Chemical Constituents and Structural Characterization of Polysaccharides from Four Typical Bamboo Species Leaves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Components and Content of Polysaccharides in Different Bamboo Leave Varieties
| No. | Varieties of Bamboo Leaves | Total Polysaccharides (%) | Rhamnose (%) | Arabinose (%) | Xylose (%) | Mannose (%) | Glucose (%) | Galactose (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P. praecox C.D. Chu et C.S. Chao | 1.4 | 3.2 | 14.0 | 48.8 | 4.7 | 15.9 | 13.1 |
| 2 | CV. Ventricousinternode | 1.5 | 4.6 | 16.3 | 50.3 | 1.4 | 17.2 | 10.1 |
| 3 | Bambusa multiplex cv. Alphonse-Karr | 1.5 | 2.7 | 16.4 | 44.2 | - | 20.7 | 15.7 |
| 4 | P. elegans McClure | 1.6 | 1.1 | 15.9 | 56.1 | - | 15.3 | 11.3 |
| 5 | Sasa pygmaea (Miq.) E. G. Camus | 1.6 | 2.5 | 17.4 | 55.5 | 0.9 | 13.6 | 9.7 |
| 6 | Pseudosasa viridula S. L. Chen et G. Y. Sheng | 1.9 | 6.7 | 13.8 | 50.2 | 1.6 | 18.4 | 10.6 |
| 7 | P. heterocycla (Carr.) Mitford cv. Pubescens | 1.9 | 2.6 | 14.2 | 58.5 | - | 16.1 | 8.3 |
| 8 | P. vivax McClure Aureocaulis | 1.9 | 1.2 | 14.5 | 59.2 | - | 14.7 | 10.2 |
| 9 | P. viridis | 2.0 | 2.1 | 15.2 | 62.7 | 0.8 | 10.2 | 8.6 |
| 10 | Bambusa albo-lineata (McClure) Chia | 2.2 | 1.8 | 20.5 | 56.0 | - | 12.3 | 9.1 |
| 11 | P. propinqua McClure | 2.2 | 1.1 | 17.0 | 56.2 | - | 15.1 | 10.2 |
| 12 | P. glauca McClure | 2.2 | 1.4 | 14.5 | 57.5 | 1.3 | 16.0 | 8.9 |
| 13 | Phyllostachys | 2.2 | 2.2 | 18.0 | 54.6 | - | 16.8 | 7.7 |
| 14 | P. heterocycla cv. Huamozhu | 2.3 | 0.6 | 14.2 | 56.4 | - | 19.9 | 8.5 |
| 15 | P. propinqua McClure | 2.5 | - | 14.7 | 56.7 | - | 17.6 | 10.8 |
