Anti-Melanogenic Properties of Greek Plants. A Novel Depigmenting Agent from Morus alba Wood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Tyrosinase Inhibition Properties of Greek Extracts
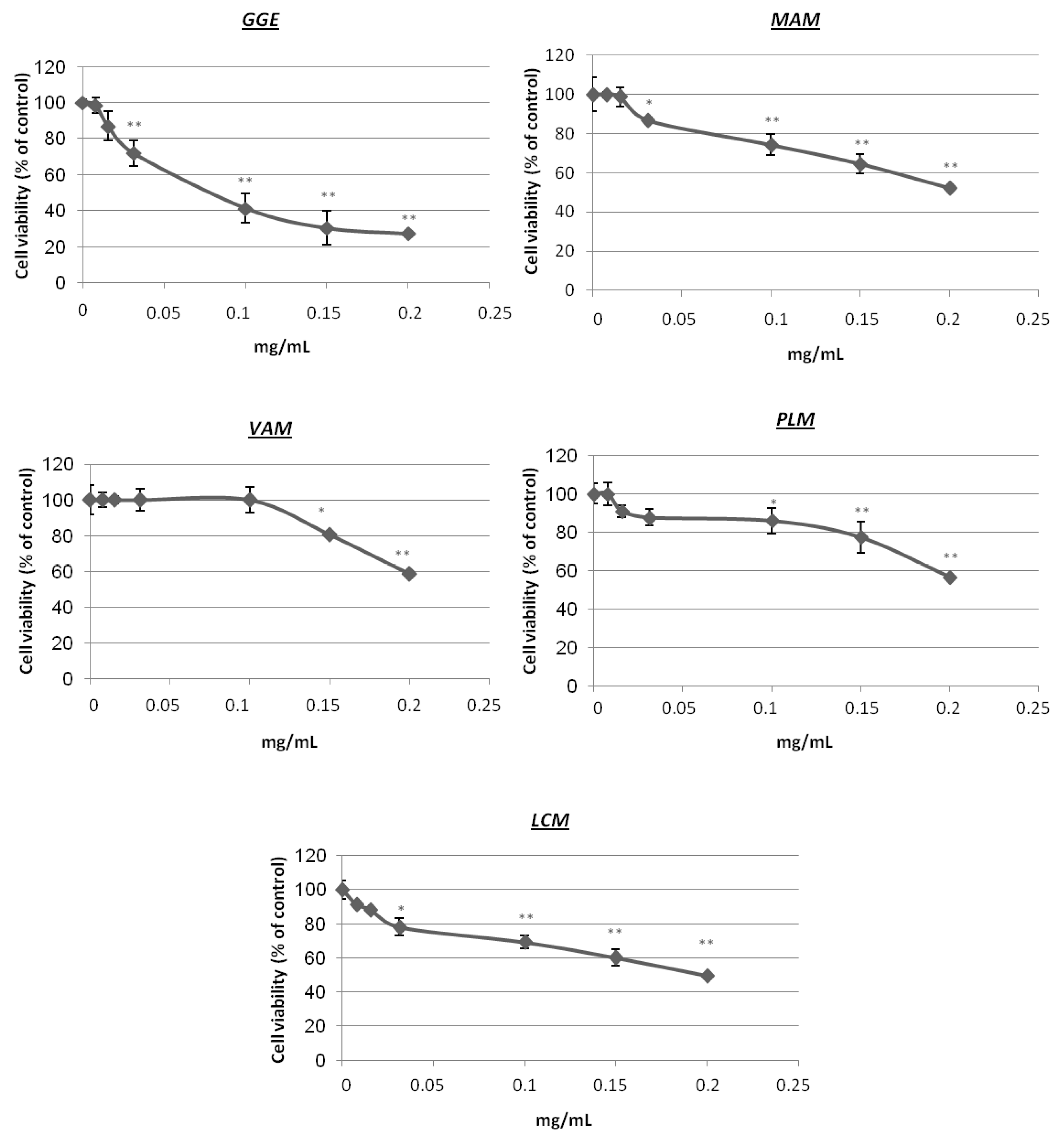
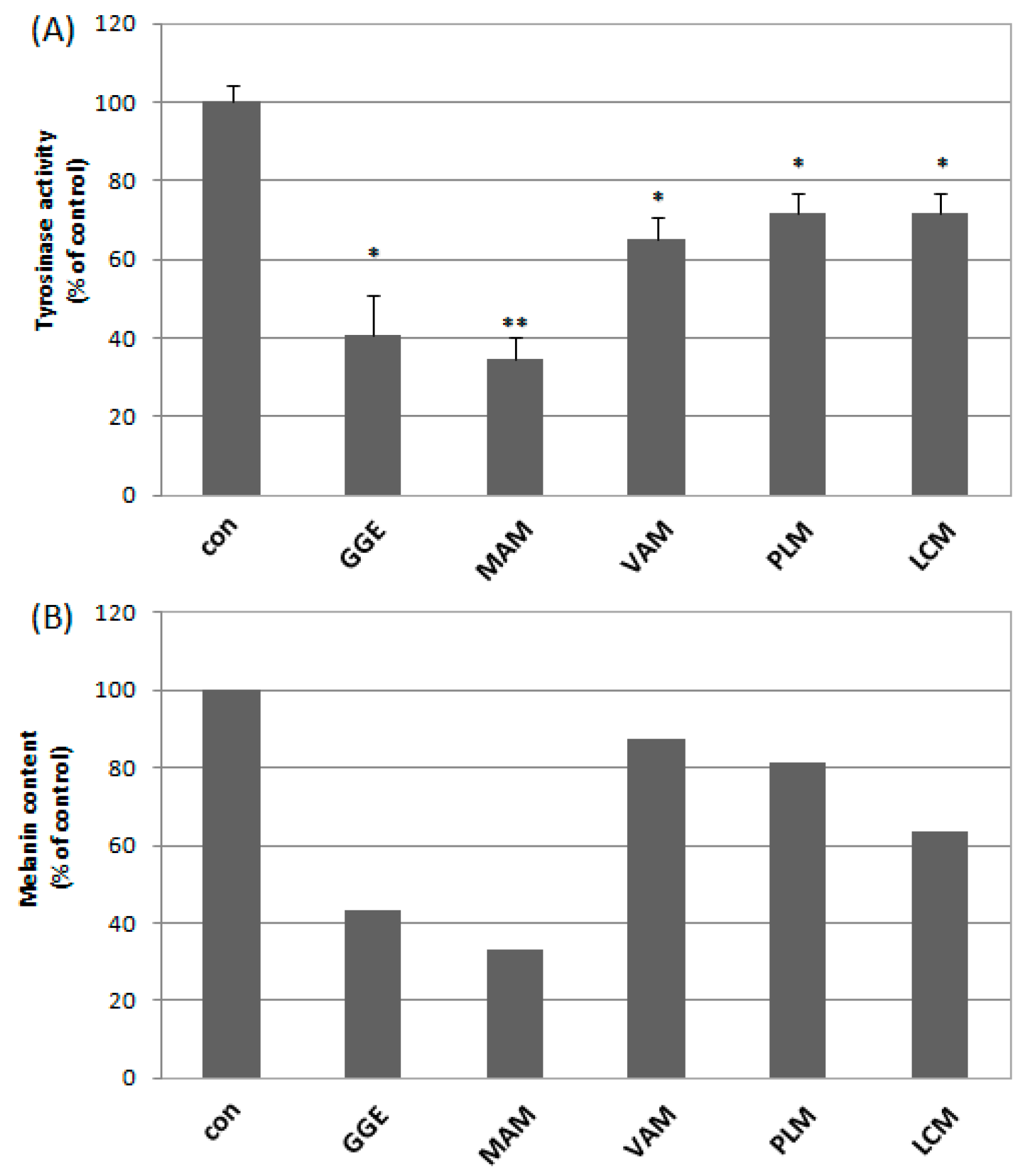
2.2. Cytotoxicity and Determination of Melanin Content and Cellular Tyrosinase Activity
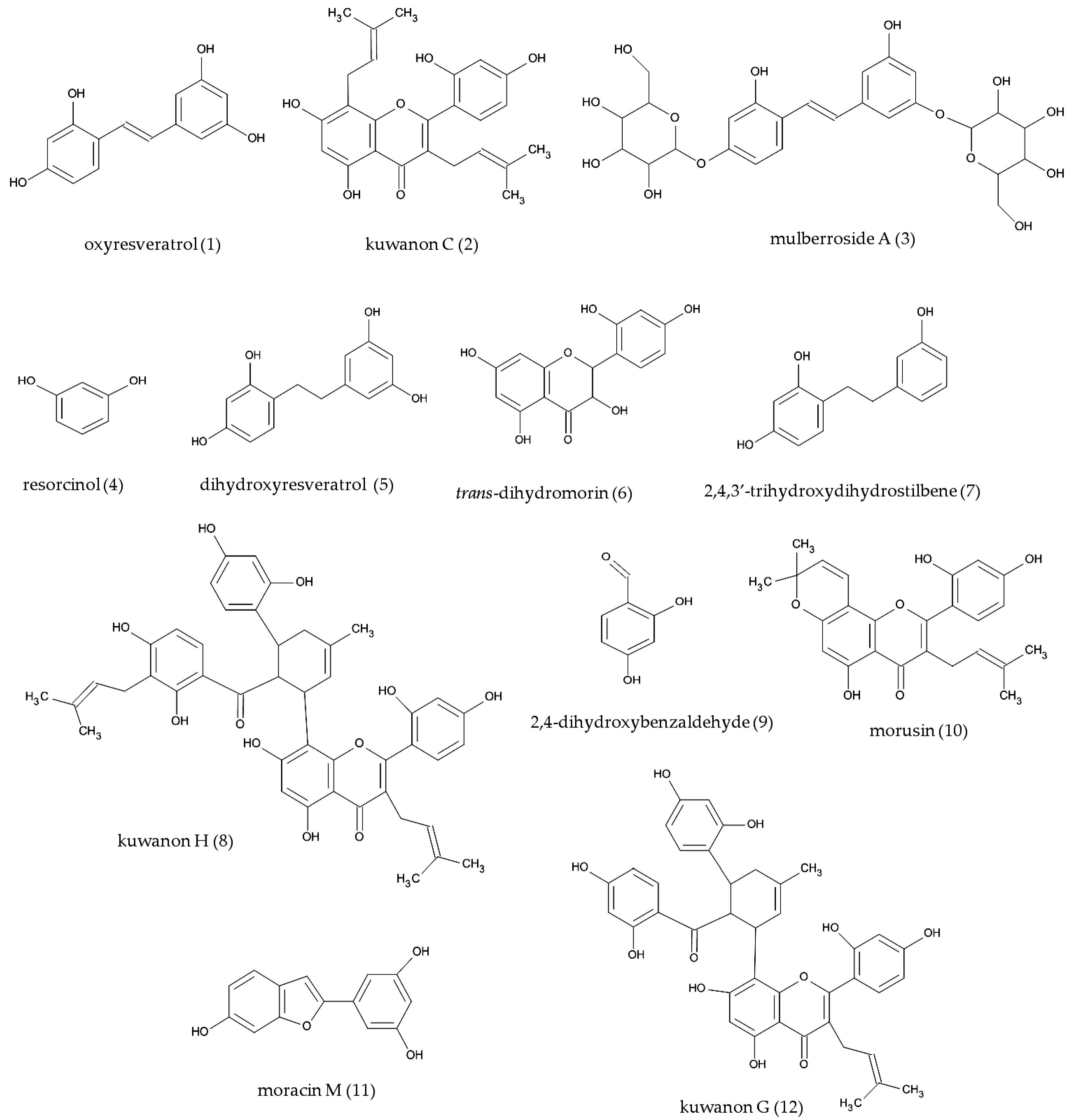
2.3. Structure Elucidation of Isolated Compounds
2.4. Tyrosinase Inhibition of Isolated Compounds
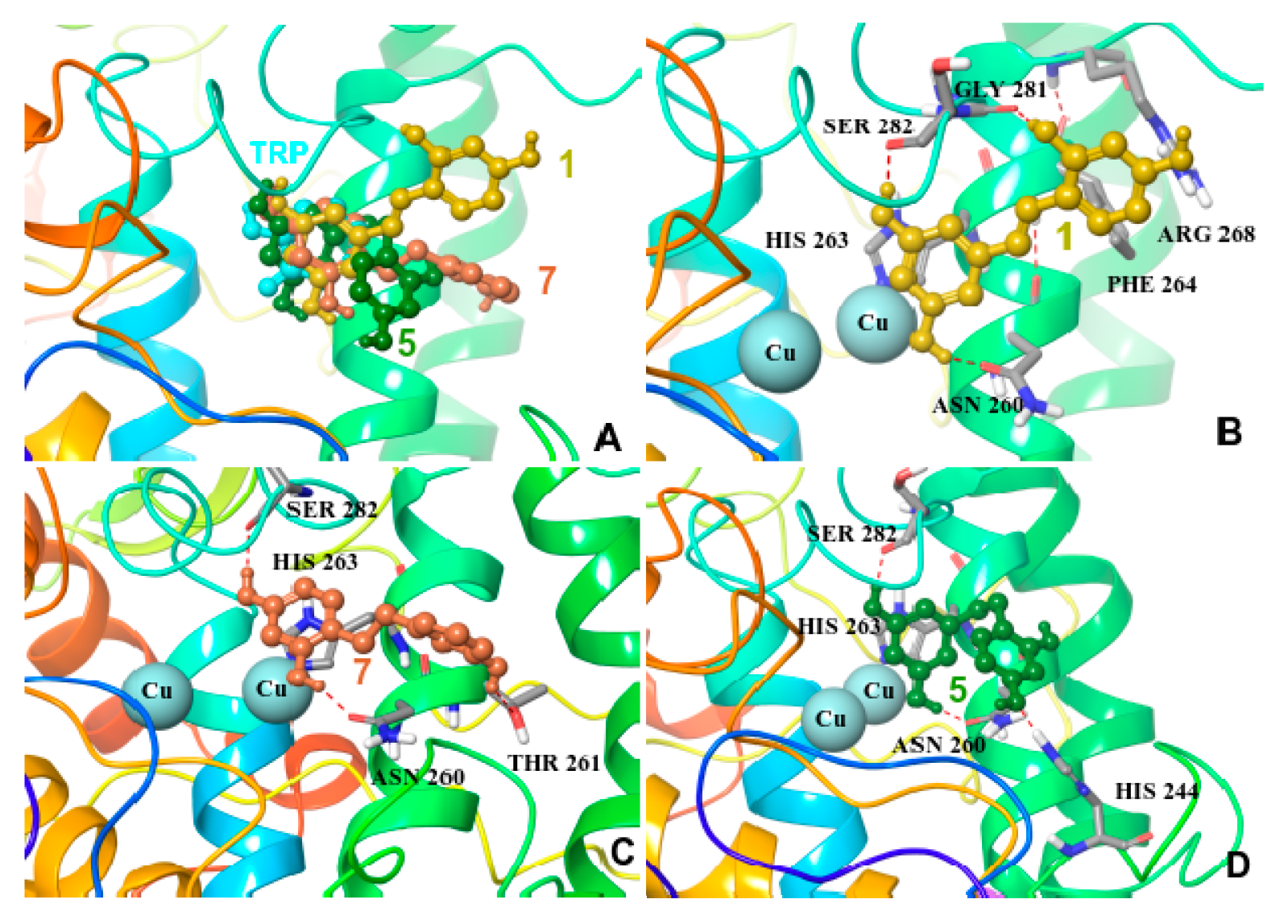
2.5. Molecular Docking on Mushroom Tyrosinase
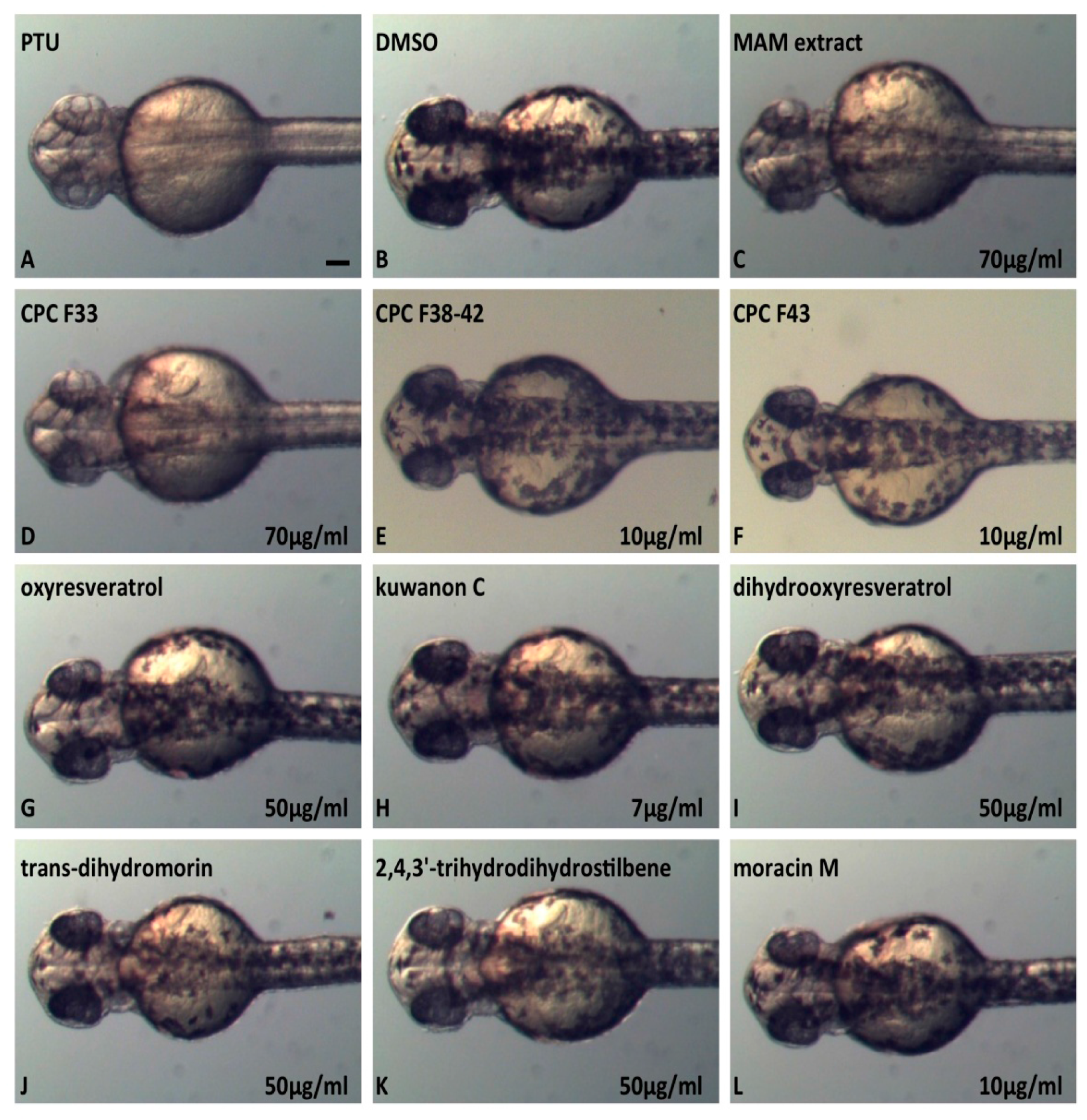
2.6. In Vivo Inhibition of Melanogenesis Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Instrumentation
3.2. Extract Preparation
3.3. Characterization data of Compounds 5 and 7
3.4. Tyrosinase Inhibition Assay
3.5. Cell Lines and Cell Culture Conditions
3.5.1. MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
3.5.2. Melanin Content Assay
3.5.3. Cellular Tyrosinase Activity Assay
3.6. FCPC-Based Bioguided Isolation from Morus alba Extracts
3.7. Molecular Docking on Mushroom Tyrosinase
3.8. Zebrafish Maintenance, Breeding and Exposure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.J.; Uyama, H. Tyrosinase inhibitors from natural and synthetic sources: Structure, inhibition mechanism and perspective for the future. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2005, 62, 1707–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillbro, J.M.; Olsson, M.J. The melanogenesis and mechanisms of skin-lightening agents—Existing and new approaches. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 33, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, S.; Kang, M.; Chung, H.-S.; Cho, C.; Hong, M.-C.; Shin, M.-K.; Bae, H. Survey and mechanism of skin depigmenting and lightening agents. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.C.; Callender, V.D. