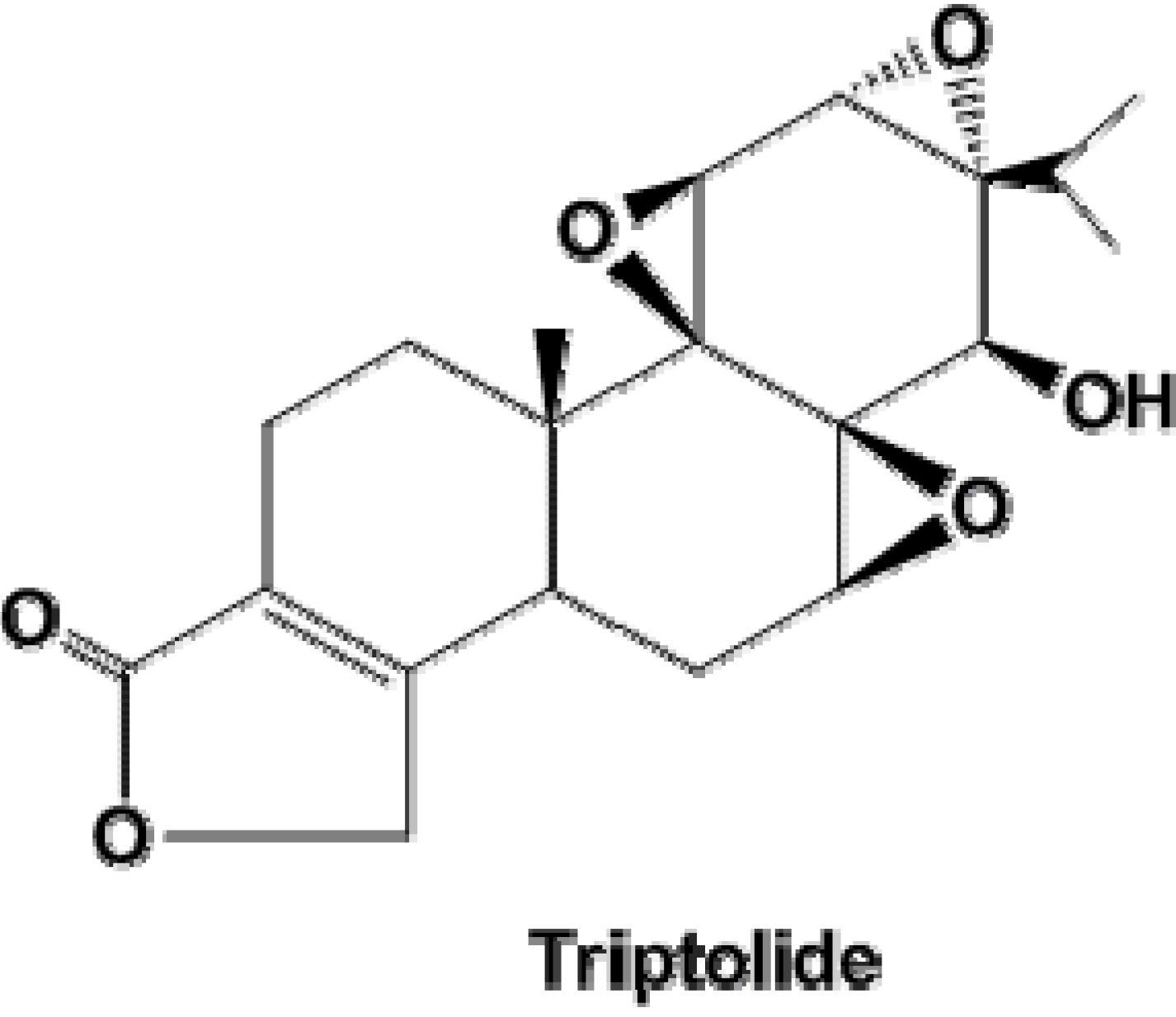
Triptolide Induces S Phase Arrest and Apoptosis in Gallbladder Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
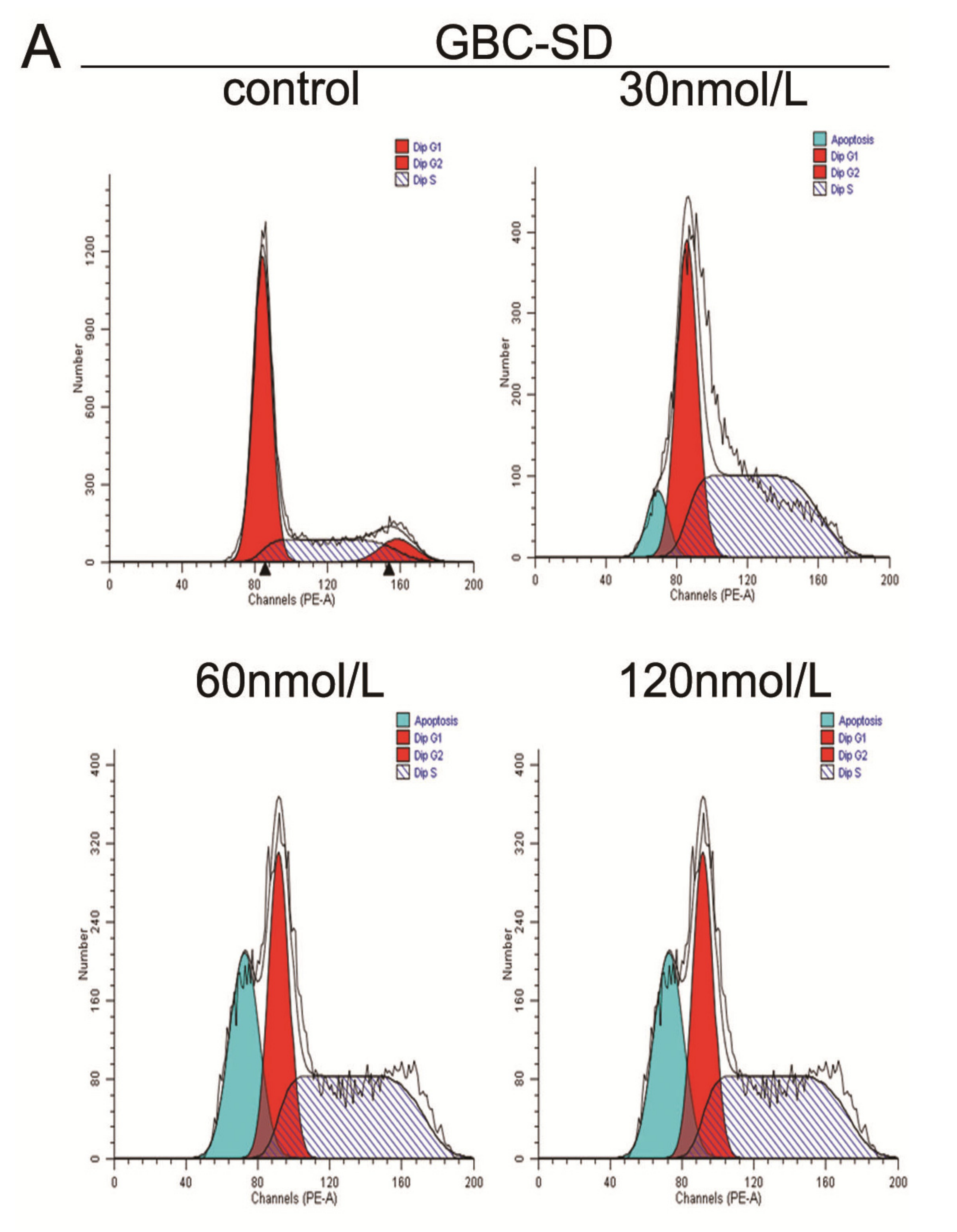
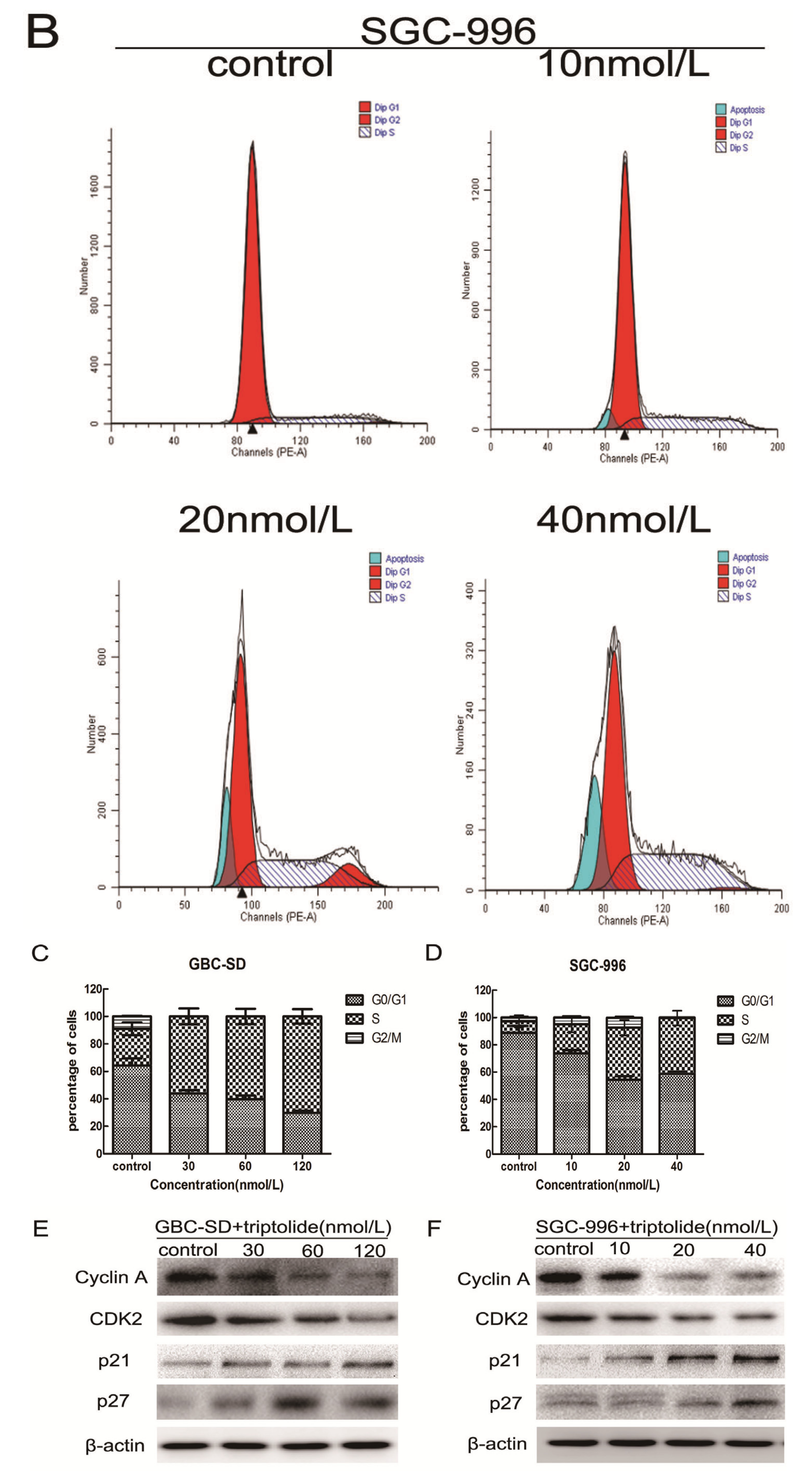
2.1. Triptolide Decreases Proliferation and Viability of Gallbladder Cancer Cells in a Dose-dependent Manner
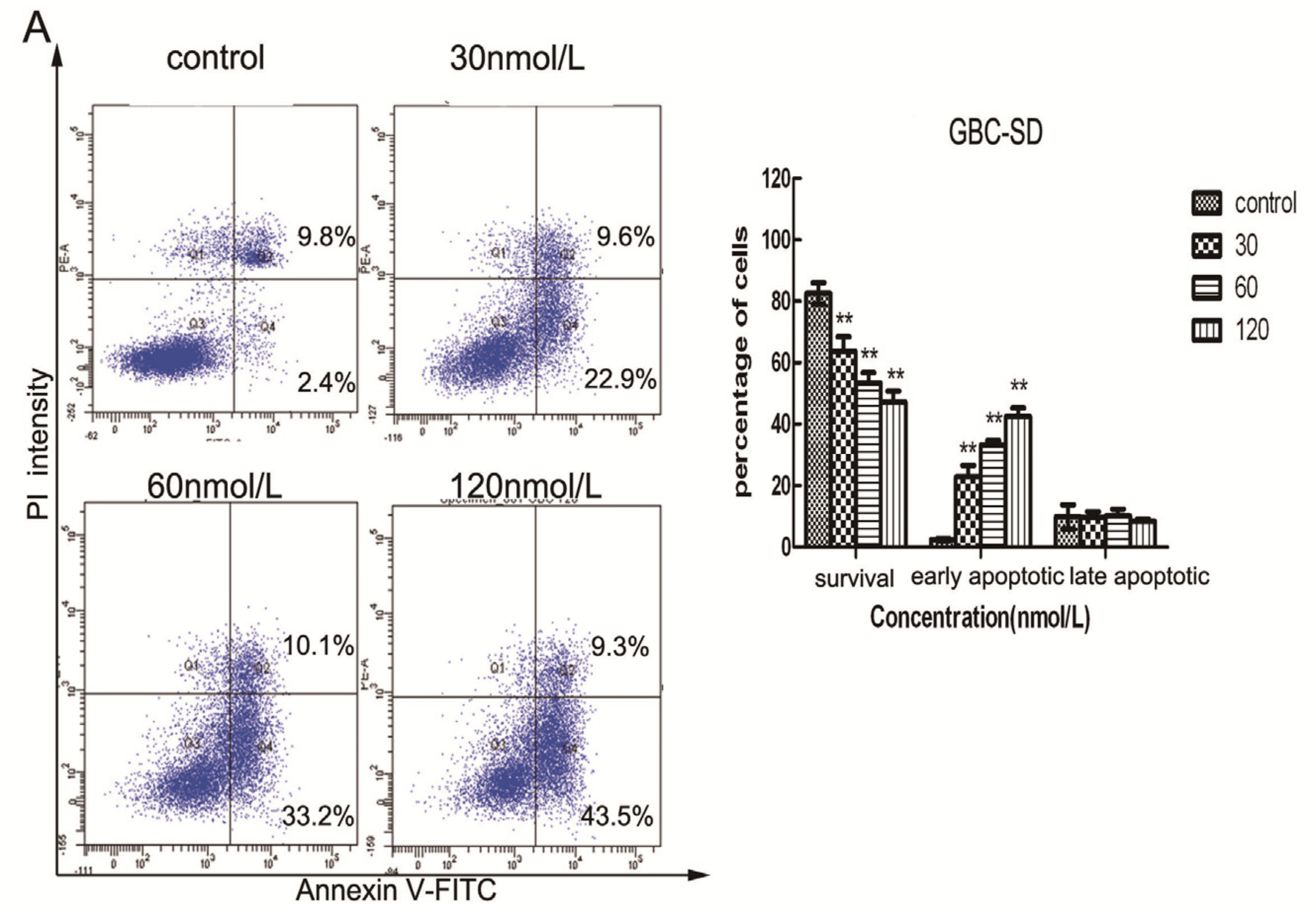
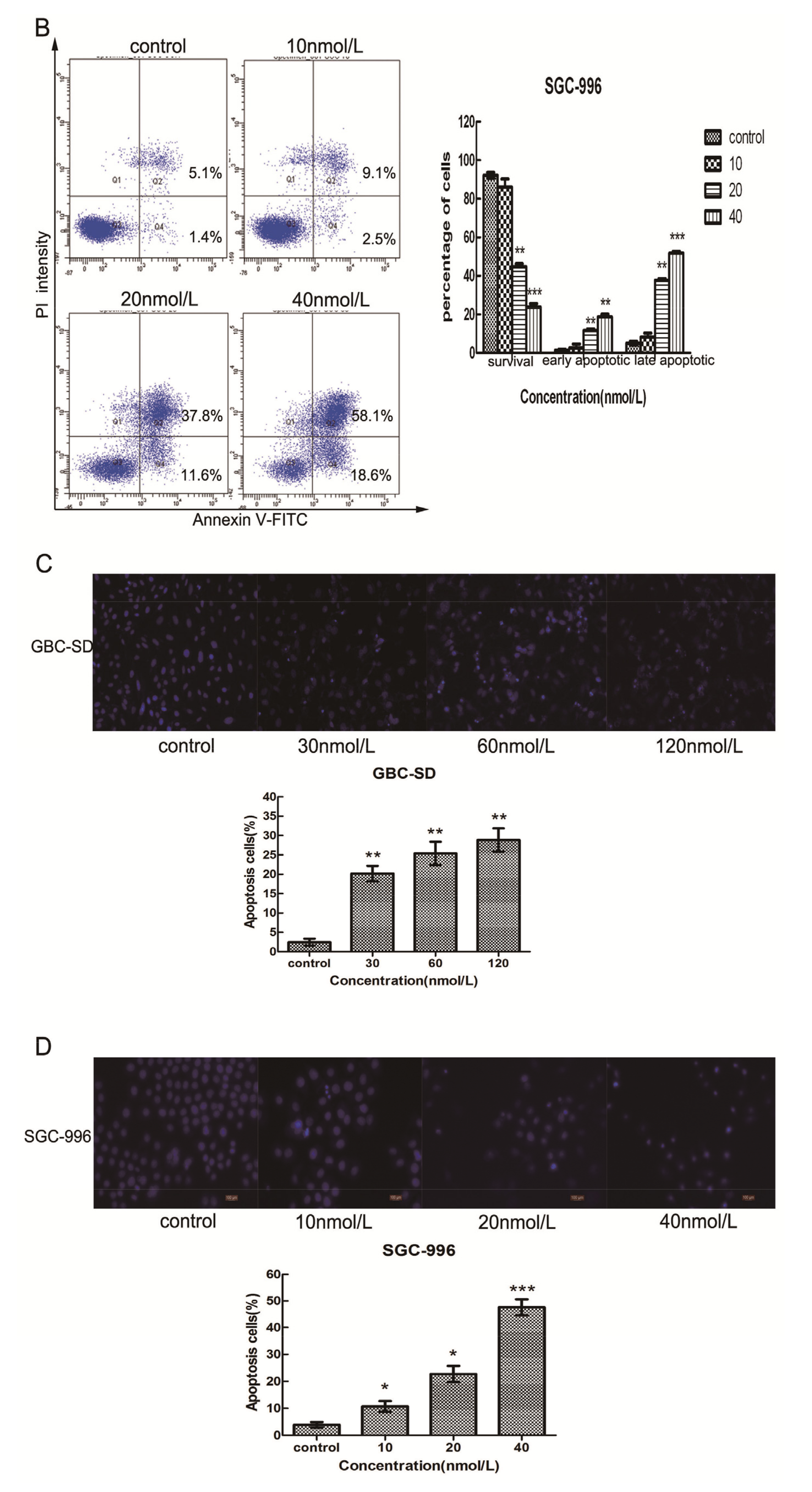
2.3. Triptolide Induces Apoptosis in Human Gallbladder Cancer Cells
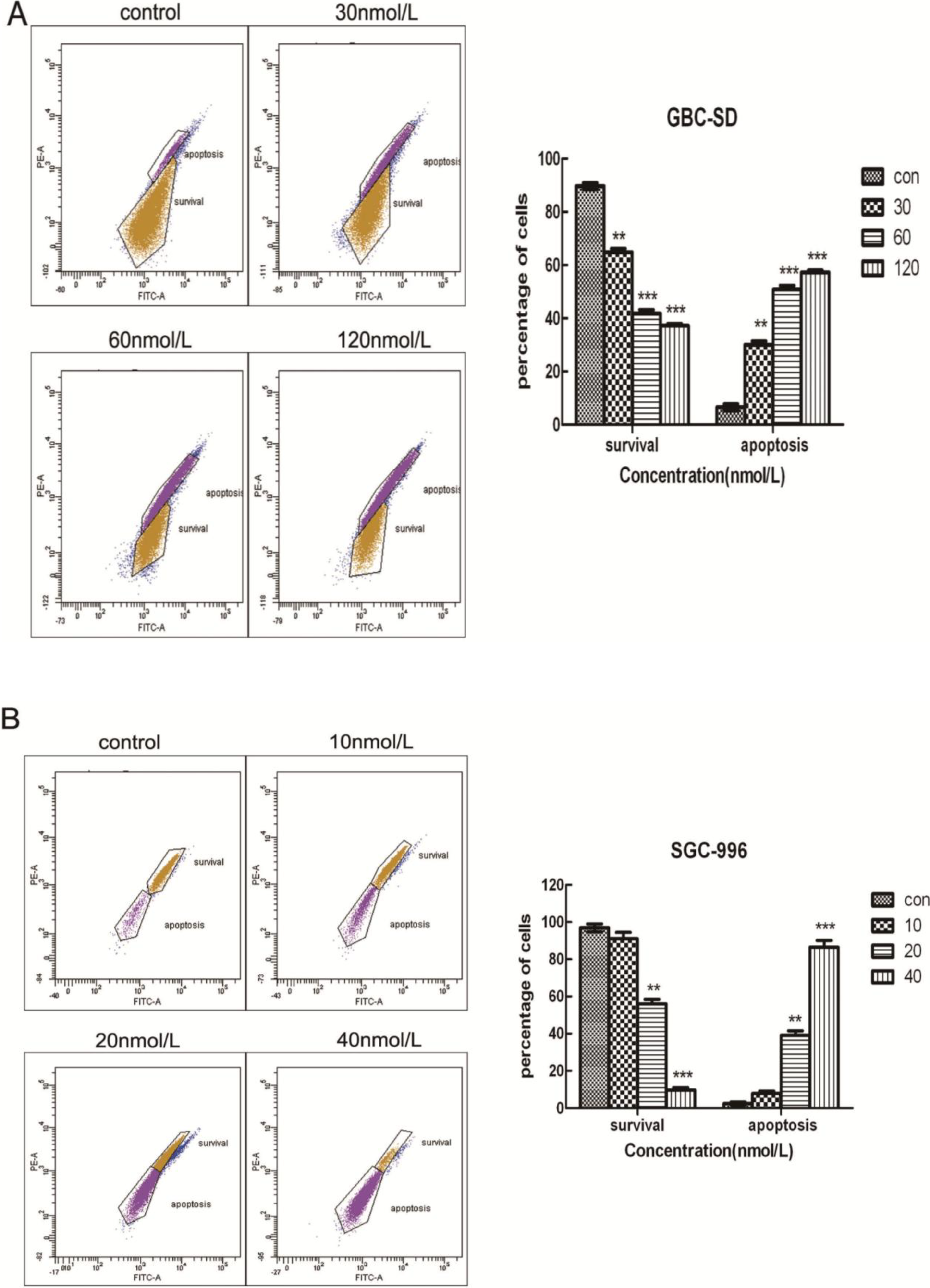
2.4. Triptolide Decreases Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm)
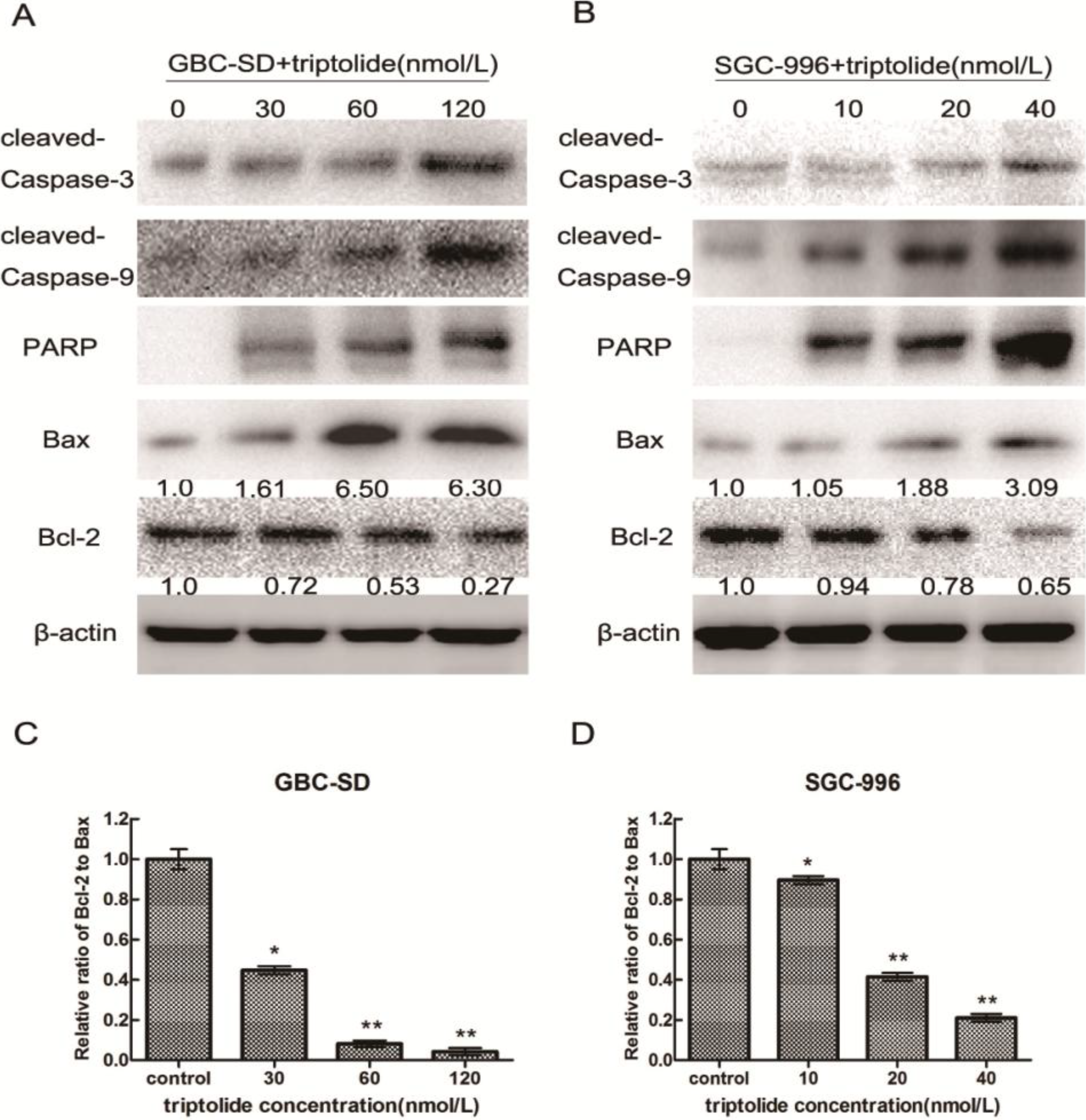
2.5. Triptolide-induced Apoptosis via Regulation of Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 Family Members in Gallbladder Cancer Cells
3. Experimental
3.1. Drugs and Antibodies
3.2. Cell Lines and Culture
3.3. Cell Viability Assay
3.4. Colony Formation Assay
3.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
3.6. Cell Apoptosis Assay
3.7. Hoechst 33342 Staining Assay
3.8. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm) Assay
3.9. Western Blot Analysis
3.10. Statistical analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pitt, H.A.; Dooley, W.C.; Yeo, C.J.; Cameron, J.L. Malignancies of the biliary tree. Curr. Probl. Surg. 1995, 32, 