Synthesis, Molecular Structure and Spectroscopic Investigations of Novel Fluorinated Spiro Heterocycles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of 3a,b
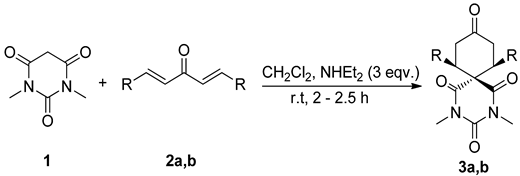
| Entries a | Diarylidene 2a,b | R | 3 | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2a | p-FPh | 3a | 98 |
| 2 | 2b | p-CF3Ph | 3b | 94 |
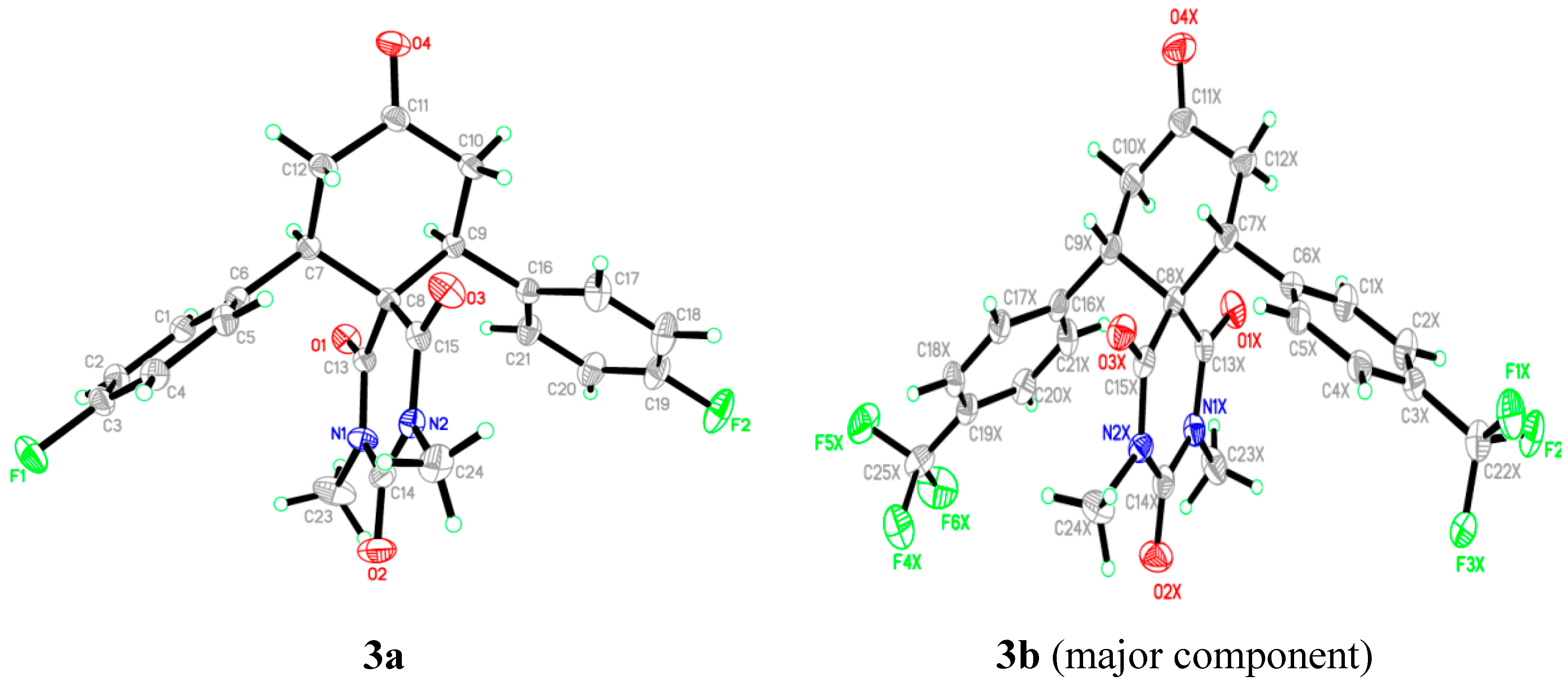
2.2. X-ray Crystal Structures of 3a,b
| Properties | Compound 3a | Compound 3b |
|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C23H20F2N2O4 | C25H20F6N2O4 |
| Formula weight | 426.41 | 526.43 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Tetragonal |
| Space group | C2/c | P-421c |
| Unit cell dimensions | a = 33.1745 (16)Å, α = 90.00° b = 7.7860 (3)Å β = 100.68 (3)° c = 15.866 (7)Å, γ = 90.00° | a = 22.1813 (10)Å, α = 90.00° b = 22.1813 (10) Å, β = 90.00° c = 9.2692 (4)Å, γ = 90.00° |
| Volume | 4027.2 (3)Å3 | 4560.5 (5)Å3 |
| Density (calculated) | 1.407Mg/m3 | 1.533 Mg/m3 |
| Absorption coefficient | 0.11 mm−1 | 0.14 mm−1 |
| F(000) | 1776 | 2160 |
| Crystal size | 0.65 × 0.27 × 0.15 mm | 0.59 × 0.33 × 0.21mm |
| Theta range for data collection | 2.5°–30.5°. | 2.4°–30.5°. |
| Index ranges | −47 ≤ h ≤ 47, −11 ≤ k ≤ 11, −22 ≤ l ≤ 22 | −26 ≤ h ≤ 26, −26 ≤ k ≤ 26, −10 ≤ l ≤ 11 |
| Reflections collected/ unique | 112794/ 4917 [R(int) = 0.038] | 35961 / 4754 [R(int) = 0.024] 82456/4010[R(int) = 0.053] |
| Completeness to theta = 30.57° | 99.7% | 99.9% |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.03 | 1.09 |
| Largest diff. peak and hole | 0.54 and −0.27 e·Å−3 | 0.27 and −0.26 e·Å−3 |
| CCDC number | 1034099 | 1034833 |
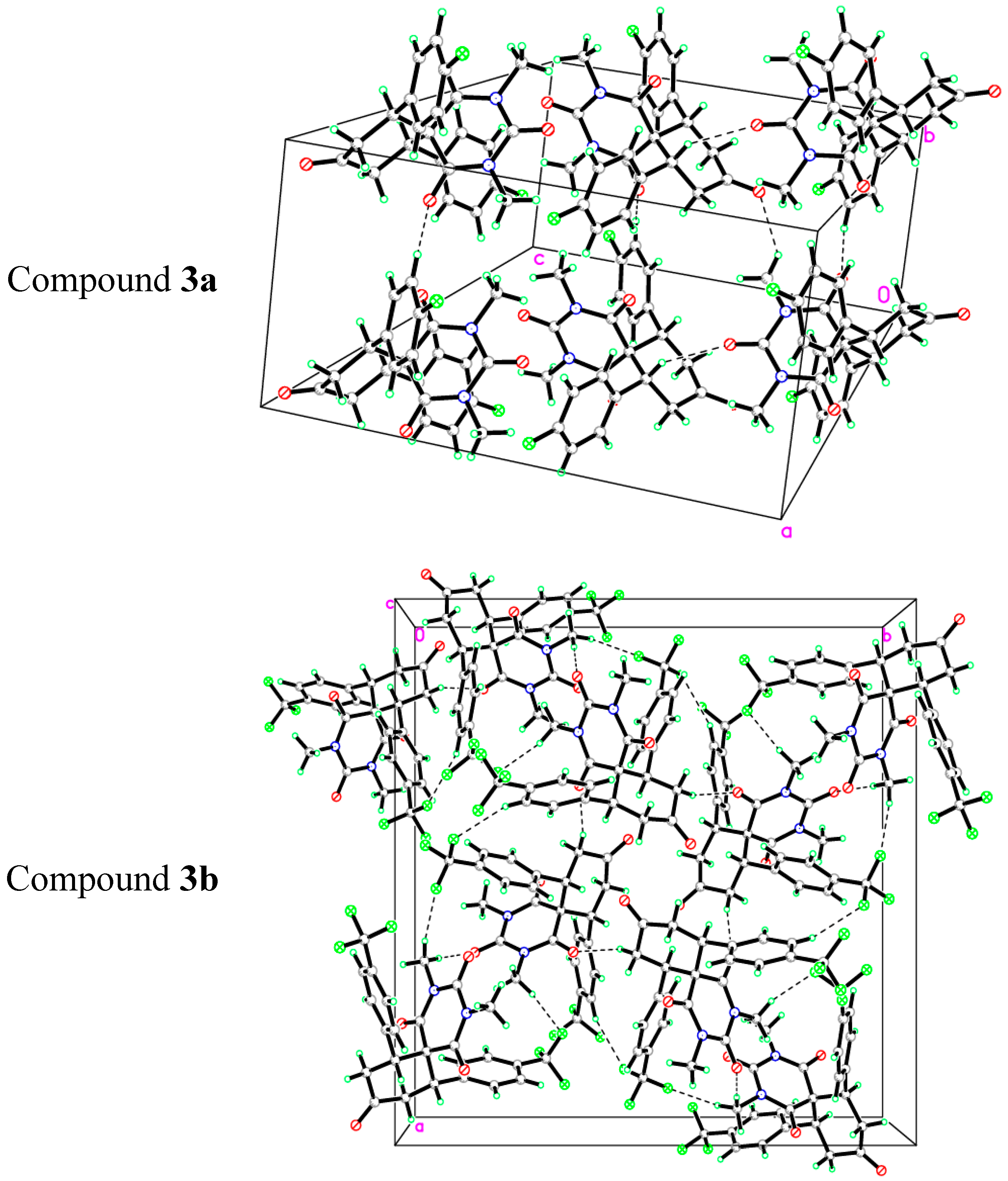
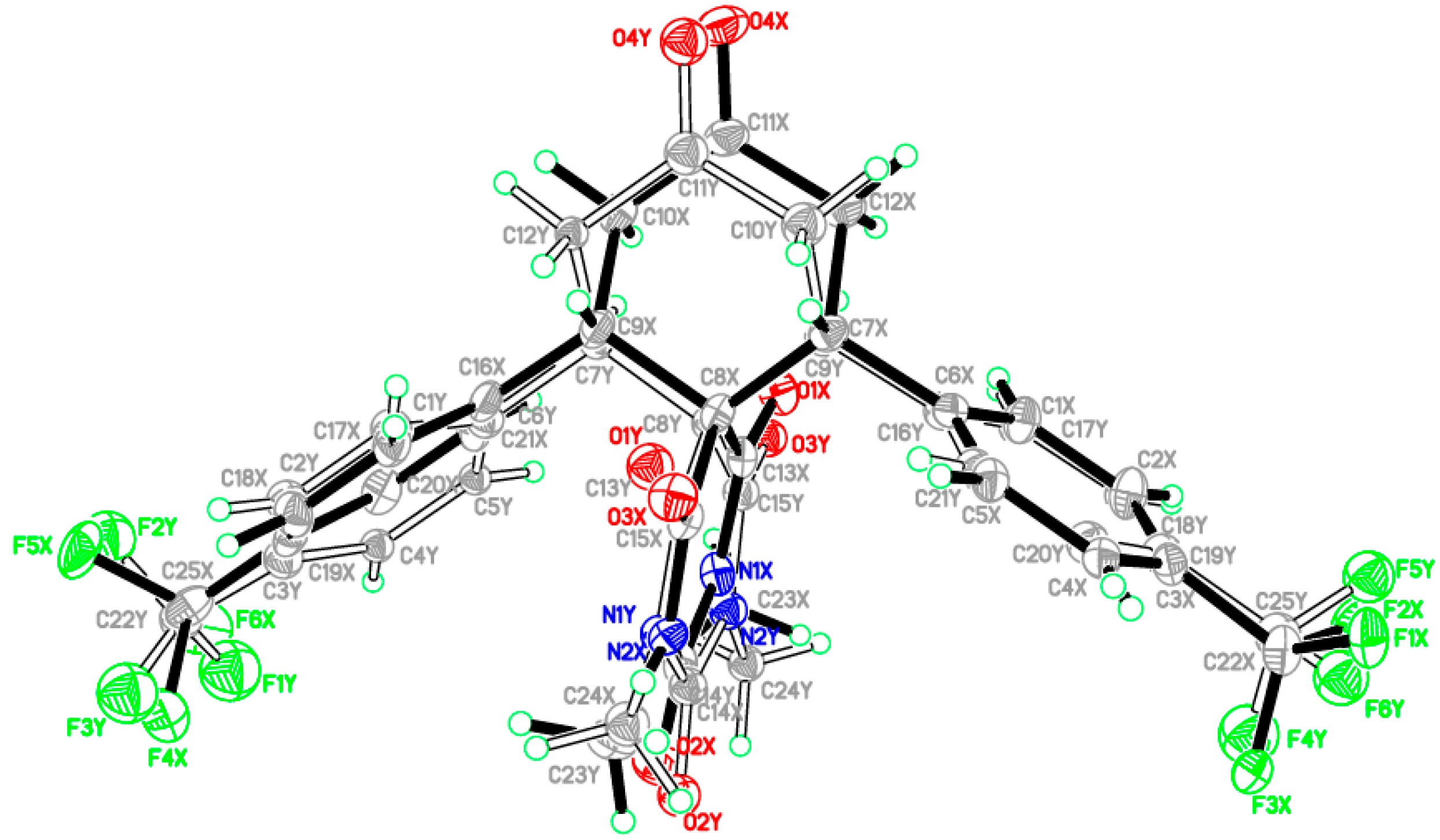
2.3. Computational Details
2.3.1. Optimized Molecular Geometry
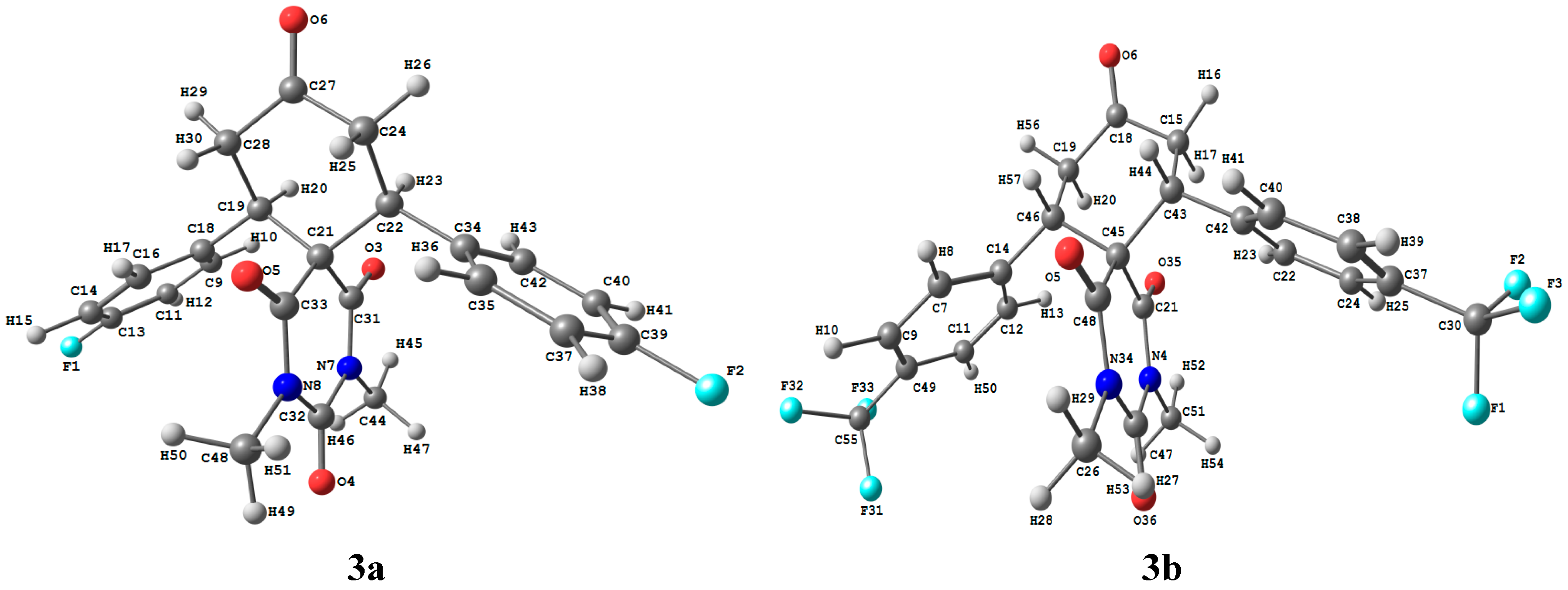
| 3a | 3b | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | −0.3468 | H29 | 0.2283 | F1 | −0.3625 | H29 | 0.2228 |
| F2 | −0.3468 | H30 | 0.2368 | F2 | −0.3629 | C30 | 1.1118 |
| O3 | −0.6191 | C31 | 0.7398 | F3 | −0.3634 | F31 | −0.3620 |
| O4 | −0.5981 | C32 | 0.8567 | N4 | −0.4888 | F32 | −0.3634 |
| O5 | −0.6260 | C33 | 0.7240 | O5 | −0.6182 | F33 | −0.3637 |
