Review of Natural Compounds for Potential Skin Cancer Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Natural Sources of Anti-Cancer Compounds
2.1. Marine Sources
2.2. Microbial Sources
2.3. Plant Sources
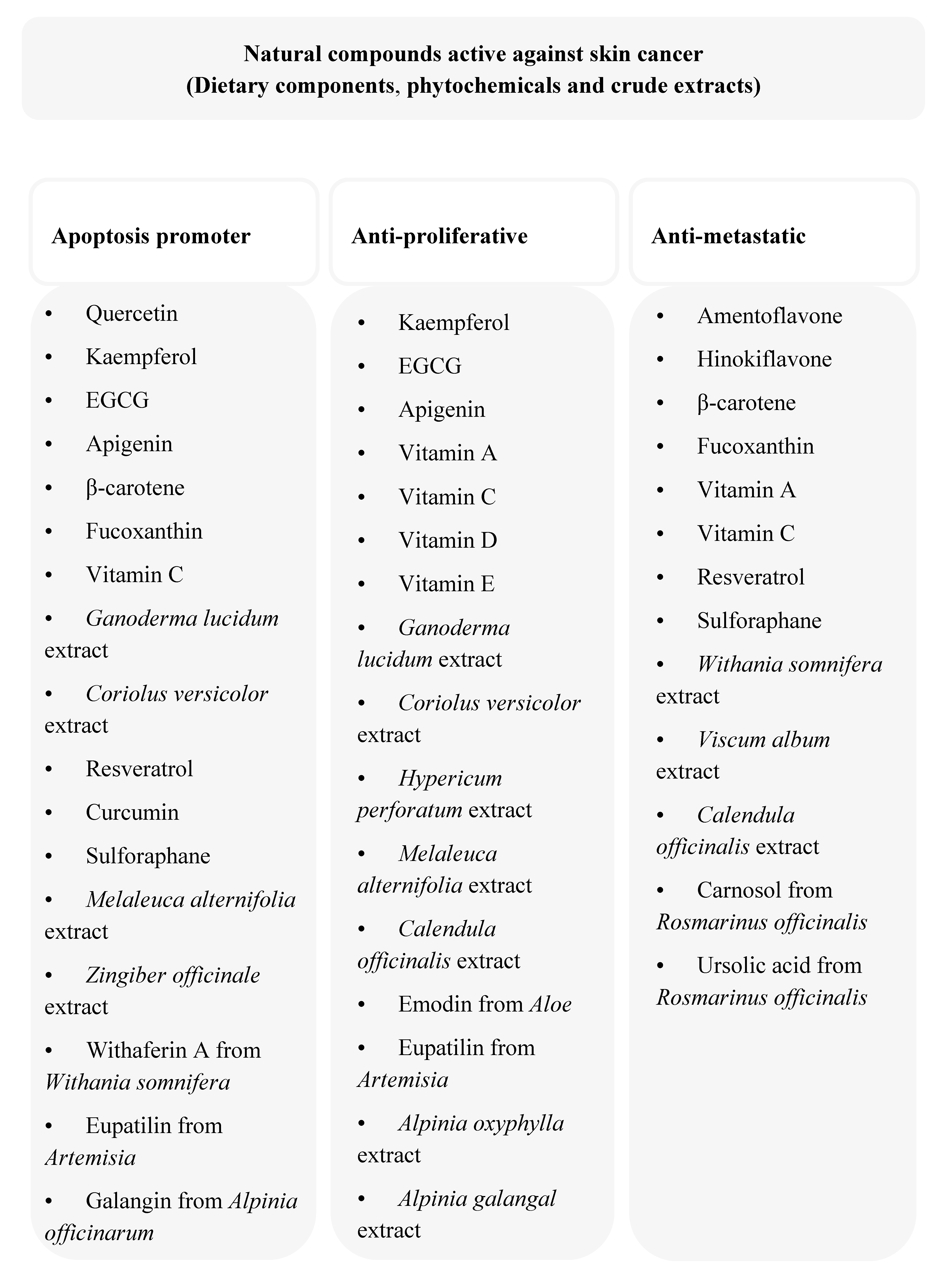
3. Anti-Cancer Dietary Components and Phytochemicals
3.1. Flavonoids
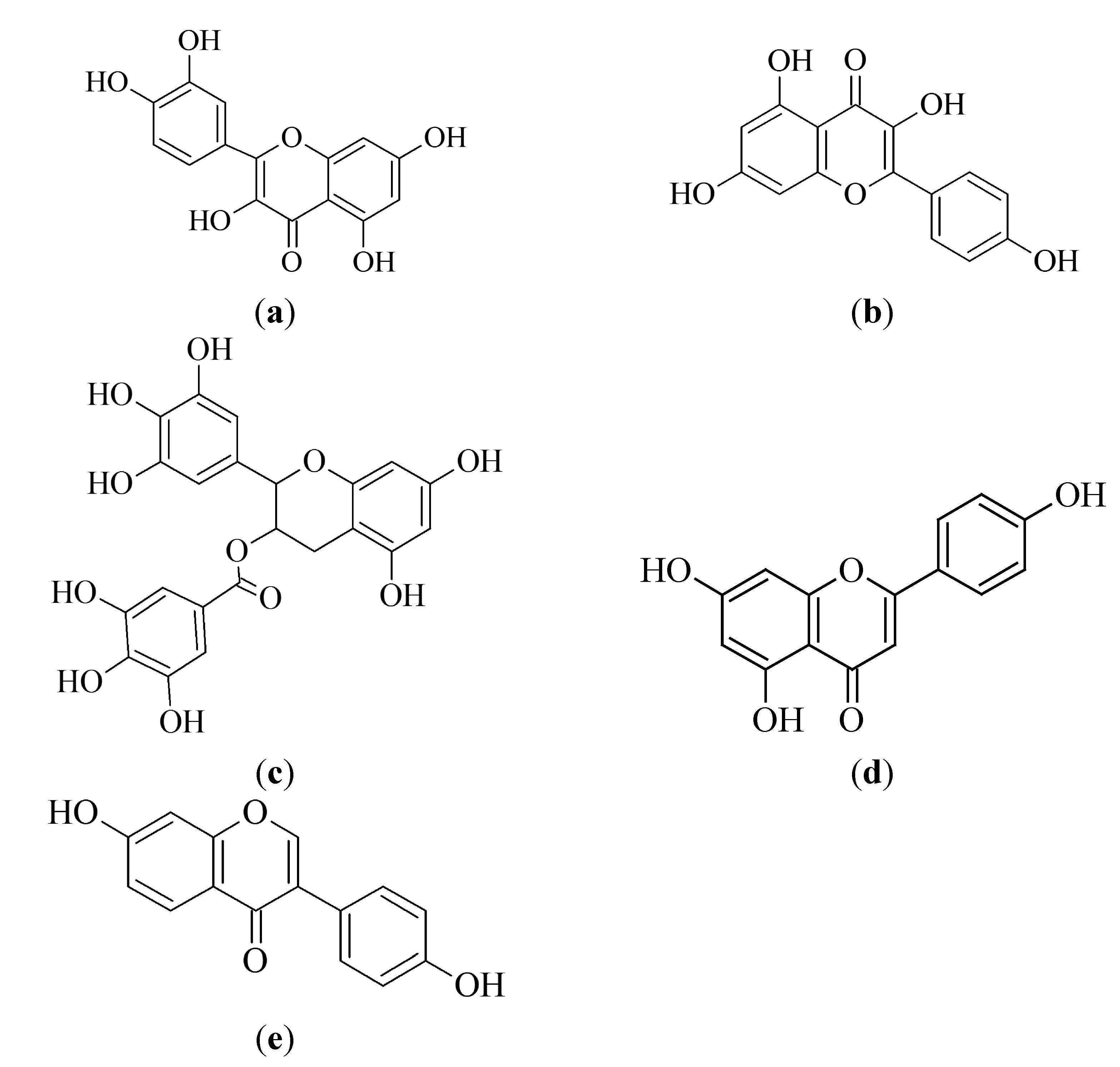
3.1.1. Quercetin
3.1.2. Kaempferol
3.1.3. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
3.1.4. Apigenin
3.1.5. Daidzein
3.1.6. Biflavonoids
3.2. Carotenoids
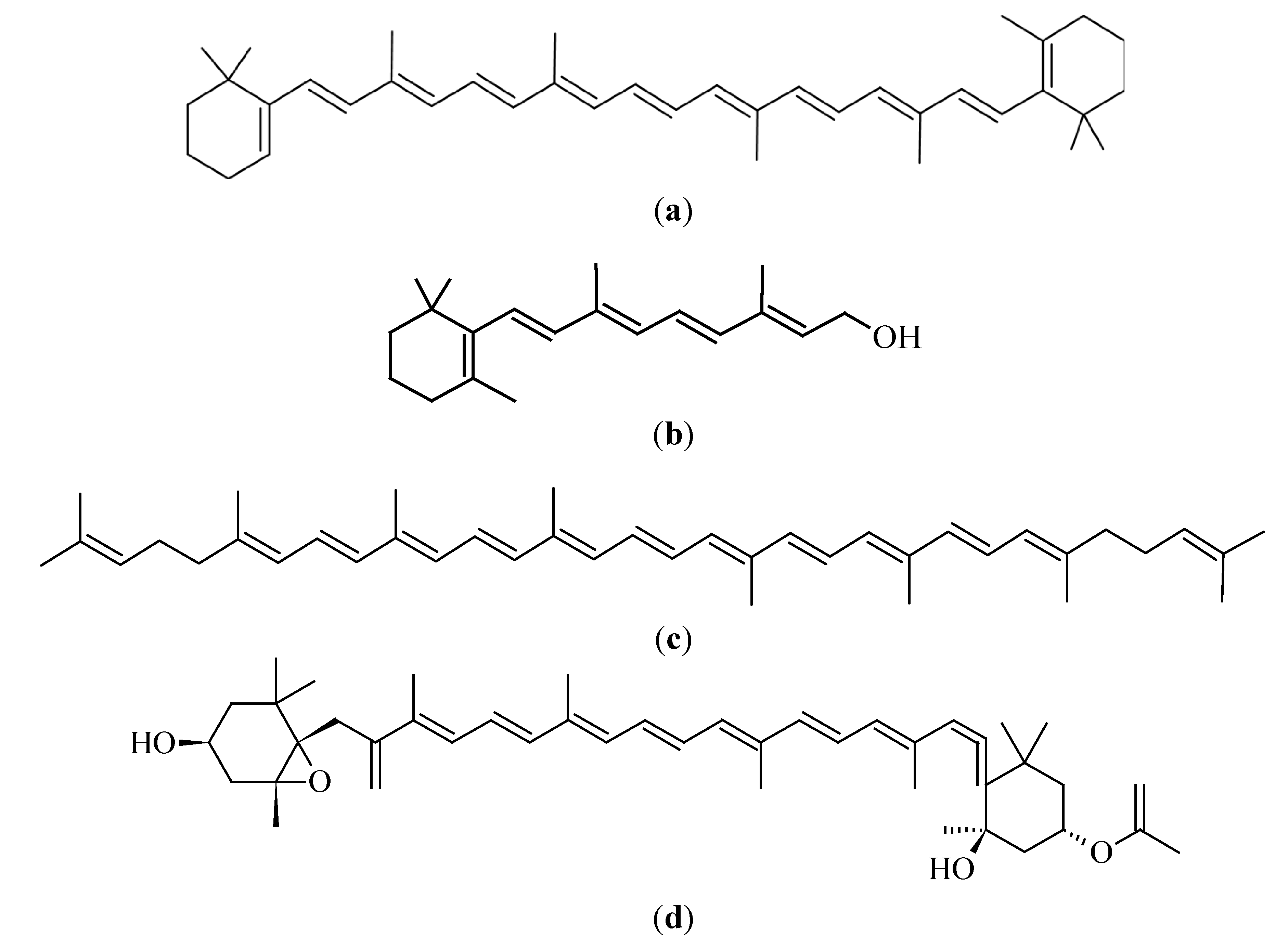
3.2.1. β-Carotene
3.2.2. Lycopene
3.2.3. Fucoxanthin
3.3. Vitamins
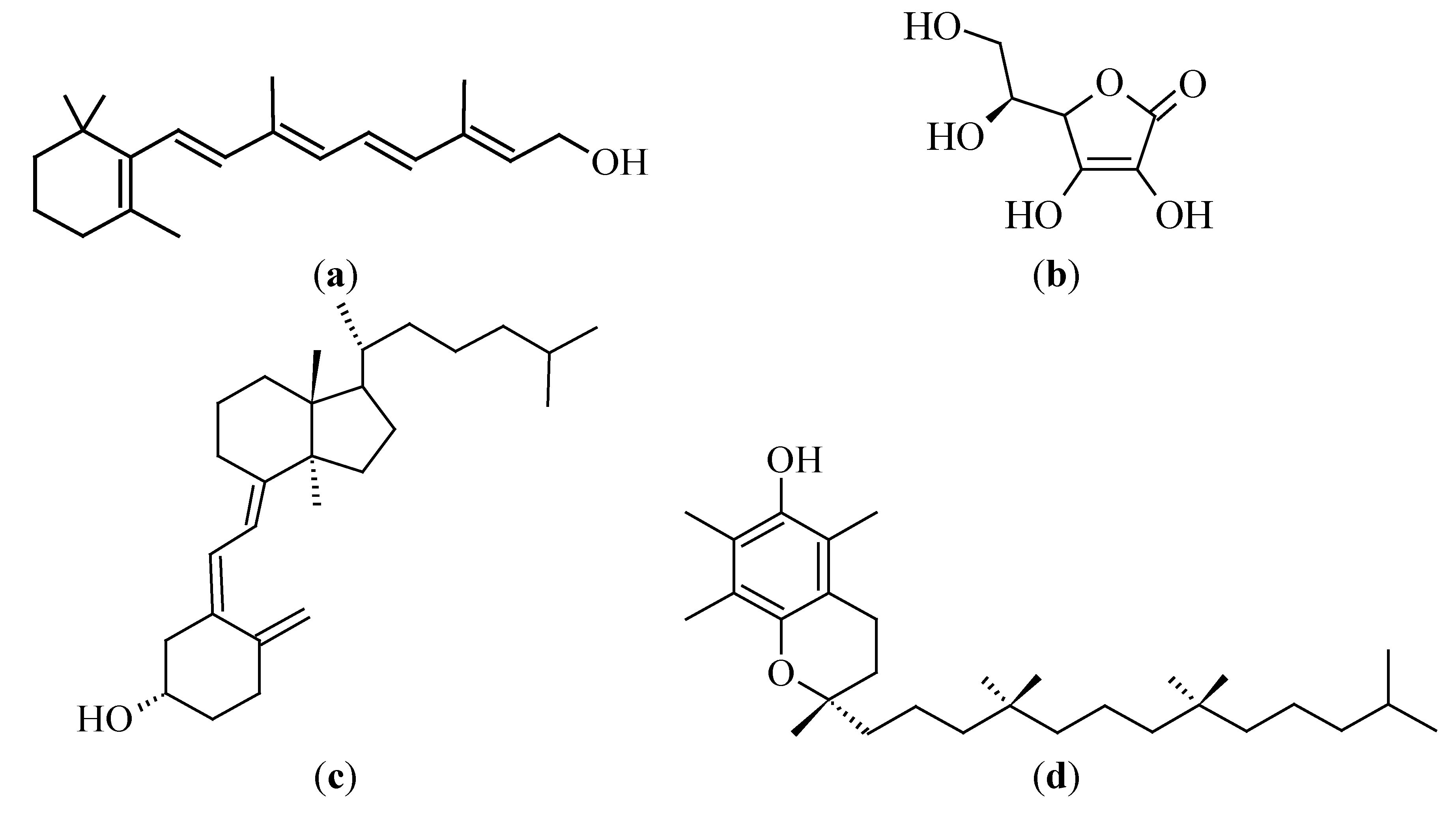
3.3.1. Vitamin A (Retinol)
3.3.2. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
3.3.3. Vitamin D
3.3.4. Vitamin E (Tocopherol)
3.4. Terpenoids
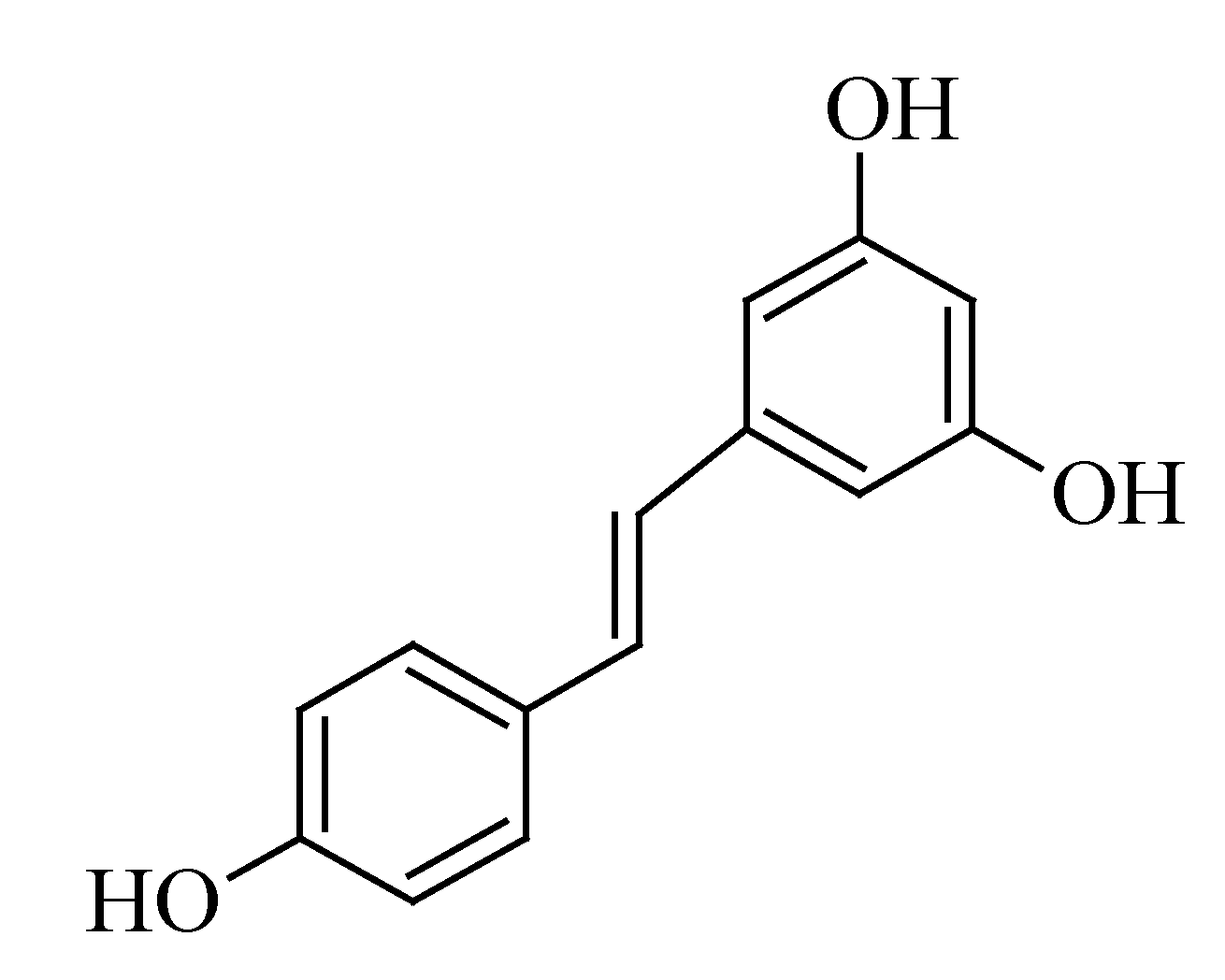
3.5. Resveratrol
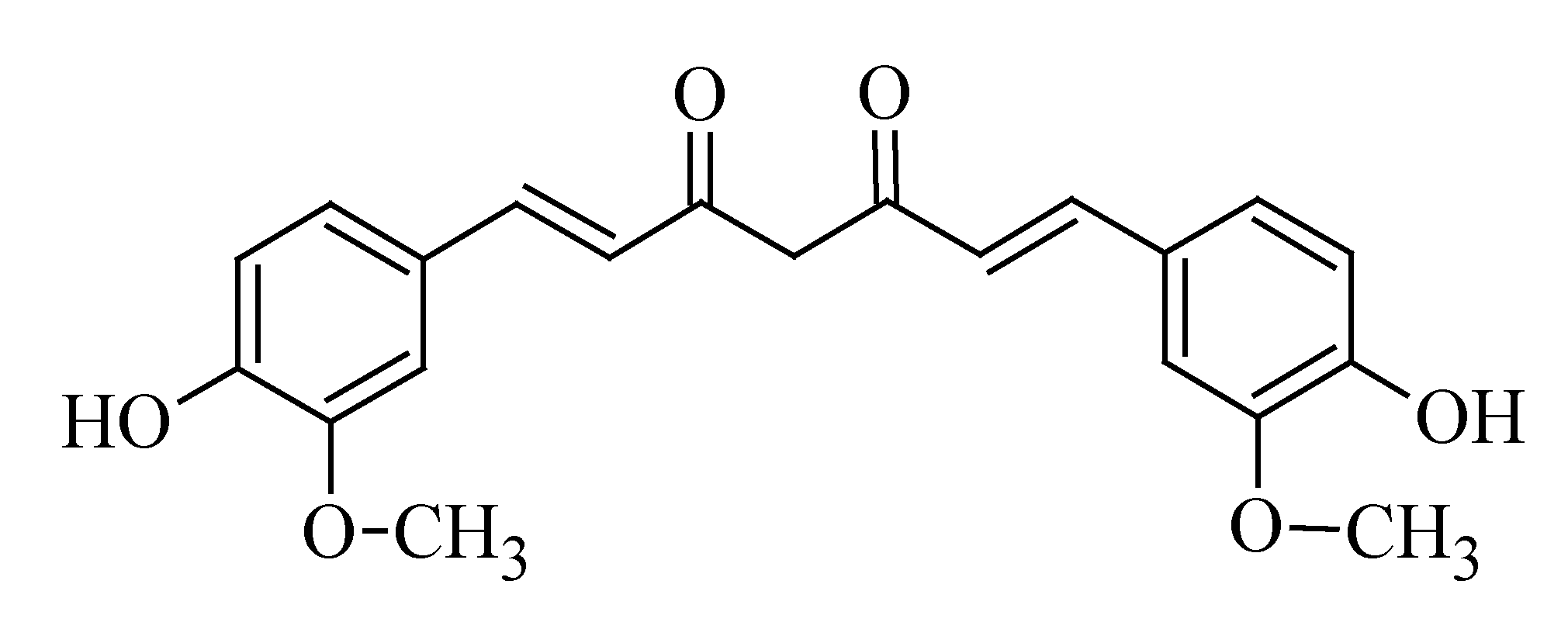
3.6. Curcumin
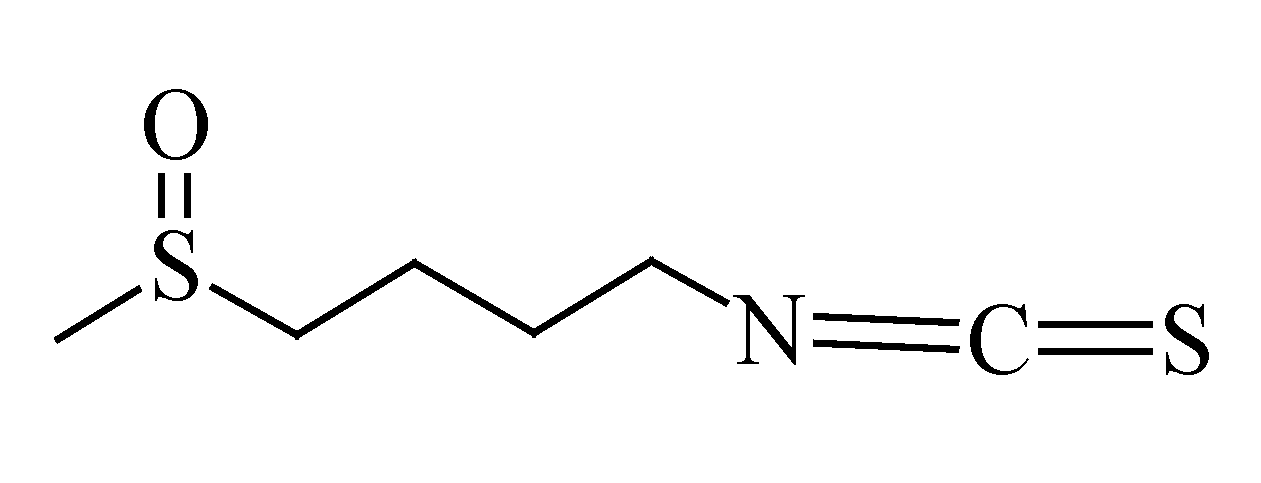
3.7. Sulforaphane
4. Anti-melanoma Activity of Crude Plant Extracts
4.1. Hypericum perforatum
4.2. Withania somnifera
4.3. Melaleuca alternifolia
4.4. Zingiber officinale
4.5. Viscum album
4.6. Calendula officinalis
4.7. Rosmarinus officinalis
4.8. Aloe Species
4.9. Artemisia Species
4.10. Alpinia Species
5. Conclusions
Abbreviations
| AMPK | adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase |
| Bax | Bcl-2 associated X protein |
| BCC | basal cell carcinoma |
| Bcl-2 | B cell lymphoma 2 |
| CAM | complementary and alternative medicine |
| CDK | cyclin dependent kinase |
| Cip | CDK interacting protein |
| CMM | cutaneous malignant melanoma |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase 2 |
| CXCR4 | C-X-C receptor 4 |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EGCG | epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FADD | Fas-Associated protein with Death Domain |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GM-CSF | granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| IC50 | 50% inhibitory concentration |
| IFN | interferon |
| IGF-1R | Type 1 insulin like growth factor receptor |
| IL | interleukin |
| lncRNA | long non-coding RNA |
| MAPK | mitogen activated protein kinase |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| mPTP | mitochondrial permeability transition pore |
| mRNA | m-ribonucleic acid |
| NCCAM | National Centre for Complementary and Alternative Medicine |
| NCI | National Cancer Institute |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NIH | National Institute of Health |
| PCNA | proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
| PDT | photodynamic therapy |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide-3 kinase |
| RAR | retinoic acid receptor |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SCC | squamous cell carcinoma |
| STAT-3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TNF-R | tumor necrosis factor receptor |
| TRAIL-R | TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand receptor |
| USA | United States of America |
| UV | ultra-violet |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kachuri, L.; De, P.; Ellison, L.F.; Semenciw, R.; Advisory Committee on Canadian Cancer Statistics. Cancer incidence, mortality and survival trends in Canada, 1970–2007. Chronic Dis. Inj. Can. 2013, 33, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Erb, P.; Ji, J.; Wernli, M.; Kump, E.; Glaser, A.; Büchner, S.A. Role of apoptosis in basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma formation. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 100, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippens, S.; Hoste, E.; Vandenabeele, P.; Declercq, W. Cell death in skin. In Apoptosis: Physiology and Pathology; Reed, J.C., Green, D.R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 323–332. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, V.J.; Hanson, N.W. Non-melanoma skin cancer. In Sauer’s Manual of Skin Diseases; Hall, B.J., Hall, J.C., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer Health: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; Volume 10, pp. 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Freedman, M.L.; Nierodzik, M.L.R. Cancer and age. In Encyclopedia of Gerontology, 2nd ed.; Birren, J.E., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 191–212. [Google Scholar]
- Conroy, M.L.; Davis, K.R.; Embree, J.L.; Madara, B.; Magaletto, P.; Roach, R.R.; Sauls, B.L.; Scemons, D.; Shen, Q.; Skoruppa, D.; et al. Atlas of Pathophysiology, 3rd ed.; Eckman, M., Labus, D., Thompson, G., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer Health: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–455. [Google Scholar]
- Raasch, B. Management of superficial basal cell carcinoma: Focus on imiquimod. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 2, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, S.C. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference, 37th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2011; pp. 1–4142. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, A.K.; Singh, A.; Ganta, S.; Amiji, M.M. Role of integrated cancer nanomedicine in overcoming drug resistance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1784–1802. [Google Scholar]
- Kunjachan, S.; Rychlik, B.; Storm, G.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Multidrug resistance: Physiological principles and nanomedical solutions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1852–1865. [Google Scholar]
- Markman, J.L.; Rekechenetskiy, A.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.Y. Nanomedicine therapeutic approaches to overcome cancer drug resistance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1866–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alifrangis, C.; Koizia, L.; Rozario, A.; Rodney, S.; Harrington, M.; Somerville, C.; Peplow, T.; Waxman, J. The experiences of cancer patients. QJM 2011, 104, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Slevin, M.L.; Stubbs, L.; Plant, H.J.; Wilson, P.; Gregory, W.M.; Armes, P.J.; Downer, S.M. Attitudes to chemotherapy: Comparing views of patients with cancer with those of doctors, nurses, and general public. Brit. Med. J. 1990, 300, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, M.; Parry, M.; Gill, P.; Mead, D.; Macbeth, F. Hard choices: A qualitative study of influences on the treatment decisions made by advanced lung cancer patients. Int. Palliat. Nurs. 2011, 17, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Molassiotis, A.; Fernandez-Ortega, P.; Pud, D.; Ozden, G.; Scott, J.A.; Panteli, V.; Margulies, A.; Browall, M.; Magri, M.; Selvekerova, S. Use of complementary and alternative medicine in cancer patients: A European survey. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 655–663. [Google Scholar]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural products: A continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3670–95. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, M.B.J.; Gibbons, S.; Williamson, E.M. Fundamentals of Pharmacognosy and Phytotherapy, 1st ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, S.N.; Ermakova, S.P.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. Anticancer and cancer preventive properties of marine polysaccharides: Some results and prospects. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4876–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeriote, F.A.; Tenney, K.; Media, J.; Pietraszkiewicz, H.; Edelstein, M.; Johnson, T.A.; Amagata, T.; Crews, P. Discovery and development of anticancer agents from marine sponges: Perspectives based on a chemistry-experimental therapeutics collaborative program. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2012, 10, 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.; Garcia, M.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Costa, M.S.; Ribeiro, M.J.; Fernandes, M.H.; Barros, P.; Barreiro, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Martins, R. Exploring bioactive properties of marine cyanobacteria isolated from the Portuguese coast: High potential as a source of anticancer compounds. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 98–114. [Google Scholar]
