Optimization of Fermentation Conditions and Bench-Scale for Improvement of a Novel Glycoprotein GP-1 Production by Streptomyces kanasenisi ZX01
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Inoculum Volume, Initial pH and Rotating Speed on Glycoprotein GP-1 Production
2.2. Optimization of Fermentation Conditions by RSM
2.3. Verification of the Model
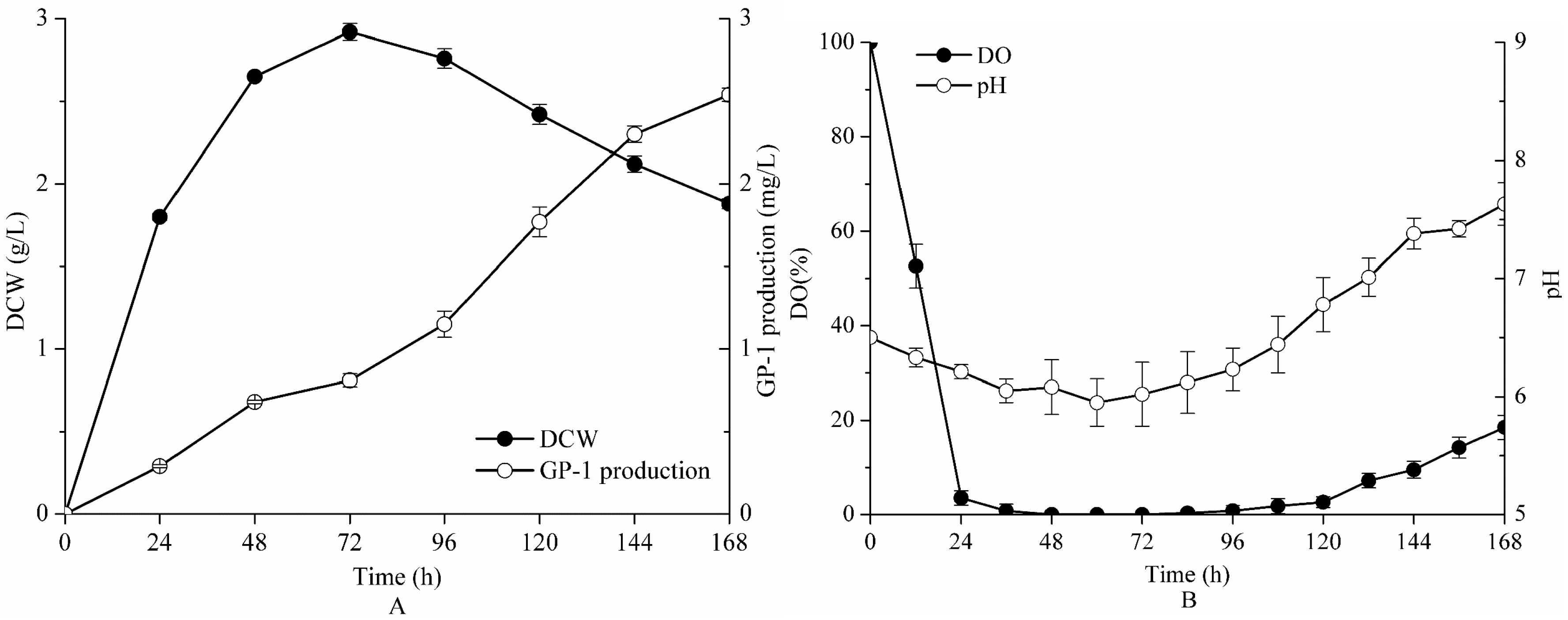
2.4. Fermentation in a 5-L Bioreactor
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganism
4.2. Cultivation and Media
4.3. Extraction and Determination of Glycoprotein GP-1 Production
4.4. Determination of Dry Cell Weight
4.5. Determination of Anti-TMV Activity
4.6. Experiment Design by Response Surface Methodology
4.7. Fermentation in Bench-Scale Fermentor
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berdy, J. Bioactive microbial metabolites. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibb, M.J. Regulation of secondary metabolism in streptomycetes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wezel, G.P.; McDowall, K.J. The regulation of the secondary metabolism of streptomycetes: New links and experimental advances. Natl. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 1311–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watve, M.G.; Tickoo, R.; Jog, M.M.; Bhole, B.D. How many antibiotics are produced by the genus streptomycetes? Arch. Microbiol. 2001, 176, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lima Procópio, R.E.; da Silva, I.R.; Martins, M.K.; de Azevedo, J.L.; de Araújo, J.M. Antibiotics produced by streptomycetes. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdy, J. The discovery of new bioactive microbial metabolites: Screening and identification. Prog. Ind. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Donadio, S.; Monciardini, P.; Alduina, R.; Mazza, P.; Chiocchini, C.; Cavaletti, L.; Sosio, M.; Puglia, A.M. Microbial technologies for the discovery of novel bioactive metabolites. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 99, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwodo, U.U.; Agunbiade, M.O.; Green, E.; Mabinya, L.V.; Okoh, A.I. A freshwater streptomycetes, isolated from tyume river, produces a predominantly extracellular glycoprotein bioflocculant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8679–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Xia, F.; Feng, K.; Sun, G.; Gao, X.; Sun, L.; Jiang, R.; Tian, D.; Sun, X. Structural characterization and in vitro antitumor activity of a novel polysaccharide isolated from the fruiting bodies of pleurotus ostreatus. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1682–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, R.C.; Sêmedo, L.T.A.S.; Soares, R.M.A.; Linhares, L.F.; Ulhoa, C.J.; Alviano, C.S.; Coelho, R.R.R. Purification of a thermostable endochitinase from streptomycetes rc1071 isolated from a cerrado soil and its antagonism against phytopathogenic fungi. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Zhang, G.; Miao, G.; Zhang, X.; Feng, J. Streptomyces kanasensis sp. Nov., an antiviral glycoprotein producing actinomycete isolated from forest soil around kanas lake of China. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Han, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Feng, J. Purification and characterization of a novel glycoprotein from streptomyces sp. Zx01. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Feng, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, X. Antiviral activity of glycoprotein gp-1 isolated from streptomyces kanasensis zx01. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.-B.; He, H.-W.; Feng, J.-T.; Zhang, X.; Han, L.-R. Optimization of medium compositions to improve a novel glycoprotein production by Streptomyces kanasenisi zx01. AMB Express 2017, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; An, F.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X. Improvement of antibiotic activity of xenorhabdus bovienii by medium optimization using response surface methodology. Microb. Cell Factor. 2011, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morowvat, M.H.; Babaeipour, V.; Memari, H.R.; Vahidi, H. Optimization of fermentation conditions for recombinant human interferon beta production by escherichia coli using the response surface methodology. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e16236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Fan, F.; Wang, P.; Jiang, X. Culture medium optimization of a new bacterial extracellular polysaccharide with excellent moisture retention activity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 2841–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Santelli, R.E.; Oliveira, E.P.; Villar, L.S.; Escaleira, L.A. Response surface methodology (rsm) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 2008, 76, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Sun, L.-P.; Shi, Y.-Z.; Wu, Y.-H.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, D.-Q. Optimization of cultivation conditions for extracellular polysaccharide and mycelium biomass by morchella esculenta as51620. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 39, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalil, S.J.; Maugeri, F.; Rodrigues, M.I. Response surface analysis and simulation as a tool for bioprocess design and optimization. Proc. Biochem. 2000, 35, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S.; CUQ, J.L. Edible wheat gluten films: Influence of the main process variables on film properties using response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Bruns, R.E.; da Silva, E.G.P.; Dos Santos, W.N.L.; Quintella, C.M.; David, J.M.; de Andrade, J.B.; Breitkreitz, M.C.; Jardim, I.C.S.F.; Neto, B.B. Statistical designs and response surface techniques for the optimization of chromatographic systems. J. Chromatog. A 2007, 1158, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaraj, V.; Murugan, N. Application of response surface methodology for predicting weld bead quality in submerged arc welding of pipes. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 1999, 88, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Optimization of growth medium and fermentation conditions for improved antibiotic activity of xenorhabdus nematophila tb using a statistical approach. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 8068–8077. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, W.; Makeen, K.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qirong, S. Optimization, purification, characterization and antioxidant activity of an extracellular polysaccharide produced by paenibacillus polymyxa sqr-21. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6095–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, B.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, P.; Yang, R.; Yan, X. Response surface methodology optimization of fermentation conditions for rapid and efficient accumulation of macrolactin a by marine bacillus amyloliquefaciens esb-2. Molecules 2012, 18, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, G.; Shi, X.; Chen, H.; Ji, Z.; Meng, J. Optimization of goat milk with ace inhibitory peptides fermented by lactobacillus bulgaricus lb6 using response surface methodology. Molecules 2017, 22, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushida, K.; Sakata, T. Effect of ph on oligosaccharide fermentation by porcine cecal digesta. Anim. Sci. Technol. (Jpn.) 1998, 69, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, C.; LeDuy, A.; Noel, G.; Choplin, L. Effect of ph on the batch fermentation of pullulan from sucrose medium. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1985, 27, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.-H.; Zhong, J.-J. Effect of initial ph on production of ganoderic acid and polysaccharide by submerged fermentation of ganoderma lucidum. Proc. Biochem. 2002, 37, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, W.R.; Westby, C.A. Effects of inoculum size on solid-phase fermentation of fodder beets for fuel ethanol production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1986, 52, 960–962. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castillo, M.; Lucey, J.; Payne, F. The effect of temperature and inoculum concentration on rheological and light scatter properties of milk coagulated by a combination of bacterial fermentation and chymosin. Cottage cheese-type gels. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcı́a-Ochoa, F.; Castro, E.G.; Santos, V. Oxygen transfer and uptake rates during xanthan gum production. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2000, 27, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, G.V.; Hebert, T.T. A simple technique for purification of tobacco mosaic virus in large quantities. Phytopathology 1967, 57, 1285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the Glycoprotein GP-1 is available from the authors. |
