Evaluation of Extraction and Degradation Methods to Obtain Chickpeasaponin B1 from Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
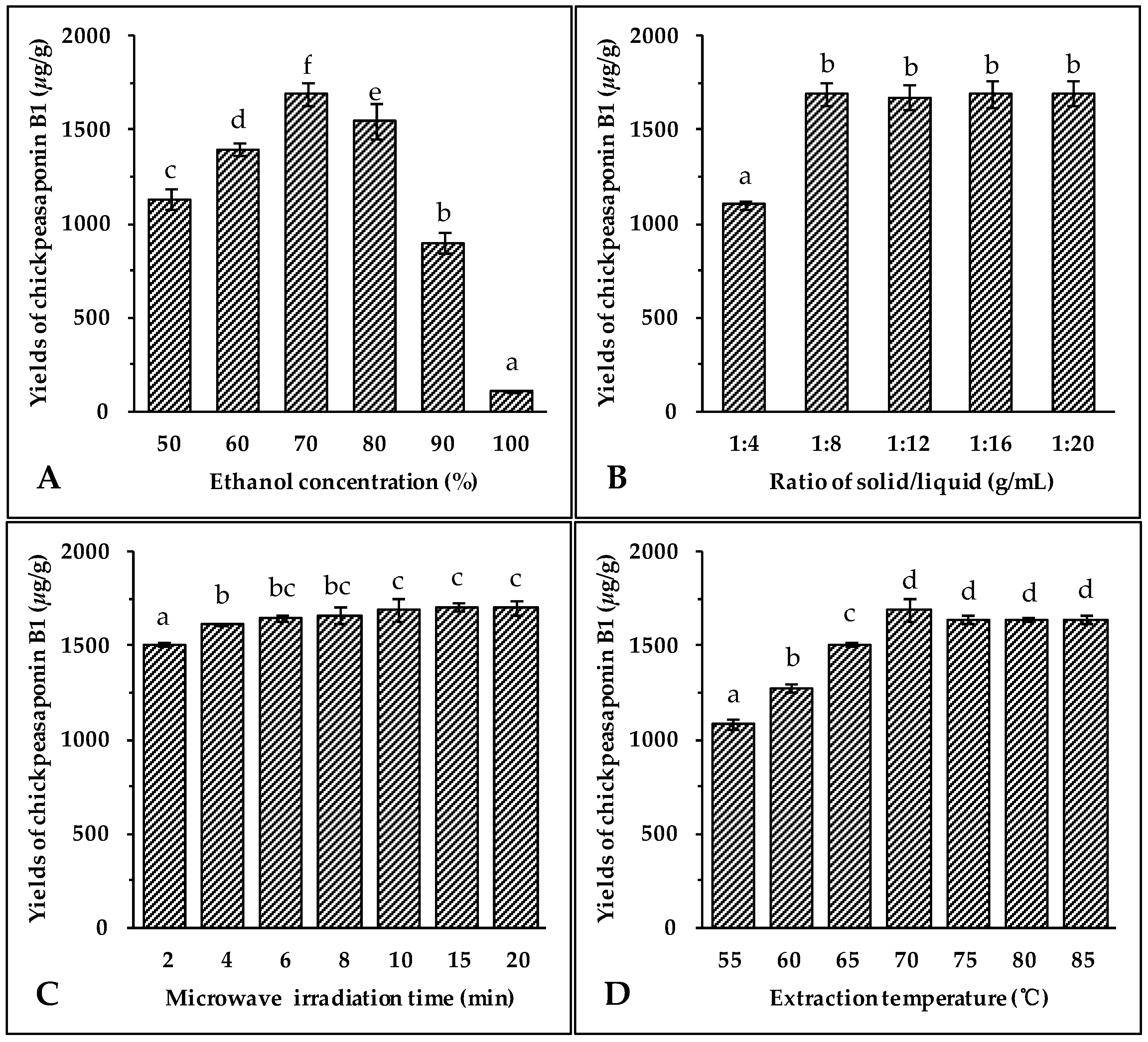
2.1. Optimization of MAE Conditions
2.1.1. Effect of Ethanol Concentration
2.1.2. Effect of Solvent/Solid Ratio
2.1.3. Effect of Irradiation Time
2.1.4. Effect of Extraction Temperature
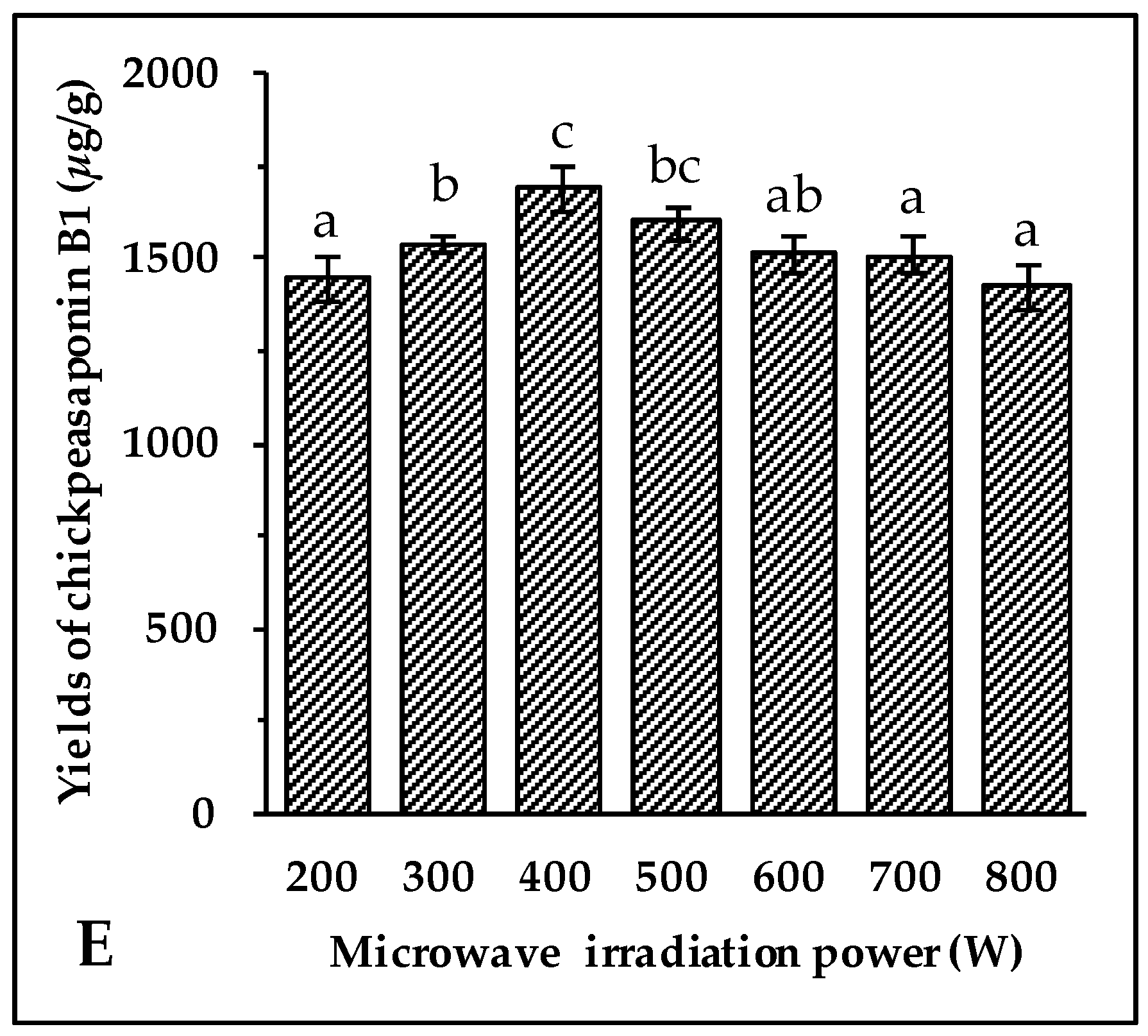
2.1.5. Effect of Irradiation Power
2.2. Comparison of Different Extraction Methods
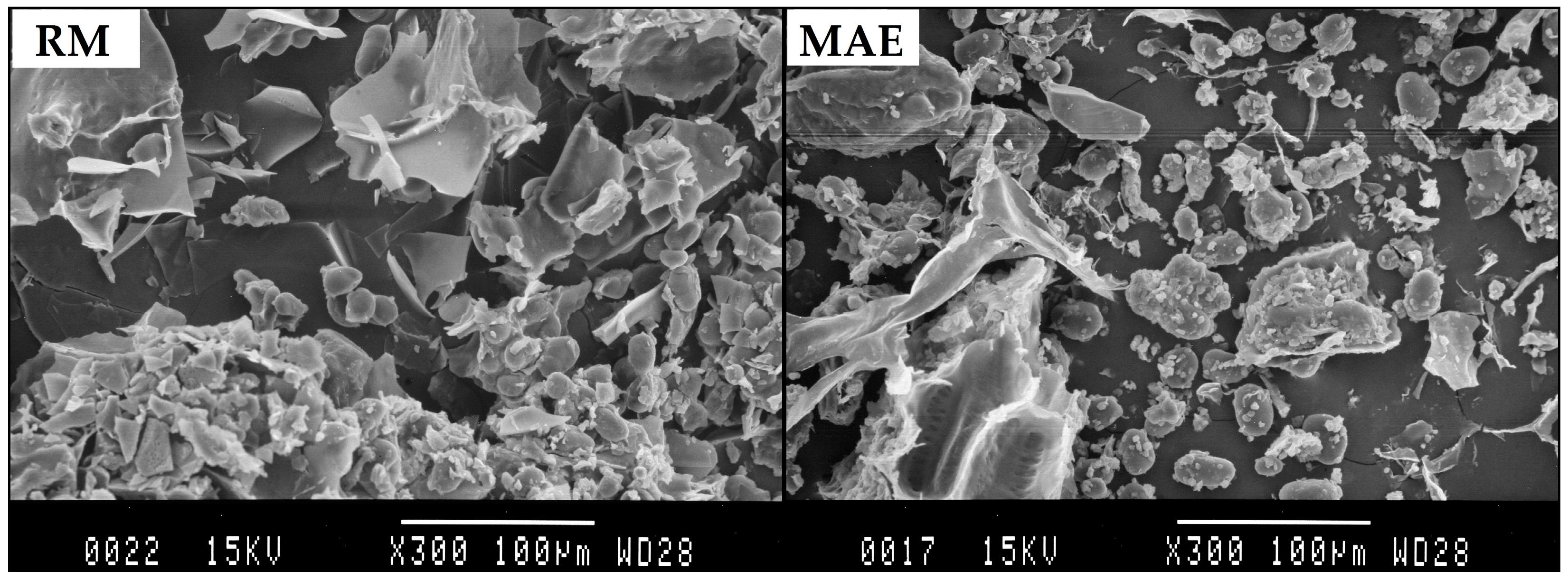
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation
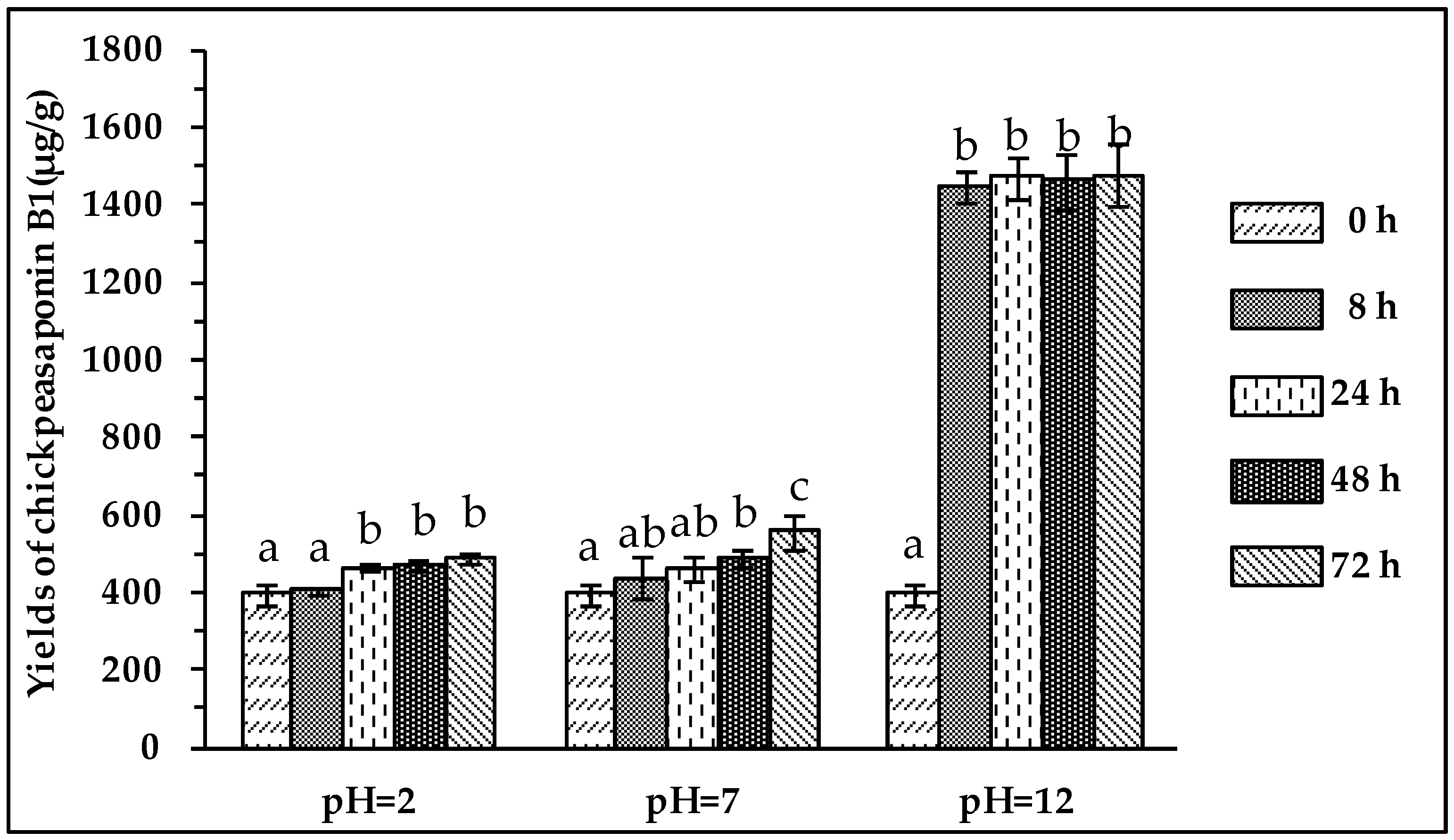
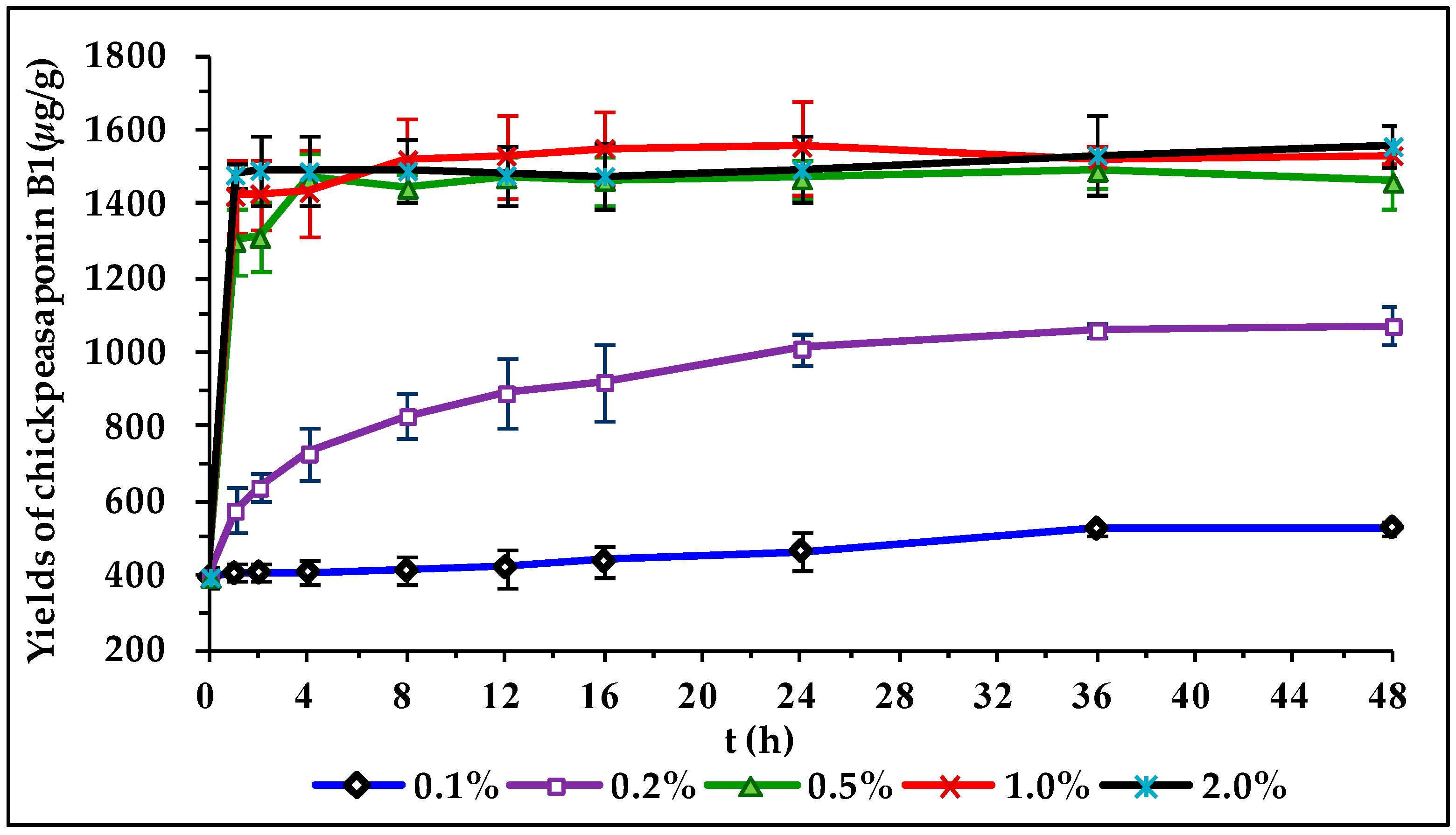
2.4. Comparison of Degradation Methods
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
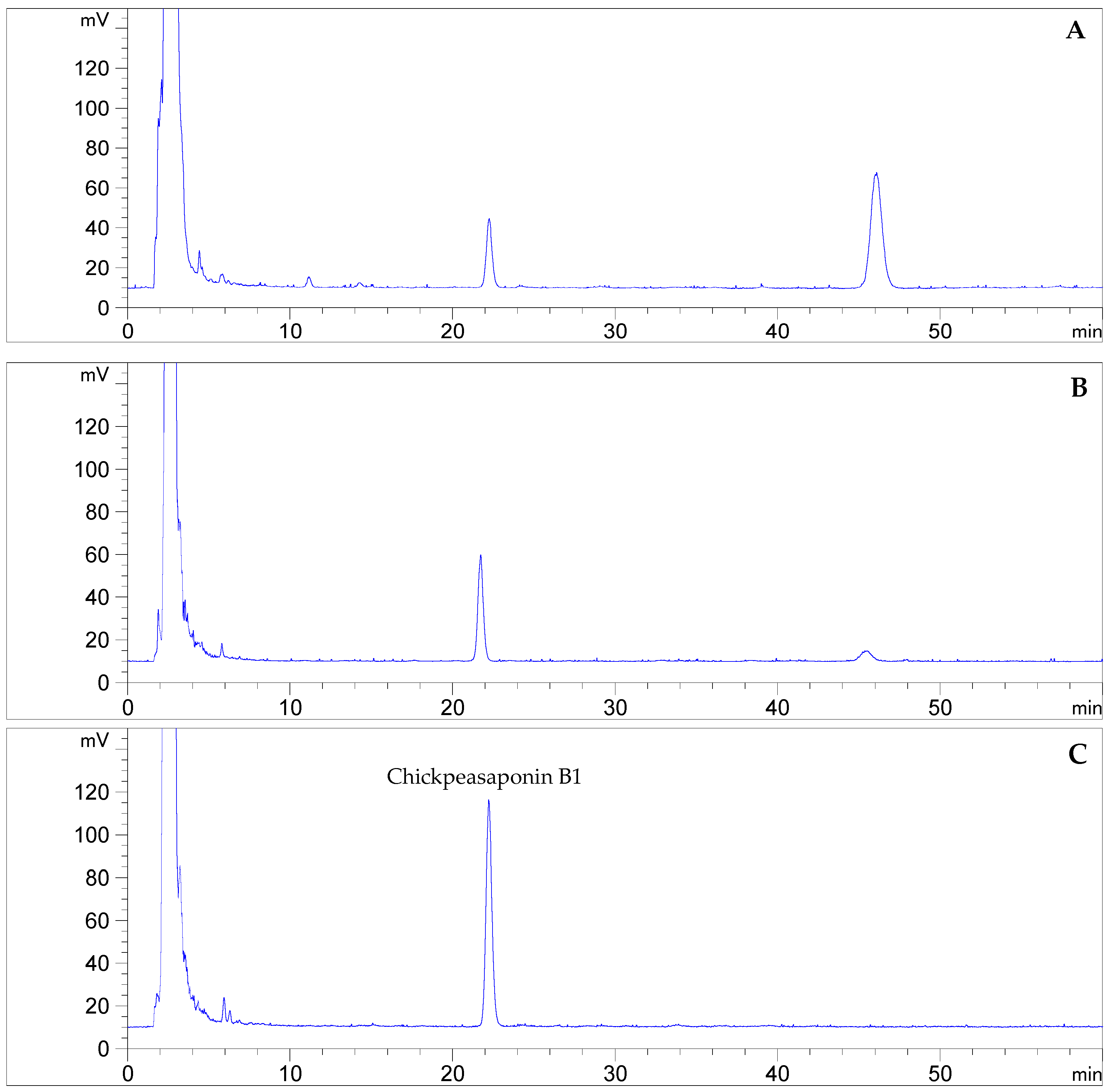
3.2. HPLC Analysis
3.3. Comparison of Extraction Methods
3.3.1. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
3.3.2. Heat Reflux Extraction (HRE)
3.3.3. Soxhlet Extraction (SE)
3.3.4. Ultrasonic Extraction (UE)
3.4. Optimization of MAE Conditions
3.5. Extract Concentration
3.6. Comparison of Degradation Methods
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chitisankul, W.T.; Shimada, K.; Omizu, Y.; Uemoto, Y.; Varanyanond, W.; Tsukamoto, C. Mechanism of DDMP-saponin degradation and maltol production in soymilk preparation. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Tsukamato, C.; Singh, R.J.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.S.; Yang, S.H.; Chung, G. The Sg-6 saponins, new components in wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. and Zucc.): Polymorphism, geographical distribution and inheritance. Euphytica 2014, 198, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, I.; Saito, M.; Taniyama, T.; Yoshikawa, M. Saponin and sapogenol. XXXIX. Structure of soyasaponins A1, a bisdeamoside of soyasapogenol A, from soybean, the seeds of Glycine max MERRIL. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, I.; Wang, K.H.; Taniyama, T.; Yoshikawa, M. Saponin and sapogenol. XLI. Reinvestigation of the structures of soyasapogenols A, B, and E, oleanene-sapogenols from soybean. Structures of soyasaponins I, II, and III. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniyama, T.; Nagahama, Y.; Yoshikawa, M.; Kitagawa, I. Saponin and sapogenol. XLIII. Acetyl-soyasaponins A4, A5, and A6, new astringent bisdeamosides of soyasapogenol A, from Japanese soybean, the seeds of Glycine max MERRIL. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 2829–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Yamauchi, F.; Harada, K.; Okubo, K. Inheritance of “group A saponin” in soybean seed. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1990, 54, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Kudo, S.; Shimoyamada, M.; Harada, K.; Okubo, K. Composition and structure of “group A saponin” in soybean seed. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1991, 55, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, C.; Kikuchi, A.; Kudou, S.; Harada, K.; Kitamura, K.; Okubo, K. Group A acetyl saponin-deficient mutant from the wild soybean. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 4139–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudou, S.; Tonomura, M.; Tsukamoto, C.; Shimoyamada, M.; Uchida, T.; Okubo, K. Isolation and structural elucidation of the major genuine soybean saponin. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudou, S.; Tonomura, M.; Tsukamoto, C.; Uchida, T.; Sakabe, T.; Tamura, N.; Okubo, K. Isolation and structural elucidation of DDMP-conjugated soyasaponins as genuine saponins from soybean seeds. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1993, 57, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudou, S.; Tonomura, M.; Tsukamoto, C.; Tsukamoto, C.; Uchida, T.; Yoshikoshi, M.; Okubo, K. Structural elucidation and physiological properties of genuine soybean saponina. ACS Symp. 1994, 547, 340–348. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Teng, S.P.; Popovich, D.G. Generation of group B soyasaponins I and III by hydrolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3620–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daveby, Y.D.; Aman, P.; Betz, J.M.; Musser, S.M. Effect of storage and extraction on ratio of soyasaponin I to 2,3-dihydro-2,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4-pyrone-conjugated soyasaponin I in dehulled peas (Pisum sativum L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 1998, 78, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lee, S.O.; Hendrich, S.; Murphy, P.A. Quantification of the group B soyasaponins by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reim, V.; Rohn, S. Characterization of saponins in peas (Pisumsativum L.) by HPTLC coupled to mass spectrometry and a hemolysis assay. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorent-Martínez, E.J.; Spínola, V.; Gouveia, S.; Castilho, P.C. HPLC-ESI-MSn characterization of phenolic compounds, terpenoidsaponins, and other minor compounds in Bituminaria bituminosa. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 69, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.G.; Sutherland, D.H.; Richards, K.W.; Zhang, H.X. Oleanane triterpenoid saponins of Caragana arborescens and their quantitative determination. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 77, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Esa, N.M.; Loh, S.P. In vitro inhibitory activity of selected legumes against pancreatic lipase. J. Food Biochem. 