Platinum(II) Oxalato Complexes Involving Adenosine-Based N-Donor Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization and Cytotoxicity Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion

2.1. IR and Raman Spectroscopy
2.2. ESI Mass Spectrometry

2.3. Multinuclear NMR Spectroscopy
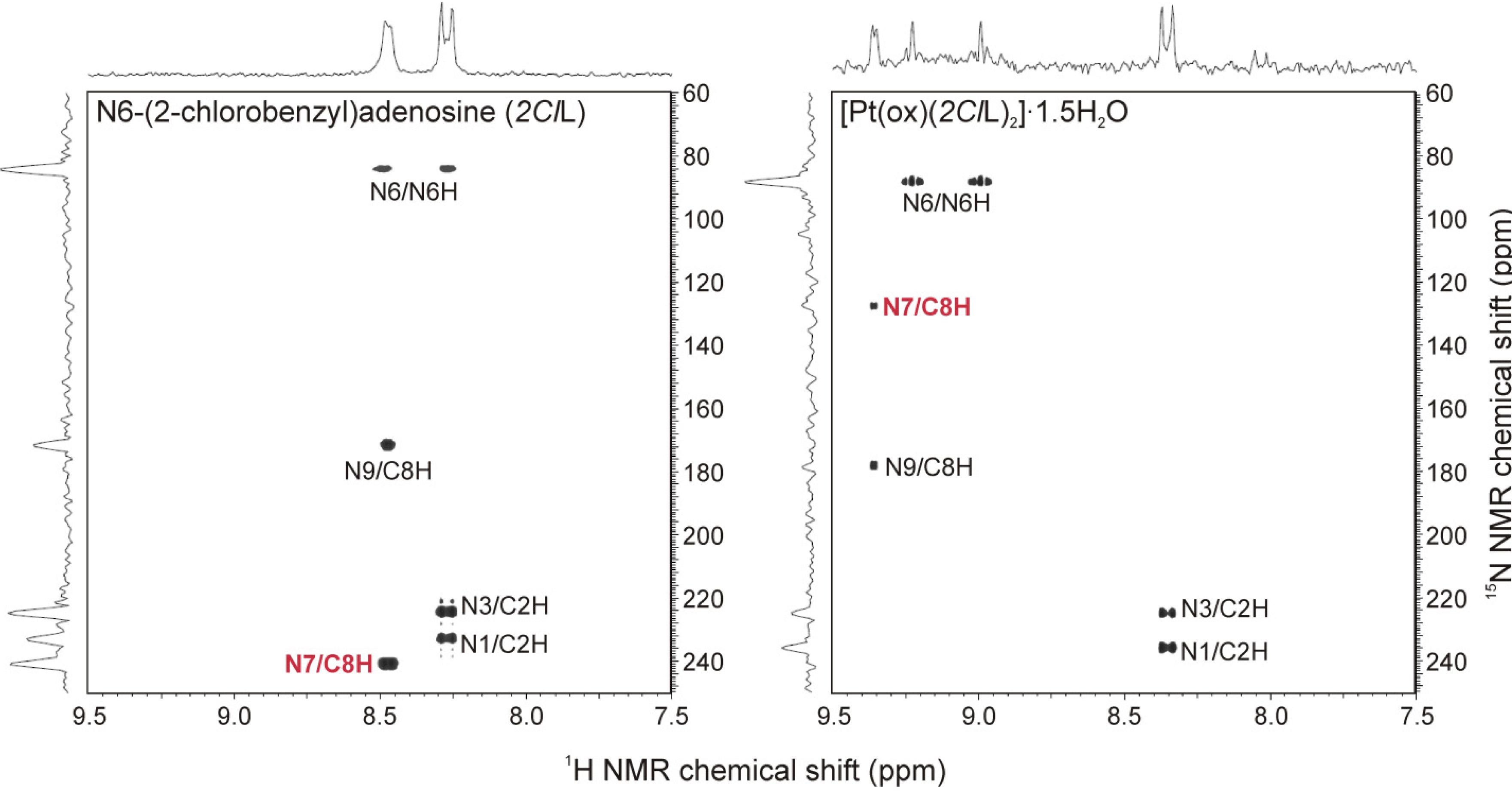
| 1H-NMR | 13C-NMR | 15N NMR | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2H | N6H | C8H | C2H | C4 | C5 | C6 | C8 | N1 | N3 | N6 | N7 | N9 | |
| 1 | 0.11 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.40 | −0.87 | −3.75 | −1.57 | 3.14 | 3.10 | −0.01 | 4.23 | −113.28 | 6.68 |
| 2 | 0.06 | 0.63 | 0.78 | 0.15 | −0.88 | −3.77 | −1.38 | 3.12 | 4.17 | 0.52 | 3.5 | −113.11 | 6.40 |
| 3 | 0.07 | 0.67 | 0.81 | 0.32 | −0.75 | −3.65 | −1.35 | 3.22 | 4.12 | 0.38 | 2.61 | −113.06 | 6.73 |
| 4 | 0.08 | 0.73 | 0.89 | 1.31 | −0.85 | −3.63 | −2.38 | 3.00 | 2.85 | −0.16 | 2.87 | −113.47 | 5.77 |
| 5 | 0.08 | 0.67 | 0.81 | 1.47 | −0.88 | −3.77 | −2.67 | 3.14 | 3.33 | −0.75 | 3.17 | −113.46 | 6.46 |
2.4. Quantum Chemical Calculations
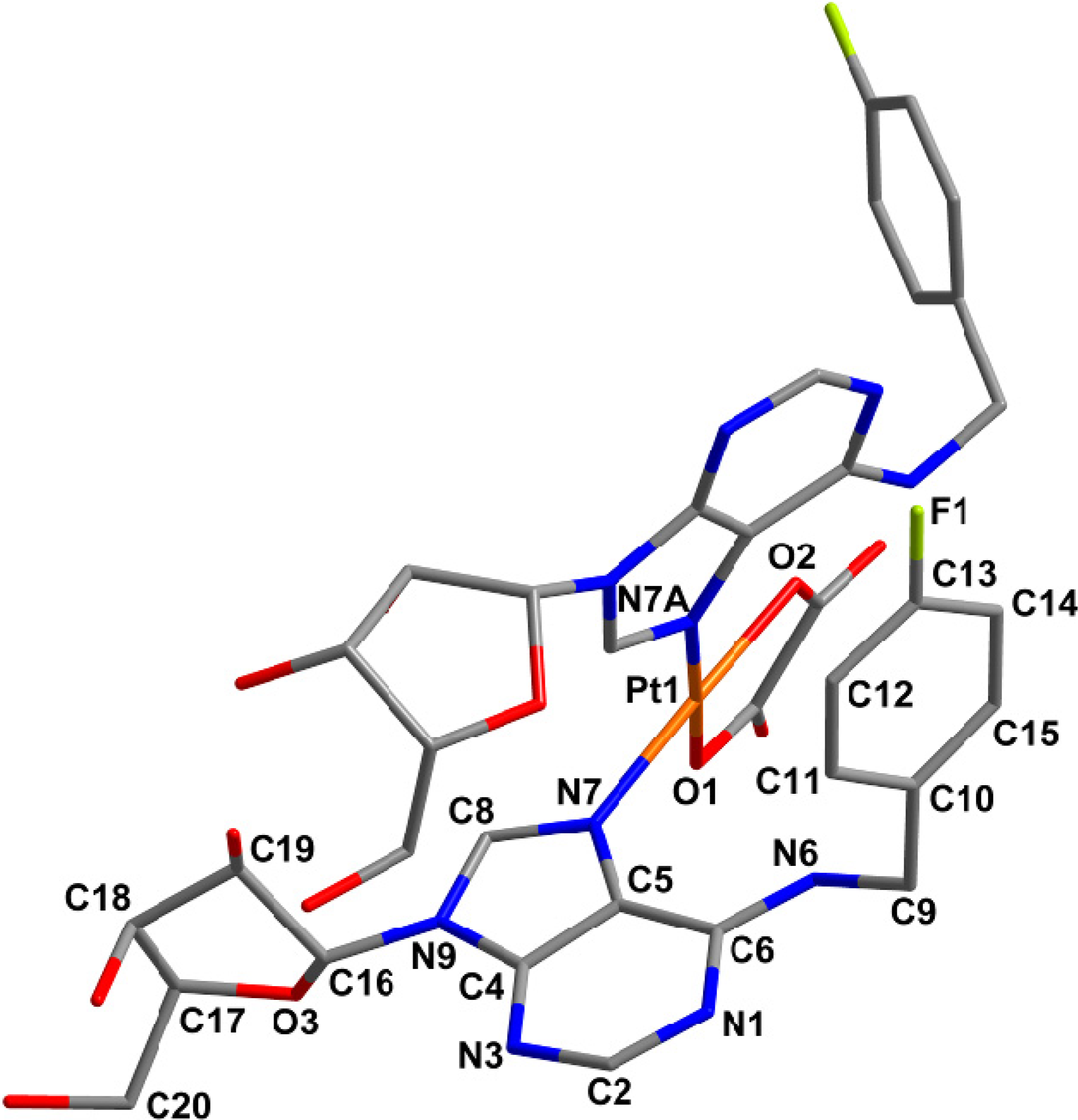
| Parameter | [Pt(ox)(4FL)] (5) a | [Pt(ox)(4FL)] (5) b | [Pt(NH3)2(ado)2]2+ | [Pt(ox)(L1)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt–N7 | 2.054 | 2.053 | 2.046(11) | 2.001(3) |
| Pt–N7A | 2.103 | 2.105 | 2.022(11) | 2.001(3) |
| Pt–O1 | 2.011 | 2.012 | – | 1.994(2) |
| Pt–O2 | 2.019 | 2.017 | – | 2.010 (2) |
| N7–Pt–N7A | 91.91 | 90.66 | 91.90(4) | 89.74(11) |
