Nerolidol: A Sesquiterpene Alcohol with Multi-Faceted Pharmacological and Biological Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Chemical Structure and Physical Properties
- (i)
- Physical description: A clear pale yellow to yellow liquid having a faint floral odor reminiscent of rose and apple.
- (ii)
- Chemical formula: C15H26O
- (iii)
- Flash point: >212° F; CC.
- (iv)
- Boiling point: 276 °C.
- (v)
- LogKow (calculated): 5.68.
- (vi)
- Vapor pressure (calculated): 0.1 mm Hg 20 °C.
- (vii)
- Specific gravity: 0.8744.
- (viii)
- Water solubility (calculated): 1.532 mg/L at 25 °C.
3. Sources, Extraction and Analytical Methods of Nerolidol
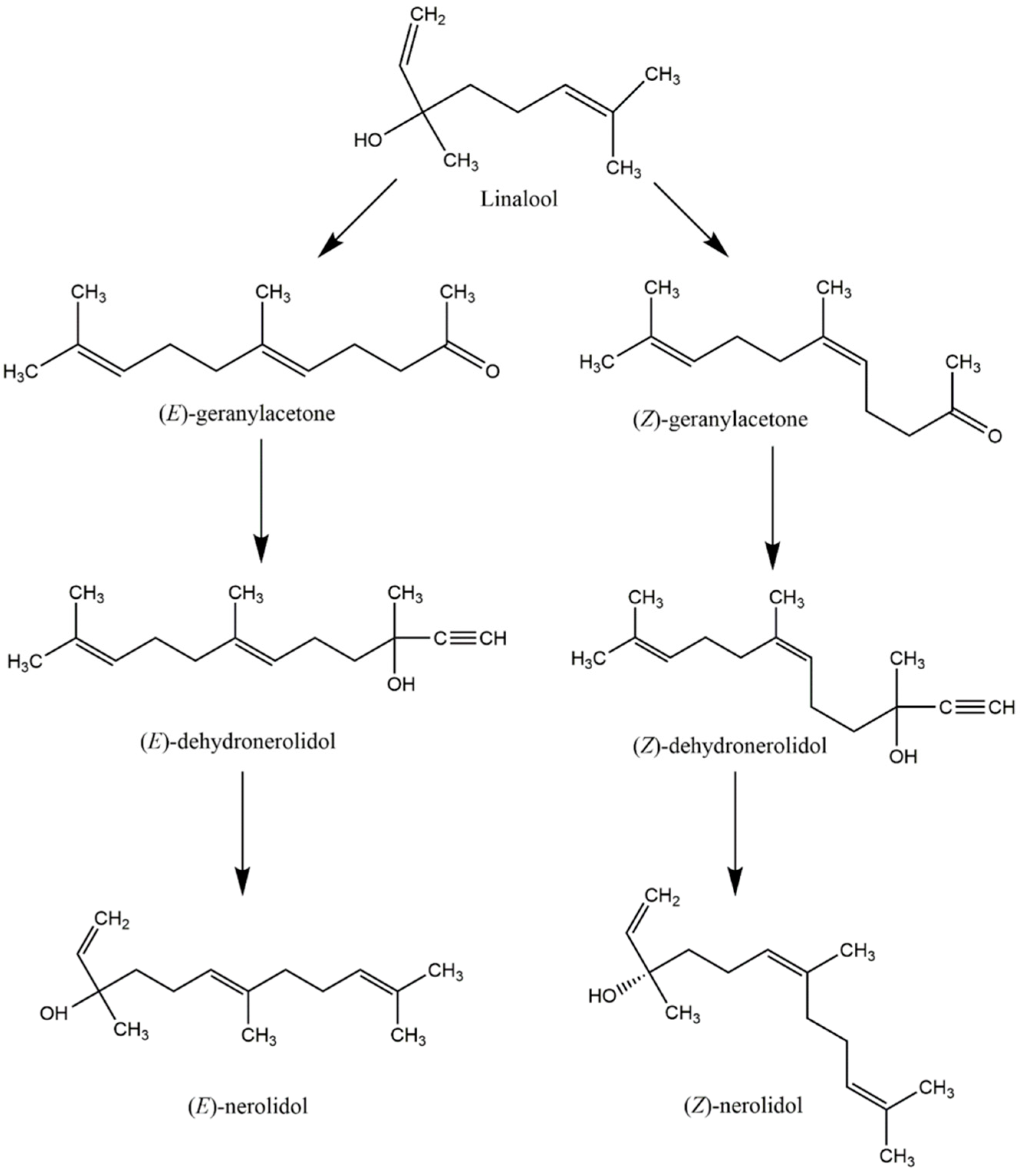
4. Industrial Synthesis of Nerolidol
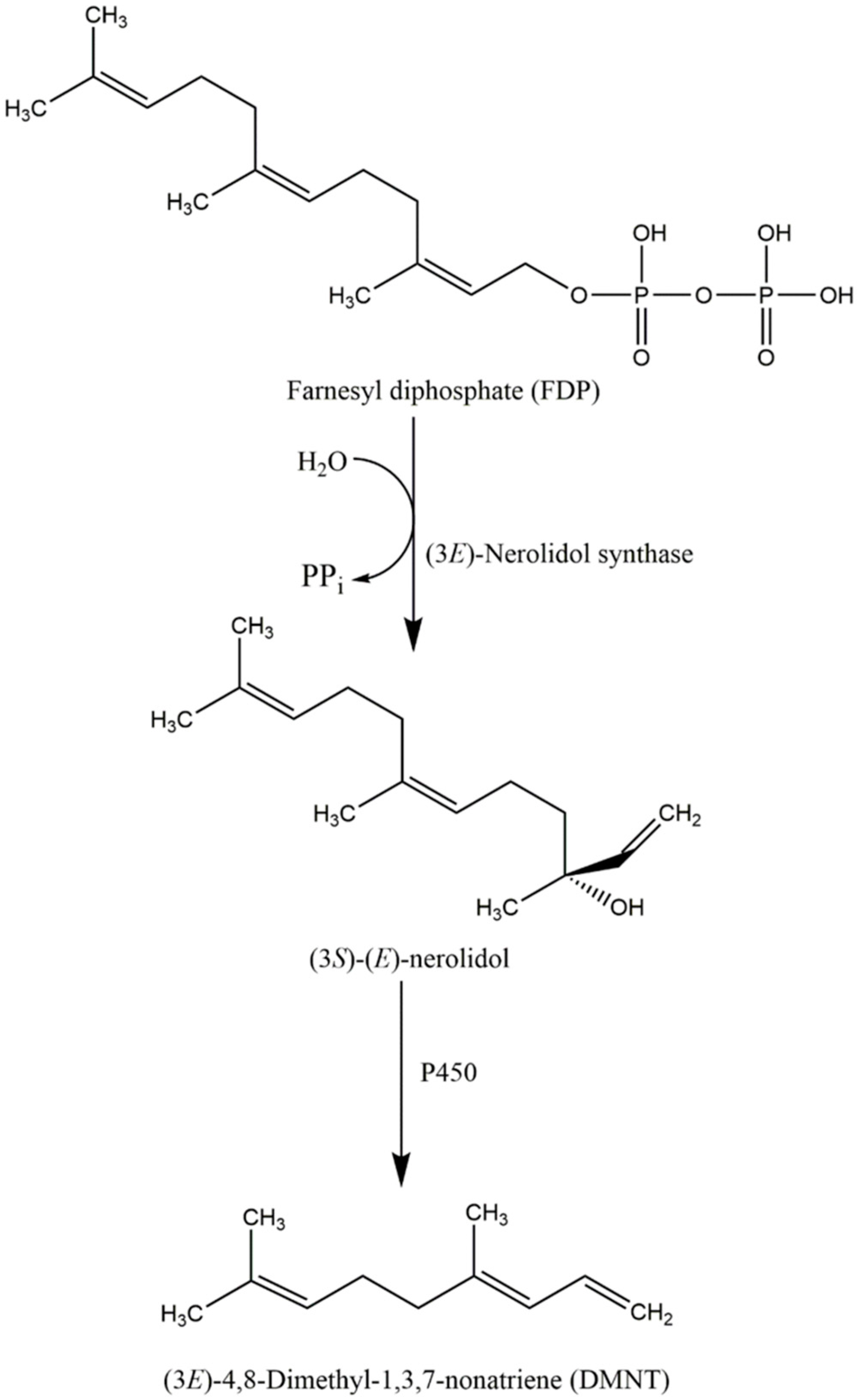
5. The Ecological Role and Biosynthesis of Nerolidol
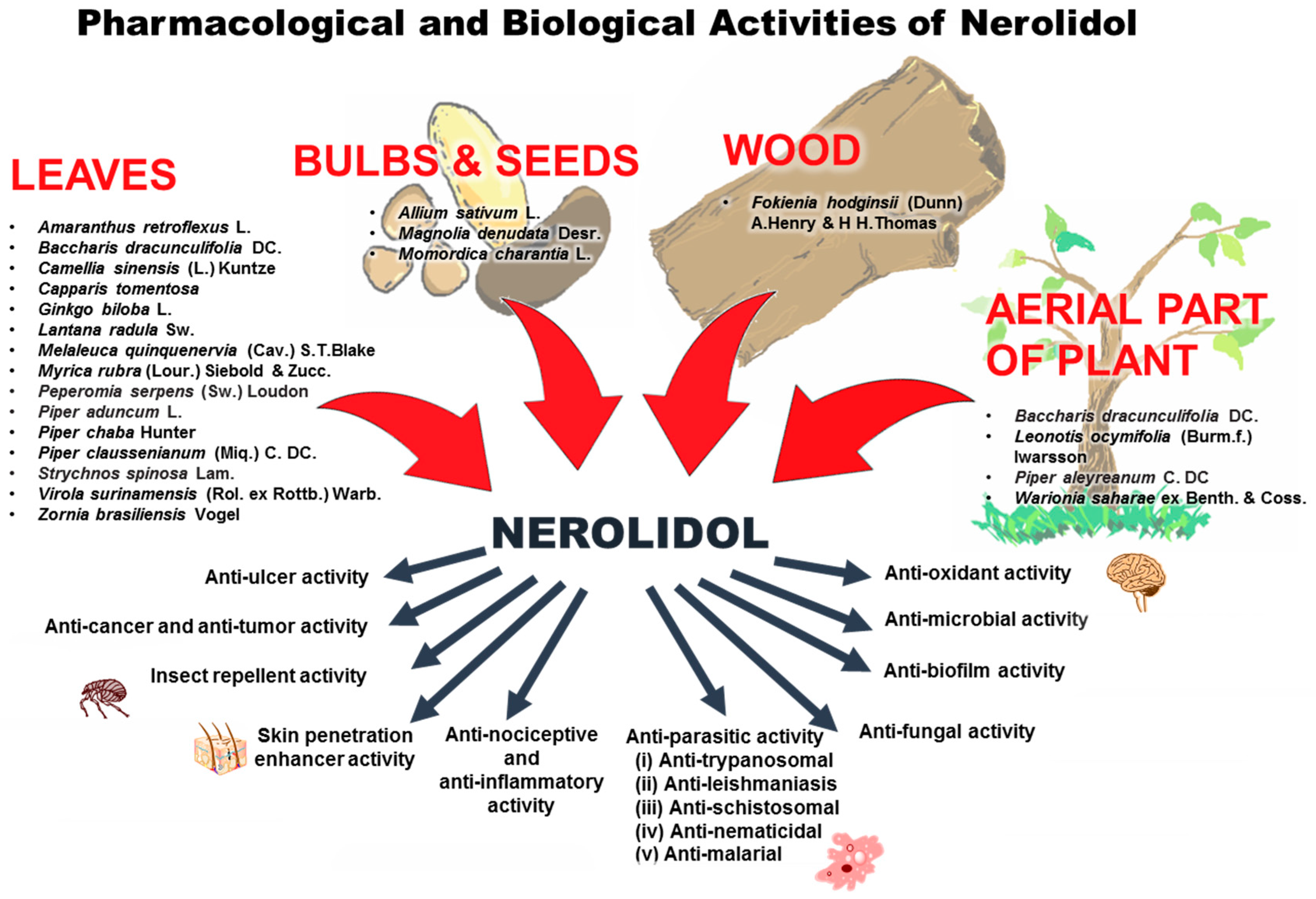
6. Pharmacological and Biological Activities of Nerolidol
6.1. Antioxidant Activity
6.2. Antibacterial Activity
6.3. Anti-Biofilm Activity
6.4. Anti-Fungal Activity
6.5. Anti-Parasitic Activity
6.5.1. Anti-Leishmaniasis
6.5.2. Anti-Trypanosomal Activity
6.5.3. Anti-Schistosomal Activity
6.5.4. Anti-Malarial Activity
6.5.5. Other Anti-Parasitic Activities
6.6. Insect Repellent Activity
6.7. Anti-Ulcer Activity
6.8. Skin Penetration Enhancer Activity
6.9. Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Activity
6.10. Anti-Cancer and Anti-Tumor Activity
6.10.1. In Vitro Studies
6.10.2. In Vivo Studies
7. Pharmacokinetic Studies
7.1. In Vitro Studies
7.2. In Vivo Studies
7.3. Toxicological Studies
7.3.1. Acute Toxicity
7.3.2. Skin Irritation and Sensitization Studies
7.3.3. Mucous Membrane Irritation
7.3.4. Phototoxicity and Photoallergenicity
7.3.5. Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity
7.3.6. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity
7.3.6.1. In Vitro Studies
7.3.6.2. In Vivo Studies
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petrovska, B.B. Historical review of medicinal plants’ usage. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2012, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils—A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, B.; Al-Wabel, N.A.; Shams, S.; Ahamad, A.; Khan, S.A.; Anwar, F. Essential oils used in aromatherapy: A systemic review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 5, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perricone, M.; Arace, E.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Bevilacqua, A. Bioactivity of essential oils: A review on their interaction with food components. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical insecticides, deterrents, and repellents in modern agriculture and an increasingly regulated world. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edris, A.E. Pharmaceutical and therapeutic Potentials of essential oils and their individual volatile constituents: A review. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braca, A.; Siciliano, T.; D’Arrigo, M.; Germanò, M.P. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of Momordica charantia seed essential oil. Fitoterapia 2008, 79, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parreira, N.A.; Magalhaes, L.G.; Morais, D.R.; Caixeta, S.C.; de Sousa, J.P.; Bastos, J.K.; Cunha, W.R.; Silva, M.L.; Nanayakkara, N.P.; Rodrigues, V.; et al. Antiprotozoal, schistosomicidal, and antimicrobial activities of the essential oil from the leaves of Baccharis dracunculifolia. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.M.; Barreto, A.L.S.; Curvelo, J.A.d.R.; Romanos, M.T.V.; Soares, R.M.d.A.; Kaplan, M.A.C. Antileishmanial activity of nerolidol-rich essential oil from Piper claussenianum. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2011, 21, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.K.S.; Ballico, L.J.; Rocha Lapa, F.; Gonçalves, H.P.; de Souza, L.M.; Iacomini, M.; Werner, M.F.d.P.; Baggio, C.H.; Pereira, I.T.; da Silva, L.M.; et al. Evaluation of the antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory and gastric antiulcer activities of the essential oil from Piper aleyreanum C.DC in rodents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.T.; Lee, L.H.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, C.K.; Abdul Kadir, H.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, and bioactivities of Cananga odorata (ylang-ylang). Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, F.M.; Palmeira, C.M.; Oliveira, M.M.; Santos, D.; Simões, A.M.; Rocha, S.M.; Coimbra, M.A.; Peixoto, F. Nerolidol effects on mitochondrial and cellular energetics. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapczynski, A.; Bhatia, S.P.; Letizia, C.S.; Api, A.M. Fragrance material review on nerolidol (isomer unspecified). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, S247–S250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinty, D.; Letizia, C.S.; Api, A.M. Addendum to fragrance material review on nerolidol (isomer unspecified). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48 (Suppl. 3), S43–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, V.; Dietrich, A.; Ulrich, T.; Mosandl, A. The stereoisomers of nerolidol: Separation, analysis and olfactoric properties. Z. Naturforsch. C 1992, 47, 304–307. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.J.; Gwak, K.S.; Yang, I.; Kim, K.W.; Jeung, E.B.; Chang, J.W.; Choi, I.G. Effect of citral, eugenol, nerolidol and α-terpineol on the ultrastructural changes of Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Fitoterapia 2009, 80, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batish, D.R.; Singh, H.P.; Kohli, R.K.; Kaur, S. Eucalyptus essential oil as a natural pesticide. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 256, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grulova, D.; de Martino, L.; Mancini, E.; Salamon, I.; de Feo, V. Seasonal variability of the main components in essential oil of Mentha × piperita L. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.M.; Kaplan, M.A.C. Seasonal evaluation and chemical composition of volatile fractions from Piper claussenianum by hydrodistillation and SPME. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2011, 23, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, J.P.B.; Jorge, R.F.; Leite, M.F.; Furtado, N.A.J.C.; Bastos, J.K.; da Silva Filho, A.A.; Queiroga, C.L.; de Magalhães, P.M.; Soares, A.E.E. Seasonal variation of the (E)-nerolidol and other volatile compounds within ten different cultivated populations of Baccharis dracunculifolia D.C. (Asteraceae). J. Essent. Oil Res. 2009, 21, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Determination of nerolidol in teas using headspace solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.Y.; Sussmann, R.A.C.; Kimura, E.A.; Cassera, M.B.; Katzin, A.M. Quantification of nerolidol in mouse plasma using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 111, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, S.; Kirby, J.; Denby, C.M.; Keasling, J.D. Production and quantification of sesquiterpenes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, including extraction, detection and quantification of terpene products and key related metabolites. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1980–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.J. Principles and applications of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in clinical biochemistry. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2009, 30, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, Y.-S.; Sun, W.; Zhang, B.-Y.; Xu, L.-H.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Qi, L.-W.; Li, P.; Wen, X.-D. Application of a sensitive liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method to a pharmacokinetic study of nerolidol in rat plasma. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znini, M.; Cristofari, G.; Majidi, L.; El Harrak, A.; Paolini, J.; Costa, J. In vitro antifungal activity and chemical composition of Warionia saharae essential oil against 3 apple phytopathogenic fungi. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibret, E.; Wink, M. Trypanocidal and antileukaemic effects of the essential oils of Hagenia abyssinica, Leonotis ocymifolia, Moringa stenopetala, and their main individual constituents. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaltsa, H.D.; Lazari, D.M.; Mavromati, A.S.; Tiligada, E.A.; Constantinidis, T.A. Composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of Scutellaria albida ssp. albida from Greece. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, N.P.; Kato, M.J.; Eloısa, H.d.A.; Maia, J.G.; Yoshida, M.; Planchart, A.R.; Katzin, A.M. Antimalarial use of volatile oil from leaves of Virola surinamensis (Rol.) Warb. by Waiapi Amazon Indians. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 67, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndung’u, M.; Gitu, L. Repellent activity of the essential oil from Capparis tomentosa against maize weevil Sitophilus zeamais. J. Resour. Dev. Manag. 2013, 1, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Wang, C.-Z.; Kong, Z.