The Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability of Lignans and Malabaricones from the Seeds of Myristica fragrans in the MDCK-pHaMDR Cell Monolayer Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
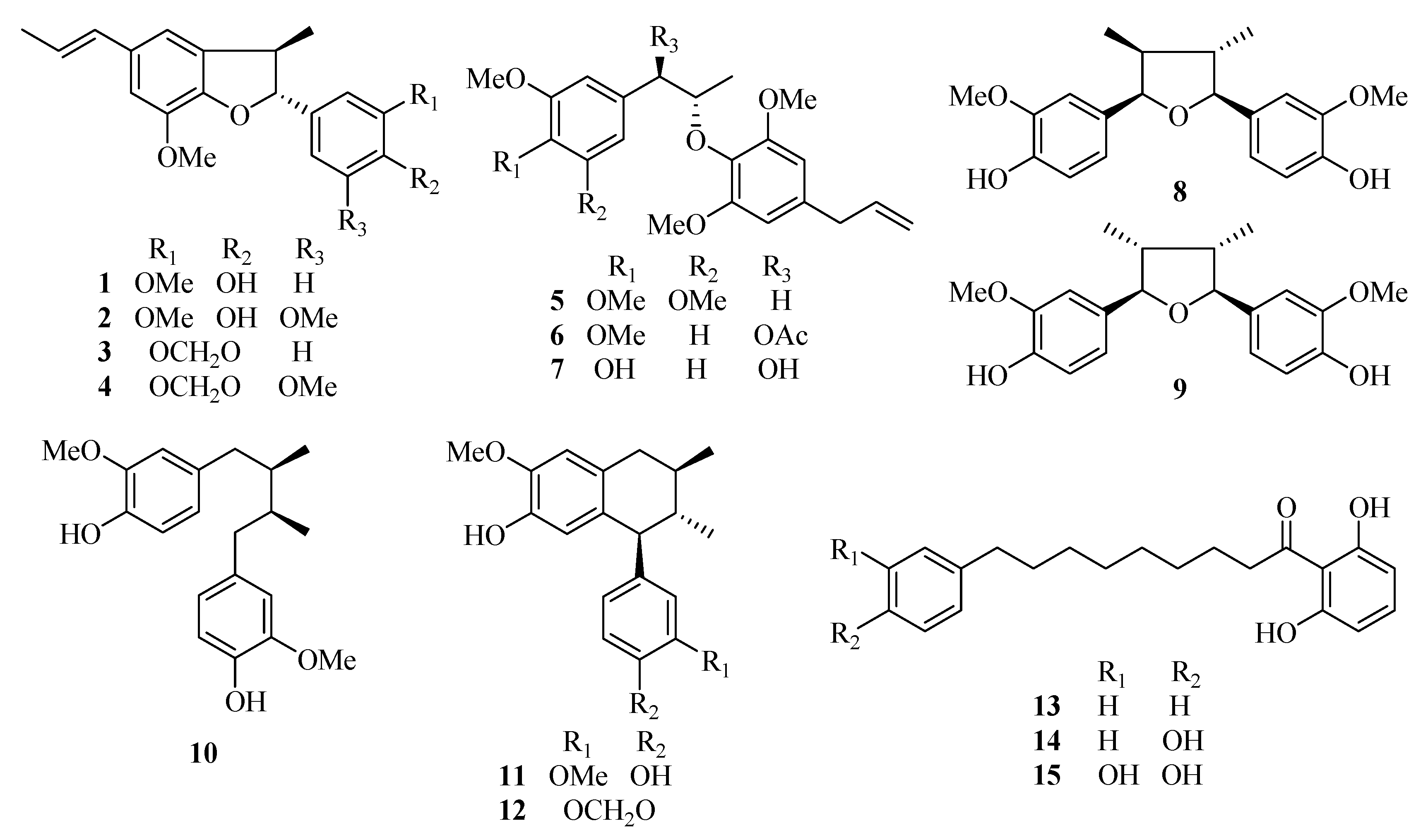
2. Results and Discussion
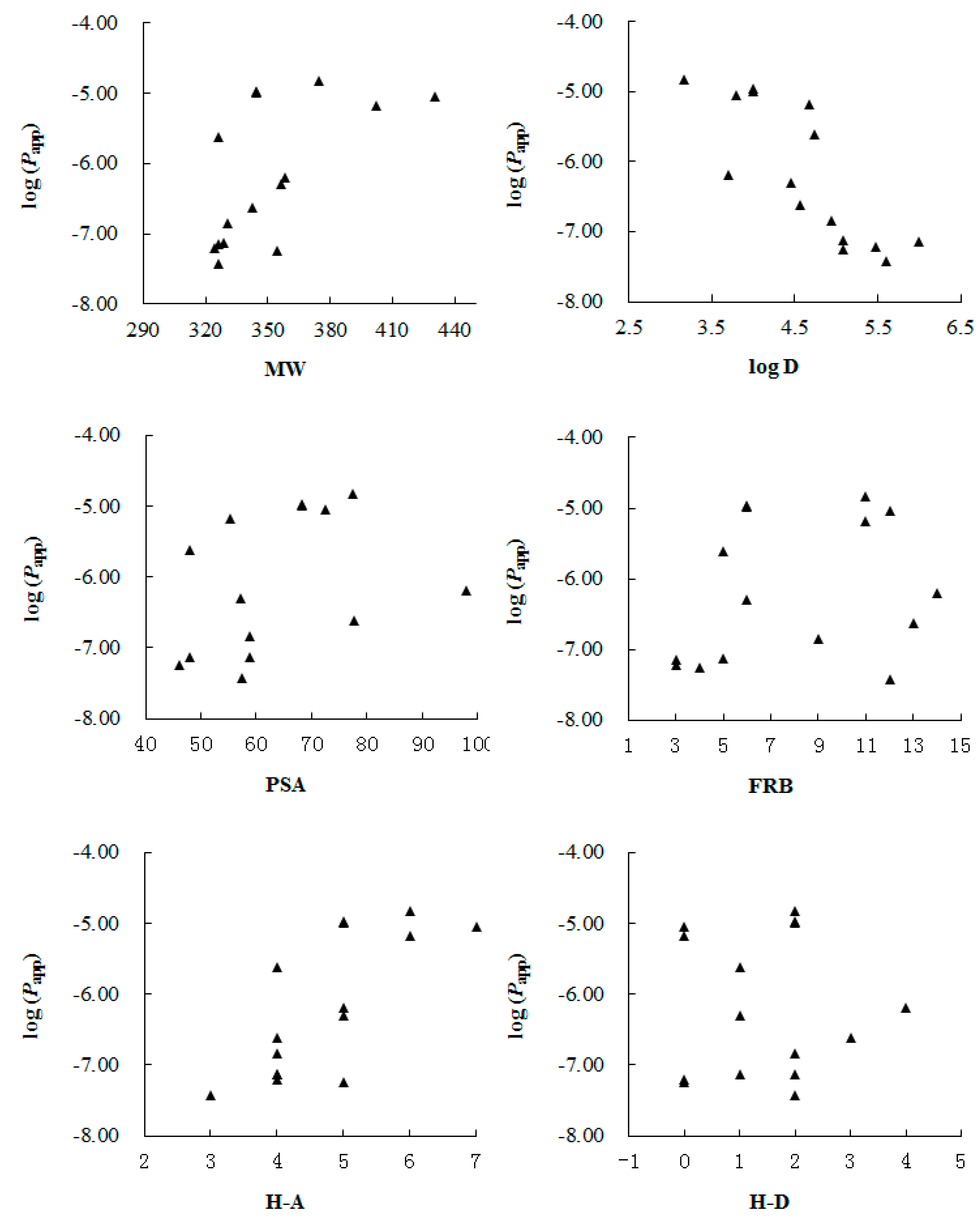
| No. | Papp A→B (×10−6, cm/s) | Papp B→A (×10−6, cm/s) | Efflux ratio (Papp B→A/Papp A→B) | MW (Da) | Log D (pH 7.35) | PSA (Å2) | FRB | H-A | H-D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.43 ± 0.32 | 1.82 ± 0.18 | 0.75 | 326.4 | 4.74 | 47.9 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
| 2 | 0.51 ± 0.07 | 1.32 ± 0.17 | 2.59 | 356.4 | 4.45 | 57.2 | 6 | 5 | 1 |
| 3 | <0.062 * | <0.060 * | – | 324.4 | 5.48 | 36.9 | 3 | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | <0.057 * | <0.055 * | – | 354.4 | 5.09 | 46.2 | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| 5 | 6.67 ± 0.56 | 8.52 ± 0.08 | 1.28 | 402.5 | 4.67 | 55.4 | 11 | 6 | 0 |
| 6 | 9.10 ± 0.21 | 21.0 ± 0.96 | 2.31 | 430.5 | 3.79 | 72.5 | 12 | 7 | 0 |
| 7 | 14.87 ± 0.94 | 13.57 ± 0.50 | 0.91 | 374.4 | 3.17 | 77.4 | 11 | 6 | 2 |
| 8 | 10.93 ± 0.32 | 20.44 ± 0.97 | 1.87 | 344.4 | 4.00 | 68.2 | 6 | 5 | 2 |
| 9 | 10.38 ± 1.49 | 14.99 ± 1.27 | 1.44 | 344.4 | 4.00 | 68.2 | 6 | 5 | 2 |
| 10 | <0.145 * | <0.140 * | – | 330.4 | 4.94 | 58.9 | 9 | 4 | 2 |
| 11 | <0.075 * | <0.073 * | – | 328.4 | 5.09 | 58.9 | 5 | 4 | 2 |
