Inkjet Printing of Drug-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles—A Platform for Drug Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
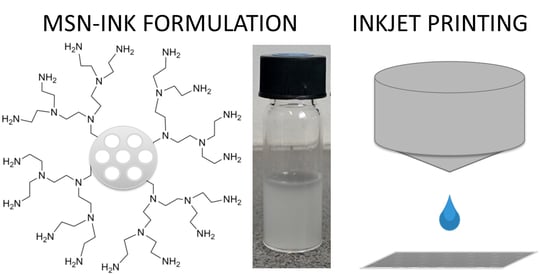
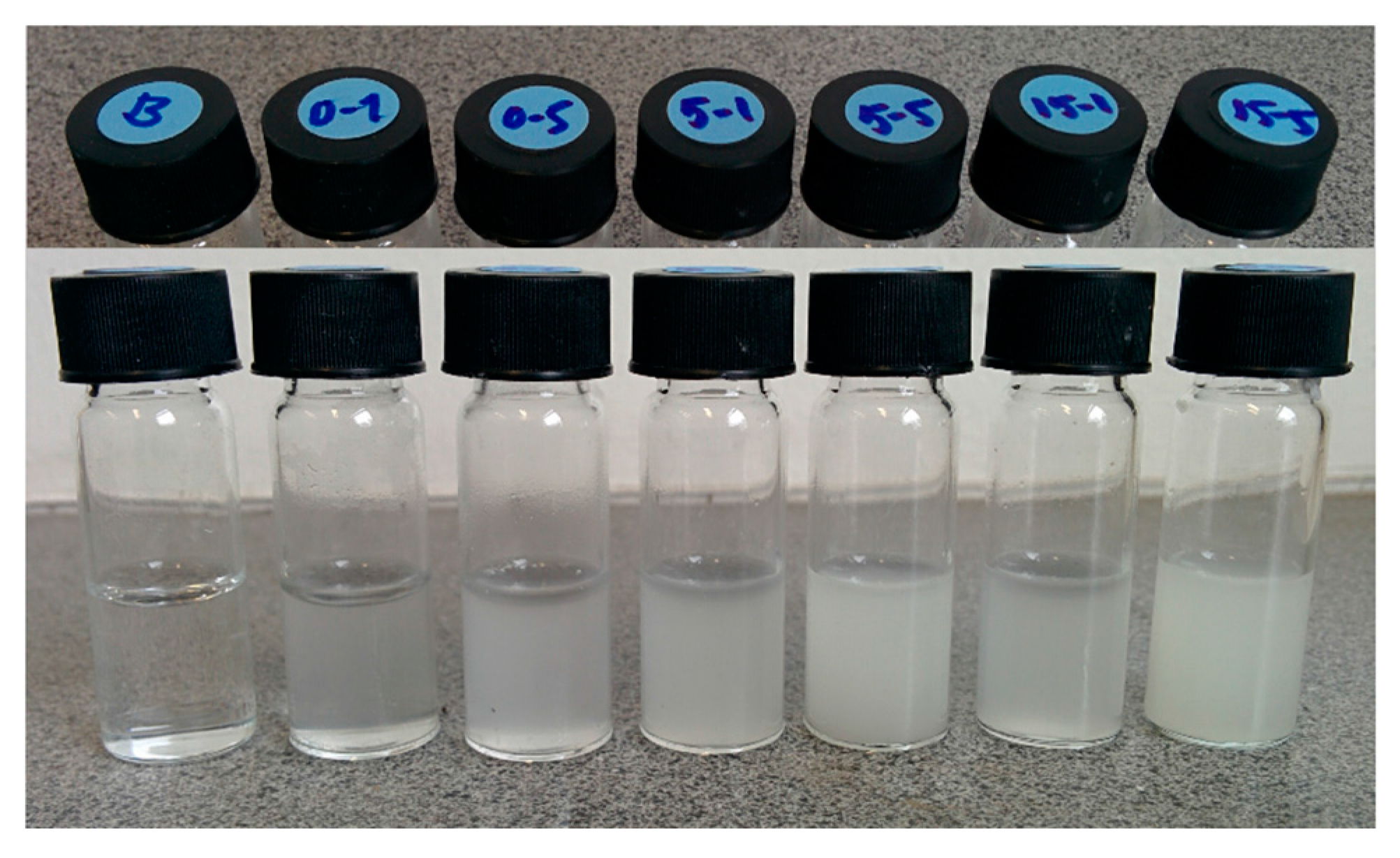
2.1. Ink Development
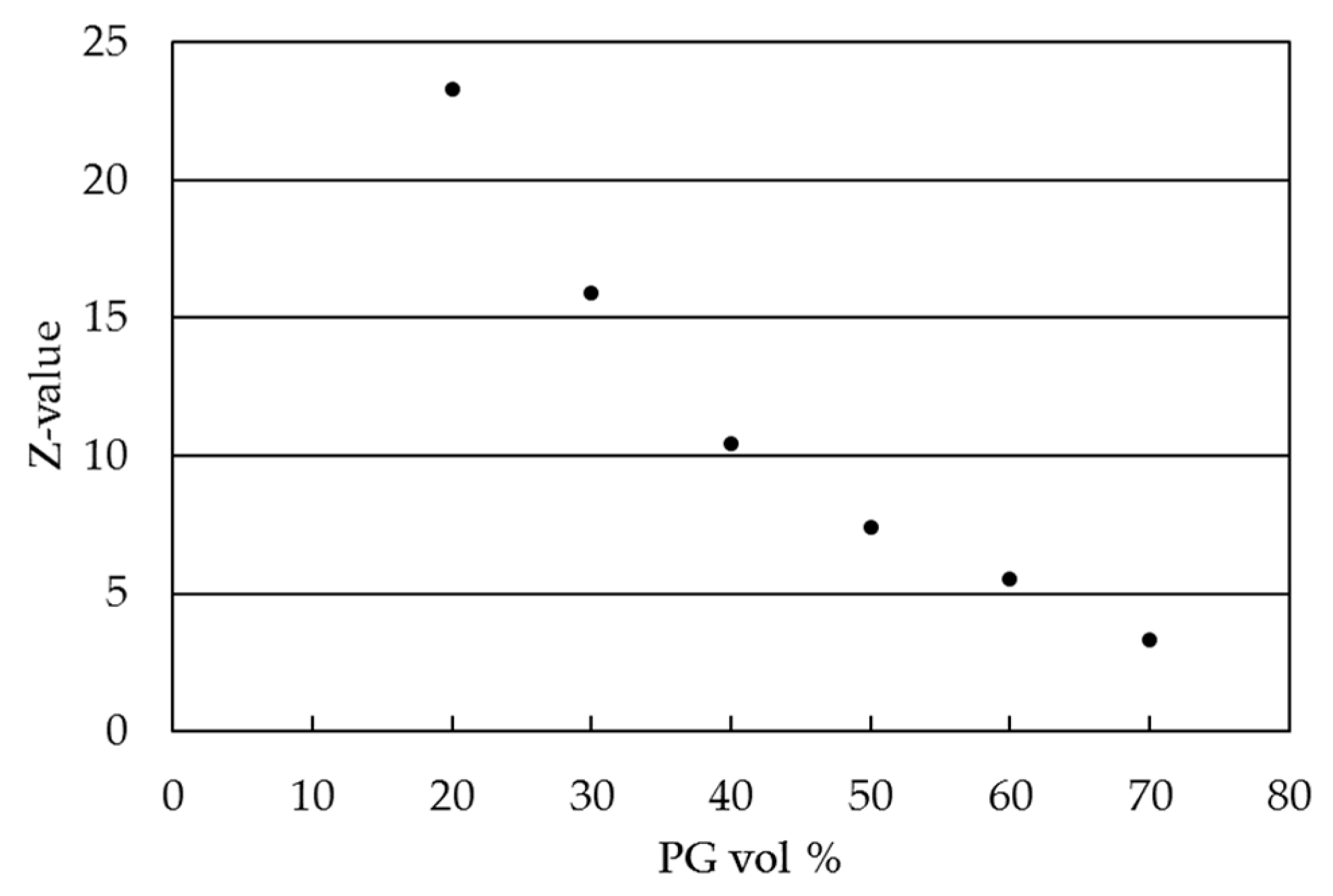
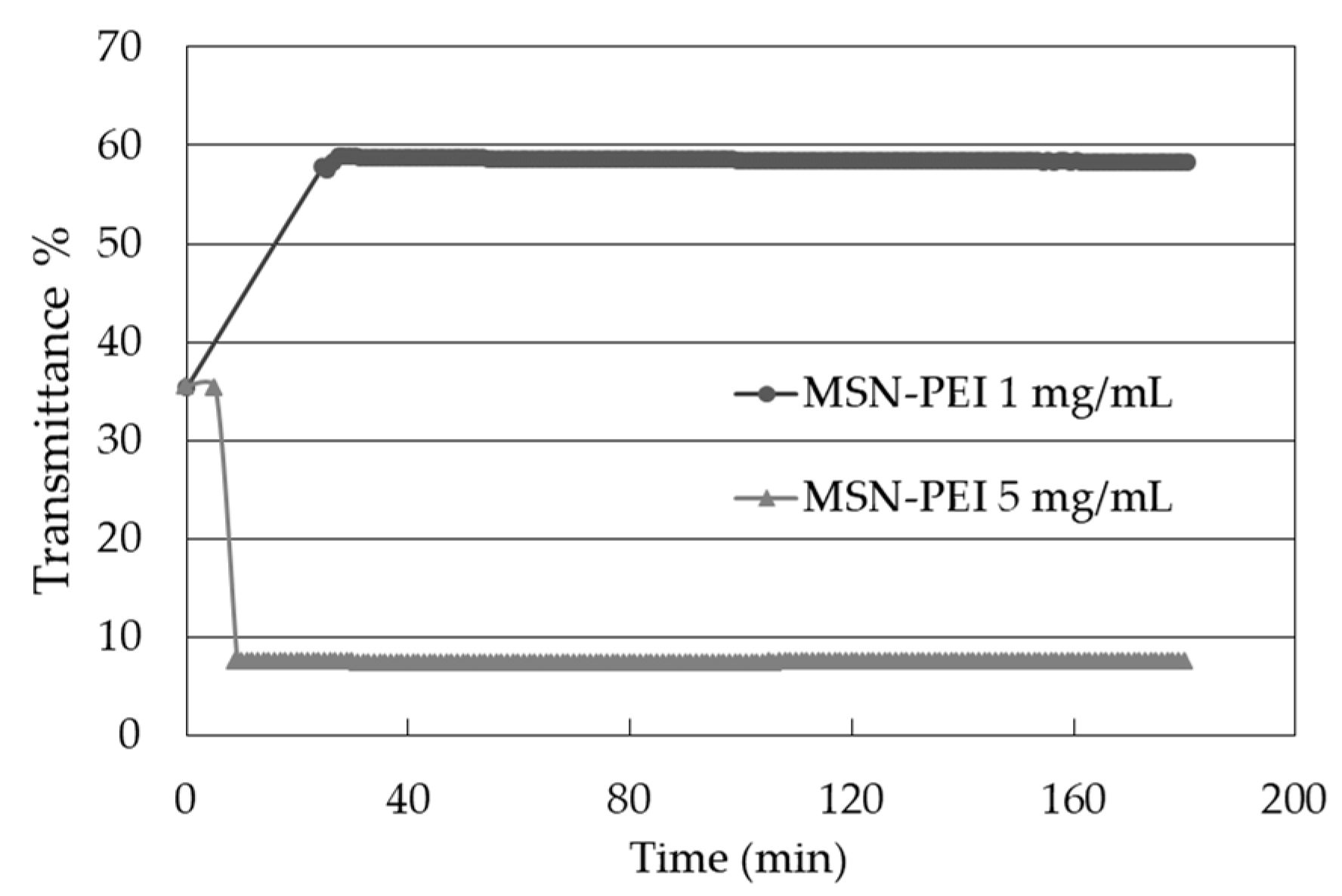
2.2. Ink Characterization
2.3. Drug Loading and Drug Leaching into Ink
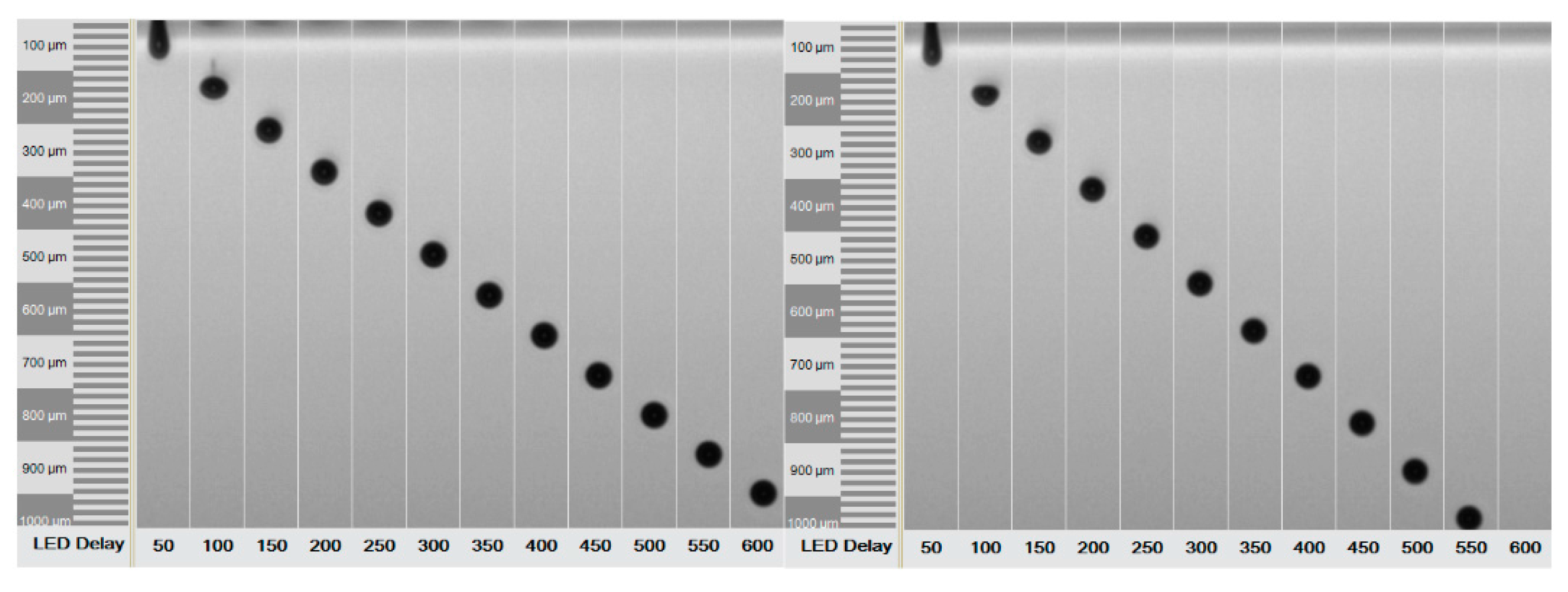
2.4. Printing Process
2.5. Dose Quantification
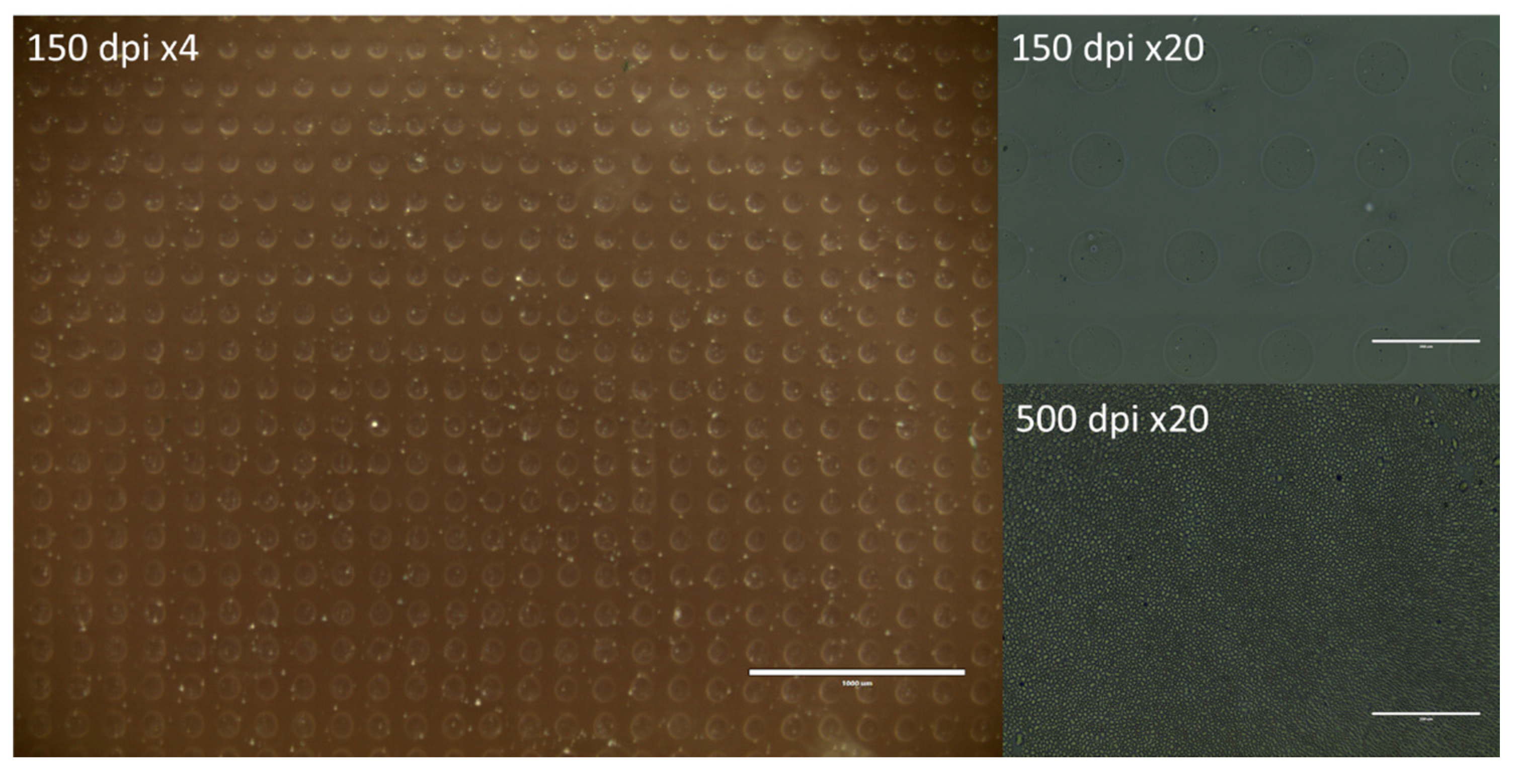
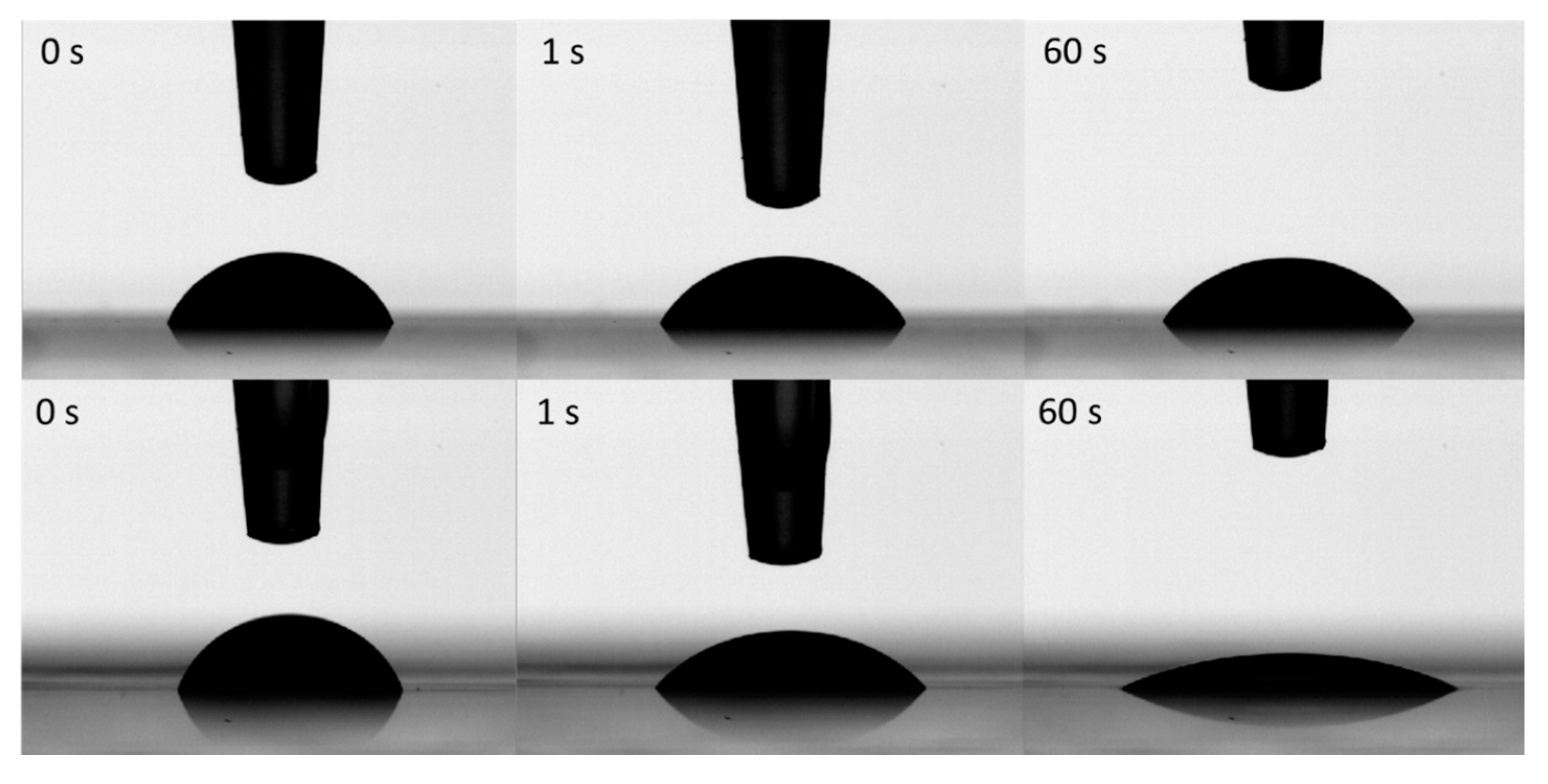
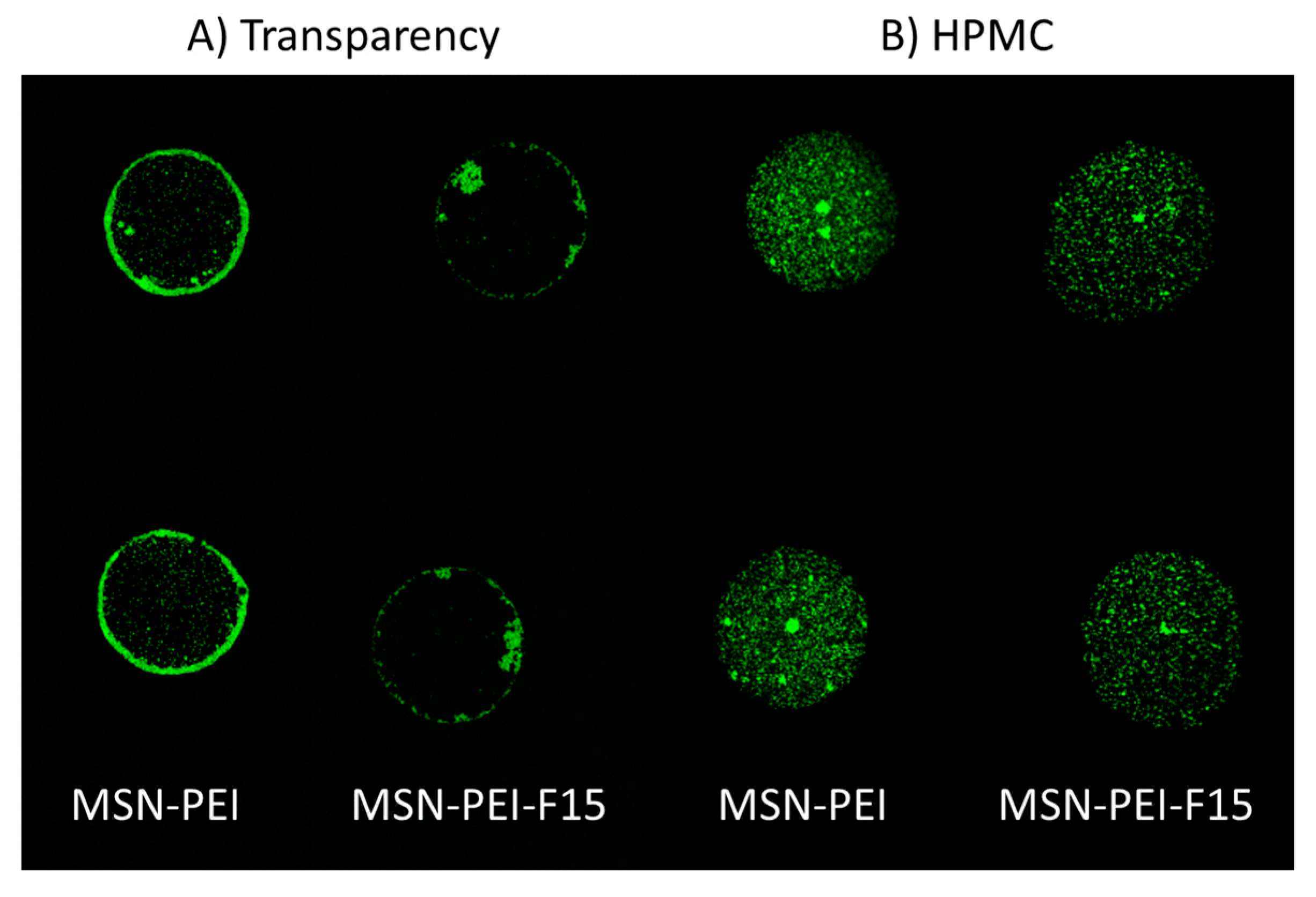
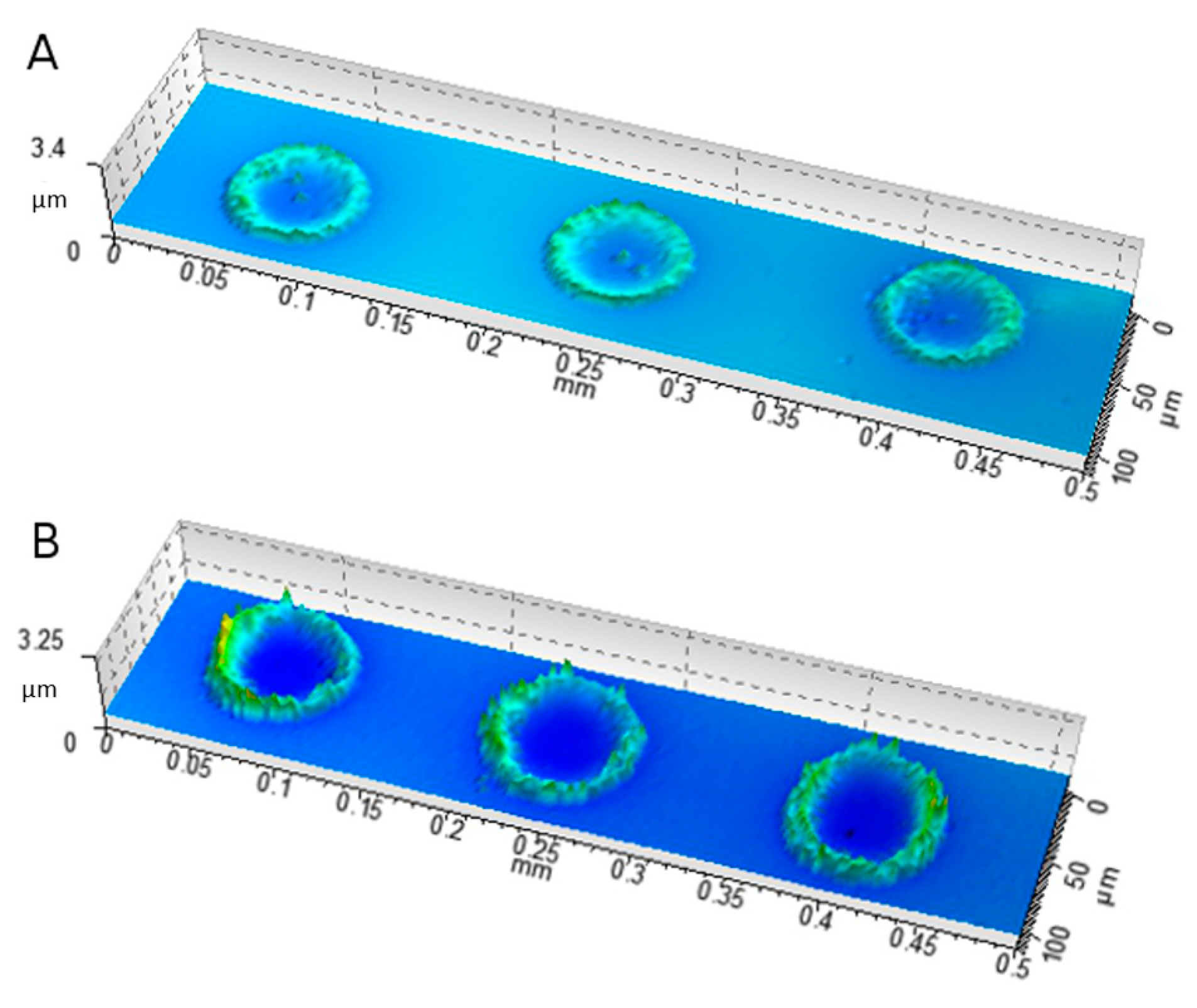
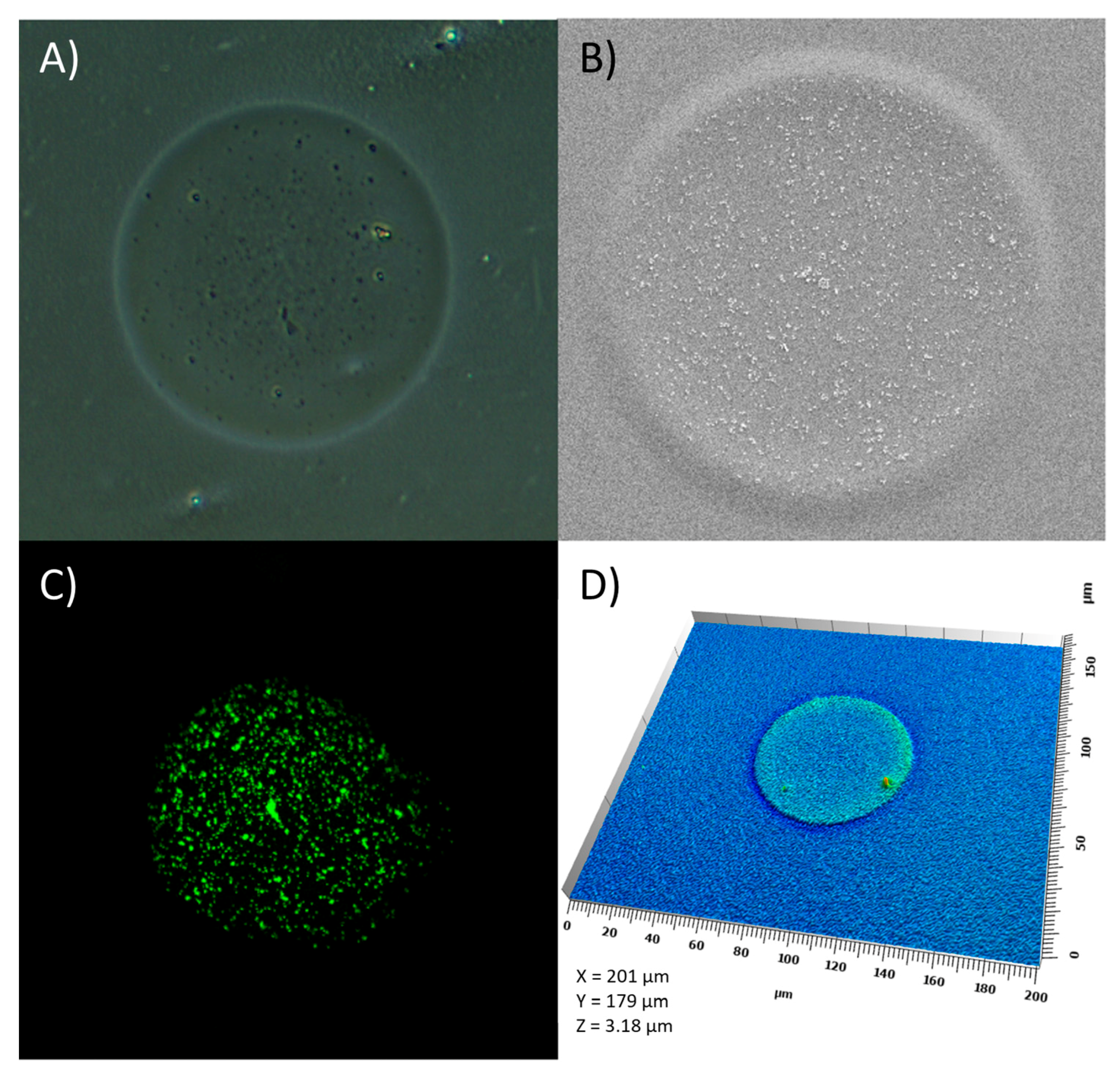
2.6. Characterization of Ink–Substrate Interactions
3. Discussion
3.1. Ink Formulation
3.2. Characterization Methods
3.3. Current Trends in MSN–Cell Interaction Studies and Potential Screening Platforms
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of MSNs
4.2. Characterization of MSN and MSN-PEI
4.3. Drug Loading
4.4. Ink Preparation and Characterization
4.4.1. Dynamic Viscosity
4.4.2. Surface Tension and Density
4.4.3. Colloidal Stability of MSN-PEI Suspensions
4.4.4. Drug Release in Ink
4.5. Inkjet Printing
4.6. Substrate
4.7. Quantification of the Prints
4.8. Contact Angle
4.9. Visual Characterization of the Prints
4.9.1. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
4.9.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4.9.3. Optical Microscopy
4.9.4. Scanning White Light Interferometry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calvert, P. Inkjet Printing for Materials and Devices. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, T.; Xu, T.; Damon, B.; Cui, X. Application of inkjet printing to tissue engineering. Biotechnol. J. 2006, 1, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katstra, W.; Palazzolo, R.; Rowe, C.; Giritlioglu, B.; Teung, P.; Cima, M. Oral dosage forms fabricated by Three Dimensional PrintingTM. J. Control. Release 2000, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genina, N.; Fors, D.; Palo, M.; Peltonen, J.; Sandler, N. Behavior of printable formulations of loperamide and caffeine on different substrates—Effect of print density in inkjet printing. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchette, C.; Pichler, H.; Wimmer-Teubenbacher, M.; Gruber, M.; Gruber-Woelfler, H.; Mohr, S.; Tetyczka, C.; Hsiao, W.-K.; Paudel, A.; Roblegg, E.; et al. Printing medicines as orodispersible dosage forms: Effect of substrate on the printed micro-structure. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 509, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, S.A.; Burley, J.C.; Alexander, M.R.; Yang, J.; Roberts, C.J. 3D printing of tablets containing multiple drugs with defined release profiles. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preis, M.; Sandler, N. Printing technologies and tailored dosing. Hostpital Pharamcy Eur. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, Y.; Wada, K.; Nakatani, M.; Yamada, S.; Onoue, S. Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: Basic approaches and practical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardeike, J.; Strohmeier, D.M.; Schrödl, N.; Voura, C.; Gruber, M.; Khinast, J.G.; Zimmer, A. Nanosuspensions as advanced printing ink for accurate dosing of poorly soluble drugs in personalized medicines. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palo, M.; Kolakovic, R.; Laaksonen, T.; Määttänen, A.; Genina, N.; Salonen, J.; Peltonen, J.; Sandler, N. Fabrication of drug-loaded edible carrier substrates from nanosuspensions by flexographic printing. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nganga, S.; Moritz, N.; Kolakovic, R.; Jakobsson, K.; Nyman, J.O.; Borgogna, M.; Travan, A.; Crosera, M.; Donati, I.; Vallittu, P.K.; et al. Inkjet printing of Chitlac-nanosilver—A method to create functional coatings for non-metallic bone implants. Biofabrication 2014, 6, 041001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheow, W.S.; Kiew, T.Y.; Hadinoto, K. Combining inkjet printing and amorphous nanonization to prepare personalized dosage forms of poorly-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 96, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varan, C.; Wickström, H.; Sandler, N.; Aktaş, Y.; Bilensoy, E. Inkjet printing of antiviral PCL nanoparticles and anticancer cyclodextrin inclusion complexes on bioadhesive film for cervical administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.K.; Yun, Y.H.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, Y.C.; Kim, J.D.; Cho, Y.W. Fabrication of drug-loaded polymer microparticles with arbitrary geometries using a piezoelectric inkjet printing system. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 427, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyobula, M.; Adedeji, A.; Alexander, M.R.; Saleh, E.; Wildman, R.; Ashcroft, I.; Gellert, P.R.; Roberts, C.J. 3D inkjet printing of tablets exploiting bespoke complex geometries for controlled and tuneable drug release. J. Control. Release 2017, 261, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, M.; Lin, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Hong, Y.; Dong, Y.; Jin, G.; Xu, F. Three-dimensional quick response code based on inkjet printing of upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles for drug anti-counterfeiting. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 10096–10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfandyarpour, R.; DiDonato, M.J.; Yang, Y.; Durmus, N.G.; Harris, J.S.; Davis, R.W. Multifunctional, inexpensive, and reusable nanoparticle-printed biochip for cell manipulation and diagnosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1306–E1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrabito, G.; Pignataro, B. Inkjet Printing Methodologies for Drug Screening. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3104–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celiz, A.D.; Hook, A.L.; Scurr, D.J.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R.; Davies, M.C.; Alexander, M.R. ToF-SIMS imaging of a polymer microarray prepared using ink-jet printing of acrylate monomers: ToF-SIMS imaging of an ink-jet printed polymer microarray. Surf. Interface Anal. 2013, 45, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Choi, J.; Lee, K.J.; Stott, N.E.; Kim, D. Large-scale synthesis of copper nanoparticles by chemically controlled reduction for applications of inkjet-printed electronics. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 415604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallan, H.C.; Sadie, J.A.; Kitsomboonloha, R.; Volkman, S.K.; Subramanian, V. Systematic Design of Jettable Nanoparticle-Based Inkjet Inks: Rheology, Acoustics, and Jettability. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13470–13477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deegan, R.D. Pattern formation in drying drops. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.-Y.; Park, J.; Shin, H.; Moon, J. Rapid Self-Assembly of Monodisperse Colloidal Spheres in an Ink-Jet Printed Droplet. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4212–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Moon, J. Control of Colloidal Particle Deposit Patterns within Picoliter Droplets Ejected by Ink-Jet Printing. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3506–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Gao, L.; Sharma, V.; Chiang, Y.-M.; Wong, C.C. Particle and Substrate Charge Effects on Colloidal Self-Assembly in a Sessile Drop. Langmuir 2008, 24, 11518–11522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-L.; Kao, Z.-K.; Liao, Y.-C. Preserving Precision of Inkjet-Printed Features with Solvents of Different Volatilities. Langmuir 2013, 29, 11330–11336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhu, S.; Wang, T.; Yang, B. Suppression of the Coffee Ring Effect by Hydrosoluble Polymer Additives. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2775–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera Gil, P.; Hühn, D.; del Mercato, L.L.; Sasse, D.; Parak, W.J. Nanopharmacy: Inorganic nanoscale devices as vectors and active compounds. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepic, I.; Hafner, A.; Lovric, J.; Perina Lakos, G. Nanotherapeutics in the EU: An overview on current state and future directions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barei, F. The generic pharmaceutical industry: Moving beyond incremental innovation towards re-innovation. Generics Biosimilars Initiat. J. 2013, 2, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Increasing the Oral Bioavailability and Permeation of Poorly Water Soluble Drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, H.I.; Yi, Z.; Rookes, J.E.; Kong, L.X.; Cahill, D.M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a biomolecule delivery vehicle in plants. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- des Rieux, A.; Fievez, V.; Garinot, M.; Schneider, Y.-J.; Préat, V. Nanoparticles as potential oral delivery systems of proteins and vaccines: A mechanistic approach. J. Control. Release 2006, 116, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, A.; Biswas, N.; Bhattacharjee, K.; Sahoo, N.; Kuotsu, K. pH responsive cylindrical MSN for oral delivery of insulin-design, fabrication and evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3552–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamaeva, V.