Alkaloids from the Tribe Bocconieae (Papaveraceae): A Chemical and Biological Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Chemical Constituents
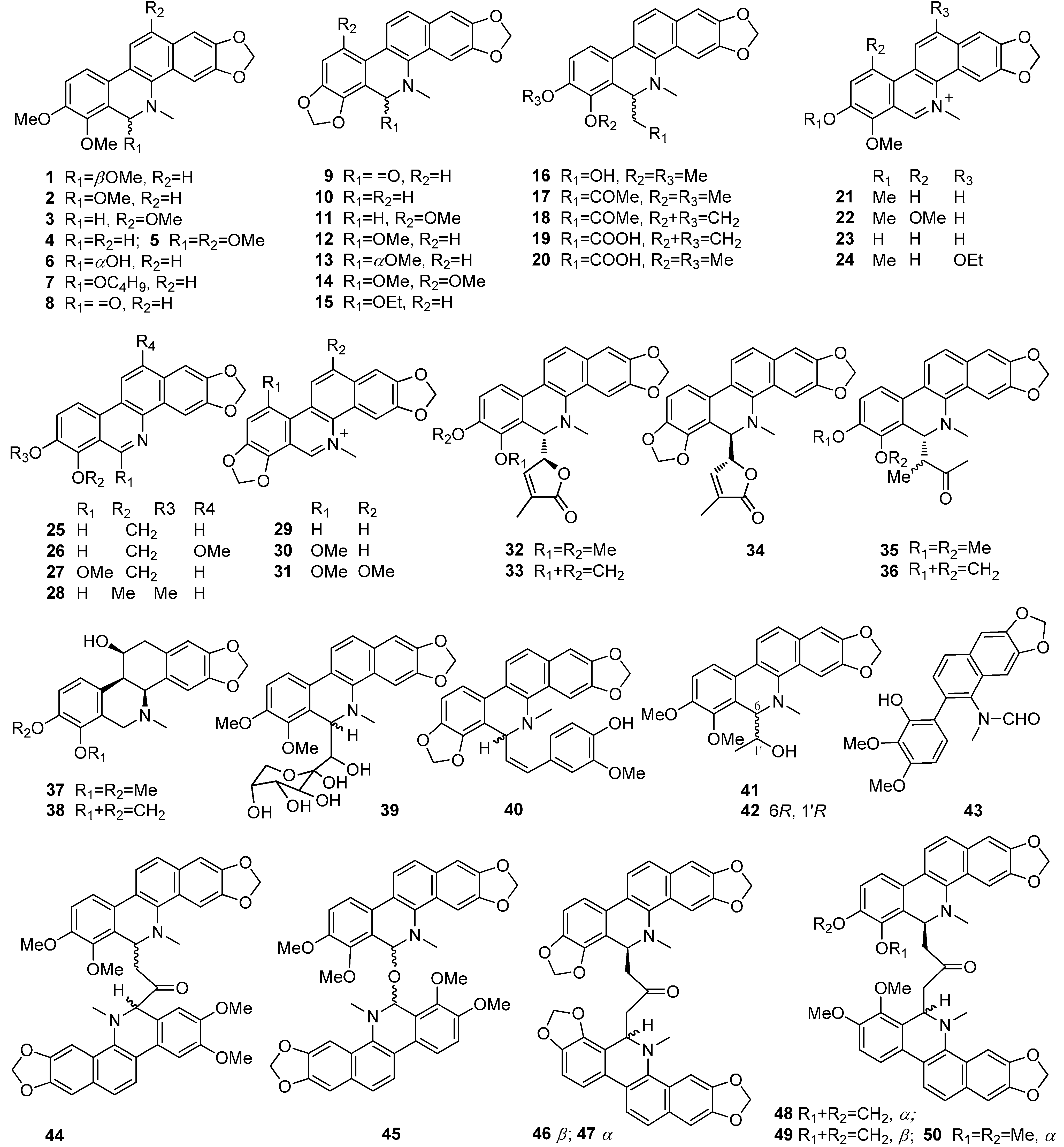
| Name | Type | Plant | Part | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11-O-Methyldihydrochelerythrine | IA | B. arborea | — | [16] | ||||
| 2 | Angoline ((±)-6-methoxydihydro-chelerythrine) | IA | M. cordata | Stems | [17] | ||||
| B. arborea | Leaves, stems | [2] | |||||||
| M. microcarpa | Aerial parts, roots | [14,18,19] | |||||||
| 3 | 12-Methoxydihydrochelerythrine | IA | B. integrifolia | Leaves | [20] | ||||
| 4 | Dihydrochelerythrine | IA | B. integrifolia | Leaves | [20] | ||||
| B. arborea | Aerial parts | [4] | |||||||
| B. frutescens | Leaves | [3] | |||||||
| M. microcarpa | Roots, leaves, whole plant | [14,21,22] | |||||||
| M. cordata | Fruits | [23] | |||||||
| B. pearcei | Fruits | [24] | |||||||
| 5 | 6, 12-Dimethoxydihydrocheleritrine | IA | B. arborea | — | [25] | ||||
| 6 | 8-Hydroxydihydrochelerythrine | IA | M. cordata. | Seeds | [26] | ||||
| 7 | 6-Butoxydihydrochelerythrine | IA | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| 8 | Oxychelerythrine | IA | B. pearcei | Fruits | [24] | ||||
| 9 | Oxysanguinarine | IA | B. latisepala | Leaves, roots, seeds | [27] | ||||
| B. arborea | — | [16] | |||||||
| B. pearcei | Fruits | [24] | |||||||
| M. cordata | — | [10] | |||||||
| 10 | Dihydrosanguinarine | IA | M. cordata | Fruits | [23] | ||||
| B. integrifolia | Leaves | [20] | |||||||
| B. arborea | Aerial parts | [4,16] | |||||||
| M. microcarpa | Roots, leaves, whole plant | [14,21,22] | |||||||
| B. Pearcei | Fruits | [24] | |||||||
| 11 | Dihydrochelirubine | IA | B. integrifolia | Leaves | [20] | ||||
| B. pearcei | Fruits | [24] | |||||||
| 12 | 6-Methoxydihydrosanguinarine | IA | M. cordata | Fruits | [10] | ||||
| M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | |||||||
| 13 | 8-Methoxydihydrosanguinarine | IA | M. cordata | Seeds | [26] | ||||
| 14 | 6-Methoxydihydrochelirubine | IA | B. arborea | — | [25] | ||||
| 15 | 6-Ethoxysanguinarine | IA | M. cordata | — | [10] | ||||
| M. microcarpa | Whole plant | [21] | |||||||
| 16 | Bocconoline | IA | B. cordata | — | [28] | ||||
| M. cordata | — | [10] | |||||||
| 17 | (±)-6-Acetonyldihydrochelerythrine | IA | B. arborea | Barks, aerial parts | [2,15] | ||||
| B. frutescens | Leaves | [3] | |||||||
| M. cordata | Fruits | [10,23] | |||||||
| 18 | (±)-6-Acetonyldihydrosanguinarine | IA | B. arborea | Aerial parts | [2] | ||||
| B. frutescens | Leaves | [3] | |||||||
| M. cordata | Fruits | [10,23] | |||||||
| M. microcarpa | Whole plant | [21] | |||||||
| 19 | Spallidamine(6-Carboxymethyldihydrosanguinarie) | IA | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| M. cordata | Whole plant | [12] | |||||||
| 20 | 6-Carboxymethyldihydrochelerythrine | IA | M. cordata | Whole plant | [12] | ||||
| 21 | Chelerythrine | IB | B. latisepala | Barks, stems, seeds | [27] | ||||
| M. cordata | — | [29] | |||||||
| B. frutescens | Roots, stalks and leaves | [30] | |||||||
| M. microcarpa | — | [31] | |||||||
| 22 | Chelilutine | IB | M. cordata | Roots | [10] | ||||
| M. microcarpa | — | [31] | |||||||
| 23 | 8-O-Demethylchelerythrine | IB | M. cordata | — | [29] | ||||
| 24 | 6-Ethoxychelerythrine | IB | M. cordata | — | [10] | ||||
| 25 | Norsanguinarine | IC | M. cordata | Fruits | [10] | ||||
| 26 | 12-Methoxynorchelerythrine | IC | B. pearcei | Fruits | [24] | ||||
| 27 | Pancorine | IC | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| 28 | Norchelerythrine | IC | M. cordata | Whole plant | [12] | ||||
| 29 | Sanguinarine | IB | B. latisepala | Barks, stems | [27] | ||||
| B. cordata | Leaves | [32] | |||||||
| B. frutescens | Roots, stalks and leaves | [30] | |||||||
| M. cordata. | Fruits | [29,33] | |||||||
| M. microcarpa | Aerial parts | [18,19,34] | |||||||
| 30 | Bocconine (chelirubine) | IB | B. cordata | — | [35] | ||||
