Identification of Catechol as a New Marker for Detecting Propolis Adulteration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
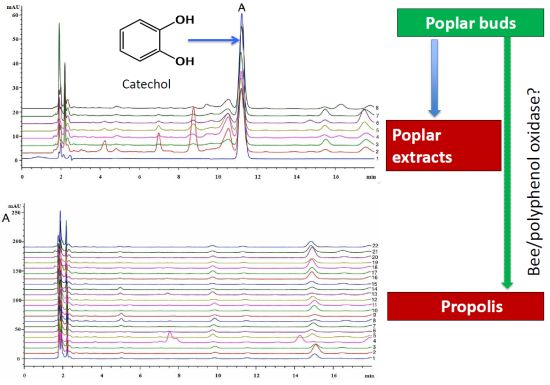
2. Results and Discussion
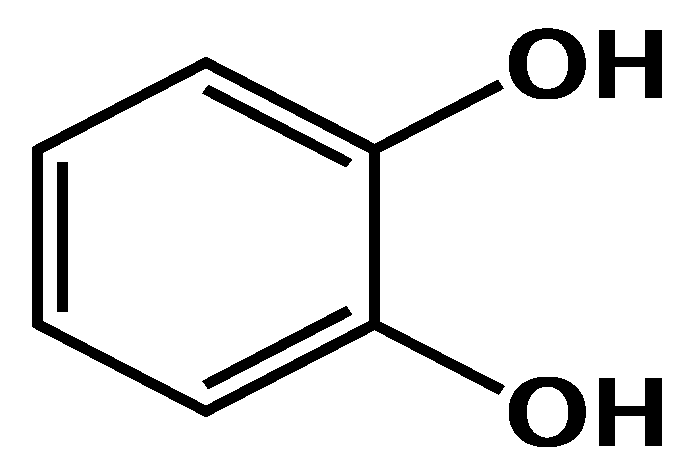
2.1. The Identification of Catechol in Poplar Extract
| Atoms | 1H-NMR | 13C-NMR |
|---|---|---|
| 1 and 2 | - | 146.3 (q) |
| 3 and 6 | 6.65 (2H, dd, J = 3.8, 7.3 Hz) | 120.9 (d) |
| 4 and 5 | 6.75 (2H, dd, J = 3.8, 7.3 Hz) | 116.4 (d) |
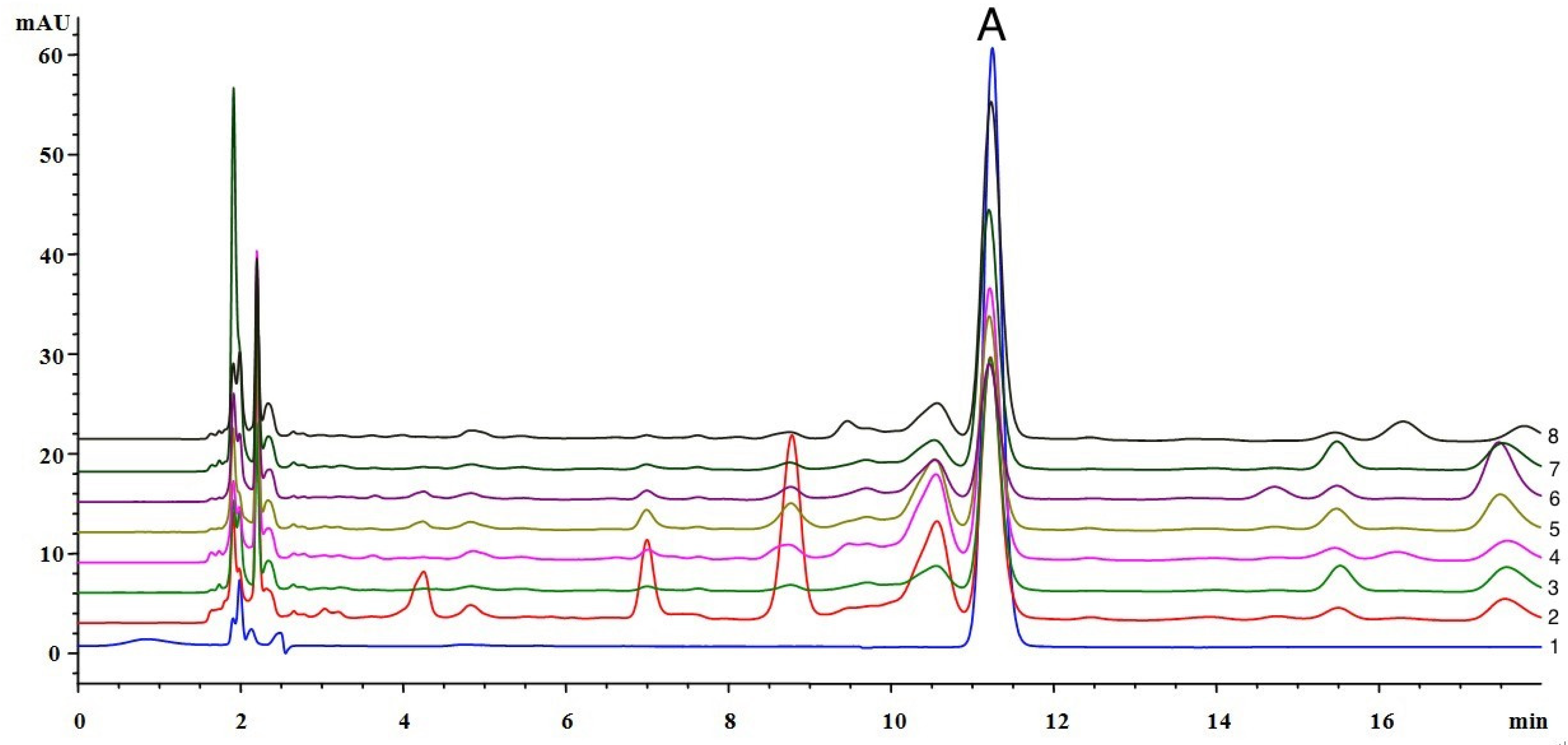
2.2. Determination of Catechol in Poplar Tree Extract and Propolis Samples
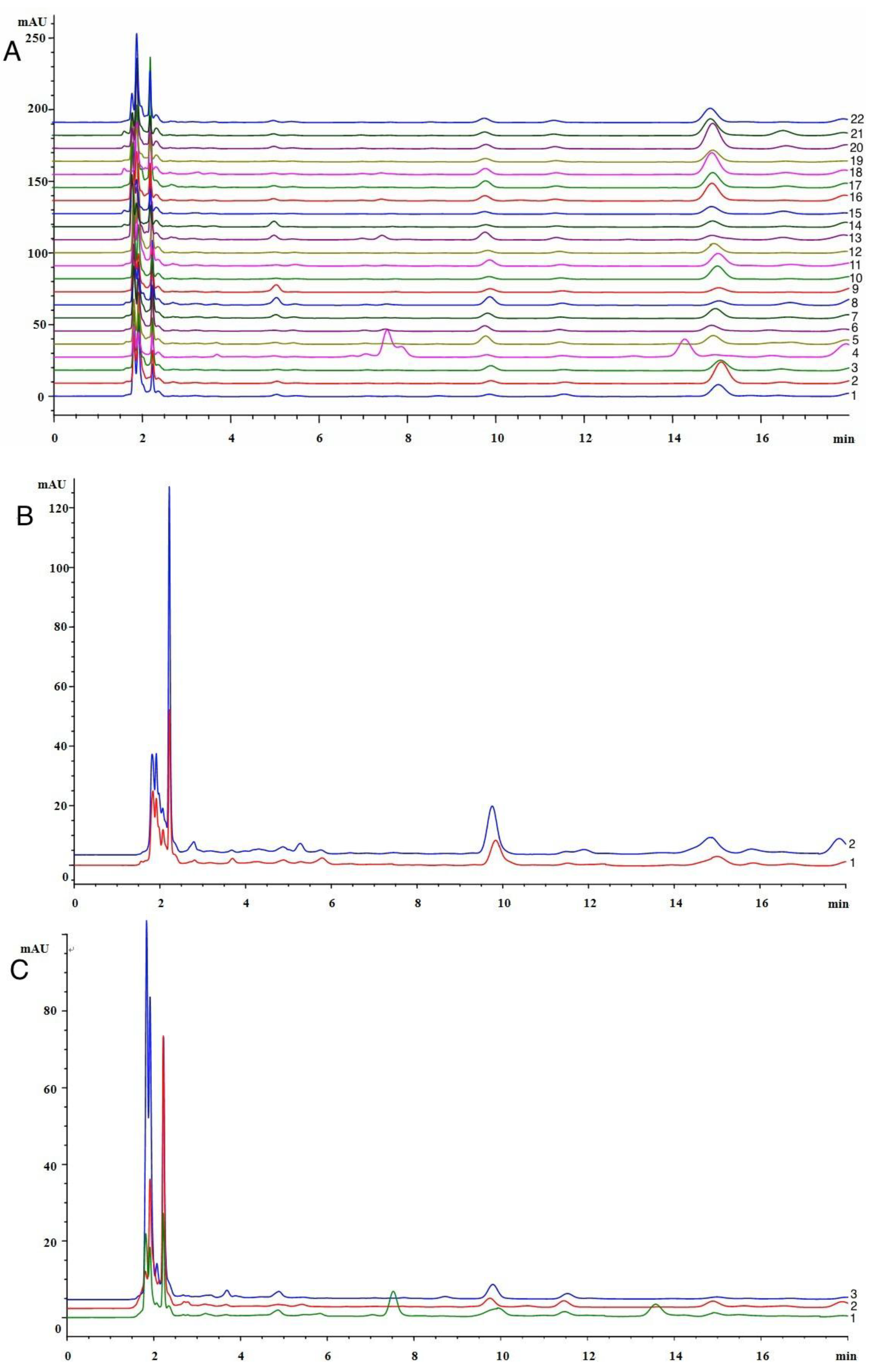
2.3. Detection the Polyphenol Oxidase (PPO) in Propolis and Poplar Buds
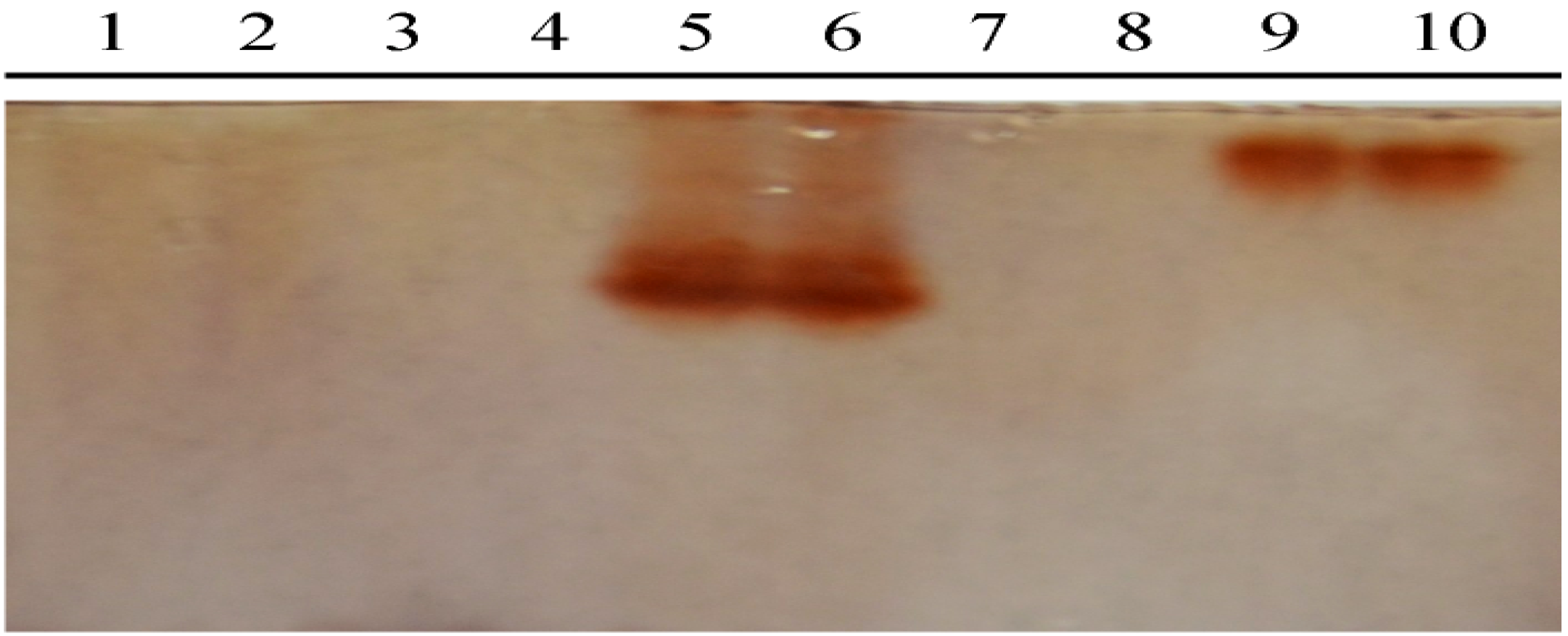
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Materials
| No. | Geographical Origin | Date of Collection |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shangshui, Henan | August 2013 |
| 2 | Qiuxian, Hebei | May 2013 |
| 3 | Shijiazhuang, Hebei | June 2013 |
| 4 | Yicheng, Hubei | June 2013 |
| 5 | Laodongkou, Hubei | June 2013 |
| 6 | Meishan, Sichuan | July 2013 |
| 7 | Wusong, Jilin | August 2013 |
| 8 | Baishan, Jilin | August 2013 |
| 9 | Ji’an, Jilin | July 2013 |
| 10 | Dashiqiao, Liaoning | July 2013 |
| 11 | Zhuanghe, Liaoning | July 2013 |
| 12 | Faku, Liaoning | July 2013 |
| 13 | Kongliu, Xinjiang | August 2013 |
| 14 | Yilan, Heilongjiang | May 2013 |
| 15 | Shuangyashan, Heilongjiang | August 2013 |
| 16 | Fuyang, Anhui | June 2013 |
| 17 | Huaibei, Anhui | June 2013 |
| 18 | Tongcheng, Anhui | August 2013 |
| 19 | Beijing | July 2013 |
| 20 | Penglai, Shandong | May 2013 |
| 21 | Longkou, Shandong | July 2013 |
| 22 | Dong’e, Shandong | August 2013 |
