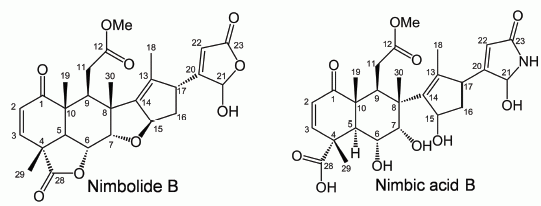
Nimbolide B and Nimbic Acid B, Phytotoxic Substances in Neem Leaves with Allelopathic Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
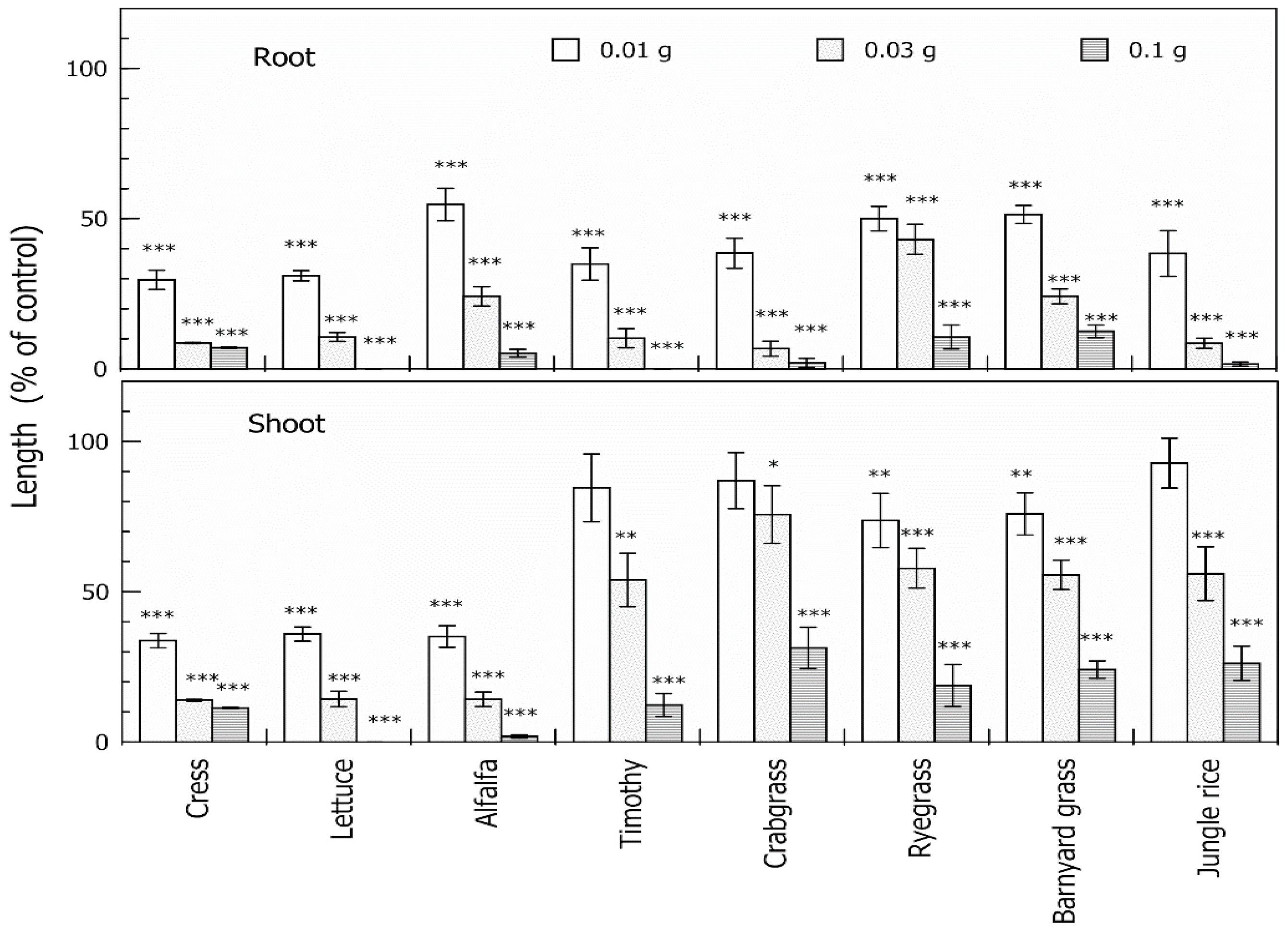
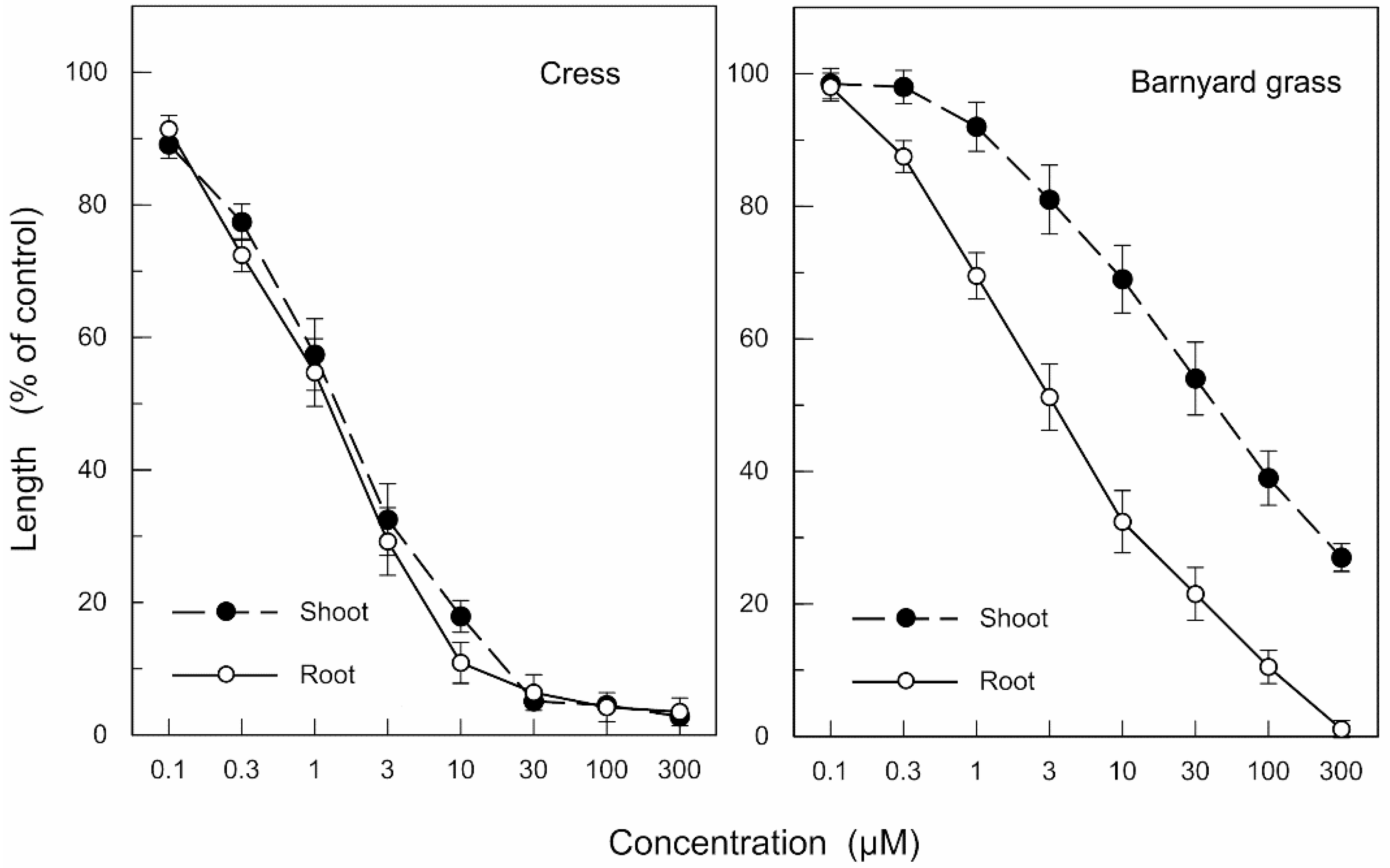
2.1. Allelopathic Activity of the Extracts of Neem Leaves
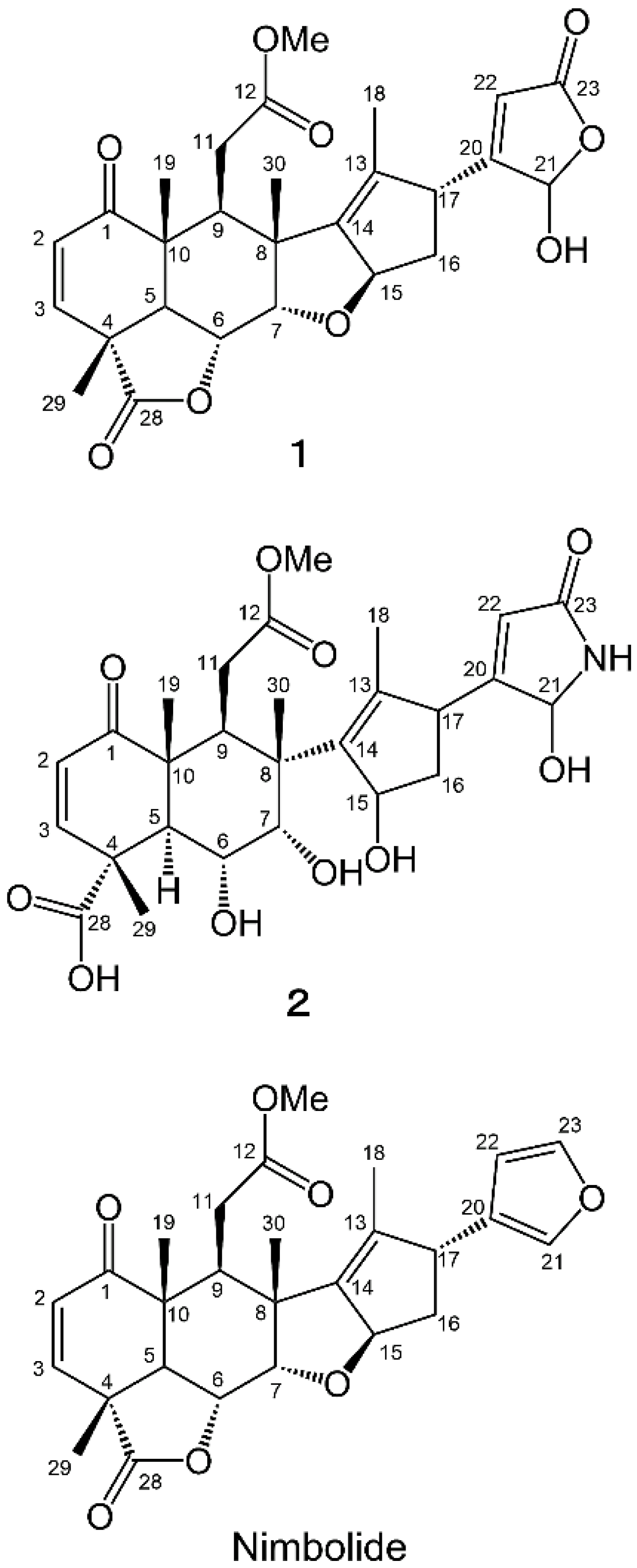
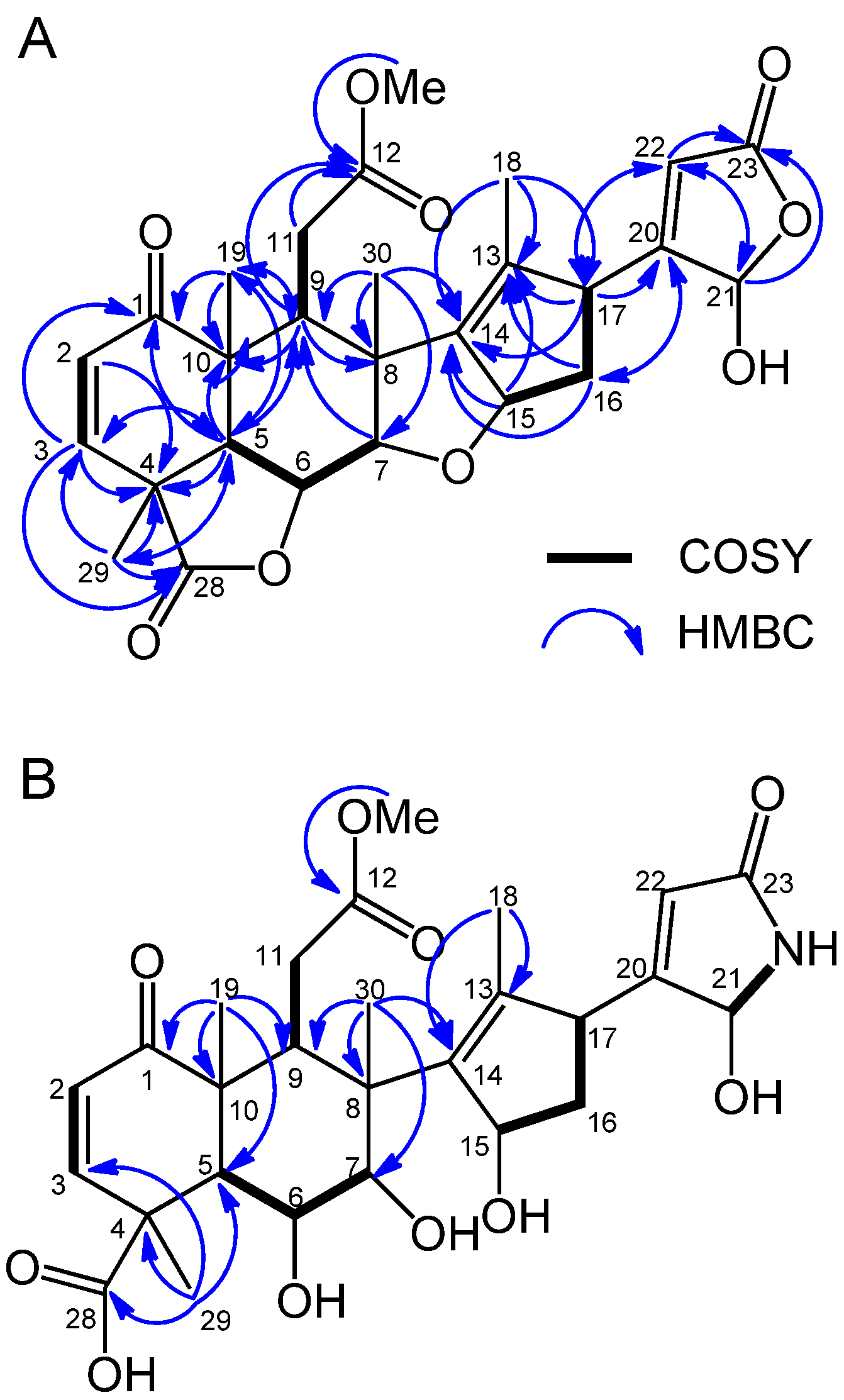
2.2. Isolation and Identification of Allelopathic Active Substances
| Compound 1 | Compound 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH/ppm (mult., J in Hz) a | δC/ppm b | δH/ppm (mult., J in Hz) a | δC/ppm c | |
| 1 | 200.8 | 202.2 | ||
| 2 | 5.91 (d, 9.9) | 130.8 | 5.85 (d, 10.1) | 126.0 |
| 3 | 7.28 (d, 9.9) | 150.0 | 6.44 (d, 10.1) | 148.5 |
| 4 | 43.7 | 43.0 | ||
| 5 | 3.08 (d, 12.5) | 47.8 | 3.31 (d, 11.4) | 47.9 |
| 6 | 4.60 (dd, 2.9, 12.5) | 73.2 | 3.92 (m) | n.d. d |
| 7 | 4.32 (d, 3.4) | 83.1 | 4.07 (d, 3.6) | 87.9 |
| 8 | 50.6 | 46.9 | ||
| 9 | 2.60 (m) | 41.4 | 2.61 (m) | 39.1 |
| 10 | 45.4 | 43.3 | ||
| 11a | 2.30 (m) | 32.8 | 2.12 (dd, 2.5, 16.5) | 35.0 |
| 11b | 3.18 (m) | 2.83 (dd, 6.4, 16.5) | ||
| 12 | 175.0 | 175.8 | ||