| 16 | Bambusa ventricosa McClure | 2.7 | - | 19.6 | 52.8 | - | 16.2 | 11.4 |
| 17 | Bambusa multiplex (Lour.) Raeusch. ex Schult. | 2.8 | - | 17.6 | 48.9 | - | 20.6 | 12.9 |
| 18 | Sinobambusa tootsik(sieb.) Makino | 2.8 | 2.3 | 15.9 | 47.6 | 1.6 | 20.0 | 12.4 |
| 19 | P. heterocycla (Carr.) Mit Ford | 2.8 | 1.3 | 13.6 | 58.0 | - | 16.4 | 10.4 |
| 20 | Pseudosasa amabilis (McClure) | 2.9 | - | 18.6 | 60.2 | - | 11.7 | 9.5 |
| 21 | P. aureosuleata McClure cv. Pekinensis | 2.9 | - | 14.5 | 57.5 | - | 19.0 | 8.9 |
| 22 | P. iridescins C.Y.Yao et S.Y.Chen | 2.9 | - | 17.2 | 57.2 | - | 16.8 | 8.5 |
| 23 | P. aureosulcata f. spectabilis | 3.1 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 48.9 | 1.2 | 21.2 | 11.5 |
| 24 | P. gramineus (Bean) Nakai | 3.2 | 1.8 | 15.7 | 53.7 | 0.6 | 19.6 | 8.2 |
| 25 | Bambusa rutila McClure | 3.3 | 3.7 | 11.3 | 55.9 | 0.4 | 18.1 | 10.5 |
| 26 | Pleioblastus amarus (Keng) keng | 3.7 | 0.8 | 21.2 | 52.4 | - | 14.2 | 11.4 |
| 27 | Pleioblastus kongosanensis f. aureostriaus | 3.9 | 4.7 | 17.6 | 47.9 | 0.5 | 16.2 | 12.9 |
| 28 | Cyperus alternifolius | 3.9 | 5.3 | 15.7 | 53.7 | 2.2 | 12.3 | 10.8 |
| 29 | P. nigra (Lodd.) Munro | 5.4 | - | 15.4 | 30.2 | - | 20.1 | 34.1 |
| 30 | P. vivax McClure | 4.7 | - | 21.3 | 33.2 | - | 17.4 | 27.8 |
| 31 | Chimonobambusa quadrangularis (Fenzi) Makino | 4.6 | - | 21.6 | 29.8 | - | 16.8 | 31.4 |
| 32 | P. bambussoides cv.Tanakae | 4.2 | - | 24.6 | 32.6 | - | 20.8 | 21.5 |
2.2. Purification of BLPS by Sevag and Ion Exchange Resin

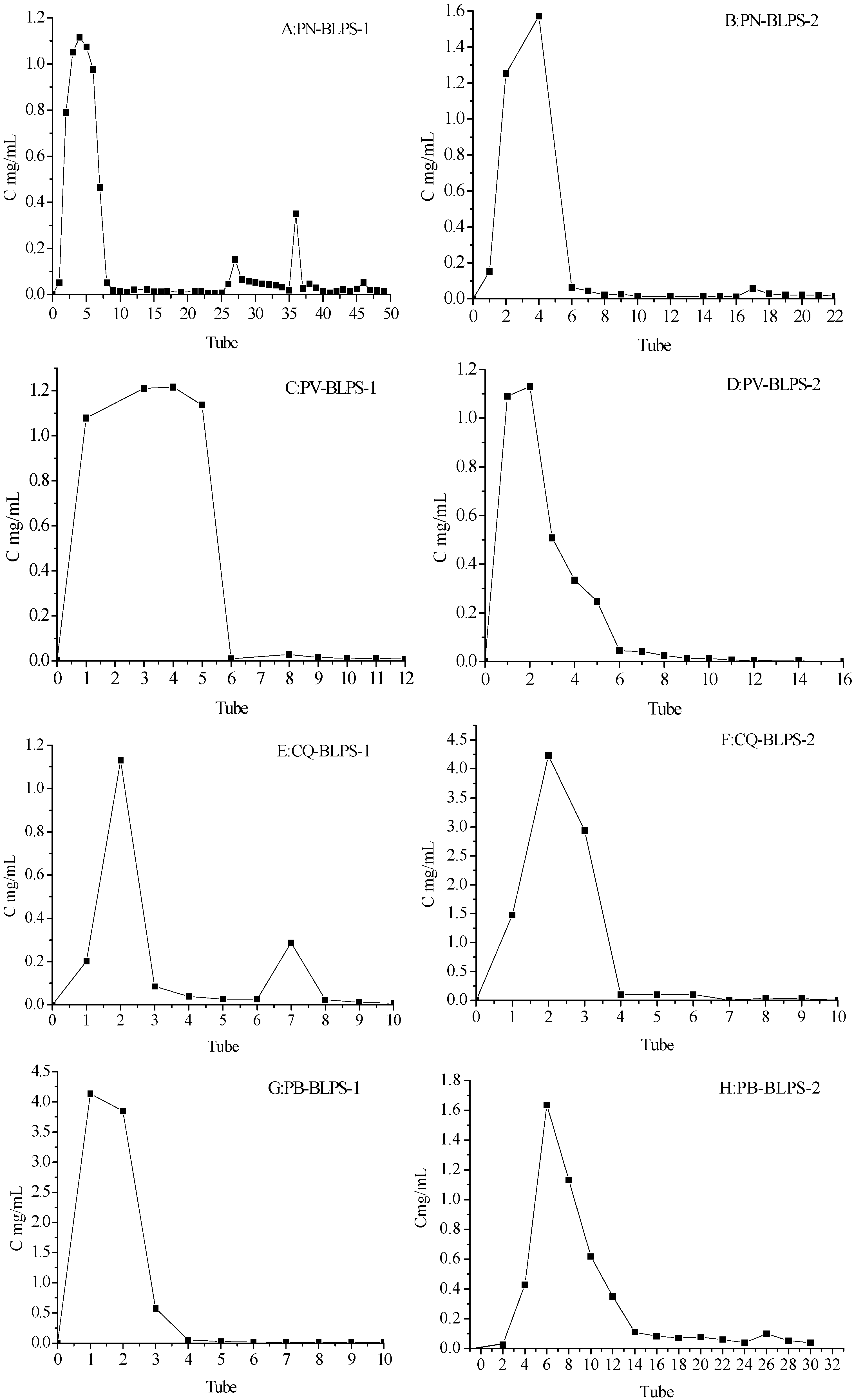
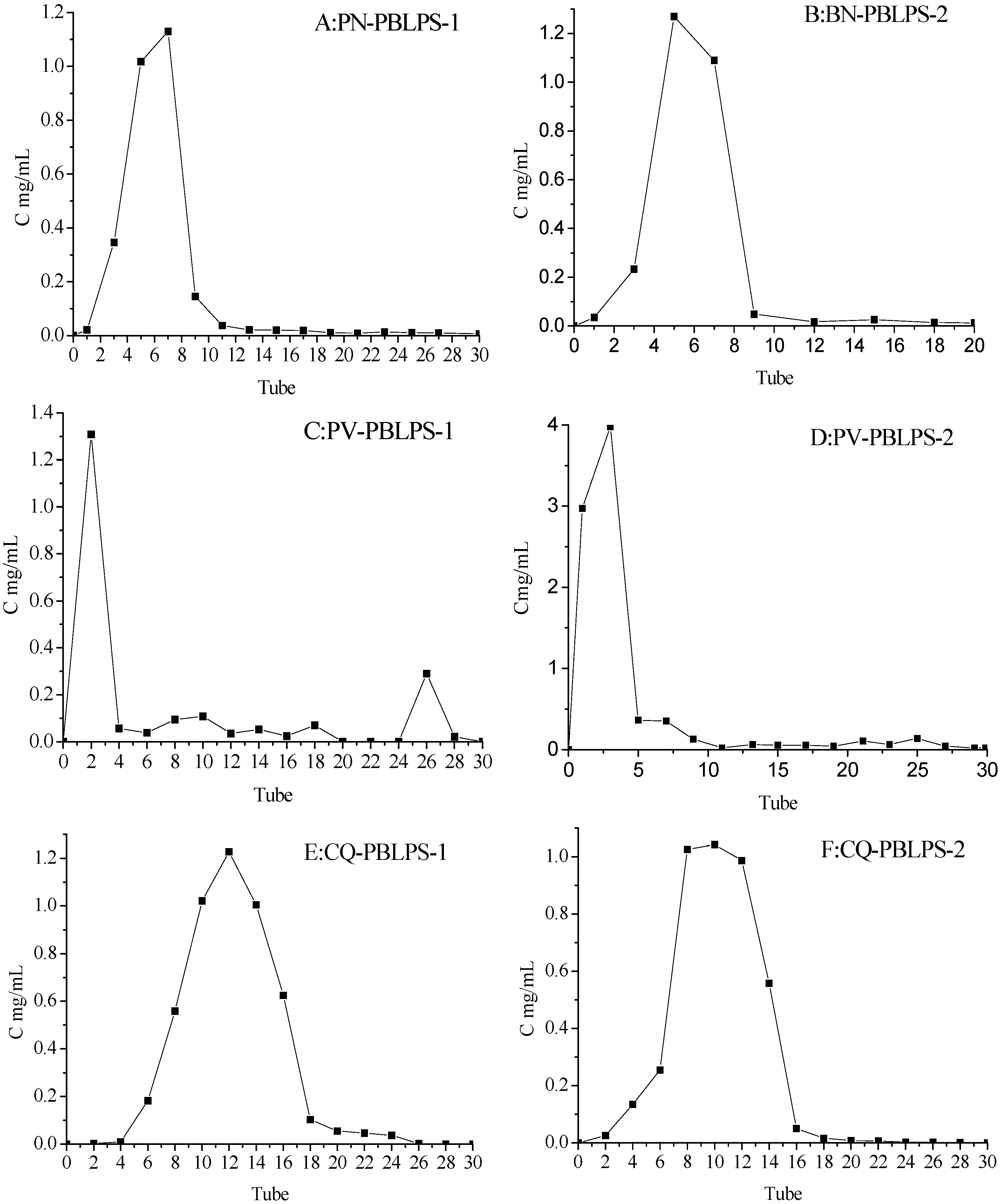