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, K.; Srivastava, A.; Sharma, K.L.; Mittal, B. Candidate gene studies in gallbladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mutat. Res. 2011, 728, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.; Jarnagin, W. Gallbladder carcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 34, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; He, X.-W.; Gu, J.; Wu, W.-G.; Li, M.-I.; Yang, J.-H.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Q.-C.; LU, J.-H.; MU, J.-S. Vimentin significantly promoted gallbladder carcinoma metastasis. Chin. Med. J. (Beijing) 2011, 124, 4236–4244. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Weng, H.; Ding, Q.; Cao, Y.; Bao, R.; Shu, Y.; Mu, J.; et al. Regulation of cell proliferation and migration in gallbladder cancer by zinc finger X-chromosomal protein. Gene 2013, 528, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Peng, S.Y.; Li, J.T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, D.Q.; Weng, W.H.; Wu, X.S.; Fei, X.Z.; et al. Identification of metastasis-associated proteins involved in gallbladder carcinoma metastasis by proteomic analysis and functional exploration of chloride intracellular channel 1. Cancer Lett. 2009, 281, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagorney, D.M.; McPherson, G.A. Carcinoma of the gallbladder and extrahepatic bile ducts. Semin. Oncol. 1988, 15, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Batra, Y.; Pal, S.; Dutta, U.; Desai, P.; Garg, P.K.; Makharia, G.; Ahuja, V.; Pande, G.K.; Sahni, P.; Chattopadhyay, T.K.; et al. Gallbladder cancer in India: A dismal picture. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 20, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazuma, S.; Kajiyama, G. Carcinogenesis of malignant lesions of the gall bladder. Langenbeck's Arch. Surg. 2001, 386, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Chijiiwa, K.; Saiki, S.; Nishihara, K.; Takashima, M.; Kawakami, K.; Tanaka, M. Retrospective analysis of 70 operations for gallbladder carcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 1997, 84, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, R.; Kaushik, S.P.; Sikora, S.S.; Bhattacharya, B.N.; Pandey, C.M.; Kapoor, V.K. Predictors of survival in patients with carcinoma of the gallbladder. Cancer 1995, 76, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X.; Weng, H.; Ding, Q.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, N.; Mu, J. Prognostic significance of nemo-like kinase (NLK) expression in patients with gallbladder cancer. Tumor Biol. 2013, 34, 3995–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Li, M.; Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Q.; Wu, X.; Mu, J.; Liu, Y. NLK is a key regulator of proliferation