| 13 | 132.5 | 130.9 | ||
| 14 | 148.6 | 150.4 | ||
| 15 | 5.60 (dd, 7.1, 7.1) | 88.8 | 5.66 (m) | 87.5 |
| 16a | 2.16 (m) | 38.9 | 2.10 (dd, 2.0, 12.5) | 38.4 |
| 16b | 2.39 (m) | 2.41 (dd, 6.7, 12.5) | ||
| 17 | 3.81 (d, 9.4) | 53.0 | 3.86 (m) | 57.6 |
| 18 | 1.74 (s, 3H) | 13.1 | 1.73 (s, 3H) | 13.0 |
| 19 | 1.23 (s, 3H) | 14.9 | 1.23 (s, 3H) | 15.7 |
| 20 | 168.4 | n.d. d | ||
| 21 | 5.77 (s) | 97.4 | 5.74 (d, 7.6) | 97.1 |
| 22 | 5.92 (s) | 120.3 | 5.95 (s) | 120.0 |
| 23 | 170.2 | n.d. d | ||
| 28 | 174.7 | 174.8 | ||
| 29 | 1.48 (s, 3H) | 18.7 | 1.60 (s, 3H) | 17.0 |
| 30 | 1.35 (s, 3H) | 17.1 | 1.28 (s, 3H) | 17.1 |
| 12OCH3 | 3.76 (s, 3H) | 52.7 | 3.80 (s, 3H) | 52.2 |
| 21NH | 5.56 (d, 7.6) | |||
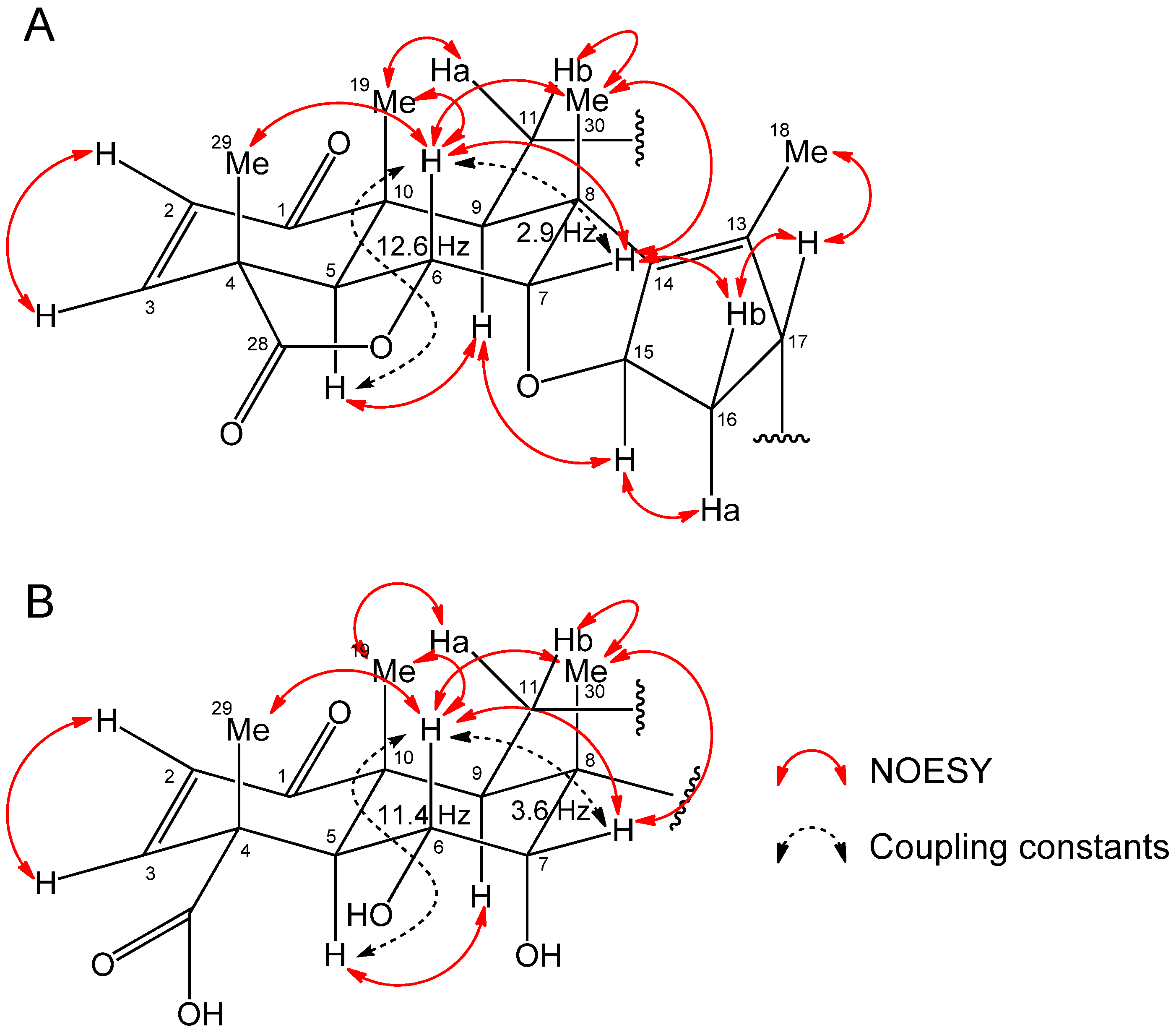
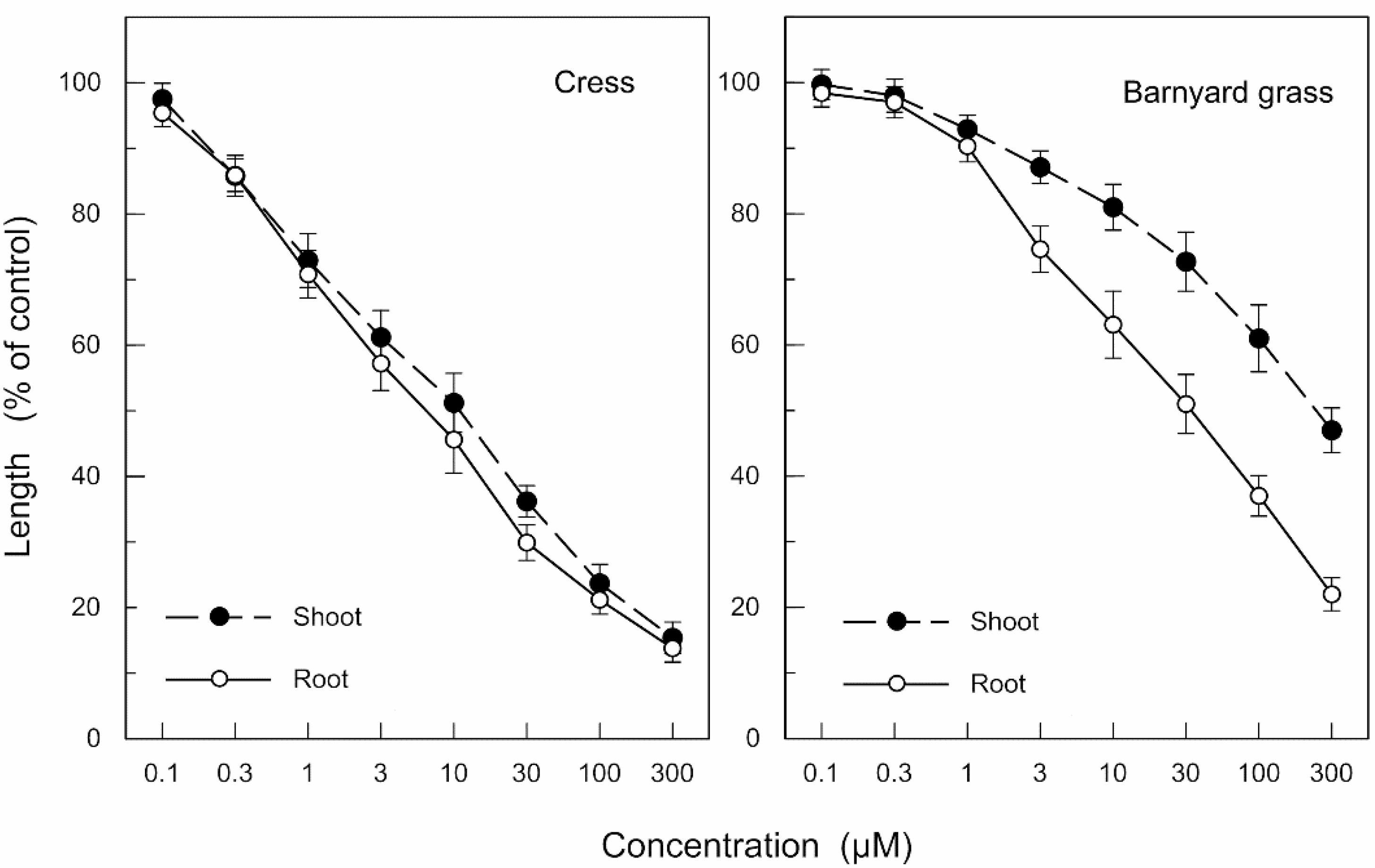
2.3. Biological Activity
3. Experimental
3.1. Plant Materials
3.2. Extraction and Bioassay
3.3. Purification of Active Substances
3.4. Spectral Data
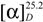 = +133.5 ° (c 0.3, CHCl3); HRESIMS m/z 499.1969 [M+H]+ (calcd for C27H31O9, 499.1968, Δ = +0.1 mmu), 497.1809 [M−H]− (calcd for C27H29O9, 497.1812, Δ = −0.3 mmu); IR (neat) 3395 (br), 2926, 2857, 1780, 1762, 1734, 1676, 1456, 1293, 1240, 1128 cm−1; NMR data (Table 1).