- Indumathy, S.; Dass, C.R. Finding chemo: The search for marine-based pharmaceutical drugs active against cancer. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 1280–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Marine-sourced anti-cancer and cancer pain control agents in clinical and late preclinical development. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartsmann, G.; da Rocha, A.B.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Jimeno, J. Marine organisms as a source of new anticancer drugs. Lancet. Oncol. 2001, 2, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cann, S.A.H.; van Netten, J.P.; van Netten, C. Dr William Coley and tumour regression: A place in history or in the future. Postgrad. Med. 2003, 79, 672–680. [Google Scholar]
- Bhanot, A.; Sharma, R.; Noolvi, M.N. Natural sources as potential anti-cancer agents: A review. Int. Phytomed. 2011, 3, 9–26. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk, B.; van Oudtshoorn, B.; Gericke, N. Medicinal Plants of South Africa, 1st ed.; Briza Publications: Pretoria, South Africa, 1997; pp. 1–304. [Google Scholar]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balunas, M.J.; Kinghorn, A.D. Drug discovery from medicinal plants. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, S.; Lippi, D.; Witort, E.; Donnini, M.; Bausi, L.; Mini, E.; Capaccioli, S. Natural compounds for cancer treatment and prevention. Pharmacol. Res. 2009, 59, 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Mansky, P.J.; Wallerstedt, D.B.; Sannes, T.S.; Stagl, J.; Johnson, L.L.; Blackman, M.R.; Grem, J.L.; Swain, S.M.; Monahan, B.P. NCCAM/NCI phase 1 study of mistletoe extract and gemcitabine in patients with advanced solid tumors. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Call, T.G.; Zent, C.S.; Leis, J.F.; LaPlant, B.; Bowen, D.A.; Roos, M.; Laumann, K.; Ghosh, A.K.; Lesnick, C.; et al. Phase 2 trial of daily, oral polyphenon E in patients with asymptomatic, Rai stage 0 to II chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 2013, 119, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Tabasum, S.; Singh, R.P. Berberine in combination with doxorubicin suppresses growth of murine melanoma B16F10 cells in culture and xenograft. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Moon, E.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, K.R. Lignan constituents of Tilia amurensis and their biological evaluation on antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3680–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Katiyar, S.K. Green tea polyphenol, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, induces toxicity in human skin cancer cells by targeting β-catenin signaling. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 273, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.; Chou, T.; Ding, H.; Chen, P.; Chiang, F.; Kuo, P.; Liang, C. Apigenin induces apoptosis via tumor necrosis factor receptor- and Bcl-2-mediated pathway and enhances susceptibility of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. S. 2012, 1820, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N.; Mukhtar, H.; Wood, G.S. Anti-proliferative and proapoptotic effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on human melanoma: Possible implications for the chemoprevention of melanoma. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 513–521. [Google Scholar]
- Katiyar, S.K. Green tea prevents non-melanoma skin cancer by enhancing DNA repair. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 508, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Meckling, K.A.; Marcone, M.F.; Kakuda, Y.; Tsao, R. Can phytochemical antioxidant rich foods act as anticancer agents? Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2545–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidnia, S.; Abdollahi, M. Antioxidants: Friends or foe in prevention or treatment of cancer: The debate of the century. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 271, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, P.; Sharma, A.K. Anti-cancer potential of flavonoids: Recent trends and future perspectives. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 439–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttan, G.; Pratheeshkumar, P.; Manu, K.A.; Kuttan, R. Inhibition of tumor progression by naturally occurring terpenoids. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, K.A.; Potter, J.D. Vegetables, fruit, and cance. II. Mechanisms. Cancer Causes Control 1991, 2, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, J.B. The Molecules of Nature: A Survey of The Biosynthesis And Chemistry of Natural Products; W.A. Benjamin, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran, M.P.; McKay, D.L.; Blumberg, J.B. Flavonoid basics: Chemistry, sources, mechanisms of action, and safety. J. Nutr. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 31, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A. Pharmacological Activities of Flavonoids: A Review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotech. 2011, 4, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Harborne, J.B.; Williams, C.A. Advances in flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saewan, N.; Jimtaisong, A. Photoprotection of natural flavonoids. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, G.S. Quercetin. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 172–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.S.; Tsai, P.H.; Kandaswami, C.C.; Cheng, C.H.; Ke, F.C.; Lee, P.P.; Hwang, J.J.; Lee, M.T. Effects of dietary flavonoids, luteolin, and quercetin on the reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A431 epidermal cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Bu, S.; Tak, K.; Park, J.; Kim, E. Anticarcinogenic effect of quercetin by inhibition of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 signaling in mouse skin cancer. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2013, 7, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derenne, A.; van Hemelryck, V.; Lamoral-Theys, D.; Kiss, R.; Goormaghtigh, E. FTIR spectroscopy: A new valuable tool to classify the effects of polyphenolic compounds on cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2013, 1832, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sak, K. Site-specific anticancer effects of dietary flavonoid quercetin. Nutr. Cancer 2014, 66, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlund, I. Review of the flavonoids quercetin, hesperetin, and naringenin: Dietary sources, bioactivities, bioavailability, and epidemiology. Nutr. Res. 2004, 24, 851–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollman, P.C.H.; van Trijp, J.M.P.; Mengelers, M.J.B.; de Vries, J.H.M.; Katan, M.B. Bioavailability of the dietary antioxidant flavonol quercetin in man. Cancer Lett. 1997, 114, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensi, M.; Ortega, A.; Mena, S.; Feddi, F.; Estrela, J.M. Natural polyphenols in cancer therapy. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2011, 48, 197–216. [Google Scholar]
- Caltagirone, S.; Rossi, C.; Poggi, A.; Ranelletti, F.O.; Natali, P.G.; Brunetti, M.; Aiello, F.B.; Piantelli, M. Flavonoids apigenin and quercetin inhibit melanoma growth and metastatic potential. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 87, 595–600. [Google Scholar]
