New Alkaloid and Aromatic Glucoside from the Flowers of Cymbidium Lunagrad Eternal Green
Abstract
:1. Introduction
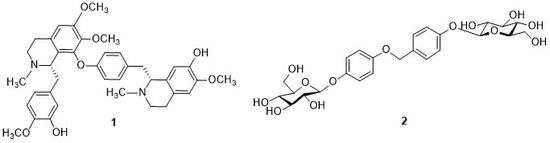
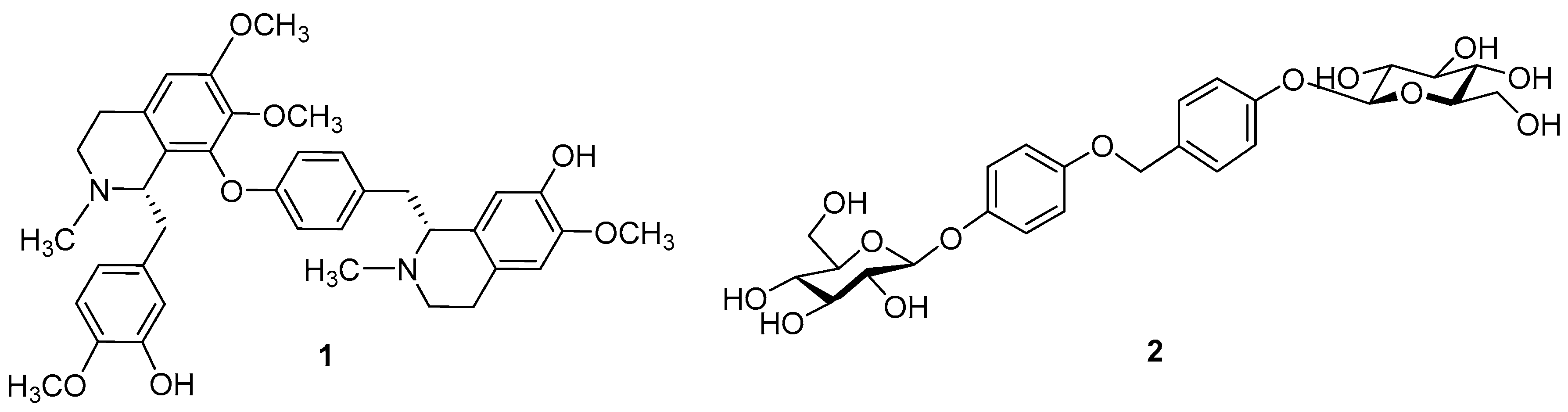
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Spectral Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shang, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Miao, X.; Zhang, J. Gymnadenia conopsea (L.) R. Br.: A systemic review of the ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of an important Asian folk medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Van Staden, J. Ansellia africana (Leopard orchid): A medicinal orchid, species with untapped reserves of important biomolecules—A mini review. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 106, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M. Therapeutic orchids: Traditional uses and recent advances—An overview. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 102–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Ito, T.; Iseki, K.; Baba, C.; Imagawa, H.; Yagi, Y.; Morita, H.; Asakawa, Y.; Kawano, S.; Hashimoto, T. Phenanthrene derivatives from Cymbidium Great Flower Marie Laurencin and their biological activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Otsu, M.; Ito, T.; Asakawa, Y.; Kawano, S.; Hashimoto, T. Aromatic constituents of Cymbidium Great Flower Marie Laurencin and their antioxidative activity. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 67, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Baba, C.; Iseki, K.; Ito, T.; Asakawa, Y.; Kawano, S.; Hashimoto, T. Phenanthrene and phenylpropanoid constituents from the roots of Cymbidium Great Flower ‘Marylaurencin’ and their antimicrobial activity. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 68, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Okahuji, M.; Iseki, K.; Ito, T.; Asakawa, Y.; Kawano, S.; Hashimoto, T. Two novel aromatic glucosides, marylaurencinosides D and E, from the fresh flowers of Cymbidium Great Flower ‘Marylaurencin’. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 68, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EI Bialy, S.A.A.; Braun, H.; Tietze, L.F. Enantioselective synthesis of a-alkyl-malates as the pharmacophoric group of several natural alkaloids and glycosides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 14, 2965–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahakitpichan, P.; Mahidol, C.; Disadee, W.; Chimnoi, N.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kanchanapoom, T. Glucopyranosyloxybenzyl deriva-tives of (R)-2-benzylmalic acid and (R)-eucomic acid, and an aromatic glucoside from the pseudobulbs of Grammatophyllum speciosum. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Woo, M.H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, B.S.; Chang, H.W.; San, J.K. Two new benzofurans from Gastrodia elata and their DNA topoisomerases I and II inhibitory activities. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, C.; Petereit, F.; Anke, J.; Hensel, A. A new arbutin derivative from the herb of Myrothamnus flabellifolia Welw. Pharmazie 2007, 62, 558–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Fu, D.X.; Hou, A.J.; Lei, G.Q.; Liu, Z.J.; Chen, J.K.; Zhou, T.S. Antioxidative phenols and phenolic glycosides from Curculigo orchioides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.; Silvan, A.M.; Abad, M.J.; Bermejo, P.; Villar, A. Isolation of two flavonoids from Tanacetum microphyllum as PMA-induced ear edema inhibitors. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haribal, M.; Renwick, A.A. Oviposition stimulants for the monarch butterfly: Flavonol glycosides from Asclepias curassavica. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcnally, D.J.; Wurms, K.V.; Labbe, C.; Quideau, S.; Belanger, R.R. Complex C-glycosyl flavonoid phytoalexins from Cucumis sativus. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1280–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, K.P.; Mukherjee, B.; Mukherjee, R. Bisbenzylisoquinoline Alkaloids—A Review. J. Nat. Prod. 1979, 42, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, P.L., Jr. Bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 645–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angerhofer, C.K.; Guinaudeau, H.; Wongpanich, V.