Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classes of Antimalarial Drugs
3. Mechanism of Antimalarial Drug Resistance
3.1. Mechanism of Resistance in Quinolines
3.2. Mechanism of Resistance in Artemisinins
3.3. Mechanism of Resistance to 4-Quinolinemethanols
3.4. Mechanism of Resistance to Hydroxynaphthoquinones and Diaminopyrimidines
3.5. Mechanism of Resistance to Sulphonamides
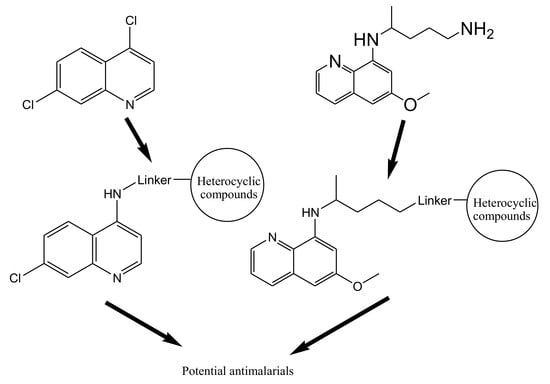
4. Hybrid Compounds
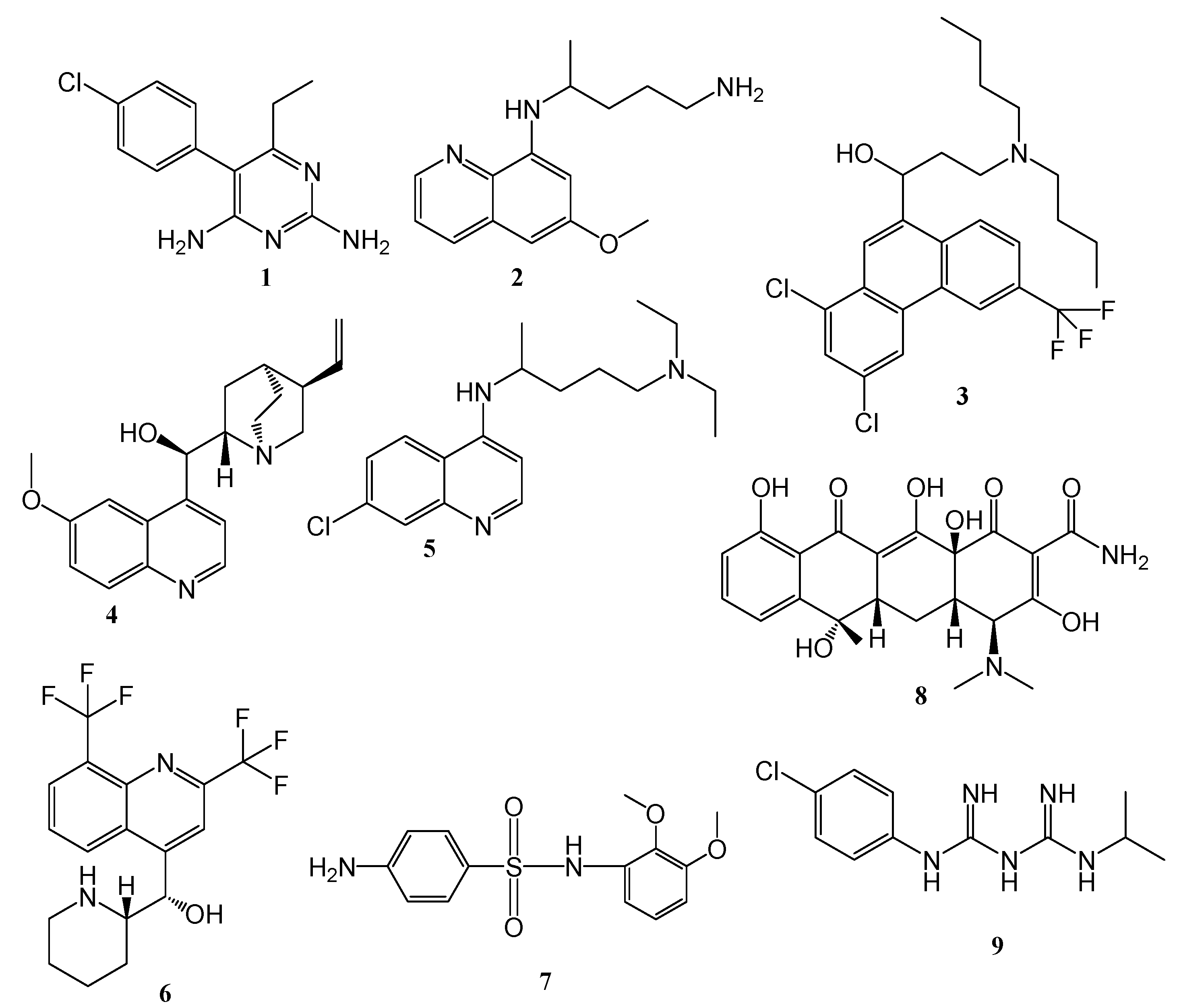
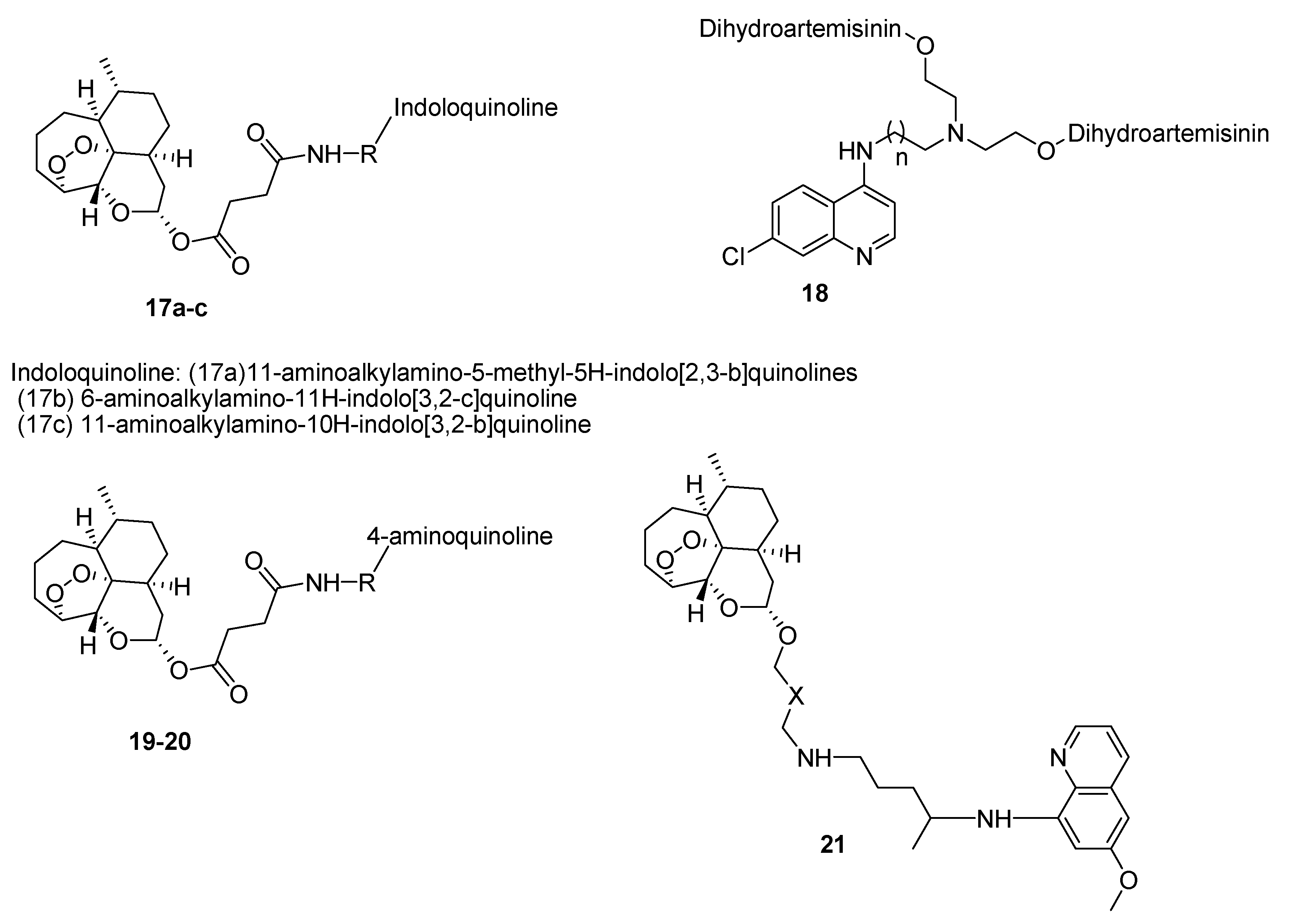
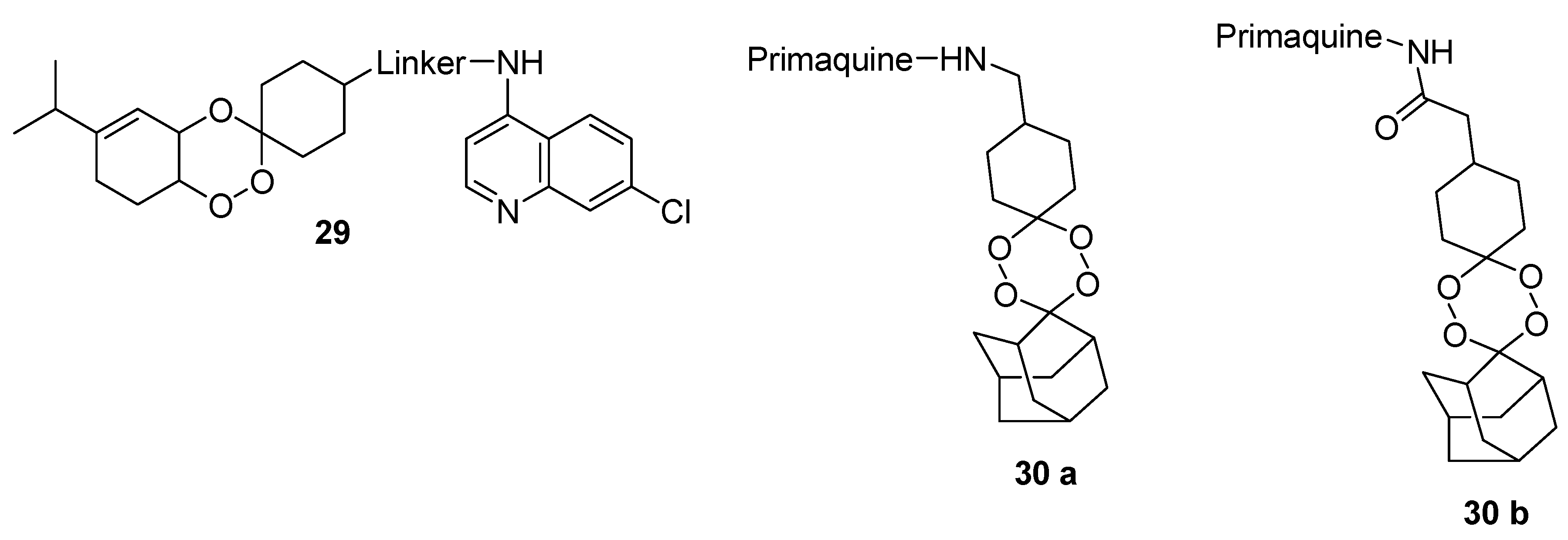
4.1. Quinoline–Artemisinin Derivatives Hybrid Compounds
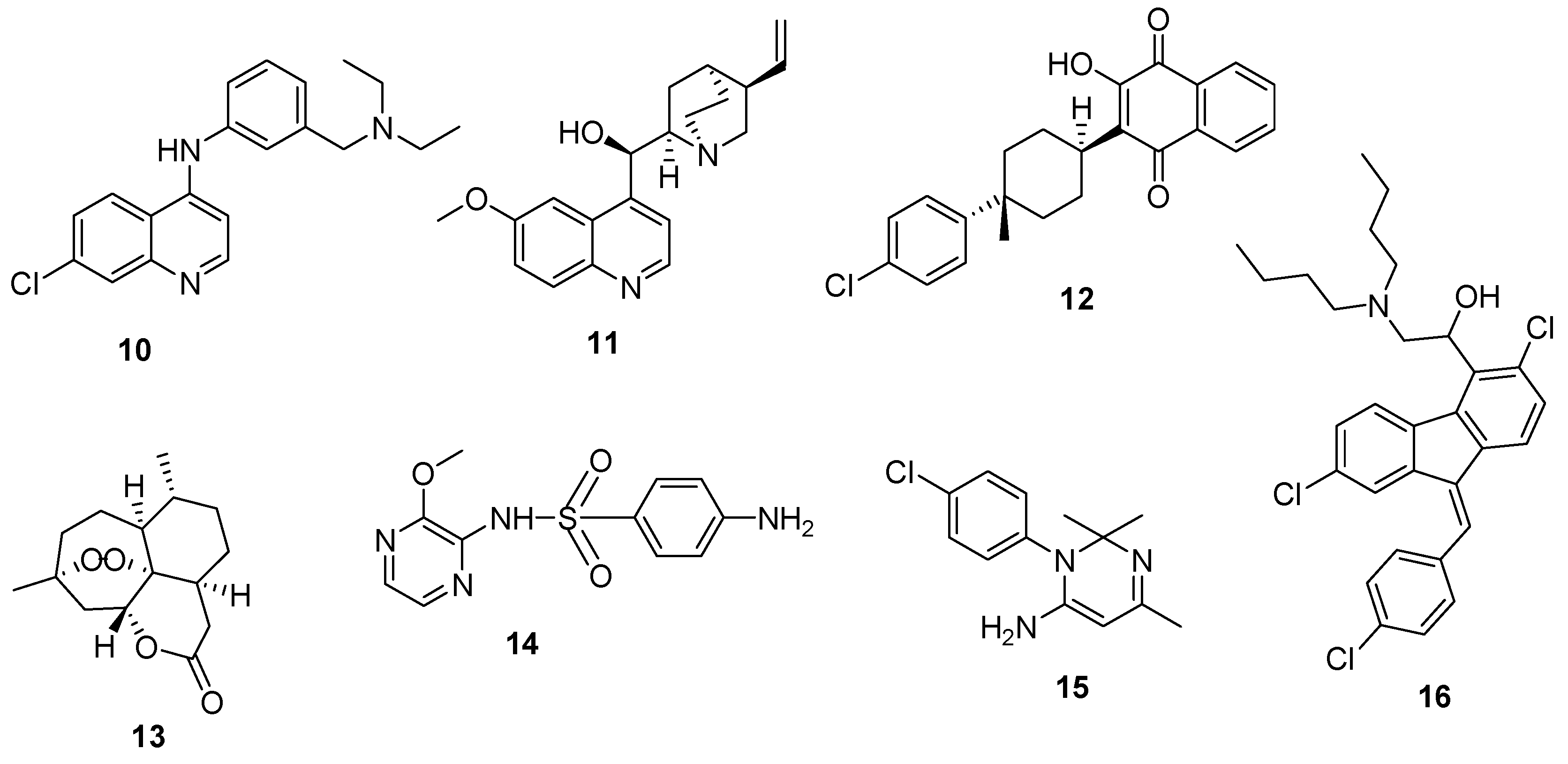
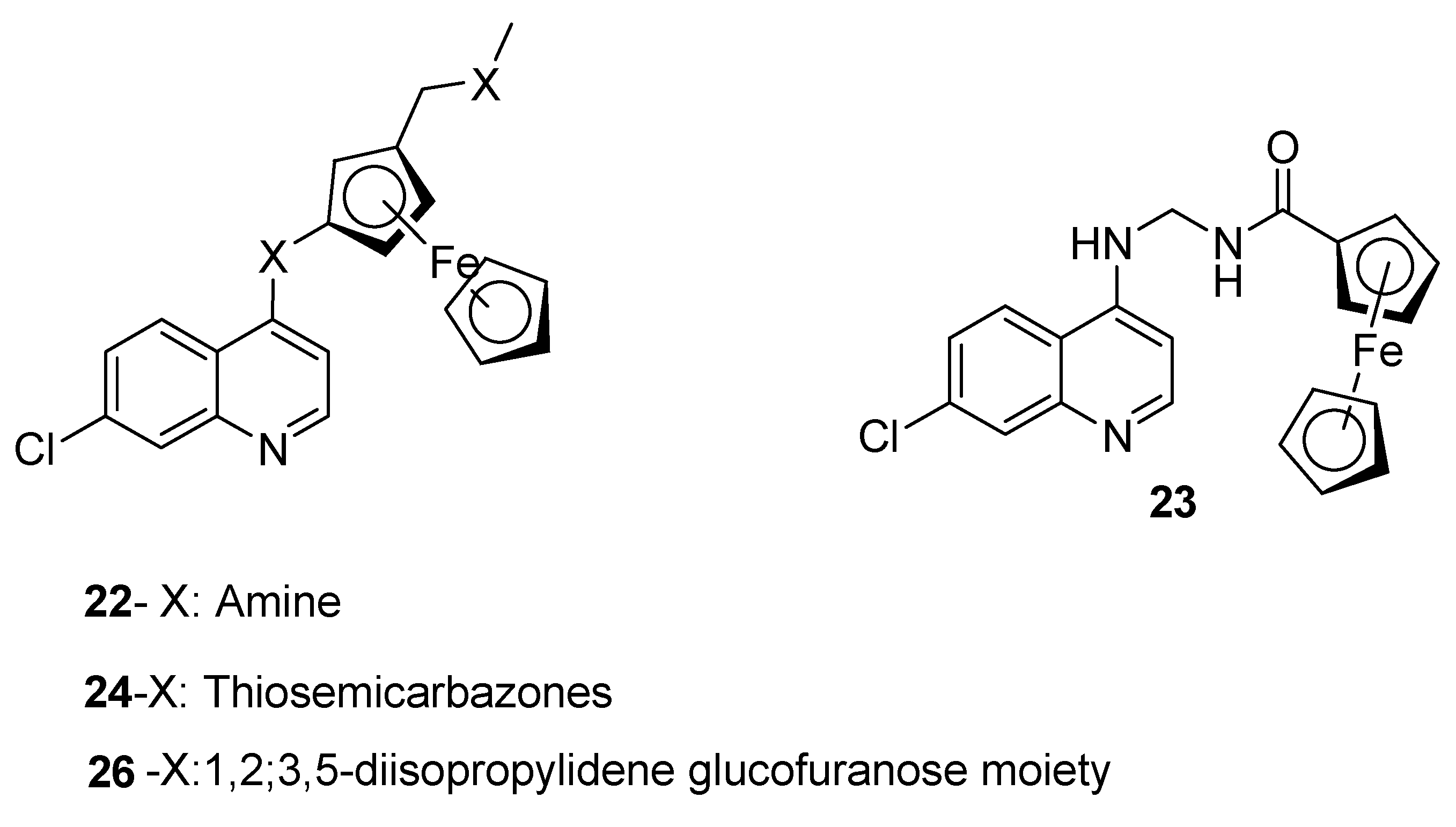