= +133.5 ° (c 0.3, CHCl3); HRESIMS m/z 499.1969 [M+H]+ (calcd for C27H31O9, 499.1968, Δ = +0.1 mmu), 497.1809 [M−H]− (calcd for C27H29O9, 497.1812, Δ = −0.3 mmu); IR (neat) 3395 (br), 2926, 2857, 1780, 1762, 1734, 1676, 1456, 1293, 1240, 1128 cm−1; NMR data (Table 1).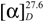 = +43.0 ° (c 0.03, CHCl3); HRESIMS m/z 534.2364 [M+H]+ (calcd for C27H36NO10, 534.2339, Δ = +2.5 mmu), 532.2198 [M−H]− (calcd for C27H34NO10, 532.2183, Δ = +1.5 mmu); IR (neat) 3402 (br), 2955, 2924, 2853, 1761, 1732, 1715, 1682, 1437, 1265, 1144 cm−1; NMR data (Table 1).
= +43.0 ° (c 0.03, CHCl3); HRESIMS m/z 534.2364 [M+H]+ (calcd for C27H36NO10, 534.2339, Δ = +2.5 mmu), 532.2198 [M−H]− (calcd for C27H34NO10, 532.2183, Δ = +1.5 mmu); IR (neat) 3402 (br), 2955, 2924, 2853, 1761, 1732, 1715, 1682, 1437, 1265, 1144 cm−1; NMR data (Table 1).3.5. Bioassay of the Isolated Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Research Council. Neem.: A Tree for Solving Global Problems; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; p. 141. [Google Scholar]
