A Palladium Catalyst System for the Efficient Cross-Coupling Reaction of Aryl Bromides and Chlorides with Phenylboronic Acid: Synthesis and Biological Activity Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
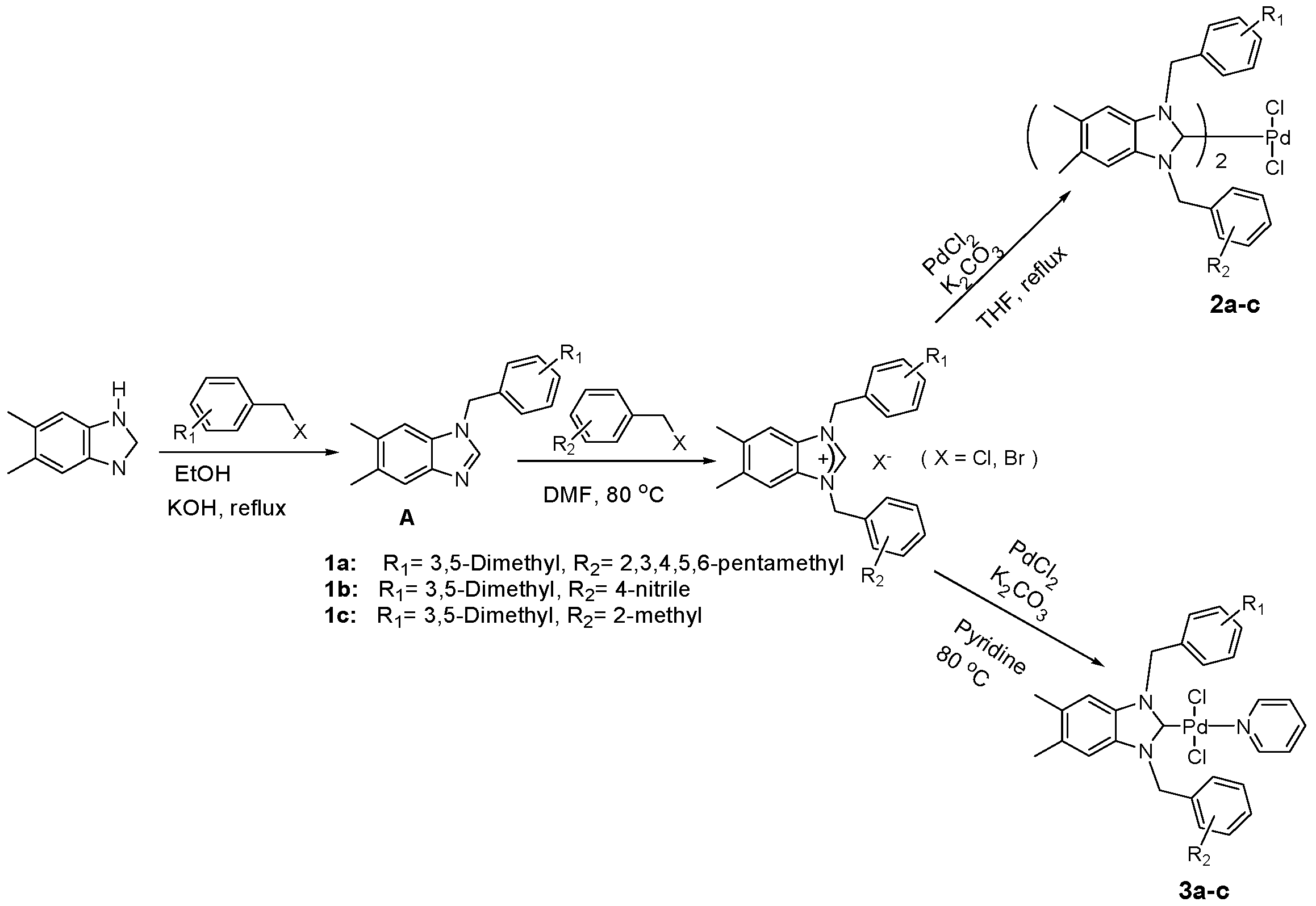
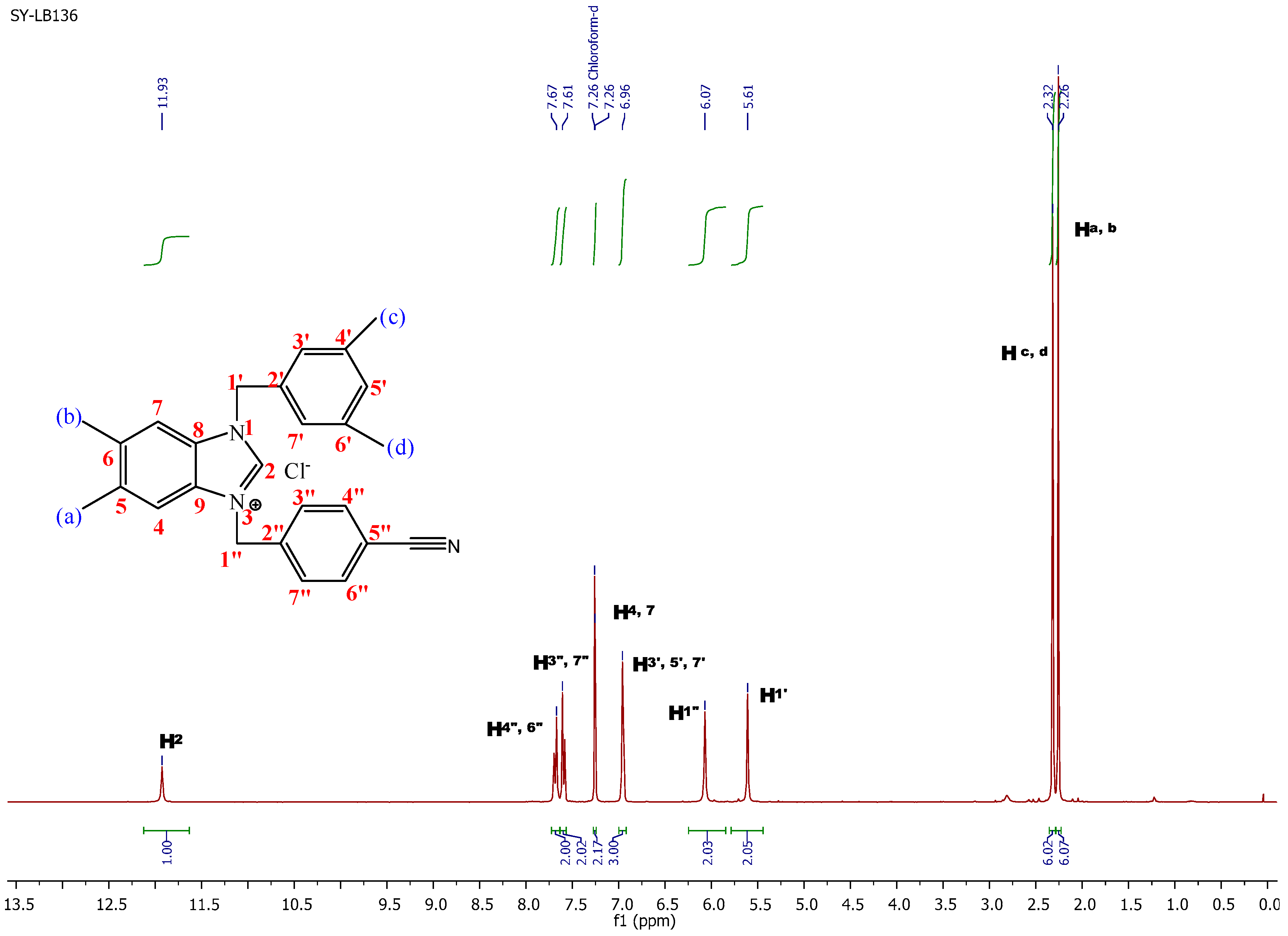
2.1. Preparation of Benzimidazolium Salts 1a–c
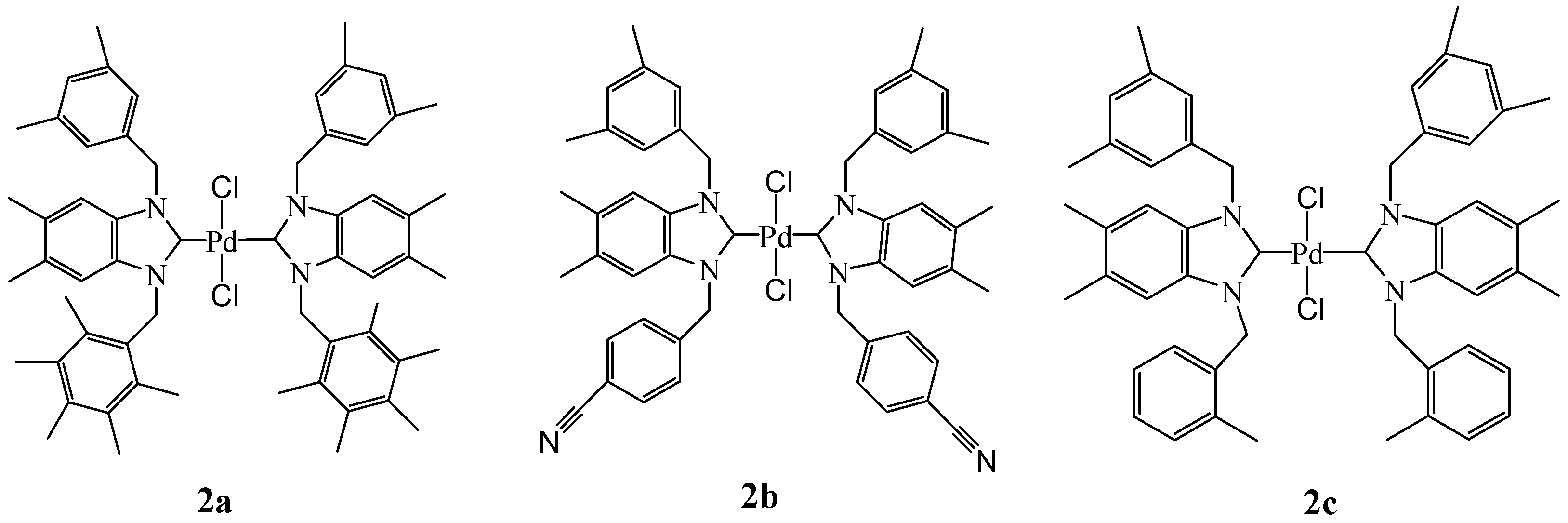
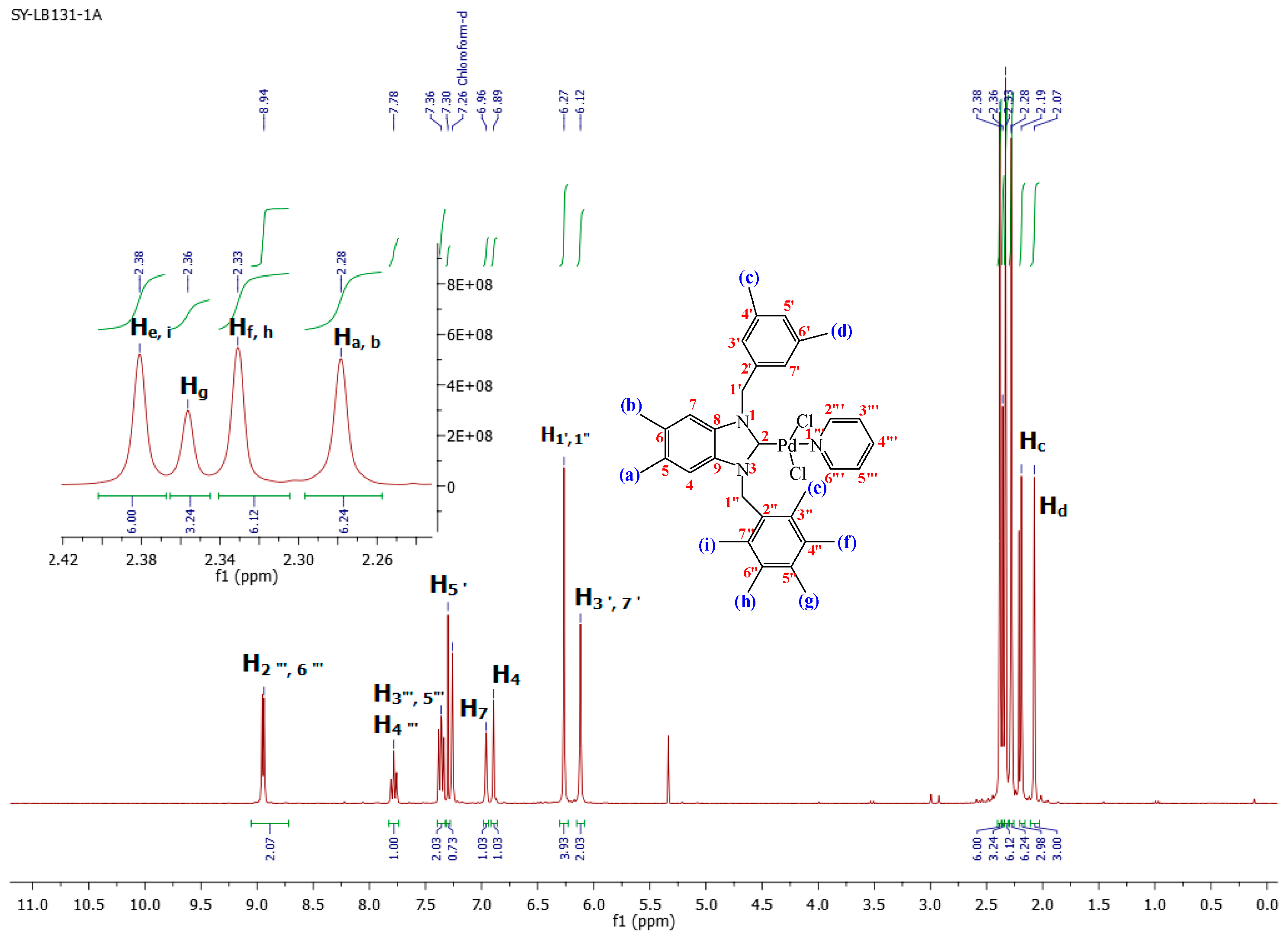
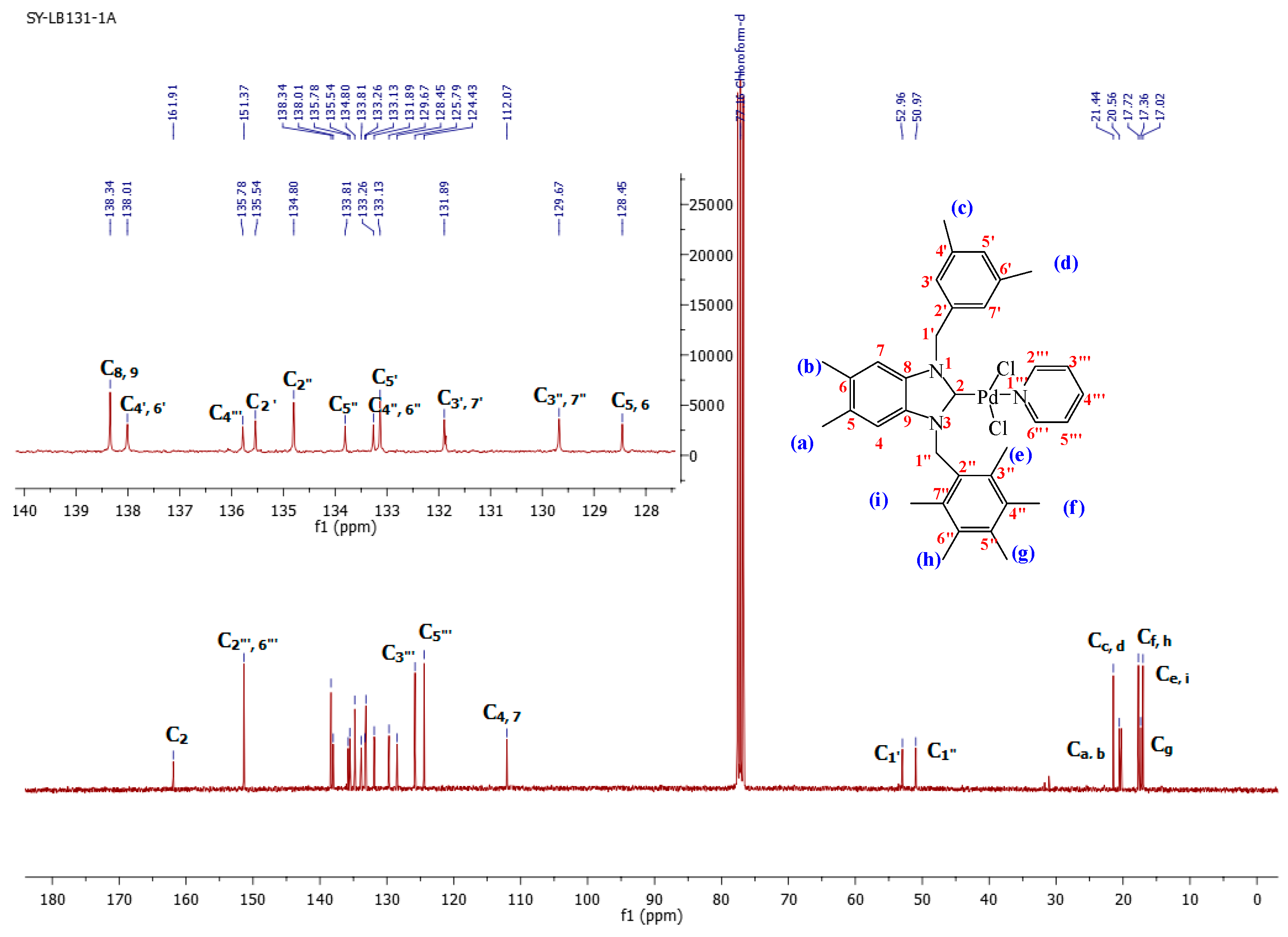
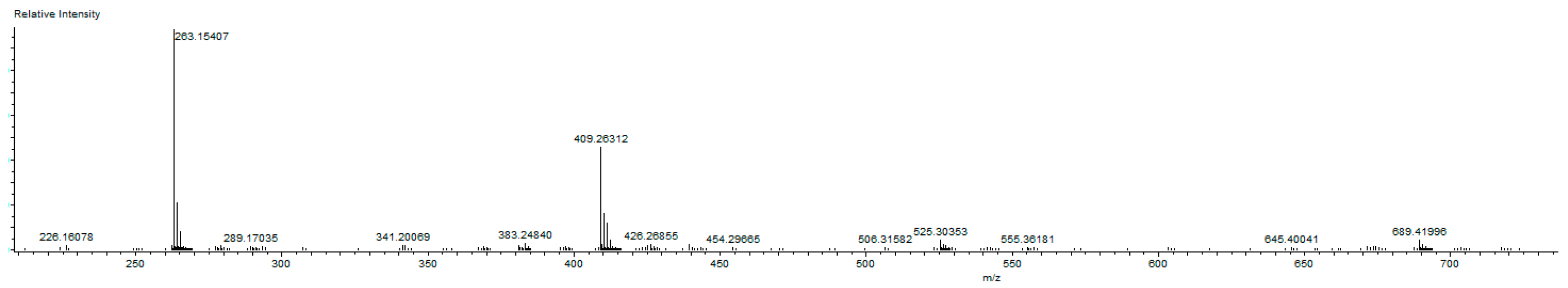
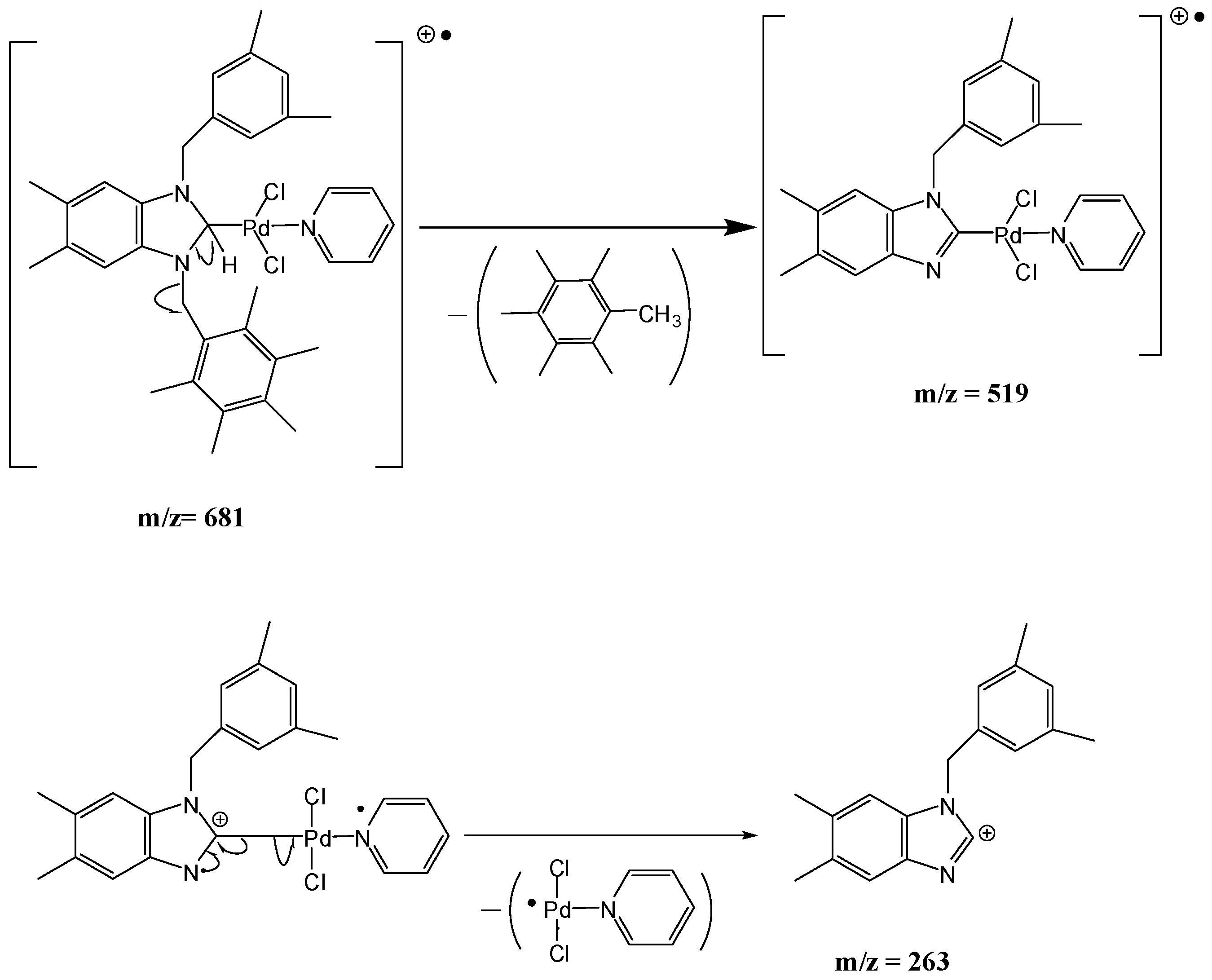
2.2. Preparation of bis-NHC-palladium Complexes 2a–c and PEPPSI-type Complexes 3a–c
2.3. Suzuki Coupling Reaction of Aryl Chlorides/Bromides with Phenylboronic Acid
2.4. Biological Activities
2.4.1. Antibacterial Activity
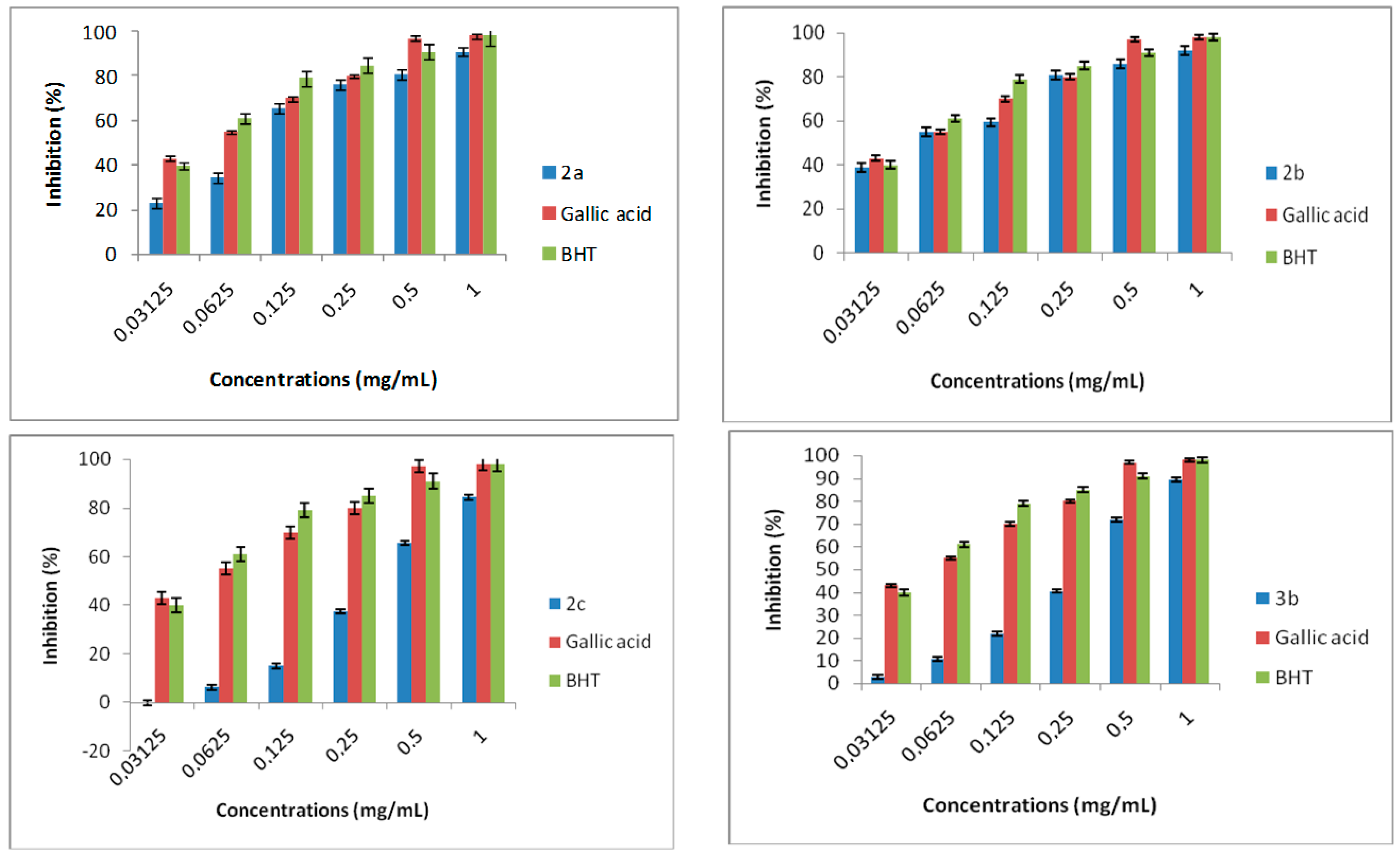
2.4.2. DPPH Radical Scavenging
2.4.3. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthesis of 1-(3,5-Dimethylbenzyl)-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole (A)
3.3. General Preparation of Benzimidazolium Salts 1a–c
3.4. General Preparation of Palladium-bis-NHCs Complexes 2a–c
3.5. General Preparation of PEPPSI Complexes 3a–c
3.6. General Procedure for the Suzuki Miyaura Reaction
3.7. Antibacterial Activity
3.7.1. Bacterial Strains, Media and Growth Conditions
3.7.2. Agar Well Diffusion Method
3.7.3. MIC Determination
3.8. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.9. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Potential
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Natalie, M.S.; Steven, P. Stabilization of Organometallic Species Achieved by the Use of N-Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 1815–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Christmann, U.; Vilar, R. Monoligated Palladium Species as Catalysts in Cross-Coupling Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfgang, A.H. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: A New Concept in Organometallic Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1290–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Hadei, N.; Kantchev, A.E.B.; Christopher, J.O.; Organ, M.G. Electronic Nature of N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands: Effect on the Suzuki Reaction. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 1991–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Hartwig, J.F. Improved Catalysts for the Palladium-Catalyzed Synthesis of Oxindoles by Amide α-Arylation. Rate Acceleration, Use of Aryl Chloride Substrates, and a New Carbene Ligand for Asymmetric Transformations. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 3402–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalho, T.C.; Tanos, C.C.F.; Rennó, M.N.; Ana, P.G.; da Cunha, E.F.F.; Kuča, K. Development of new acetylcholinesterase reactivators: Molecular modeling versus in vitro data. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2010, 185, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, R.; Ahmad Dar, B.; Majeed, R.; Hamid, A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of ursolic acid-triazolyl derivatives as potential anti-cancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 128, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willian, E.A.D.L.; Pereira, A.F.; Alexandre, A.D.C.; Elaine, F.F.D.C.; Ramalho, T.C. Flexibility in the Molecular Design of Acetylcholinesterase Reactivators: Probing Representative Conformations by Chemometric Techniques and Docking/QM Calculations. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2016, 13, 360–371. [Google Scholar]
- Sedat, Y.; Çağlar, Ş.; Murat, A.; Özdemir, İ. Synthesis, characterization and the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions of N-heterocyclic carbene–Pd(II)–pyridine (PEPPSI) complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 776, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Suzan, Ç.; Sedat, Y.; Özdemir, İ. Palladium(II)-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic application. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 28, 423–431. [Google Scholar]
- Matthias, E.; Gregory, C.F. The First Applications of Carbene Ligands in Cross-Couplings of Alkyl Electrophiles: Sonogashira Reactions of Unactivated Alkyl Bromides and Iodides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13642–13643. [Google Scholar]
- Alois, F.; Oliver, R.; Thiel, L.; Ackermann, H.-J.; Schanz, S.P.N. Ruthenium Carbene Complexes with N,N′-Bis(mesityl)imidazol-2-ylidene Ligands: RCM Catalysts of Extended Scope. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 2204–2207. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, A. Recent advances in the cross-coupling reactions of organoboron derivatives with organic electrophiles. J. Organomet. Chem. 1999, 576, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennifer, C.; Dougherty, D.A. The Cation−π Interaction. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1303–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Rische, T.; Eilbracht, P. One-pot synthesis of pharmacologically active secondary and tertiary 1-(3,3-diarylpropyl)amines via rhodium-catalysed hydroamino methylation of 1,1-diarylethenes. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, P.S. Catalytic Cross-coupling Reactions in Biaryl Synthesis. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 263–303. [Google Scholar]