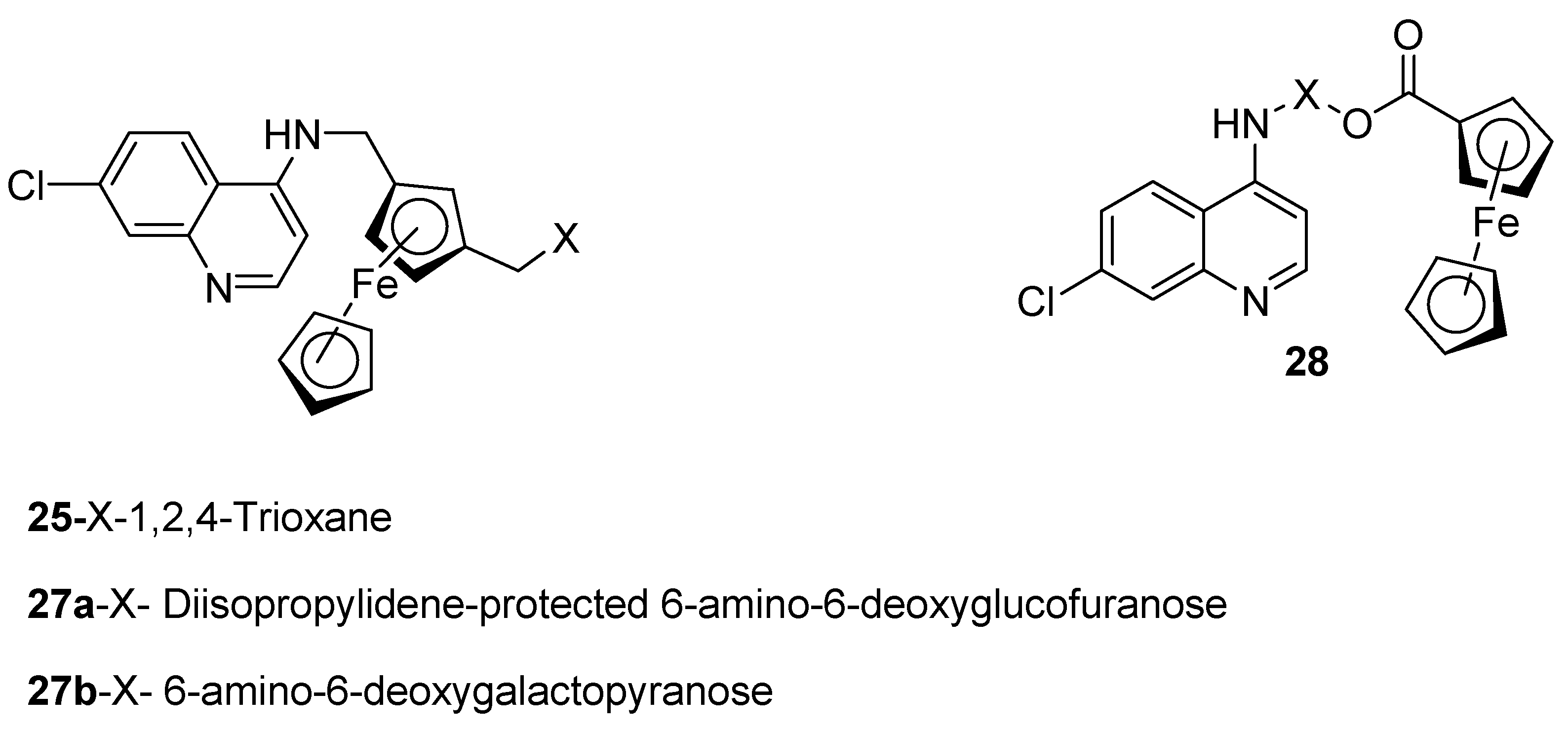
4.2. Quinoline–Ferrocene Hybrid Compounds
4.3. Quinoline-Trioxolanes Hybrid Compounds
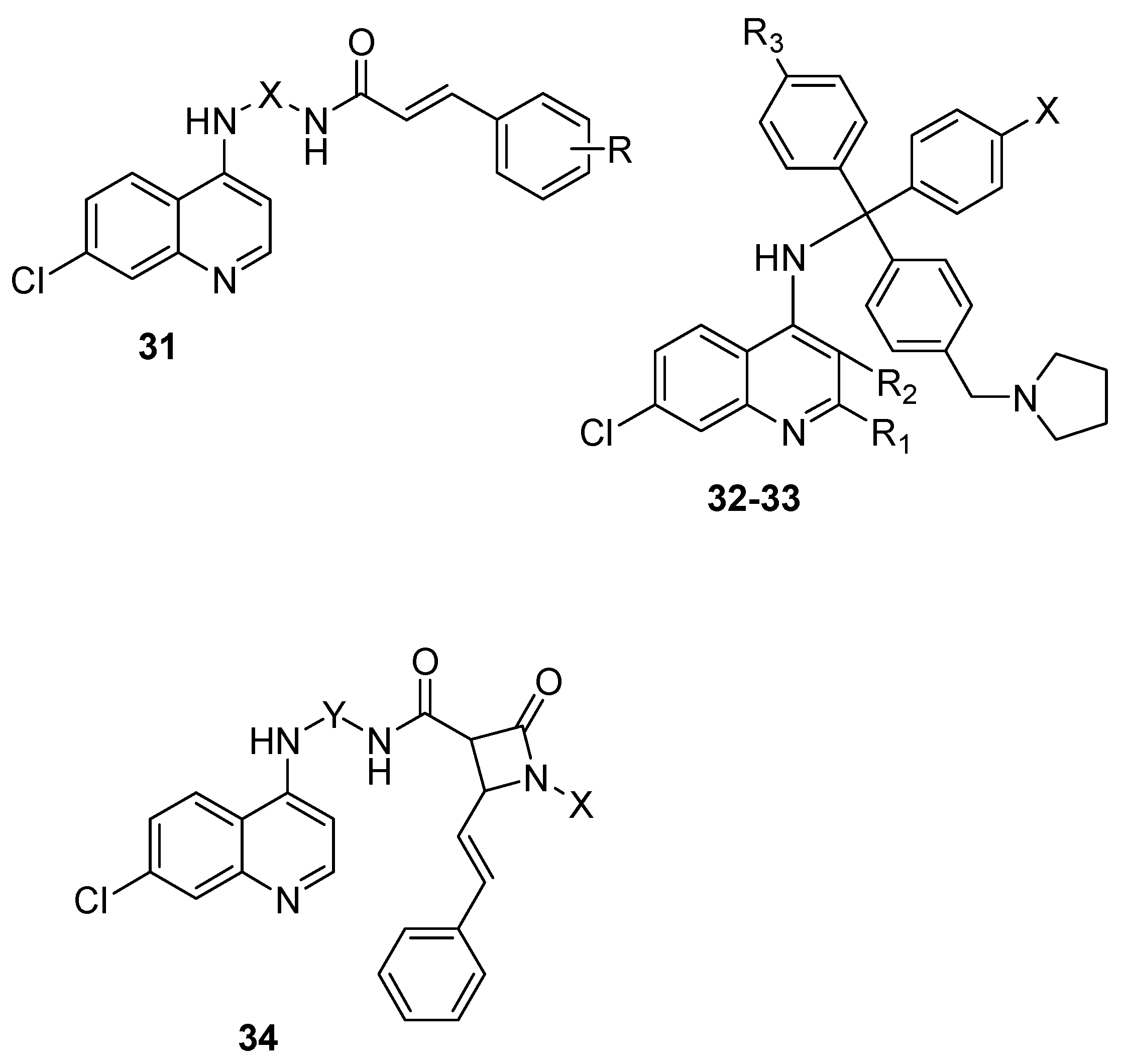
4.4. Hybrid Compounds Containing Quinoline Derivatives and Antibacterial Agents
4.5. Quinoline-Mercaptopurine Hybrid
4.6. Quinoline-Pyrimidine Hybrid Compounds
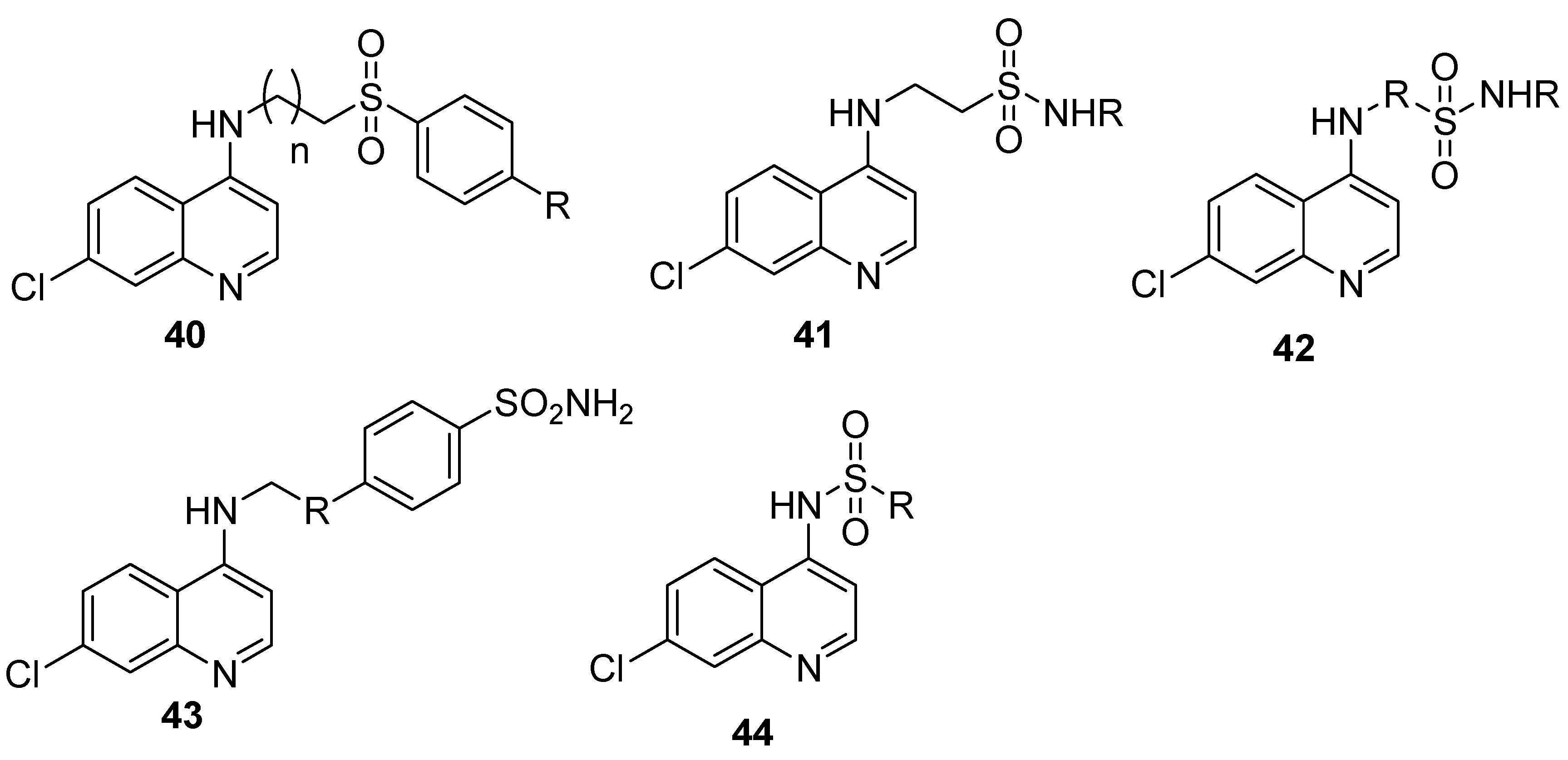
4.7. Quinoline–Sulfonamide Hybrids
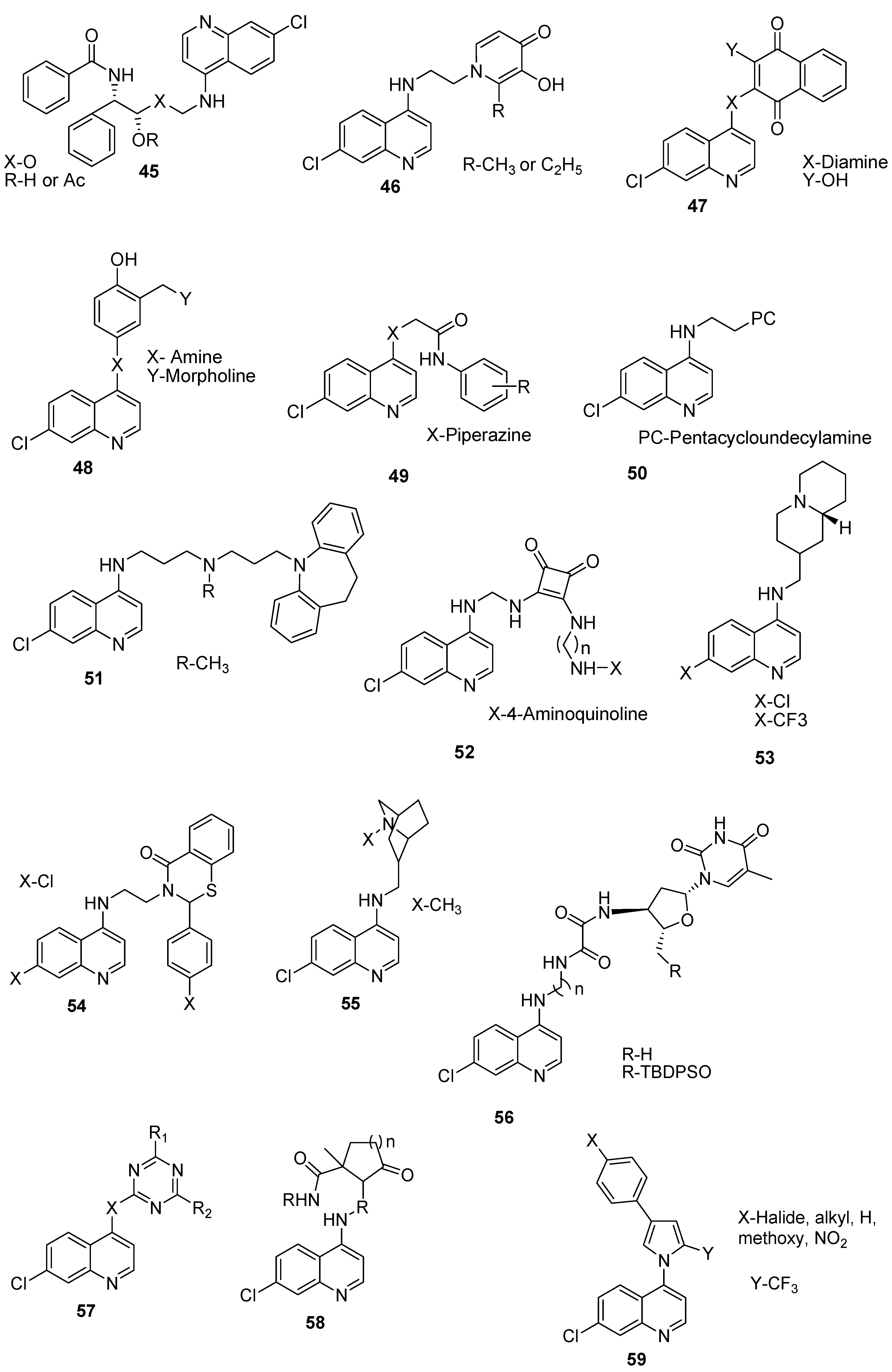
4.8. Hybrid Compounds Containing Quinoline and Other Ring Systems
5. Lipinski Rules
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, P.L.; Khan, S.I.; Ponnan, P.; Tripathi, M.