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: A review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2010, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Yun, J.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, H.; Min, K.R.; Kim, Y. Oxyresveratrol and hydroxystilbene compounds. Inhibitory effect on tyrosinase and mechanism of action. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 16340–16344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-S. An Updated Review of Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2440–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vontzalidou, A.; Zoidis, G.; Chaita, E.; Makropoulou, M.; Aligiannis, N.; Lambrinidis, G.; Mikros, E.; Skaltsounis, A.-L. Design, synthesis and molecular simulation studies of dihydrostilbene derivatives as potent tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5523–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tao, G.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Z.-P. Characterization of a New Flavone and Tyrosinase Inhibition Constituents from the Twigs of Morus alba L. Molecules 2016, 21, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korac, R.R.; Khambholja, K.M. Potential of herbs in skin protection from ultraviolet radiation. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2011, 5, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asanuma, M.; Miyazaki, I.; Ogawa, N. Dopamine- or L-DOPA-induced neurotoxicity: The role of dopamine quinone formation and tyrosinase in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox. Res. 2003, 5, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Iuliis, A.; Arrigoni, G.; Andersson, L.; Zambenedetti, P.; Burlina, A.; James, P.; Arslan, P.; Vianello, F. Oxidative metabolism of dopamine: A colour reaction from human midbrain analysed by mass spectrometry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.M.; Yang, Y.J.; Huang, H.S.; Lim, S.C.; Kai, M.; Lee, M.K. Induction of dopamine biosynthesis by l-DOPA in PC12 cells: Implications of l-DOPA influx and cyclic AMP. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 591, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solano, F.; Briganti, S.; Picardo, M.; Ghanem, G. Hypopigmenting agents: An updated review on biological, chemical and clinical aspects. Pigment Cell Res. Spons. Eur. Soc. Pigment Cell Res. Int. Pigment Cell Soc. 2006, 19, 550–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamakshi, R. Fairness via formulations: A review of cosmetic skin-lightening ingredients. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2012, 63, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- MacRae, C.A.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as tools for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beis, D.; Stainier, D.Y. In vivo cell biology: Following the zebrafish trend. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colanesi, S.; Taylor, K.L.; Temperley, N.D.; Lundegaard, P.R.; Liu, D.; North, T.E.; Ishizaki, H.; Kelsh, R.N.; Patton, E.E. Small molecule screening identifies targetable zebrafish pigmentation pathways. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012, 25, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, P.M.; Elias, S.T.; Simeoni, L.A.; de Paula, J.E.; Gomes, S.M.; Guerra, E.N.; Fonseca, Y.M.; Silva, E.C.; Silveira, D.; Magalhaes, P.O. Plants from Brazilian Cerrado with potent tyrosinase inhibitory activity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, K.S.; Mohanta, K.Y.; Padhi, L.; Park, Y.-H.; Mohanta, K.T.; Bae, H. Large Scale Screening of Ethnomedicinal Plants for Identification of Potential Antibacterial Compounds. Molecules 2016, 21, 293. [Google Scholar]
