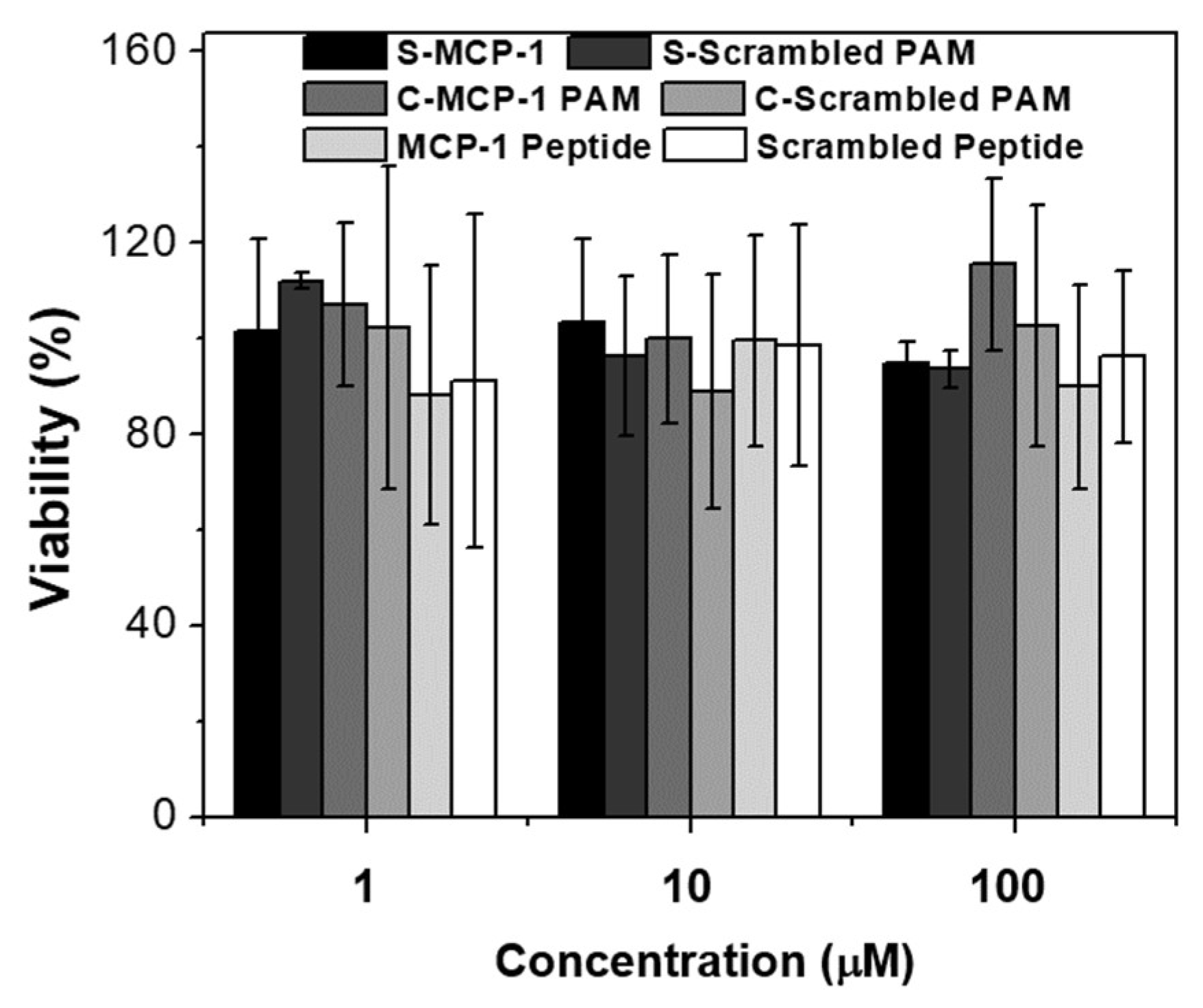
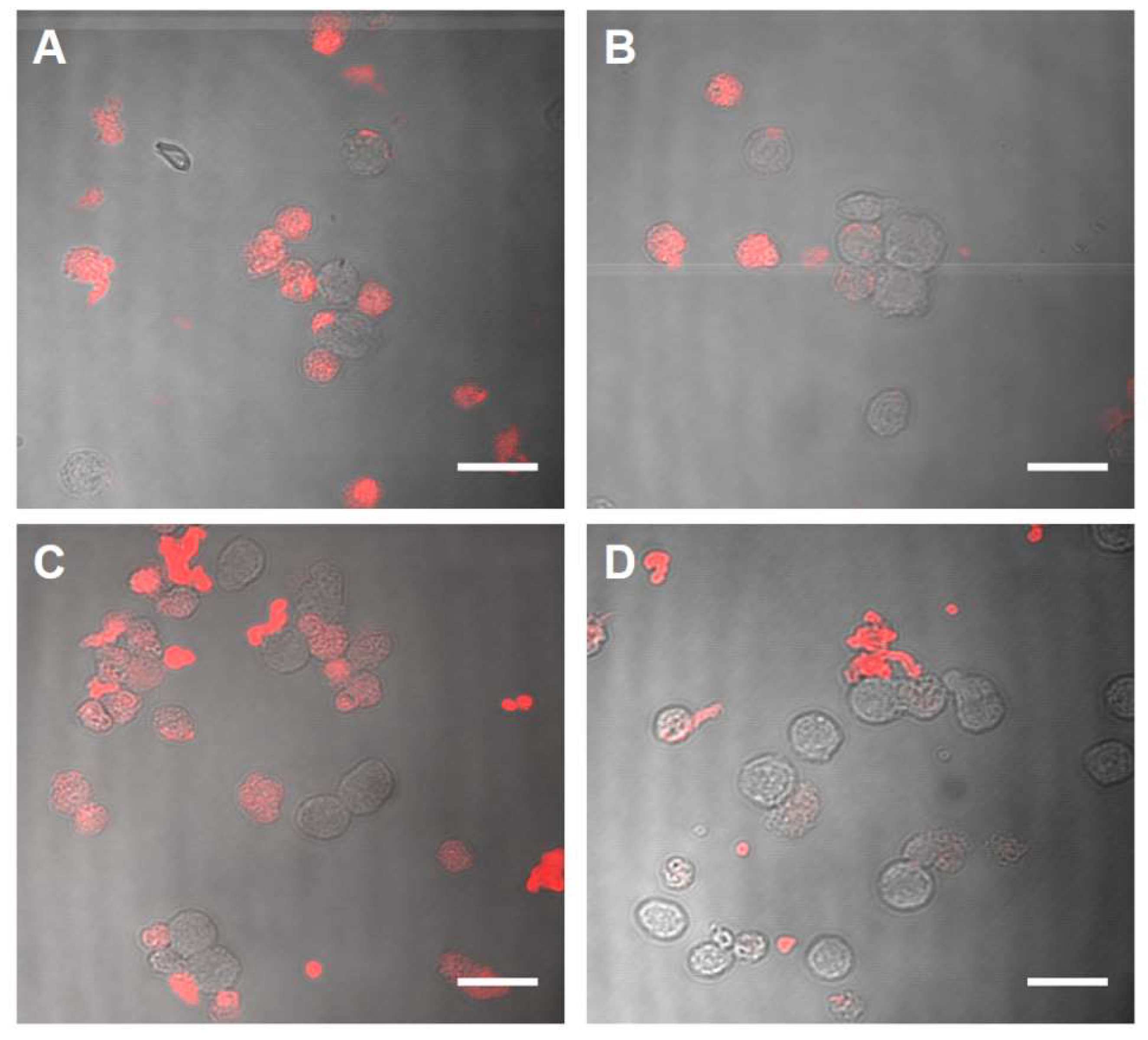
2.2. Biocompatibility and Binding to Monocytes
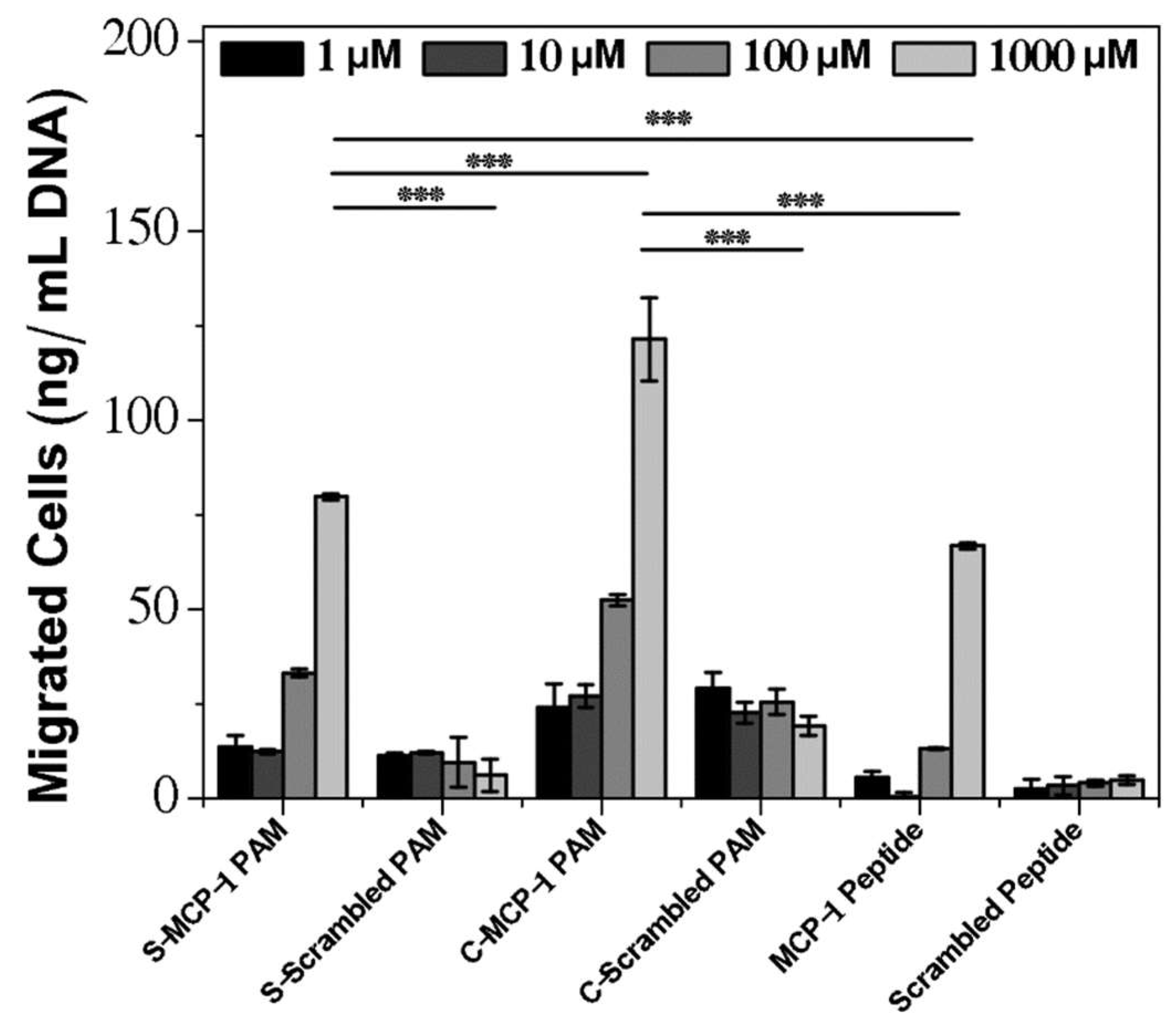
2.3. Chemoattractant Properties of PAMs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Peptides and Peptide Amphiphile Synthesis
4.3. Fluorescently Labeled Amphiphiles
4.4. Peptide Amphiphile Micelle (PAM) Assembly
4.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.6. Particle Characterization
4.7. Particle Stability
4.8. Circular Dichroism
4.9. Cell-Culture
4.10. In Vitro Biocompatibility
4.11. Binding Assay
4.12. Chemotaxis Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, E.J. Targeting and therapeutic peptides in nanomedicine for atherosclerosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, C.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuo, C.H.; Fang, Y.; Alenghat, F.J.; Hyatt, D.; Kani, K.; Gross, M.E.; Chung, E.J. Protein Mimetic and Anticancer Properties of Monocyte-Targeting Peptide Amphiphile Micelles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3273–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thundimadathil, J. Cancer Treatment Using Peptides: Current Therapies and Future Prospects. J. Amino Acids 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.J.; Nord, K.; Sugimoto, M.J.; Wonder, E.; Tirrell, M.; Mlinar, L.B.; Alenghat, F.J.; Fang, Y. Monocyte-Targeting Supramolecular Micellar Assemblies: A Molecular Diagnostic Tool for Atherosclerosis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missirlis, D.; Khant, H.; Tirrell, M. Mechanisms of Peptide Amphiphile Internalization by SJSA-1 Cells in Vitro. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 3304–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.J.; Cheng, Y.; Morshed, R.; Nord, K.; Han, Y.; Wegscheid, M.L.; Auffinger, B.; Wainwright, D.A.; Lesniak, M.S.; Tirrell, M.V. Fibrin-binding, peptide amphiphile micelles for targeting glioblastoma(☆). Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Masehi-Lano, J.J.; Chung, E.J. Peptide and antibody ligands for renal targeting: Nanomedicine strategies for kidney disease. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.P.; Pineda, F.; Barrett, J.C.; Poon, C.; Tirrell, M.; Chung, E.J. Gadolinium-Functionalized Peptide Amphiphile Micelles for Multimodal Imaging of Atherosclerotic Lesions. ACS Omega 2016, 1, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, H.; Srivastava, S.; Chung, E.J.; Schnorenberg, M.R.; Barrett, J.C.; LaBelle, J.L.; Tirrell, M. Self-Assembling Peptide-Based Building Blocks in Medical Applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 110–111, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raha, S.; Paunesku, T.; Woloschak, G. Peptide mediated cancer targeting of nanoconjugates. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 3, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulijn, R.V.; Smith, A.M. Designing peptide based nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trent, A.; Marullo, R.; Lin, B.; Black, M.; Tirrell, M. Structural properties of soluble peptide amphiphile micelles. Soft Matter 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; p. 631. [Google Scholar]
- Lukyanov, A.N.; Torchilin, V.P. Micelles from lipid derivatives of water-soluble polymers as delivery systems for poorly soluble drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1273–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berndt, P.; Fields, G.B.; Tirrell, M. Synthetic lipidation of peptides and amino acids: Monolayer structure and properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 9515–9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missirlis, D.; Krogstad, D.V.; Tirrell, M. Internalization of p5314−29 Peptide Amphiphiles and Subsequent Endosomal Disruption Results in SJSA-1 Cell Death. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 2173–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmali, P.P.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Kastantin, M.; Black, M.; Missirlis, D.; Tirrell, M.; Ruoslahti, E. Targeting of albumin-embedded paclitaxel nanoparticles to tumors. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009, 5, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Liu, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Zou, H.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, W.; et al. iRGD-conjugated DSPE-PEG2000 nanomicelles for targeted delivery of salinomycin for treatment of both liver cancer cells and cancer stem cells. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2677–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, T.J.; Kassam, H.A.; Bahnson, E.S.M.; Morgan, C.E.; Tantakitti, F.; Chew, T.L.; Kibbe, M.R.; Stupp, S.I. Shape Dependent Targeting of Injured Blood Vessels by Peptide Amphiphile Supramolecular Nanostructures. Small 2015, 11, 2750–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groß, A.; Hashimoto, C.; Sticht, H.; Eichler, J. Synthetic Peptides as Protein Mimics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1): An Overview. J. Int. Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Fujita, K.; Tanigawa, G.; Kawashima, A.; Nagahara, A.; Ujike, T.; Uemura, M.; Takao, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nonomura, N. Serum monocyte fraction of white blood cells is increased in patients with high Gleason score prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 35255–35261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlmark, K.R.; Tacke, F.; Dunay, I.R. Monocytes in health and disease—Minireview. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 2, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacke, F.; Alvarez, D.; Kaplan, T.J.; Jakubzick, C.; Spanbroek, R.; Llodra, J.; Garin, A.; Liu, J.; Mack, M.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. Monocyte subsets differentially employ CCR2, CCR5, and CX3CR1 to accumulate within atherosclerotic plaques. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.J.; Mlinar, L.B.; Sugimoto, M.J.; Nord, K.; Roman, B.B.; Tirrell, M. In vivo biodistribution and clearance of peptide amphiphile micelles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamley, I.W. PEG–Peptide Conjugates. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1543–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; O’Mara, M.L.; Surawski, P.P.T.; Trau, M.; Mark, A.E. Effect of Poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG) Spacers on the Conformational Properties of Small Peptides: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Langmuir 2011, 27, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5577–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunov, O.; Syrovets, T.; Loos, C.; Beil, J.; Delacher, M.; Tron, K.; Nienhaus, G.U.; Musyanovych, A.; Mailänder, V.; Landfester, K.; et al. Differential Uptake of Functionalized Polystyrene Nanoparticles by Human Macrophages and a Monocytic Cell Line. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anachkov, S.E.; Danov, K.D.; Basheva, E.S.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P. Determination of the aggregation number and charge of ionic surfactant micelles from the stepwise thinning of foam films. Adv. Coll. Int. Sci. 2012, 183–184, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguli, D.; Ganguli, M. Inorganic Particle Synthesis via Macro and Microemulsions: A Micrometer to Nanometer Landscape; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2003; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, E.J.; Tirrell, M. Recent Advances in Targeted, Self-Assembling Nanoparticles to Address Vascular Damage Due to Atherosclerosis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 2408–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lameijer, M.A.; Tang, J.; Nahrendorf, M.; Beelen, R.H.J.; Mulder, W.J.M. Monocytes and macrophages as nanomedicinal targets for improved diagnosis and treatment of disease. Exp. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 13, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahrendorf, M.; Zhang, H.; Hembrador, S.; Panizzi, P.; Sosnovik, D.E.; Aikawa, E.; Libby, P.; Swirski, F.K.; Weissleder, R. Nanoparticle PET-CT Imaging of Macrophages in Inflammatory Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2008, 117, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodabandehlou, K.; Masehi-Lano, J.J.; Poon, C.; Wang, J.; Chung, E.J. Targeting cell adhesion molecules