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis and evaluation of 4-aminoquinoline-purine hybrids as potential antiplasmodial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, S.S.; Khan, S.I.; Bahuguna, A.; Kumar, D.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis, antimalarial activity, heme binding and docking studies of N-substituted 4-aminoquinoline-pyrimidine molecular hybrids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 129, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Kumar, V. 4-Aminoquinoline-ferrocenyl-chalcone conjugates: Synthesis and anti-plasmodial evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.A.; Panda, S.S.; Hall, C.D. Quinine conjugates and quinine analogues as potential antimalarial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, K.; Raichurkar, A.V.; Rahman, F.; Khan, N.; Iyer, P.S. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of novel 8-aminoquinoline—Pyrazolopyrimidine hybrids as potent antimalarial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar]
- White, N.J.; Pukrittayakamee, S.; Hien, T.T.; Faiz, M.A.; Mokuolu, O.A.; Dondorp, A.M. Malaria. Lancet 2014, 383, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Land, K.M.; Kumar, V. 4-Aminoquinoline-hybridization en route towards the development of rationally designed antimalarial agents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82676–82698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Agarwal, D.; Sharma, K.; Sharma, M.; Nielsen, M.A.; Alifrangis, M.; Singh, A.K.; Gupta, R.D.; Awasthi, S.K. 4-Aminoquinoline derivatives: Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo antiplasmodial activity against chloroquine-resistant parasites. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 122, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Pedrosa, M.; da Cruz, D.; Marques, R.; Viana, O.; de Moura, R.O.; Ishiki, H.M.; Barbosa, F.; Maria, J.; Diniz, M.F.; Scotti, M.T.; et al. Hybrid Compounds as Direct Multitarget Ligands: A Review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1044–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antimalarial Drugs. Available online: http://www.malariasite.com/malaria-drugs (accessed on 16 October 2017).