-W. Antibacterial/antifungal activity and synergistic interactions between polyprenols and other lipids isolated from Ginkgo biloba L. Leaves. Molecules 2013, 18, 2166–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curvelo, J.A.R.; Marques, A.M.; Barreto, A.L.S.; Romanos, M.T.V.; Portela, M.B.; Kaplan, M.A.C.; Soares, R.M.A. A novel nerolidol-rich essential oil from Piper claussenianum modulates Candida albicans biofilm. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, J.L.; Barbosa, L.C.A.; Demuner, A.J.; Alvarenga, E.S.; Silva, C.M.d.; Barreto, R.W. Chemical characterization of volatile compounds of Lantana camara L. and L. radula Sw. and their antifungal activity. Molecules 2012, 17, 11447–11455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Al-Reza, S.; Kang, S. Antifungal activity of essential oil and extracts of Piper chaba Hunter against phytopathogenic fungi. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoet, S.; Stevigny, C.; Hérent, M.-F.; Quetin-Leclercq, J. Antitrypanosomal compounds from the leaf essential oil of Strychnos spinosa. Planta Med. 2006, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-M.; Kim, J.; Chang, K.-S.; Kim, B.-S.; Yang, Y.-J.; Kim, G.-H.; Shin, S.-C.; Park, I.-K. Larvicidal activity of myrtaceae essential oils and their components against Aedes aegypti, acute toxicity on Daphnia magna, and aqueous residue. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, M.C.; Câmara, C.G.; Born, F.; Moraes, M.; Badji, C. Acaricidal activity and repellency of essential oil from Piper aduncum and its components against Tetranychus urticae. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 57, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, B.G.; Silva, A.S.B.; Souza, G.E.P.; Figueiredo, J.G.; Cunha, F.Q.; Lahlou, S.; da Silva, J.K.R.; Maia, J.G.S.; Sousa, P.J.C. Chemical composition, antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects in rodents of the essential oil of Peperomia serpens (SW.) Loud. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.V.; Menezes, L.R.A.; Rocha, S.L.A.; Baliza, I.R.S.; Dias, R.B.; Rocha, C.A.G.; Soares, M.B.P.; Bezerra, D.P. Antitumor properties of the leaf essential oil of Zornia brasiliensis. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrož, M.; Boušová, I.; Skarka, A.; Hanušová, V.; Králová, V.; Matoušková, P.; Szotáková, B.; Skálová, L. The influence of sesquiterpenes from Myrica rubra on the antiproliferative and pro-oxidative effects of doxorubicin and its accumulation in cancer cells. Molecules 2015, 20, 15343–15358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simionatto, E.; Porto, C.; Dalcol, I.I.; da Silva, U.F.; Morel, A.F. Essential oil from Zanthoxylum hyemale. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzakou, O.; Loukis, A.; Said, A. Essential oil from the flowers and leaves of Cassia fistula L. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2007, 19, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stashenko, E.; Martínez, J.R.; Medina, J.D.; Durán, D.C. Analysis of essential oils isolated by steam distillation from Swinglea glutinosa fruits and leaves. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2015, 27, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garneau, F.-X.; Collin, G.; Gagnon, H.; Jean, F.-I.; Strobl, H.; Pichette, A. The essential oil composition of devil’s club, Oplopanax horridus J.E. Smith Miq. Flavour. Fragr. J. 2006, 21, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, S.-I.; Cho, M.; Lee, J. Anti-biofilm, anti-hemolysis, and anti-virulence activities of black pepper, cananga, myrrh oils, and nerolidol against Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9447–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judzentiene, A.; Mockutë, D. Chemical composition of essential oils produced by pink flower inflorescences of wild Achillea millefolium L. Chemija 2004, 15, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Perumalsamy, H.; Wang, M.; Shu, S.; Ahn, Y.J. Larvicidal activity of Magnolia denudata seed hydrodistillate constituents and related compounds and liquid formulations towards two susceptible and two wild mosquito species. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, I.; Singh, B.; Singh, G.; Isidorov, V.; Szczepaniak, L. Chemistry, antifungal and antioxidant activities of cardamom (Amomum subulatum) essential oil and oleoresins. Int. J. Essent. Oil Ther. 2008, 2, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Koudou, J.; Abena, A.A.; Ngaissona, P.; Bessière, J.M. Chemical composition and pharmacological activity of essential oil of Canarium schweinfurthii. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, Y.-T.; Chua, M.-T.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chang, S.-T. Anti-inflammation activities of essential oil and its constituents from indigenous cinnamon (Cinnamomum osmophloeum) twigs. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3908–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gretchen, E.P.; Junwei, Z.; Lyric, B.; Joel, R.C. Amyris and siam-wood essential oils: Insect activity of sesquiterpenes. In Pesticides in Household, Structural and Residential Pest Management; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; Volume 1015, pp. 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, B.; Hauser, A.; Ohloff, G. New sesquiterpenoids from cabreuva oil. Helv. Chim. Acta 1986, 69, 2026–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, M.; Estell, R.; Tellez, M.; Fredrickson, E. A retention index calculator simplifies identification of plant volatile organic compounds. Phytochem. Anal. 2009, 20, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babushok, V.I.; Zenkevich, I.G. Retention indices for most frequently reported essential oil compounds in GC. Chromatographia 2008, 69, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orav, A. Identification of terpenes by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. In Current Practice of Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 483–494. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, T.Y.; Eiserich, J.P.; Shibamoto, T. Volatile compounds isolated from edible Korean chamchwi (Aster scaber Thunb). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-S. Character impact odorants of citrus hallabong [(C. unshiu Marcov × C. sinensis Osbeck) × C. reticulata Blanco] cold-pressed peel oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2687–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.; Nagarajan, S.; Jagan Mohan Rao, L. Microwave heating and conventional roasting of cumin seeds (Cuminum cyminum L.) and effect on chemical composition of volatiles. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigmatov, A.G.; Serebryakov, é.P.; Yanovskaya, L.A. Improved method for the isolation of geranyl esters of (4E/Z,8E)- and (4E/Z,8Z)-farnesylacetic acid. Pharm. Chem. J. 1987, 21, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofner, A.; Kimel, W.; Holmgren, A.; Forrester, F. Synthetisches nerolidol und verwandte c15-alkohole. Helv. Chim. Acta 1959, 42, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, C.V.; Morlacchi, P.; Baevich, A.; Matsuda, S.P.T. Nerolidol, Terpene, and Terpene Deriviative Synthesis. U.S. Patent 8173405, 8 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Iason, G. The role of plant secondary metabolites in mammalian herbivory: Ecological perspectives. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2005, 64, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichersky, E.; Gershenzon, J. The formation and function of plant volatiles: Perfumes for pollinator attraction and defense. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlings, T.C.; Ton, J. Exploiting scents of distress: The prospect of manipulating herbivore-induced plant odours to enhance the control of agricultural pests. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudareva, N.; Pichersky, E.; Gershenzon, J. Biochemistry of plant volatiles. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudareva, N.; Negre, F.; Nagegowda, D.A.; Orlova, I. Plant volatiles: Recent advances and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2006, 25, 417–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.-X.; Lou, Y.-G.; Mao, Y.-B.; Lu, S.; Wang, L.-J.; Chen, X.-Y. Plant terpenoids: Biosynthesis and ecological functions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2007, 49, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, J.; Köllner, T.G.; Gershenzon, J. Monoterpene and sesquiterpene synthases and the origin of terpene skeletal diversity in plants. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagegowda, D.A.; Gutensohn, M.; Wilkerson, C.G.; Dudareva, N. Two nearly identical terpene synthases catalyze the formation of nerolidol and linalool in snapdragon flowers. Plant J. 2008, 55, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenhardt, J.; Gershenzon, J. Demonstration and characterization of (E)-nerolidol synthase from maize: A herbivore-inducible terpene synthase participating in (3E)-4,8-dimethyl-1,3,7-nonatriene biosynthesis. Planta 2000, 210, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnee, C.; Köllner, T.G.; Gershenzon, J.; Degenhardt, J. The maize gene terpene synthase 1 encodes a sesquiterpene synthase catalyzing the formation of (E)-β-farnesene, (E)-nerolidol, and (E,E)-farnesol after herbivore damage. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwmeester, H.J.; Verstappen, F.W.; Posthumus, M.A.; Dicke, M. Spider mite-induced (3S)-(E)-nerolidol synthase activity in cucumber and lima bean. The first dedicated step in acyclic c11-homoterpene biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinholes, J.; Gonçalves, P.; Martel, F.; Coimbra, M.A.; Rocha, S.M. Assessment of the antioxidant and antiproliferative effects of sesquiterpenic compounds in in vitro Caco-2 cell models. Food Chem. 2014, 156, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinholes, J.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Gonçalves, P.; Martel, F.; Coimbra, M.A.; Rocha, S.M. Hepatoprotection of sesquiterpenoids: A quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) approach. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira Neto, J.; de Almeida, A.; da Silva Oliveira, J.; dos Santos, P.; de Sousa, D.; de Freitas, R. Antioxidant effects of nerolidol in mice hippocampus after open field test. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hada, T.; Shiraishi, A.; Furuse, S.; Inoue, Y.; Hamashima, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Masuda, K.; Shiojima, K.; Shimada, J. Inhibitory effects of terpenes on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Med. 2003, 57, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, Y.; Shiraishi, A.; Hada, T.; Hirose, K.; Hamashima, H.; Shimada, J. The antibacterial effects of terpene alcohols on Staphylococcus aureus and their mode of action. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 237, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togashi, N.; Hamashima, H.; Shiraishi, A.; Inoue, Y.; Takano, A. Antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus aureus of terpene alcohols with aliphatic carbon chains. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2010, 22, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, I. Antimicrobial activity of green tea flavor components. In Bioactive Volatile Compounds from Plants; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 525, pp. 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, O.; Pereira, R.; Gonçalves, F.; Mendo, S.; Coimbra, M.A.; Rocha, S.M. Evaluation of the mutagenicity of sesquiterpenic compounds and their influence on the susceptibility towards antibiotics of two clinically relevant bacterial strains. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. 2011, 723, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brehm-Stecher, B.F.; Johnson, E.A. Sensitization of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli to antibiotics by the sesquiterpenoids nerolidol, farnesol, bisabolol, and apritone. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3357–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, M.; Rocha, S.; Coimbra, M.A.; Vieira, M.J. Enhancement of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus antibiotic susceptibility using sesquiterpenoids. Med. Chem. 2008, 4, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-J.; Han, J.-I.; Lee, G.-S.; Park, M.-J.; Choi, I.-G.; Na, K.-J.; Jeung, E.-B. Antifungal effect of eugenol and nerolidol against Microsporum gypseum in a guinea pig model. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontin, M.; Bottini, R.; Burba, J.L.; Piccoli, P. Allium sativum produces terpenes with fungistatic properties in response to infection with Sclerotium cepivorum. Phytochemistry 2015, 115, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd-Shukri, H.; Zainal-Abidin, B. The effects of nerolidol, allicin and berenil on the morphology of Trypanosoma evansi in mice: A comparative study using light and electron microscopic approaches. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2011, 40, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Arruda, D.C.; D’Alexandri, F.L.; Katzin, A.M.; Uliana, S.R.B. Antileishmanial activity of the terpene nerolidol. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargos, H.S.; Moreira, R.A.; Mendanha, S.A.; Fernandes, K.S.; Dorta, M.L.; Alonso, A. Terpenes increase the lipid dynamics in the Leishmania plasma membrane at concentrations similar to their IC50 values. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.P.; Oliveira, G.L.; de Carvalho, R.B.; de Sousa, D.P.; Freitas, R.M.; Pinto, P.L.; de Moraes, J. Antischistosomal activity of the terpene nerolidol. Molecules 2014, 19, 3793–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.M.; Peixoto, A.C.C.; de Paula, R.C.; Nascimento, M.F.A.; Soares, L.F.; Velozo, L.S.; Guimarães, E.F.; Kaplan, M.A.C. Phytochemical investigation of anti-plasmodial metabolites from Brazilian Native Piper species. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2015, 18, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Goulart, H.; Kimura, E.A.; Peres, V.J.; Couto, A.S.; Aquino Duarte, F.A.; Katzin, A.M. Terpenes arrest parasite development and inhibit biosynthesis of isoprenoids in Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2502–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Macedo, C.S.; Uhrig, M.L.; Kimura, E.A.; Katzin, A.M. Characterization of the isoprenoid chain of coenzyme Q in Plasmodium falciparum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 207, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, M.F.; Saito, A.Y.; Peres, V.J.; Oliveira, A.C.; Katzin, A.M. In vitro antimalarial activity of different inhibitors of the plasmodial isoprenoid synthesis pathway. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5084–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbouLaila, M.; Sivakumar, T.; Yokoyama, N.; Igarashi, I. Inhibitory effect of terpene nerolidol on the growth of Babesia parasites. Parasitol. Int. 2010, 59, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Rahman, F.H.; Alaniz, N.M.; Saleh, M.A. Nematicidal activity of terpenoids. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2013, 48, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Moll, M.C.; Romero, M.C.; Montilla, M.P.; Valero, A. In vitro and in vivo activity of three sesquiterpenes against L3 larvae of Anisakis type I. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Campli, E.; di Bartolomeo, S.; Delli Pizzi, P.; Di Giulio, M.; Grande, R.; Nostro, A.; Cellini, L. Activity of tea tree oil and nerolidol alone or in combination against Pediculus capitis (head lice) and its eggs. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Assis Lage, T.C.; Montanari, R.M.; Fernandes, S.A.; de Oliveira Monteiro, C.M.; de Oliveira Souza Senra, T.; Zeringota, V.; da Silva Matos, R.; Daemon, E. Chemical composition and acaricidal activity of the essential oil of Baccharis dracunculifolia De Candole (1836) and its constituents nerolidol and limonene on larvae and engorged females of Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 148, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klopell, F.C.; Lemos, M.; Sousa, J.P.B.; Comunello, E.; Maistro, E.L.; Bastos, J.K.; Andrade, S.F.d. Nerolidol, an antiulcer constituent from the essential oil of Baccharis dracunculifolia DC (Asteraceae). Z. Naturforsch. C 2007, 62, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, P.A.; Barry, B.W. Sesquiterpene components of volatile oils as skin penetration enhancers for the hydrophilic permeant 5-fluorouracil. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanthi, D.; Lakshmi, P.K. Terpenes: Effect of lipophilicity in enhancing transdermal delivery of alfuzosin hydrochloride. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2012, 3, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnaiah, Y.S.; Al-Saidan, S.M.; Jayaram, B. Effect of nerodilol, carvone and anethole on the in vitro transdermal delivery of selegiline hydrochloride. Pharmazie 2006, 61, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Kattan, A.F.; Asbill, C.S.; Kim, N.; Michniak, B.B. The effects of terpene enhancers on the percutaneous permeation of drugs with different lipophilicities. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 215, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonsêca, D.V.; Salgado, P.R.R.; de Carvalho, F.L.; Salvadori, M.G.S.S.; Penha, A.R.S.; Leite, F.C.; Borges, C.J.S.; Piuvezam, M.R.; Pordeus, L.C.d.M.; Sousa, D.P.; et al. Nerolidol exhibits antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activity: Involvement of the GABAergic system and proinflammatory cytokines. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 30, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryabchenko, B.; Tulupova, E.; Schmidt, E.; Wlcek, K.; Buchbauer, G.; Jirovetz, L. Investigation of anticancer and antiviral properties of selected aroma samples. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Boris, R.; Elena, T.; Erich, S.; Walter, J.; Gerhard, B.; Leopold, J. Cytotoxic properties of selected sesquiterpene alcohols on human cervix carcinoma cell lines. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2011, 14, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, I.; Morimitsu, Y. Cytotoxicity of green tea flavor compounds against two solid tumor cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 1626–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattenberg, L.W. Inhibition of azoxymethane-induced neoplasia of the large bowel by 3-hydroxy-3,7,11-trimethyl-l,6,10-dodecatriene (nerolidol). Carcinogenesis 1991, 12, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatman, D.; Mo, H. Volatile isoprenoid constituents of fruits, vegetables and herbs cumulatively suppress the proliferation of murine B16 melanoma and human HL-60 leukemia cells. Cancer Lett. 2002, 175, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanušová, V.; Skálová, L.; Ambrož, M.; Králová, V.; Langhansová, L.; Matoušková, P. The effect of Myrica rubra essential oil and its components α-humulene and trans-nerolidol on adhesion and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Cell Microenviron. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, K. Studies on free radicals, antioxidants, and co-factors. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uttara, B.; Singh, A.V.; Zamboni, P.; Mahajan, R.T. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hana, B.; Veronika, H.; Lenka, S.; Martin, A.; Iva, B. Antioxidant, pro-oxidant and other biological activities of sesquiterpenes. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 2478–2494. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Burgos, E.; Gomez-Serranillos, M.P. Terpene compounds in nature: A review of their potential antioxidant activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 5319–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Antioxidants in human health and disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1996, 16, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, C.T. Increasing antioxidant activity and reducing decay of blueberries by essential oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3587–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J.V. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, I.; Muroi, H.; Masaki, H.; Kubo, A. Antibacterial activity of long-chain alcohols: The role of hydrophobic alkyl groups. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1993, 3, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlan, R.M. Biofilms: Microbial life on surfaces. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, E.S.D.; Lewis, R.; Lewis, J.S.; Martin, C.; Andes, D. Pharmacology of systemic antifungal agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, S28–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemba, D.; Kunicka, A. Antibacterial and antifungal properties of essential oils. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 813–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattnaik, S.; Subramanyam, V.R.; Kole, C. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of ten essential oils in vitro. Microbios 1996, 86, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Renslo, A.R.; McKerrow, J.H. Drug discovery and development for neglected parasitic diseases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, J.P.; Fyfe, L.; Smith, H. Plant active components—A resource for antiparasitic agents? Trends Parasitol. 2005, 21, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, P.; Scott, P. Leishmaniasis: Complexity at the host-pathogen interface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiuman, T.S.; Santos, A.O.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Filho, B.P.D.; Nakamura, C.V. Recent advances in leishmaniasis treatment. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e525–e532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, A.S.; Kimura, E.A.; Peres, V.J.; Uhrig, M.L.; Katzin, A.M. Active isoprenoid pathway in the intra-erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium falciparum: Presence of dolichols of 11 and 12 isoprene units. Biochem. J. 1999, 341, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendanha, S.A.; Alonso, A. Effects of terpenes on fluidity and lipid extraction in phospholipid membranes. Biophys. Chem. 2015, 198, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, T.; Esmat, G. Hepatic and intestinal schistosomiasis: Review. J. Adv. Res. 2013, 4, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.G.P.; Bartley, P.B.; Sleigh, A.C.; Olds, G.R.; Li, Y.; Williams, G.M.; McManus, D.P. Schistosomiasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangpukdee, N.; Duangdee, C.; Wilairatana, P.; Krudsood, S. Malaria diagnosis: A brief review. Korean. J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonhosolo, R.; D’Alexandri, F.L.; Genta, F.A.; Wunderlich, G.; Gozzo, F.C.; Eberlin, M.N.; Peres, V.J.; Kimura, E.A.; Katzin, A.M. Identification, molecular cloning and functional characterization of an octaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase in intra-erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem. J. 2005, 392, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukeh, D.A.; Birkett, M.A.; Pickett, J.A.; Bowman, A.S.; Jennifer Mordue, A. Repellent activity of alligator pepper, Aframomum melegueta, and ginger, Zingiber officinale, against the maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isman, M.B. Plant essential oils for pest and disease management. Crop Prot. 2000, 19, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, V.; Tripathi, A.K.; Aggarwal, K.K.; Khanuja, S.P.S. Insecticidal, repellent and oviposition-deterrent activity of selected essential oils against Anopheles stephensi, Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, F.K.L.; Leung, W.K. Peptic-ulcer disease. Lancet 2002, 360, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Mitragotri, S.; Langer, R. Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Leu, Y.-L.; Hwang, T.-L.; Cheng, H.-C.; Hung, C.-F. Development of sesquiterpenes from Alpinia oxyphylla as novel skin permeation enhancers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 19, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Singh, J. In vitro percutaneous absorption enhancement of a lipophilic drug tamoxifen by terpenes. J. Control. Release 1998, 51, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, W.; Neeck, G. Nociception, pain, and antinociception: Current concepts. Z. Rheumatol. 2001, 60, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, B.L.; Urban, L.A. Mechanisms of inflammatory pain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2001, 87, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, F.Y. The role of innate cytokines in inflammatory response. Immunol. Lett. 2003, 85, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroon, J.C.; Bost, J.W.; Maroon, A. Natural anti-inflammatory agents for pain relief. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Supriady, H.; Goh, B.H.; Kadir, H.A. Elephantopus scaber induces apoptosis through ROS-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway in HCT116 human colorectal carcinoma cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Singh, A. Ocular adverse effects of anti-cancer chemotherapy. J. Cancer Ther. Res. 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.W.; Ruefli, A.A.; Lowe, S.W. Apoptosis: A link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell 2002, 108, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, N.; Mantha, A.K.; Mittal, S. Essential oils and their constituents as anticancer agents: A mechanistic view. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, B.H.; Chan, C.K.; Kamarudin, M.N.A.; Abdul Kadir, H. Swietenia macrophylla King induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis through p53 upregulation in HCT116 colorectal carcinoma cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvestre, M.; Pichette, A.; Lavoie, S.; Longtin, A.; Legault, J. Composition and cytotoxic activity of the leaf essential oil of Comptonia peregrina (L.) Coulter. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golias, C.; Tsoutsi, E.; Matziridis, A.; Makridis, P.; Batistatou, A.; Charalabopoulos, K. Leukocyte and endothelial cell adhesion molecules in inflammation focusing on inflammatory heart disease. In Vivo 2007, 21, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casey, P.J.; Solski, P.A.; Der, C.J.; Buss, J.E. p21ras is modified by a farnesyl isoprenoid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 8323–8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smet, P.A.G.M. Clinical risk management of herb-drug interactions. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 63, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.J.; Dickinson, J.R. Biotransformation of hop aroma terpenoids by ale and lager yeasts. FEMS Yeast Res. 2003, 3, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longenecker, H.E.; Musulin, R.R.; Tully, R.H.; King, C.G. An acceleration of Vitamin C synthesis and excretion by feeding known organic compounds to rats. J. Biol. Chem. 1939, 129, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Mendanha, S.A.; Moura, S.S.; Anjos, J.L.V.; Valadares, M.C.; Alonso, A. Toxicity of terpenes on fibroblast cells compared to their hemolytic potential and increase in erythrocyte membrane fluidity. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, S. Drug administration, absorption, and bioavailability. In Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: An Integrated Textbook and Computer Simulations, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 36–59. [Google Scholar]