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Cordell, G.A. Antiplasmodial and cytotoxic activity of natural bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, D.; Chen, X.; Zheng, J. Identification of Quinone Methide Metabolites of dauricine in human liver microsomers and in rat bile. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F. Dauricine. In Handbook of Metabolic Pathways of Xenobiotics; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 3, pp. 1181–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, G.R.M.; Hennig, L.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Bussmann, R.W.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Giannis, A. Curare alkaloids: Constituents of a matisdart poison. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of all compounds in the manuscripts are available from the authors. |
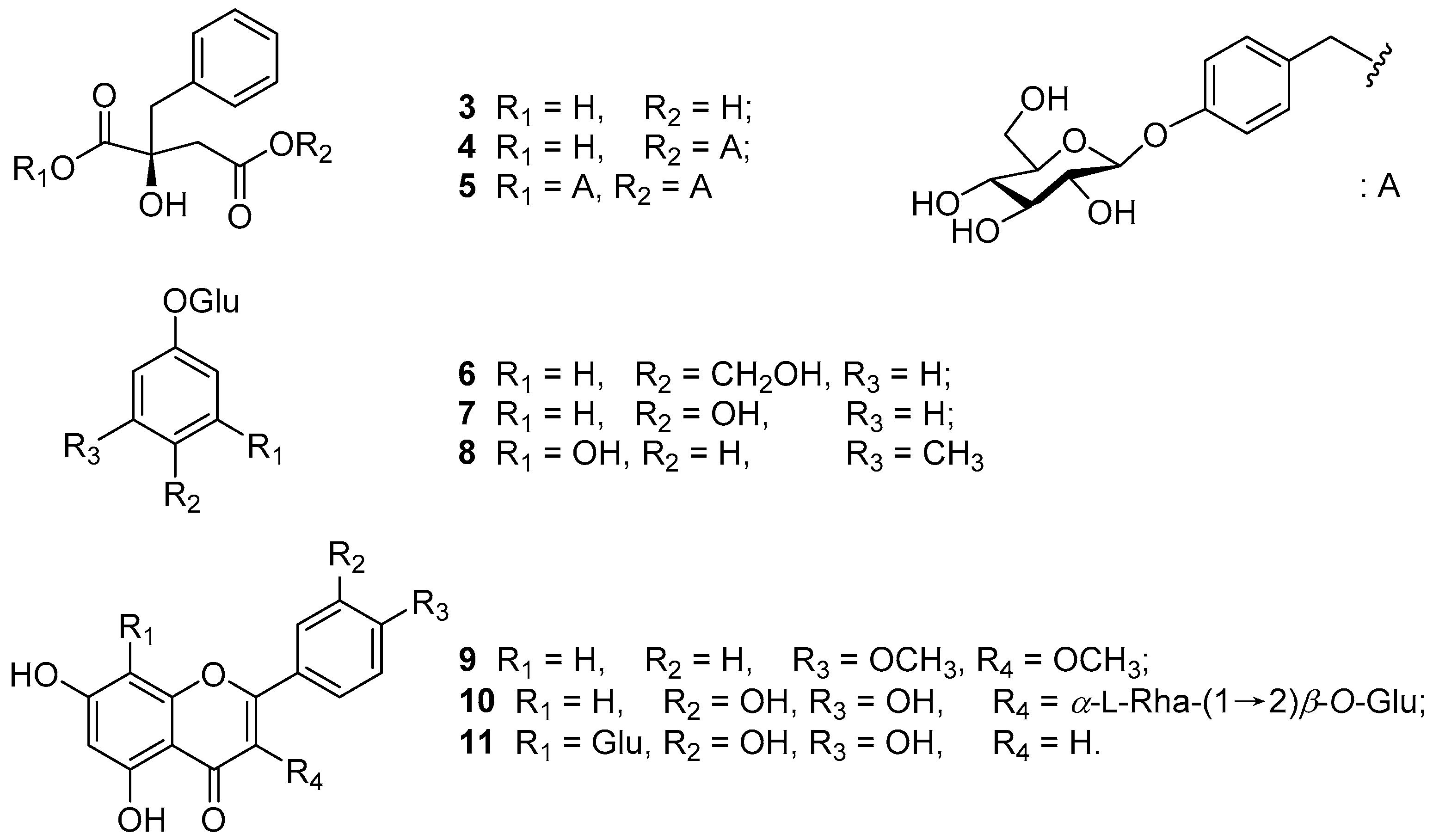
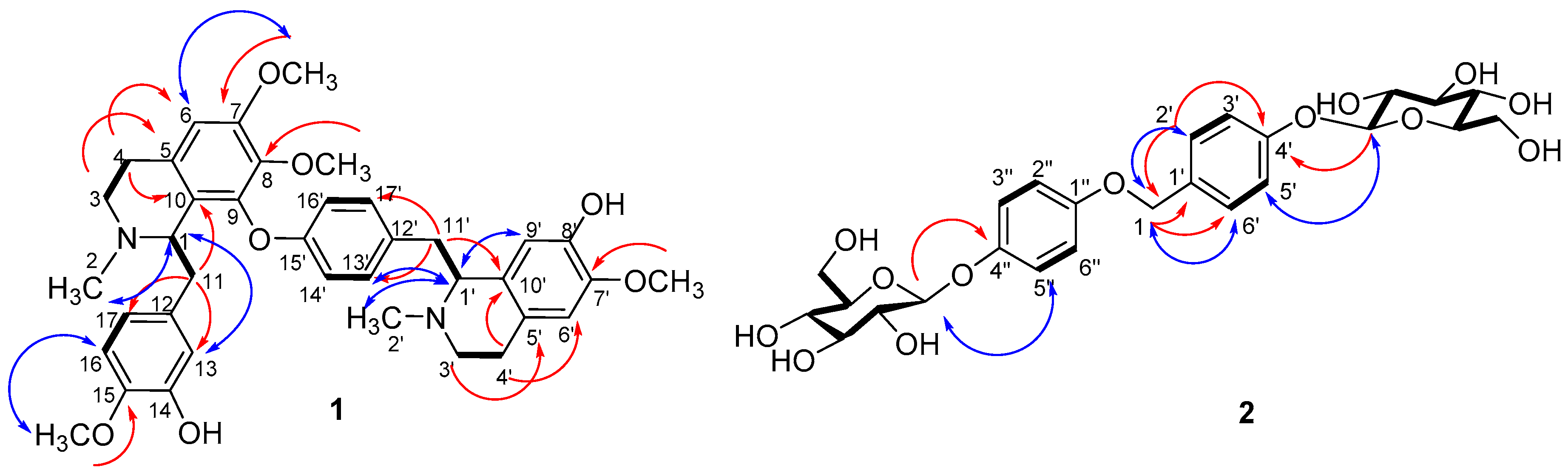
| No. | 1H-NMR | 13C-NMR | No. | 1H-NMR | 13C-NMR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CH | 3.82, d, 10.0 | 63.0 | 1′ | CH | 4.00, dd, 11.0, 6.0 | 64.5 |
| 2 | CH3 | 2.27, s | 43.1 | 2′ | CH3 | 2.62, s | 42.5 |
| 3 | CH2 | 3.49, overlap 2.91, overlap | 45.3 | 3′ | CH2 | 3.47, m 2.78, overlap | 45.7 |
| 4 | CH2 | 2.92, overlap 2.53, dd, 14.5, 4.5 | 23.7 | 4′ | CH2 | 3.01, m 2.86, overlap | 26.0 |
| 5 | C | - | 124.0 | 5′ | C | - | 129.1 |
| 6 | CH | 6.42, s | 107.3 | 6′ | CH | 6.66, s | 113.7 |
| 7 | C | - | 153.0 | 7′ | C | - | 150.3 |
| 7-OMe | CH3 | 3.73, s | 56.4 | 7′-OMe | CH3 | 3.37, s | 56.1 |
| 8 | C | - | 139.3 | 8′ | C | - | 145.2 |
| 8-OMe | CH3 | 3.15, s | 60.7 | - | |||
| 9 | C | - | 149.4 | 9′ | CH | 6.01, s | 121.4 |
| 10 | C | - | 129.3 | 10′ | C | - | 129.0 |
| 11 | CH2 | 2.76, dd, 14.5, 10.0 2.46, d, 14.5 | 42.6 | 11′ | CH2 | 3.27, dd, 12.5, 6.0 2.87, overlap | 37.5 |
| 12 | C | - | 135.8 | 12′ | C | - | 136.7 |
| 13 | CH | 6.56, d, 1.6 | 116.7 | 13′ | CH | 7.43, d, 8.2 | 131.8 |
| 14 | C | - | 151.0 | 14′ | CH | 7.05, d, 8.2 | 122.9 |
| 15 | C | - | 148.7 | 15′ | C | - | 155.1 |
| 15-OMe | CH3 | 3.89, s | 56.8 | - | - | - | - |
