Inhibition of Hypoxia-Induced Retinal Angiogenesis by Specnuezhenide, an Effective Constituent of Ligustrum lucidum Ait., through Suppression of the HIF-1α/VEGF Signaling Pathway
Abstract
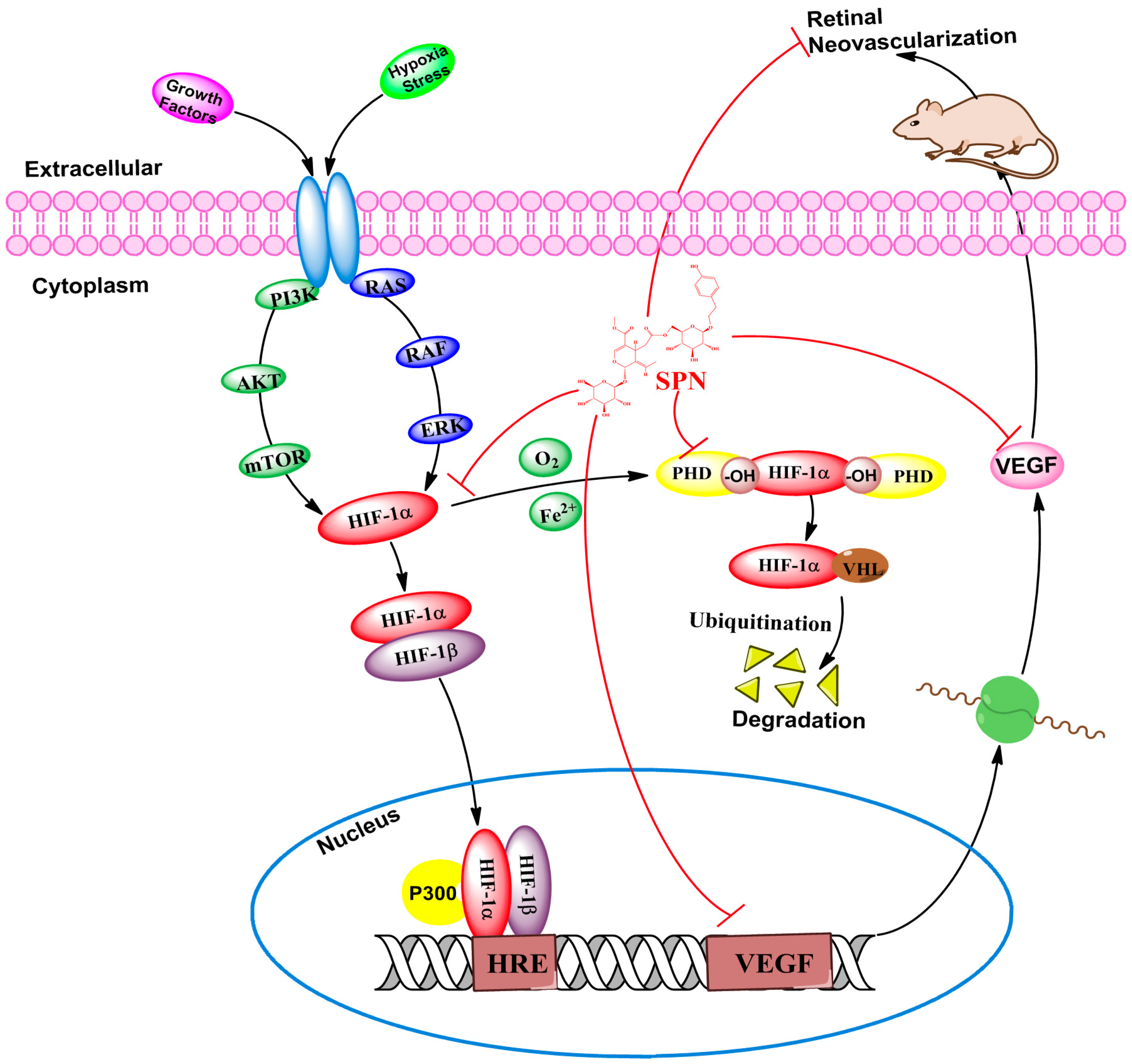
:1. Introduction
2. Results
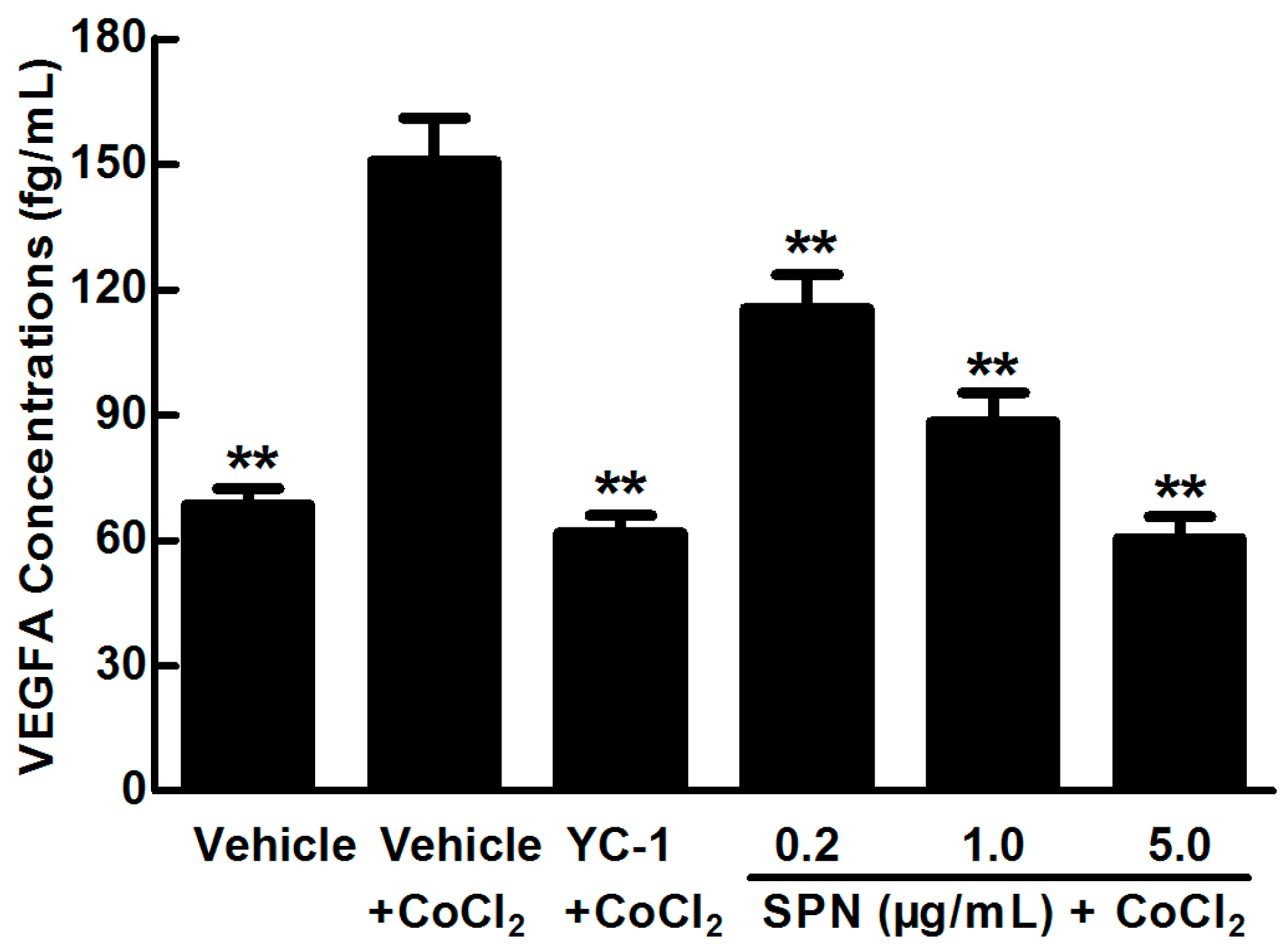
2.1. SPN Inhibits the Secretion of VEGFA in ARPE-19 Cells under Hypoxia
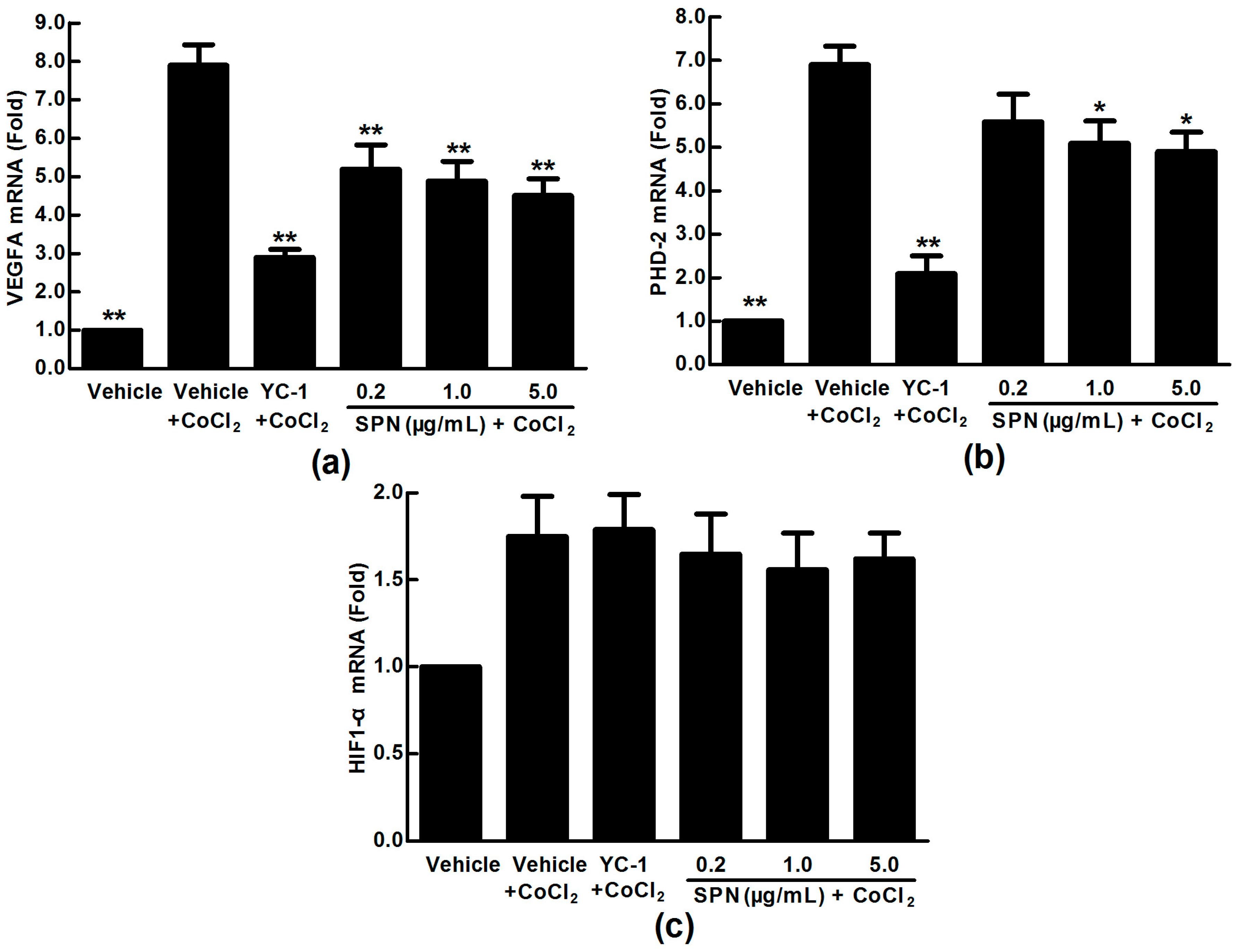
2.2. Effects of SPN on the mRNA Expressions of VEGFA, HIF-1α and PHD-2 in ARPE-19 Cells
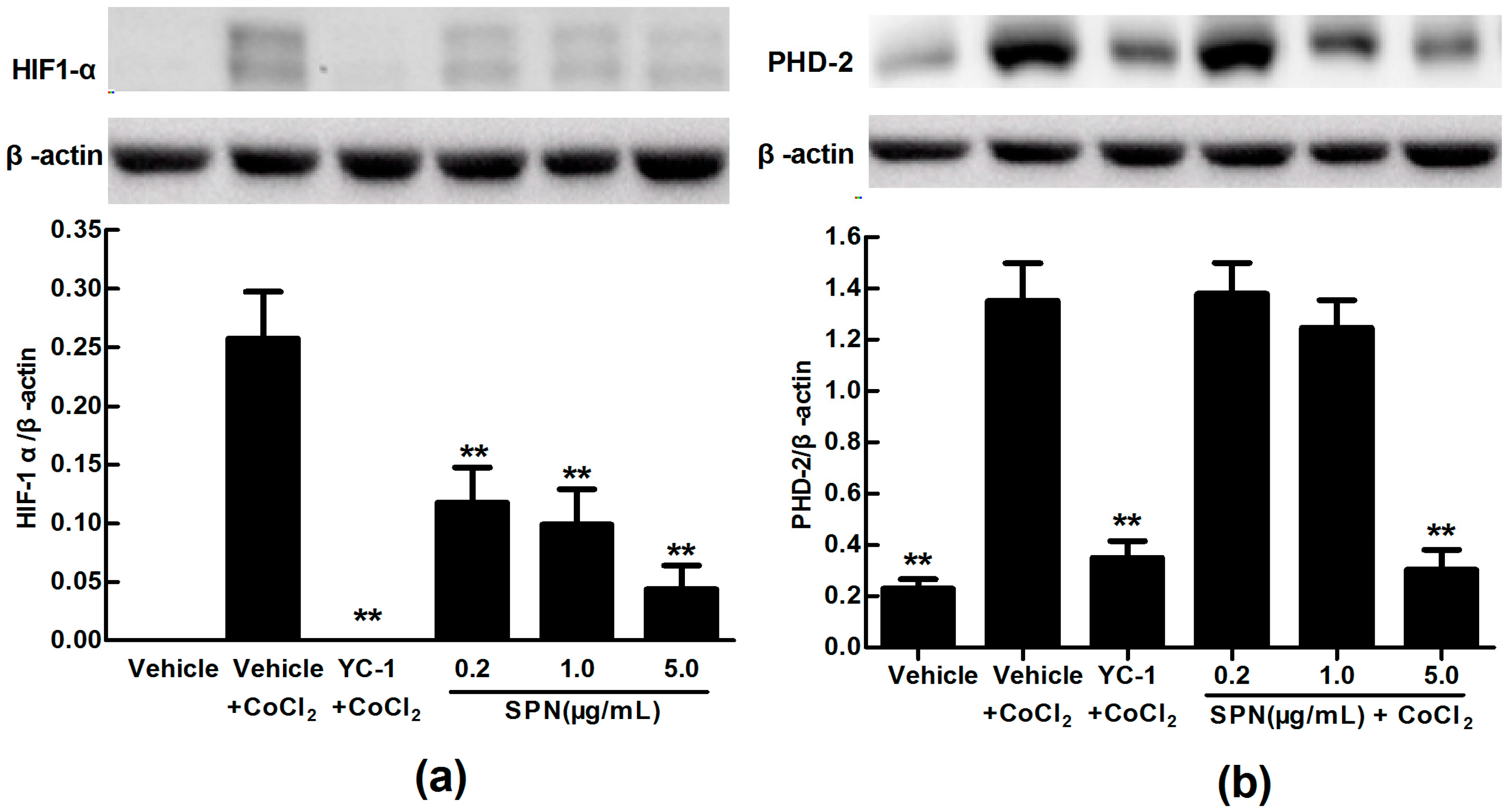
2.3. Effects of SPN on the Intracellular Protein Levels of HIF-1α and PHD-2 in ARPE-19 Cells
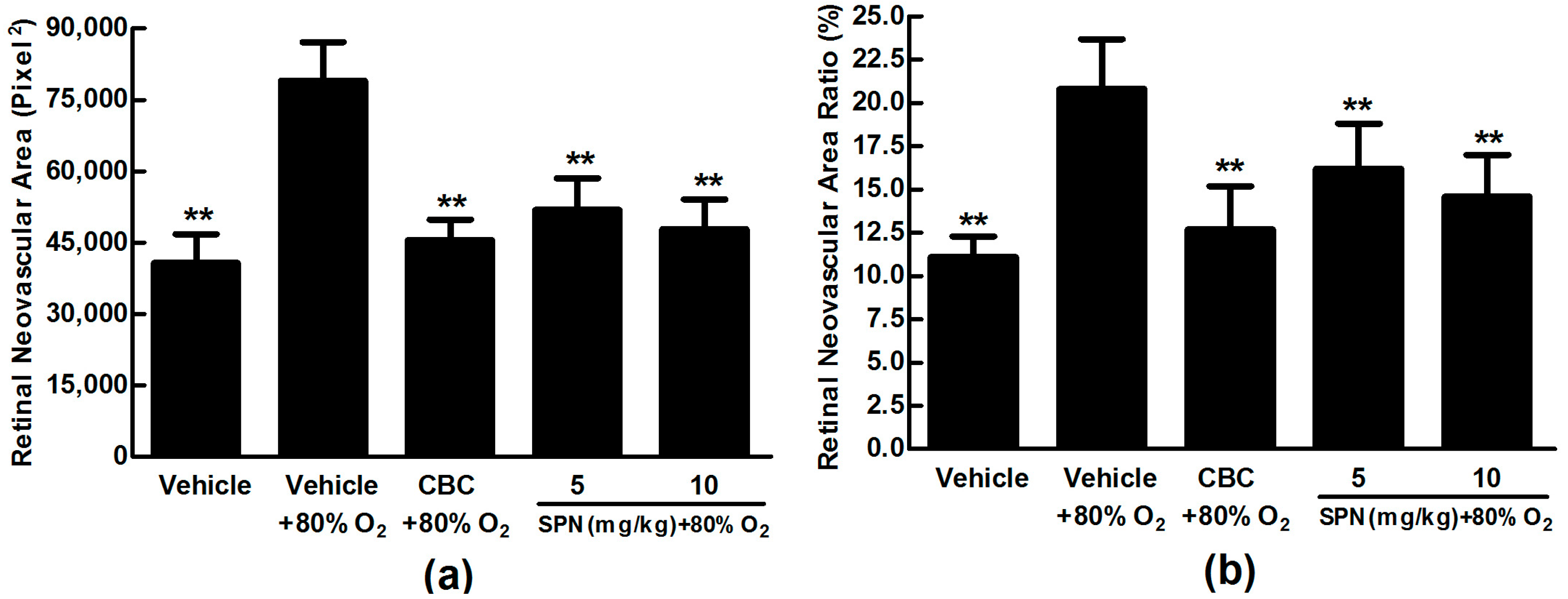
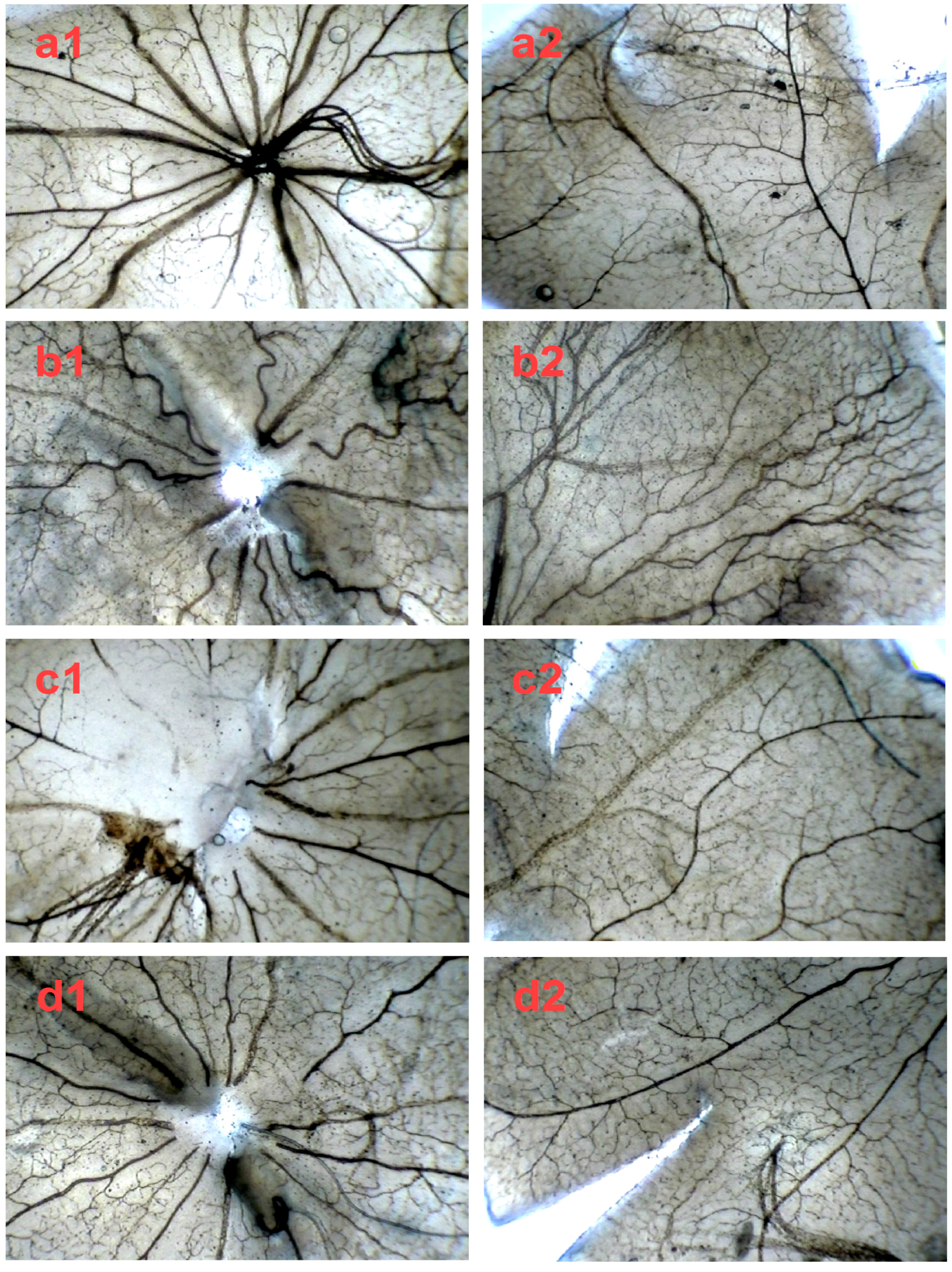
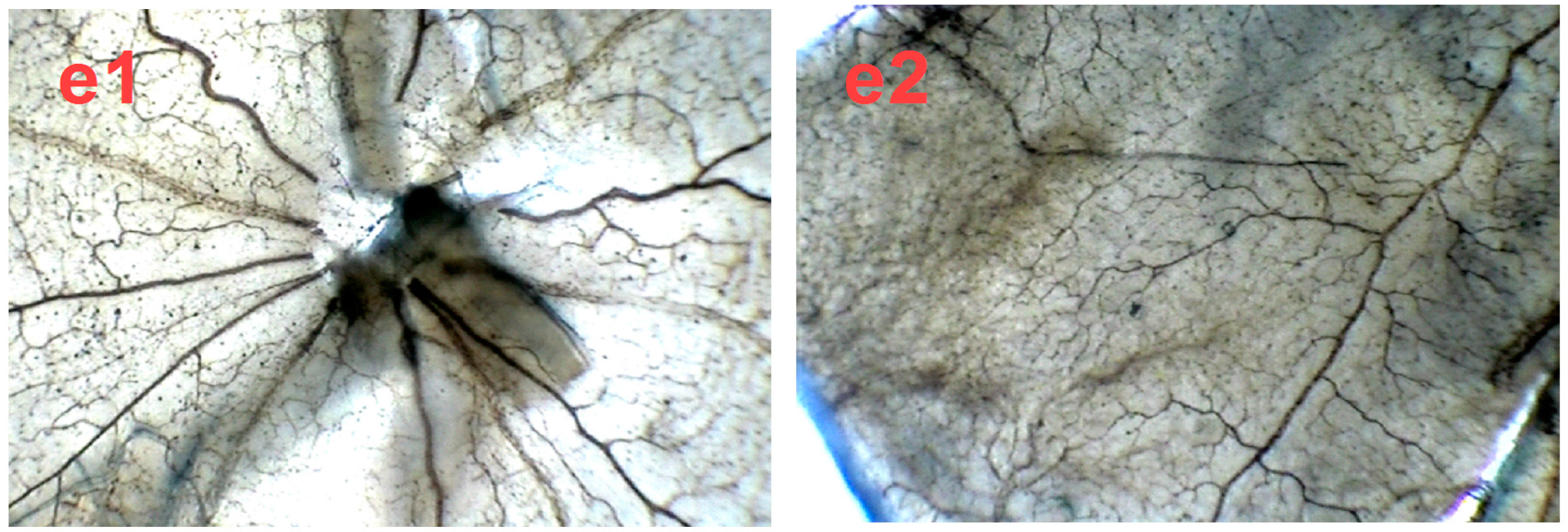
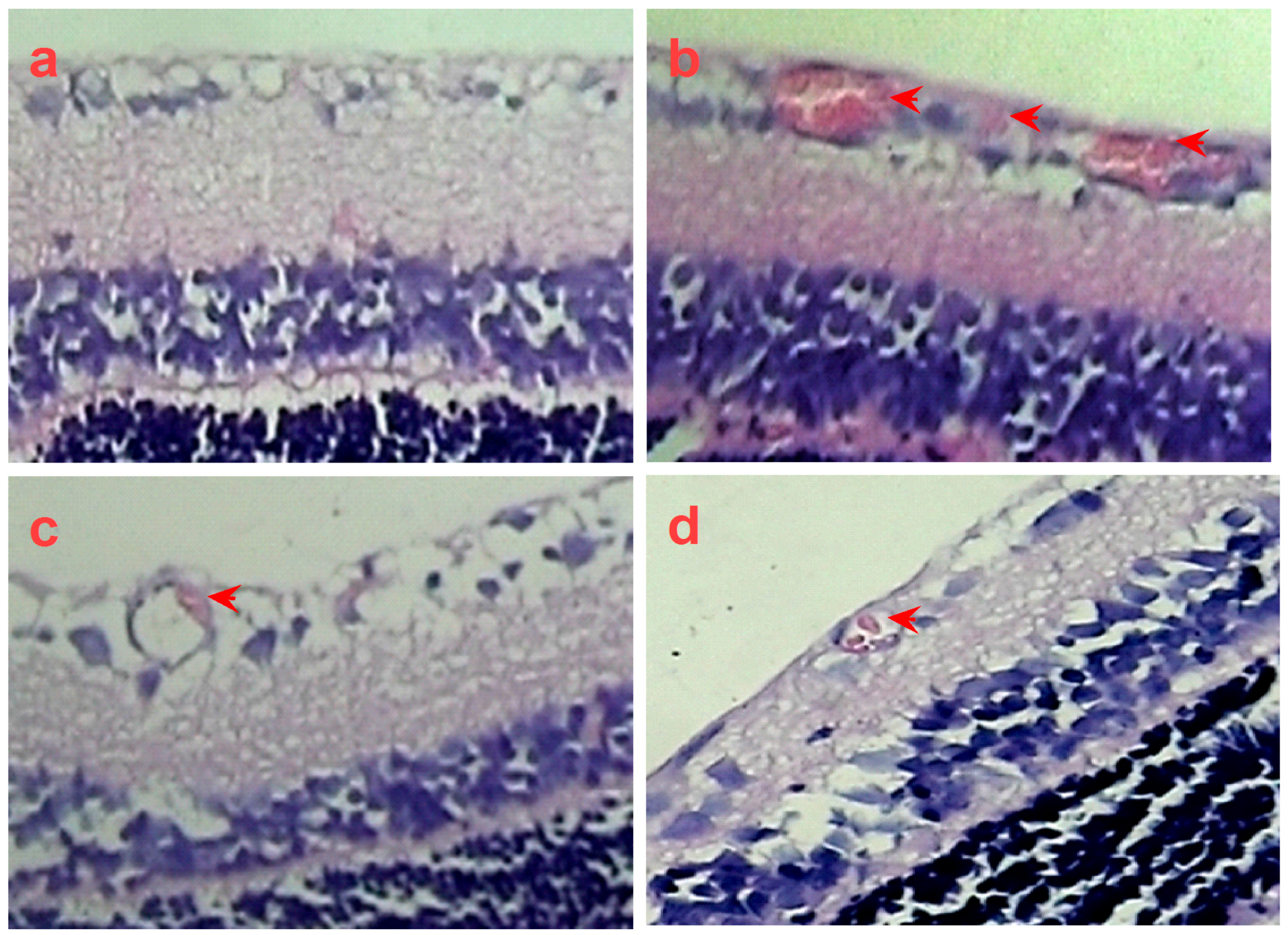
2.4. SPN Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Retinal Neovascularization In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Reagents and Antibodies
4.3. Cell Culture
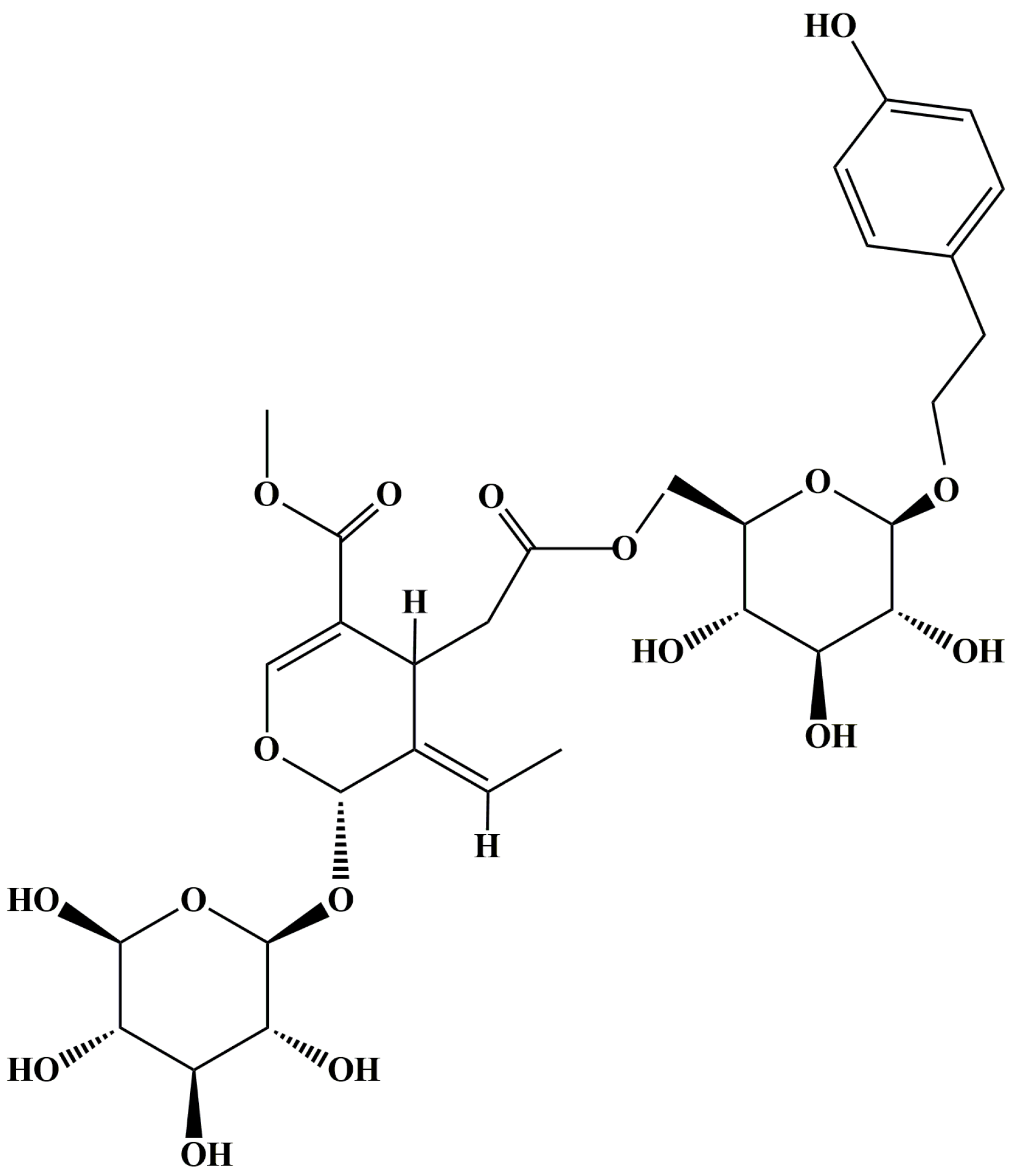
4.4. Extraction and Isolation of SPN
4.5. Determination of VEGFA Secretion by ARPE-19 Cells under Chemical Induced Hypoxia
4.6. RNA Isolation and Analysis of the mRNA Expressions of VEGFA, HIF-1α and PHD-2
4.7. Western Blots Analysis of HIF-1α and PHD-2 Proteins
4.8. Rat Model of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy (OIR)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, N.; Yu, Y.; Ablajan, K.; Li, L.; Fan, B.; Peng, J.; Yan, H.; Ma, F.; Nie, Y. Seasonal variations in metabolite profiling of the fruits of Ligustrum lucidum Ait. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H.; Bauer, R.; Melchart, D.; Xiao, P.G.; Staudinger, A. Fructus Ligustri lucidi – Nüzhenzi. In Chromatographic Fingerprint Analysis of Herbal Medicines; Wagner, H., Bauer, R., Melchart, D., Xiao, P.G., Staudinger, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shan, A.; Liu, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z. In vitro immunomodulatory effects of an oleanolic acid-enriched extract of Ligustrum lucidum fruit (Ligustrum lucidum supercritical CO2 extract) on piglet immunocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.M.; Yen, F.L.; Ng, L.T.; Lin, C.C. Protective effects of Ligustrum lucidum fruit extract on acute butylated hydroxytoluene-induced oxidative stress in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 111, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Shan, A.