- Rosner, K.; Röpke, C.; Pless, V.; Skovgaard, G.L. Late type apoptosis and apoptosis free lethal effect of quercetin in human melanoma. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-M.; Chen, J.; Xia, Y.-G.; Xu, Q. Apoptosis of murine melanoma B16-BL6 cells induced by quercetin targeting mitochondria, inhibiting expression of PKC-α and translocating PKC-δ. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2005, 55, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, E.R.; Melton, T.; Dickinson, S.E.; Dong, Z.; Alberts, D.S.; Bowden, G.T. Quercetin potentiates UVB-Induced c-Fos expression: Implications for its use as a chemopreventive agent. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 3, 876–884. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Li, W.; Son, Y.O.; Sun, L.; Lu, J.; Kim, D.; Wang, X.; Yao, H.; Wang, L.; Pratheeshkumar, P.; et al. Quercitin protects skin from UVB-induced oxidative damage. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 269, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.H.; Tse, A.K.W.; Kwan, H.Y.; Yu, H.; Cheng, C.Y.; Su, T.; Fong, W.F.; Yu, Z.L. Quercetin exerts anti-melanoma activities and inhibits STAT3 signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 87, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, R.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Dorta, D.J.; dos Santos, A.C.; Fonseca, M.J.V. Protective effect of topical formulations containing quercetin against UVB-induced oxidative stress in hairless mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2006, 84, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-F.; Leu, Y.-L.; Al-Suwayeh, S.A.; Ku, M.-C.; Hwang, T.-L.; Fang, J.-Y. Anti-inflammatory activity and percutaneous absorption of quercetin and its polymethoxylated compound and glycosides: The relationships to chemical structures. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneha, S.; Swarnlata, S.; Kaur, C.D.; Shailendra, S. Biocompatible nanoparticles for sustained topical delivery of anticancer phytoconstituent quercetin. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 16, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, R.; Martena, V.; Hoti, E.; Malaj, L.; di Martino, P. Permeation and skin retention of quercetin from microemulsions containing Transcutol® P. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albishi, T.; John, J.A.; Al-Khalifa, A.S.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidative phenolic constituents of skins of onion varieties and their activities. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, Y.C.; Yi Charlie, C. Review: A review of the dietary flavonoid, kaempferol on human health and cancer chemoprevention. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miean, K.H.; Mohamed, S. Flavonoid (myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, and apigenin) content of edible tropical plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3106–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon-Montano, J.M.; Burgos-Moron, E.; Perez-Guerrero, C.; Lopez-Lazaro, M. A review on the dietary flavonoid kaempferol. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 298–344. [Google Scholar]
- Casagrande, F.; Darbon, J. Effects of structurally related flavonoids on cell cycle progression of human melanoma cells: Regulation of cyclin-dependent kinases CDK2 and CDK1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 61, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Huang, C.T.; Fu, L.T.; Huang, Y.B.; Tsai, Y.H.; Wu, P.C. The effect of submicron emulsion systems on transdermal delivery of kaempferol. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.N.; Kim, S.Y.; Lim, G.N.; Jo, N.R.; Lee, M.H. In vitro skin permeation and cellular protective effects of flavonoids isolated from Suaeda asparagoides extracts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 18, 680–683. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.Y.; Ou, N.; Lu, Q.B. Antioxidant induces DNA damage, cell death and mutagenicity in human lung and skin normal cells. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3169–3169. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, M.; Tedesco, I.; Iacomino, G.; Palumbo, R.; Galano, G.; Russo, G.L. Dietary phytochemicals in chemoprevention of cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. Immunol. Endocr. Metab. Agents 2005, 5, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Miura, Y.; Yagasaki, K. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in cancer cells by in vivo metabolites of teas. Nutr. Cancer 2000, 38, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihal, M.; Roelke, C.T.; Wood, G.S. Anti-melanoma effects of vorinostat in combination with polyphenolic antioxidant (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihal, M.; Ahsan, H.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Mukhtar, H.; Ahmad, N.; Wood, G.S. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) sensitizes melanoma cells to interferon induced growth inhibition in a mouse model of human melanoma. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.Y.; Hong, W.; Guang Xun, L.; Zhihong, Y.; Fei, G.; Huanyu, J. Review: Cancer prevention by tea: Evidence from laboratory studies. Pharm. Res. 2011, 64, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, N.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R. Differential responses of skin cancer-chemopreventive agents silibinin, quercetin, and epigallocatechin 3-gallate on mitogenic signaling and cell cycle regulators in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Nutr. Cancer 2001, 39, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, V.; Vaid, M.; Katiyar, S.K. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate reactivates silenced tumor suppressor genes, Cip1/p21 and p16INK4a, by reducing DNA methylation and increasing histones acetylation in human skin cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevın, A.; Özta, P.; Senen, D.; Han, Ü.; Karaman, Ç.; Tarimci, N.; Kartal, M.; Erdogan, B. Effects of polyphenols on skin damage due to ultraviolet A rays: An experimental study on rats. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2007, 21, 650–656. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.; Gupta, S. Apigenin and cancer chemoprevention. In Bioactive Foods in Promoting Health: Fruits and Vegetables; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.; Gupta, S. Apigenin: A promising molecule for cancer prevention. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Das, J.; Paul, A.; Samadder, A.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A.R. Research article: Apigenin, a bioactive flavonoid from lycopodium lavatum, stimulates nucleotide excision repair genes to protect skin keratinocytes from ultraviolet B-induced reactive oxygen species and DNA damage. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2013, 6, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.; Park, J.; Lee, E.; Lim, S.; Yu, J.G.; Lee, S.J.; Chen, H.; Dong, Z.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, H.J. Src kinase is a direct target of apigenin against UVB-induced skin inflammation. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Na, S.; Yong-Tai, Z.; Qin, W.; Ling, X.; Nian-Ping, F. Pharmaceutical nanotechnology: Enhanced in vitro and in vivo skin deposition of apigenin delivered using ethosomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 460, 280–288. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Das, J.; Samadder, A.; Paul, A.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A.R. Strategic formulation of apigenin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for intracellular trafficking, DNA targeting and improved therapeutic effects in skin melanoma in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 223, 124–138. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Das, S.; Samadder, A.; Paul, A.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A.R. Efficacy of PLGA-loaded apigenin nanoparticles in Benzo[a]pyrene and ultraviolet-B induced skin cancer of mice: Mitochondria mediated apoptotic signalling cascades. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Hung, C.; Lin, Y.; Fang, J. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of topical delivery and potential dermal use of soy isoflavones genistein and daidzein. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Tournas, J.A.; Burch, J.A.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Zielinski, J. Topical isoflavones provide effective photoprotection to skin. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2008, 24, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovine, B.; Iannella, M.L.; Gasparri, F.; Monfrecola, G.; Bevilacqua, M.A. Synergic effect of genistein and daidzein on UVB-induced DNA damage: An effective photoprotective combination. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, L.P.; Yu, X.Y.; Zhang, R.Q. Effects of genistein and daidzein on the cell growth, cell cycle, and differentiation of human and murine melanoma cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.Y.; Cai, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y. Natural phenolic compounds from medicinal herbs and dietary plants: Potential use for cancer prevention. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chang, H.W.; Kim, H.P.; Park, H. Synthesis of phospholipase A2 inhibitory biflavonoids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2373–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.M.; Horinouchi, C.D.; Prudente Ada, S.; Cechinel-Filho, V.; Cabrini Dde, A.; Otuki, M.F. Effect of a Garcinia gardneriana (Planchon and Triana) Zappi hydroalcoholic extract on melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruvayoorappan, C.; Kuttan, G. Amentoflavone inhibits experimental tumor metastasis through a regulatory mechanism involving MMP-2, MMP-9, prolyl hydroxylase, lysyl oxidase, VEGF, ERK-1, ERK-2, STAT-1, NM23 and cytokines in lung tissues of C57BL/6 mice. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2008, 30, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarallo, V.; Lepore, L.; Marcellini, M.; Dal Piaz, F.; Tudisco, L.; Ponticelli, S.; Lund, F.W.; Roepstorff, P.; Orlandi, A.; Pisano, C.; et al. The biflavonoid amentoflavone inhibits neovascularization preventing the activity of proangiogenic vascular endothelial growth factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 19641–19651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruvayoorappan, C.; Kuttan, G. Effect of amentoflavone on the inhibition of pulmonary metastasis induced by B16F-10 melanoma cells in C57BL/6 mice. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalva, S.; Azhagiya Singam, E.R.; Rajapandian, V.; Saleena, L.M.; Subramanian, V. Discovery of potent inhibitor for matrix metalloproteinase-9 by pharmacophore based modeling and dynamics simulation studies. J. Mol. Graphics Modell. 2014, 49, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Krinsky, N.I.; Johnson, E.J. Carotenoid actions and their relation to health and disease. Mol. Aspects. Med. 2005, 26, 459–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. A Guide to Carotenoid Analysis in Foods; ILSI Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Vainio, H.; Rautalahti, M. An international evaluation of the cancer preventive potential of carotenoids. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1998, 7, 725–728. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, W.; Sies, H. Bioactivity and protective effects of natural carotenoids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2005, 1740, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Shnimizu, M.; Moriwaki, H. Cancer chemoprevention by carotenoids. Molecules 2012, 17, 3202–3242. [Google Scholar]
- Payette, M.J.; Whalen, J.; Grant-Kels, J.M. Nutrition and nonmelanoma skin cancers. Clin. Dermatol. 2010, 28, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, E.; Vahlquist, A.; Rosdahl, I. β-carotene uptake and bioconversion to retinol differ between human melanocytes and keratinocytes. Nutr. Cancer 2001, 39, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palozza, P.; Serini, S.; Torsello, A.; di Nicuolo, F.; Maggiano, N.; Ranelletti, F.O.; Wolf, F.I.; Calviello, G. mechanism of activation of caspase cascade during β-carotene-induced apoptosis in human tumor cells. Nutr. Cancer 2003, 47, 76–87. [Google Scholar]
- Guruvayoorappan, C.; Kuttan, G. β-Carotene down-regulates inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression and induces apoptosis by suppressing bcl-2 expression and activating caspase-3 and p53 genes in B16F-10 melanoma cells. Nutr. Res. 2007, 27, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruvayoorappan, C.; Kuttan, G. Beta-carotene inhibits tumor-specific angiogenesis by altering the cytokine profile and inhibits the nuclear translocation of transcription factors in B16F-10 melanoma cells. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzioch, M.; Dembinska-Kiec, A.; Hartwich, J.; Lapicka-Bodzioch, K.; Banas, A.; Polus, A.; Grzybowska, J.; Wybranska, I.; Dulinska, J.; Gil, D.; et al. The microarray expression analysis identifies BAX as a mediator of β-carotene effects on apoptosis. Nutr. Cancer 2005, 51, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialy, T.L.; Rothe, M.J.; Grant-Kels, J.M. Dietary factors in the prevention and treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer and melanoma. Dermatol. Surg. 2002, 28, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Millen, A.E.; Tucker, M.A.; Hartge, P.; Halpern, A.; Elder, D.E.; Guerry, D.T.; Holly, E.A.; Sagebiel, R.W.; Potischman, N. Diet and melanoma in a case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2004, 13, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, A.; Hedayati, B.; Dalgleish, A.G. Disease regression in malignant melanoma: Spontaneous resolution or a result of treatment with antioxidants, green tea, and pineapple cores? A case report. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hercberg, S.; Ezzedine, K.; Guinot, C.; Preziosi, P.; Galan, P.; Bertrais, S.; Estaquio, C.; Briancon, S.; Favier, A.; Latreille, J.; et al. Antioxidant supplementation increases the risk of skin cancers in women but not in men. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2098–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzedine, K.; Latreille, J.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Guinot, C.; Malvy, D. Incidence of skin cancers during 5-year follow-up after stopping antioxidant vitamins and mineral supplementation. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 3316–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennekens, C.H.; Buring, J.E.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.; Rosner, B.; Cook, N.R.; Belanger, C.; LaMotte, F.; Gaziano, J.M.; Ridker, P.M.; et al. Lack of effect of long-term supplementation with beta carotene on the incidence of malignant neoplasms and cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslow, R.A.; Alberg, A.J.; Helzlsouer, K.J.; Bush, T.L.; Norkus, E.P.; Morris, J.S.; Spate, V.E.; Comstock, G.W. Serological precursors of cancer: Malignant melanoma, basal and squamous cell skin cancer, and prediagnostic levels of retinol, beta- carotene, lycopene, alpha-tocopherol, and selenium. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1995, 4, 837–842. [Google Scholar]
- Comstock, G.W.; Helzlsouer, K.J.; Bush, T.L. Prediagnostic serum levels of carotenoids and vitamin E as related to subsequent cancer in Washington County, Maryland. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 260S–264S. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, H.-S.; Wu, W.-B.; Fang, J.-Y.; Chen, D.-F.; Chen, B.-H.; Huang, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-T.; Hung, C.-F. Lycopene inhibits PDGF-BB-induced signaling and migration in human dermal fibroblasts through interaction with PDGF-BB. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.B.; Chiang, H.S.; Fang, J.Y.; Hung, C.F. Inhibitory effect of lycopene on PDGF-BB-induced signalling and migration in human dermal fibroblasts: A possible target for cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1377–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, N.; Gemello, E.; Gammone, M.A.; de Girolamo, M.; Ficoneri, C.; Riccioni, G. Fucoxantin: A treasure from the sea. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbs, T.I.; Ermakova, S.P.; Fedoreyev, S.A.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Isolation of fucoxanthin and highly unsaturated monogalactosyldiacylglycerol from brown alga Fucus evanescens C Agardh and in vitro investigation of their antitumor activity. Mar. Biotechnol. 2013, 15, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.; Masashi, H.; Kazuo, M. Fucoxanthin: A marine carotenoid exerting anti-cancer effects by affecting multiple mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 5130–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Ahn, G.; Heo, S.J.; Kang, S.M.; Kang, M.C.; Yang, H.M.; Kim, D.; Roh, S.W.; Kim, S.K.; Jeon, B.T.; et al. Inhibition of tumor growth in vitro and in vivo by fucoxanthin against melanoma B16F10 cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 35, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.W.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Jeong, H.S.; Kim, C.H.; Joo, M.; Choi, J.Y.; Han, C.