| M. microcarpa | — | [31] | |||||||
| 31 | Macarpine | IB | M. cordata | Callus tissues | [10,36] | ||||
| M. microcarpa | — | [31] | |||||||
| 32 | Maclekarpine A | IA | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| 33 | Maclekarpine B | IA | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| 34 | Maclekarpine C | IA | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| 35 | 6 α-Isobutanonyldihydrochelerythrine | IA | M. cordata | Fruits | [23] | ||||
| 36 | 6 α-Isobutanonyldihydrosanguinarine | IA | M. cordata | Fruits | [23] | ||||
| 37 | Homochelidonine | ID | M. cordata | — | [10] | ||||
| 38 | Chelidonine | ID | B. frutescens | Roots | [37] | ||||
| 39 | Maclekarpine D | IA | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| 40 | Maclekarpine E | IA | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| 41 | 6-(1'-hydroxyethyl)-dihydrochelerythrine | IA | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| 42 | R-6-((R)-1-Hydroxyethyl)-dihydrochelerythrie | IA | M. cordata | Whole plant | [12] | ||||
| 43 | Arnottianamide | IF | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| 44 | Chelerythridimerine | IE | B. arborea | Barks | [38] | ||||
| 45 | Bis[6-(5, 6-dihydrochelerythrinyl)]ether | IE | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] | ||||
| 46 | (±)-Sanguidimerine | IE | B. arborea | Aerial parts | [2] | ||||
| M. cordata | Leaves | [10] | |||||||
| 47 | Chelidimerine | IE | B. arborea | Aerial parts | [2] | ||||
| M. cordata | Leaves | [10] | |||||||
| 48 | (±)-Bocconarborine A | IE | B. arborea | Aerial parts | [2] | ||||
| M. cordata | Leaves | [10] | |||||||
| M. microcarpa | Whole plant | [21] | |||||||
| 49 | (±)-Bocconarborine B | IE | B. arborea | Aerial parts | [2] | ||||
| M. cordata | Leaves | [10] | |||||||
| 50 | 1, 3-Bis(1l-hydrochelerythriny1)acetone | IE | B. arborea | — | [16] | ||||
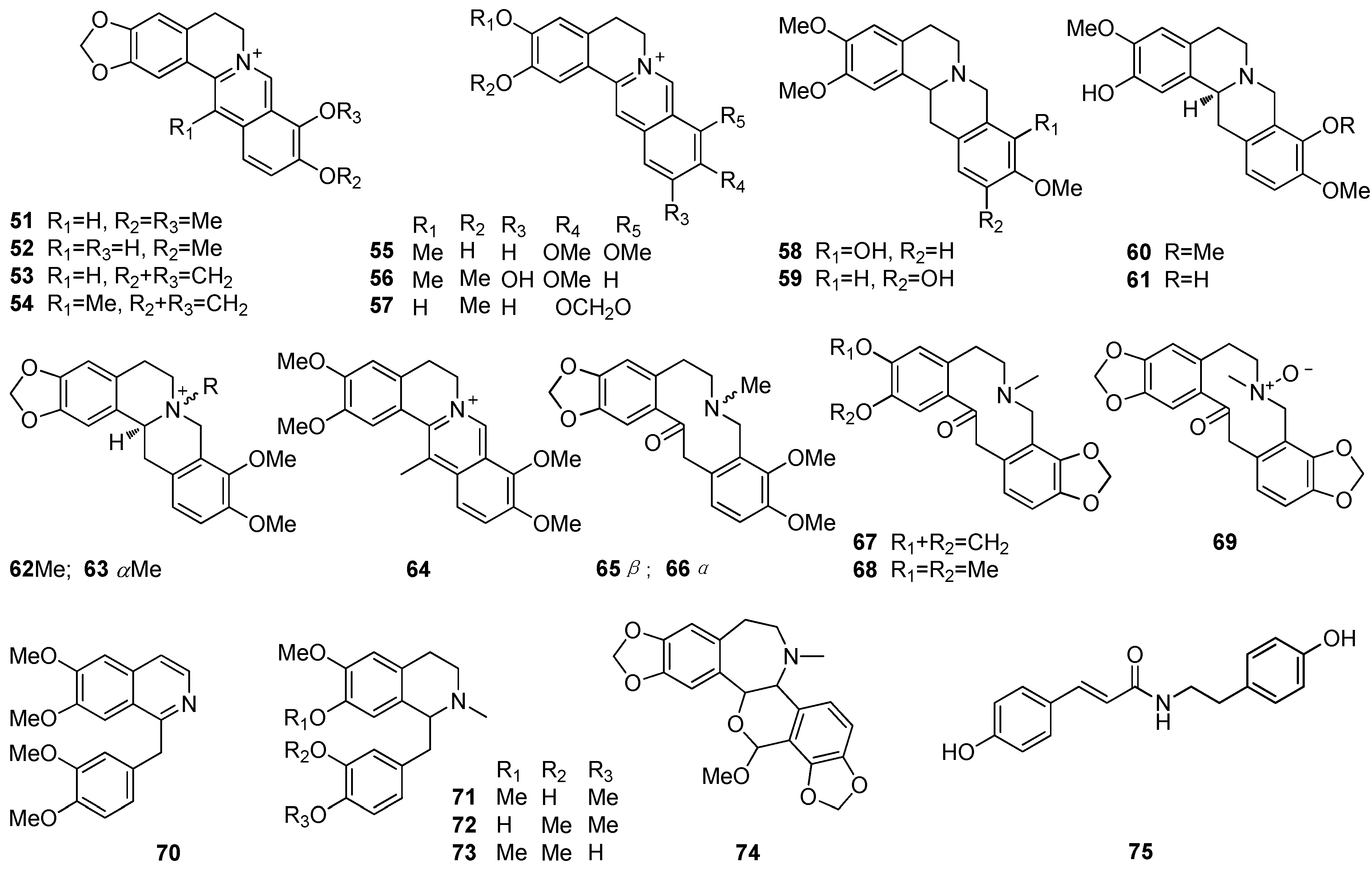
| Name | Type | Plant | Part | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 | Berberine | II | B. frutescens M. cordata M. microcarpa | Roots, stalks, leaves — Roots | [30] [10] [31] |
| 52 | Berberrabine | II | M. microcarpa | Whole plant | [21] |
| 53 | Coptisine | II | B. frutescens M. microcarpa | Roots, stalks and leaves Roots | [30] [31] |
| 54 | Corysamine | II | B. frutescens | — | [37] |
| 55 | Columbamine | II | B. frutescens | Roots, stalks, leaves | [30] |
| 56 | Dehydrocorytenchine | II | M. cordata | Cultured cells | [39] |
| 57 | Dehydrocheilanthifoline | II | M. cordata | — | [40] |
| 58 | Tetrahydropalmatrubine | II | M. cordata | Cultured cells | [39] |
| 59 | Corytenchine | II | M. cordata | Cultured cells | [39] |
| 60 | (–)-Isocorypalmine | II | B. frutescens | Leaves, roots | [30,37,41] |
| 61 | (–)-Scoulerine | II | B. frutescens | Roots, leaves | [30,37] |
| 62 | (–)-cis-N-Methylcanadinium | II | B. frutescens | Roots | [37] |
| 63 | (–)-α-Canadine | II | B. frutescens | Roots, stalks, leaves | [30] |
| 64 | Dehydrocicanthifoline | II | M. cordata | — | [40] |
| 65 | β-Allocryptopine | III | M. microcarpa | Aerial parts, whole plant | [18,19,21] |
| 66 | α-Allocryptopine | III | B. cordata M. cordata B. latisepala M. microcarpa | Leaves Fruits Roots Whole plant | [32] [10] [27] [21] |
| 67 | Protopine | III | B. latisepala B.cordata B. frutescens M. cordata M. microcarpa | Leaves, roots Leaves Roots, stalks, leaves Cultured cells Aerial parts, whole plant | [27] [32] [30,41] [39] [19,21] |
| 68 | Cryptopine | III | M. cordata M. microcarpa | Fruits Aerial parts | [10] [18] |
| 69 | Protopine N-oxide | III | B. cordata | Whole plant | [10,42] |
| 70 | Papaverine | IV | M. cordata | Cultured cells | [39] |
| 71 | Laudanine | IV | M. cordata | Cultured cells | [43] |
| 72 | Codamine | IV | M. cordata | Cultured cells | [43] |
| 73 | Pseudocodamine | IV | M. cordata | Cultured cells | [43] |
| 74 | Rhoeadine | IV | B. frutescens | Leaves, stalks | [30,41] |