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Bate-Eya, L.T.; Bergman, L.; Peuhu, E.; Duchanoy, A.; Fortelius, L.E.; Landor, S.; Toivola, D.M.; Lindén, M.; et al. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems for Targeted Inhibition of Notch Signaling in Cancer. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Meng, H.; Kabehie, S.; George, S.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Polyethyleneimine Coating Enhances the Cellular Uptake of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Allows Safe Delivery of siRNA and DNA Constructs. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3273–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukara, K.; Schueller, L.; Rosier, J.; Martens, M.A.; Daems, T.; Verheyden, L.; Eelen, S.; Van Speybroeck, M.; Libanati, C.; Martens, J.A.; et al. Ordered mesoporous silica to enhance the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs: Proof of concept in man. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbé, C.; Bartlett, J.; Kong, L.; Finnie, K.; Lin, H.Q.; Larkin, M.; Calleja, S.; Bush, A.; Calleja, G. Silica Particles: A Novel Drug-Delivery System. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Lindén, M. Towards establishing structure–activity relationships for mesoporous silica in drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, A.; Kettiger, H.; Schoubben, A.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Ambrogi, V.; Hamidi, M. Mesoporous silica materials: From physico-chemical properties to enhanced dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Control. Release 2017, 262, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoncheva, K.; Popova, M.; Szegedi, A.; Mihaly, J.; Tzankov, B.; Lambov, N.; Konstantinov, S.; Tzankova, V.; Pessina, F.; Valoti, M. Functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for