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, J.S.; et al. Marine algal fucoxanthin inhibits the metastatic potential of cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 580–585. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda, H.; Tanaka, J.; Shan, S.J.; Maoka, T. Anti-pigmentary activity of fucoxanthin and its influence on skin mRNA expression of melanogenic molecules. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju Hye, L.; Kishikawa, M.; Kumazoe, M.; Yamada, K.; Tachibana, H. Vitamin A enhances antitumor effect of a green tea polyphenol on melanoma by upregulating the polyphenol sensing molecule 67-kDa laminin receptor. PLoS One 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Eastham, L.; Varney, M.E.; Hall, A.; Adkins, N.L.; Sollars, V.E.; Georgel, P.; Niles, R.M. Silencing and re-expression of retinoic acid receptor beta2 in human melanoma. Pigm. Cell Melanoma Res. 2010, 23, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Marchand, L.; Saltzman, B.S.; Hankin, J.H.; Wilkens, L.R.; Franke, A.A.; Morris, S.J.; Kolonel, L.N. Sun exposure, diet, and melanoma in Hawaii Caucasians. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, M.M.; Brasky, T.M.; White, E. Association of vitamin A and carotenoid intake with melanoma risk in a large prospective cohort. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, M.E.; Wang, S.Q. Current sunscreen controversies: A critical review. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2011, 27, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganroth, P.A.; Lim, H.W.; Burnett, C.T. Ultraviolet radiation and the skin: An in-depth review. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2013, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruvayoorappan, C.; Kuttan, G. 13 cis-Retinoic acid regulates cytokine production and inhibits angiogenesis by disrupting endothelial cell migration and tube formation. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2008, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Meyskens, F.L., Jr.; Fuller, B.B. Characterization of the effects of different retinoids on the growth and differentiation of a human melanoma cell line and selected subclones. Cancer Res. 1980, 40, 2194–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.P.C.; Silva, F.S.G.; Paixão, J.; Santos, A.E.; Custódio, J.B.A. The combination of the antiestrogen endoxifen with all-trans-retinoic acid has anti-proliferative and anti-migration effects on melanoma cells without inducing significant toxicity in non-neoplasic cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 715, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feskanich, D.; Willett, W.C.; Hunter, D.J.; Colditz, G.A. Dietary intakes of vitamins A, C, and E and risk of melanoma in two cohorts of women. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Cho, D.; Kim, Y.I.; Hahm, E.; Yang, Y.; Kim, D.; Hur, D.; Park, H.; Bang, S.; Hwang, Y.I.; et al. L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) induces the apoptosis of B16 murine melanoma cells via a caspase-8-independent pathway. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2003, 52, 693–698. [Google Scholar]
- Neena, P.; Thomas, K.; Carol, H. Reciprocal effects of ascorbate on cancer cell growth and the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and transforming growth factor-β. Cancer Lett. 2007, 256, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, E.; Jin, D.H.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Hong, S.W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.N.; Jung, D.J.; Kim, J.E.; Shin, D.H.; et al. The molecular mechanisms of vitamin C on cell cycle regulation in B16F10 murine melanoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 102, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Kim, H.; Kong, J.; Bae, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, N.; Cho, B.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Hwang, Y.; et al. Vitamin C down-regulates VEGF production in B16F10 murine melanoma cells via the suppression of p42/44 MAPK activation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.L.; Seung, J.K.; da Jung, J.; Young, D.H.; Eun, J.K.; Eunsil, H.; Seyeon, B.; Woo, H.K.; Daejin, K.; Joo, B.C.; et al. Vitamin C suppresses proliferation of the human melanoma cell SK-MEL-2 through the inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and the modulation of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) production. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 216, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandini, S.; Raimondi, S.; Gnagnarella, P.; Doré, J.F.; Maisonneuve, P.; Testori, A. Vitamin D and skin cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandini, S.; Francesco, F.; Johanson, H.; Bonanni, B.; Testori, A. Why vitamin D for cancer patients? Ecancermedicalscience 2009, 3, 160–160. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.Y.; Fu, T.; Lau, C.; Oh, D.H.; Bikle, D.D.; Asgari, M.M. Vitamin D in cutaneous carcinogenesis: Part I. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, J.M.; Kiruthu, C.; Weinstein, S.J.; Horst, R.L.; Snyder, K.; Virtamo, J.; Albanes, D. Pre-diagnostic circulating vitamin D and risk of melanoma in men. PLoS One 2012, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Asgari, M.M.; Maruti, S.S.; Kushi, L.H.; White, E. A cohort study of vitamin D intake and melanoma risk. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar]
- Geyu, L.; Hongmei, N.; Qureshi, A.A.; Jiali, H. Pre-diagnostic plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and risk of non-melanoma skin cancer in women. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinceti, M.; Malagoli, C.; Fiorentini, C.; Longo, C.; Crespi, C.M.; Albertini, G.; Ricci, C.; Lanzoni, A.; Reggiani, M.; Virgili, A.; et al. Inverse association between dietary vitamin D and risk of cutaneous melanoma in a northern Italy population. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozyna, A.A.; Jozwicki, W.; Janjetovic, Z.J.; Slominski, A.T. Original contribution: Expression of vitamin D receptor decreases during progression of pigmented skin lesions. Hum. Pathol. 2011, 42, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuohimaa, P.; Pukkala, E.; Scélo, G.; Olsen, J.H.; Brewster, D.H.; Hemminki, K.; Tracey, E.; Weiderpass, E.; Kliewer, E.V.; Pompe-Kirn, V.; et al. Does solar exposure, as indicated by the non-melanoma skin cancers, protect from solid cancers: Vitamin D as a possible explanation. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafa, M.P.; Fokum, F.D.; Mowlavi, A.; Abusief, M.; King, M. Vitamin E inhibits melanoma growth in mice. Surgery 2002, 131, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairfield, K.M.; Fletcher, R.H. Vitamins for chronic disease prevention. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2002, 287, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.N.; Yap, W.N.; Lee, D.T.W.; Ling, M.T.; Wong, Y.C.; Yap, Y.L. Evidence of gamma-tocotrienol as an apoptosis-inducing, invasion-suppressing, and chemotherapy drug-sensitizing agent in human melanoma cells. Nutr. Cancer 2009, 61, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Ottino, P.; Duncan, J.R. Human study: Effect of vitamin E succinate on free radical formation, lipid peroxidation levels and cyclooxygenase activity in murine melanoma cells. Nutr. Res. 1997, 17, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.N.; Edwards-Prasad, J. Effects of tocopherol (vitamin E) acid succinate on morphological alterations and growth inhibition in melanoma cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 550–555. [Google Scholar]