| O1–Pt–O2 | 82.46 | 82.40 | – | 83.90(9) |
| N7–Pt–O2 | 172.41 | 173.19 | – | 175.93 (10) |
| N7A–Pt–O1 | 176.19 | 176.54 | – | 176.98 (10) |
2.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
2.6. Cellular Accumulation Study
2.7. ESI-MS and NMR Studies on Hydrolysis
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. Synthesis
4. Conclusions
Abbreviations
| Δδ | coordination shift (calculated as δcomplex − δligand) |
| COSY | correlation spectroscopy |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| gs | gradient selected |
| HMBC | heteronuclear multiple bond coherence |
| HMQC | heteronuclear multiple quantum coherence |
| MCF7 | human breast adenocarcinoma cancer cell line |
| HOS | human osteosarcoma cancer cell line |
| 2ClL | N6-(2-chlorobenzyl)adenosine |
| 2OMeL | N6-(2-methoxybenzyl)adenosine |
| 4FL | N6-(4-fluorobenzyl)adenosine |
| 4OMeL | N6-(4-methoxy- benzyl)adenosine |
| 4MeL | N6-(4-methylbenzyl)adenosine |
| nL | N6-(substituted-benzyl)-adenosine derivatives in general |
| ESI– | negative-ion mode electrospray ionization |
| ESI+ | positive-ion mode electrospray ionization |
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflictts of Interest
References
- Kelland, L.R.; Farrell, N.P. Platinum based Drugs in Cancer Therapy; Humana Press: Totowa, New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, R.N.; Cornelius, R.D.; Viola, R.E. Multinuclear NMR studies and the kinetics of formation of