| 12 | <0.073 * | <0.070 * | – | 326.4 | 6.00 | 47.9 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 13 | <0.038 * | <0.037 * | – | 326.4 | 5.61 | 57.5 | 12 | 3 | 2 |
| 14 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ± 0.04 | 1.33 | 342.4 | 4.56 | 77.8 | 13 | 4 | 3 |
| 15 | 0.64 ± 0.07 | 0.63 ± 0.04 | 0.98 | 358.4 | 3.71 | 98.0 | 14 | 5 | 4 |
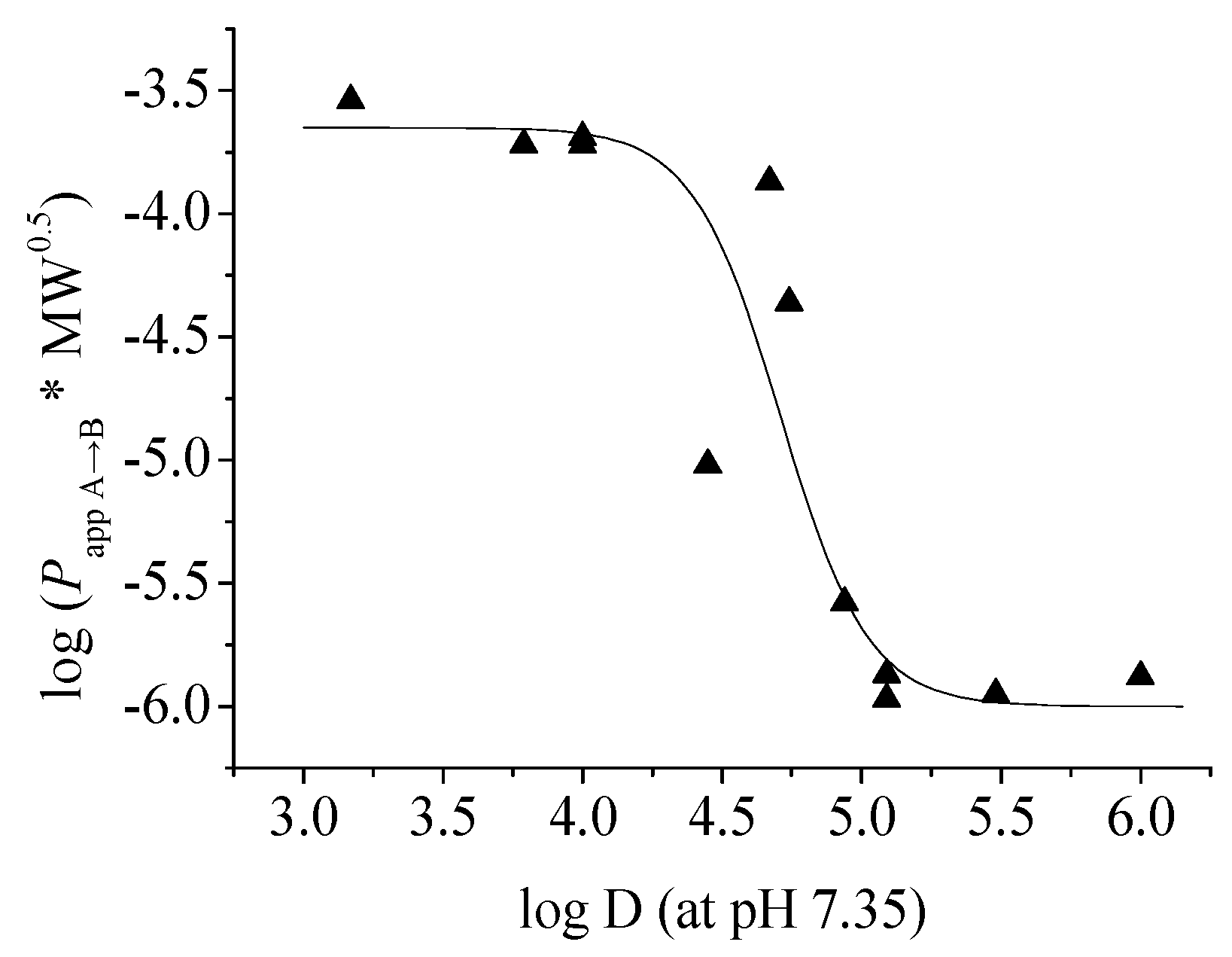
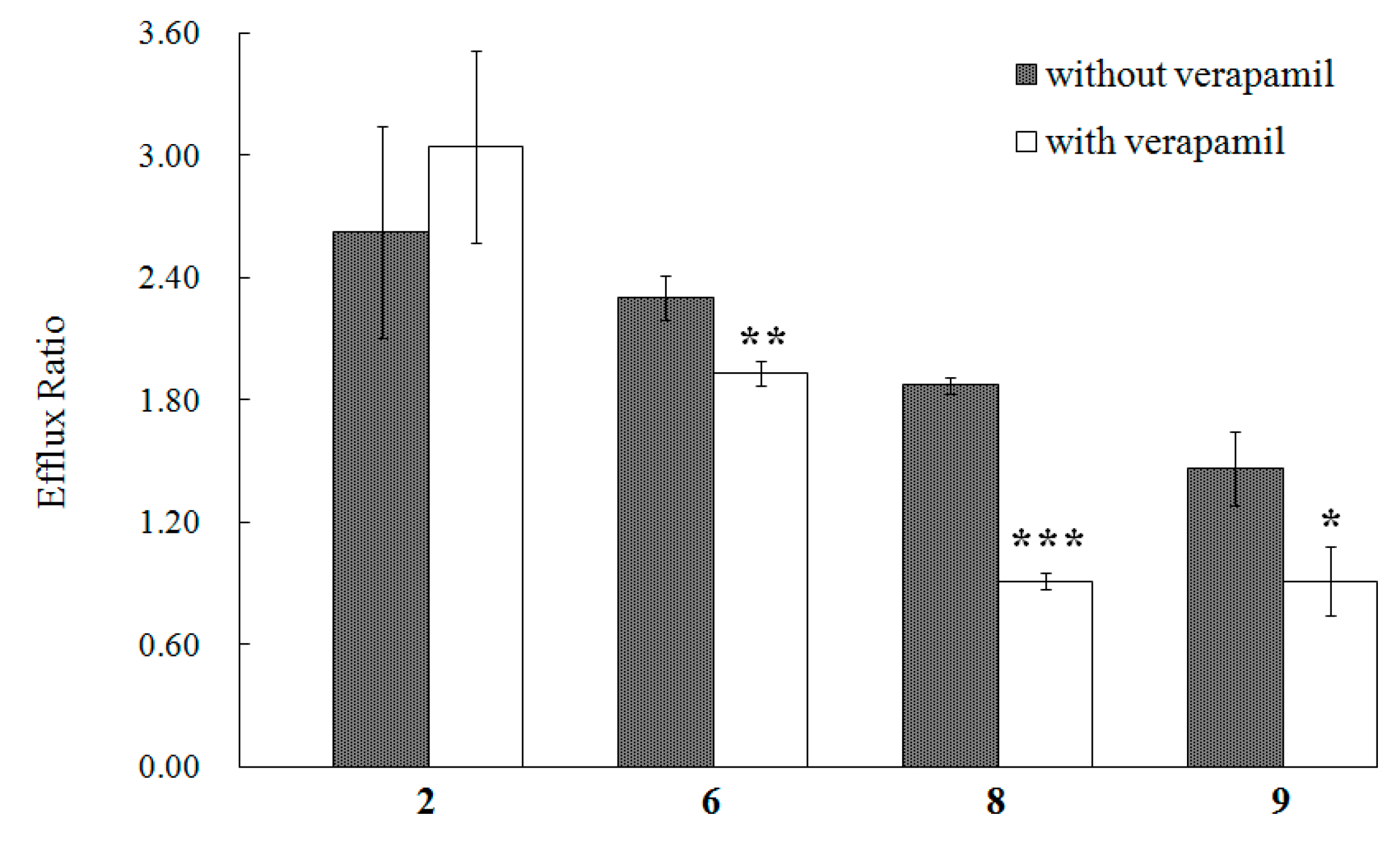
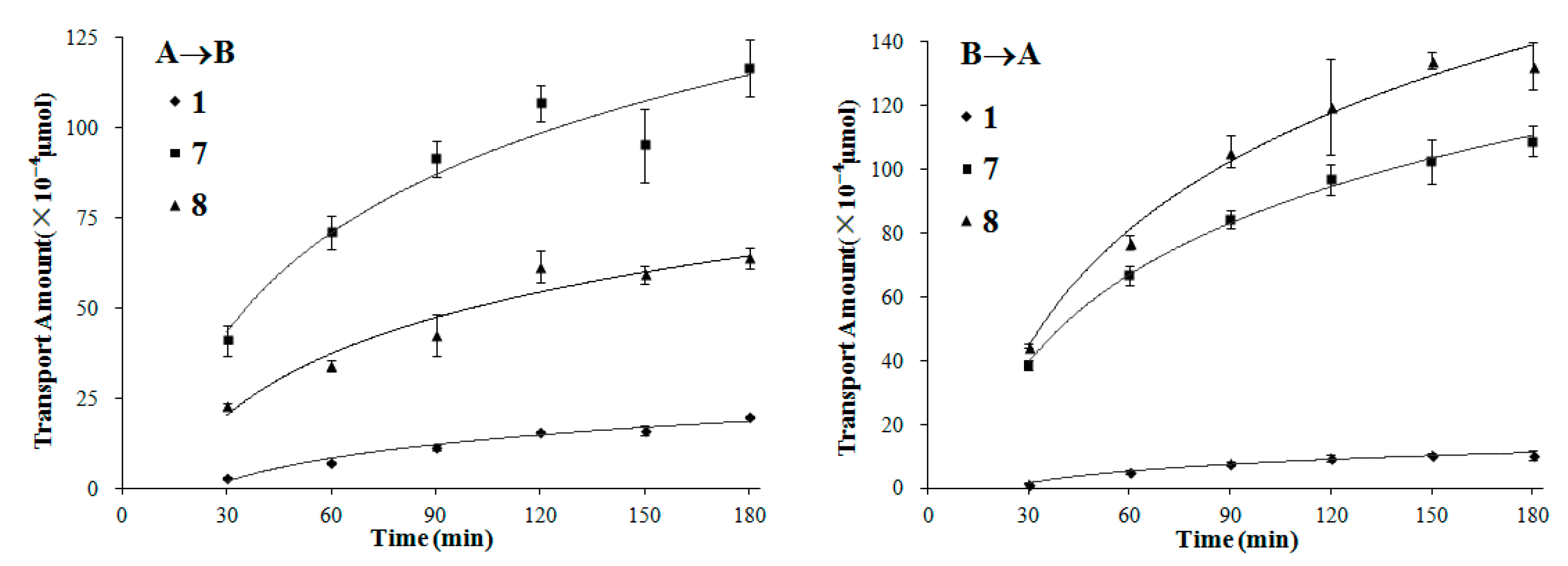
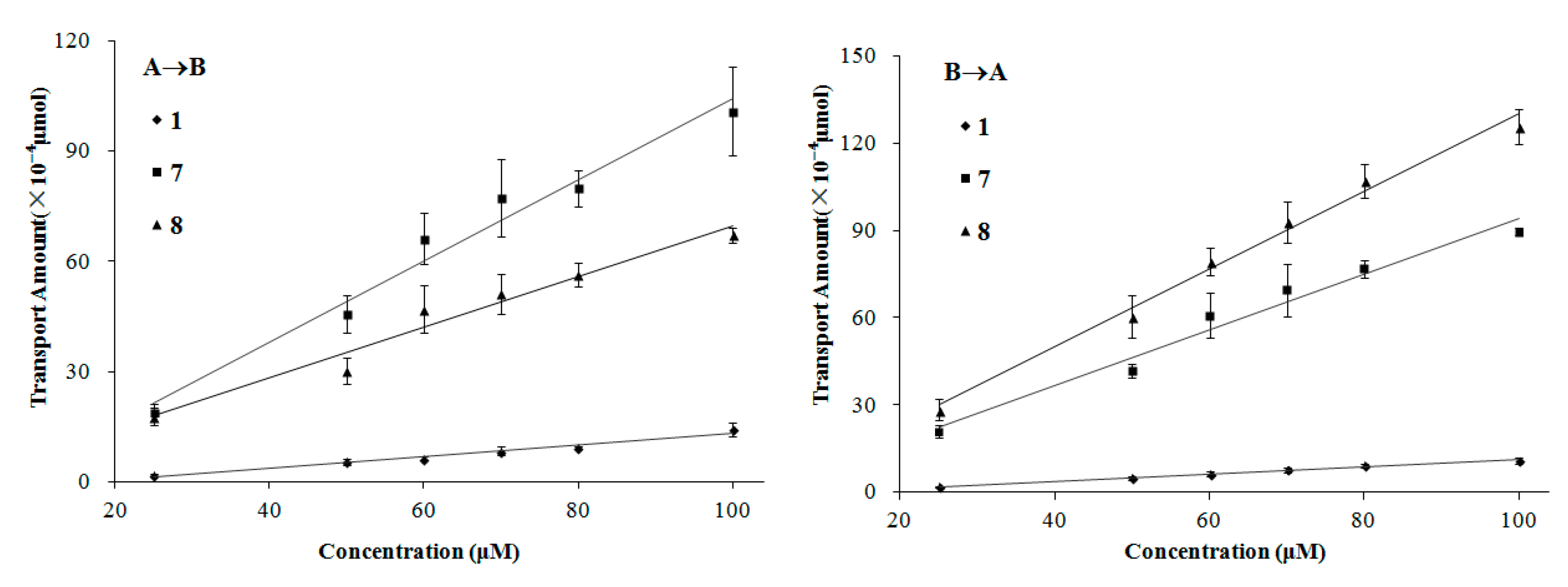
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. Transport Studies and Sample Preparation
3.4. HPLC Analysis
3.5. Data Analysis
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bendayan, R.; Lee, G.; Bendayan, M. Functional expression and localization of P-glycoprotein at the blood brain barrier. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2002, 57, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J. Prediction of blood–brain barrier permeation in drug discovery from in vivo, in vitro and in silico models. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.W.; Yang, X.D.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.G.; Wang, K. Establishment of Caco-2 cell monolayer model and standard operation procedure for assessing intestinal absorption of chemical components of traditional Chinese medicine. J. Chin. Integr. Med. 2007, 5, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M.; Ueda, K.; Lovelace, E.; Rutherford, A.V.; Willingham, M.C. A retrovirus carrying an MDR1 cDNA confers multidrug resistance and polarized expression of P-glycoprotein in MDCK cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 4486–4490. [Google Scholar]