- Ottino, P.; Duncan, J.R. The role of adenylate cyclase, cAMP and PGE2 in the in vitro growth regulation of murine melanoma cells by vitamin E. Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Essent. Fatty Acids 1996, 54, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafa, M.P.; Fokum, F.D.; Smith, L.; Louis, A. Inhibition of angiogenesis and promotion of melanoma dormancy by vitamin E succinate. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2002, 9, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrelli, V.F.; Lauriola, M.M.; Pigatto, P.D. Clinical evaluation of photoprotective effect by a topical antioxidants combination (tocopherols and tocotrienols). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, E.M.; Tober, K.L.; Riggenbach, J.A.; Kusewitt, D.F.; Young, G.S.; Oberyszyn, T.M. Differential effects of topical vitamin E and C E Ferulic® treatments on ultraviolet light B-induced cutaneous tumor development in Skh-1 mice. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, D.; Fabienne, D.; Véronique, P. Review: Vitamin E-based nanomedicines for anti-cancer drug delivery. J. Controlled Release 2014, 182, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banthorpe, D.V. Terpenoids. In Natural Products: Their Chemistry and Biological Significance; Mann, J., Davidson, R.S., Hobbs, J.B., Banthorpe, D.V., Harbone, J.B., Eds.; Addison Wesley Longman: Edinburgh, UK, 1994; pp. 289–359. [Google Scholar]
- Trajković, L.M.H.; Mijatović, S.A.; Maksimović-Ivanić, D.D.; Stojanović, I.D.; Momčilović, M.B.; Tufegdzic, S.J.; Maksimović, V.M.; Marjanović, Ž.S.; Stošic-Grujičić, S.D. Anticancer properties of Ganoderma Lucidum methanol extracts in vitro and in vivo. Nutr. Cancer 2009, 61, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harhaji, L.J.; Mijatović, S.; Maksimović-Ivanić, D.; Stojanović, I.; Momčilović, M.; Maksimović, V.; Tufegdžić, S.; Marjanović, Z.; Mostarica-Stojković, M.; Vučinić, Z.; et al. Anti-tumor effect of Coriolus versicolor methanol extract against mouse B16 melanoma cells: In vitro and in vivo study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiahdi, S.M.; Iranshahi, M.; Sahebkar, A. Cytotoxic activities of phytochemicals from Ferula species. Daru J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, A.N.; Labuda, I.; Burns, F.J. A novel mechanism of filaggrin induction and sunburn prevention by β-damascenone in Skh-1 mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 265, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, K.A.; Carson, C.F.; Riley, T.V.; Nielsen, J.B. A review of the toxicity of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, D.J.; Greay, S.J.; Hooper, C.M.; Kissick, H.T.; Filion, P.; Riley, T.V.; Beilharz, M.W. Topically applied Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil causes direct anti-cancer cytotoxicity in subcutaneous tumour bearing mice. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 67, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Zhang, H.J.; Xuan, L.J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.M.; Bai, D.L. Stilbenoids: Chemistry and bioactivities. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Rahman, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 34, pp. 453–646. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, T.; Xie, C.F.; Wang, X.N.; Luo, H.X. Stilbenoids. In Natural Products; Ramawat, K.G., Merillon, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 1901–1949. [Google Scholar]
- Delmas, D.; Lancon, A.; Colin, D.; Jannin, B.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol as a chemopreventive agent: A promising molecule for fighting cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niles, R.M.; McFarland, M.; Weimer, M.B.; Redkar, A.; Fu, Y.M.; Meadows, G.G. Resveratrol is a potent inducer of apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2003, 190, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatouillat, G.; Balasse, E.; Joseph-Pietras, D.; Morjani, H.; Madoulet, C. Resveratrol induces cell-cycle disruption and apoptosis in chemoresistant B16 melanoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 110, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Chang, W.W.; Kuan, Y.D.; Lin, S.T.; Hsu, H.C.; Lee, C.H. Resveratrol inhibits LPS-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mouse melanoma model. Innate Immun. 2012, 18, 685–693. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Bradley, M.J.; Cook, K.M.; Herrick, E.J.; Nicholl, M.B. A potential role for resveratrol as a radiation sensitizer for melanoma treatment. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 183, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmond, G.W.; Augustine, C.K.; Zipfel, P.A.; Padussis, J.; Tyler, D.S. Enhancing melanoma treatment with resveratrol. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 172, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niles, R.M.; Cook, C.P.; Meadows, G.G.; Fu, Y.M.; McLaughlin, J.L.; Rankin, G.O. Resveratrol is rapidly metabolized in athymic (Nu/Nu) mice and does not inhibit human melanoma xenograft tumor growth. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2542–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Asensi, M.; Medina, I.; Ortega, A.; Carretero, J.; Baño, M.C.; Obrador, E.; Estrela, J.M. Original contribution: Inhibition of cancer growth by resveratrol is related to its low bioavailability. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Singh, N.P.; Singh, U.P.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Resveratrol prevents endothelial cells injury in high-dose interleukin-2 therapy against melanoma. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, A.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.S. Curcumin in various cancers. Biofactors 2013, 39, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Patchva, S.; Koh, W.; Aggarwal, B.B. Discovery of curcumin, a component of golden spice, and its miraculous biological activities. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2012, 39, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Sundaram, C.; Jhurani, S.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin and cancer: An “old-age” disease with an “age-old” solution. Cancer Lett. 2008, 267, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Yu, T.; Wang, W.; Pan, K.; Shi, D.; Sun, H. Curcumin-induced melanoma cell death is associated with mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 448, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, J.A.; Cheung, K.J.J., Jr.; Li, G. Curcumin induces apoptosis in human melanoma cells through a Fas Receptor/Caspase-8 Pathway Independent of p53. Exp. Cell. Res. 2001, 271, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.D.; Yang, S.M.; Tseng, M.J.; Lin, J.C.; Hsu, J.D.; Lee, Y.J.; Cherng, J.M. Curcumin protects against UVB-induced skin cancers in SKH-1 hairless mouse: Analysis of early molecular markers in carcinogenesis. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmke, I.N.; Backes, C.; Rudzitis-Auth, J.; Laschke, M.W.; Leidinger, P.; Menger, M.D.; Meese, E.; Mahlknecht, U. Curcumin intake affects miRNA signature in murine melanoma with mmu-miR-205-5p most significantly altered. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.M.; Clark, C.; Herman-Ferdinandez, L.; Moore-Medlin, T.; Rong, X.H.; Gill, J.R.; Clifford, J.L.; Abreo, F.; Nathan, C.A.O. Curcumin inhibits skin squamous cell carcinoma tumor growth in vivo. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 145, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naksuriya, O.; Okonogi, S.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Hennink, W.E. Curcumin nanoformulations: A review of pharmaceutical properties and preclinical studies and clinical data related to cancer treatment. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3365–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimeault, M.; Batra, S.K. Potential applications of curcumin and its novel synthetic analogs and nanotechnology-based formulations in cancer prevention and therapy. Chin. Med. 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Z.; Lu, C.T.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Y.P.; Tian, J.L.; Xu, Y.Y.; Feng, Z.G.; Xu, C.Y. Selection of high efficient transdermal lipid vesicle for curcumin skin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 302–309. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.H.; Chang, F.Y.; Hung, D.K. Terpene microemulsions for transdermal curcumin delivery: Effects of terpenes and cosurfactants. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 82, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthi, C.; Kathiresan, K. Curcumin-Piperine/Curcumin-Quercetin/Curcumin-Silibinin dual drug-loaded nanoparticulate combination therapy: A novel approach to target and treat multidrug-resistant cancers. J. Med. Hypotheses Ideas 2013, 7, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fimognari, C.; Hrelia, P. Sulforaphane as a promising molecule for fighting cancer. Mutat. Res. 2007, 635, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsa, T.P.; Thejass, P.; Kuttan, G. Induction of apoptosis by sulforaphane in highly metastatic B16F-10 melanoma cells. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 34, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, K.; Cervinka, M.; Rudolf, E. Sulforaphane-induced apoptosis involves p53 and p38 in melanoma cells. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thejass, P.; Kuttan, G. Modulation of cell-mediated immune response in B16F-10 melanoma-induced metastatic tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice by sulforaphane. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2007, 29, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thejass, P.; Kuttan, G. Antimetastatic activity of Sulforaphane. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 3043–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eylen, D.V.; Oey, I.; Hendrickx, M.; Loey, A.V. Kinetics of the stability of broccoli (Brassica oleracea cv. italica) myrosinase and isothiocyanates in broccoli juice during pressure/temperature treatments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.P.; Pai, S.B.; Rizvi, S.A.A.; D’Souza, M.J. Development of sulforaphane-encapsulated microspheres for cancer epigenetic therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 386, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Enriquez, G.G.; Rizvi, S.A.A.; D’Souza, M.J.; Do, D.P. Formulation and evaluation of drug-loaded targeted magnetic microspheres for cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Davids, L.M.; Kleemann, B.; Kacerovská, D.; Pizinger, K.; Kidson, S.H. Hypericin phototoxicity induces different modes of cell death in melanoma and human skin cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2008, 91, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis, P.; Vantieghem, A.; Merlevede, W.; de Witte, P.A.M. Hypericin in cancer treatment: More light on the way. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34, 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- Boiy, A.; Roelandts, R.; de Witte, P.A.M. Photodynamic therapy using topically applied hypericin: Comparative effect with methyl-aminolevulinic acid on UV induced skin tumours. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2011, 102, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalkos, D.; Gioti, E.; Stalikas, C.D.; Meyer, H.; Papazoglou, T.G.; Filippidis, G. Photophysical properties of Hypericum perforatum L. extrSacts-novel photosensitizers for PDT. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2006, 82, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Menichini, G.; Alfano, C.; Marrelli, M.; Toniolo, C.; Provenzano, E.; Statti, G.A.; Nicoletti, M.; Menichini, F.; Conforti, F. Hypericum perforatum L. subsp. perforatum induces inhibition of free radicals and enhanced phototoxicity in human melanoma cells under ultraviolet light. Cell Prolif. 2013, 46, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Samadi, A.; Cohen, M.S.; Timmermann, B. Antiproliferative withanolides from the Solanaceae: A structure-activity study. Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 84, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Kalthur, G.; Mutalik, S.; Pathirissery, U.D. Effect of withaferin A on the development and decay of thermotolerance in B16F1 melanoma: A preliminary study. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalthur, G.; Pathirissery, U.D. Enhancement of the response of B16F1 melanoma to fractionated radiotherapy and prolongation of survival by withaferin A and/or hyperthermia. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayola, E.; Gallerne, C.; Esposti, D.D.; Martel, C.; Pervaiz, S.; Larue, L.; Debuire, B.; Lemoine, A.; Brenner, C.; Lemaire, C. Withaferin A induces apoptosis in human melanoma cells through generation of reactive oxygen species and down-regulation of Bcl-2. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyon, P.V.; Kuttan, G. Effect of Withania somnifera on B16F-10 melanoma induced metastasis in mice. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greay, S.J.; Ireland, D.J.; Kissick, H.T.; Levy, A.; Beilharz, M.W.; Riley, T.V.; Carson, C.F. Induction of necrosis and cell cycle arrest in murine cancer cell lines by Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil and terpinen-4-ol. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 65, 877–888. [Google Scholar]
- Greay, S.J.; Ireland, D.J.; Kissick, H.T.; Heenan, P.J.; Carson, C.F.; Riley, T.V.; Beilharz, M.W. Inhibition of established subcutaneous murine tumour growth with topical Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcabrini, A.; Stringaro, A.; Toccacieli, L.; Meschini, S.; Marra, M.; Colone, M.; Salvatore, G.; Mondello, F.; Arancia, G.; Molinari, A. Terpinen-4-ol, the main component of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil inhibits the in vitro growth of human melanoma cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eok-Cheon, K.; Jeong-Ki, M.; Tae-Yoon, K.; Shin-Jeong, L.; Hyun-Ok, Y.; Sanghwa, H.; Young-Myeong, K.; Young-Guen, K. [6]-Gingerol, a pungent ingredient of ginger, inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, N.; Bhui, K.; Prasad, S.; George, J.; Shukla, Y. [6]-Gingerol induces reactive oxygen species regulated mitochondrial cell death pathway in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 181, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.J.; Yoo, Y.C.; Kang, T.B.; Song, S.K.; Lee, K.B.; Her, E.; Song, K.S.; Kim, J.B. Antitumor activity of the Korean mistletoe lectin is attributed to activation of macrophages and NK cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.J.; Yoo, Y.C.; Kang, T.B.; Baek, Y.J.; Huh, C.S.; Song, S.K.; Lee, K.H.; Azuma, I.; Kim, J.B. Prophylactic effect of Korean mistletoe (Viscum album coloratum) extract on tumor metastasis is mediated by enhancement of NK cell activity. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1998, 20, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, T.J.; Yoo, Y.C.; Choi, O.B.; Do, M.S.; Kang, T.B.; Lee, S.W.; Azuma, I.; Kim, J.B. Inhibitory effect of Korean mistletoe (Viscum album coloratum) extract on tumour angiogenesis and metastasis of haematogenous and non-haematogenous tumour cells in mice. Cancer Lett. 1995, 97, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, A.; Nugel, D.; Pfuller, U.; Moll, I.; Schumacher, U. Influence of mistletoe lectins and cytokines induced by them on cell prolifertion of human melanoma cells in vitro. Toxicology 2005, 207, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huyen, J.D.; Delignat, S.; Bayry, J.; Kazatchkine, M.D.; Bruneval, P.; Nicoletti, A.; Kaveri, S.V. Interleukin-12 is associated with the in vivo anti-tumor effect of mistletoe extracts in B16 mouse melanoma. Cancer Lett. 2006, 243, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Strüh, C.M.; Jäger, S.; Schempp, C.M.; Scheffler, A.; Martin, S.F. A novel triterpene extract from mistletoe induces rapid apoptosis in murine B16.F10 melanoma cells. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar]