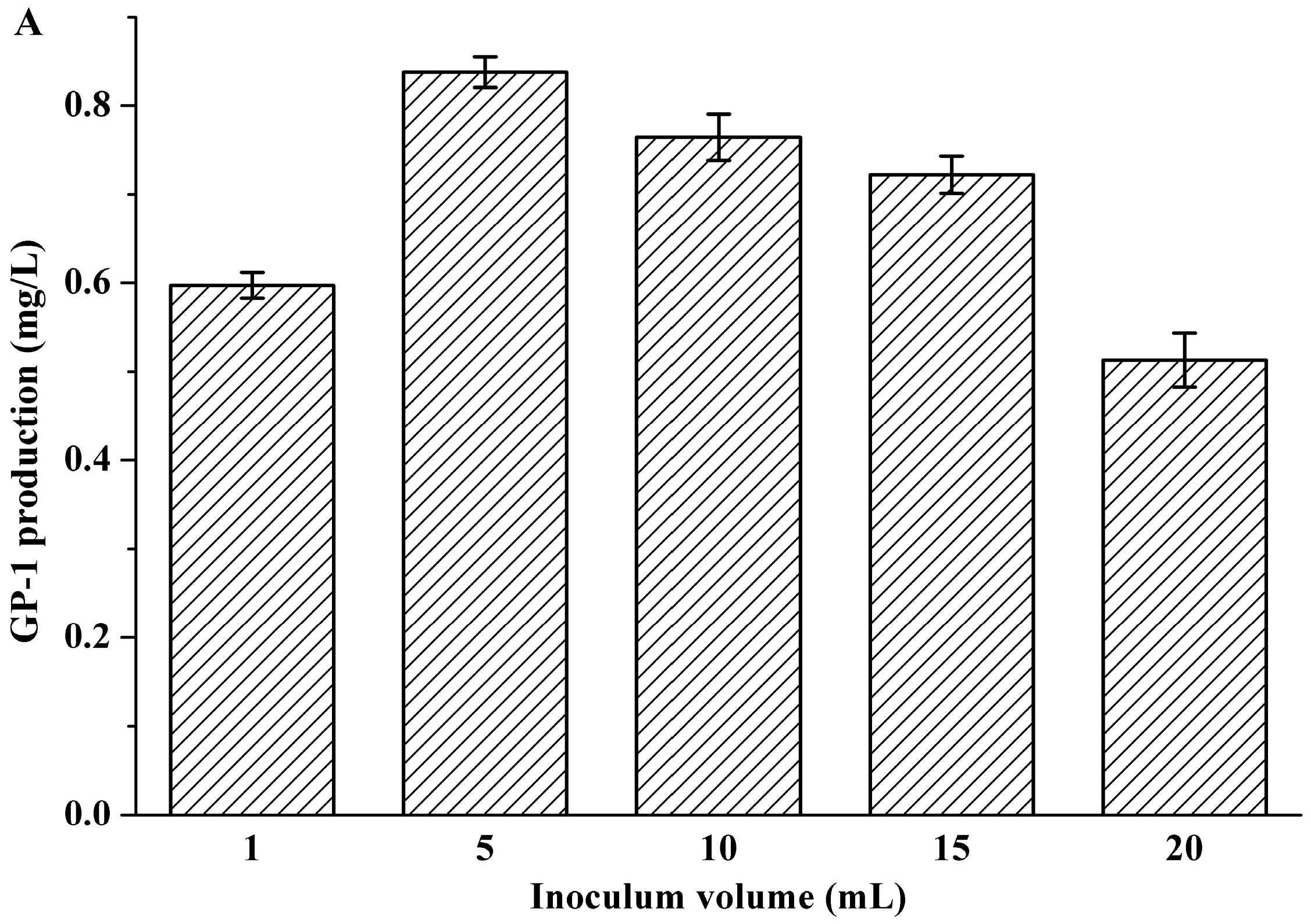
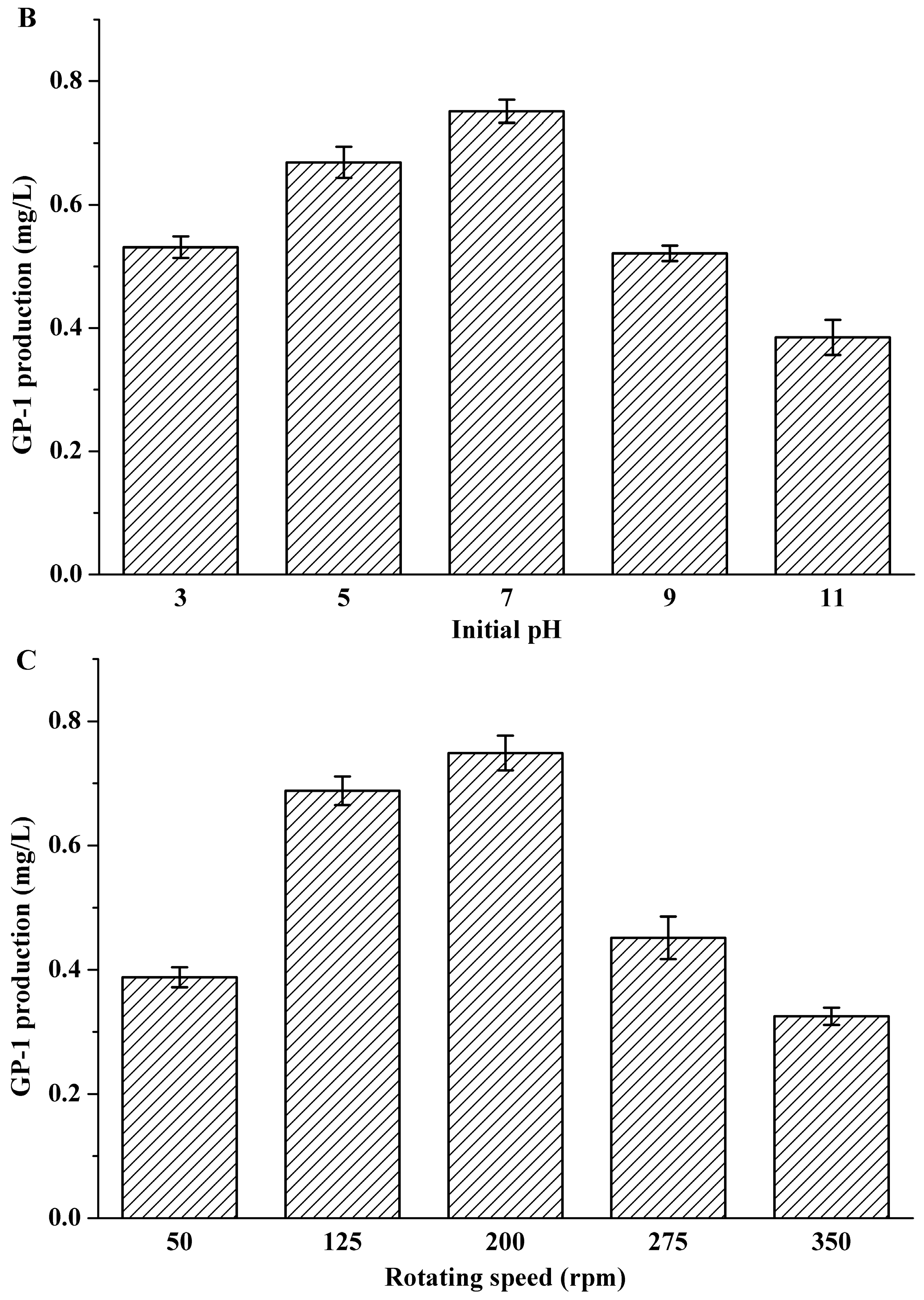
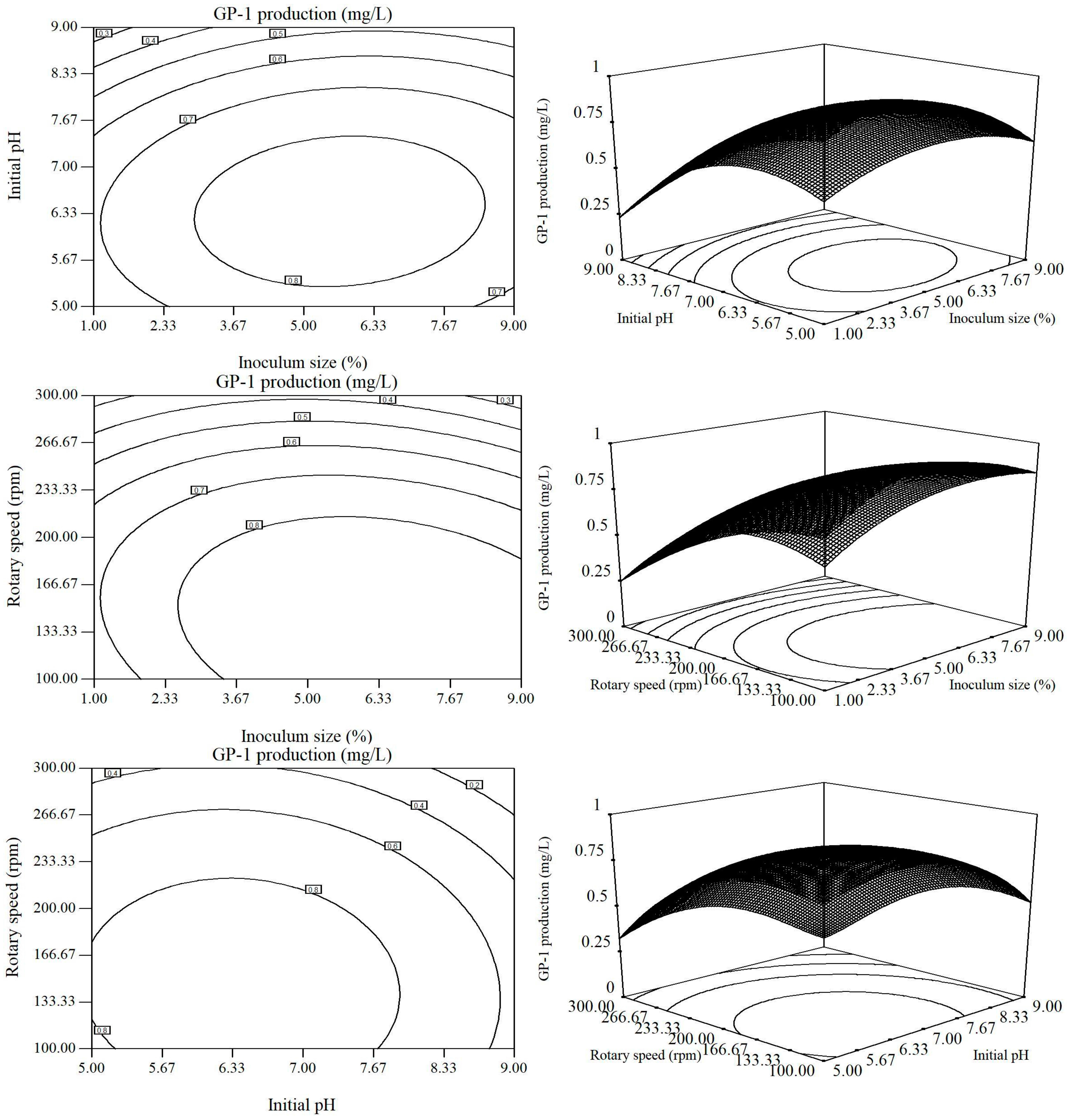
| Factors | Variables | Levels of Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.682 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 1.682 | ||
| Inoculum volume (%) | X1 | 1.64 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 7.00 | 8.36 |
| Initial pH | X2 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 8.7 |
| Rotating speed (rpm) | X3 | 116 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 284 |
| Run | x1 | x2 | x3 | Experimental Values (mg/L) | Predicted Values (mg/L) | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 0.8276 | 0.802 | 0.0256 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8315 | 0.830 | 0.0015 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | −1.682 | 0.8301 | 0.872 | −0.0419 |
| 4 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 0.6838 | 0.666 | 0.0178 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 0.6753 | 0.660 | 0.0153 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8356 | 0.830 | 0.0056 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8211 | 0.830 | −0.0089 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8151 | 0.830 | −0.0149 |
| 9 | 0 | 1.682 | 0 | 0.5352 | 0.566 | −0.0308 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8332 | 0.830 | 0.0032 |
| 11 | 0 | −1.682 | 0 | 0.7669 | 0.802 | −0.0351 |
| 12 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 0.8435 | 0.837 | 0.0065 |
| 13 | 1.682 | 0 | 0 | 0.7296 | 0.790 | −0.0604 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8490 | 0.830 | 0.0190 |
| 15 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5567 | 0.517 | 0.0397 |
| 16 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 0.7317 | 0.704 | 0.0277 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 1.682 | 0.4760 | 0.486 | −0.0100 |
| 18 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 0.9286 | 0.890 | 0.0386 |
| 19 | −1.682 | 0 | 0 | 0.7027 | 0.703 | −0.0003 |
| 20 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 0.4558 | 0.474 | −0.0182 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F Value | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.34 | 9 | 0.0370 | 29.61 | <0.0001 |
