Crystallization of Esomeprazole Magnesium Water/Butanol Solvate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
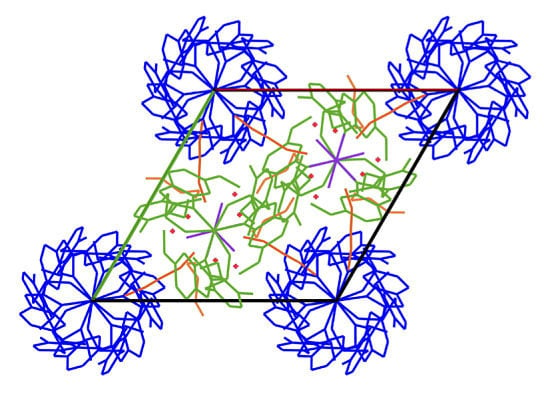
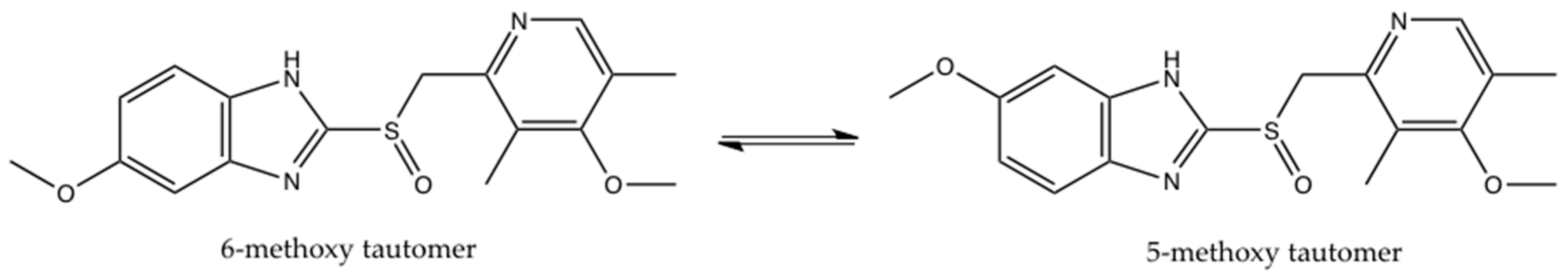
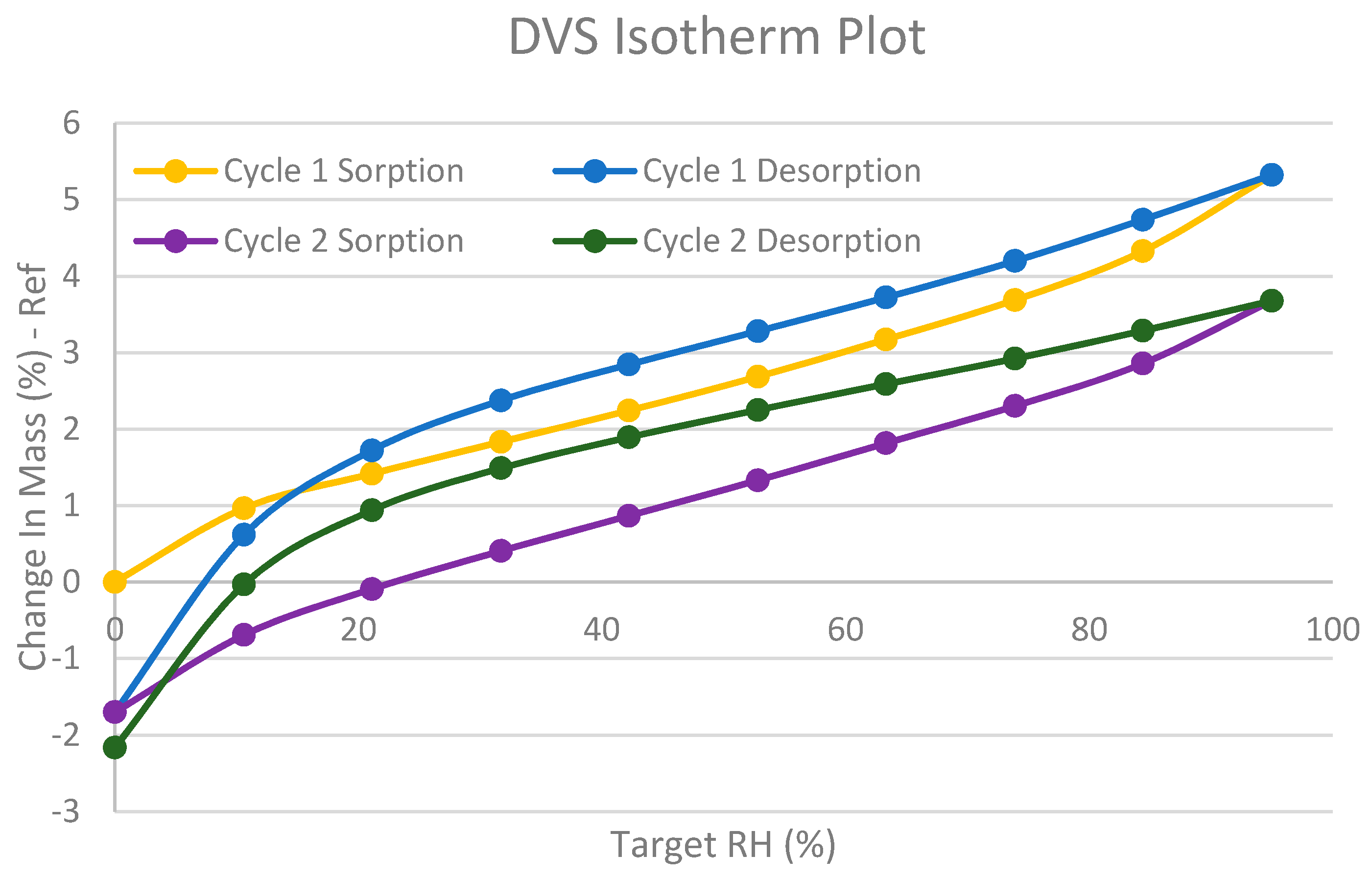
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| API | Active pharmaceutical ingredient |
| FDA | US Food and Drug Administration |
| DFT | Density functional theory |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| DVS | Dynamic vapor sorption |
| IR | Infrared |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| PXRD | Powder X-ray diffraction |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
References
- Robins, G.W.; Scott, L.J.; Levy, B.I.; Federatif, I.; Circulation, D.R.; Lariboisiere, H. Esomeprazole: A Review of its Use in the Management of Hypertension. Drugs 2002, 62, 1503–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg, P.; Nordberg, P.; Alminger, T.; Braendstroem, A.; Wallmark, B. The mechanism of action of the antisecretory agent omeprazole. J. Med. Chem. 1986, 29, 1327–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalwade, S.U.; Reddy, V.R.; Rao, D.D.; Morisetti, N.K. A validated stability indicating ultra performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of impurities in Esomeprazole magnesium gastro resistant tablets. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 57, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, A.G.; McCallum, A. A survey of the stability of omeprazole products from 13 countries. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1996, 22, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AstraZeneca Nexium. Available online: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2007/021153s027s028,021689s008s011lbl.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2015).