platinum(II)-adenine nucleotide complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 4403–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtinger–Schepman, A.M.J.; van der Veer, J.L.; den Hartog, J.H.J.; Lohman, P.H.M.; Reedijk, J. Adducts of the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) with DNA: Formation, identification, and quantitation. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 707–713. [Google Scholar]
- Cleare, M.J.; Hoeschele, J.D. Studies on the antitumor activity of group VIII transition metal complexes Part I Platinum(II) Complexes. Bioinorg. Chem. 1973, 2, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štarha, P.; Popa, I.; Trávníček, Z.; Vančo, J. N6-Benzyladenosine derivatives as novel N-donor ligands of platinum(II) dichlorido complexes. Molecules 2013, 18, 6990–7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trávníček, Z.; Štarha, P.; Popa, I.; Vrzal, R.; Dvořák, Z. Roscovitine-based CDK inhibitors acting as N-donor ligands in the platinum(II) oxalato complexes: Preparation, characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 4609–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trávníček, Z.; Matiková-Maľarová, M.; Novotná, R.; Vančo, J.; Štěpánková, K.; Suchý, P. In vitro and in vivo biological activity screening of Ru(III) complexes involving 6-benzylaminopurine derivatives with higher pro-apoptotic activity than NAMI-A. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trávníček, Z.; Štarha, P.; Vančo, J.; Šilha, T.; Hošek, J.; Suchý, P.; Pražanová, G. Anti-inflammatory active gold(I) complexes involving 6-substituted purine derivative. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 4568–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, L.; Borgne, A.; Mulner, O.; Chong, J.P.J.; Blow, J.J.; Inagaki, N.; Inagaki, M.; Delcros, J.G.; Moulinoux, J.P. Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 243, 527–536. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, C.; Kaye, S.; Workman, P.; Garret, M.; Walton, M.; de Bono, J. Clinical anticancer drug development: Targeting the cyclin-dependent kinases. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrzal, R.; Štarha, P.; Dvořák, Z.; Trávníček, Z. Evaluation of in vitro cytotoxicity and hepatotoxicity of platinum(II) and palladium(II) oxalato complexes with adenine derivatives as carrier ligands. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szüčová, L.; Trávníček, Z.; Popa, I.; marek, J. Preparation and cis-to-trans transformation study of square-planar [Pt(Ln)2Cl2] complexes bearing cytokinins derived from 6-benzylaminopurine (Ln) by view of NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. Polyhedron 2008, 27, 2710–2720. [Google Scholar]
- Dvořák, L.; Popa, I.; Štarha, P.; Trávníček, Z. In vitro cytotoxic-active platinum(II) complexes derived from carboplatin and involving purine derivatives. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 3441–3448.