| 0.0083 | 1 | 0.0082 | 6.56 | 0.0283 | |
| 0.0660 | 1 | 0.0660 | 52.43 | <0.0001 | |
| 0.1800 | 1 | 0.1800 | 140.81 | <0.0001 | |
| 0.0013 | 1 | 0.0013 | 1.06 | 0.3278 | |
| 0.0006 | 1 | 0.0006 | 0.51 | 0.4917 | |
| 0.0022 | 1 | 0.0022 | 1.78 | 0.2119 | |
| 0.0130 | 1 | 0.0130 | 10.47 | 0.0089 | |
| 0.0410 | 1 | 0.0410 | 32.48 | 0.0002 | |
| 0.0400 | 1 | 0.0400 | 31.63 | 0.0002 | |
| Residual | 0.0130 | 10 | 0.0013 | ||
| Lack of fit | 0.0120 | 5 | 0.0024 | 16.94 | 0.0037 |
| Pure error | 0.0007 | 5 | 0.0001 | ||
| Cor Total | 0.3500 | 19 |
| Fermentor | Bench-Scale |
|---|---|
| Total volume (L) | 5 |
| Working volume (L) | 3.5 |
| Diameter of fermentor (m) | 0.15 |
| Diameter of impeller (m) | 0.07 |
| Height of fermentor (m) | 0.30 |
| Baffle | 3 |
| Impeller | Two impellers with four flat blades |
| Type of drive | Magnetic stirred |
| Sterilization | Off-situ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, D.-L.; Sang, B.; Feng, J.-T.; Han, L.-R.; Zhang, X. Optimization of Fermentation Conditions and Bench-Scale for Improvement of a Novel Glycoprotein GP-1 Production by Streptomyces kanasenisi ZX01. Molecules 2018, 23, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010137
Zhou Y, Zhou X, Yu D-L, Sang B, Feng J-T, Han L-R, Zhang X. Optimization of Fermentation Conditions and Bench-Scale for Improvement of a Novel Glycoprotein GP-1 Production by Streptomyces kanasenisi ZX01. Molecules. 2018; 23(1):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010137
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yong, Xin Zhou, Dai-Lin Yu, Bu Sang, Jun-Tao Feng, Li-Rong Han, and Xing Zhang. 2018. "Optimization of Fermentation Conditions and Bench-Scale for Improvement of a Novel Glycoprotein GP-1 Production by Streptomyces kanasenisi ZX01" Molecules 23, no. 1: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010137
APA StyleZhou, Y., Zhou, X., Yu, D.-L., Sang, B., Feng, J.-T., Han, L.-R., & Zhang, X. (2018). Optimization of Fermentation Conditions and Bench-Scale for Improvement of a Novel Glycoprotein GP-1 Production by Streptomyces kanasenisi ZX01. Molecules, 23(1), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010137