- Medail, F.Q. Pierre Hot-Spots Analysis for Conservation of Plant Biodiversity in the Mediterranean Basin. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1997, 84, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanou, C.; Bourou, G.; Dervishi, A.; Aligiannis, N.; Angelis, A.; Komiotis, D.; Skaltsounis, A.-L.; Kouretas, D. Antioxidant and Chemopreventive Properties of Polyphenolic Compounds Derived from Greek Legume Plant Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6967–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagos, D.; Portesis, N.; Spanou, C.; Mossialos, D.; Aligiannis, N.; Chaita, E.; Panagoulis, C.; Reri, E.; Skaltsounis, L.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; et al. Correlation of total polyphenolic content with antioxidant and antibacterial activity of 24 extracts from Greek domestic Lamiaceae species. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 4115–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Lim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, D.-S. Dioscin: A synergistic tyrosinase inhibitor from the roots of Smilax china. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1146–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, G.M.; Abdel Bar, F.M.; Baraka, H.N.; Gohar, A.A.; Lahloub, M.-F. A new antioxidant stilbene and other constituents from the stem bark of Morus nigra L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, M.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Sun, S.; Xia, B.; Wu, F.-H. In vivo hypoglycemic effects of phenolics from the root bark of Morus alba. Fitoterapia 2009, 80, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poumale, H.M.P.; Randrianasolo, R.; Rakotoarimanga, J.V.; Raharisololalao, A.; Krebs, H.C.; Tchouankeu, J.C.; Ngadjui, B.T. Flavonoid glycosides and other constituents of Psorospermum androsaemifolium BAKER (Clusiaceae). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 1428–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likhitwitayawuid, K.; Sornsute, A.; Sritularak, B.; Ploypradith, P. Chemical transformations of oxyresveratrol (trans-2,4,3′,5′-tetrahydroxystilbene) into a potent tyrosinase inhibitor and a strong cytotoxic agent. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 5650–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.P.; Zhu, Q.; Fan, C.L.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, M. Phenolic tyrosinase inhibitors from the stems of Cudrania cochinchinensis. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nomura, T.; Fukai, T.; Narita, T.; Terada, S.; Uzawa, J.; Iitaka, Y.; Takasugi, M.; Ishikawa, S.I.; Nagao, S.; Masamune, T. Confirmation of the structures of kuwanons G and H (albanins F and G) by partial synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 2195–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downie, I.M.; Earle, M.J.; Heaney, H.; Shuhaibar, K.F. Vilsmeier formylation and glyoxylation reactions of nucleophilic aromatic compounds using pyrophosphoryl chloride. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 4015–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Curtis-Long, M.J.; Lee, B.W.; Ryu, Y.B.; Park, K.H. Isolation of Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Flavonoids from Morus lhou. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4589–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, R.; Harmalkar, D.S.; Xu, X.; Jang, K.; Lee, K. Bioactive benzofuran derivatives: Moracins A-Z in medicinal chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90C, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, Y.; Konno, C.; Hikino, H.; Matsushita, K. Structure of moracenin B, a hypotensive principle of Morus root barks. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21, 3381–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, V.H.; Srinivasan, R.; Rao, A.V. Wood phenolics of Morus species. IV. Phenolics of the heartwood of five Morus species. Ind. J. Chem. 1975, 13, 453–457. [Google Scholar]