and migration in gallbladder carcinoma cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 369, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piehler, J.M.; Crichlow, R.W. Primary carcinoma of the gallbladder. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1978, 147, 929–942. [Google Scholar]
- Boutros, C.; Gary, M.; Baldwin, K.; Somasundar, P. Gallbladder cancer: Past, present and an uncertain future. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 21, e183–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Dwary, A.D.; Mohanti, B.K.; Deo, S.V.; Pal, S.; Sreenivas, V.; Raina, V.; Shukla, N.K.; Thulkar, S.; Garg, P.; et al. Best supportive care compared with chemotherapy for unresectable gall bladder cancer: A randomized controlled study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4581–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducreux, M.; Rougier, P.; Fandi, A.; Clavero-Fabri, M.C.; Villing, A.L.; Fassone, F.; Fandi, L.; Zarba, J.; Armand, J.P. Effective treatment of advanced biliary tract carcinoma using 5-fluorouracil continuous infusion with cisplatin. Ann. Oncol. 1998, 9, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.L.; Sun, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, Y.L.; Hu, D.W.; Shi, Y.P.; Zhu, Q.L.; Dai, H.; Zhang, N.Z. A prospective, controlled, double-blind, cross-over study of tripterygium wilfodii hook F in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin. Med. J. 1989, 102, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X. Clinical observations on the use of the Chinese herbTripterygium wilfordii Hook for the treatment of nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 1994, 8, 343–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.Z.; Zhu, G.D.; Yang, S.M.; Han, K.Y.; Wang, J. Clinical observations on Tripterygium wilfordii in treatment of 26 cases of discoid lupus erythematosus. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1983, 3, 131–132. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, F.M.; Chen, Y.L.; Huang, A.C.; Hsiao, Y.P.; Yang, J.S.; Chung, M.T.; Chueh, F.S.; Lu, H.F.; Chung, J.G. Triptolide induces S phase arrest via the inhibition of cyclin E and CDC25A and triggers apoptosis via caspase- and mitochondrial-dependent signaling pathways in A375.S2 human melanoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.H.; Wong, B.C.; Lin, M.C.; Zhu, G.H.; Kung, H.F.; Jiang, S.H.; Yang, D.; Lam, S.K. Functional p53 is required for triptolide-induced apoptosis and AP-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB activation in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 8009–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengchaisri, T.; Chawengkirttikul, R.; Rachaphaew, N.; Reutrakul, V.; Sangsuwan, R.; Sirisinha, S. Antitumor