- Doležal, K.; Popa, I.; Hauserová, E.; Spíchal, L.; Chakrabarty, K.; Novák, O.; Kryštof, V.; Voller, J.; Holub, J.; Strnad, M. Preparation, biological activity and endogenous occurrence of N6-benzyladenosines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 3737–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, 5th ed.; Willey-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Pouchert, C.J. The Aldrich Library of Infrared Spectra; Aldrich Chemical Company Press: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Malek, K.; Podstawka, E.; Milecki, J.; Schroeder, G.; Proniewicz, L.M. Structural features of the adenosine conjugate in means of vibrational spectroscopy and DFT. Biophys. Chem. 2009, 142, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čajan, M.; Trávníček, Z. Structural (X-ray), spectral (FT-IR and Raman) and quantum chemical investigations of a series of 6-benzylaminopurine derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 994, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, S.; Jia, B.; Wei, D.; Liao, X.; Lu, J.; Zhao, Y. A theoretical and mass spectrometry study of the novel mechanism of N-glycosidic bond cleavage in nukleoside. Int. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2009, 282, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S. Accurate description of van der Waals complexes by density functional theory including empirical corrections. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S. Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, D. The role of databases in support of computational chemistry calculations. J. Comp. Chem. 1996, 17, 1571–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchardt, K.L.; Didier, B.T.; Elsethagen, T.; Sun, L.; Gurumoorthi, V.; Chase, J.; Li, J.; Windus, T.L. Basis set exchange: a community database for computational sciences. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Binkley, J.S.; Seeger, R.; Pople, J.A. Self‐consistent molecular orbital methods. XX. A basis set for correlated wave functions. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. ORCA — An ab initio, Density Functional and Semiempirical Program Package; Version 2.8; Universität Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rochon, F.D.; Melanson, R.; Macquet, J.P.; Belanger-Gariepy, F.; Beauchamp, A.L. Crystal structures of diammine(oxalato)platinum(II)and diammine(malonato)platinum(II). Inorg. Chim. Acta 1985, 108, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štarha, P.; Marek, J.; Trávníček, Z. Cisplatin and oxaliplatin derivatives involving 7-azaindole: Structural characterisations. Polyhedron 2012, 33, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štarha, P.; Trávníček, Z.; Popa, I. Platinum(II) oxalato complexes with adenine-based carrier ligands showing significant in vitro antitumor activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meelich, K.; Galanski, M.; Arion, V.B.; Keppler, B.K. Bis(2-amino alcohol-κN)dicarboxylatoplatinum(II) complexes — elegant synthesis via ring-opening of bis(2-amino alcoholato-κ2N, O)platinum(II) species with dicarboxylic acids. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, F.A. The Cambridge Structural Database: a quarter of a million crystal structures and rising. Acta Crystallogr. 2002, B58, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikola, M.; Klika, K.D.; Arpalahti, J. The Kinetics of substitution reactions of mixed platinum(II)–bis(nucleoside) complexes in aqueous solution in the presence of thiourea; X-ray crystal structure determination of cis-[Pt(NH3)2(adenosine-N7)2](ClO4)2∙3.5H2O. Chem. Eur. J. 2000, 6, 3404–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, H.; Kassack, M.U.; Wiese, M. Comparison of the usefulness of the MTT, ATP, and Calcein assays to predict the potency of cytotoxic agents in various human cancer cell lines. J. Biomol. Screen. 2004, 9, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.V.; Hambley, T.W. Platinum drug distribution in cancer cells and tumors. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4911–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, Z.H. Cisplatin: Mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7265–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berners-Price, S.J.; Ronconi, L.; Sadler, P.J. Insights into the mechanism of action of platinum anticancer drugs from multinuclear NMR spectroscopy. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2006, 49, 65–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnle, J.A.; Fuller, G.; Corse, J.; Mackey, B.E. Anti-senescent activity of natural cytokinins. Physiol. Plant. 1977, 41, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–5 are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Štarha, P.; Popa, I.; Trávníček, Z. Platinum(II) Oxalato Complexes Involving Adenosine-Based N-Donor Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization and Cytotoxicity Evaluation. Molecules 2014, 19, 3832-3847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19033832
Štarha P, Popa I, Trávníček Z. Platinum(II) Oxalato Complexes Involving Adenosine-Based N-Donor Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization and Cytotoxicity Evaluation. Molecules. 2014; 19(3):3832-3847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19033832
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠtarha, Pavel, Igor Popa, and Zdeněk Trávníček. 2014. "Platinum(II) Oxalato Complexes Involving Adenosine-Based N-Donor Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization and Cytotoxicity Evaluation" Molecules 19, no. 3: 3832-3847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19033832
APA StyleŠtarha, P., Popa, I., & Trávníček, Z. (2014). Platinum(II) Oxalato Complexes Involving Adenosine-Based N-Donor Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization and Cytotoxicity Evaluation. Molecules, 19(3), 3832-3847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19033832







