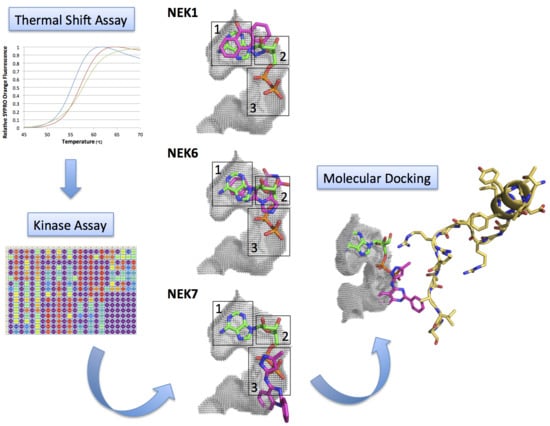
Kinase Inhibitor Profile for Human Nek1, Nek6, and Nek7 and Analysis of the Structural Basis for Inhibitor Specificity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Screening of ATP-Competitive Inhibitors for Recombinant Human Neks 1, 2, 6, and 7 by Thermal Shift Assay
| Nek | CAS Number | Compound Description | Δ Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nek1(Δ262-1258)-(T162A) | 667463-62-9 | GSK-3 Inhibitor IX | 3.5 |
| Nek1(Δ262-1258)-(T162A) | 444723-13-1 | Cdk2 Inhibitor IV, NU6140 | 3.1 |
| Nek1(Δ262-1258)-(T162A) | 879127-16-9 | Aurora Kinase Inhibitor III | 3.6 |
| Nek1(Δ262-1258)-(T162A) | 443798-55-8 | Cdk1/2 Inhibitor III | 2.6 |
| Nek1(Δ262-1258)-(T162A) | 220792-57-4 | Aminopurvalanol A | 2.5 |
| Nek1(Δ262-1258)-(T162A) | 4129-56-6 | JNK Inhibitor II | 4.0 |
| Nek2(Δ272-445)-(T175A) | 220792-57-4 | Aminopurvalanol A | 4.0 |
| Nek2(Δ272-445)-(T175A) | 866405-64-3 | AMPK Inhibitor, Compound C | 2.5 |
| Nek2(Δ272-445)-(T175A) | 326914-10-7 | SU11652 | 9.6 |
| Nek2(Δ272-445)-(T175A) | 4129-56-6 | JNK Inhibitor II | 4.8 |
| Nek2(Δ272-445)-(T175A) | 97161-97-2 | K-252a, Nocardiopsis sp. | 5.4 |
| Nek2(Δ272-445)-(T175A) | 522629-08-9 | MNK1 Inhibitor | 2.1 |
| Nek2(Δ272-445)-(T175A) | 545380-34-5 | NF-kB Activation Inhibitor | 4.2 |
| Nek2(Δ272-445)-(T175A) | 601514-19-6 | GSK3b Inhibitor XII, TWS119 | 2.3 |
| Nek6(S206A) | 62996-74-1 | Staurosporine, Streptomyces sp. | 2.1 |
| Nek6(S206A) | 852527-97-0 | Alsterpaullone, 2-Cyanoethyl | 2.5 |
| Nek6(S206A) | 244148-46-7 | Isogranulatimide | 6.5 |
| Nek7wt | 345987-15-7 | JNK Inhibitor V | 4.9 |
| Nek7wt | 443798-55-8 | Cdk1/2 Inhibitor III | 4.2 |
| Nek7wt | 135897-06-2 | SB 218078 | 11.5 |
| Nek7wt | 152121-53-4 | PD 169316 | 4.4 |
| Nek7wt | 62996-74-1 | Staurosporine, Streptomyces sp. | 3.2 |
| Nek7wt | 97161-97-2 | K-252a, Nocardiopsis sp. | 8.8 |
| Nek7wt | 244148-46-7 | Isogranulatimide | 8.3 |
| Nek7wt | 404828-08-6 | GSK-3 Inhibitor XIII | 4.3 |
| Nek7wt | 220792-57-4 | Aminopurvalanol A | 3.0 |
| Nek7wt | 41179-33-3 | MK2a Inhibitor | 5.3 |
| Nek7wt | 854171-35-0 | Indirubin Derivative E804 | 9.7 |
| Nek7wt | 160807-49-8 | Indirubin-3'-monoxime | 7.9 |
| Nek7wt | 487021-52-3 | GSK-3b Inhibitor VIII | 3.3 |
| Nek7wt | 4129-56-6 | JNK Inhibitor II | 2.6 |
| CompoundDescription | Nek6wt | Nek6wtD | Nek6(S206A) | Nek6(S206A)D | Nek6(Δ1-44) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alsterpaullone | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.4 | 2.9 | −0.5 |
| Alsterpaullone, 2-Cyanoethyl | 0.0 | −0.1 | 2.5 | 2.5 | −0.2 |
| Aminopurvalanol A | 0.3 | −1.8 | 0.8 | _ | −0.2 |
| Aminopyrazole1 | −0.4 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 2.4 | 0.0 |