- Mario, R.; Paul, K. New multi-coupling benzylic zinc reagents for the preparation of flexible aromatic compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 1749–1752. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, O.; Yetkin, G.; Özlem, Ö.; Murat, K.; Henri, D.; Christian, B. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: Useful Ligands for the Palladium-Catalysed Direct C5 Arylation of Heteroaromatics with Aryl Bromides or Electro N-Deficient Aryl Chlorides. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 41, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.T.; Sakamuru, S.; Huang, R.L.; Teneva, N.; Simmons, S.O.; Xia, M.H.; Tice, R.R.; Austin, C.P.; Myung, K. High-throughput genotoxicity assay identifies antioxidants as inducers of DNA damage response and cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5423–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalauni, S.K.; Choudhary, M.I.; Khalid, A.; Manandhar, M.D.; Shaheen, F.; Atta-ur-Rahman, G.M.B. New cholinesterase inhibiting steroidal alkaloids from the leaves of Sarcococca coriacea of Nepalese origin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 1423–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta-ur-Rahman, W.A.T.; Nawas, S.A.; Choudhary, M.I. New cholinesterase inhibiting bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids from Cocculus pendulus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, B.; Ahmad, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Nisar, M.; Ahmad, M. In vitro inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase and lipoxygenase by crude extract of Myricaria elegans Royle. J. Biol. Sci. 2003, 11, 1046–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Güven, K.; Yücel, E.; Cetintas, F. Antimicrobial activities of fruits of Crataegus and Pyrus species. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standard. Referece method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Conidium-Forming Filamentous Fungi. Proposed Standard M38-P; National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standard: Wayne, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, A.J.; Schmidt, R. The anti-oxidant activity of Chinese herbs for eczema and of placebo herbs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1997, 56, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.J.R.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaivani, P.; Umadevi, C.; Prabhakaran, R.; Dallemer, F.; Mohan, P.S.; Natarajan, K. New palladium(II) complexes of 3-methoxysalicylaldehyde-4(N)-substituted thiosemicarbazones: Synthesis, spectroscopy, X-ray crystallography and DNA/protein binding study. Polyhedron 2014, 80, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, T.T.; Paschoal, D.; Motta, E.V.S.; Carpanez, A.G.; Lopes, M.T.P.; Fontes, E.S.; Dos Santos, H.F.; Silva, H.; Grazul, A.P.S.R.M. Platinum (II) and palladium (II) aryl-thiosemicarbazone complexes: Synthesis, characterization, molecular modeling, cytotoxicity, and antimicrobial activity. J. Coord. Chem. 2014, 67, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, H.; Iftikhar, H.B.; Saqib, A.; Saira, S.; Muhammad, S.; Khurram, S.M. Synthesis and spectroscopic and thermogravimetric characterization of heterobimetallic complexes with Sn (IV) and Pd (II); DNA binding, alkaline phosphatase inhibition and biological activity studies. J. Coord. Chem. 2015, 68, 662–677. [Google Scholar]
- EN-Jun, G.; Qiong, W.; Chuan-Sheng, W.; Ming-Chang, Z.; Lei, W.; Hong-Yan, L.; Yun, H.; Ya-Guang, S. Synthesis, interaction with double-helical DNA and biological activity of new Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes with phenylglycine. J. Coord. Chem. 2009, 62, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–3 are available from the authors.