2.3. Seperation of DPS by DEAE-52 Cellulose and Sephadex Gel Chromatography

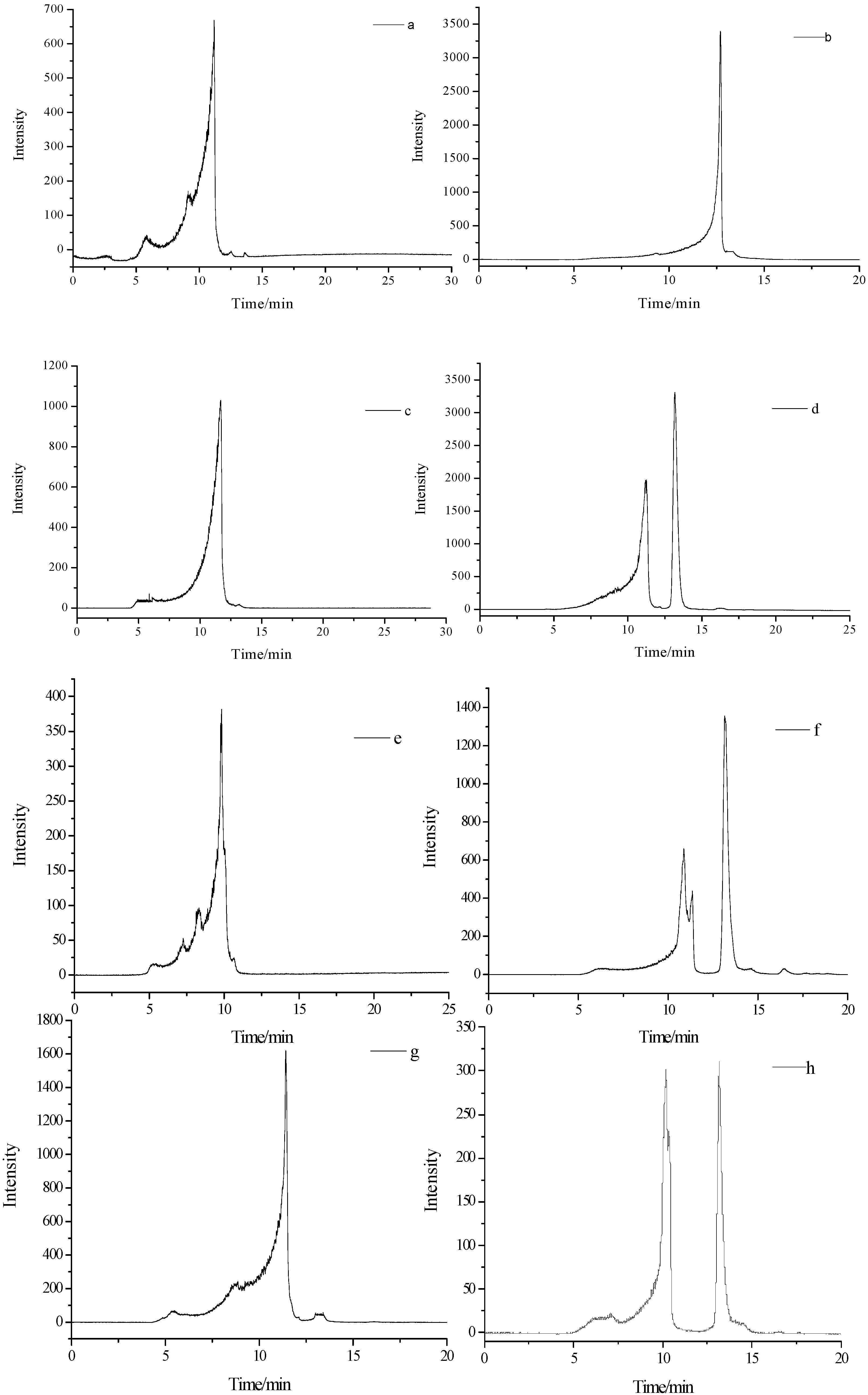
2.4. Molecular Weight of PBLPS
2.5. Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FTIR) Spectroscopy of PBLPS

2.6. NaIO4-HIO4 Oxidation and Smith Degradation of PBLPS-1

3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Apparatus and Chemicals
3.3. Experimental Methods
3.3.1. Colorimetric Analysis of BLPS
- C: concentration of polysaccharides from the linear regression equation, μg/mL
- V: volume of polysaccharide, mL
- w: sample weight of bamboo leaves, g
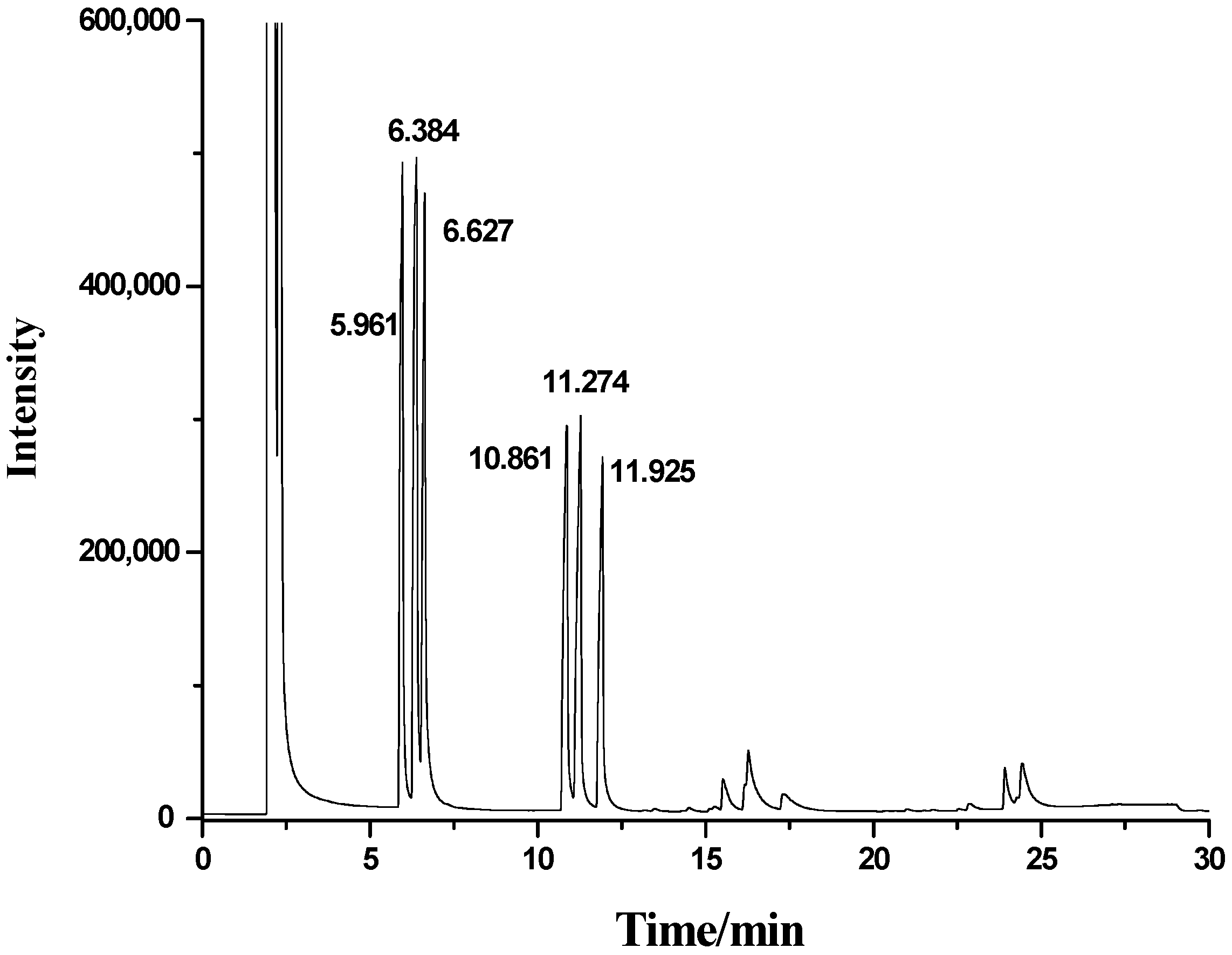
3.3.2. Gas Chromatography
3.3.3. Extraction and Purification of BLPS
3.3.4. Ion-Exchange and Sephadex Gel Chromatography of DPS
3.3.5. Determination of Relative Molecular Weight of PBLPS
3.3.6. Fourier Transform Infra-Red Spectroscopy (FTIR) of PBLPS
3.3.7. NaIO4—HIO4 Oxidation and Smith Reduction of PBLPS
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aspinall, G.O.; Mahomed, R.S. The constitution of a wheat-straw xylan. J. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 1731–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.F.; Sun, R.C.; Fowler, P.; Baird, M.S. Extraction and characterization of original lignin and hemicelluloses from wheat straw. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuya, H.; Ayumi, T.; Akiko, H.; Fumihide, T.; Tomihisa, O. Antioxidant C-glycosyl flavones from the leaves of Sasa kurilensis varigantean. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuke, E.; Tadashi, I. Hemicelucosic polysaccharides from bamboo shoot cell-walls. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.Q.; Yuan, K.; Zhu, M.X. GC-MS analysis of chemical constituents of the essential oil from Phyllostachys pubescens. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2009, 29, 954–960. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.B.; Yao, H.; Bao, G.H.; Zhang, H.P.; Qin, G.W. Flavone glucosides with immunomodulatory activity from the leaves of Pleioblastus amarus. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, J.J.; Liu, C.M.; Wu, X.Q.; Zhang, Y. Isolation and purification of four flavone C-glycosides from antioxidant of bamboo leaves by macroporous resin column chromatography and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.Y.; Wu, X.Q.; Tie, X.W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Toxicology and safety of antioxidant of bamboo leaves. Part 1, Acute and subchronic toxicity studies on antioxidant of bamboo leaves. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 783–792. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.L.; Ding, X.L. Study on extraction isolation and biological activity of bamboo-leaves polysaccharide. Food Res. Dev. 2000, 21, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.Q.; Yue, Y.D.; Peng, Z.H. Evaluation of extracts from bamboo for biological activity against CULEX PIPIENS PALLENS. Entomol. Sin. 2004, 11, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Ikm, I.; Krylova, R.G.; Usvo, A.I. Preliminary investigation of the water-soluble polysaccharides from the leaves of the bamboo sasamorpha chiisanensis. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1987, 23, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Shiozawa, R.; Takeda, S.; Ito, S.; Matsuda, K. Structural investigation of a β-d-glucan and a xyloglucan from bamboo—shoot cell—walls. Carbohydr. Res. 1982, 109, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Saito, T.; Uchiyama, M.; Okiya, S. Isolation of hemicelluloses from Yakushima bamboo and their growth inhibitory activities against S180 tumor. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1968, 16, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.Z.; Chen, W.Y.; Wang, C.Z. Screening of Polysaccharide and study on their analysis forhigh quality bamboo leaves. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2008, 10, 268–270. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.C.; Wang, C.Z.; Chen, W.Y. Sutdy on Chemical Characteristics and Content of Polvsaccharides from Bamboo Leaves of Different Species. Chem. Ind. For. Prod. 2009, 29, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Xie, B. Analysis of the active components in bamboo leaves and the anti-microbial effect of their Extracts. J. Cent. South For. Univ. 2004, 24, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y. Chain conformation and rheological behavior ofan extracellular heteropolysaccharide Erwinia gum in aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singthong, J.; Ningsanond, S.; Cui, S.W. Extraction and physicochemical characterization of polysaccharide gum from Yanang leaves. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacurakova, M.; Wilson, R.H. Developments in mid-infrared FTIR spectroscopy of selected carbohydrated. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 44, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L.M. Chemical structural and chain conformation characterization of some bioactive polysacchrides isolated from natural source. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whistler, R.L.; Wolfrom, M.L. Periodate oxidation: De-termination of periodate, Methods. Carbohydr. Chem. 1962, 1, 435–441. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.-Z.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Li, W.-J.; Ye, J.-Z. Chemical Constituents and Structural Characterization of Polysaccharides from Four Typical Bamboo Species Leaves. Molecules 2015, 20, 4162-4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20034162
Wang C-Z, Zhang H-Y, Li W-J, Ye J-Z. Chemical Constituents and Structural Characterization of Polysaccharides from Four Typical Bamboo Species Leaves. Molecules. 2015; 20(3):4162-4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20034162
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cheng-Zhang, Hong-Yu Zhang, Wen-Jun Li, and Jian-Zhong Ye. 2015. "Chemical Constituents and Structural Characterization of Polysaccharides from Four Typical Bamboo Species Leaves" Molecules 20, no. 3: 4162-4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20034162
APA StyleWang, C.-Z., Zhang, H.-Y., Li, W.-J., & Ye, J.-Z. (2015). Chemical Constituents and Structural Characterization of Polysaccharides from Four Typical Bamboo Species Leaves. Molecules, 20(3), 4162-4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20034162