- Ohishi, H.; In, Y.; Ishida, T.; Inoue, M.; Sato, F.; Okitsu, M.; Ohno, T. Structure of 5-methoxy-2-{[4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridinylmethyl]sulfinyl}-1H-benzimidazole (omeprazole). Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Cryst. Struct. Commun. 1989, 45, 1921–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.M.; Desiraju, G.R. Tautomeric polymorphism in omeprazole. Chem. Commun. 2007, 2057–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, J.; Bolte, M.; Schmidt, M.U. New Toluene Hemi Solvate of the Proton Pump Inhibitor Piperazinium Esomeprazolate. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2008, 39, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, T.; Hassan-Alin, M.; Hasselgren, G.; Röhss, K.; Weidolf, L. Pharmacokinetic studies with esomeprazole, the (S)-isomer of omeprazole. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2001, 40, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claramunt, R.M.; López, C.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Yang, R.; Schulman, S. The tautomerism of Omeprazole in solution: A 1H- and 13C-NMR study. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2004, 42, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claramunt, R.M.; López, C.; Elguero, J. The structure of Omeprazole in the solid state: A 13C and 15N-NMR/CPMAS study. Arkivoc 2005, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, H.G. Polymorphism in Pharmaceutical Solids, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pangarkar, P.A.; Tayade, A.M.; Uttarwar, S.G.; Wanare, R.S. Drug polymorphism: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. Technol. 2012, 5, 2374–2402. [Google Scholar]
- Savanovic, L.V.; Ham, Z.; Rzen, J. Crystalline Solvate of Omeprazole Sodium. Patent US8247566 B2, 7 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, D.R.; Pathi, S.L.; Kankan, R.N.; Curtis, P.A. Esomeprazole Potassium Polymorph and Its Preparation. Patent WO2010097583 A1, 2 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gonikberg, E. Esomeprazole Magnesium; United States Pharmacopeia: Rockvill, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Khankari, R.K. Pharmaceutical hydrates. Thermochim. Acta 1995, 248, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.; Erdemir, D.; Myerson, A.S. Crystal Polymorphism in Chemical Process Development. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2011, 2, 259–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casar, R.T. Process for the Preparation of Esomeprazole Magnesium in a Stable Form. Patent US20100016370 A1, 21 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, H.; Kronström, A.; Mattson, A.; Möller, E. Form