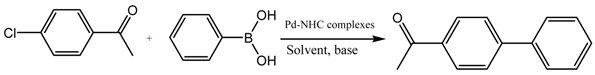
| Entry | Pd-NHC Complexes | Solvent | Base | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2a | Toluene | KOtBu | 73 |
| 2 | 3a | 60 | ||
| 4 | 2a | DMF/H2O | KOtBu | 0 |
| 5 | 3a | 89 | ||
| 6 | 2a | DMF/H2O | K2CO3 | 1 |
| 7 | 3a | 90 |
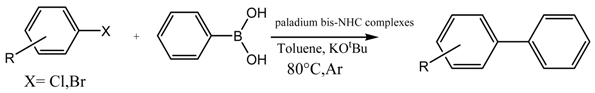
| Entry | Ar-X | Pd-NHC Complexes | Time (h) | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 2a | 3 | 73 |
| 2 | 2b | 3 | 66 | |
| 3 | 2c | 3 | 83 | |
| 4 | 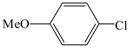 | 2a | 12 | 6 |
| 5 | 2b | 12 | 4 | |
| 6 | 2c | 12 | 5 | |
| 7 | 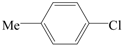 | 2a | 12 | 6 |
| 8 | 2b | 12 | 2 | |
| 9 | 2c | 12 | 2 | |
| 10 | 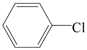 | 2a | 12 | 28 |
| 11 | 2b | 12 | 25 | |
| 12 | 2c | 12 | 20 | |
| 13 |  | 2a | 12 | 4 |
| 14 | 2b | 12 | 14 | |
| 15 | 2c | 12 | 14 | |
| 16 | 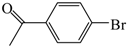 | 2a | 3 | 85 |
| 17 | 2b | 3 | 90 | |
| 18 | 2c | 3 | 91 | |
| 19 | 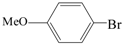 | 2a | 6 | 76 |
| 20 | 2b | 6 | 91 | |
| 21 | 2c | 6 | 84 | |
| 22 | 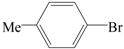 | 2a | 6 | 47 |
| 23 | 2b | 6 | 75 | |
| 24 | 2c | 6 | 85 | |
| 25 | 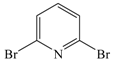 | 2a | 6 | Mono = 42 Di = 58 |
| 26 | 2b | 6 | Mono = 44 Di = 56 | |
| 27 | 2c | 6 | Mono = 25 Di = 75 |
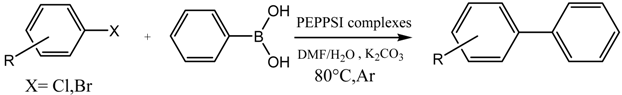
| Entry | Ar-X | Pd-NHC Complexes | Time (h) | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 3a | 3 | 90 |
| 2 | 3b | 3 | 100 | |
| 3 | 3c | 3 | 99 | |
| 4 |  | 3a | 12 | 28 |
| 5 | 3b | 12 | 9 | |
| 6 | 3c | 12 | 25 | |
| 7 |  | 3a | 12 | 34 |