- Jambhekar, S.S.; Breen, P.J. Bioavailability/bioequivalence. In Basic Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2012; pp. 137–159. [Google Scholar]
- Bunel, V.; Ouedraogo, M.; Nguyen, A.T.; Stévigny, C.; Duez, P. Methods applied to the in vitro primary toxicology testing of natural products: State of the art, strengths, and limits. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1210–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausen, B.M.; Evers, P.; Stüwe, H.T.; König, W.A.; Wollenweber, E. Propolis allergy (IV) studies with further sensitizers from propolis and constituents common to propolis, poplar buds and Balsam of Peru. Contact Dermat. 1992, 26, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausen, B.M.; Simatupang, T.; Bruhn, G.; Evers, P.; Koenig, W.A. Identification of new allergenic constituents and proof of evidence for coniferyl benzoate in Balsam of Peru. Am. J. Contact Dermat. 1995, 6, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsito, D.; Bickers, D.; Bruze, M.; Calow, P.; Greim, H.; Hanifin, J.M.; Rogers, A.E.; Saurat, J.H.; Sipes, I.G.; Tagami, H. A safety assessment of non-cyclic alcohols with unsaturated branched chain when used as fragrance ingredients: The RIFM expert panel. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48 (Suppl. 3), S1–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, K.; Jiang, Y.; Crumrine, D.; Bass, N.M.; Appel, R.; Elias, P.M.; Williams, M.L.; Feingold, K.R. Activators of the nuclear hormone receptors PPARalpha and FXR accelerate the development of the fetal epidermal permeability barrier. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, M.D.; Nicholls, D.G. Assessing mitochondrial dysfunction in cells. Biochem. J. 2011, 435, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Péres, V.F.; Moura, D.J.; Sperotto, A.R.M.; Damasceno, F.C.; Caramão, E.B.; Zini, C.A.; Saffi, J. Chemical composition and cytotoxic, mutagenic and genotoxic activities of the essential oil from Piper gaudichaudianum Kunth leaves. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2389–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperotto, A.R.M.; Moura, D.J.; Péres, V.F.; Damasceno, F.C.; Caramão, E.B.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Saffi, J. Cytotoxic mechanism of Piper gaudichaudianum Kunth essential oil and its major compound nerolidol. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 57, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijne, W.H.M.; Kienhuis, A.S.; van Ommen, B.; Stierum, R.H.; Groten, J.P. Systems toxicology: Applications of toxicogenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics in toxicology. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2005, 2, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youns, M.; Hoheisel, J.D.; Efferth, T. Toxicogenomics for the prediction of toxicity related to herbs from traditional Chinese medicine. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pículo, F.; Guiraldeli Macedo, C.; de Andrade, S.F.; Luis Maistro, E. In vivo genotoxicity assessment of nerolidol. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
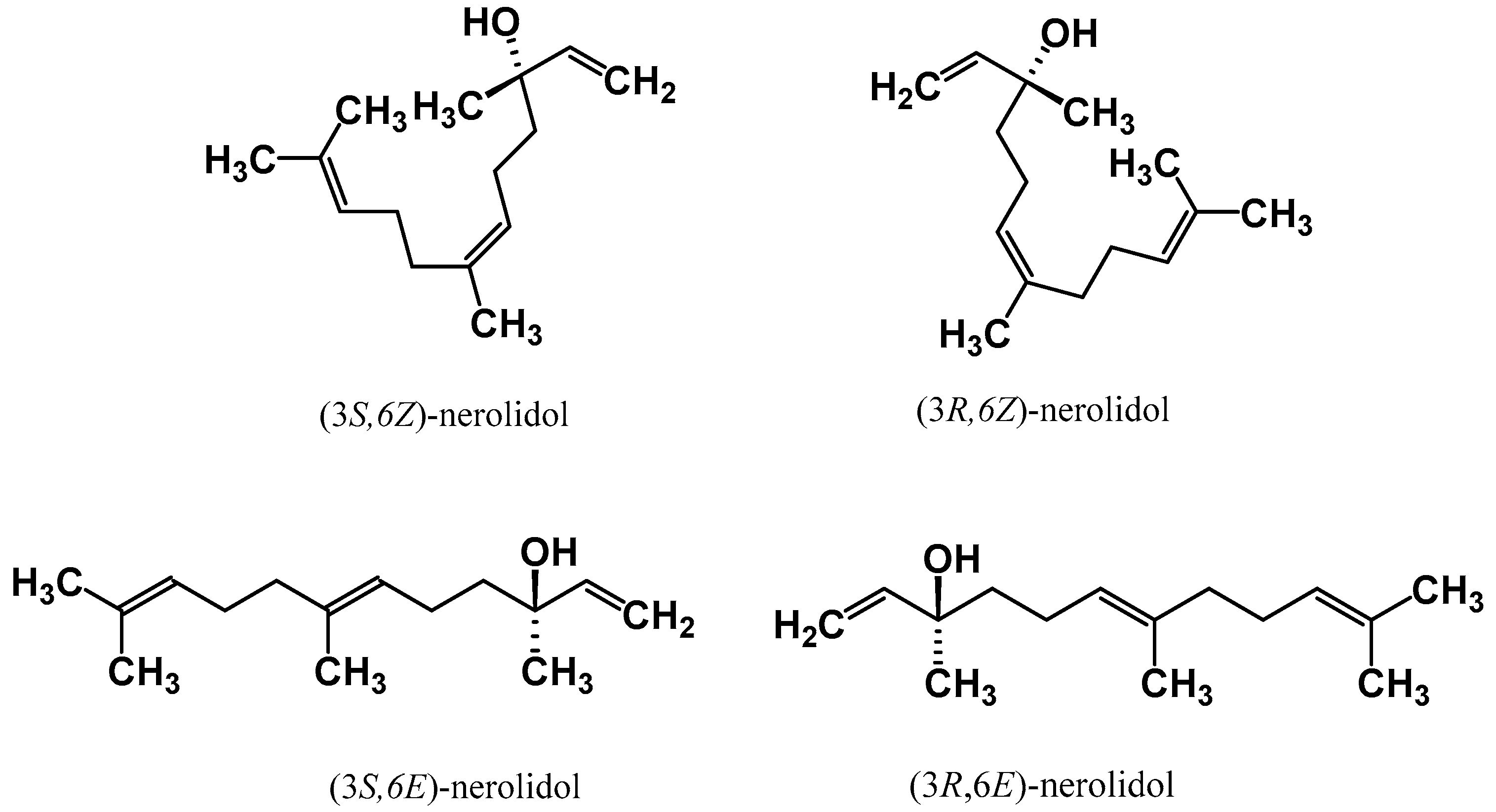
| Cis-Nerolidol | Trans-Nerolidol |
|---|---|
| (i) (±)-cis-nerolidol | (i) (±)-trans-nerolidol |
| (ii) (6Z)-3,7,11-trimethyl-1,6,10-dodecatrien-3-ol | (ii) (6E)-3,7,11-trimethyl-1,6,10-dodecatrien-3-ol |
| (iii) (6Z)-3,7,11-trimethyldodeca-1,6,10-trien-3-ol | (iii) (6E)-3,7,11-trimethyldodeca-1,6,10-trien-3-ol |
| (iv) (6Z)-nerolidol | (iv) (6E)-nerolidol |
| (v) 1,6,10-dodecatrien-3-ol, 3,7,11-trimethyl-, (6Z)- | (v) 1,6,10-dodecatrien-3-ol, 3,7,11-trimethyl-, (6E)- |
| (vi) (Z)-nerolidol | (vi) (E)-nerolidol |
| Plant Part | Type of Nerolidol Found in the Essential Oil | Nerolidol Purified from the Essential Oil of the Respective Plants (%) | Extraction Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerial parts | trans-nerolidol | (i) Warionia saharae ex Benth. & Coss. (23.0%) | Hydrodistillation technique using the Clevenger-type apparatus | [10,26,27,28] |
| (ii) Scutellaria abida L. ssp. albida (9.03%) | ||||
| (iii) Piper aleyreanum C. DC (1.2%) | ||||
| (iv) Leonotis ocymifolia (Burm.f.) Iwarsson (0.41%) | ||||
| Leaf | Nerolidol (n.s.) | (i) Capparis tomentosa Lam. (5.14%) | Hydrodistillation technique using the Clevenger-type apparatus | [29,30] |
| (ii) Virola surinamensis (Rol. ex Rottb.) Warb. (3.0%) | ||||
| Ginkgo biloba L. (0.12%) | Molecular distillation at a feed temperature of 60 °C, distillation temperature of 280 °C, feed flow rate of 180 mL per hour, scraper rate of 300 rpm, and operating pressure of 0.1–0.5 Pa | [31] | ||
| trans-Nerolidol | (i) Baccharis dracunculifolia DC. (33.51%) | Hydrodistillation technique using the Clevenger-type apparatus | [8,9,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43] | |
| (ii) Cassia fistula L. (2.2%) | ||||
| (iii) Comptonia peregrina (L.) Coult. (2.11% and 3.43% after 0–30 min fraction and 30–60 min fraction respectively) | ||||
| (iv) Melaleuca quinquenervia (Cav.) S.T.Blake (24.19%) | ||||
| (v) Myrica rubra (Lour.) Siebold & Zucc. (2%) | ||||
| (vi) Lantana radula Sw. (19.0%) | ||||
| (vii) Peperomia serpens (Sw.) Loudon (38.0%) | ||||
| (viii) Piper aduncum L. (0.2%) | ||||
| (ix) Piper chaba Hunter (5.1%) | ||||
| (x) Piper claussenianum (Miq.) C. DC. (81.4%) | ||||
| (xi) Strychnos spinosa Lam. (0.7%) | ||||
| (xii) Swinglea glutinosa (Blanco) Merr. (28.4%) | ||||
| (xiii) Zanthoxylum hyemale A.St.-Hil. (51.0%) | ||||
| (xiv) Zornia brasiliensis Vogel (48.0%) | ||||
| Stem | trans-Nerolidol | Oplopanax horridus (Sm.) Miq. (54.5%) | Steam distillation using a low pressure system with an external steam source | [44] |
| Flower | trans-Nerolidol | (i) Achillea millefolium L. (11.6%–31.9%) | Hydrodistillation technique using the Clevenger-type apparatus | [42,45,46] |
| (ii) Cananga odorata (Lam.) Hook.f. & Thomson (0.32%) | ||||
| (iii) Cassia fistula L. (38.0%) | ||||
| Root | trans-Nerolidol | Oplopanax horridus (Sm.) Miq. (54.6%) | Steam distillation using a low pressure system with an external steam source | [44] |
| Seed/grain | Nerolidol (n.s.) | Magnolia denudata Desr. (2.18%) | Hydrodistillation technique using the Clevenger-type apparatus | [47] |
| trans-Nerolidol | (i) Elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton (3.6%) | Hydrodistillation technique using the Clevenger-type apparatus | [7,48] | |
| (ii) Momordica charantia L. (61.6%) | ||||
| Fruit | trans-Nerolidol | Swinglea glutinosa (Blanco) Merr. (19.1%) | Hydrodistillation technique using the Clevenger-type apparatus | [43] |
| Resin | trans-Nerolidol | Canarium schweinfurthii Engl. (14%) | Hydrodistillation technique using the Clevenger-type apparatus | [49] |
| Twig/wood | Trans-Nerolidol | Cinnamomum osmophloeum Kaneh. (1.05%) | Hydrodistillation technique using the Clevenger-type apparatus | [50] |
| Fokienia hodginsii (Dunn) A.Henry & H H.Thomas (34.8%) | Solid-phase microextraction | [51] | ||
| cis-Nerolidol | Myrocarpus fastigiatus Allemao (80.0%) | Hydrodistillation technique using the Clevenger-type apparatus | [52] |
| Types of Column/Equipment Used | Cis-Nerolidol | Trans-Nerolidol | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| (A) Retention time of different chromatographic columns of GC (minutes) | |||
| (i) A-100 or 154-C column | 14 | 16 | [22] |
| (ii) DB-5 capillary column | n.a. | 10.5 | [21] |
| (iii) TR-5MS capillary column | 5.87 | 5.98 | [22] |
| (B) Retention time of different chromatographic columns of LC (minutes) | |||
| (i) Hypersil BDS C18 column | 11.9 | 13.1 | [25] |
| (C) Major peaks of mass spectrometry (MS) (m/z) | |||
| (i) M-80B gas chromatograph double focusing mass spectrometer | 41, 69, 134, 91, 93, 79 | 69, 41, 93, 43, 71, 55 | [55] |
| (ii) Y2K ion trap (MS) PolarisQ System mass spectrometer | 93, 91, 67, 107, 79, 161, 121, 133, 55, 147, 189, 175 | 93, 121, 67, 107, 79, 161, 136, 55, 189, 148, 175 | [22] |
| (D) Retention indices of different chromatographic columns of GC | |||
| (i) HP-101 | n.a. | 1564 | [56] |
| (ii) HP-20M | n.a. | 2009 | [56] |
| (iii) HP-FFAP | n.a. | 2055 | [56] |
| (iv) Fused silica capillary column coated with DB-5 | n.a. | 1564 | [29] |
| (v) OV-101 | 1533 | 1549 | [55] |
| (vi) PEG 20M | 2028 | 2035 | [55] |
| (vii) DB-5 | 1565 | 1539 | [57] |
| (viii) DB-Wax | 2010 | 2054 | [57] |
| (ix) SPB-1 | 1543 | n.a. | [58] |
| (x) Dimethylsilicone (DIMS) | 1524.4 (a) | 1550.1 (a) | [54] |
| (xi) Dimethylsilicone with 5% phenyl groups (DIMS5P) | 1543.6 (a) | 1560.9 (a) | [54] |
| (xii) Polyethylene glycol (PEG) | 2007.3 (a) | 2036.3 (a) | [54] |