activity of triptolide against cholangiocarcinoma growth in vitro and in hamsters. Cancer Lett. 1998, 133, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Guo, Z.; Xu, X.M.; Wang, L.; Pei, X.F.; Yang, J.; Underhill, C.B.; Zhang, L. Triptolide inhibits the growth and metastasis of solid tumors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2003, 2, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.Y.; Park, J.S.; Jee, Y.K.; Rosen, G.D. Triptolide sensitizes lung cancer cells to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis by inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2002, 34, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiviharju, T.M.; Lecane, P.S.; Sellers, R.G.; Peehl, D.M. Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of triptolide (PG490), a natural product entering clinical trials, on primary cultures of human prostatic epithelial cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2666–2674. [Google Scholar]
- Nigg, E.A. Cyclin-dependent protein kinases: Key regulators of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Bioessays 1995, 17, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.L.; Sorger, P.K. Measuring and modeling apoptosis in single cells. Cell 2011, 144, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, S.W.; Green, D.R. Mitochondria and cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zelenski, N.G.; Yang, J.; Sakai, J.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Cleavage of sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) by CPP32 during apoptosis. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Emoto, Y.; Manome, Y.; Meinhardt, G.; Kisaki, H.; Kharbanda, S.; Robertson, M.; Ghayur, T.; Wong, W.W.; Kamen, R.; Weichselbaum, R.; et al. Proteolytic activation of protein kinase C delta by an ICE-like protease in apoptotic cells. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 6148–6156. [Google Scholar]
- Tewari, M.; Quan, L.T.; O'Rourke, K.; Desnoyers, S.; Zeng, Z.; Beidler, D.R.; Poirier, G.G.; Salvesen, G.S.; Dixit, V.M. Yama/CPP32 beta, a mammalian homolog of CED-3, is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cell 1995, 81, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walensky, L.D. BCL-2 in the crosshairs: Tipping the balance of life and death. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Tan, Z.J.; Jiang, L.; Gu, J.F.; Wu, X.S.; Cao, Y.; Li, M.L.; Wu, K.J.; Liu, Y.B. Curcumin induces apoptosis in gallbladder carcinoma cell line GBC-SD cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.Q.; Wang, J.H.; Ma, H.X.; Cheng, P.F.