| AR-A014418 | 0.3 | −0.5 | 1.4 | 2.6 | −0.2 |
| Indolinone1 | _ | −0.4 | −0.2 | 2.1 | −0.5 |
| Indolocarbazole1 | −0.3 | −0.1 | 1.7 | 0.7 | −1.3 |
| Isogranulatimide | 1.2 | 0.6 | 6.5 | 2.3 | −0.7 |
| JNJ-7706621 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 2.1 | −0.7 |
| Pyrazolanthrone | 0.3 | −1.1 | 1.8 | 2.3 | 0.1 |
| Staurosporine | 0.3 | −0.7 | 2.1 | 2.3 | _ |
| TPCA-1 | 0.0 | −0.7 | 0.9 | 2.0 | −1.7 |
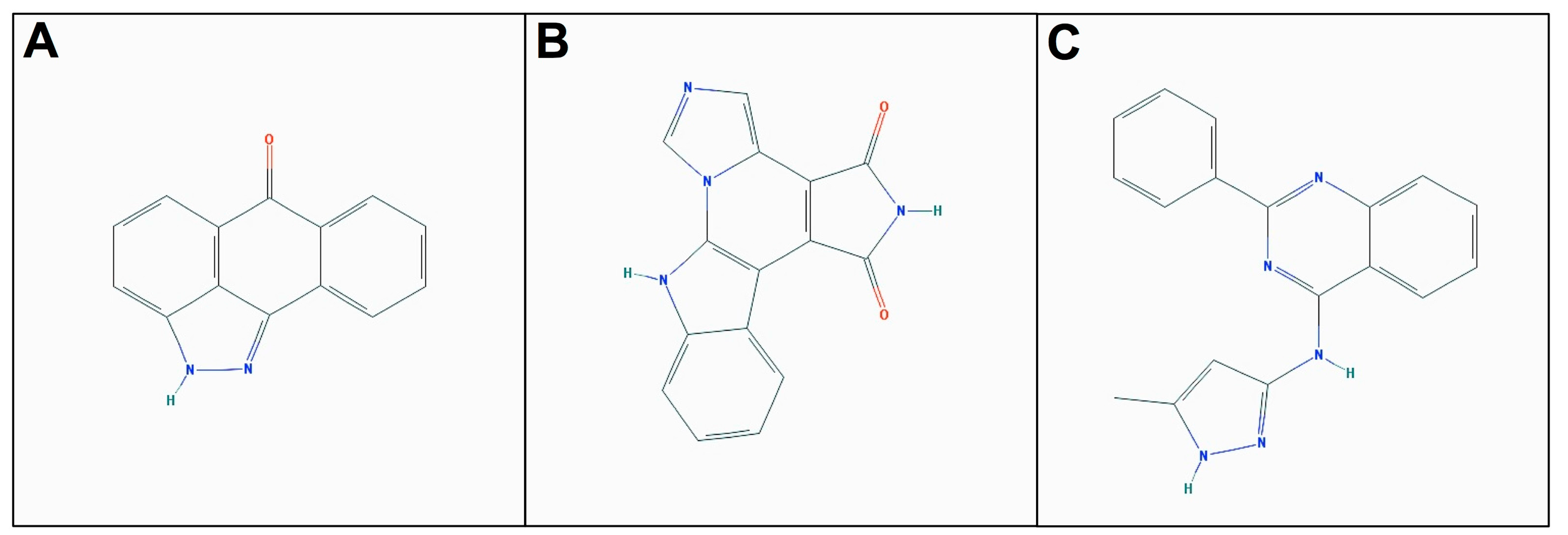
2.2. Kinase Assays of Selected Candidate Compounds for Recombinant Human Neks 1, 6, and 7
2.3. Molecular Docking of Selected Inhibitors for Recombinant Human Neks 1, 6, and 7
| Nek | CAS Number | Compound Description | ΔTm (°C) | Docked/Predicted Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Phosphorylation (%) 2× b | Phosphorylation (%) 1× b | Phosphorylation (%) 0.5× b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nek1(Δ262-1258)-(T162A) | 4129-56-6 | JNK Inhibitor II | 4.0 | −7.345 | 71.5 ± 0.1 | 87.3 ± 18.3 | - |
| Nek6(S206A) | 244148-46-7 | Isogranulatimide a | 6.5 | −8.917 | - | 74.9 ± 10.4 | 100.2 ± 1.3 |
| Nek7wt | 220792-57-4 | Aminopurvalanol A | 3.0 | −8.626 | 41.0 ± 13.5 | 35.9 ± 3.3 | 64.4 ± 3.4 |
| Nek7wt | 487021-52-3 | GSK-3b Inhibitor VIII | 3.3 | −7.572 | 58.1 ± 3.2 | 47.5 ± 4.4 | 44.3 ± 3.3 |
| Nek7wt | 404828-08-6 | GSK-3 Inhibitor XIII | 4.3 | −8.629 | 46.3 ± 2.9 | - | 43.3 ± 10.1 |

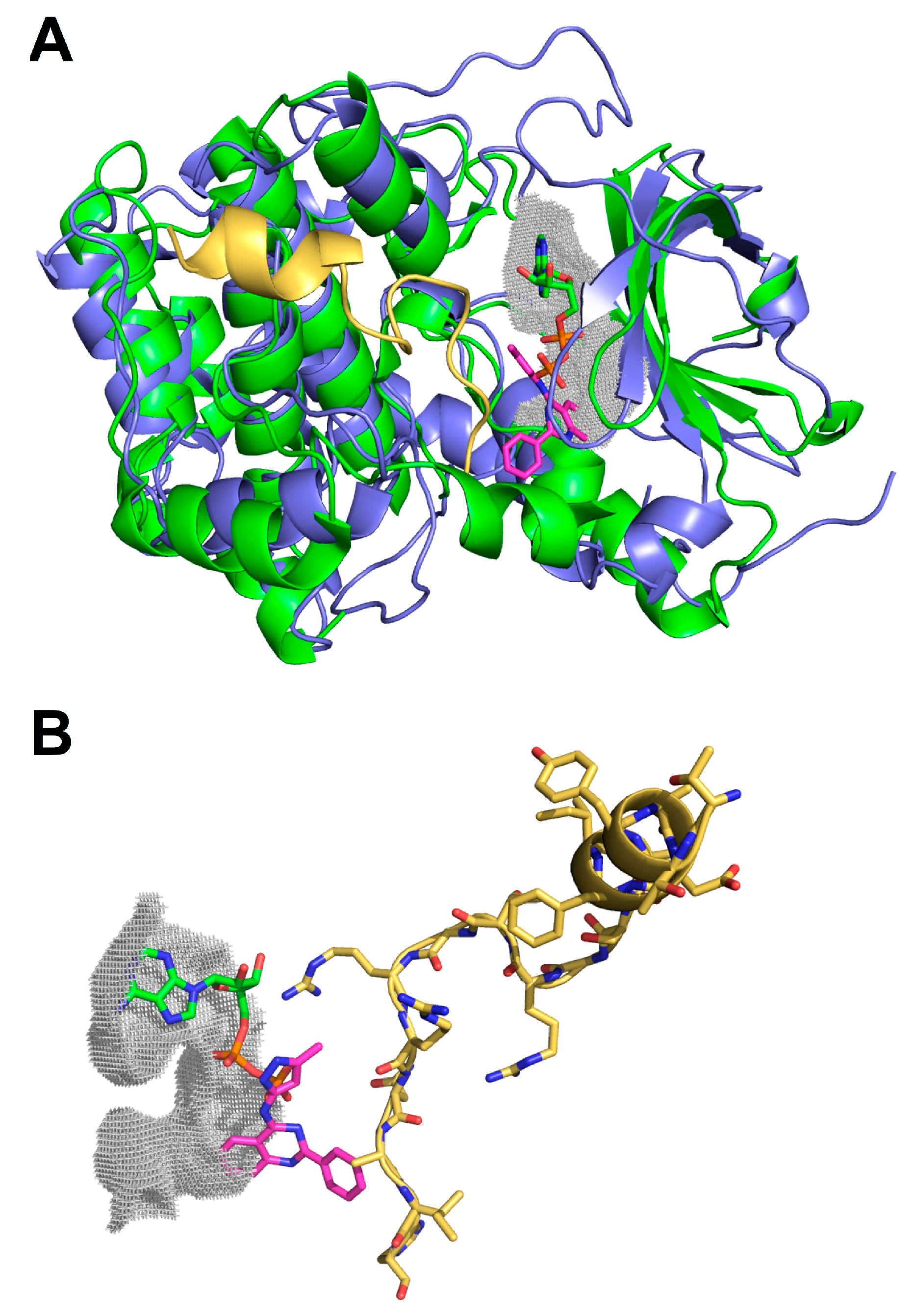
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plasmid Constructions
3.2. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
3.3. Protein Expression, Purification, and Dephosphorylation
3.4. Thermal Shift Assays
3.5. Kinase Assays
3.6. Homology Molecular Modeling
3.7. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubin, G.M.; Yandell, M.D.; Wortman, J.R.; Gabor Miklos, G.L.; Nelson, C.R.; Hariharan, I.K.; Fortini, M.E.; Li, P.W.; Apweiler, R.; Fleischmann, W.; et al. Comparative genomics of the eukaryotes. Science 2000, 287, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.N.; Lowe, E.D.; Noble, M.E.; Owen, D.J. The Eleventh Datta Lecture. The structural basis for substrate recognition and control by protein kinases. FEBS Lett. 1998, 430, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hanks, S.K. Eukaryotic protein kinases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1991, 1, 369–383. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, P.D.; Russo, A.A.; Polyak, K.; Gibbs, E.; Hurwitz, J.; Massagué, J.; Pavletich, N.P. Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex. Nature 1995, 376, 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Hendrickson, W.A. Structural basis for activation of human lymphocyte kinase Lck upon tyrosine phosphorylation. Nature 1996, 384, 484–489. [Google Scholar]