- Ismaya, W.T.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Weijn, A.; Mes, J.J.; Fusetti, F.; Wichers, H.J.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystal Structure of Agaricus bisporus Mushroom Tyrosinase: Identity of the Tetramer Subunits and Interaction with Tropolone. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 5477–5486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, T.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Ko, D.H.; Kim, C.H.; Hwang, J.S.; Ahn, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, T.J. Zebrafish as a new model for phenotype-based screening of melanogenic regulatory compounds. Pigment Cell Res. Spons. Eur. Soc. Pigment Cell Res. Int. Pigment Cell Soc. 2007, 20, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Odaka, Y.; Ogawa, N.; Nakamoto, K.; Kuninaga, H. Identification of geranic acid, a tyrosinase inhibitor in lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklirou, A.D.; Ralli, M.; Dominguez, M.; Papassideri, I.; Skaltsounis, A.-L.; Trougakos, I.P. Hexapeptide-11 is a novel modulator of the proteostasis network in human diploid fibroblasts. Redox Biol. 2015, 5, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.R.; Habasi, M.; Xie, L.Z.; Aisa, H.A. Effect of chlorogenic acid on melanogenesis of B16 melanoma cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 12940–12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamei, Y.; Otsuka, Y.; Abe, K. Comparison of the inhibitory effects of vitamin E analogues on melanogenesis in mouse B16 melanoma cells. Cytotechnology 2009, 59, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakyriakou, A.; Kefalos, P.; Sarantis, P.; Tsiamantas, C.; Xanthopoulos, K.P.; Vourloumis, D.; Beis, D. A zebrafish in vivo phenotypic assay to identify 3-aminothiophene-2-carboxylic acid-based angiogenesis inhibitors. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