| 75 | N-p-Coumaroyltyramine | IV | M. microcarpa | Roots | [14] |
3. Biological Activities
3.1. Cytotoxicity against Tumor Cells
3.2. Insecticidal Activities
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Property
3.5. Effect on Cardiovascular System
3.6. Other Activities
4. Toxicity and Side Effects
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Institute of Botany, the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Iconographia Cormophytorum Sinicorum; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994; Volume 2, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Julian, A.; Delgado, G. (±)-Bocconarborines A and B, novel 1, 3-bis-benzo[c]phenanthridinyl acetone alkaloids from Bocconia arborea. Rev. Soc. Quim. Mex. 2001, 45, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Arreola, E.; Hernandez-Molina, L.R.; Sanchez-Salas, J.L.; Martinez-Espino, G. Alkaloids from Bocconia frutescens and biological activity of their extracts. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.; Delgado, G. Two antimicrobial alkaloids from Bocconia arborea. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 66, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, G.P.; Ren, P.; Yu, J.M.; Shi, R.F.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.H. Separation of sanguinarine and chelerythrine in Macleaya cordata (Willd) R. Br. based on methyl acrylate-co-divinylbenzene macroporous adsorbents. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1192, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Q.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, C.; Chai, X.Y.; Tu, P.F. Chemical constituents from the aerial parts of Meconopsis horridula (Papaveraceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 55, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaninova, I.; Pencikova, K.; Urbanova, J.; Slanina, J.; Taborska, E. Antitumour activities of sanguinarine and related alkaloids. Phytochem. Rev. 2014, 13, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.W. The chemotaxonomy of angiosperms families (V): Papaveraceae. J. Int. Pharm. Res. 1981, 2, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Ruecker, G.; Breitmaier, E.; Nieger, M.; Mayer, R.; Steinbeck, C. Alkaloids from Dactylicapnos torulosa. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosina, P.; Gregorova, J.; Gruz, J.; Vacek, J.; Kolar, M.; Vogel, M.; Roos, W.; Naumann, K.; Simanek, V.; Ulrichova, J. Phytochemical and antimicrobial characterization of Macleaya cordata herb. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.J.; Zhou, S.Y.; Shi, H.Z.; Yin, J. Determination of Chemical Composition of the Essential Oil from Macleaya cordata by GC-MS. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2009, 25, 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.J. Study on the Chemical Constituents and their Bioactivities from Macleaya cordata. Master Thesis, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, M.I.; Julian, A.; Delgado, G. Structure elucidation and 13C-NMR spectral assignments of 3α-hydroxyolean-12-en-30-oic acid, a new triterpene from Bocconia arborea. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2003, 41, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.J.; Qin, H.L. Cytotoxic dihydrobenzophenanthridine alkaloids from the roots of Macleaya microcarpa. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Martinez, F.J.; Padilla-Martinez, I.I.; Hernandez-Carlos, B.; Perez-Gutierrez, R.M.; Garcia-Baez, E.V. X-ray diffraction and total 1H and 13C NMR assignment of (RS)-5,6-dihydro-7, 8-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-(2-oxopropyl)-(2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl)-[c]-phenanthridine ((RS)-6-acetonyldihydrochelerythrine). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2002, 32, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, D.B.; Gracey, D.E.F.; Saunders, J.K.; Rodrigo, R.; Manske, R.H.F. Benzophenanthridine alkaloids from Bocconia arborea. Can. J. Chem. 1969, 47, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Qing, W.G.; Mar, W.; Luyengi, L.; Mehta, R.G.; Kawanishi, K.; Fong, H.H.S.; Beecher, C.W.W.