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.J. Polyamine transporter recognization and antitumor effects of anthracenymethyl homospermidine. Toxicology 2009, 263, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.-P.; Tan, Z.-J.; Wu, X.-S.; Liu, T.-Y.; Jiang, L.; Bao, R.-F.; Shu, Y.-J.; Li, M.-L.; Weng, H.; Ding, Q.; et al. Triptolide Induces S Phase Arrest and Apoptosis in Gallbladder Cancer Cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 2612-2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022612
Hu Y-P, Tan Z-J, Wu X-S, Liu T-Y, Jiang L, Bao R-F, Shu Y-J, Li M-L, Weng H, Ding Q, et al. Triptolide Induces S Phase Arrest and Apoptosis in Gallbladder Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2014; 19(2):2612-2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022612
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yun-Ping, Zhu-Jun Tan, Xiang-Song Wu, Tian-Yu Liu, Lin Jiang, Run-Fa Bao, Yi-Jun Shu, Mao-Lan Li, Hao Weng, Qian Ding, and et al. 2014. "Triptolide Induces S Phase Arrest and Apoptosis in Gallbladder Cancer Cells" Molecules 19, no. 2: 2612-2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022612
APA StyleHu, Y.-P., Tan, Z.-J., Wu, X.-S., Liu, T.-Y., Jiang, L., Bao, R.-F., Shu, Y.-J., Li, M.-L., Weng, H., Ding, Q., Tao, F., & Liu, Y.-B. (2014). Triptolide Induces S Phase Arrest and Apoptosis in Gallbladder Cancer Cells. Molecules, 19(2), 2612-2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022612