- Canagarajah, B.J.; Khokhlatchev, A.; Cobb, M.H.; Goldsmith, E.J. Activation mechanism of the MAP kinase ERK2 by dual phosphorylation. Cell 1997, 90, 859–869. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, S.R. Crystal structure of the activated insulin receptor tyrosine kinase in complex with peptide substrate and ATP analog. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5572–5581. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, A.M.; O’Regan, L.; Sabir, S.R.; Bayliss, R. Cell cycle regulation by the NEK family of protein kinases. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4423–4433. [Google Scholar]
- Meirelles, G.V.; Perez, A.M.; Souza, E.E.; Basei, F.L.; Papa, P.F.; Melo Hanchuk, T.D.; Cardoso, V.B.; Kobarg, J. “Stop Ne(c)king around”: How systems biology can help to characterize the functions of Nek family kinases from cell cycle regulation to DNA damage response. World J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 5, 141–160. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, A.M.; Mayor, T.; Meraldi, P.; Stierhof, Y.D.; Tanaka, K.; Nigg, E.A. C-Nap1, a novel centrosomal coiled-coil protein and candidate substrate of the cell cycle-regulated protein kinase Nek2. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 141, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Quarmby, L.M.; Mahjoub, M.R. Caught Nek-ing: Cilia and centrioles. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 5161–5169. [Google Scholar]
- Meirelles, G.V.; Silva, J.C.; Mendonça, Y.A.; Ramos, C.H.; Torriani, I.L.; Kobarg, J. Human Nek6 is a monomeric mostly globular kinase with an unfolded short N-terminal domain. BMC Struct. Biol. 2011, 11, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Belham, C.; Roig, J.; Caldwell, J.A.; Aoyama, Y.; Kemp, B.E.; Comb, M.; Avruch, J. A mitotic cascade of NIMA family kinases. Nercc1/Nek9 activates the Nek6 and Nek7 kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34897–34909. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, M.J.; Shao, L.; Voehringer, D.; Smeal, T.; Jallal, B. The serine/threonine kinase Nek6 is required for cell cycle progression through mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52454–52460. [Google Scholar]