with nanoparticles using in vivo and flow-based in vitro models of atherosclerosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B.A. Protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopy: Methods and reference databases. Biopolymers 2007, 89, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds MCP-1, DSPE-PEG2000 MCP-1, and diC16 MCP-1 are available from the authors on reasonable request. |
| S-MCP-1 PAM | S-Scrambled PAM | MCP-1 Peptide | Scrambled MCP-1 Peptide | C-MCP-1 PAM | C-Scrambled PAM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW (g/mol) | 5830 | 5830 | 2892 | 2892 | 3571 | 3571 |
| Diameter (nm) | 18.7 ± 4.0 a (14.9 ± 6.0) b | 18.4 ± 5.8 a (15.1 ± 7.1) b | 24.7 ± 6.2 a (10.7 ± 0.3) b | 23.7 ± 1.6 a (9.3 ± 2.0) b | ||
| Length (nm) | - | - | 62.2 ± 41.3 | 51.7 ± 15.8 | ||
| PDI | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.06 | ||
| Zeta Potential (mV) | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 17.6 ± 5.7 | 18.8 ± 3.4 | ||
| Secondary Structure | ||||||
| Beta Sheet (%) | 50.9 | 46.3 | 36.2 | 43.9 | 55.4 | 55.6 |
| Random Coil (%) | 36.8 | 37.0 | 54.5 | 47.5 | 32.6 | 31.6 |
| Alpha Helix (%) | 12.2 | 16.6 | 9.2 | 8.6 | 8.7 | 12.7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joo, J.; Poon, C.; Yoo, S.P.; Chung, E.J. Shape Effects of Peptide Amphiphile Micelles for Targeting Monocytes. Molecules 2018, 23, 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112786
Joo J, Poon C, Yoo SP, Chung EJ. Shape Effects of Peptide Amphiphile Micelles for Targeting Monocytes. Molecules. 2018; 23(11):2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112786
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoo, Johan, Christopher Poon, Sang Pil Yoo, and Eun Ji Chung. 2018. "Shape Effects of Peptide Amphiphile Micelles for Targeting Monocytes" Molecules 23, no. 11: 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112786
APA StyleJoo, J., Poon, C., Yoo, S. P., & Chung, E. J. (2018). Shape Effects of Peptide Amphiphile Micelles for Targeting Monocytes. Molecules, 23(11), 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112786