| Bioactivity | Type of Nerolidol | Plant and Part of Plant Used (If Any) | Target Organism(s) | Screening Assay and Methods Used | Results | Possible Mechanisms of Action | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant activity | cis-Nerolidol (Aldrich Chemical Co., Milwaukee, WI, USA) | - | - | DPPH and hydroxyl radical scavenging activity | (i) Exhibited DPPH radical scavenging activity | Mediates antioxidant activities via free radical scavenging activity | [73] |
| (ii) Exhibited scavenging activity against hydroxyl radical with IC50 = 1.48 mM | |||||||
| cis-Nerolidol (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | - | Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) assay | (i) Demonstrated 25.60% ± 0.98% malonaldehyde (MDA) reduction in hepatocytes at 1 mM under physiological conditions | Mediates antioxidant activity via lipid peroxidation inhibitory effect | [74] | |
| (ii) Demonstrated higher MDA reduction with value of 36.50% ± 4.47% at 1 mM in hepatocytes under oxidative stress induced by tert-BuOOH | |||||||
| Mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (Sigma Chemical Company, St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | - | TBARS assay, nitrite assay, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and catalase activity | (i) At doses of 25, 50 and 75 mg/kg of nerolidol caused a significant decrease in lipid peroxidation by 59.97%, 74.79% and 91.31% respectively when compared to negative control | (i) Suggested to prevent oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids | ||
| (ii) At doses of 25, 50 and 75 mg/kg of nerolidol caused a significant decrease in nitrite level by 71.1%, 66.6% and 63.35 % respectively when compared to negative control | |||||||
| (iii) At doses of 25, 50 and 75 mg/kg of nerolidol increased superoxide dismutase activity by 31.1%, 34.8% and 66.1%, respectively when compared to negative control | (ii) Suggested to inactivate the enzyme nitric oxide synthase | [75] | |||||
| (iv) At doses of 25, 50 and 75 mg/kg of nerolidol increased catalase enzymatic activity by 109%, 148% and 177.7%, respectively when compared to negative control | |||||||
| Antibacterial activity | Mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (Sigma Chemical Company, St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | Staphylococcus aureus FDA 209P, 14 strains of methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) and 20 strains of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) | Broth-dilution with shaking method (BDS) | Exhibited dose-related inhibition against 34 clinical isolates of S. aureus. Inhibitory dose 50% (ID50) ranged from 5.0 to 22.0 μg/mL and from 2.6 to 10.6 μg/mL against MSSA and MRSA respectively. | Suggested the aliphatic chain of nerolidol mediates the antibacterial activity by damaging the bacterial cell membrane | [76] |
| Mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (Sigma Chemical Company, (St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | Staphylococcus aureus FDA209P | Broth dilution with shaking (BDS) method and quantitation of the leakage of K+ ions using K+-selective electrode | Treatment of nerolidol caused a dose-dependent increase in amount of K+ ions leakage from bacterial cells. | Mediates the antibacterial activity via cell membrane-distrupting mechanism and hence resulting in the leakage of K+ ions from bacterial cells | [77] | |
| Mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (Sigma Chemical Company, St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | Staphylococcus aureus FDA209P | Broth dilution with shaking (BDS) method and quantitation of the leakage of K+ ions using K+-selective electrode | (i) Caused a dose-dependent increase in K+ ions leakage from bacterial cells | [78] | ||
| (ii) Exhibited minimum inhibitory concentration at 40 μg/mL | |||||||
| trans-Nerolidol | Momordica charantia L., seed | Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 | Broth microdilution method (MIC) | (i) Exhibited anti-microbial activity with MIC ranged from 125–500 μg/mL. | - | [7] | |
| Nerolidol (n.s.) | Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze, leaves | Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus mutans | Broth dilution method | Exhibited antibacterial activity against S. aureus and S. mutans with MIC measured at 200 and 25 μg/mL respectively | - | [79] | |
| Nerolidol (n.s.) | Ginkgo biloba L., leaves | Salmonella enterica, Staphylococcus aureus and Aspergillus niger | Disc-diffusion and broth dilution methods | (i) Exhibited antibacterial activity against S. enterica, S. aureus and A. niger with MIC, MBC and MFC values measured ranging from 3.9–15.6 μg/mL, 31.3–62.5 μg/mL and 62.5 μg/mL respectively. | - | [31] | |
| cis-Nerolidol and the racemic mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (Aldrich Chemical Co., Milwaukee, WI, USA) | - | Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus | Agar-disc diffusion assay | Nerolidol (cis-nerolidol and the racemic mixture of cis- and trans-isomers) potentiated the action of antibiotics: | - | [80] | |
| (i) amoxicillin/clavulanic acid against S. aureus and | |||||||
| (ii) amoxicilline/clavulanic acid, ceftadizine and imipenem against E. coli | |||||||
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus | Disc-diffusion assay | (i) Nerolidol concentrations ranged from 0.5 to 2 mM enhanced the susceptibility of S. aureus to ciprofloxacin, clindamycin, erythromycin, gentamicin, tetracycline, and vancomycin | - | [81] | ||
| (ii) Nerolidol (1 mM) enhanced the susceptibility of E. coli to polymyxin B | |||||||
| Racemic mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (1:1) (Aldrich, Madrid, Spain) | - | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | Antibiotic disc assay | Nerolidol (20 mM) potentiated the susceptibility of E. coli and S. aureus towards ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, gentamicin and vancomycin | - | [82] | |
| Anti-biofilm activity | Mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol | Black pepper, cananga, and myrrh EOs (Berjé (Bloomfield, NJ, USA), Jin Aromatics (Anyang, Gyeonggi Province, Korea) and Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, USA)) | Staphylococcus aureus | Crystal violet biofilm assay | Cis-nerolidol at 0.01% (v/v) inhibited S. aureus biofilm formation by > 80 %; trans-nerolidol at similar concentration exerted 45% inhibition | - | [45] |
| trans-Nerolidol | Piper claussenianum (Miq.) C. DC., leaves | Candida albicans | MTT assay | Concentrations of 0.06%–1.0% inhibited biofilm formation by 30% and 50% after 24 and 48 h incubation respectively | - | [32] | |
| cis,trans-Nerolidol and cis-nerolidol (Sigma Aldrich) | - | Candida albicans | MTT assay | 1.0% of cis,trans-nerolidol exerted 76.1% reduction in the viability of pre-formed biofilm while only 67.0% reduction observed from 1.0% cis-nerolidol | - | [32] | |
| Anti-fungal activity | Nerolidol (n.s.) | Chamaecyparis obtusa (Siebold & Zucc.) Endl. (Japanese cypress) | Microsporum gypseum | Broth microdilution method Skin lesion scoring in guinea pig model | (i) Exhibited MIC concentrations of 0.5%–2% against M. gypseum | - | [83] |
| (ii) Nerolidol-treated group exhibited a significant improvement (p < 0.05) in lesion as compared to eugenol and econazole (positive control) treated groups | |||||||
| trans-Nerolidol | Piper claussenianum (Miq.) C. DC., Piperaceae, leaves | Candida albicans | Broth microdilution and trypan blue exclusion method | (i) Exhibited anti-fungal activity with MIC values ranging from 0.24% to 1.26%. | - | [32] | |
| (ii) Exhibited inhibitory effect on yeast-to-hyphae transition by 81% | |||||||
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Sigma-Aldrich, Yongin, Korea) | - | Trichophyton mentagrophytes | Agar dilution method | Inhibited the hyphal growth of T. mentagrophytes at the concentration of 0.4 mg/mL. | - | [16] | |
| Nerolidol (n.s.) | Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze, leaves | Broth dilution method | Inhibited the growth of T. mentagrophytes at 12.5 μg/mL | - | [79] | ||
| trans-Nerolidol | Lantana radula Sw., leaves | Corynespora cassiicola | Poison food (PF) technique | (i) L. radula EO at the concentration of 1000 mg/L and 3000 mg/L inhibited the growth of C. cassiicola by 17.2% and 40.6% respectively | - | [33] | |
| (ii) L. radula EO at the concentration of 5000 mg/L and 10,000 mg/L completely inhibited the growth of C. cassiicola | |||||||
| trans-Nerolidol | Piper chaba Hunter, leaves | Fusarium oxysporum, Phytophthora capsici, Colletotrichum capsici, Fusarium solani and Rhizoctonia solani | Spore germination assay and agar dilution method | Caused 55.1%–70.3% growth inhibition at concentration ranging from 125 to 500 µg/mL. | - | [34] | |
| trans-Nerolidol | Warionia saharae ex Benth. & Coss., aerial part | Alternaria sp., Penicillium expansum and Rhizopus stolonifer | Poisoned food (PF) technique and volatile activity (VA) assay | Inhibited the fungal spore production of Alternaria sp., P. expansum and R. stolonifera at 1, 2 and 2 µL/mL air respectively | - | [26] | |
| Nerolidol | Allium sativum L., bulb | Sclerotium cepivorum | Disc diffusion method; scanning electron microscopy | (i) Nerolidol ranged from 2.0 to 5.0 µg/disc displayed fungistatic property by inhibiting mycelial growth by ~85% | - | [84] | |