oral delivery of budesonide. J. Solid State Chem. 2014, 211, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Rámila, A.; del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A New Property of MCM-41: Drug Delivery System. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, N. Modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhancing oral bioavailability and antihypertensive activity of poorly water soluble valsartan. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapino, S.; Ugazio, E.; Gastaldi, L.; Miletto, I.; Berlier, G.; Zonari, D.; Oliaro-Bosso, S. Mesoporous silica as topical nanocarriers for quercetin: Characterization and in vitro studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.; Singh, R.K.; Perez, R.A.; Abou Neel, E.A.; Kim, H.-W.; Chrzanowski, W. Silica-based mesoporous nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. J. Tissue Eng. 2013, 4, 204173141350335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, D.; Karaman, D.S.; Prabhakar, N.; Tadayon, S.; Duchanoy, A.; Toivola, D.M.; Rajput, S.; Näreoja, T.; Rosenholm, J.M. Design considerations for mesoporous silica nanoparticulate systems in facilitating biomedical applications. Mesoporous Biomater. 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.-Y.; Kao, Z.-K.; Liao, Y.-C.; Yamauchi, Y.; Wu, K.C.-W. Self-Assembled Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Controlled Patterns Produced by Soft-Lithography and Ink-Jet Printing. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 2804–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, D.; Kim, D.; Moon, J. Influence of Fluid Physical Properties on Ink-Jet Printability. Langmuir 2009, 25, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Product Data: Spectra SL-128 AA Rev. 08; FUJIFILM Dimatix, Inc.: Tokyo, Japan, 21 January 2015.