| O6 | −0.5416 | C34 | −0.0596 | O6 | −0.5377 | N34 | −0.4900 |
| N7 | −0.4909 | C35 | −0.1934 | C7 | −0.1889 | O35 | −0.6309 |
| N8 | −0.4889 | H36 | 0.2154 | H8 | 0.2176 | O36 | −0.5886 |
| C9 | −0.1784 | C37 | −0.2606 | C9 | −0.1661 | C37 | −0.1514 |
| H10 | 0.2162 | H38 | 0.2212 | H10 | 0.2209 | C38 | −0.1676 |
| C11 | −0.2624 | C39 | 0.4327 | C11 | −0.1643 | H39 | 0.2222 |
| H12 | 0.2221 | C40 | −0.2624 | C12 | −0.2038 | C40 | −0.1892 |
| C13 | 0.4327 | H41 | 0.2221 | H13 | 0.2178 | H41 | 0.2177 |
| C14 | −0.2606 | C42 | −0.1784 | C14 | −0.0235 | C42 | −0.0237 |
| H15 | 0.2212 | H43 | 0.2162 | C15 | −0.4814 | C43 | −0.1975 |
| C16 | −0.1934 | C44 | −0.3530 | H16 | 0.2295 | H44 | 0.2294 |
| H17 | 0.2154 | H45 | 0.2226 | H17 | 0.2381 | C45 | −0.1819 |
| C18 | −0.0596 | H46 | 0.2051 | C18 | 0.6236 | C46 | −0.1975 |
| C19 | −0.1937 | H47 | 0.2052 | C19 | −0.4813 | C47 | 0.8539 |
| H20 | 0.2275 | C48 | −0.3535 | H20 | 0.2382 | C48 | 0.7362 |
| C21 | −0.1845 | H49 | 0.2266 | C21 | 0.7232 | C49 | −0.1515 |
| C22 | −0.1937 | H50 | 0.2021 | C22 | −0.2037 | H50 | 0.2192 |
| H23 | 0.2275 | H51 | 0.2021 | H23 | 0.2179 | C51 | −0.3552 |
| C24 | −0.4814 | C24 | −0.1625 | H52 | 0.2223 | ||
| H25 | 0.2368 | H25 | 0.2174 | H53 | 0.2068 | ||
| H26 | 0.2283 | C26 | −0.3536 | H54 | 0.2069 | ||
| C27 | 0.6238 | H27 | 0.2061 | C55 | 1.1118 | ||
| C28 | −0.4814 | H28 | 0.2068 | H56 | 0.2294 | ||
2.3.2. Infrared Vibrational Studies
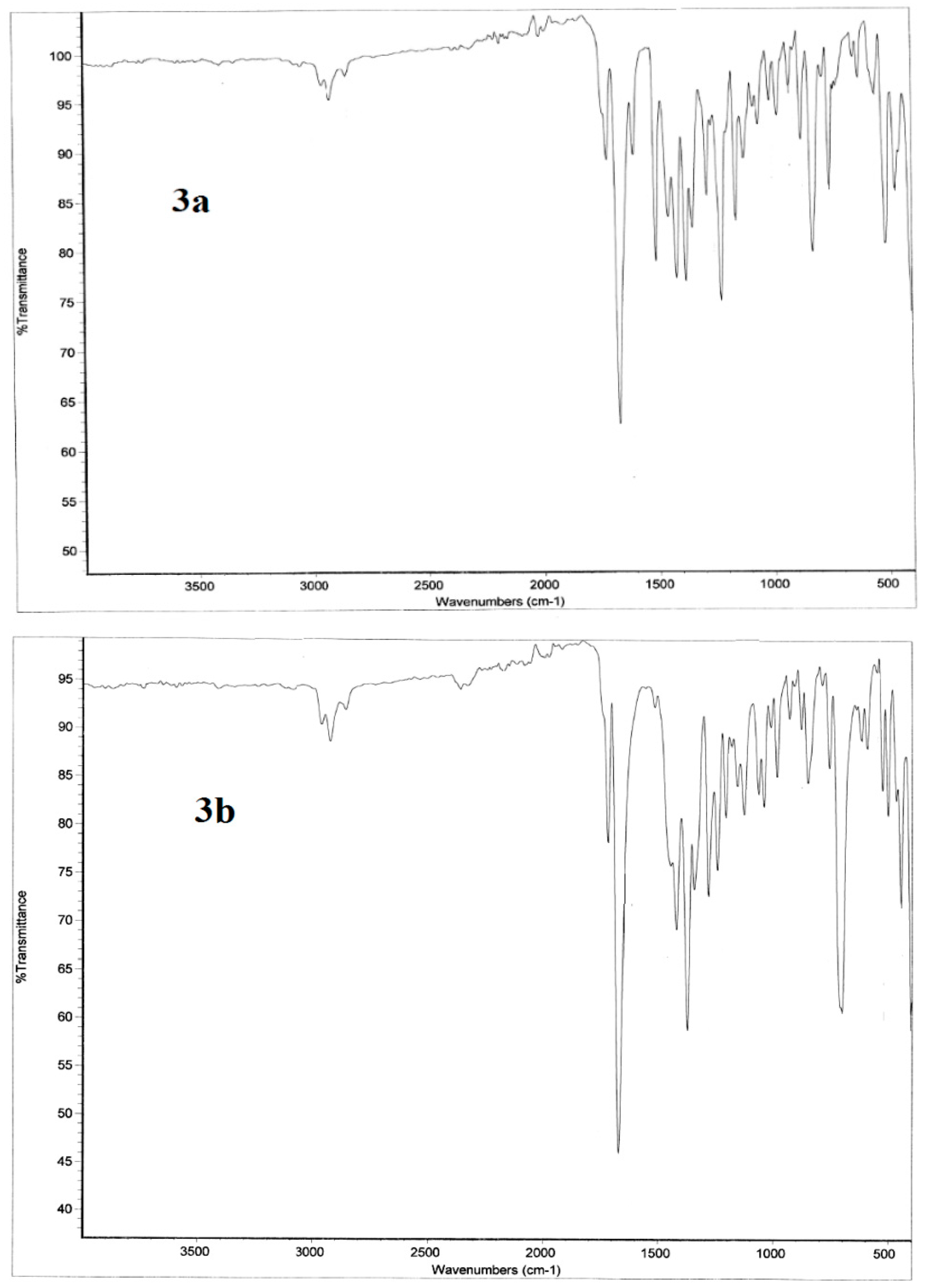
Region below 1650 cm−1
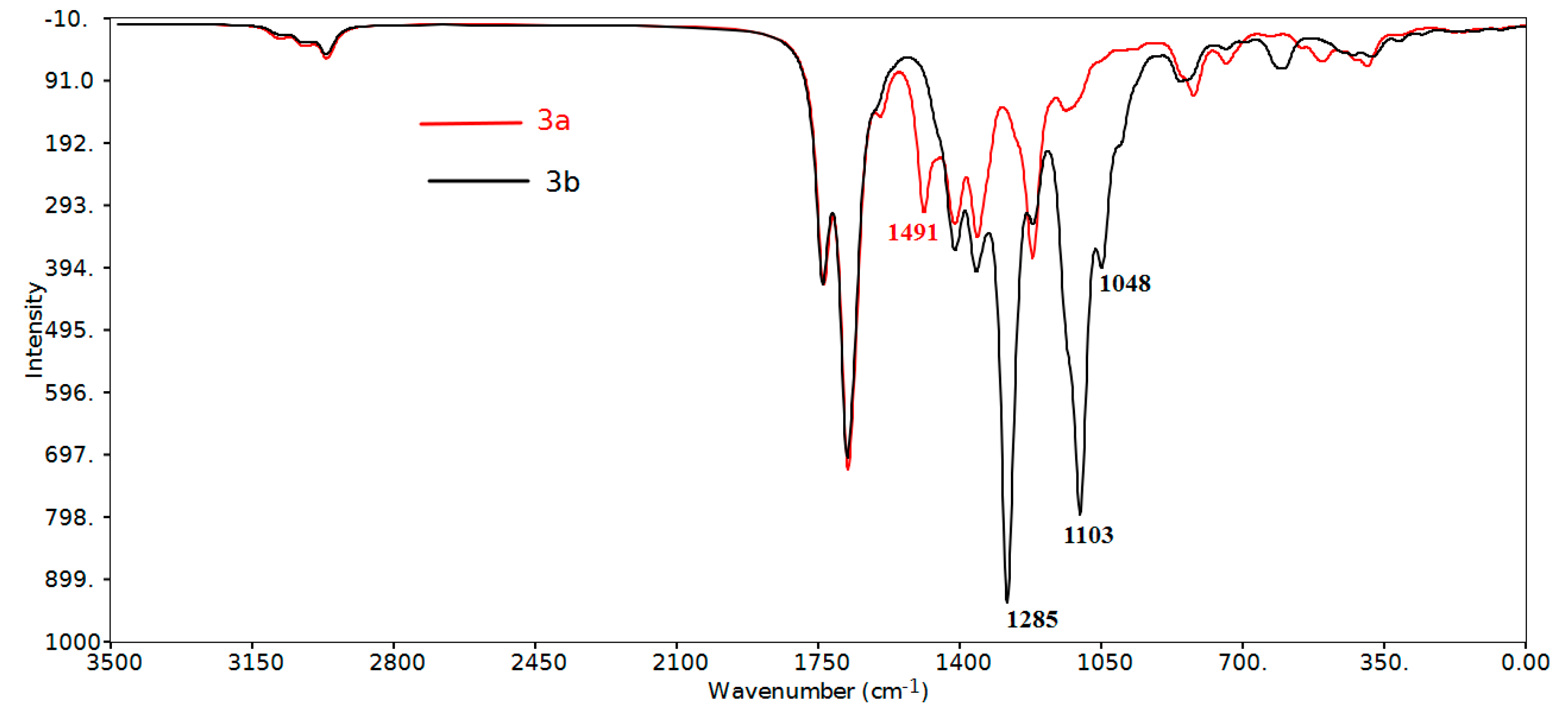
| Assignment | 3a | 3b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated | Experimental | Calculated | Experimental | |
| υ(CH, aromatic) | 3096, 3095, 3080, 3073 | 2956 | 3101–3093, 3082–3074 | 2956 |
| υ(CHasym, aliphatic) | 3087, 3084, 3033–3007 | 2921 | 3085, 3033–3008 | 2919 |
| υ(CHsym, aliphatic) | 2970–2952 | 2850 | 2971–2954 | 2851 |
| υ(C=O) | 1740–1668 | 1718-1688 | 1743–1661 | 1715–1669 |
| υC=C (aromatic) | 1595–1491 | 1604, 1508 | 1604–1497 | 1512 |
| δCH asym methyl | 1460–1449 | 1454 | 1463–1448 | 1448 |
| δCH sym methyl | 1422, 1403–1355 | 1378, 1349 | 1423, 1400–1355 | 1373, 1343 |
| δCH rocking CH2 | 1416–1404 | 1418 | 1416-1405 | 1419 |