2015, 39, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xu, B.J. Inhibitory effects of phenolics and saponins from commonly consumed food legumes in China against digestive enzymes pancreatic lipase and α-glycosidase. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 2246–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melek, F.R.; Kassem, I.A.A.; Miyase, T.; Fayad, W. Caspicaosides E-K, triterpenoid saponins and cytotoxic acylated saponins from fruits of Gleditsia caspica Desf. Phytochemistry 2014, 100, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lev-Yadun, S.; Gopher, A.; Abbo, S. The cradle of agriculture. Science 2000, 288, 1602–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés-Giraldo, I.; Megías, C.; Alaiz, M.; Girón-Calle, J.; Vioque, J. Purification of free arginine from chickpea (Cicer arietinum) seeds. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archak, S.; Tyagi, R.K.; Harer, P.N.; Mahase, L.B.; Singh, N.; Dahiya, O.P.; Nizar, M.A.; Singh, M.; Tilekar, V.; Kumar, V. Characterization of chickpea germplasm conserved in the Indian National Genebank and development of a core set using qualitative and quantitative trait data. Crop J. 2016, 4, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.H.; Zhang, L.P.; Gao, P.; Shao, Z.Y. Isolation and characterisation of the isoflavones from sprouted chickpea seeds. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, K.R.; Eagles, J.; Fenwick, G.R. Saponin composition of 13 varieties of legume seed using fast atom bombardment mass-spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1988, 42, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerem, Z.; German-Shashoua, H.; Yarden, O. Microwave-assisted extraction of bioactive saponins from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Watanabe, T.; Uchida, T.; Kanazawa, T.; Osanai, T.; Okumura, K. Hypoglycemic effect of soyasaponin B extracted from hypocotyl on the increasing blood glucose in diabetic mice (KK-Ay/Ta). J. Jpn. Soc. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 27, 358–366. [Google Scholar]