| Plant Species | Plant Family | Plant Part | Extraction Solvent | Tyrosinase Inhibition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 μg/mL | 75 μg/mL | IC50 (μg/mL) * | ||||
| Morus alba | Moraceae | wood | MeOH | 97 | 98 | 0.4 ± 0.02 |
| Morus alba | Moraceae | wood | EtOAc | 83 | 96 | 1.3 ± 0.1 |
| Glycyrrhiza glabra | Leguminosae | roots | EtOAc | 82 | 89 | 2.1 ± 0.1 |
| Glycyrrhiza glabra | Leguminosae | roots | MeOH | 92 | 88 | 4.7 ± 0.3 |
| Veratrum album | Liliaceae | whole plant | MeOH | 78 | 60 | 23.5 ± 3.8 |
| Pistacia lentiscus var. chia | Anacardiaceae | branches & leaves | MeOH | 76 | 58 | 62.0 ± 1.2 |
| Cistus salvifolius | Cistaceae | aerial parts | MeOH | 79 | 45 | 85.6 ± 10.8 |
| Umbilicus horizontalis | Crassulaceae | whole plant | MeOH | 81 | 51 | 86.6 ± 11.2 |
| Cistus salvifolius | Cistaceae | aerial parts | EtOAc | 71 | 41 | 95.3 ± 11.3 |
| Lathyrus clymenum | Leguminosae | perisperm | MeOH | 75 | 40 | 95.5 ± 2.1 |
| Sedum sediforme | Crassulaceae | aerial parts | MeOH | 70 | 40 | 116.6 ± 10.2 |
| Paeonia mascula ssp hellenica | Paeoniaceae | aerial parts | MeOH | 70 | 42 | 135.2 ± 12.2 |
| Armeria canescens | Plubaginaceae | whole plant | MeOH | 76 | 43 | 138.1 ± 9.0 |
| Cercis siliquastrum | Leguminosae | aerial parts | MeOH | 70 | 25 | >150 |
| Pistacia terebinthus | Anacardiaceae | leaves & stems | MeOH | 70 | 35 | >150 |
| kojic acid | 1.9 ± 0.1 | |||||
| Compound | Tyrosinase Inhibition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| % ± STD (300 μM) | % ± STD (60 μM) | IC50 ± STD (μΜ) * | |
| Oxyresveratrol (1) | 97.8 ± 0.1 | 93.1 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.04 |
| Kuwanon C (2) | 75.6 ± 1.2 | 46.5 ± 1.3 | 76.2 ± 1.1 |
| Mulberroside A (3) | 58.3 ± 1.4 | 43.1 ± 0.7 | >100 |
| Resorcinol (4) | 60.4 ± 1.0 | 38.0 ± 1.1 | 162.6 ± 18.2 |
| Dihydrooxyresveratrol (5) | 98.2 ± 0.5 | 97.6 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.05 |