| δCH aromatic in planea | 1492, 1491, 1281–998 | 1508, 1286–980 | 1497, 1300–1020 | 1512, 1281–1008 |
| υ(C-CF3) | 1285, 1284 | 1281 | ||
| υ(C-F) | 1223–1219 | 1224 | 1103, 1048 (asym) 1000 (sym) | 1038 (asym) 1008 (sym) |
| δCH aromatic out-of-plane | 948–806 | 928–784 | 965–823 | 980–847 |
Region above 1650 cm−1
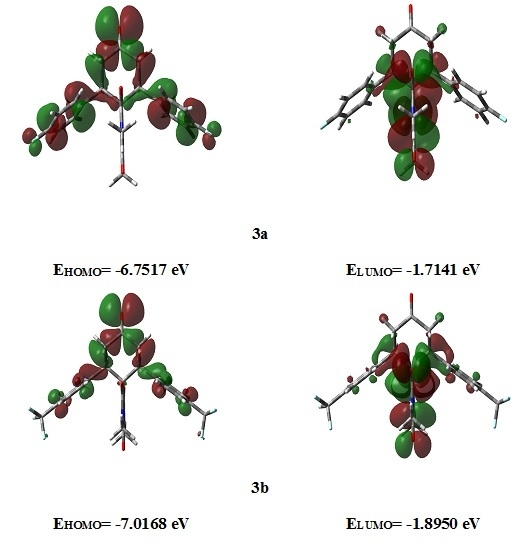
2.3.3. Frontier Molecular Orbitals
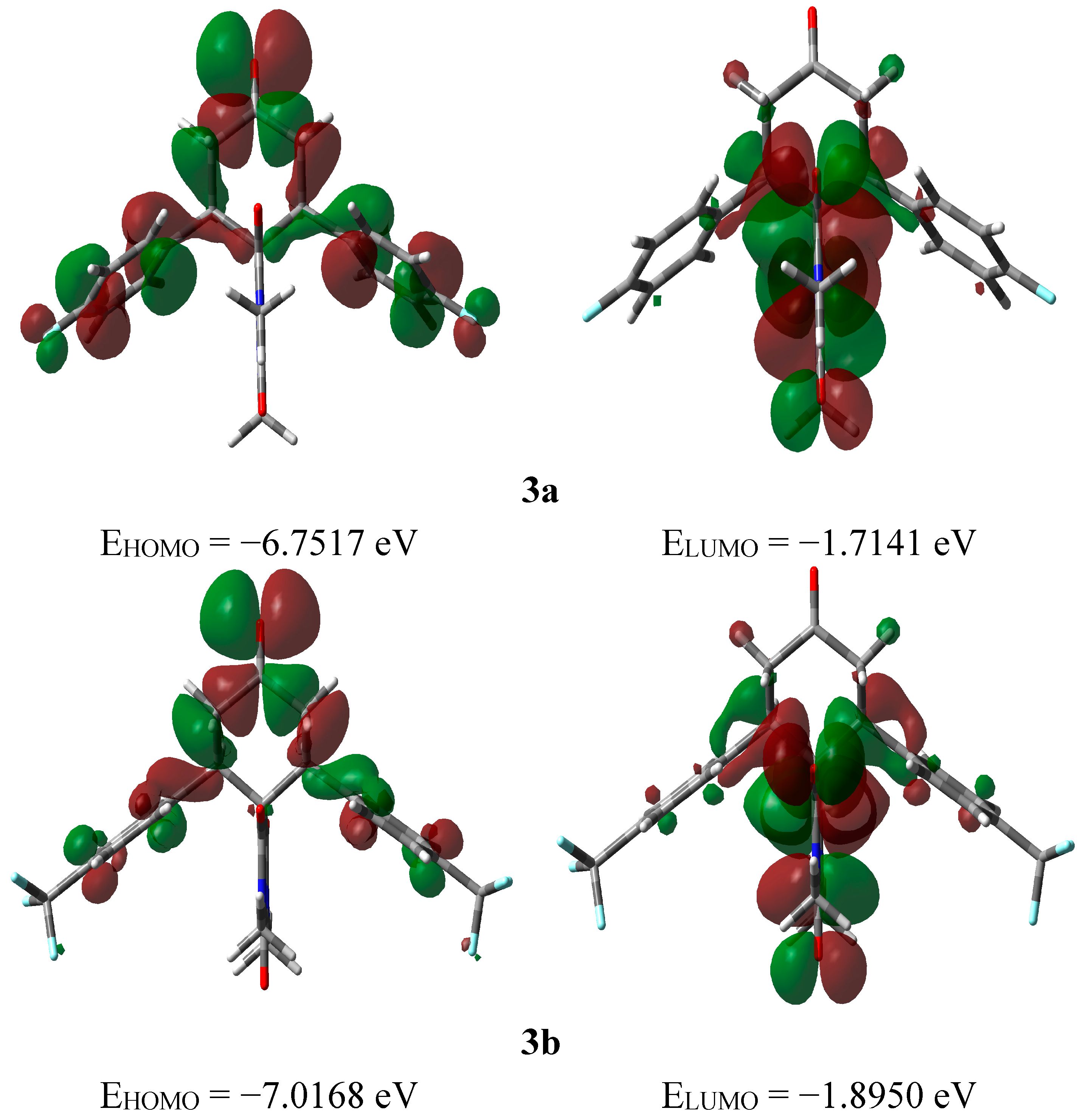
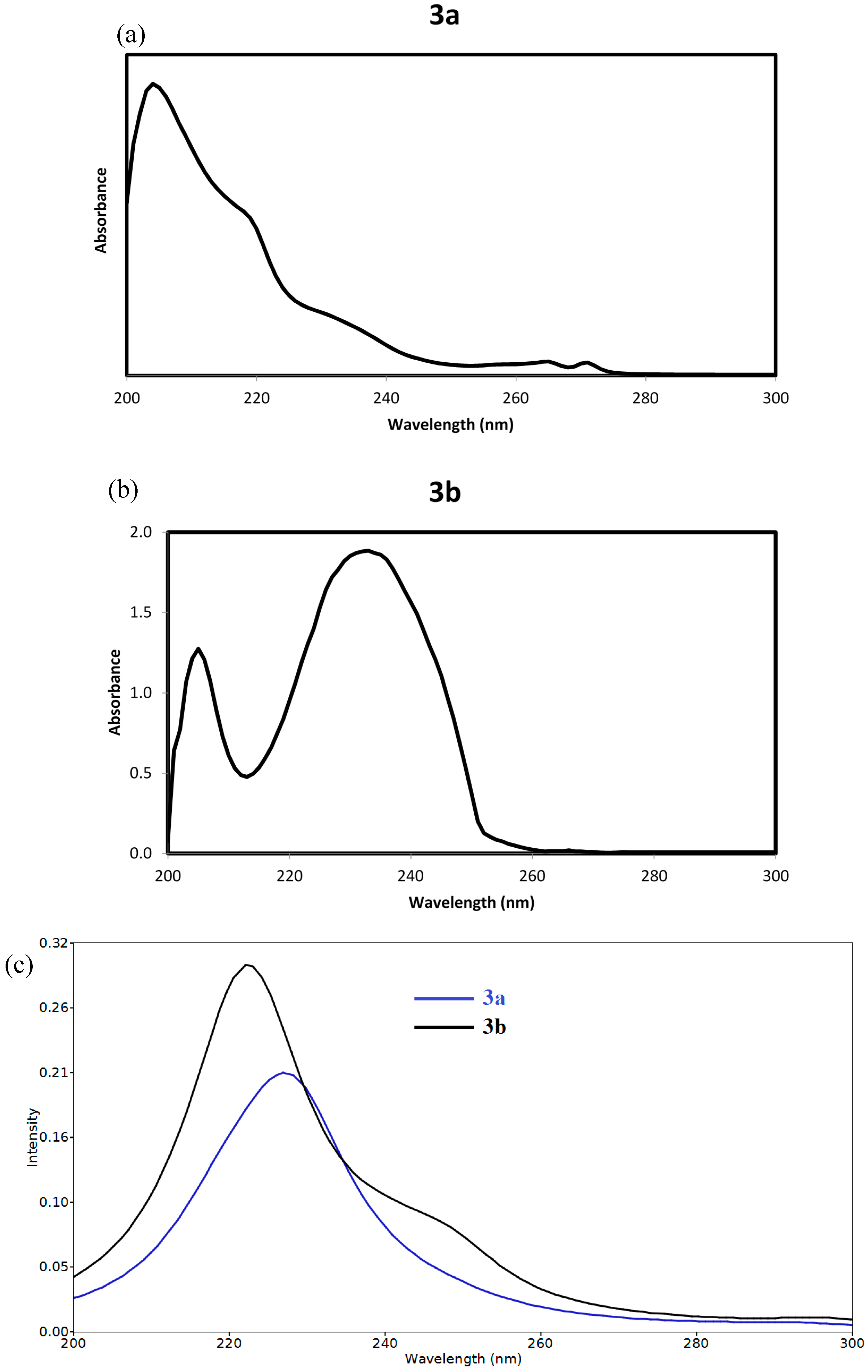
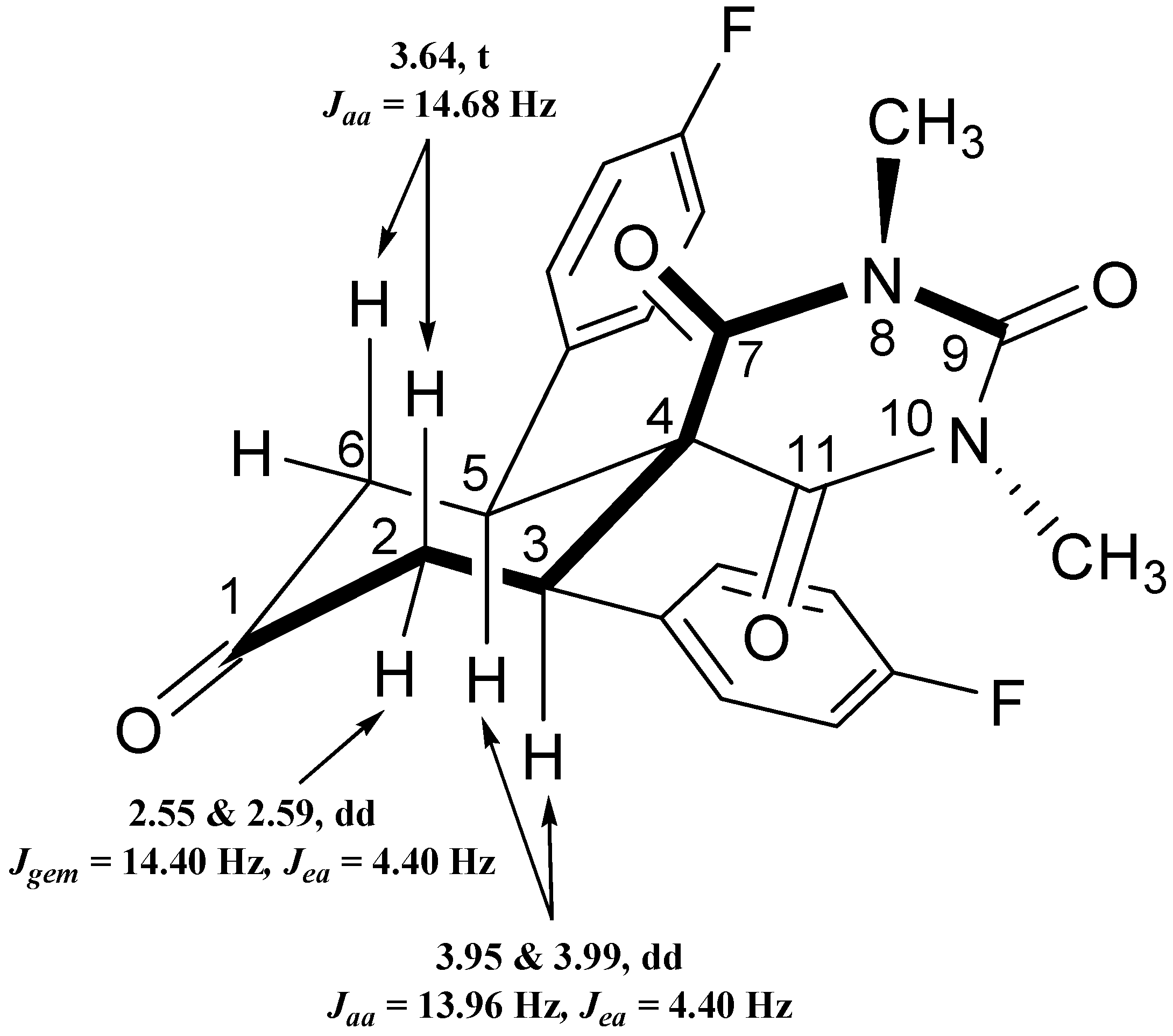
2.3.4. NMR Spectra
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. General Procedure of Double Michael Addition Reaction for the Synthesis of Spiro-Compounds 3a,b (GP1)
3.2.1. 7,11-bis(4-Fluorophenyl)-2,4-dimethyl-2,4-diazaspiro[5.5]undecane-1,3,5,9-tetraone (3a)
3.2.2. 2,4-Dimethyl-7,11-bis (4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2,4-diazaspiro[5.5]undecane-1,3,5,9-tetraone (3b)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pradhan, R.; Patra, M.; Behera, A.K.; Mishra, B.K.; Behera, R.K. A synthon approach to spiro compounds. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 779–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatholuvhu, M.S.; Sinclair, A.; Newton, A.F.; Alcaraz, M.-L.; Stockman, R.A.; Fuchs, P.L. A concise total synthesis of DL-histrionicotoxin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12656–12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.C.; Berrier, J.V.; Cocuzza, A.J.; Kobylecki, R.; McCormack, J.J. Pteridines. 41. Synthesis and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitory activity of some cycloalka[g]pteridines. J. Med. Chem. 1977, 20, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naydenova, E.; Pencheva, N.; Popova, J.; Stoyanov, N.; Lazarova, M.; Aleksiev, B. Aminoderivatives of cycloalkanespirohydantoins: Synthesis and biological activity. Il Farmaco 2002, 57, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Witkop, B.; Brossi, A.; Maleque, M.A.; Albuquerque, E.X. Total synthesis and electrophysiological properties of natural (–)-perhydrohistrionicotoxin, its unnatural (+) antipode and their 2-depentyl analogs. Helv. Chim. Acta 1982, 65, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Nagai, Y.; Ono, K.; Begum, K.; Wataya, Y.; Hamada, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Masuyama, A.; Nojima, M.; McCullough, K.J. Synthesis and antimalarial activity of novel medium-sized 1,2,4,5-tetraoxacycloalkanes. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 2357–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, D.M.; Qazi, N.A.; Sawant, S.D.; Bandey, A.H.; Srinivas, J.; Shankar, M.; Singh, S.K.; Verma, M.; Chashoo, G.; Saxena, A.; et al. Design and synthesis of spiro derivatives of parthenin as novel anti-cancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 3210–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastav, N.; Mittal, A.; Kumar, A. A novel chiral auxiliary from chiral spiranes. cis, cis-(+)-and (–)-spiro [4.4] nonane-1, 6-diol as chiral modifier in lithium aluminium hydride reduction of phenyl alkyl ketones. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 493–494. [Google Scholar]
- Longeon, A.; Guyot, M.; Vacelet, J. Araplysillins-I and -II: Biologically active dibromotyrosine derivatives from the sponge Psammaplysilla Arabica. Experentia 1990, 46, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.N.; Kandeel, M.M.; Said, M.M.; Ahmed, E.M. Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of some spiro compound derived from barbituric and thiobarbituric acids. Indian. J. Chem. Sect. B Org. Chem. Incl. Med. Chem. 1996, 35, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Kesharwani, S.; Sahu, N.K.; Kohli, D.V. Synthesis and biological evaluation of some new spiro derivatives of barbituric acid. Pharm. Chem. J. 2009, 43, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, R.K.; Behera, A.K.; Pradhan, R.; Pati, A.; Patra, M. Studies on spiroheterocycles Part-II: Heterocyclisation of the spiro compounds containing cyclohexanone and thiobarbituric acid with different bidentate nucleophilic reagents. Synth. Commun. 2006, 36, 3729–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, R.K.; Behera, A.K.; Pradhan, R.; Pati, A.; Patra, M. Phosphorus, Studies on spiroheterocycles part-III: Synthesis of diazaspiroundecanetetraone derivatives containing biological active heterocycles. Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2009, 184, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, B.; Sharma, S.; Bajaj, K.; Bansal, D.; Singh, T.; Malik, N.; Lata, S.; Tyagi, C.; Panwar, H.; Agarwal, A.; Kumar, A. Synthesis and CNS depressant of newer spirobarbiturates. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 67, 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Tamejiro, H.; Yamamoto, H. Organofluorine Compounds: Chemistry and Applications, 1st ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.K.; Kitteringham, N.L.; O’Neill, P.M. Metabolism of fluorine-containing drugs. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 443–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, P. Modern Fluoroorganic Chemistry; Wiley-VHC: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nyffeler, P.T.; Duron, S.G.; Burkart, M.D.; Vincent, S.P.; Wong, C.-H. Selectfluor: Mechanistic Insight and Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 44, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.L. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry: Recent therapeutic application of fluorinated small molecules. J. Fluor. Chem. 2006, 127, 1013–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinoiu, V. Chemical fluorination of organic compounds. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2007, 52, 219–234. [Google Scholar]
- Hagmann, W.K. The many roles for fluorine in medicinal chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4359–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filler, R.; Saha, R. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry: A century of progress and a 60 year retrospective of selected highlights. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 5, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janin, Y.L. Preparation and Chemistry of 3/5-Halogenopyrazoles. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3924–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Neumann, C.N.; Ritter, T. Introduction of Fluorine and Fluorine-Containing Functional Groups. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8214–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.J. Ueber die Addition von Natriumacetessig-und Natriummalonsäureäthern zu den Aethern ungesättigter Säuren. Prakt. Chem. 1887, 35, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.E. Comprehensive Organic Synthesis; Trost, B.M., Fleming, I., Semmelhack, M.F., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 4, pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter, P. Conjugate Addition Reactions in Organic Synthesis; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Barakat, A.; Islam, M.S.; Al Majid, A.M.A.; Al-Othman, Z.A. Highly Enantioselective Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of Indoles with α,β-Unsaturated Ketones with simple Cu(II)-Oxazoline-Imidazoline Catalysts. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 5185–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Al Majid, A.M.A.; Al-Othman, Z.A.; Barakat, A. Highly enantioselective Friedel-Crafts alkylation of indole with electron deficient trans-b-nitroalkenes using Zn(II)-oxazoline-imidazoline catalysts. Tetrahedron-Asymmetry 2014, 25, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Al-Najjar, H.J.; Al-Majid, A.M.; Soliman, S.M.; Mabkhot, Y.N.; Al-Agamy, M.H.M.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Fun, H-K. Synthesis, molecular structure investigations and antimicrobial activity of 2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1081, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Al Majid, A.M.A.; Al-Najjar, H.J.; Mabkhot, Y.N.; Sumaira, J.; Sammer, Y.; Choudhary, M.I. Zwitterionic pyrimidinium adducts as antioxidants with therapeutic potential as nitric oxide scavenger. Euro. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 84, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Barakat, A.; Al Majid, A.M.A.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Fun, H.-K.; Siddiqui, M.R. Stereoselective synthesis of diazaspiro[5.5]undecane derivatives via base promoted [5+1] double Michael addition of N,N-dimethylbarbituric acid to diaryliedeneacetones. Arab. J. Chem 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, 112, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, 148, 