| 16 | CH | 6.92, d, 8.2 | 113.2 | 16′ | CH | 6.76, d, 8.2 | 122.8 |
| 17 | CH | 6.86, d, 8.2 | 124.4 | 17′ | CH | 6.38, d, 8.2 | 133.9 |
| No. | 1H-NMR | 13C-NMR | No. | 1H-NMR | 13C-NMR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1′ | C | - | 136.6 | 1″ | C | - | 153.9 |
| 2′, 6′ | CH | 7.27, d, 8.4 | 129.5 | 2″, 6″ | CH | 6.69, d, 8.8 | 116.6 |
| 3′, 5′ | CH | 7.07, d, 8.4 | 117.7 | 3″, 5″ | CH | 6.96, d, 8.8 | 119.4 |
| 4′ | C | - | 158.5 | 4″ | C | - | 152.5 |
| 4′-O-Glu-1 | CH | 4.89, d, 7.2 | 102.4 | 4″-O-Glu-1 | CH | 4.73, d, 7.2 | 103.7 |
| 4′-O-Glu-2 | CH | 3.42, overlap | 75.1 | 4″-O-Glu-2 | CH | 3.42, overlap | 75.0 |
| 4′-O-Glu-3 | CH | 3.41, overlap | 78.2 | 4″-O-Glu-3 | CH | 3.41, overlap | 78.0 |
| 4′-O-Glu-4 | CH | 3.34, overlap | 71.5 | 4″-O-Glu-4 | CH | 3.34, overlap | 71.4 |
| 4′-O-Glu-5 | CH | 3.36, overlap | 78.1 | 4″-O-Glu-5 | CH | 3.36, overlap | 78.0 |
| 4′-O-Glu-6 | CH2 | 3.88, br.d, 12.0 3.69, br.d, 12.0 | 62.6 | 4″-O-Glu-6 | CH2 | 3.88, br.d, 12.0 3.69, br.d, 12.0 | 62.5 |
| 1 | CH2 | 4.54, s | 64.9 | - | - | - | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, L.-Y.; Huang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.-J.; Ouyang, M.-A. New Alkaloid and Aromatic Glucoside from the Flowers of Cymbidium Lunagrad Eternal Green. Molecules 2018, 23, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010099
Song L-Y, Huang F, Wang Y, Wu Z-J, Ouyang M-A. New Alkaloid and Aromatic Glucoside from the Flowers of Cymbidium Lunagrad Eternal Green. Molecules. 2018; 23(1):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010099
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Li-Yan, Fang Huang, Yan Wang, Zu-Jian Wu, and Ming-An Ouyang. 2018. "New Alkaloid and Aromatic Glucoside from the Flowers of Cymbidium Lunagrad Eternal Green" Molecules 23, no. 1: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010099
APA StyleSong, L.-Y., Huang, F., Wang, Y., Wu, Z.-J., & Ouyang, M.-A. (2018). New Alkaloid and Aromatic Glucoside from the Flowers of Cymbidium Lunagrad Eternal Green. Molecules, 23(1), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010099