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. MS and NMR
3.5. Application of Catechol to Distinguish Poplar Extract and Propolis
3.6. Polyphenol Oxidase (PPO) Preparation and 1-D SDS-PAGE
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bankova, V.S. Recent trends and important developments in propolis research. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2005, 2, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, S.I.; Tomás, A.; Vale, N.; Gomes, P.; Freire, C.; Vilas-Boas, M. Phenolic quantification and botanical origin of Portuguese propolis. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 49, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatino, A.; Fernandes-Silva, C.C.; Righi, A.A.; Salatino, M.L.F. Propolis research and the chemistry of plant products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ping, S.; Huang, S.; Hu, L.; Xuan, H.Z.; Zhang, C.P.; Hu, F.L. Molecular mechanisms underlying the in vitro anti-inflammatory effects of a Ffavonoid-rich ethanol extract from Chinese propolis (poplar type). Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 127672:1–127672:11. [Google Scholar]
- Banskota, A.H.; Tezuka, Y.; Kadota, S. Recent progress in pharmacological research of propolis. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.R.; Kumazawa, S.; Usui, Y.; Nakamura, J.; Matsuka, M.; Zhu, F.; Nakayama, T. Antioxidant activity and constituents of propolis collected in various areas of China. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforcin, J.M.; Bankova, V. Propolis: Is there a potential for the development of new drugs? J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petelinc, T.; Polak, T.; Demšar, L.; Jamnik, P. Fractionation of phenolic compounds extracted from propolis and their activity in the yeast saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS One 2013, 8, e56104. [Google Scholar]