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Pezzuto, J.M. Angoline and chelerythrine, benzophenanthridine alkaloids that do not inhibit protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 19829–19833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Yi, Y.L.; Zhang, C.; Wu, S.Q.; Shi, C.B.; Wang, G.X. Bioassay-guided isolation and identification of active compounds from Macleaya microcarpa (Maxim) Fedde against fish pathogenics bacteria. Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.X.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, D.X.; Han, J.; Wang, J.F.; Zhao, L.W.; Li, J. In vivo anthelmintic activity of five alkaloids from Macleaya microcarpa (Maxim) Fedde against Dactylogyrus intermedius in Carassius auratus. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 171, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oechslin, S.M.; Koenig, G.M.; Oechslin-Merkel, K.; Wright, A.D.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Sticher, O.; Miyagawa, M. An NMR study of four benzophenanthridine alkaloids. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Miao, F.; Zheng, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Geng, H.L.; Sun, W. Isolation and identification of alkaloids from Macleaya microcarpa (Maxim.) Fedde. Acta Bot. Boreal-Occident. Sin. 2010, 30, 405–411. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.Y.; Zhou, Z.M.; Li, X.L.; Yin, W.L.; Ru, H.S.; Pan, X.Y.; Hao, G.J.; Xu, Y.; Shen, J.Y. Antiparasitic efficacy of dihydrosanguinarine and dihydrochelerythrine from Macleaya microcarpa against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in richadsin (Squaliobarbus. curriculus). Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 183, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Ye, F.Z.; Li, C.L.; Liu, W.Y.; Xie, N. New benzophenanthridine isoquinoline alkaloids from Macleaya cordata. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2012, 10, 378–382. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchino, H.; Kawano, M.; Mori-Yasumoto, K.; Sekita, S.; Satake, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Kiuchi, F.; Kawahara, N. In vitro leishmanicidal activity of benzophenanthridine alkaloids from Bocconia pearcei and related compounds. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayo Camacho-Corona, M.; Jesus Favela-Hernandez, J.M.; Gonzalez-Santiago, O.; GarzaGonzalez, E.; Molina-Salinas, G.M.; Said-Fernandez, S.; Delgado, G.; Luna-Herrera, J. Evaluation of some plant-derived secondary metabolites against sensitive and multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2009, 53, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, M.Y.; Park, H.J.; Kim, G.M.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, G.Y.; Moon, S.J.; Ahn, E.M.; Kim, G.S.; Bang, M.H.; Baek, N.I. Insecticidal alkaloids from the seeds of Macleaya cordata on cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii). J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2013, 56, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, X.A.; Delgado, J.G.; Monroy C., A.; Armendariz, L.G.; Alcala, A.; Quevedo, J.; Rojas, P. A chemical study of Bocconia latisepala Wat. Can. J. Chem. 1965, 43, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Hosoya, K.; Takao, N. Bocconoline: A new type dihydrobenzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloid possessing a unique substituent at C6 position. Tetrahedron Lett. 1971, 12, 2429–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkachev, O.N.; Savina, A.A.; Sheichenko, V.I.; Proskudina, V.V. 8-O-demethylchelerythrine from Macleaya cordata. Pharm. Chem. J. 1999, 33, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taborska, E.; Veznik, F.; Slavik, J. Alkaloids of the Papaveraceae. LXXI. Alkaloids from Bocconia frutescens L. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 1980, 45, 1301–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pěnčíková, K.; Urbanová, J.; Musil, P.; Táborská, E.; Gregorová, J. Seasonal variation of bioactive alkaloid contents in Macleaya microcarpa (Maxim.) Fedde. Molecules 2011, 16, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryakov, N.G.; Kitova, M.S.; Georgieva, A.V. Alkaloids of Bocconi acordata. Cr. Acad. Bulg. Sci. 1967, 20, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.B.; Chen, B.; Yao, S.Z. Rapid determination of protopine, allocryptopine, sanguinarine and chelerythrine in fruits of Macleaya cordata by microwave-assisted solvent extraction and HPLC-ESI/MS. Phytochem. Anal. 2006, 17, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, M.; Abe, K.; Yonezawa, K.; Esumi, N.; Suzuki, T. Constituents of Bocconia cordata. II. Bocconine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1970, 18, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konda, Y.; Harigaya, Y.; Onda, M. Studies on the constituents of Bocconia cordata. III. Structure elucidation of bocconine by means of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic studies. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1986, 23, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takao, N.; Kamigauchi, M.; Okada, M. Biosynthesis of benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids sanguinarine, chelirubine and macarpine. Helv. Chim. Acta 1983, 66, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-George, C.; Vanderheyden, P.M.L.; Apers, S.; van den Heuvel, H.; Solis, P.N.; Gupta, M.P.; Claeys, M.; Pieters, L.; Vauquelin, G.; Vlietinck, A.J. Inhibitory activity on binding of specific ligands to the human angiotensin II AT1 and endothelin 1 ETA receptors: Bioactive benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids from the root of Bocconia frutescents. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, R.M.; Vargas Solis, R.; Diaz Gutierrez, G.; Martinez-Martinez, F.J. Identification of benzophenanthridine alkaloids from Bocconia arborea by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2002, 13, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, K.; Cui, W.; Sugiura, M.; Takeuchi, A.; Moriyasu, M.; Takeda, K. Structural analyses of metabolites of phenolic 1-benzyltetrahydroisoquinolines in plant cell cultures by LC/NMR, LC/MS, and LC/CD. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.L.; Zhang, D.Z.; Xu, Q.J.; Xie, R.R.; Li, Q.Q. Advance in studies on Macleaya cordata. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2009, 5, 144–145. [Google Scholar]
- Slavik, J.; Slavikova, L. Alkaloids of Papaveraceae. LIX. Alkaloids from the leaves of Bocconia frutescens L. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 1975, 40, 3206–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, K.; Okada, M.; Takao, N. Protopine-N.-oxide, an alkaloid from Bocconia cordata. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, K.; Doi, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Cui, W.; Nishiyama, Y.; Tode, C.; Moriyasu, M.; Takeda, K.; Minami, H.; Ikezawa, N.; et al. Enantiomeric separation of racemic 1-benzyl-N-methyltetrahydroisoquinolines on chiral columns and chiral purity determinations of the O-methylated metabolites in plant cell cultures by HPLC-CD on-line coupling in combination with HPLC-MS. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, X.R.; Liao, C.C.; Poo, W.K. In vitro assessment of Macleaya cordata crude extract bioactivity and anticancer properties in normal and cancerous human lung cells. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.L.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, Y.; An, C.X.; Fu, J.M. Study on the effects of total alkaloids from Macleaya cordata on transplantable animal tumors. Shanxi Oncol. Med. 2000, 8, 174–149. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.X.; Ma, R.Q.; Liu, L.M.; Jiang, Y.P.; Sun, L.S. Total alkaloid of Macleaya cordata: In vitro cytotoxic effect on Hep3B cells and in vivo antitumor effect in mice. J. First Mil. Med. Univ. 2005, 25, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.W.; Zhang, J.B.; Wei, X.H. Chelerythrine chloride from Macleaya cordata induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in human gastric cancer BGC-823 cells. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2012, 2, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhami, V.M.; Aziz, M.H.; Reagan-Shaw, S.R.; Nihal, M.; Mukhtar, H.; Ahmad, N. Sanguinarine causes cell cycle blockade and apoptosis of human prostate carcinoma cells via modulation of cyclin kinase inhibitor-cyclin-cyclin-dependent kinase machinery. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 933–940. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsan, H.; Reagan-Shaw, S.; Breur, J.; Ahmad, N. Sanguinarine induces apoptosis of human pancreatic carcinoma AsPC-1 and BxPC-3 cells via modulations in Bcl-2 family proteins. Cancer Lett. 2007, 249, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.C.; Park, J.G.; Song, D.K.; Baek, W.K.; Yoo, S.K.; Jung, K.H.; Park, G.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Suh, S.L. Sanguinarine induces apoptosis in A549 human lung cancer cells primarily via cellular glutathione depletion. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, K.A.; Meyer, A.; Jerabkova, L.; Korhonen, L.E.; Rahnasto, M.; Juvonen, R.O.; Imming, P.; Raunio, H. Inhibition of human drug metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes by plant isoquinoline alkaloids. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 533–538. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.Y.; Shen, J.Y.; Li, X.L.; Xu, Y.; Hao, G.J.; Pan, X.Y.; Wang, G.X.; Yin, W.L. Effect of sanguinarine from the leaves of Macleaya cordata against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Li, G.Y.; Zeng, J.G.; Zhang, L.; Huang, K.L.; She, J.M.; Li, X.; Wei, W.Y. Evaluation of molluscicidal activities of benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids from Macleaya cordata (Wild) R. Br. on snail hosts of Schistosoma japonicum. J. Med. Plant. Res. 2011, 5, 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, V.; Rojas, G.; Delgado, G.; Lozoya, X. Antimicrobial compounds detected in Bocconia arborea extracts by a direct bioautographic method. Arch. Med. Res. 1998, 29, 191–194. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, V.; Villarreal, M.L.; Rojas, G.; Lozoya, X. Antimicrobial evaluation of some plants used in Mexican traditional medicine for the treatment of infectious diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1996, 53, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Vega, D.E.; Verde-Star, M.J.; Salinas-Gonzalez, N.; Rosales-Hernandez, B.; Estrada-Garcia, I.; Mendez-Aragon, P.; Carranza-Rosales, P.; Gonzalez-Garza, M.T.; Castro-Garza, J. Antimycobacterialactivity of Juglans regia, Juglans mollis, Carya illinoensis and Bocconia frutescens. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cheng, P.; Chen, J.L.; Zeng, J.G. Extraction of quaternary benzophenanthridine alkaloids (QBAs) from Macleaya cordata and antibacterial activity, acute toxicity of the QBAs bisulfate. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2013, 15, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, S.E.; Roll, M.J.; Harkrader, R.J. A naturally occurring compound for controlling powdery mildew of greenhouse roses. Hortscience 1999, 34, 686–689. [Google Scholar]