- Sevene, E.; González, R.; Menéndez, C. Current knowledge and challenges of antimalarial drugs for treatment and prevention in pregnancy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 1277–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Classification of Antimalarial Drugs. Available online: http://www.medworldonline.com/classification-anti-malarial-drugs (accessed on 16 October 2017).
- Chinappi, M.; Via, A.; Marcatili, P.; Tramontano, A. On the mechanism of chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogstad, D.J.; Gluzman, I.Y.; Kyle, D.E.; Oduola, A.M.J.; Martin, S.K.; Milhous, W.K. Schlesinger PHEfflux of chloroquine from Plasmodium falciparum: Mechanism of chloroquine resistance. Science 1987, 238, 1283–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, P.G.; Janneh, O.; Ward, S.A. Chloroquine uptake and activity is determined by binding to ferriprotoporphyrin IX in Plasmodium falciparum. Novartis Found. Symp. 1999, 226, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.A.; Hartwig, C.L.; Ferdig, M.T. pfcrt is more than the Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance gene: A functional and evolutionary perspective. Acta Trop. 2005, 94, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbengue, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Pandharkar, T.; Liu, H.; Estiu, G.; Stahelin, R.V.; Rizk, S.S.; Njimoh, D.L.; Ryan, Y.; Chotivanich, K.; et al. A molecular mechanism of artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature 2015, 520, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassonville-Klimpt, A.; Jonet, A.; Pillon, M.; Mullié, C.; Sonnet, P. Mefloquine derivatives: Synthesis, mechanisms of action, antimicrobial activities. In Science against Microbial Pathogens: Communicating Current Research and Technological Advances; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex Publishers: Badarjoz, Spain, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Price, R.N.; Nosten, F.; Luxemburger, C.; Kham, A.; Brockman, A.; Chongsuphajaisiddhi, T.; White, N.J. Artesunate versus artemether in combination with mefloquine for the treatment of multidrug-resistant falciparum malaria. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 89, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoon, B.A.; Singh, K.P.; Varshney, M.; Gupta, S.K.; Shukla, Y.; Gupta, S.K. Understanding the mechanism of atovaquone drug resistance in Plasmodium falciparum cytochrome b mutation Y268S using computational methods. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirichaiwat, C.; Intaraudom, C.; Kamchonwongpaisan, S.; Vanichtanankul, J.; Thebtaranonth, Y.; Yuthavong, Y. Target guided synthesis of 5-benzyl-2,4-diamonopyrimidines: Their antimalarial activities and binding affinities to wild type and mutant dihydrofolate reductases from Plasmodium falciparum. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayak, S.; Alam, M.T.; Mixson-Hayden, T.; McCollum, A.M.; Sem, R.; Shah, N.K.; Lim, P.; Muth, S.; Rogers, W.O.; Fandeur, T.; et al. Origin and evolution of sulfadoxine resistant Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloland, P.B. Drug Resistance in Malaria; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- White, N. Antimalarial drug resistance and combination chemotherapy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 354, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lödige, M.; Hiersch, L. Design and synthesis of novel hybrid molecules against malaria. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 2015, 458319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muregi, F.W.; Ishih, A. Next-generation antimalarial drugs: Hybrid molecules as a new strategy in drug design. Drug Dev. Res. 2010, 71, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wicht, K.J.; Shaban, E.; Ngoc, T.A.; Wang, M.Q.; Hayashi, I.; Hossain, M.I.; Takemasa, Y.; Kaiser, M.; El Sayed, I.E.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of artesunate–indoloquinoline hybrids as antimalarial drug candidates. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, M.C.; N’Da, D.D.; Breytenbach, J.C.; Kolesnikova, N.I.; Van Ba, C.T.; Wein, S.; Norman, J.; Denti, P.; Vial, H.; Wiesner, L. Antimalarial and anticancer activities of artemisinin–quinoline hybrid-dimers and pharmacokinetic properties in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.J.; Coughlan, D.; Heneghan, N.; Gaynor, C.; Bell, A. A novel artemisinin–quinine hybrid with potent antimalarial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 3599–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombard, M.C.; N’Da, D.D.; Breytenbach, J.C.; Smith, P.J.; Lategan, C.A. Synthesis, in vitro antimalarial and cytotoxicity of artemisinin-aminoquinoline hybrids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1683–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombard, M.C.; N’Da, D.D.; Van Ba, C.T.; Wein, S.; Norman, J.; Wiesner, L.; Vial, H. Potent in vivo anti-malarial activity and representative snapshot pharmacokinetic evaluation of artemisinin-quinoline hybrids. Malar. J. 2013, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capela, R.; Cabal, G.G.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Gut, J.; Mota, M.M.; Moreira, R.; Lopes, F.; Prudêncio, M. Design and evaluation of primaquine-artemisinin hybrids as a multistage antimalarial strategy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4698–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barends, M.; Jaidee, A.; Khaohirun, N.; Singhasivanon, P.; Nosten, F. In vitro activity of ferroquine (SSR 97193) against Plasmodium falciparum isolates from the Thai-Burmese border. Malar. J. 2007, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biot, C.; Taramelli, D.; Forfar-Bares, I.; Maciejewski, L.; Boyce, M.; Nowogrocki, G.; Brocard, J.; Basilico, N.; Olliaro, P.; Egan, T.J. Insights into the mechansims of action of ferroquine. Relationship between physicochemical properties and antiplasmodial activity. Mol. Pharm. 2005, 2, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Domarle, O.; Blampain, G.; Agnaniet, H.; Nzadiyabi, T.; Lebibi, J.; Brocard, J.; Maciejewski, L.; Biot, C.; Georges, A.J.; Millet, P. In vitro antimalarial activity of a new organometallic analog, ferrocene-chloroquine. Antimicrob. Agents Chem. 1998, 42, 540–544. [Google Scholar]
- Biot, C.; Dessolin, J.; Ricard, I.; Dive, D. Easily synthesized antimalarial ferrocene triazacyclononane quinoline conjugates. J. Organomet. Chem. 2004, 689, 4678–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Da, D.D.; Smith, P.J. Synthesis, in vitro antiplasmodial and antiproliferative activities of a series of quinoline–ferrocene hybrids. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, C.; Daher, W.; Chavain, N.; Fandeur, T.; Khalife, J.; Dive, D.; De Clercq, E. Design and synthesis of hydroxyferroquine derivatives with antimalarial and antiviral activities. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biot, C.; Pradines, B.; Sergeant, M.H.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Chibale, K. Design, synthesis, and antimalarial activity of structural chimeras of thiosemicarbazone and ferroquine analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 6434–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavain, N.; Davioud-Charvet, E.; Trivelli, X.; Mbeki, L.; Rottmann, M.; Brun, R.; Biot, C. Antimalarial activities of ferroquine conjugates with either glutathione reductase inhibitors or glutathione depletors via a hydrolyzable amide linker. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 8048–8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellot, F.; Coslédan, F.; Vendier, L.; Brocard, J.; Meunier, B.; Robert, A. Trioxaferroquines as new hybrid antimalarial drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4103–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, C.; Salas, P.F.; Cawthray, J.F.; de Kock, C.; Patrick, B.O.; Smith, P.J.; Adam, M.J.; Orvig, C. 1,1′-Disubstituted ferrocenyl carbohydrate chloroquine conjugates as potential antimalarials. Organometallics 2012, 31, 5736–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, C.; Salas, P.F.; Patrick, B.O.; Kock, C.D.; Smith, P.J.; Adam, M.J.; Orvig, C. Modular synthesis of 1,2- and 1,1′-disubstituted ferrocenyl carbohydrate chloroquine and mefloquine conjugates as potential antimalarial agents. Organometallics 2012, 31, 5748–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, P.F.; Herrmann, C.; Cawthray, J.F.; Nimphius, C.; Kenkel, A.; Chen, J.; de Kock, C.; Smithm, P.J.; Patrick, B.O.; Adam, M.J.; et al. Structural characteristics of chloroquine-bridged ferrocenophane analogues of ferroquine may obviate malaria drug-resistance mechanisms. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1596–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biot, C.; Nosten, F.; Fraisse, L.; Ter-Minassian, D.; Khalife, J.; Dive, D. The antimalarial ferroquine: From bench to clinic. Parasite 2011, 18, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, D.N.; Breytenbach, J.C.; Smith, P.J.; Lategan, C. Synthesis and in vitro antiplasmodial activity of quinoline-ferrocene esters. Arzneimittelforschung 2011, 61, 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, N.C.; Barton, V.; Jones, M.; Stocks, P.A.; Ward, S.A.; Davies, J.; Bray, P.G.; Shone, A.E.; Cristiano, M.L.; O’Neill, P.M. Semi-synthetic and synthetic 1,2,4-trioxaquines and 1,2,4-trioxolaquines: Synthesis, preliminary SAR and comparison with acridine endoperoxide conjugates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2038–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, B. Hybrid molecules with a dual mode of action: Dream or reality? Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 41, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousejra-El Garah, F.; Claparols, C.; Benoit-Vical, F.; Meunier, B.; Robert, A. The antimalarial trioxaquine DU1301 alkylates heme in malaria-infected mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chem. 2008, 52, 2966–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, D.; Capela, R.; Albuquerque, I.S.; Meireles, P.; Paiva, I.; Nogueira, F.; Amewu, R.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Oliveira, R.; et al. Novel endoperoxide-based transmission-blocking antimalarials with liver-and blood-schizontocidal activities. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, B.; Teixeira, C.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Gomes, J.R.; Gomes, P. Cinnamic Acid/Chloroquinoline Conjugates as Potent Agents against Chloroquine-Resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Chem. Med. Chem. 2012, 7, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardley, S.C.; Keller-Maerki, S.; Rottmann, M.; Brun, R.; Coletta, M.; Marini, S.; Guiso, G.; Caccia, S.; Fattorusso, C. Combining 4-aminoquinoline-and clotrimazole-based pharmacophores toward innovative and potent hybrid antimalarials. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 502–513. [Google Scholar]
- Gemma, S.; Camodeca, C.; Coccone, S.S.; Joshi, B.P.; Bernetti, M.; Moretti, V.; Brogi, S.; Bonache de Marcos, M.C.; Savini, L.; Taramelli, D.; et al. Optimization of 4-aminoquinoline/clotrimazole-based hybrid antimalarials: Further structure–activity relationships, in vivo studies, and preliminary toxicity profiling. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 5, 6948–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.S.; Bajaj, K.; Meyers, M.J.; Sverdrup, F.M.; Katritzky, A.R. Quinine bis-conjugates with quinolone antibiotics and peptides: Synthesis and antimalarial bioassay. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 8985–8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, B.C.; Teixeira, C.; Figueiras, M.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Gomes, J.R.; Gomes, P. Novel cinnamic acid/4-aminoquinoline conjugates bearing non-proteinogenic amino acids: Towards the development of potential dual action antimalarials. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, B.C.; Teixeira, C.; Albuquerque, I.S.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Gomes, J.R.; Prudêncio, M.; Gomes, P. N-Cinnamoylated chloroquine analogues as dual-stage antimalarial leads. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Singh, P.; Kumar, M.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, V.; Mahajan, M.P.; Bisetty, K. Synthesis, docking and in vitro antimalarial evaluation of bifunctional hybrids derived from β-lactams and 7-chloroquinoline using click chemistry. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, R.; Biot, C.; Carrère-Kremer, S.; Kremer, L.; Guérardel, Y.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Kumar, V. 4-Aminoquinoline-β-Lactam Conjugates: Synthesis, Antimalarial, and Antitubercular Evaluation. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 83, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Raj, R.; Singh, P.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Kumar, V. Urea/oxalamide tethered β-lactam-7-chloroquinoline conjugates: Synthesis and in vitro antimalarial evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 71, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellotti de Souza, N.; Carvalhaes, R.; Maria Lino do Carmo, A.; Jose Martins Alves, M.; Soares Coimbra, E.; Maria Neumann Cupolilo, S.; Abramo, C.; David Da Silva, A. Synthesis and In Vivo Antimalarial Activity of Quinoline/Mercaptopurine Conjugates. Lett. Drug. Des. Discov. 2012, 9, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Khan, S.I.; Ponnan, P.; Kholiya, R.; Rawat, D.S. Aminoquinoline-Pyrimidine-Modified Anilines: Synthesis, In Vitro Antiplasmodial Activity, Cytotoxicity, Mechanistic Studies and ADME Predictions. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 9074–9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, S.; Rajesh, U.C.; Khan, S.I.; Tekwani, B.L.; Rawat, D.S. Novel 4-aminoquinoline-pyrimidine based hybrids with improved in vitro and in vivo antimalarial activity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Khan, S.I.; Tekwani, B.L.; Ponnan, P.; Rawat, D.S. 4-Aminoquinoline-Pyrimidine hybrids: Synthesis, antimalarial activity, heme binding and docking studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Khan, S.I.; Tekwani, B.L.; Ponnan, P.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis, antimalarial activity, heme binding and docking studies of 4-aminoquinoline–pyrimidine based molecular hybrids. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 63655–63669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.B.; Valand, N.N.; Sutariya, P.G.; Menon, S.K. Design, synthesis and characterization of quinoline–pyrimidine linked calix [4] arene scaffolds as anti-malarial agents. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2016, 84, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Balzarini, J.; de Kock, C.; Smith, P.J.; Chibale, K.; Singh, K. Synthesis, antiplasmodial activity and mechanistic studies of pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile and quinoline hybrids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Khan, S.I.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis of piperazine tethered 4-aminoquinoline-pyrimidine hybrids as potent antimalarial agents. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 20729–20736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Kaur, H.; Chibale, K.; Balzarini, J.; Little, S.; Bharatam, P.V. 2-aminopyrimidine based 4-aminoquinoline anti-plasmodial agents. Synthesis, biological activity, structure–activity relationship and mode of action studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 52, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, S.I.; Breytenbach, W.J.; De Kock, C.; Smith, P.J.; N’Da, D.D. Synthesis, characterization and antimalarial activity of quinoline–pyrimidine hybrids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, L.C.; Boechat, N.; Maria de Lourdes, G.F.; Júnior, C.C.; Jesus, A.M.; Leite, M.M.; Souza, N.B.; Krettli, A.U. Anti-Plasmodium falciparum activity of quinoline–sulfonamide hybrids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 5979–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Pandey, S.; Agarwal, P.; Verma, P.; Deshpande, S.; Saxena, J.K.; Srivastava, K.; Chauhan, P.M.; Prabhakar, Y.S. N-(7-Chloroquinolinyl-4-aminoalkyl) arylsulfonamides as antimalarial agents: Rationale for the activity with reference to inhibition of hemozoin formation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 25584–25593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.R.; da Silva, J.M.; Carlos, B.C.; da Fonseca, C.C.; de Souza, L.S.; Lopes, F.V.; de Paula Dias, R.M.; Moreira, P.O.; Abramo, C.; Viana, G.H.; et al. New quinoline derivatives demonstrate a promising antimalarial activity against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro and Plasmodium berghei in vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2308–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, G.M.; Tanpure, R.P.; Douchez, A.; Andrews, K.T.; Poulsen, S.A. Synthesis and Evaluation of Antimalarial Properties of Novel 4-Aminoquinoline Hybrid Compounds. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 84, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahuddin, A.; Inam, A.; van Zyl, R.L.; Heslop, D.C.; Chen, C.T.; Avecilla, F.; Agarwal, S.M.; Azam, A. Synthesis and evaluation of 7-chloro-4-(piperazin-1-yl) quinoline-sulfonamide as hybrid antiprotozoal agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3080–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njogu, P.M.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Chibale, K. Design, Synthesis, and Antiplasmodial Activity of Hybrid Compounds Based on (2R,3S)-N-Benzoyl-3-phenylisoserine. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 4, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andayi, W.A.; Egan, T.J.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Chibale, K. Synthesis, Antiplasmodial Activity, and β-Hematin Inhibition of Hydroxypyridone–Chloroquine Hybrids. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, A.; Chetia, D.; Rudrapal, M. Synthesis, Antimalarial Activity Evaluation and Drug likeness Study of Some New Quinoline-Lawsone Hybrids. Ind. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 78, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Chetia, D.; Puri, S.K.; Srivastava, K.; Prakash, A. Synthesis and in vitro and in vivo antimalarial activity of novel 4-anilinoquinoline Mannich base derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2011, 20, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, A.; Van Zyl, R.L.; van Vuuren, N.J.; Chen, C.T.; Avecilla, F.; Agarwal, S.M.; Azam, A. Chloroquinoline–acetamide hybrids: A promising series of potential antiprotozoal agents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48368–48381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, J.; Fortuin, E.E.; Taylor, D.; Smith, P.J.; Malan, S.F. Pentacycloundecylamines and conjugates thereof as chemosensitizers and reversed chloroquine agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5516–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.J.; Selzer, A.; Kelly, J.X.; Smilkstein, M.J.; Riscoe, M.K.; Peyton, D.H. A chloroquine-like molecule designed to reverse resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5623–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.; Burgess, S.J.; Skaalrud, D.; Kelly, J.X.; Peyton, D.H. Reversal agent and linker variants of reversed chloroquines: Activities against Plasmodium falciparum. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 53, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.J.; Kumar, S.P.; Gut, J.; Goncalves, L.M.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Moreira, R.; Santos, M.M. Squaric acid/4-aminoquinoline conjugates: Novel potent antiplasmodial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparatore, A.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Romeo, S.; Novelli, F.; Sparatore, F.; Taramelli, D. 4-Aminoquinoline quinolizidinyl-and quinolizidinylalkyl-derivatives with antimalarial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5338–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, V.R.; Haq, W.; Srivastava, K.; Puri, S.K.; Katti, S.B. Synthesis and antimalarial activity of side chain modified 4-aminoquinoline derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.F.; Levi, M.S.; Tekwani, B.L.; Wilson, N.H.; Borne, R.F. Synthesis of isoquinuclidine analogs of chloroquine: Antimalarial and antileishmanial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 3919–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornut, D.; Lemoine, H.; Kanishchev, O.; Okada, E.; Albrieux, F.; Beavogui, A.H.; Bienvenu, A.L.; Picot, S.; Bouillon, J.P.; Médebielle, M. Incorporation of a 3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-γ-hydroxy-γ-lactam motif in the side chain of 4-aminoquinolines. Syntheses and antimalarial activities. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunduru, N.; Sharma, M.; Srivastava, K.; Rajakumar, S.; Puri, S.K.; Saxena, J.K.; Chauhan, P.M. Synthesis of oxalamide and triazine derivatives as a novel class of hybrid 4-aminoquinoline with potent antiplasmodial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6451–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musonda, C.C.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Yardley, V.; De Souza, R.C.; Chibale, K. Application of multicomponent reactions to antimalarial drug discovery. Part 2: New antiplasmodial and antitrypanosomal 4-aminoquinoline γ- and δ-lactams via a ‘catch and release’ protocol. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 5605–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunico, W.; Cechinel, C.A.; Bonacorso, H.G.; Martins, M.A.; Zanatta, N.; de Souza, M.V.; Freitas, I.O.; Soares, R.P.; Krettli, A.U. Antimalarial activity of 4-(5-trifluoromethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-chloroquine analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wilkinson, B. Drug discovery beyond the ‘rule-of-five’. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doak, B.C.; Kihlberg, J. Drug discovery beyond the rule of 5-Opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Chetia, D.; Rudrapal, M. Design, synthesis and antimalarial activity of some new 2-hydroxy-1, 4-naphthoquinone-4-hydroxyaniline hybrid mannich bases. Asian J. Chem. 2016, 28, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, F.A.; Kouznetsov, V.V. Property-based design and synthesis of new chloroquine hybrids via simple incorporation of 2-imino-thiazolidin-4-one or 1h-pyrrol-2,5-dione fragments on the 4-amino-7-chloroquinoline side chain. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2011, 22, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Khan, S.I.; Ponnan, P.; Rawat, D.S. Triazine–pyrimidine based molecular hybrids: Synthesis, docking studies and evaluation of antimalarial activity. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 5087–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nqoro, X.; Tobeka, N.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity. Molecules 2017, 22, 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122268
Nqoro X, Tobeka N, Aderibigbe BA. Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity. Molecules. 2017; 22(12):2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122268
Chicago/Turabian StyleNqoro, Xhamla, Naki Tobeka, and Blessing A. Aderibigbe. 2017. "Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity" Molecules 22, no. 12: 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122268
APA StyleNqoro, X., Tobeka, N., & Aderibigbe, B. A. (2017). Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity. Molecules, 22(12), 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122268