Resveratrol-4-O-D-(2'-galloyl)-glucopyranoside Isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum Exhibits Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Viability by Inducing Apoptosis via the JNK and ERK Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
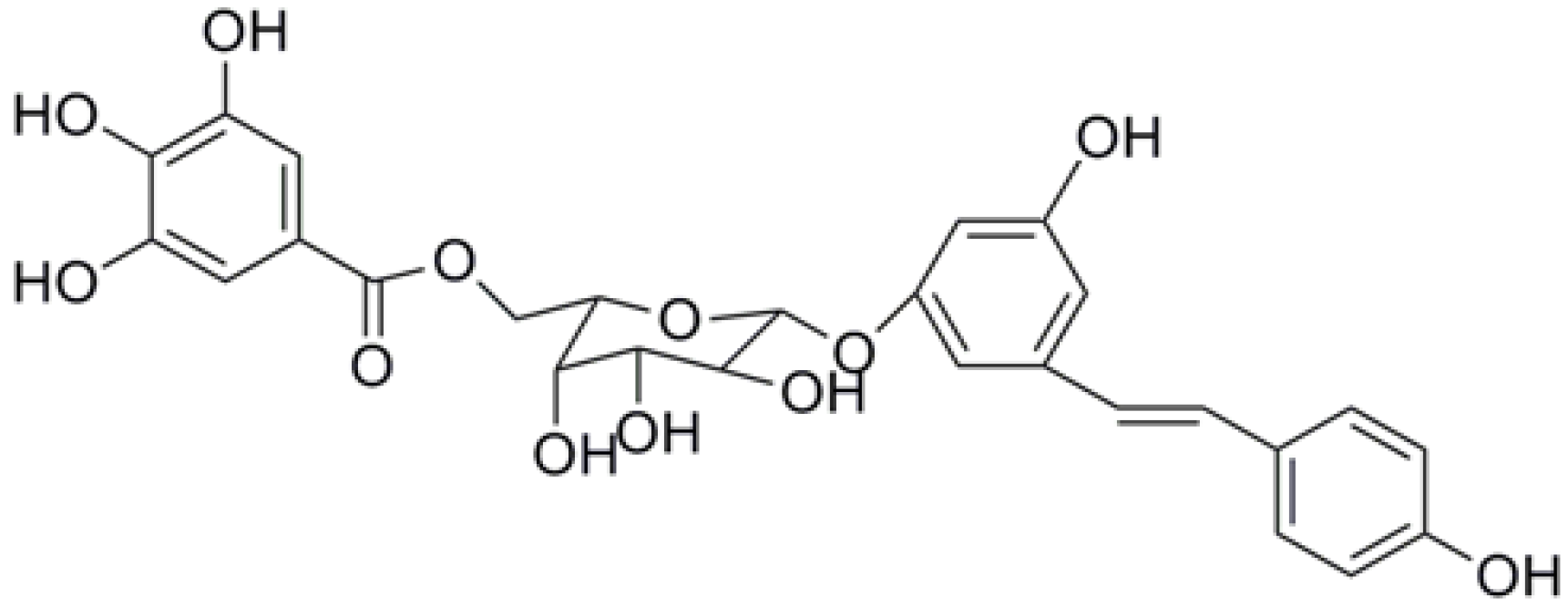
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. RESG Has In Vitro Antitumor Activity
2.1.1. RESG Inhibited Human Hepatoma Cells Activity
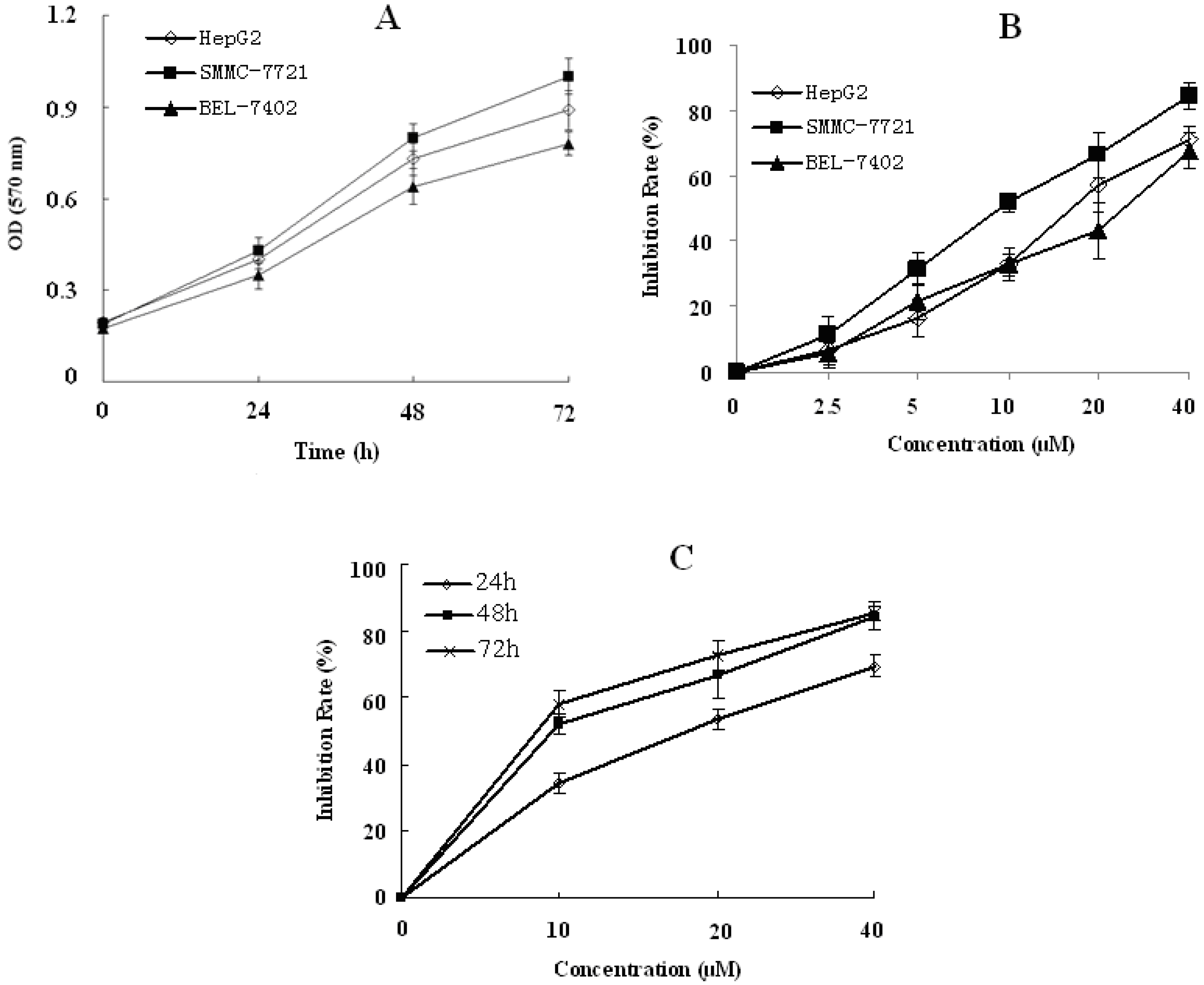
2.1.2. RESG Induced SMMC-7721 Cell Apoptosis

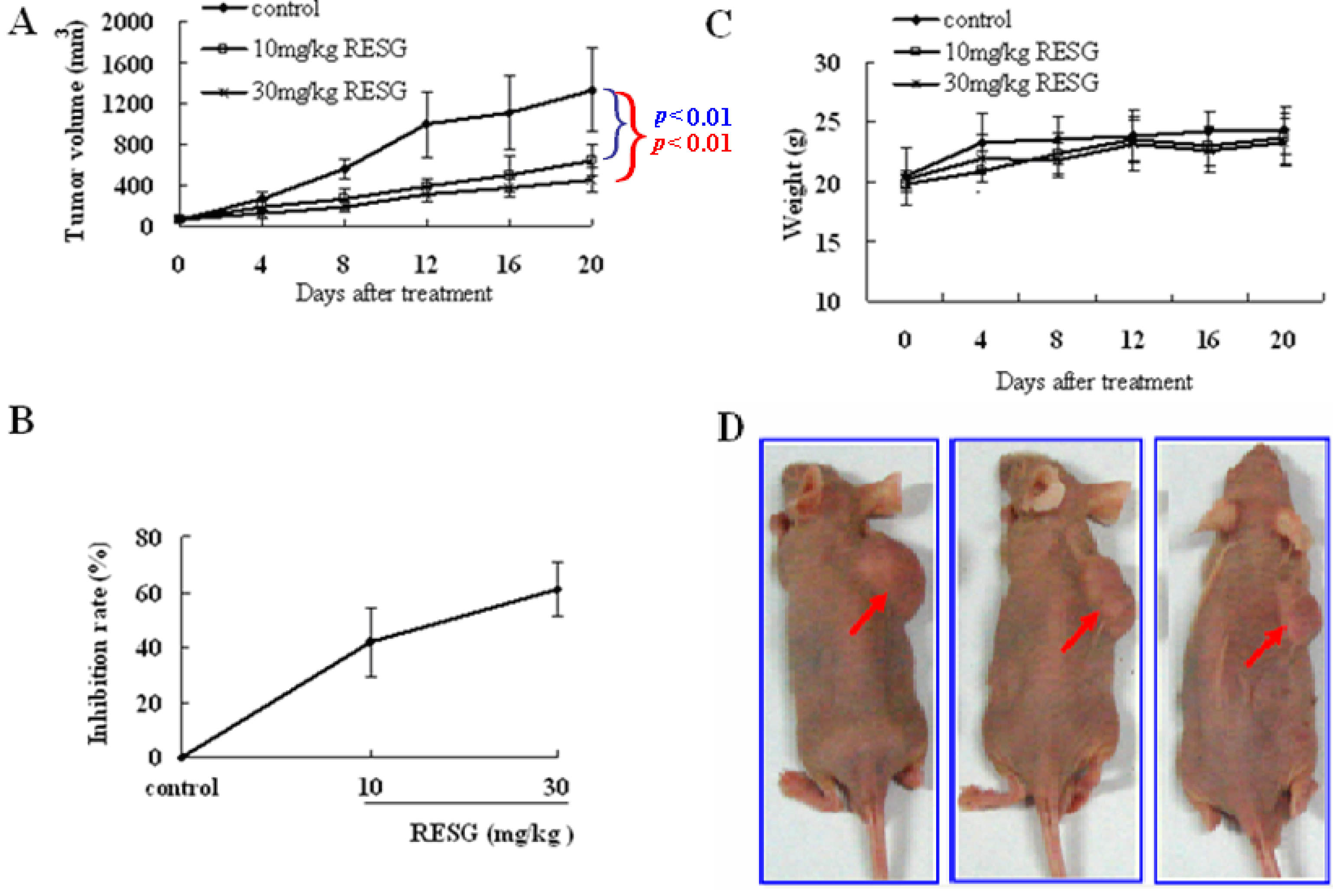
2.2. RESG Exhibits Antitumor Effects on SMMC-7721 Xenograft Model Mice
2.3. Investigation of the Antitumor Mechanisms of RESG In Vitro
2.3.1. RESG Affected the MAPK Pathways
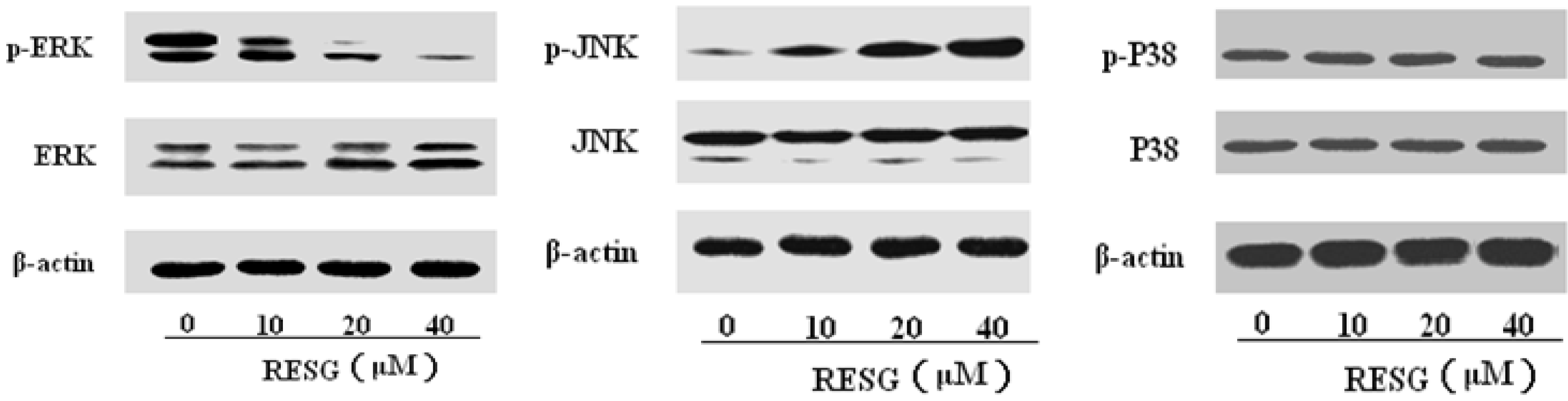
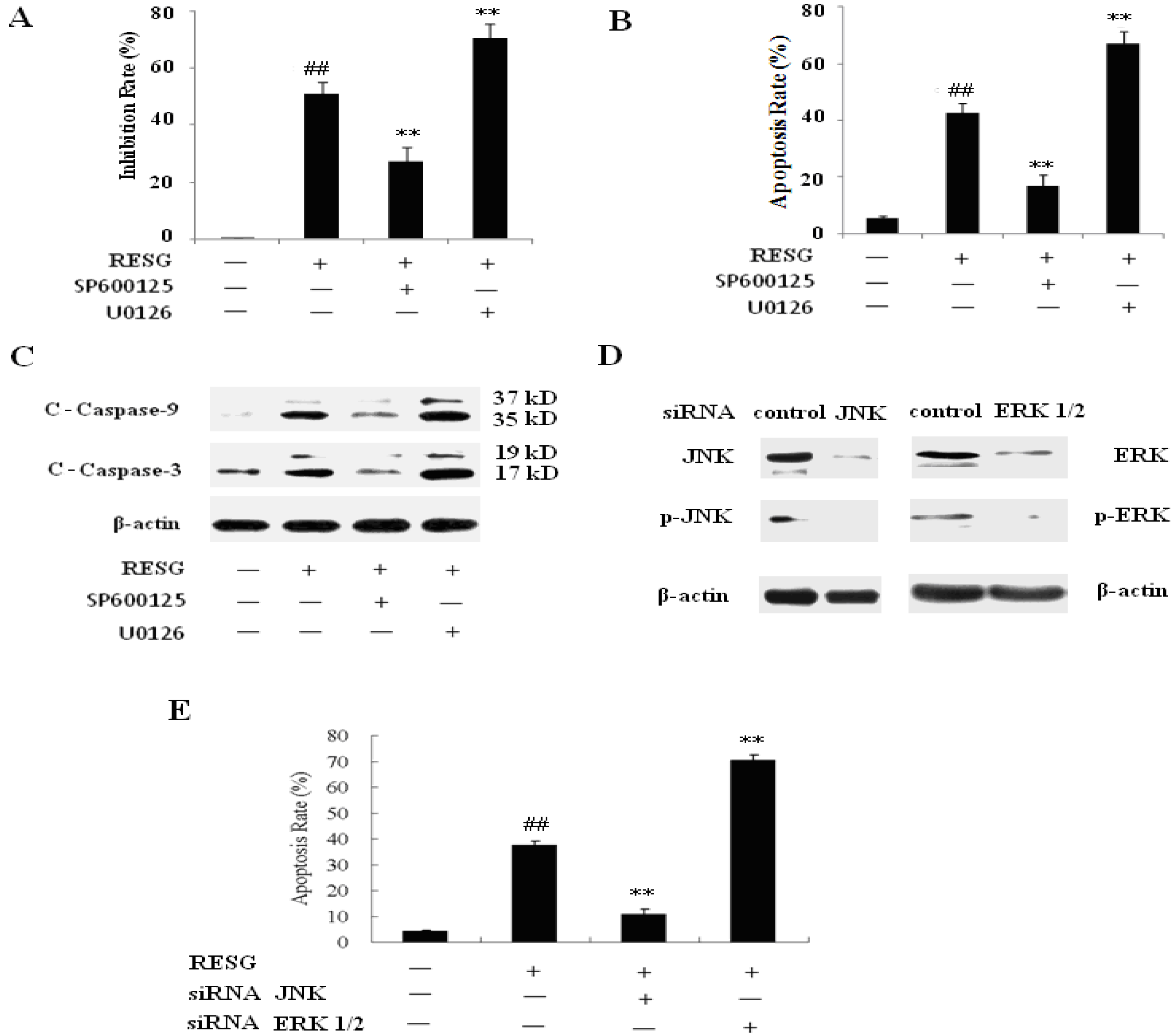
2.3.2. Activation of JNK and ERK Play Important Roles in RESG-Mediated Apoptosis in SMMC-7721 Cells
3. Experimental
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Isolation and Preparation of RESG
3.3. Cells Culture
3.4. Cell Viability and Apoptosis Assay
3.5. Western Blot Analysis
3.6. Gene Silencing Using Small RNA (siRNA)
3.7. Xenograft Assay In Vivo
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, W.; Qin, R.X.; Li, X.L.; Zhou, H. Botany, Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and potential application of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb.et Zucc: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial Board of Flora of China. Flora of China, 1st ed.; Science Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 277–350. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Song, Z.F.; Ma, C. Emodin Studies on pharmacokinetics and distribution in rat liver after Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb.et Zucc extract administration. Mode Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Med. 2008, 10, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.H.; Koh, W.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, E.O.; Lee, S.J.; Khil, J.H.; Kim, J.T.; Jeong, S.J.; Kim, S.H. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of ethyl acetate fraction of Polygonum cuspidatum in experimental animals. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 34, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial Committee of Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Chinese Pharmacopoeia; Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 194–195. [Google Scholar]
- Hegde, V.R.; Pu, H.Y.; Patel, M.; Black, T.; Soriano, A.; Zhao, W.J.; Gullo, V.P.; Chan, T.M. Two new bacterial DNA primase inhibitors from the plant Polygonum cuspidatum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 2275–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Xuan, L.J.; Xu, Y.M.; Bai, D.L.; Zhong, D.X. Constituents from Polygonum cuspidatum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.H.; Hay, A.E.; Marston, A.; Lou, H.X.; Hostettmann, K. Chemical variability of the invasive neophytes Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. and Zucc. and Polygonum sachalinensis F. Schmidt ex Maxim. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2009, 37, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Gao, Y.Y.; Liu, B.Q.; Niu, X.F.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, H.Q. Resveratrol-induced cytotoxicity in human Burkitt’s lymphoma cells is coupled to the unfolded protein response. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, A.; Hori, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Saitoh, A.; Yasuda, I.; Maekawa, T.; Uchida, T.; Asakura, K.; Nakazato, T.; Kaneda, T.; et al. Emodin has a cytotoxic activity against human multiple myeloma as a Janus-activated kinase 2 inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 987–994. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ginkel, P.R.; Sareen, D.; Subramanian, L. Resveratrol inhibits tumor growth of human neuroblastoma and mediates apoptosis by directly targeting mitochondria. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5162–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.X.; Zhang, X.Q.; Kang, L.D.; Zhang, P.J.; Chen, W.W.; Liu, W.W.; Liu, Q.W.; Zhang, J.Y. Emodin induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cell LNCaP. Asian J. Androl. 