of S-Omeprazole. Patent US7411070 B2, 12 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Lu, J.; Wu, D. Preparation, Characterization and Transformation of Esomeprazole Magnesium Polymorphs. Chin. J. Pharm. 2014, 45, 377–380. [Google Scholar]
- Bhesaniya, K.; Baluja, S. Solubility of esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate in alcohols at temperatures from 298.15 to 318.15 K. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 87, 2187–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruker-AXS, SAINT version 2013.8; Bruker-AXS: Madison, WI, USA, 2013.
- Bruker-AXS, SADABS version 2012.1; Bruker-AXS: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C.F.; Bruno, I.J.; Chisholm, J.A.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; van de Streek, J.; Wood, P.A. Mercury CSD 2.0—New Features for the Visualization and Investigation of Crystal Structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 2008, 41, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.G.; Vega Hissi, E.G.; Rizzi, A.C.; Brondino, C.D.; Salinas Ibañez, Á.G.; Vega, A.E.; Silva, H.J.; Mercader, R.; Narda, G.E. Synthesis, physicochemical characterization, DFT calculation and biological activities of Fe(III) and Co(II)-omeprazole complexes. Potential application in the Helicobacter pylori eradication. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1061, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koilpillai, J.P.; Kulkami, P.B.; Dabe, A.D.; Khan, M.A. Process for the Preparation of Esomeprazole Magnesium Dihydrate. Patent EP2186807 A1, 19 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Seenivasaperumal, M.; Federsel, H.-J.; Szabo, K.J. Mechanism of the asymmetric sulfoxidation in the esomeprazole process: Effects of the imidazole backbone for the enantioselection. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 903–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, I.C.; Sharman, G.J.; Pidgeon, J. 1H- and 13C-NMR data to aid the identification and quantification of residual solvents by NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2005, 43, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S. Solvation Number and Solvent Exchange Rate of Al(DMSO)n3+ in DMSO. J. Chem. Phys. 1966, 44, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, J. Organic Analytical Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Alpha Science International Limited: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Ravi Teja, M.; Pariyani, L.; Balamuralidhara, V.; Gupta, N.V. Formulation and Evaluation of Spray-Dried Esomeprazole Magnesium Microspheres. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroshenko, I.; Pogorelov, V.; Sablinskas, V. Infrared Absorption Spectra of Monohydric Alcohols. Dataset Pap. Chem. 2013, 2013, 329406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolugoddu, V.; Lilakar, J.D.; Koilkonda, P.; PingiliI, R.R.; Lekkala, A.R.; Kammili, V.R.; Dudipala, S.R.; Narasapur, S.P.; Malina, S.R.; Akula, R. Process for Preparing Amorphous Salts. Patent WO2006096709 B1, 7 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
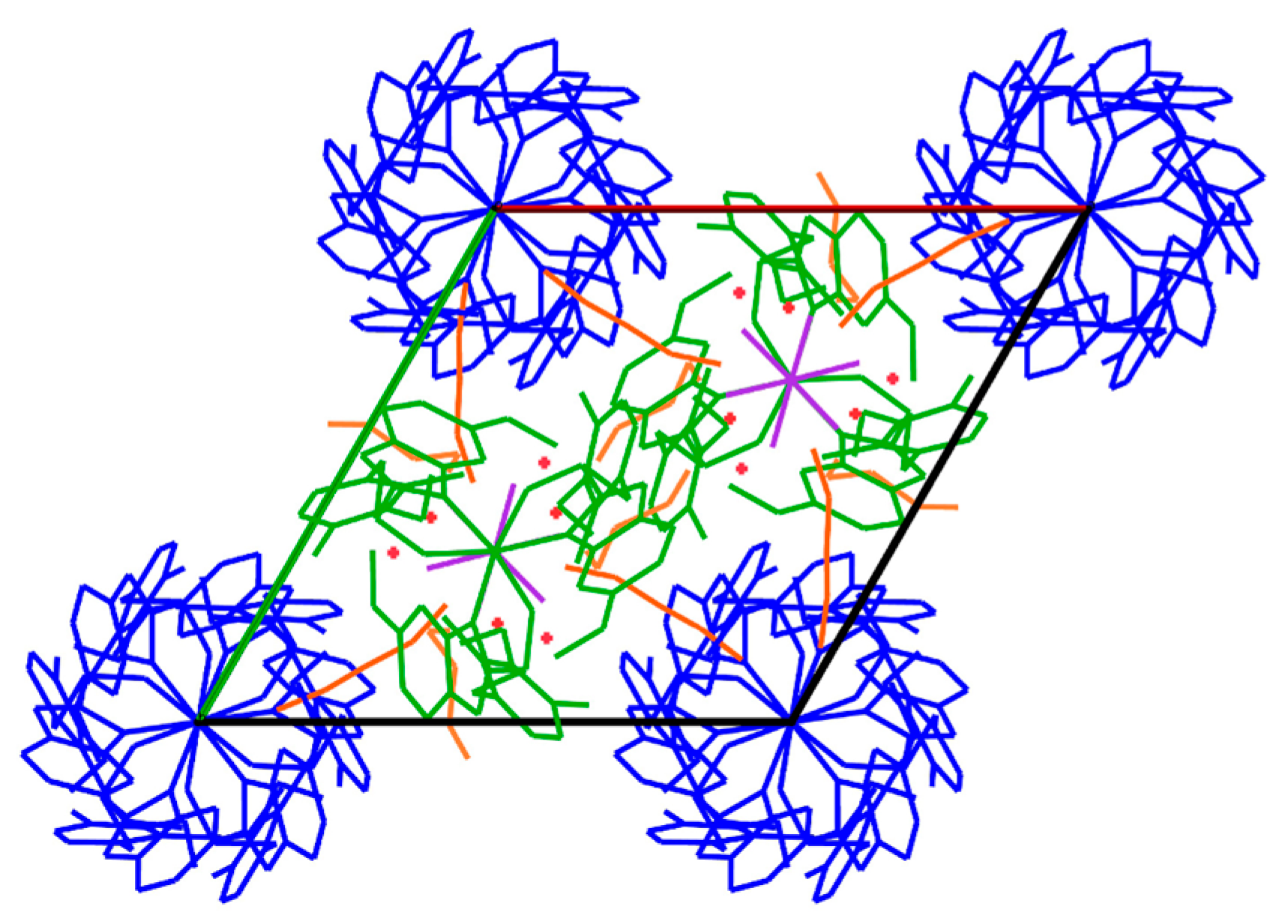
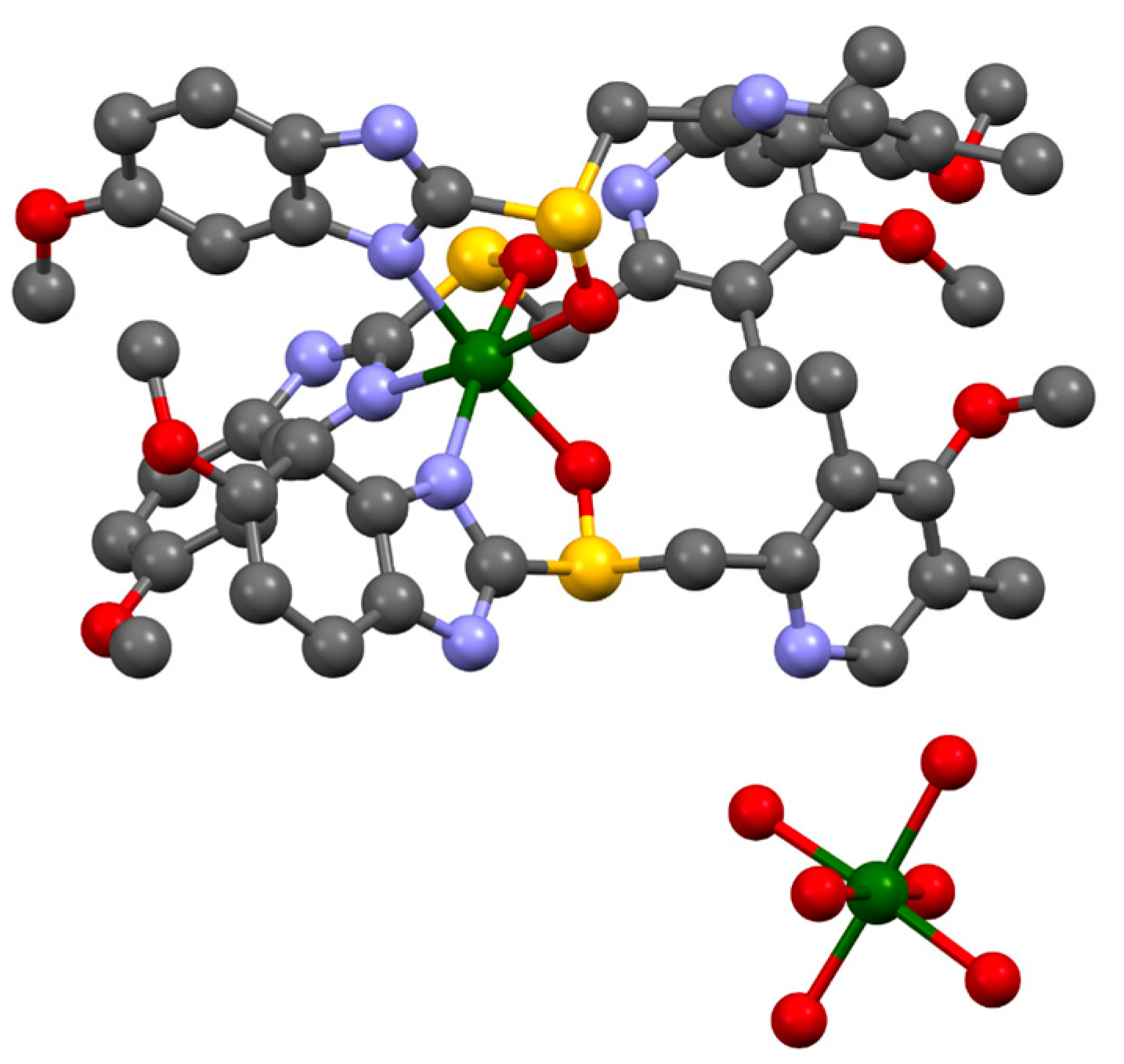
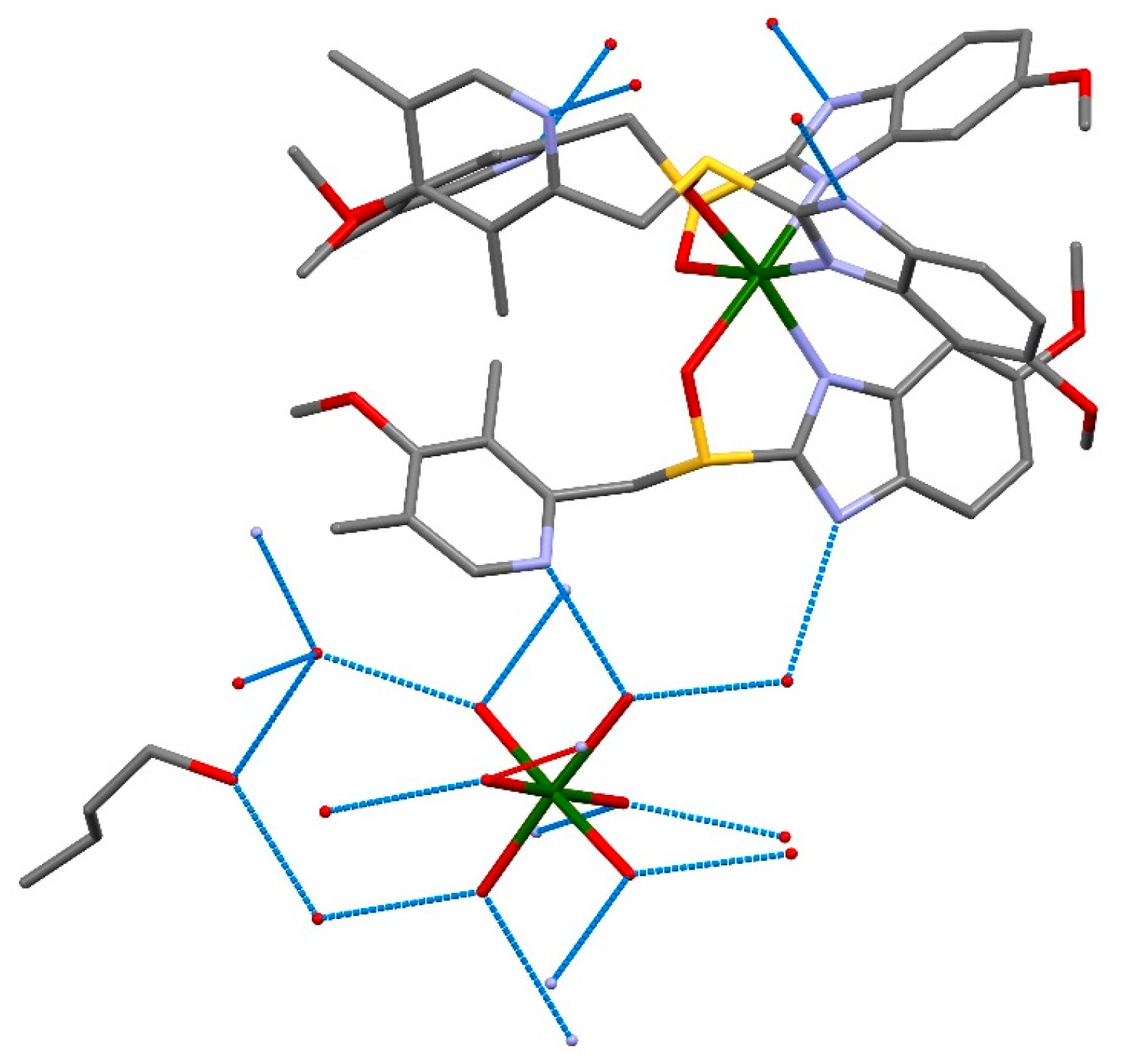
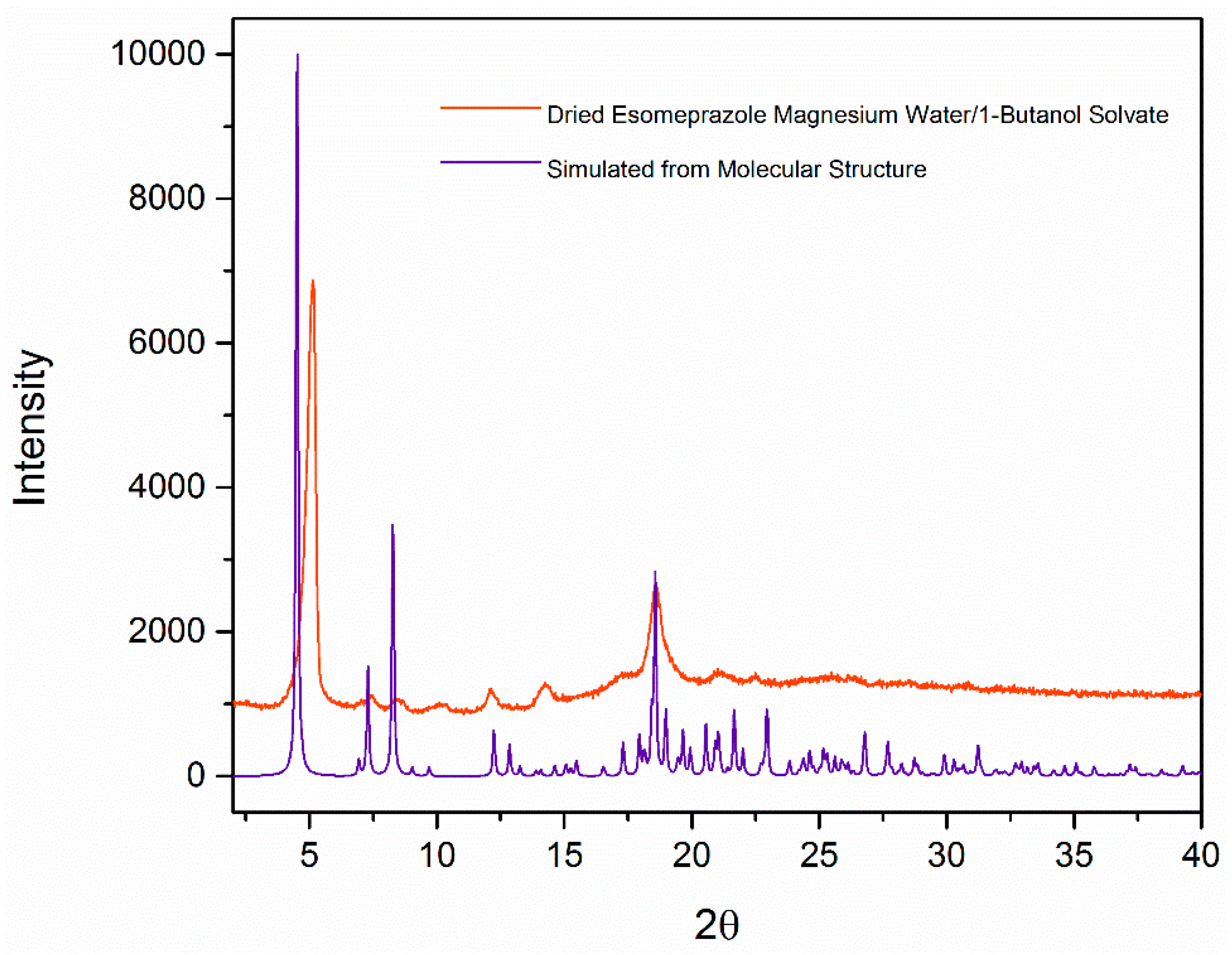
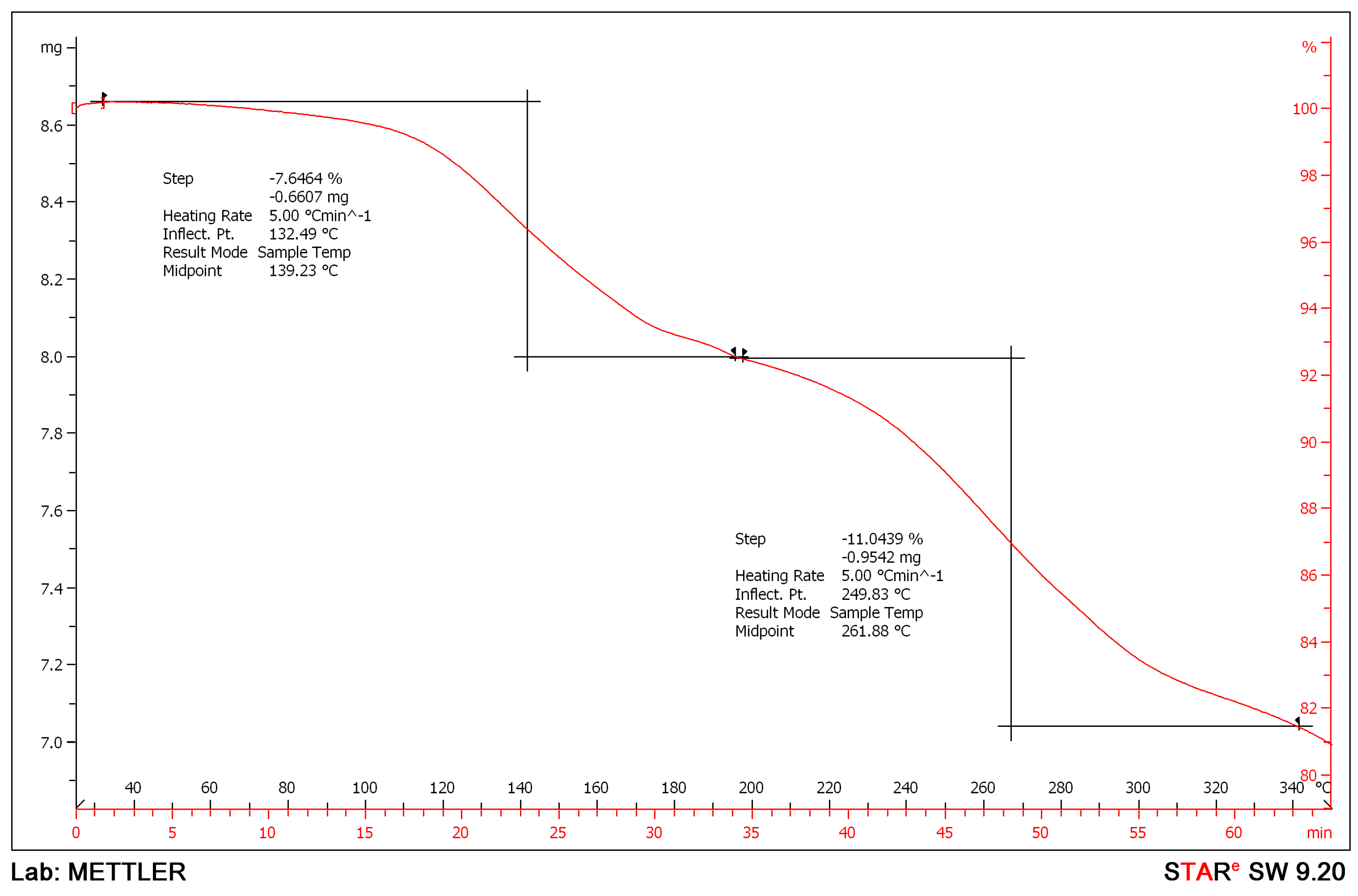

| Formula | C126H198Mg3N18O36S6 |
| Formula Weight (g/mol) | 2806.30 |
| Crystal Dimensions (mm) | 0.185 × 0.142 × 0.092 |
| Crystal System | Hexagonal |
| Space Group | P 63 |
| Temperature, K | 110 |
| a, Å | 14.701(4) |
| b, Å | 14.701 |
| c, Å | 39.123(11) |
| α, ° | 90 |
| β, ° | 90 |
| γ, ° | 120 |
| V, Å3 | 7323(5) |
| Z | 2 |
| F(000) | 3000 |
| ρ (g/cm) | 1.273 |
| λ, Å, (MoKα) | 0.71073 |
| μ, (cm−1) | 0.185 |
| R1 | 0.0674 |
| wR2 | 0.1733 |
| GOF | 1.032 |
| Maximum shift/error | 0.000 |
| Min & Max peak heights on final ΔF Map (e−/Å) | −0.497, 0.487 |
| Functional Group | Absorption Frequency (cm−1) | Type of Vibration |