| 8 | 3b | 12 | 15 | |
| 9 | 3c | 12 | 22 | |
| 10 |  | 3a | 12 | 77 |
| 11 | 3b | 12 | 67 | |
| 12 | 3c | 12 | 67 | |
| 13 |  | 3a | 3 | 100 |
| 14 | 3b | 3 | 100 | |
| 15 | 3c | 3 | 100 | |
| 16 |  | 3a | 6 | 100 |
| 17 | 3b | 6 | 100 | |
| 18 | 3c | 6 | 100 | |
| 19 |  | 3a | 6 | 100 |
| 20 | 3b | 6 | 100 | |
| 21 | 3c | 6 | 100 | |
| 22 |  | 3a | 6 | 100 Diarylated |
| 23 | 3b | 6 | 100 Diarylated | |
| 45 | 3c | 6 | 100 Diarylated |
| Microorganism Indicator | Compounds | Inhibition Zone (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Micrococcus luteus LB 14110 | 2a | 18 ± 0.5 |
| 2b | 23 ± 0.2 | |
| 2c | 24 ± 0.1 | |
| 3a | 25 ± 0.3 | |
| 3b | 30 ± 0.5 | |
| 3c | 22 ± 0.4 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 | 2a | 16 ± 1.1 |
| 2b | 17 ± 0.5 | |
| 2c | 15 ± 0.3 | |
| 3a | 15 ± 0.3 | |
| 3b | 16 ± 0.5 | |
| 3c | 12 ± 0.4 | |
| Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19117 | 2a | 20 ± 0.4 |
| 2b | 16 ± 1.5 | |
| 2c | 19 ± 0.5 | |
| 3a | 16 ± 0.3 | |
| 3b | 16 ± 0.3 | |
| 3c | 14 ± 0.5 | |
| Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 14028 | 2a | 14 ± 0.4 |
| 2b | 16 ± 0.4 | |
| 2c | 13 ± 0.3 | |
| 3a | 12 ± 0.1 | |
| 3b | 16 ± 0.5 | |
| 3c | - | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 49189 | 2a | - |
| 2b | 16 ± 0.2 | |
| 2c | - | |
| 3a | - | |
| 3b | - | |
| 3c | - |
| Microorganism Indicator | Compounds | MIC (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Micrococcus luteus LB 14110 | 2a | 0.039 |
| 2b | 0.0197 | |
| 2c | 0.025 | |
| 3a | 0.3125 | |
| 3b | 0.039 | |
| 3c | 0.625 | |
| Ampicillin | 0.0195 | |
| Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19117 | 2a | 1.25 |
| 2b | 0.078 | |
| 2c | 1.25 | |
| 3a | 2.5 | |
| 3b | 0.3125 | |
| 3c | 1.25 | |
| Ampicillin | 0.039 | |
| Salmonella typhimurium ATCC14028 | 2a | 2.5 |