| (ii) Nerolidol ranged from 2.0 to 5.0 µg/disc inhibited the production of sclerotial by ~84% | |||||||
| (ii) Nerolidol at 4.0 µg/disc caused morphological alterations such as shorter branching, hyphal shrinkage and partial distortion | |||||||
| Anti-trypanosomal activity | trans-Nerolidol | Strychnos spinosa Lam., leaves | Trypanosoma brucei | Alamar Blue™ assay. | Exhibited anti-trypanosomal activity with IC50 measured at 1.7 µg/mL (7.6 µM) | - | [35] |
| cis-Nerolidol | Leonotis ocymifolia (Burm.f.) Iwarsson, aerial part | Trypanocidal and cytotoxic assays | Exhibited anti-trypanosomal activity with IC50 measured at 15.78 µg/mL | - | [27] | ||
| Mixture of ±40% cis-nerolidol and ±55% of trans-nerolidol (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) | - | Trypanosoma evansi | Collection of blood samples from T. evansi-infected mice for observation using light and electron microscopes | (i) Adverse morphological changes observed in nerolidol-treated group. The parasites lost their undulating membrane after 23 day post-treatment. | - | [85] | |
| (ii) Total disfigurement observed after 27 day post-treatment | |||||||
| Anti-leishmanial activity | A mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol | - | Leishmania (L.) amazonensis, L. braziliensis, and L. chagasi | MTT assay and metabolic labeling with [2-14C] mevalonic acid, [1-14C] acetic acid, [1(n)-3H] farnesyl pyrophosphate and l-[35S]methionine | (i) Inhibited the growth of L. amazonensis, L. braziliensis and L. chagasi promastigotes, and L. amazonensis amastigotes with IC50 of 85, 74, 75, and 67 µM respectively | Inhibition of the isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway | [86] |
| (ii) Nerolidol at 100 µM reduced the percentage of intracellular parasitism of L. amazonensis by 95% from the pre-infected macrophages culture | |||||||
| trans-Nerolidol | Baccharis dracunculifolia DC., leaves | Leishmania donovani | Parasite lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH) assay, antileishmanial assay, schistosomicidal assay and cytotoxicity assay using the mammalian cells Vero. | Exhibited anti-leishmanial activity against promastigotes of L. donovani with IC50 and IC90 values of 42 and 85 µg/mL respectively. | - | [8] | |
| Nerolidol | Piper claussenianum (Miq.) C. DC., Piperaceae, leaves | Leishmania amazonensis | Protozoal arginase activity, nitrite determination and cytotoxicity assay using L929 fibroblast cells (mouse) and Raw cells (mouse macrophages) | (i) Nerolidol inhibited the arginase activity by 62.17% in the promastigotes of Leishmania amazonensis | Interferes with parasite-host cell interaction | [9] | |
| (ii) Nerolidol caused an increase in NO production (20.5%) | |||||||
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Acros Organics, Geel, Belgium) | - | Promastigotes of Leishmania amazonensis | Anti-proliferative activity assay and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy of the spin-labeled 5-doxyl stearic acid | Nerolidol modulated the molecular dynamics of the lipid component in the Leishmania plasma membrane | Insertion of nerolidol into the lipid bilayer increased the fluidity of membranes, thus causing leakage of cytoplasmic content and eventually the death of Leishmania cells | [87] | |
| Anti-schistosomal activity | Nerolidol (n.s.) | Baccharis dracunculifolia DC. (Asteraceae), leaves | Schistosoma mansoni | Schistosomicidal assay | 100% mortality of S. mansoni adult worms after 24 h incubation with 10 to 100 mg/mL of EO containing nerolidol as the main constituent | - | [8] |
| Racemic mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (1:1) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | In vitro anti-schistosomal assay and microscopy studies | Exhibited anti-schistosomal activity by reducing worm motor activity and caused 100% mortality of male and female schistosomes at concentration of 31.2 and 62.5 µM respectively | (i) Induced severe tegumental damage in adult schistosomes. | [88] | ||
| (ii) Caused alterations on the tubercles of male parasites | |||||||
| Anti-malarial activity | Nerolidol (n.s.) | Virola surinamensis (Rol. ex Rottb.) Warb., leaves | Plasmodium falciparum | In vitro anti-plasmodial assay | Treatment with 100 µg/mL of nerolidol caused 100% inhibition in the development of young trophozoite to the schizont stage after 48 h | - | [29] |
| trans-Nerolidol | Piper claussenianum (Miq.) C. DC., leaves | Exerted anti-malarial activity with IC50 of 11.1 μg/mL | - | [89] | |||
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | Immunoprecipitation assays and metabolic labeling | Exhibited inhibitory activity on the biosynthesis of the isoprenic side chain of the benzoquinone ring in ubiquinones during the schizont stage | Interferes with the elongation of isoprenic chains via inhibition of isoprenyl diphosphate synthases | [90] | ||
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | Nerolidol at 50 nM inhibited the synthesis of the isoprenic chain attached to coenzyme Q at all intraerythrocytic stages | - | [91] | |||
| Nerolidol (n.s.) | - | Isobolographic analysis | Nerolidol mediated supra-additive (the sum of the fractions of IC50 of < 1) interaction with fosmidomycin and squalestatin with average IC50 values of 0.57 and 0.62 µM, respectively in the inhibition of plasmodial isoprenoid pathway | - | [92] | ||
| Other anti-parasite activities | Mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | Four Babesia species (B. bovis, B. bigemina, B. ovata, and B. caballi) | In vitro growth inhibition assay | Inhibited in vitro growth of B. bovis, B. bigemina, B. ovata, and B. caballi with IC50 values of 21 ± 1, 29.6 ± 3, 26.9 ± 2, and 23.1 ± 1 µM respectively | Inhibits the isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway in a similar mechanism with that of P. falciparum | [93] |
| Mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (Sigma Chemical Company, St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | Caenorhabditis elegans | Mortality assay against Caenorhabditis elegans | Caused 74.0% mortality of C. elegans at 50 µg/mL | - | [94] | |
| Nerolidol (n.s.) | - | L3 larvae of Anisakis | In vitro and in vivo larvicidal activity | (i) Nerolidol at both 31.5 and 62.5 µg/mL resulted in 100% mortality of L3 larvae of Anisakis type I after 4 h. | - | [95] | |
| (ii) Only 20% of nerolidol-treated rats were affected by gastric wall lesions caused by Anisakis larvae in comparison to 86% of the control rats | |||||||
| Insecticidal activity | trans-Nerolidol | Siam-wood (Fokienia hodginsii (Dunn) A.Henry & H H.Thomas), wood | Mosquito and house flies | House fly toxicity test | Exhibited insecticidal activity with LD50 measured at 0.17 µmol/fly | - | [51] |
| Combination of nerolidol (n.s.) and linalool | Capparis tomentosa, leaves | Maize weevil (Sitophilus zeamais) | Repellency assay using a glass Y-tube Olfactometer | Exhibited mean repellency value of 58.23% ± 2.95% against S. zeamais at 2 µL | - | [30] | |
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Moellhausen SpA,Vimercate, Milano, Italy) | Melaleuca alternifolia (Maiden & Betche) Cheel (tea tree oil) | Pediculus capitis (head lice) and its eggs | Pediculicidal and ovicidal activities | Nerolidol in combination with tea tree oil with ratio of 1:2 (tea tree oil 0.5% plus nerolidol 1%), exerted a total killing effect of lice within 30 min and abortive effect of louse eggs after 5 days. | - | [96] | |
| Nerolidol (n.s.) | Magnolia denudata Desr., seeds | Culex pipiens pallens, Aedes aegypti, Aedes albopictus and Anopheles sinensis | Direct-contact mortality bioassay | Exerted larvacidal activity against Culex pipiens pallens, Aedes aegypti, Aedes albopictus and Anopheles sinensis with LD50 value of 9.84, 13.85, 16.34 and 20.84 mg/L respectively | - | [47] | |
| trans-Nerolidol | Melaleuca quinquenervia (Cav.) S.T.Blake, leaves | Aedes aegypti | Larvicidal activity test | Exerted larvicidal activity with ≥ 95% and > 80% mortality of A. aegypti at 0.1 mg/mL and 0.05mg/mL respectively | - | [36] | |
| Piper aduncum L., leaves | Tetranychus urticae Koch | Fumigant, contact, repellency and two-choice assay | Exerted acaricidal activity with repellency value of 83.2% ± 0.59 % at 9.8 µg/mL | - | [37] | ||
| Nerolidol (n.s.) | Baccharis dracunculifolia DC., leaves | Rhipicephalus microplus | Larval packet test (LPT) and engorged female immersion test | (i) Exerted acaricidal activity when concentration more than 5mg/mL and 100% mortality of larvae at 15 mg/mL | - | [97] | |
| (ii) Reduced the quality of the egg and larval hatching rate with increasing concentration from 20 to 50 mg/mL | |||||||
| Antiulcer activity | Nerolidol (n.s.) | Baccharis dracunculifolia DC., leaves | - | In vivo antiulcer activity in male Wistar rat ulcer models induced with ethanol, indomethacin and stress | Nerolidol displayed gastroprotective activity by inhibiting the formation of ulcers induced by all physical and chemical agents in dose-dependent manner (50, 250, 500 mg/kg) | - | [98] |