2008, 10, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.G.; Yang, J.Q.; Liu, B.Z.; Jin, D.T.; Wang, C.; Zhong, L.; Zhu, D.; Wu, Y. Anti-tumor activity of emodin against human chronic myelocytic leukemia K562 cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 627, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.C.; Yang, J.S.; Lin, M.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Lin, J.J.; Lin, H.J.; Hsia, T.C.; Liao, C.L.; Yang, M.D.; Fan, M.J.; et al. Emodin has cytotoxic and protective effects in rat C6 glioma cells: Roles of Mdr1a and nuclear factor kappaB in cell survival. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.M.; Hsu, Y.A.; Tsai, Y.; Shieh, F.K.; Huang, S.H.; Wan, L.; Tsai, F.J. Emodin inhibits the growth of hepatoma cells: Finding the common anti-cancer pathway using Huh7, Hep3B, and HepG2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 392, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, G.; Gallelli, L.; Renda, T.; Fratto, D.; Falcone, D.; Caraglia, M.; Busceti, M.T.; Terracciano, R.; Vatrella, A.; Maselli, R.; et al. Effects of statins and farnesyl transferase inhibitors on ERK phosphorylation, apoptosis and cell viability in non-small lung cancer cells. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.H.; Lin, S.M.; Chen, J.C.; Su, Y.H.; Huang, H.Y.; Chen, C.K.; Lin, P.Y.; Chen, Y. Resveratrol suppresses the angiogenesis and tumor growth of gliomas in rats. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 2190–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Gibson, B.T.; Xu, B.E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.; Dickens, M.; Raingeaud, J.; Davis, R.J.; Greenberg, M.E. Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-P38 MAP kinases on apop-tosis. Science 1995, 270, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Enayat, S.; Ceyhan, M.S.; Basaran, A.A.; Gürsel, M.; Banerjee, S. Anticarcinogenic effects of the ethanolic extract of salix aegyptiaca in colon cancer cells: Involvement of Akt/PKB and MAPK pathways. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Budhraja, A.; Cheng, S.; Liu, E.H.; Huang, C.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X. Interruption of the MEK/ERK signaling cascade promotes dihydroartemisinin-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, P.; Li, H.; Gao, H.; Su, X. Anti-tumor effects of atractylenolide I isolated from Atractylodes macrocephala in human lung carcinoma cell lines. Molecules 2013, 18, 13357–13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, A.; Mitsui, S.; Yanagie, H.; Kasano, H.; Hisa, T.; Yamase, T.; Eriguchi, M. A novel anti-tumor agent, polyoxomolybdate induces apoptotic cell death in AsPC-1 human pancreatic cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2005, 59, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compound is available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhang, A.; Liu, C. Resveratrol-4-O-D-(2'-galloyl)-glucopyranoside Isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum Exhibits Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Viability by Inducing Apoptosis via the JNK and ERK Pathway. Molecules 2014, 19, 1592-1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19021592
Xie Q, Yang Y, Wang Z, Chen F, Zhang A, Liu C. Resveratrol-4-O-D-(2'-galloyl)-glucopyranoside Isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum Exhibits Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Viability by Inducing Apoptosis via the JNK and ERK Pathway. Molecules. 2014; 19(2):1592-1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19021592
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Qichao, Yupeng Yang, Zhiyi Wang, Fanglin Chen, Anmei Zhang, and Chengcheng Liu. 2014. "Resveratrol-4-O-D-(2'-galloyl)-glucopyranoside Isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum Exhibits Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Viability by Inducing Apoptosis via the JNK and ERK Pathway" Molecules 19, no. 2: 1592-1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19021592
APA StyleXie, Q., Yang, Y., Wang, Z., Chen, F., Zhang, A., & Liu, C. (2014). Resveratrol-4-O-D-(2'-galloyl)-glucopyranoside Isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum Exhibits Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Viability by Inducing Apoptosis via the JNK and ERK Pathway. Molecules, 19(2), 1592-1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19021592