| 2b | 1.25 | |
| 2c | 2.5 | |
| 3a | 2.5 | |
| 3b | 2.5 | |
| 3c | 5 | |
| Ampicillin | 0.625 |
| Compounds | (AChEI) (%) |
|---|---|
| 2a | — |
| 2b | 38.15 |
| 2c | — |
| 3a | 32.15 |
| 3b | 32.80 |
| 3c | — |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamia, B.; Chakchouk-Mtibaa, A.; Hallouma, B.; Mansour, L.; Mellouli, L.; Özdemir, I.; Yaşar, S.; Hamdi, N. A Palladium Catalyst System for the Efficient Cross-Coupling Reaction of Aryl Bromides and Chlorides with Phenylboronic Acid: Synthesis and Biological Activity Evaluation. Molecules 2017, 22, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030420
Lamia B, Chakchouk-Mtibaa A, Hallouma B, Mansour L, Mellouli L, Özdemir I, Yaşar S, Hamdi N. A Palladium Catalyst System for the Efficient Cross-Coupling Reaction of Aryl Bromides and Chlorides with Phenylboronic Acid: Synthesis and Biological Activity Evaluation. Molecules. 2017; 22(3):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030420
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamia, Boubakri, Ahlem Chakchouk-Mtibaa, Bilel Hallouma, Lamjed Mansour, Lotfi Mellouli, Ismail Özdemir, Sedat Yaşar, and Naceur Hamdi. 2017. "A Palladium Catalyst System for the Efficient Cross-Coupling Reaction of Aryl Bromides and Chlorides with Phenylboronic Acid: Synthesis and Biological Activity Evaluation" Molecules 22, no. 3: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030420
APA StyleLamia, B., Chakchouk-Mtibaa, A., Hallouma, B., Mansour, L., Mellouli, L., Özdemir, I., Yaşar, S., & Hamdi, N. (2017). A Palladium Catalyst System for the Efficient Cross-Coupling Reaction of Aryl Bromides and Chlorides with Phenylboronic Acid: Synthesis and Biological Activity Evaluation. Molecules, 22(3), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030420