- Brahmachari, G. Neem—An omnipotent plant: A retrospection. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 408–421. [Google Scholar]
- Ogbuewu, I.P.; Odoemenam, Y.U.; Obikaonu, H.O.; Opara, M.N.; Emenalom, O.O.; Uchegbu, M.C.; Okoli, I.C.; Esonu, B.O.; Iloeje, M.U. The growing importance of neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) in agriculture, industry, medicine and environment: A review. Res. J. Med. Plant. 2011, 5, 230–245. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, T.D.; Tsuzuki, E.; Hiroyuki, T.; Mitsuhiro, M.; Khanh, T.D.; Chung, I.-M. Evaluation on phytotoxicity of neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) to crops and weeds. Crop. Prot 2004, 23, 335–345. [Google Scholar]
- Subapriya, R.; Nagini, S. Medicinal properties of neem leaves: A review. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Cancer Agent. 2005, 5, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Chutia, M.; Sarma, S. Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss), a potent biopesticide and medicinal plant: A review. J. Plant. Sci. 2007, 2, 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Gahukar, R.T. Evaluation of plant-derived products against pests and diseases of medicinal plants. Crop. Prot. 2012, 42, 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Sindhu, A.; Kumar, S.; Sindhu, G.; Ali, H.; Abdulla, M.K. Effect of neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) leachates on germination and seedling growth of weeds. Allelopathy. J. 2005, 16, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Rickli, H.C.; Fortes, A.M.T.; da Silva, P.S.S.; Pilatti, D.M.; Hutt, D.R. Allelopathic effect of aqueous extract of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. On lettuce, soybeans, maize, beans and bidens pilosa. Semina. Ciencias. Agrarias. 2011, 32, 473–484. [Google Scholar]
- Rajashekhara, R.B.K.; Shivananda, T.N.; Joshi, S.; Siddaramappa, R. Effects of allelochemicals from selected carbon sources under flooded soil conditions on histological abnormalities induced in rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. Allelopathy J. 2007, 20, 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Putnam, A.R. Allelochemicals from plants as herbicides. Weed Technol. 