- Calzada, F.; Yepez-Mulia, L.; Tapia-Contreras, A. Effect of Mexican medicinal plant used to treat trichomoniasis on Trichomonas vaginalis trophozoites. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 113, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchilla, M.; Valerio, I.; Sanchez, R.; Mora, V.; Bagnarello, V.; Martinez, L.; Gonzalez, A.; Vanegas, J.C.; Apestegui, A. In vitro antimalarial activity of extracts of some plants from a biological reserve in Costa Rica. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2012, 60, 881–891. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.Q. Inhibitory activity of dihydrosanguinarine and dihydrochelerythrine against phytopathogenic fungi. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.H.; Zhao, J.L.; Lu, S.Q.; Wang, J.G.; Jiang, W.B.; Ma, Z.H.; Zhou, L.G. Isoquinoline alkaloids from Macleaya cordata active against plant microbial pathogens. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1557–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Vrublova, E.; Vostalova, J.; Ehrmann, J.; Palikova, I.; Vrbkova, J.; Vacek, J.; Cibicek, N.; Vecera, R.; Ulrichova, J.; Simanek, V. The phytogenetic feed additive Sangrovit modulates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in rats. Vet. Med.-Czech 2010, 55, 610–618. [Google Scholar]
- Vrba, J.; Orolinova, E.; Ulrichova, J. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 by Macleaya cordata extract and its constituent sanguinarine in RAW264.7 cells. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Alvarado, C.; Rojas, A.; Mendoza, S.; Bah, M.; Gutierrez, D.M.; Hernandez-Sandoval, L.; Martinez, M. Vasoactive and antioxidant activities of plants used in Mexican traditional medicine for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-George, C.; Vanderheyden, P.M.L.; Solis, P.N.; Pieters, L.; Shahat, A.A.; Gupta, M.P.; Vauquelin, G.; Vlietinck, A.J. Biological screening of selected medicinal Panamanian plants by radioligand-binding techniques. Phytomedicine 2001, 8, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-George, C.; Vanderheyden, P.M.L.; Solis, P.N.; Gupta, M.P.; Pieters, L.; Vauquelin, G.; Vlietinck, A. In vitro effect of sanguinarine alkaloid on binding of [3H] candesartan to the human angiotensin AT1 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 458, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez, C.; Calzada, F.; Torres, J.; Gonzalez, F.; Ceballos, G. Antisecretory activity of plants used to treat gastrointestinal disorders in Mexico. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 103, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.S.; Fang, X.M. Experimental studies on pharmacodynamic effect of Macleaya cordata. Chin. Med. Mat. 1999, 22, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Son, K.H.; Kang, S.S.; Choi, J.S. Scavenging effect of Korean medicinal plants on the peroxynitrite and total ROS. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2003, 9, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, M.; Huang, K.L.; Zeng, J.G.; Li, S.; Zhang, L. Determination of contents of eight alkaloids in fruits of Macleaya cordata (Willd) R. Br. from different habitats and antioxidant activities of extracts. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2010, 17, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedo, A.; Vlasicova, K.; Bartak, P.; Vespalec, R.; Vicar, J.; Simanek, V.; Ulrichova, J. Quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids as inhibitors of aminopeptidase N and dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sedo, A.; Malik, R.; Vicar, J.; Simanek, V.; Ulrichova, J. Quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids as inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase IV-like activity bearing enzymes in human blood plasma and glioma cell lines. Physiol. Res. 2003, 52, 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski, J.; Zdunczyk, Z.; Juskiewicz, J.; Kozlowski, K.; Lecewicz, A.; Jeroch, H. Gastrointestinal tract and metabolic response of broilers to diets with the Macleaya cordata alkaloid extract. Arch. Geflugelk. 2009, 73, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Juskiewicz, J.; Gruzauskas, R.; Zdunczyk, Z.; Semaskaite, A.; Jankowski, J.; Totilas, Z.; Jarule, V.; Sasyte, V.; Zdunczyk, P.; Raceviciute-Stupeliene, A.; et al. Effects of dietary addition of Macleaya cordata alkaloid extract on growth performance, caecal indices and breast meat fatty acids profile in male broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2011, 95, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.G. A report of poisoning by food containing Macleaya cordata. Chin. J. Med. 1980, 11, 23–23. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.K. Report of a case: Poisoning by Macleaya cordata. Hunan Med. J. 1991, 8, 159. [Google Scholar]