- Kinjo, J.; Imagire, M.; Udayama, M.; Arao, T.; Nohara, T. Structure-hepatoprotective relationships study of soyasaponin I–IV having soyasapogenol B as aglycone. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Park, Y.; Joh, E.; Kim, D. Soyasaponin I attenuates TNBS-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting NF-κB pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10929–10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.A.; Berhow, M.; Singletary, K.W. Induction of macroautophagy in human colon cancer cell by soybean B-group triterpenoid saponins. Carcinogensis 2005, 26, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinela, J.; Prieto, M.A.; Carvalho, A.M.; Barreiro, M.F.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, L.C.F.R. Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic acids and flavonoids and production of antioxidant ingredients from tomato: A nutraceutical-oriented optimization study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 164, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.B.; Wu, H.F.; Li, H.W.; Jia, Q.; Song, Y. Comparison of microwave-assisted and conventional extraction of mangiferin from mango (Mangifera indica L.) leaves. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 3457–3462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Renoe, B.W. Microwave-assisted extraction. Am. Lab. 1994, 26, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Eskilsson, P.C.; Björklund, E. Analytical-scale microwave-assisted extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 902, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.X. Development of microwave assisted extraction. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2003, 31, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Ondruschka, B.; Asghari, J. Microwave-assisted extraction—a state-of-the-art overview of varieties. Chimia 2006, 60, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Weller, C.L. Recent advances in extraction of nutraceuticals from plants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, E.; Collina, S.; Rossi, D.; Bazzoni, D.; Gaggeri, R.; Bracco, F.; Azzolina, O. Influence of the extraction mode on the yield of hyperoside, vitexin and vitexin-2′′-O-rhamnoside from Crataegus monogyna Jacq. (Hawthorn). Phytochem. Anal. 2008, 19, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.L.; Shi, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.Q. Development of an aqueous polyethylene glycol-based extraction and recovery method for almond (Prunus armeniaca L.) protein. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 3319–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nescatelli, R.; Carradori, S.; Marini, F.; Caponigro, V.; Bucci, R.; De Monte, C.; Mollica, A.; Mannina, L.; Ceruso, M.; Supuran, C.T.; Secci, D. Geographical characterization by MAE-HPLC and NIR methodologies and carbonic anhydrase inhibition of Saffron components. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belwal, T.; Bhatt, I.D.; Rawal, R.S.; Pande, V. Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) conditions using polynomial design for improving antioxidant phytochemicals in Berberis asiatica Roxb. ex DC. leaves. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 95, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Qiao, L.; Gu, H.Y.; Yang, F.J.; Yang, L. Development of brӧnsted acidic ionic liquid based microwave assisted method for simultaneous extraction of pectin and naringin from pomelo peels. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemwimon, S.; Pavasant, P.; Shotipruk, A. Microwave-assisted extraction of antioxidative anthraquinones from roots of Morinda citrifolia. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 54, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, B.H.; Wu, H.; Lai, F.R.; Li, X.F. Microwave-assisted extraction and a new determination method for total steroid saponins from Dioscorea zingiberensis C.H. Wright. Steroids 2015, 104, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Liu, Y.B.; Liang, Z.S.; Wang, W.L. Investigation on ultrasound-assisted extraction of salvianolic acid B from Salvia miltiorrhiza root. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010, 17, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, E.; Ramaiola, I.; Urbano, M.; Bracco, F.; Collina, S. Microwave-assisted extraction of coumarin and related compounds from Melilotus officinalis (L.) Pallas as an alternative to Soxhlet and ultrasound-assisted extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1125, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.S.; Liu, Z.B.; Wang, J.H. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of five isoflavones from Iris tectorum Maxim. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 78, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmakani, M.T.; Rezaei, K. Comparison of microwave-assisted hydrodistillation with the traditional hydrodistillation method in the extraction of essential oils from Thymus vulgaris L. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Sample of chickpeasaponin B1 is available from the authors.
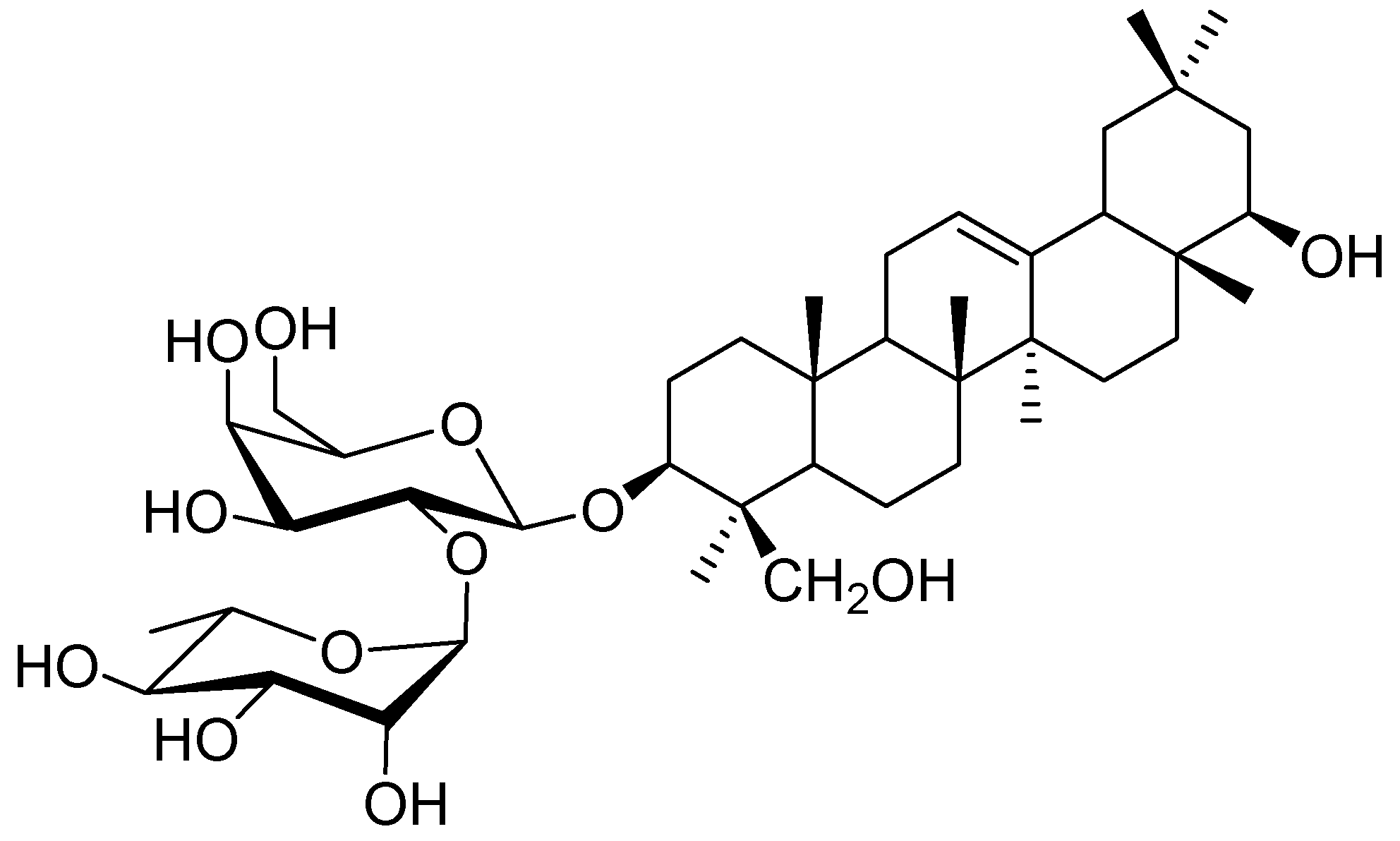

| MAE | HRE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction Time (min) | Yields (μg/g) | Extraction Time (min) | Yields (μg/g) |
| 2 | 1505.31 ± 10.22 | 10 | 1277.34 ± 19.39 |
| 4 | 1613.20 ± 7.80 | 20 | 1433.34 ± 17.94 |
| 6 | 1651.91 ± 17.64 | 30 | 1490.64 ± 70.29 |
| 8 | 1666.89 ± 43.85 | 60 | 1557.67 ± 54.23 |
| 10 | 1692.27 ± 63.72 | 90 | 1610.18 ± 23.13 |