1988, 2, 510–518. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, D.; Paritheir, B. Novel natural substances acting in plant growth regulation. J. Plant. Grow. Regul. 1994, 13, 93–114. [Google Scholar]
- Seigler, D.S. Chemistry and mechanisms of allelopathic interactions. Agron. J. 1996, 88, 876–885. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, S.O.; Dayan, F.E.; Romagni, J.G.; Rimando, A.M. Natural products as sources of herbicide, current status and future trends. Weed. Res. 2000, 40, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Macías, F.A.; Molinillo, J.M.G.; Varela, R.M.; Galindo, J.G.G. Allelopathy—a natural alternative for weed control. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 327–348. [Google Scholar]
- Weston, L.A. Utilization of allelopathy for weed management in agroecosystems. Agron. J. 1996, 88, 860–866. [Google Scholar]
- Narwal, S.S. Allelopathy in weed managemen. In Allelopathy Update. Vol. 2. Basic and Applied Aspects; Narwal, S.S., Ed.; Science Publishers Inc: Enfield, NH, USA, 1999; pp. 203–254. [Google Scholar]
- Semidey, N. Allelopathic crops for weed management in cropping systems. In Allelopathy Update. Vol. 2. Basic and Applied Aspects; Narwal, S.S., Ed.; Science Publishers Inc: Enfield, NH, USA, 1999; pp. 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Caamal-Maldonado, J.A.; Jiménez-Osornio, J.J.; Torres-Barragán, A.; Anaya, A.L. The use of allelopathic legume cover and mulch species for weed control in cropping systems. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Inderjit. Plant phenolics in allelopathy. Bot. Rev. 1996, 62, 186–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ekong, D.E.U. Chemistry of the meliacins (limonoids). The structure of nimbolide, a new meliacin from Azadirachta. indica. Chem. Commun 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Kigodi, P.G.; Blaskó, G.; Thebtaranonth, Y.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Cordell, G.A. Spectroscopic and biological investigation of nimbolide and 28-deoxonimbolide from Azadirachta indica. J. Nat. Prod. 1989, 52, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Bokel, M.; Cramer, R.; Cutzeit, H.; Reeb, S.; Kraus, W. Tetranortriterpenoids related to nimbin and nimbolide from Azadirachta indica A. Juss (Meliaceae). Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 775–782. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kato-Noguchi, H.; Salam, M.A.; Ohno, O.; Suenaga, K. Nimbolide B and Nimbic Acid B, Phytotoxic Substances in Neem Leaves with Allelopathic Activity. Molecules 2014, 19, 6929-6940. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19066929
Kato-Noguchi H, Salam MA, Ohno O, Suenaga K. Nimbolide B and Nimbic Acid B, Phytotoxic Substances in Neem Leaves with Allelopathic Activity. Molecules. 2014; 19(6):6929-6940. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19066929
Chicago/Turabian StyleKato-Noguchi, Hisashi, Md Abdus Salam, Osamu Ohno, and Kiyotake Suenaga. 2014. "Nimbolide B and Nimbic Acid B, Phytotoxic Substances in Neem Leaves with Allelopathic Activity" Molecules 19, no. 6: 6929-6940. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19066929
APA StyleKato-Noguchi, H., Salam, M. A., Ohno, O., & Suenaga, K. (2014). Nimbolide B and Nimbic Acid B, Phytotoxic Substances in Neem Leaves with Allelopathic Activity. Molecules, 19(6), 6929-6940. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19066929