- Psotova, J.; Vecera, R.; Zdarilova, A.; Anzenbacherova, E.; Kosina, P.; Svobodova, A.; Hrbac, J.; Jirovsky, D.; Stiborova, M.; Lichnovsky, V.; et al. Safety assessment of sanguiritrin, alkaloid fraction of Macleaya cordata, in rats. Vet. Med.-Czech. 2006, 51, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zdunczyk, Z.; Gruzauskas, R.; Juskiewicz, J.; Semaskaite, A.; Jankowski, J.; Godycka-Klos, I.; Jarule, V.; Miezeliene, A.; Alencikiene, G. Growth performance, gastrointestinal tract responses, and meat characteristics of broiler chickens fed a diet containing the natural alkaloid sanguinarine from Macleaya cordata. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2010, 19, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawling, M.D.; Merrifield, D.L.; Davies, S.J. Preliminary assessment of dietary supplementation of Sangrovit on red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth performance and health. Aquaculture 2009, 294, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosina, P.; Walterova, D.; Ulrichova, J.; Ulrichova, J.; Lichnovsky, V.; Stiborova, M.; Rydlova, H.; Vicar, J.; Krecman, V.; Brabec, M.J.; Simanek, V. Sanguinarine and chelerythrine: assessment of safety on pigs in ninety days feeding experiment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacek, J.; Papoušková, B.; Kosina, P.; Galandáková, A.; Ulrichová, J. Mass spectrometric investigation of chelerythrine and dihydrochelerythrine biotransformation patterns in human hepatocytes. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 941, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancula, D.; Suchomelova, J.; Gregor, J.; Smutna, M.; Marsalek, B.; Taborska, E. Effects of aqueous extracts from five species of the family Papaveraceae on selected aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. 2007, 22, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiborova, M.; Vostalova, J.; Zdarilova, A.; Ulrichova, J.; Hudecek, J.; Tschirner, K.; Simanek, V. Macleaya cordata extract and Sangrovit genotoxicity. Assessment in vivo. Biomed. Pap. 2008, 152, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambault, J.; Williams, R.D.; Bedard, C.; Chavarie, C. Production of sanguinarine by elicited plant cell culture. I. Shake flask suspension cultures. J. Biotechnol. 1996, 46, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Gao, X.; Zhu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tu, P.; Chai, X. Alkaloids from the Tribe Bocconieae (Papaveraceae): A Chemical and Biological Review. Molecules 2014, 19, 13042-13060. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913042
Yu X, Gao X, Zhu Z, Cao Y, Zhang Q, Tu P, Chai X. Alkaloids from the Tribe Bocconieae (Papaveraceae): A Chemical and Biological Review. Molecules. 2014; 19(9):13042-13060. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913042
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xuelong, Xiaoli Gao, Zhixiang Zhu, Yuan Cao, Qian Zhang, Pengfei Tu, and Xingyun Chai. 2014. "Alkaloids from the Tribe Bocconieae (Papaveraceae): A Chemical and Biological Review" Molecules 19, no. 9: 13042-13060. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913042
APA StyleYu, X., Gao, X., Zhu, Z., Cao, Y., Zhang, Q., Tu, P., & Chai, X. (2014). Alkaloids from the Tribe Bocconieae (Papaveraceae): A Chemical and Biological Review. Molecules, 19(9), 13042-13060. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913042