- Augustin, M.; Bock, P.R.; Hanisch, J.; Karasmann, M.; Schneider, B. Safety and efficacy of the long-term adjuvant treatment of primary intermediate- to high-risk malignant melanoma (UICC/AJCC stage II and III) with a standardized fermented European mistletoe (Viscum album L.) extract. Results from a multicenter, comparative, epidemiological cohort study in Germany and Switzerland. Arzneimittel-Forsch. 2005, 55, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch, A. Successful treatment of metastatic malignant melanoma with Viscum album extract (Iscador® M). J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2007, 13, 443–446. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Medina, E.; Garcia-Lora, A.; Paco, L.; Algarra, I.; Collado, A.; Garrido, F. A new extract of the plant Calendula officinalis produces a dual vitro effect: Cytotoxic anti-tumor activity and lymphocyte activation. BMC Cancer 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukiya, M.; Akihisa, T.; Yasukawa, K.; Tokuda, H.; Suzuki, T.; Kimura, Y. Anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor-promoting, and cytotoxic activities of constituents of marigold (Calendula officinalis) flowers. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1692–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matić, I.Z.; Juranić, Z.; Savikin, K.; Zdunić, G.; Nađvinski, N.; Gođevac, D. Chamomile and marigold tea: Chemical characterization and evaluation of anticancer activity. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, K.C.; Siveen, K.S.; Kuttan, R.; Kuttan, G. Inhibition of metastasis of B16F-10 melanoma cells in C57BL/6 mice by an extract of Calendula officinalis L flowers. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2010, 11, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, S.N.T.; Williams, D.B.; Head, R.J. Rosemary and cancer prevention: Preclinical perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Ho, C.T.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y.; Lin, J.K. Carnosol inhibits the invasion of B16/F10 mouse melanoma cells by suppressing metalloproteinase-9 through down-regulating nuclear factor-kappaB and c-Jun. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kumar, N.C.; Glickman, R.D. Modulation of photochemical damage in normal and malignant cells by naturally occurring compounds. Photochem. Photobiol. 2012, 88, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu, K.A.; Kuttan, G. Ursolic acid induces apoptosis by activating p53 and caspase-3 gene expressions and suppressing NF-κB mediated activation of bcl-2 in B16F-10 melanoma cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.J.; Tak, J.K.; Kim, S.T.; Nam, W.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, K.M.; Park, J.W. Sensitization of ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis by ursolic acid. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Wang, E.; Kumar, N.; Glickman, R.D. Ursolic acid differentially modulates apoptosis in skin melanoma and retinal pigment epithelial cells exposed to UV-VIS broadband radiation. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjoormana, M.; Kuttan, G. Antiangiogenic activity of ursolic acid. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 224–235. [Google Scholar]
- Chandu, A.N.; Kumar, S.C.; Bhattacharjee, C.; Debnath, S. Cytotoxicity study of plant Aloe vera (Linn). Chron. Young Sci. 2012, 3, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabolacci, C.; Lentini, A.; Mattioli, P.; Provenzano, B.; Oliverio, S.; Carlomosti, F.; Beninati, S. Antitumor properties of aloe-emodin and induction of transglutaminase 2 activity in B16–F10 melanoma cells. Life Sci. 2010, 87, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovic, J.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D.; Timotijevic, G.; Popadic, S.; Ramic, Z.; Trajkovic, V.; Miljkovic, D.; Stosic-Grujicic, S.; Mijatovic, S. Cell-type dependent response of melanoma cells to aloe emodin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3181–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabolacci, C.; Rossi, S.; Lentini, A.; Provenzano, B.; Turcano, L.; Facchiano, F.; Beninati, S. Aloin enhances cisplatin antineoplastic activity in B16-F10 melanoma cells by transglutaminase-induced differentiation. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shawi, A.; Rasul, A.; Khan, M.; Furhan, I.; Ma, T. Eupatilin: A flavonoid compound isolated from the artemisia plant, induces apoptosis and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in human melanoma A375 cells. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 582–588. [Google Scholar]
- Priestap, H.A.; Galvis, A.; Rivero, N.; Costantino, V.; Lopez, L.A.; Barbieri, M.A. Dehydroleucodine and dehydroparishin-B inhibit proliferation and motility of B16 melanoma cells. Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 5, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.H.; Bhat, K.A.; Naseer, S.; Rather, R.A.; Khuroo, M.A.; Tasduq, S.A. Isolation, cytotoxicity evaluation and HPLC-quantification of the chemical constituents from Artemisia amygdalina Decne. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 2013, 940, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zheng, X.; Newman, R.A.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, Z.J.; Nan, P. Chemical composition and bioactivity of the essential oil of Artemisia anomala from China. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2013, 25, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Chiu, C.; Liao, W.; Wu, P.; Chen, Y.; Huang, K.; Chou, Y.; Wen, Z.; Wang, H. Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. bioactive extracts from supercritical fluid carbon dioxide extraction. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 78, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.Y.; Liu, P.L.; Lin, L.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Hseu, Y.C.; Wen, Z.H.; Wang, H.M. Antimelanoma and antityrosinase from Alpinia galangal constituents. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Hua, Z. Galangin induces B16F10 melanoma cell apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway and sustained activation of p38 MAPK. Cytotechnology 2013, 65, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, B.; Huang, Q.; Hua, Z. Galangin inhibits tumor growth and metastasis of B16F10 melanoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, W.B. Advising patients on the use of complementary and alternative medicine. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2001, 26, 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Joos, S.; Glassen, K.; Musselmann, B. Herbal medicine in primary healthcare in Germany: The patient’s perspective. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekelle, P.G.; Morton, S.C.; Suttorp, M.J.; Buscemi, N.; Friesen, C. Challenges in systematic reviews of Complementary and Alternative Medicine topics. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Nartey, L.; Huwiler-Müntener, K.; Shang, A.; Liewald, K.; Jüni, P.; Egger, M. Matched-pair study showed higher quality of placebo-controlled trials in Western phytotherapy than conventional medicine. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2007, 60, 787–794. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsel, J.F.; Straus, S.E. Complementary and alternative therapeutics: Rigorous research is needed to support claims. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 43, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, I. Beyond randomized controlled trials: Evidence in complementary medicine. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 17, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Q.; Tao, K.M.; Zhou, Q.H.; Ling, C.Q. Scientific publications from Mainland China, Taiwan, and Hong Kong in integrative and complementary medicine journals: A ten-year literature survey. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maino, D.M. Evidence Based Medicine and CAM: A review. Optom. Vis. Dev. 2012, 43, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Price, A.; Grann, V.R. Portrayal of Complementary and Alternative Medicine for Cancer by Top Online News Sites. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2012, 18, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chinembiri, T.N.; Du Plessis, L.H.; Gerber, M.; Hamman, J.H.; Du Plessis, J. Review of Natural Compounds for Potential Skin Cancer Treatment. Molecules 2014, 19, 11679-11721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811679
Chinembiri TN, Du Plessis LH, Gerber M, Hamman JH, Du Plessis J. Review of Natural Compounds for Potential Skin Cancer Treatment. Molecules. 2014; 19(8):11679-11721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811679
Chicago/Turabian StyleChinembiri, Tawona N., Lissinda H. Du Plessis, Minja Gerber, Josias H. Hamman, and Jeanetta Du Plessis. 2014. "Review of Natural Compounds for Potential Skin Cancer Treatment" Molecules 19, no. 8: 11679-11721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811679
APA StyleChinembiri, T. N., Du Plessis, L. H., Gerber, M., Hamman, J. H., & Du Plessis, J. (2014). Review of Natural Compounds for Potential Skin Cancer Treatment. Molecules, 19(8), 11679-11721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811679