| 15 | 1710.83 ± 20.88 | 120 | 1628.20 ± 33.29 |
| 20 | 1703.22 ± 35.60 | 150 | 1595.12 ± 35.37 |
| SE | UE | ||
| Extraction Time (min) | Yields (μg/g) | Extraction Time (min) | Yields (μg/g) |
| 30 | 212.28 ± 10.96 | 10 | 434.41 ± 46.11 |
| 60 | 246.80 ± 42.79 | 20 | 479.95 ± 20.65 |
| 90 | 373.81 ± 52.17 | 30 | 675.25 ± 26.80 |
| 120 | 493.67 ± 40.35 | 40 | 690.49 ± 29.26 |
| 150 | 599.63 ± 44.92 | 50 | 708.59 ± 35.87 |
| 180 | 776.00 ± 67.17 | 60 | 773.49 ± 22.92 |
| 210 | 1079.11 ± 59.50 | 90 | 871.28 ± 27.92 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, K.; Gao, H.; Wang, R.-R.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Y.-X.; Liu, X.-H.; Liu, K.; Wang, W. Evaluation of Extraction and Degradation Methods to Obtain Chickpeasaponin B1 from Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Molecules 2017, 22, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020332
Cheng K, Gao H, Wang R-R, Liu Y, Hou Y-X, Liu X-H, Liu K, Wang W. Evaluation of Extraction and Degradation Methods to Obtain Chickpeasaponin B1 from Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Molecules. 2017; 22(2):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020332
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Kun, Hua Gao, Rong-Rong Wang, Yang Liu, Yu-Xue Hou, Xiao-Hong Liu, Kun Liu, and Wei Wang. 2017. "Evaluation of Extraction and Degradation Methods to Obtain Chickpeasaponin B1 from Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.)" Molecules 22, no. 2: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020332
APA StyleCheng, K., Gao, H., Wang, R.-R., Liu, Y., Hou, Y.-X., Liu, X.-H., Liu, K., & Wang, W. (2017). Evaluation of Extraction and Degradation Methods to Obtain Chickpeasaponin B1 from Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Molecules, 22(2), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020332