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X. Influence of an aqueous extract of Ligustrum lucidum and an ethanol extract of Schisandra chinensis on parameters of antioxidative metabolism and spleen lymphocyte proliferation of broilers. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2009, 63, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.D.; But, P.; Chan, T.W.; Dong, H.; Xu, H.X.; Lau, C.P.; Sun, H.D. Antioxidative glucosides from the fruits of Ligustrum lucidum. Chem. Pharm Bull. (Tokyo) 2001, 49, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Du, Q.; Deng, S.; An, H.M.; Pan, C.F.; Shen, K.P.; Xu, L.; Wei, M.M.; Wang, S.S. Ligustrum lucidum Ait. fruit extract induces apoptosis and cell senescence in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through upregulation of p21. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Gao, J.; Wu, C.; Han, L.; Liu, E.; Shi, P.; Gao, X.; Wang, T. New secoiridoids from the fruits of Ligustrum lucidum Ait. with triglyceride accumulation inhibitory effects. Fitoterapia 2013, 91, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Ip, F.C.; Pang, H.; Ip, N.Y. New secoiridoid glucosides from Ligustrum lucidum induce ERK and CREB phosphorylation in cultured cortical neurons. Planta. Med. 2010, 76, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Han, Z. Antidiabetic and antioxidant effects of oleanolic acid from Ligustrum lucidum Ait. in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Han, Z.; Li, J.; Li, K. Antidiabetic potential of oleanolic acid from Ligustrum lucidum Ait. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 85, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y. Prevention of experimental atherosclerosis in rabbits with Ligustrum lucidum fruit. Zhong Yao Tong Bao 1983, 8, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Fan, M.; Bian, Z.; Nie, M.; Chen, Z. Extract and identify ingredient from Ligustrum lucidum Ait. and study its effect to periodontal pathogen. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2002, 37, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yim, T.K.; Wu, W.K.; Pak, W.F.; Ko, K.M. Hepatoprotective action of an oleanolic acid-enriched extract of Ligustrum lucidum fruits is mediated through an enhancement on hepatic glutathione regeneration capacity in mice. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.C.; He, Z.D.; Deng, X.L.; But, P.P.; Ooi, V.E.; Xu, H.X.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.F. In vitro evaluation of secoiridoid glucosides from the fruits of Ligustrum lucidum as antiviral agents. Chem. Pharm Bull. (Tokyo) 2001, 49, 1471–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, F. Bioactivity-guided Isolation of antiosteoporotic compounds from Ligustrum lucidum. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.B.; Jo, Y.H.; Kim, E.S.; Hwang, B.Y.; Oh, K.; Lee, M.K. Anti-obesity effect of (8-E)-niizhenide, a secoiridoid from Ligustrum lucidum, in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 1399–1401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.N.; Zhang, Y.N.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.J.; Kong, L.B. Active components of Ligustrum lucidum inhibiting hepatitis C virus replicase activity. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2013, 48, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.T.; Wang, M. Research progress of chemical composition and pharmacological effects of fructus Figustri lucidi. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form. 2014, 20, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, C.; Lifu, S.; Jinhong, H.; Qian, S. Effects of specnuezhenide on the proliferation ability of lymphocytes and cytotoxicity of natural killer cells in murine splenocytes in vitro. P. Chem. Sens. Symp. 1998, 51, 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.; Dai, J.; Zheng, C.; Bao, B.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, L.; Ding, A.; Li, W. Quality assessment of Fructus Ligustri lucidi by the simultaneous determination of six compounds and chemometric analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1822–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Y. Therapeutic effect observation of Tangmuning on early diabetic retinopathy. Chin. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 19, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.F.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.M.; Shen, X.P.; Ke, X.; Gao, X.P. Inhibitory effects of Keluoxin capsule on hypoxia-induced angiogenesis in retina. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form. 2014, 10, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Vaziri, K.; Schwartz, S.G.; Relhan, N.; Kishor, K.S.; Flynn, H.W., Jr. New therapeutic approaches in diabetic retinopathy. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2015, 12, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, D.H.; An, H.; Chang, D.J.; Baek, Y.Y.; Cho, C.S.; Jun, H.O.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, K.W.; et al. Hypoxia-mediated retinal neovascularization and vascular leakage in diabetic retina is suppressed by HIF-1alpha destabilization by SH-1242 and SH-1280, novel hsp90 inhibitors. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2014, 92, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Cutler, A.; Shen, B.; Moss, S.E.; Iyengar, S.K.; Klein, R.; Folkman, J.; Anand-Apte, B. Inhibition of EGF signaling protects the diabetic retina from insulin-induced vascular leakage. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, R.; Vagaggini, T.; Chen, Y.; Hu, D.N. Zeaxanthin inhibits hypoxia-induced VEGF secretion by RPE cells through decreased protein levels of hypoxia-inducible factors-1alpha. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 687386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marneros, A.G.; Fan, J.; Yokoyama, Y.; Gerber, H.P.; Ferrara, N.; Crouch, R.K.; Olsen, B.R. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in the retinal pigment epithelium is essential for choriocapillaris development and visual function. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Y.Z.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, L. Temporal requirement of RPE-derived VEGF in the development of choroidal vasculature. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pages, G.; Pouyssegur, J. Transcriptional regulation of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor gene--a concert of activating factors. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, T.; Westenskow, P.D.; Friedlander, M. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in the retina. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 801, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, Y.S.; Shin, J.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, K.W. Deguelin inhibits retinal neovascularization by down-regulation of HIF-1alpha in oxygen-induced retinopathy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNiro, M.; Al-Halafi, A.; Al-Mohanna, F.H.; Alsmadi, O.; Al-Mohanna, F.A. Pleiotropic effects of YC-1 selectively inhibit pathological retinal neovascularization and promote physiological revascularization in a mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 348–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwase, T.; Fu, J.; Yoshida, T.; Muramatsu, D.; Miki, A.; Hashida, N.; Lu, L.; Oveson, B.; Lima, E.S.R.; Seidel, C.; et al. Sustained delivery of a HIF-1 antagonist for ocular neovascularization. J. Control. Release. 2013, 172, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berra, E.; Benizri, E.; Ginouvès, A.; Volmat, V.; Roux, D.; Pouysségur, J. HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1alpha in normoxia. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4082–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, L.G.; Schiavon, V.F.; Andrade, J.M.; Tiezzi, D.G.; Peria, F.M.; Marana, H.R. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor-C in locally advanced breast cancer patients. Clinics 2011, 66, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ricci, B. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the rat model. Doc. Ophthalmol. 1990, 74, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osera, C.; Martindale, J.L.; Amadio, M.; Kim, J.; Yang, X.; Moad, C.A.; Indig, F.E.; Govoni, S.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M.; et al. Induction of VEGFA mRNA translation by CoCl2 mediated by HuR. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoud, G.N.; Li, W. HIF-1alpha pathway: role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin. B 2015, 5, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Wu, M.; Fu, D.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Wilson, K.; Lyons, T.J. Effects of modified LDL and HDL on retinal pigment epithelial cells: a role in diabetic retinopathy? Diabetologia 2013, 56, 2318–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simo, R.; Villarroel, M.; Corraliza, L.; Hernandez, C.; Garcia-Ramirez, M. The retinal pigment epithelium: something more than a constituent of the blood-retinal barrier--implications for the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 190724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Petrovic, J.M.; Callaghan, D.; Jones, A.; Cui, H.; Howlett, C.; Stanimirovic, D. Evidence that hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) mediates transcriptional activation of interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) in astrocyte cultures. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 174, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, I.; Carrarelli, P.; Luisi, S.; Batteux, F.; Chapron, C.; Naldini, A.; Petraglia, F. Different expression of hypoxic and angiogenic factors in human endometriotic lesions. Reprod. Sci. 2016, 23, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelkmann, W. Regulation of erythropoietin production. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.; Kim, M.H. HIF-1 alpha: a key survival factor for serum-deprived prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2008, 68, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krotova, K.; Patel, J.M.; Block, E.R.; Zharikov, S. Hypoxic upregulation of arginase II in human lung endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 299, C1541–C1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, V.A.; Ashcroft, M. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha versus HIF-2alpha in the regulation of HIF target genes in response to hypoxia, insulin-like growth factor-I, or loss of von Hippel-Lindau function: implications for targeting the HIF pathway. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6264–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salceda, S.; Caro, J. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein is rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system under normoxic conditions. Its stabilization by hypoxia depends on redox-induced changes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 22642–22647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tug, S.; Delos, R.B.; Fandrey, J.; Berchner-Pfannschmidt, U. Non-hypoxic activation of the negative regulatory feedback loop of prolyl-hydroxylase oxygen sensors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 384, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaidi, A.; Qualtrough, D.; Williams, A.C.; Paraskeva, C. Direct transcriptional up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 promotes colorectal tumor cell survival and enhances HIF-1 transcriptional activity during hypoxia. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6683–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.H.; Zhang, X.P.; Liu, F.; Wang, W. Modeling the interplay between the HIF-1 and p53 pathways in hypoxia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eschricht, S.; Jarr, K.U.; Kuhn, C.; Lehmann, L.; Kreusser, M.; Katus, H.A.; Frey, N.; Chorianopoulos, E. Heat-shock-protein 90 protects from downregulation of HIF-1alpha in calcineurin-induced myocardial hypertrophy. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 85, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.F.; Cao, Y.Y.; Chen, H.S.; Dong, J.P. Isolation and identification of two new secoiridoids of water-soluble chemical constituents from the fruits of Ligustrum lucidum Ait. Yao Xue Xue Bao 1997, 32, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, M.; Saito, Y.; Nakanishi-Ueda, T.; Ueda, T.; Hisamitsu, T.; Koide, R.; Takahashi, H. Influence of the difference of breastfeeding volume on a rat model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2014, 55, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winners-Mendizabal, O.G.; Orge, F.H.; Di Fiore, J.M.; Martin, R.J.; Kc, P. Hypoxia-hyperoxia paradigms in the development of oxygen-induced retinopathy in a rat pup model. J. Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2014, 7, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calzia, D.; Panfoli, I.; Heinig, N.; Schumann, U.; Ader, M.; Traverso, C.E.; Funk, R.H.; Roehlecke, C. Impairment of extramitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in mouse rod outer segments by blue light irradiation. Biochimie 2016, 125, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of specnuezhenide was available from the authors.
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Ke, X.; Fu, W.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Ma, N.; Zhao, M.; Hao, X.; Zhang, Z. Inhibition of Hypoxia-Induced Retinal Angiogenesis by Specnuezhenide, an Effective Constituent of Ligustrum lucidum Ait., through Suppression of the HIF-1α/VEGF Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2016, 21, 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121756
Wu J, Ke X, Fu W, Gao X, Zhang H, Wang W, Ma N, Zhao M, Hao X, Zhang Z. Inhibition of Hypoxia-Induced Retinal Angiogenesis by Specnuezhenide, an Effective Constituent of Ligustrum lucidum Ait., through Suppression of the HIF-1α/VEGF Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2016; 21(12):1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121756
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jianming, Xiao Ke, Wei Fu, Xiaoping Gao, Hongcheng Zhang, Wei Wang, Na Ma, Manxi Zhao, Xiaofeng Hao, and Zhirong Zhang. 2016. "Inhibition of Hypoxia-Induced Retinal Angiogenesis by Specnuezhenide, an Effective Constituent of Ligustrum lucidum Ait., through Suppression of the HIF-1α/VEGF Signaling Pathway" Molecules 21, no. 12: 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121756
APA StyleWu, J., Ke, X., Fu, W., Gao, X., Zhang, H., Wang, W., Ma, N., Zhao, M., Hao, X., & Zhang, Z. (2016). Inhibition of Hypoxia-Induced Retinal Angiogenesis by Specnuezhenide, an Effective Constituent of Ligustrum lucidum Ait., through Suppression of the HIF-1α/VEGF Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 21(12), 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121756