- Crane, E. The honeybees’ plant resources. In Beekeeping: Science, Practice and World Recourses; Heinemann: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bankova, V.S.; de Castro, S.L.; Marcucci, M.C. Propolis: Recent advances in chemistry and plant origin. Apidologie 2000, 31, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toreti, V.C.; Sato, H.H.; Pastore, G.M.; Park, Y.K. Recent progress of propolis for its biological and chemical compositions and its botanical origin. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.W.; Sun, S.Q.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q. Rapid discrimination of extracts of Chinese propolis and poplar buds by FT-IR and 2D IR correlation spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 883, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.P.; Zheng, H.Q.; Liu, G.; Hu, F.L. Development and validation of HPLC method for determination of salicin in poplar buds: Application for screening of counterfeit propolis. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdock, G. Review of the biological properties and toxicity of bee propolis (propolis). Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontoh, J.; Low, N. Purification and characterization of β-glucosidase from honey bees (Apis mellifera). Insect Biochem. Molec. 2002, 32, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.P.; Zheng, H.Q.; Hu, F.L. Extraction, partial characterization, and storage stability of β-Glucosidase from Propolis. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.P.; Liu, G.; Hu, F.L. Hydrolysis of flavonoid glycosides by propolis beta-glycosidase. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, K.C.; Lax, A.R.; Duke, S.O. Polyphenol oxidase: The chloroplast oxidase with no established function. Physiol. Plant. 1988, 72, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, K.J.; Cookson, A.; Allison, G.; Sullivan, M.L.; Winters, A.L. Gene expression patterns, localization, and substrates of polyphenol oxidase in red clover (Trifolium pratense L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7421–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, K.C.; Duke, S.O. Function of polyphenol oxidase in higher plants. Physiol. Plant. 1984, 60, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-P.; Huang, S.; Wei, W.-T.; Ping, S.; Shen, X.-G.; Li, Y.-J.; Hu, F.-L. Development of high-performance liquid chromatographic for quality and authenticity control of chinese propolis. J. Food Sci. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Trémolières, M.; Bieth, J.G. Isolation and characterization of the polyphenoloxidase from senescent leaves of black poplar. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Zhao, W.L.; Gao, X.W. Communication between plants: Induced resistance in poplar seedlings following herbivore infestation, mechanical wounding, and volatile treatment of the neighbors. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2013, 149, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka, T.; Kawashima, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kanamaru, Y.; Yabe, T. Erratum to: Isolation and characterization of proteases that hydrolyze royal jelly proteins from queen bee larvae of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Apidologie 2014, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Fang, Y.; Han, B.