- Yissachar, N.; Salem, H.; Tennenbaum, T.; Motro, B. Nek7 kinase is enriched at the centrosome, and is required for proper spindle assembly and mitotic progression. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 6489–6495. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Lee, K.; Rhee, K. NEK7 is a centrosomal kinase critical for microtubule nucleation. Biochem. Biophys. Res.Commun. 2007, 360, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Roig, J.; Mikhailov, A.; Belham, C.; Avruch, J. Nercc1, a mammalian NIMA-family kinase, binds the Ran GTPase and regulates mitotic progression. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1640–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhya, P.; Birkenmeier, E.H.; Birkenmeier, C.S.; Barker, J.E. Mutations in a NIMA-related kinase gene, Nek1, cause pleiotropic effects including a progressive polycystic kidney disease in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Lu, W.; Obara, T.; Kuida, S.; Lehoczky, J.; Dewar, K.; Drummond, I.A.; Beier, D.R. A defect in a novel Nek-family kinase causes cystic kidney disease in the mouse and in zebrafish. Development 2002, 129, 5839–5846. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Yu, L. Interaction of Pin1 with Nek6 and characterization of their expression correlation in Chinese hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, P.L.; Chen, C.F.; Jiang, X.; Riley, D.J. Never-in mitosis related kinase 1 functions in DNA damage response and checkpoint control. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3194–3201. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, M.A.; Jee, H.J.; Kim, A.J.; Bae, Y.S.; Park, J.I.; Chung, J.H.; Yun, J. Nek6 is involved in G2/M phase cell cycle arrest through DNA damage induced phosphorylation. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2705–2709. [Google Scholar]
- Innocenti, P.; Cheung, K.M.; Solanki, S.; Mas-Droux, C.; Rowan, F.; Yeoh, S.; Boxall, K.; Westlake, M.; Pickard, L.; Hardy, T.; et al. Design of potent and selective hybrid inhibitors of the mitotic kinase Nek2: structure-activity relationship, structural biology, and cellular activity. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3228–3241. [Google Scholar]
- Solanki, S.; Innocenti, P.; Mas-Droux, C.; Boxall, K.; Barillari, C.; van Montfort, R.L.; Aherne, G.W.; Bayliss, R.; Hoelder, S. Benzimidazole inhibitors induce a DFG-out conformation of never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 2 (Nek2) without binding to the back pocket and reveal a nonlinear structure-activity relationship. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1626–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Whelligan, D.K.; Solanki, S.; Taylor, D.; Thomson, D.W.; Cheung, K.M.; Boxall, K.; Mas-Droux, C.; Barillari, C.; Burns, S.; Grummitt, C.G.; et al. Aminopyrazine inhibitors binding to an unusual inactive conformation of the mitotic kinase Nek2: SAR and structural characterization. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7682–7698. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, P.; ChellaPerumal, P.; Sudha, A. Discovery of novel inhibitors for Nek6 protein through homology model assisted structure based virtual screening and molecular docking approaches. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rellos, P.; Ivins, F.J.; Baxter, J.E.; Pike, A.; Nott, T.J.; Parkinson, D.M.; Das, S.; Howell, S.; Fedorov, O.; Shen, Q.Y.; et al. Structure and regulation of the human Nek2 centrosomal kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 6833–6842. [Google Scholar]
- Westwood, I.; Cheary, D.M.; Baxter, J.E.; Richards, M.W.; van Montfort, R.L.; Fry, A.M.; Bayliss, R. Insights into the conformational variability and regulation of human Nek2 kinase. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 476–485. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, M.W.; O’Regan, L.; Mas-Droux, C.; Blot, J.M.; Cheung, J.; Hoelder, S.; Fry, A.M.; Bayliss, R. An autoinhibitory tyrosine motif in the cell-cycleregulated Nek7 kinase is released through binding of Nek9. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 560–570. [Google Scholar]
- Geromichalos, G.D. Importance of molecular computer modeling in anticancer drug development. J. Buon. 2007, 12, S101–S118. [Google Scholar]
- Vedadi, M.; Niesen, F.H.; Allali-Hassani, A.; Fedorov, O.Y.; Finerty, P.J., Jr.; Wasney, G.A.; Yeung, R.; Arrowsmith, C.; Ball, L.J.; Berglund, H.; et al. Chemical screening methods to identify ligands that promote protein stability, protein crystallization, and structure determination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15835–15840. [Google Scholar]
- Lengauer, T.; Rarey, M. Computational methods for biomolecular docking. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1996, 6, 402–406. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, O.; Marsden, B.; Pogacic, V.; Rellos, P.; Müller, S.; Bullock, A.N.; Schwaller, J.; Sundström, M.; Knapp, S. A systematic interaction map of validated kinase inhibitors with Ser/Thr kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20523–20528. [Google Scholar]
- Roberge, M.; Berlinck, R.G.; Xu, L.; Anderson, H.J.; Lim, L.Y.; Curman, D.; Stringer, C.M.; Friend, S.H.; Davies, P.; Vincent, I.; et al. High-throughput assay for G2 checkpoint inhibitors and identification of the structurally novel compound isogranulatimide. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5701–5706. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Zhao, B.; Britton, R.; Lim, L.Y.; Leong, D.; Sanghera, J.S.; Zhou, B.B.; Piers, E.; Andersen, R.J.; Roberge, M. Inhibition of Chk1 by the G2 DNA damage checkpoint inhibitor isogranulatimide. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar]