- Veronesi, B. Characterization of the MDCK cell line for screening neurotoxicants. Neurotoxicology 1996, 17, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gumbleton, M.; Audus, K.L. Progress and limitations in the use of in vitro cell cultures to serve as a permeability screen for the blood–brain barrier. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 1681–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakkarainen, J.J.; Jalkanen, A.J.; Kääriäinen, T.M.; Keski-Rahkonen, P.; Venäläinen, T.; Hokkanen, J.; Mönkkönen, J.; Suhonen, M.; Forsberg, M.M. Comparison of in vitro cell models in predicting in vivo brain entry of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 402, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Rager, J.D.; Weinstein, K.; Kardos, P.S.; Dobson, G.L.; Li, J.; Hidalgo, I.J. Evaluation of the MDR-MDCK cell line as a permeability screen for the blood–brain barrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 288, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.Q.; Lim, C.S.; Hwang, J.K.; Ha, I.; Han, J.S. Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of macelignan in murine hippocampal cell line and primary culture of rat microglial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhingra, D.; Sharma, A. Antidepressant-like activity of n-hexane extract of nutmeg (Myristica fragrans) seeds in mice. J. Med. Food. 2006, 9, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.W. Quantitative determination of neolignanoids in the seeds of Myristica fragrans. Mod. Chin. Med. 2008, 10, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Purushothaman, K.K.; Sarada, A.; Connolly, J.D. Malabaricones A–D, novel diarylnonanoids from Myristica malabarica Lam (Myristicaceae). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1977, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Shoji, M.; Hirata, A.; Tanaka, S.; Yokoe, I.; Fujisawa, S. Dehydrodiisoeugenol, an isoeugenol dimer, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nuclear factor kappa B activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 434, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, I.L.; Hsieh, C.F.; Duh, C.Y.; Chen, I.S. Further study on the chemical constituents and their cytotoxicity from the leaves of Persea obovatifolia. Chin. Pharm. J. (Taipei) 1999, 51, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.Y.; Yang, X.W.; Xu, W.; Li, F. New inhibitors of nitric oxide production from the seeds of Myristica fragrans. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.Y.; Xu, W.; Yang, X.W.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Li, F. New neolignans from the seeds of Myristica fragrans that inhibit nitric oxide production. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, B.S.; Bauri, A.K.; Mishra, S.; Chattopadhyay, S. Antioxidant activity of Myristica malabarica extracts and their constituents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6912–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.P.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Weng, X.C. Isolation of some compounds from nutmeg and their antioxidant activities. Czech. J. Food Sci. 2012, 30, 164–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Tae, N.; Min, B.S.; Choe, J.; Lee, J.H. Malabaricone C suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses via inhibiting ROS-mediated Akt/IKK/NF-κB signaling in murine macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, B.; Yadav, S.K.; Patro, B.S.; Tyagi, M.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, S. Molecular mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of a natural diarylnonanoid, malabaricone C. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1680–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, C.; Mori, S.; Ando, T.; Tsuji, T. Arg-gingipain inhibition and anti-bacterial activity selective for Porphyromonas gingivalis by malabaricone C. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 1475–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, B.S.; Tyagi, M.; Saha, J.; Chattopadhyay, S. Comparative nuclease and anti-cancer properties of the naturally occurring malabaricones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7043–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, A.; Schmitz-Afonso, I.; Martin, M.T.; Awang, K.; Laprévote, O.; Guéritte, F.; Litaudon, M. Acylphenols from Myristica crassa as new acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Burgos, E.; Carretero, M.E.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. In vitro permeability study of CNS-active diterpenes from Sideritis spp. using cellular models of blood-brain barrier. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardridge, W.M.; Triguero, D.; Yang, J.; Cancilla, P.A. Comparison of in vitro and in vivo models of drug transcytosis through the blood-brain barrier. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990, 253, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wils, P.; Warnery, A.; Phung-Ba, V.; Legrain, S.; Scherman, D. High lipophilicity decreases drug transport across intestinal epithelial cells. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 1994, 269, 654–658. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.W.; Huang, X.; Ma, L.; Wu, Q.; Xu, W. The intestinal permeability of neolignans from the seeds of Myristica. fragrans in the Caco-2 cell monolayer model. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomini, K.M.; Huang, S.M.; Tweedie, D.J.; Benet, L.Z.; Brouwer, K.L.; Chu, X.; Dahlin, A.; Evers, R.; Fischer, V.; Hillgren, K.M.; et al. Membrane transporters in drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Li, S.N.; Yang, X.W. Absorption characteristics of 4 linear furocoumarins across human intestinal epithelial in a model of Caco-2 cell monolayer. Chin. J. New Drugs 2009, 18, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.W.; Huang, X.; Ahmat, M. New neolignan from seed of Myristica fragrans. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2008, 33, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, M.; Yang, X.W.; Shu, Y.Z.; Kakiuchi, N.; Tezuka, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Namba, T. New constituents of the aril of Myristica fragrans Houtt. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, N.; Tannergren, C.; Rungstad, D.; Lennernäs, H. Transport characteristics of fexofenadine in the Caco-2 cell model. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, C.N.; Zeng, S. Establishment of Madin-Darby canine kidney cell line with high P-glycoprotein expression. Chin. Pharm. J. 2009, 44, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.F.; Xu, W.; Song, W.; Ye, M.; Yang, X.W. Transport of twelve coumarins from Angelicae Pubescentis Radix across a MDCK-pHaMDR cell monolayer—An in vitro model for blood-brain barrier permeability. Molecules 2015, 20, 11719–11732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manda, V.K.; Avula, B.; Ali, Z.; Khan, I.A.; Walker, L.A.; Khan, S.I. Evaluation of in vitro absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties of mitragynine, 7-hydroxymitragynine, and mitraphylline. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, N.; Xu, W.; Cao, G.-Y.; Yang, Y.-F.; Yang, X.-B.; Yang, X.-W. The Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability of Lignans and Malabaricones from the Seeds of Myristica fragrans in the MDCK-pHaMDR Cell Monolayer Model. Molecules 2016, 21, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020134
Wu N, Xu W, Cao G-Y, Yang Y-F, Yang X-B, Yang X-W. The Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability of Lignans and Malabaricones from the Seeds of Myristica fragrans in the MDCK-pHaMDR Cell Monolayer Model. Molecules. 2016; 21(2):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020134
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Ni, Wei Xu, Gui-Yun Cao, Yan-Fang Yang, Xin-Bao Yang, and Xiu-Wei Yang. 2016. "The Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability of Lignans and Malabaricones from the Seeds of Myristica fragrans in the MDCK-pHaMDR Cell Monolayer Model" Molecules 21, no. 2: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020134
APA StyleWu, N., Xu, W., Cao, G.-Y., Yang, Y.-F., Yang, X.-B., & Yang, X.-W. (2016). The Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability of Lignans and Malabaricones from the Seeds of Myristica fragrans in the MDCK-pHaMDR Cell Monolayer Model. Molecules, 21(2), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020134