|---|---|---|
| sulfoxide | 1076 | S=O stretching [34] |
| methoxy | 1199 | C-O stretching [34] |
| methoxy | 1228 | C-O stretching [34] |
| amine | 1409 | N-H bending [28] |
| pyridine | 1569 | C=N stretching [28] |
| benzimidazole | 1612, 1588 | C=N stretching [28] |
| aromatic | 2970 | C=C-H asymmetric stretching [34] |
| alcohol/water | 3100–2800 | O-H stretching [35] |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skieneh, J.; Khalili Najafabadi, B.; Horne, S.; Rohani, S. Crystallization of Esomeprazole Magnesium Water/Butanol Solvate. Molecules 2016, 21, 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040544
Skieneh J, Khalili Najafabadi B, Horne S, Rohani S. Crystallization of Esomeprazole Magnesium Water/Butanol Solvate. Molecules. 2016; 21(4):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040544
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkieneh, Jenna, Bahareh Khalili Najafabadi, Stephen Horne, and Sohrab Rohani. 2016. "Crystallization of Esomeprazole Magnesium Water/Butanol Solvate" Molecules 21, no. 4: 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040544
APA StyleSkieneh, J., Khalili Najafabadi, B., Horne, S., & Rohani, S. (2016). Crystallization of Esomeprazole Magnesium Water/Butanol Solvate. Molecules, 21(4), 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040544