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R. Gaussian-03; Revision C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dennington, R., II; Keith, T.; Millam, J. Gauss View; Version 4.1.2; Semichem Inc.: Shawnee Mission, KS, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhurko, G.A.; Zhurko, D.A. ChemCraft: Tool for Treatment of Chemical Data, Late version build 08 (freeware). 2005. Available online: http://www.chemcraftprog.com (accessed on 5 May 2015).
- Glendening, E.D.; Reed, A.E.; Carpenter, J.E.; Weinhold, F. NBO; Version 3.1; TCI, University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sidir, I.; Sidir, Y.G.; Kumalar, M.; Tasal, E. Ab initio Hartree-Fock and density functional theory investigations on the conformational stability, molecular structure and vibrational spectra of 7-acetoxy-6-(2,3-dibromopropyl)-4,8-dimethyl -coumarin molecule. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 964, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, L.J. The Infrared Spectra of Complex Molecules; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Basseler, G.C.; Morill, C. Spectroscopic Identification of Organic Compounds; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B. Infrared Spectral Interpretation, A Systematic Approach; CRC Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dollish, F.R.; Fateley, W.G.; Bentley, F.F. Characteristic Raman Frequencies of Organic Compounds; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chamundeeswari, S.P.V.; Samuel, E.R.J.J.; Sundaraganesan, N. Theoretical and experimental studies on 2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1-imidazolyl)ethanol. Eur. J. Chem. 2011, 2, 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Fukui, K.; Yonezawa, T.; Shingu, H.J. A molecular-orbital theory of reactivity in aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmaja, L.; Ravikumar, C.; Sajan, D.; Joe, I.H.; Jayakumar, V.S.; Pettit, G.R.; Neilsen, F.O. Density functional study on the structural conformations and intramolecular charge transfer from the vibrational spectra of the anticancer drug combretastatin–A2. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, C.; Joe, I.H.; Jayakumar, V.S. Charge transfer interactions and nonlinear optical properties of push-pull chromophore benzaldehyde phenylhydrazone: A vibrational approach. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 460, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göğer, N.G.; Parlatan, H.K.; Basan, H.; Berkkan, A.; Özden, T. Quantitative determination of azathioprine in tablets by H NMR spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 21, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, A.; Al-Najjar, H.J.; Al-Majid, A.M.; Soliman, S.M.; Mabkhot, Y.N.; Rafi Shaik, M.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Fun, H.-K. Synthesis, NMR, FT-IR, X-ray structural characterization, DFT analysis and Isomerism aspects of 5-(2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2015, 147, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples 3a,b are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.S.; Al-Majid, A.M.; Barakat, A.; Soliman, S.M.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Quah, C.K.; Fun, H.-K. Synthesis, Molecular Structure and Spectroscopic Investigations of Novel Fluorinated Spiro Heterocycles. Molecules 2015, 20, 8223-8241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058223
Islam MS, Al-Majid AM, Barakat A, Soliman SM, Ghabbour HA, Quah CK, Fun H-K. Synthesis, Molecular Structure and Spectroscopic Investigations of Novel Fluorinated Spiro Heterocycles. Molecules. 2015; 20(5):8223-8241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058223
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Mohammad Shahidul, Abdullah Mohammed Al-Majid, Assem Barakat, Saied M. Soliman, Hazem A. Ghabbour, Ching Kheng Quah, and Hoong-Kun Fun. 2015. "Synthesis, Molecular Structure and Spectroscopic Investigations of Novel Fluorinated Spiro Heterocycles" Molecules 20, no. 5: 8223-8241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058223
APA StyleIslam, M. S., Al-Majid, A. M., Barakat, A., Soliman, S. M., Ghabbour, H. A., Quah, C. K., & Fun, H.-K. (2015). Synthesis, Molecular Structure and Spectroscopic Investigations of Novel Fluorinated Spiro Heterocycles. Molecules, 20(5), 8223-8241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058223