| trans-Dihydromorin (6) | 94.3 ± 0.1 | 73.1 ± 0.6 | 9.4 ± 1.3 |
| 2,4,3′-Trihydroxydihydrostilbene (7) | 97.8 ± 0.1 | 96.3 ± 0.5 | 0.8 ± 0.15 |
| Kuwanon H (8) | 49.0 ± 2.6 | 46.0 ± 2.9 | >100 |
| 2,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde (9) | 4.9 ± 0.3 | na | na |
| Morusin (10) | 49.9 ± 2.2 | 31.0 ± 3.2 | >100 |
| Moracin M (11) | 87.2 ± 0.5 | 61.3 ± 1.2 | 8.0 ± 0.6 |
| Kuwanon G (12) | 77.8 ± 2.8 | 59.1 ± 1.4 | 27.5 ± 1.2 |
| Kojic acid | 96.0 ± 0.2 | 94.2 ± 0.2 | 16.1 ± 1.4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaita, E.; Lambrinidis, G.; Cheimonidi, C.; Agalou, A.; Beis, D.; Trougakos, I.; Mikros, E.; Skaltsounis, A.-L.; Aligiannis, N. Anti-Melanogenic Properties of Greek Plants. A Novel Depigmenting Agent from Morus alba Wood. Molecules 2017, 22, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040514
Chaita E, Lambrinidis G, Cheimonidi C, Agalou A, Beis D, Trougakos I, Mikros E, Skaltsounis A-L, Aligiannis N. Anti-Melanogenic Properties of Greek Plants. A Novel Depigmenting Agent from Morus alba Wood. Molecules. 2017; 22(4):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040514
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaita, Eliza, George Lambrinidis, Christina Cheimonidi, Adamantia Agalou, Dimitris Beis, Ioannis Trougakos, Emmanuel Mikros, Alexios-Leandros Skaltsounis, and Nektarios Aligiannis. 2017. "Anti-Melanogenic Properties of Greek Plants. A Novel Depigmenting Agent from Morus alba Wood" Molecules 22, no. 4: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040514
APA StyleChaita, E., Lambrinidis, G., Cheimonidi, C., Agalou, A., Beis, D., Trougakos, I., Mikros, E., Skaltsounis, A.-L., & Aligiannis, N. (2017). Anti-Melanogenic Properties of Greek Plants. A Novel Depigmenting Agent from Morus alba Wood. Molecules, 22(4), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040514