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Li, J. Novel aspects of understanding molecular working mechanisms of salivary glands of worker honeybees (Apis mellifera) investigated by proteomics and phosphoproteomics. J. Proteomics 2013, 87, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Fang, Y.; Li, J. Proteomic analysis of honeybee worker (Apis mellifera) hypopharyngeal gland development. BMC Genomics 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Wang, Z.; Yan, S.; Ma, L.; Yang, C. Effects of Lymantria dispar feeding and mechanical wounding on defense-related enzymes in Populus simonii × Populus nigra. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 7034–7039. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Zhang, C.-P.; Li, G.Q.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Wang, K.; Hu, F.-L. Identification of Catechol as a New Marker for Detecting Propolis Adulteration. Molecules 2014, 19, 10208-10217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190710208
Huang S, Zhang C-P, Li GQ, Sun Y-Y, Wang K, Hu F-L. Identification of Catechol as a New Marker for Detecting Propolis Adulteration. Molecules. 2014; 19(7):10208-10217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190710208
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shuai, Cui-Ping Zhang, George Q. Li, Yue-Yi Sun, Kai Wang, and Fu-Liang Hu. 2014. "Identification of Catechol as a New Marker for Detecting Propolis Adulteration" Molecules 19, no. 7: 10208-10217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190710208
APA StyleHuang, S., Zhang, C.-P., Li, G. Q., Sun, Y.-Y., Wang, K., & Hu, F.-L. (2014). Identification of Catechol as a New Marker for Detecting Propolis Adulteration. Molecules, 19(7), 10208-10217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190710208