- De Castro, E.; Sigrist, C.J.A.; Gattiker, A.; Bulliard, V.; Langendijk-Genevaux, P.S.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Hulo, N. ScanProsite: Detection of PROSITE signature matches and ProRule-associated functional and structural residues in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W362–W365. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrin, L.K.; Saiah, E. Approaches to discover non-ATP site kinase inhibitors. Med. Chem. Commun. 2013, 4, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, S.H.; Ferraz, F.A.; Honorato, R.V.; Xavier-Neto, J.; Sobreira, T.J.; de Oliveira, P.S. KVFinder: Steered identification of protein cavities as a PyMOL plugin. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 197. [Google Scholar]
- Meirelles, G.V.; Lanza, D.C.F.; Silva, J.C.; Bernachi, J.S.; Leme, A.F.P.; Kobarg, J. Characterization of hNek6 Interactome Reveals an Important Role for Its Short N-Terminal Domain and Colocalization with Proteins at the Centrosome. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 6298–6316. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDockVina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors but are commercially available.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moraes, E.C.; Meirelles, G.V.; Honorato, R.V.; De Souza, T.D.A.C.B.; De Souza, E.E.; Murakami, M.T.; De Oliveira, P.S.L.; Kobarg, J. Kinase Inhibitor Profile for Human Nek1, Nek6, and Nek7 and Analysis of the Structural Basis for Inhibitor Specificity. Molecules 2015, 20, 1176-1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20011176
Moraes EC, Meirelles GV, Honorato RV, De Souza TDACB, De Souza EE, Murakami MT, De Oliveira PSL, Kobarg J. Kinase Inhibitor Profile for Human Nek1, Nek6, and Nek7 and Analysis of the Structural Basis for Inhibitor Specificity. Molecules. 2015; 20(1):1176-1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20011176
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoraes, Eduardo Cruz, Gabriela Vaz Meirelles, Rodrigo Vargas Honorato, Tatiana De Arruda Campos Brasil De Souza, Edmarcia Elisa De Souza, Mario Tyago Murakami, Paulo Sergio Lopes De Oliveira, and Jörg Kobarg. 2015. "Kinase Inhibitor Profile for Human Nek1, Nek6, and Nek7 and Analysis of the Structural Basis for Inhibitor Specificity" Molecules 20, no. 1: 1176-1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20011176
APA StyleMoraes, E. C., Meirelles, G. V., Honorato, R. V., De Souza, T. D. A. C. B., De Souza, E. E., Murakami, M. T., De Oliveira, P. S. L., & Kobarg, J. (2015). Kinase Inhibitor Profile for Human Nek1, Nek6, and Nek7 and Analysis of the Structural Basis for Inhibitor Specificity. Molecules, 20(1), 1176-1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20011176