| Skin penetration enhancer activity | Nerolidol (n.s.) (Aldrich, Gillingham, UK) | - | - | In vitro diffusion studies and stratum corneum-water partitioning studies | Increased diffusion rate by over 20-fold for transdermal delivery of drugs such as 5-fluorouracil | Nerolidol exhibits a chemical structure that allows it to align within the lipid lamellae of the stratum corneum in order to disrupt the organization of stratum corneum | [99] |
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Alfa Aesar Ltd., Haverhill, MA, USA) | - | - | Solubility studies, ex vivo permeation studies and histopathological studies | The enhancement effect is increased with the increasing lipophilicity; the rank of order (nerolidol > farnesol > limonene > linalool > geraniol > carvone > fenchone > menthol) in facilitating transdermal delivery of alfuzosin hydrochloride | [100] | ||
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Merck-Schuchardt, Hohenbrunn, Germany) | - | - | In vitro permeation studies | Exhibited the highest permeation enhancing ability with a 3.2-fold increase in permeation of selegiline hydrochloride across the rat skin, followed by the effect of carvone (2.8-fold increase) and anethole (2.6-fold increase) | - | [101] | |
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Aldrich Chemical Co. Milwaukee, WI, USA) | - | - | In vitro skin permeability studies | Most effective terpene enhancer for percutaneous permeation of four different drug models (nicardipine hydrochloride, hydrocortisone, carbamazepine, and tamoxifen) when compared to fenchone, thymol and limonene | - | [102] | |
| Anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities | trans-Nerolidol | Peperomia serpens (Sw.) Loudon, leaves | - | (i) Chemical (acetic acid and formalin) and thermal (hot plate) models of nociception | trans-Nerolidol could be responsible for the anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects displayed by essential oils of both Peperomia serpens (Sw.) Loudon and Piper aleyreanum C. DC | - | [38] |
| (ii) Carrageenan- and dextran-induced paw edema tests in rats croton oil-induced ear edema | |||||||
| (iii) Cell migration, rolling and adhesion activities | |||||||
| trans-Nerolidol | Piper aleyreanum C. DC, aerial parts | - | (i) Nociception induced by formalin | - | [10] | ||
| (ii) Evaluation of locomotor activity | |||||||
| (iii) Induction of acute gastric lesions | |||||||
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) | - | - | (i) Rotarod, acetic acid-induced writhing, formalin and hot-plate tests (ii) Involvement of ATP-sensitive opioid and GABAergic K+ channels (iii)Carrageenan-induced paw edema (iv) Analysis of leukocytes, tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) and interleukin 6 in peritoneal lavage | (i) For acetic acid-induced writhing test, at the doses of 200, 300 and 400 mg/kg, nerolidol reduced the frequency of acetic acid-induced writhing at all three doses tested compared to the mice in the control group (55% ± 1.1%, 53% ± 4.5%, and 41% ± 2.4%, respectively) (ii) For formalin test, at the doses of 200, 300 and 400 mg/kg, nerolidol significantly inhibited licking time by 20% ± 3.3%, 33% ± 5.9% and 37% ± 4.8%, respectively when compared to the control mice. (iii) For hot-plate test, no increase in the reaction time to painful stimulation in the mice treated with nerolidol when compared to the control mice. (iv) Reduced leukocytes level by 51% ± 0.7%, 37% ± 0.5% and 57% ± 0.4% at doses of 200, 300 and 400 mg/kg respectively (v) Reduced the level of tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) at doses of 300 (59.3% ± 30.2%) and 400 (62.2% ± 13.7%) in peritoneal lavage. (vi) IL-1β production was inhibited after treatment with nerolidol (1, 10, 50 and 100 µM) whereas IL-6 level was unchanged | (i) Anti-nociceptive activtity of nerolidol was indicated to be mediated by GABAA receptors, as the use of bicuculline, a GABAA antagonist inhibited the effect of nerolidol in reducing the paw licking times (ii) Anti-inflammatory activity of nerolidol was suggested to be mediated by inhibiting the production or the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α analgesic and IL-1β | [103] | |
| Anti-cancer or anti-tumor activity | Nerolidol (a combination of cis-nerolidol 40.7%, trans-nerolidol 58.3%, cis-dihydronerolidol 0.4% and trans-dihydro-nerolidol) (Kurt Kitzing Co. Wallerstein, Germany) | - | - | Cytotoxicity assay on HeLa cell lines using CytoTox-96®-assay | Exhibited anticancer effect against HeLa cells with CC50 value at 1.5 ± 0.7 µM | - | [104] |
| cis-Nerolidol (Charabot S.A. Grasse, France) | - | - | Cytotoxicity and cytoproliferative activity on HeLa cell lines using Cytotoxicity Detection Kit (LDH) and the Cell Proliferation Reagent WST-1, respectively | Exhibited cytotoxic effect (16.5 ± 6.7 μM) against HeLa cells | - | [105] | |
| Nerolidol (n.s.) | Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze, leaves | - | MTT assay | Exhibited cytotoxic effect with IC50 value of 2.96 and 3.02 µg/mL against BT-20 breast carcinoma and HeLa cells respectively | - | [106] | |
| trans-Nerolidol | Zornia brasiliensis Vogel, leaves | - | In vitro cytotoxic activity assay using Alamar blue assay, and in vivo antitumor activity assay | (i) trans-Nerolidol induced cytotoxic effect on B16-F10, HepG2, HL-60 and K562 cells with IC50 value of >25, >25, 21.99 and 17.58 µg/mL respectively | - | [39] | |
| (ii) The EO at dose of 100 mg/kg containing trans-nerolidol as major constituent reduced the weight of tumor in mice injected with B16-F10 melanoma by 38.61% | |||||||
| Myrica rubra (Lour.) Siebold & Zucc., leaves | - | Neutral red uptake (NRU) test, MTT assay and 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein-diacetate (H2DCF-DA) oxidation | Potentiated the action of doxorubicin, an anticancer drug in the modulation of CaCo-2 cancer cells | - | [40] | ||
| Nerolidol (n.s.) (Sigma Aldrich Chemical Company) | - | - | In vivo anti-cancer study | (i) Reduction of incidence of intestinal neoplasia from 82% to 33% in rats fed with nerolidol | Modulation of nerolidol on protein prenylation which responsible for the formation of cancer | [107] | |
| (ii) Reduction of number of tumors/rat from 1.5 to 0.7 in rats fed with nerolidol | |||||||
| Combination of farnesol and nerolidol (n.s.) | - | - | In vitro anti-cancer study | The combination suppressed the proliferation of human HL-60 acute promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells by 20%. Meanwhile, farnesol isomers (2.5 µmol/L) and nerolidol (5 µmol/L) individually suppressed the proliferation of HL-60 cells by 4 and 9%, respectively | Nerolidol induced cell cycle arrest at the G0-G1/S interphase in HL-60 cells and eventually lead to apoptotic cell death | [108] | |
| trans-Nerolidol | Myrica rubra (Lour.) Siebold & Zucc., leaves | - | Cell adhesion and apoptosis luminescent assays | (i) Reduced adhesion of HT29 to collagen. | Nerolidol induced apoptosis in cancer cells | [109] | |
| (ii) Suppressed cell adhesion of HT29 cells in the presence TNFα cytokines | |||||||
| (iii) Decreasing the phosphorylation of NF-κB and increased the activity of caspases |
| Parameters | Saito et al. [22] | He et al. [25] |
|---|---|---|
| Type of nerolidol | Mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (1:3) | Mixture of cis- and trans-nerolidol (2:3) |
| Analytical method used | GC-MS | LC-MS |
| Animal used | BALB/c mice | Sprague-Dawley rats |
| Route of administration | Oral | Intraperitoneal injection |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | 1000 | 25 |
| Type of sample used | Plasma | |
| Time collection taken (min) | 30, 60, 120, 180, 240, 300, 360, 480 and 720 | 10, 20, 30, 60, 90, 120, 240 and 360 |
| Peak plasma concentration (Cmax) (µg/mL) | ~0.27 ± 0.07 | 8.30 ± 1.07 |
| Peak time (Tmax) (min) | 30 | 20 |
| Elimination half life (T1/2) (min) | n.a. | 20.98 ± 7.71 |
| Mean residence time (MRT) (min) | n.a. | 27.72 ± 2.14 |
| Clearance (L/min/kg) | n.a. | 0.082 ± 0.012 |
| Time for drug to be eliminated to almost near zero | 12 | ~2 |
| Human equivalent dose a (HED) (mg/kg) | 81.08 | 4.05 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, W.-K.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H.; Goh, B.-H. Nerolidol: A Sesquiterpene Alcohol with Multi-Faceted Pharmacological and Biological Activities. Molecules 2016, 21, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050529
Chan W-K, Tan LT-H, Chan K-G, Lee L-H, Goh B-H. Nerolidol: A Sesquiterpene Alcohol with Multi-Faceted Pharmacological and Biological Activities. Molecules. 2016; 21(5):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050529
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Weng-Keong, Loh Teng-Hern Tan, Kok-Gan Chan, Learn-Han Lee, and Bey-Hing Goh. 2016. "Nerolidol: A Sesquiterpene Alcohol with Multi-Faceted Pharmacological and Biological Activities" Molecules 21, no. 5: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050529
APA StyleChan, W.-K., Tan, L. T.-H., Chan, K.-G., Lee, L.-H., & Goh, B.-H. (2016). Nerolidol: A Sesquiterpene Alcohol with Multi-Faceted Pharmacological and Biological Activities. Molecules, 21(5), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050529