- Meixner, R.M.; Cibis, D.; Krueger, K.; Goebel, H. Characterization of polymer inks for drop-on-demand printing systems. Microsyst. Technol. 2008, 14, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derby, B. Inkjet Printing of Functional and Structural Materials: Fluid Property Requirements, Feature Stability, and Resolution. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2010, 40, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuscer, D.; Stavber, G.; Trefalt, G.; Kosec, M. Formulation of an Aqueous Titania Suspension and its Patterning with Ink-Jet Printing Technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemelä, E.; Desai, D.; Nkizinkiko, Y.; Eriksson, J.E.; Rosenholm, J.M. Sugar-decorated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as delivery vehicles for the poorly soluble drug celastrol enables targeted induction of apoptosis in cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 96, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Penninkangas, A.; Lindén, M. Amino-functionalization of large-pore mesoscopically ordered silica by a one-step hyperbranching polymerization of a surface-grown polyethyleneimine. Chem. Commun. 2006, 3909–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaasalainen, M.; Aseyev, V.; von Haartman, E.; Karaman, D.Ş.; Mäkilä, E.; Tenhu, H.; Rosenholm, J.; Salonen, J. Size, Stability, and Porosity of Mesoporous Nanoparticles Characterized with Light Scattering. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebrián, V.; Yagüe, C.; Arruebo, M.; Martín-Saavedra, F.M.; Santamaría, J.; Vilaboa, N. On the role of the colloidal stability of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as gene delivery vectors. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 4097–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.I.; Aulton, M.E. Aulton’s Pharmaceutics: The Design and Manufacture of Medicines, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Edinburgh, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-443-10108-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kaasalainen, M.; Mäkilä, E.; Riikonen, J.; Kovalainen, M.; Järvinen, K.; Herzig, K.-H.; Lehto, V.-P.; Salonen, J. Effect of isotonic solutions and peptide adsorption on zeta potential of porous silicon nanoparticle drug delivery formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 431, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowade, E.; Blaudeck, T.; Baumann, R.R. Inkjet Printing of Colloidal Nanospheres: Engineering the Evaporation-Driven Self-Assembly Process to Form Defined Layer Morphologies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etheridge, M.L.; Campbell, S.A.; Erdman, A.G.; Haynes, C.L.; Wolf, S.M.; McCullough, J. The big picture on nanomedicine: The state of investigational and approved nanomedicine products. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahlgren, C.; Meinander, A.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, F.; Preis, M.; Xu, C.; Salminen, T.A.; Toivola, D.; Abankwa, D.; Rosling, A.; et al. Tailored Approaches in Drug Development and Diagnostics: From Molecular Design to Biological Model Systems. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lensing, R.; Bleich, A.; Smoczek, A.; Glage, S.; Ehlert, N.; Luessenhop, T.; Behrens, P.; Müller, P.P.; Kietzmann, M.; Stieve, M. Efficacy of nanoporous silica coatings on middle ear prostheses as a delivery system for antibiotics: An animal study in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 4815–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlert, N.; Lüßenhop, T.; Krueger, I.; Feldhoff, A.; Badar, M.; Mueller, P.P.; Stieve, M.; Lenarz, T.; Behrens, P. Nanoporous silica coatings on implant surfaces: Characterization, stability, biocompatibility and drug release properties. BioNanoMaterials 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltschka, O.; Böcking, D.; Miller, L.; Brenner, R.E.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Preparation, characterization, and preliminary biocompatibility evaluation of particulate spin-coated mesoporous silica films. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 188, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böcking, D.; Wiltschka, O.; Niinimäki, J.; Shokry, H.; Brenner, R.; Lindén, M.; Sahlgren, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based substrates for cell directed delivery of Notch signalling modulators to control myoblast differentiation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili, A.; Ahmad, M. A Review of Cell Adhesion Studies for Biomedical and Biological Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18149–18184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Paving the Way for Personalized Medicine FDA’s Role in a New Era of Medical Product Development FDA’s Role in a New Era of Medical Product Development Commissioner’s Message 2; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013.
- Lammers, T.; Aime, S.; Hennink, W.E.; Storm, G.; Kiessling, F. Theranostic Nanomedicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.V.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, M.; Fan, X.; Zhou, H. Recent advances in bioprinting techniques: Approaches, applications and future prospects. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bale, S.S.; Vernetti, L.; Senutovitch, N.; Jindal, R.; Hegde, M.; Gough, A.; McCarty, W.J.; Bakan, A.; Bhushan, A.; Shun, T.Y.; et al. In vitro platforms for evaluating liver toxicity. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.B.; Kelbauskas, L.; Brunner, A.; Meldrum, D.R. A versatile method for dynamically controlled patterning of small populations of epithelial cells on substrates via non-contact piezoelectric inkjet printing. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Lindén, M. Wet-Chemical Analysis of Surface Concentration of Accessible Groups on Different Amino-Functionalized Mesoporous SBA-15 Silicas. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 5023–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Duchanoy, A.; Lindén, M. Hyperbranching Surface Polymerization as a Tool for Preferential Functionalization of the Outer Surface of Mesoporous Silica †. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |


| Particle | Surface Area (m2;/g) | Pore Volume (cm3;/g) | Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSN | 1882 | 1.87 | 4.09 |
| MSN–PEI | 930 | 0.82 | 3.54 |
| Sample | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSN–PEI | 395.4 ± 1.6 | 0.050 ± 0.026 | 57.0 ± 0.6 |
| MSN–PEI–F5 | 289.0 ± 13.5 | 0.802 ± 1.07 | 46.6 ± 0.6 |
| MSN–PEI–F15 | 445.9 ± 117.1 | 1.00 | 38.5 ± 2.8 |
| MQ/PG | MSN–PEI (1 mg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| Average step height (nm) n = 9 | 60.5 ± 24.1 | 155.0 ± 17.8 |
| Average drop volume (pl) n = 3 | 52.9 ± 0.6 | 54.9 ± 0.2 |
| Average drop diameter (µm) n = 12 | 81.2 ± 2.2 | 85.8 ± 1.6 |
| Light Microscope | SEM | CSLM | SWLI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D | 2D | 2D | 3D | |
| Non-destructive | + | − | − | + |
| Droplet deposition | + | + | + | + |
| Drop diameter | +/− | + | + | + |
| MSN uniformity | − | + | + | − |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wickström, H.; Hilgert, E.; Nyman, J.O.; Desai, D.; Şen Karaman, D.; De Beer, T.; Sandler, N.; Rosenholm, J.M. Inkjet Printing of Drug-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles—A Platform for Drug Development. Molecules 2017, 22, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112020
Wickström H, Hilgert E, Nyman JO, Desai D, Şen Karaman D, De Beer T, Sandler N, Rosenholm JM. Inkjet Printing of Drug-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles—A Platform for Drug Development. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112020
Chicago/Turabian StyleWickström, Henrika, Ellen Hilgert, Johan O. Nyman, Diti Desai, Didem Şen Karaman, Thomas De Beer, Niklas Sandler, and Jessica M. Rosenholm. 2017. "Inkjet Printing of Drug-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles—A Platform for Drug Development" Molecules 22, no. 11: 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112020
APA StyleWickström, H., Hilgert, E., Nyman, J. O., Desai, D., Şen Karaman, D., De Beer, T., Sandler, N., & Rosenholm, J. M. (2017). Inkjet Printing of Drug-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles—A Platform for Drug Development. Molecules, 22(11), 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112020