Curcumin Protects against CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats by Inhibiting HIF-1α Through an ERK-Dependent Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Histological Examination
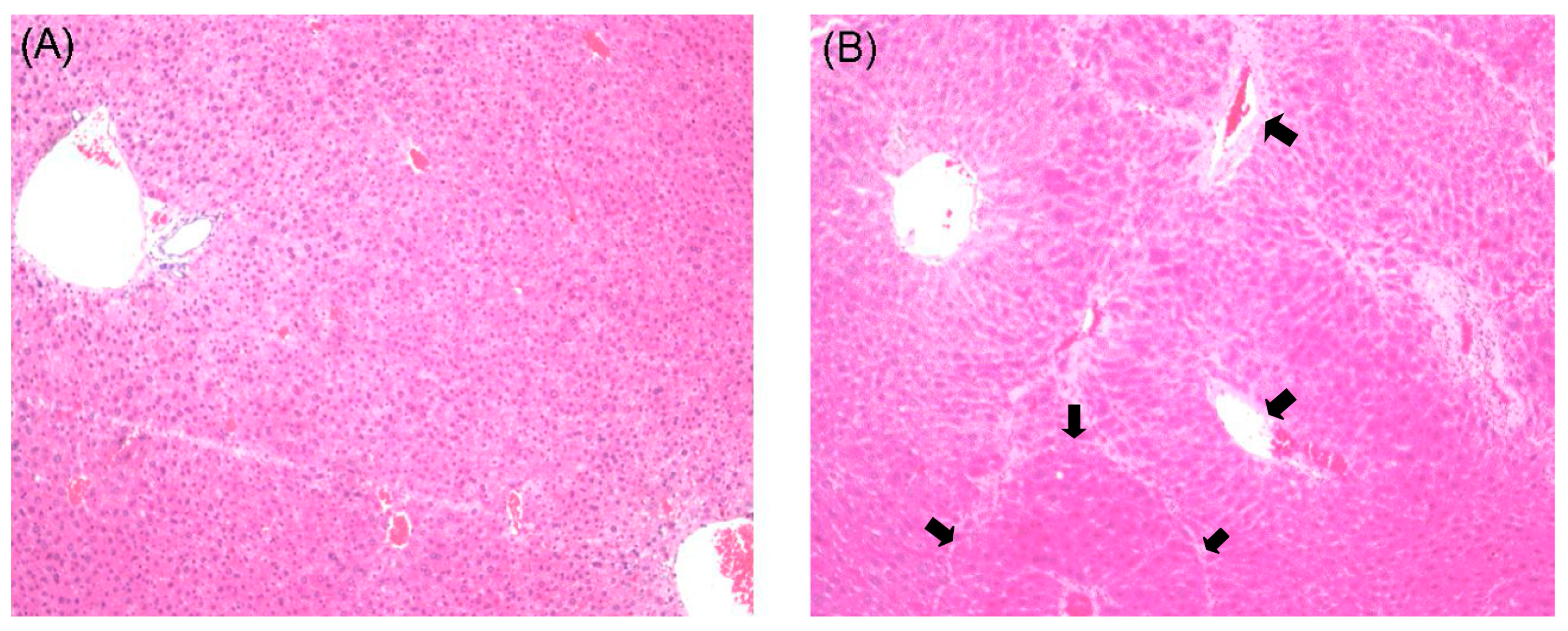
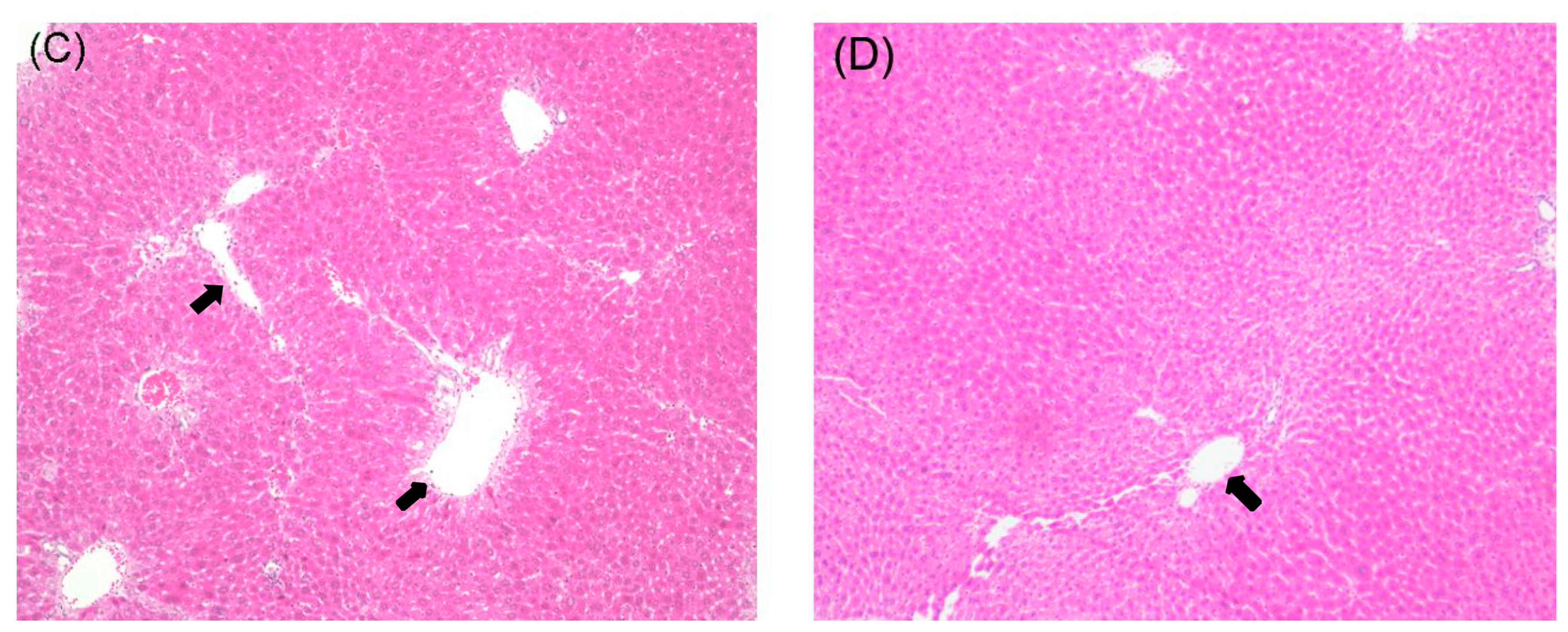
2.2. Effects of Curcumin on Serum Biochemistry
| Group | ALT (U/L) | AST (U/L) | ALP (U/L) | ALB (g/L) | TP (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 60.06 ± 15.04 | 140.23 ± 19.27 | 270.96 ± 17.82 | 41.45 ± 2.84 | 70.90 ± 6.43 |
| Model | 158.10 ± 23.50 ** | 394.28 ± 37.74 ** | 434.42 ± 52.30 ** | 23.95 ± 3.05 ** | 42.10 ± 5.13 ** |
| CUR-L | 52.98 ± 12.36 ## | 106.67 ± 19.26 ## | 260.78 ± 22.99 ## | 29.72 ± 3.27 **## | 49.17 ± 5.49 **# |
| CUR-H | 53.02 ± 15.20 ## | 100.48 ± 17.25 ## | 241.42 ± 33.11 ## | 30.60 ± 3.17 **## | 53.67 ± 7.68 **## |
2.3. Effects of Curcumin on mRNA Expression of α-SMA and Col III
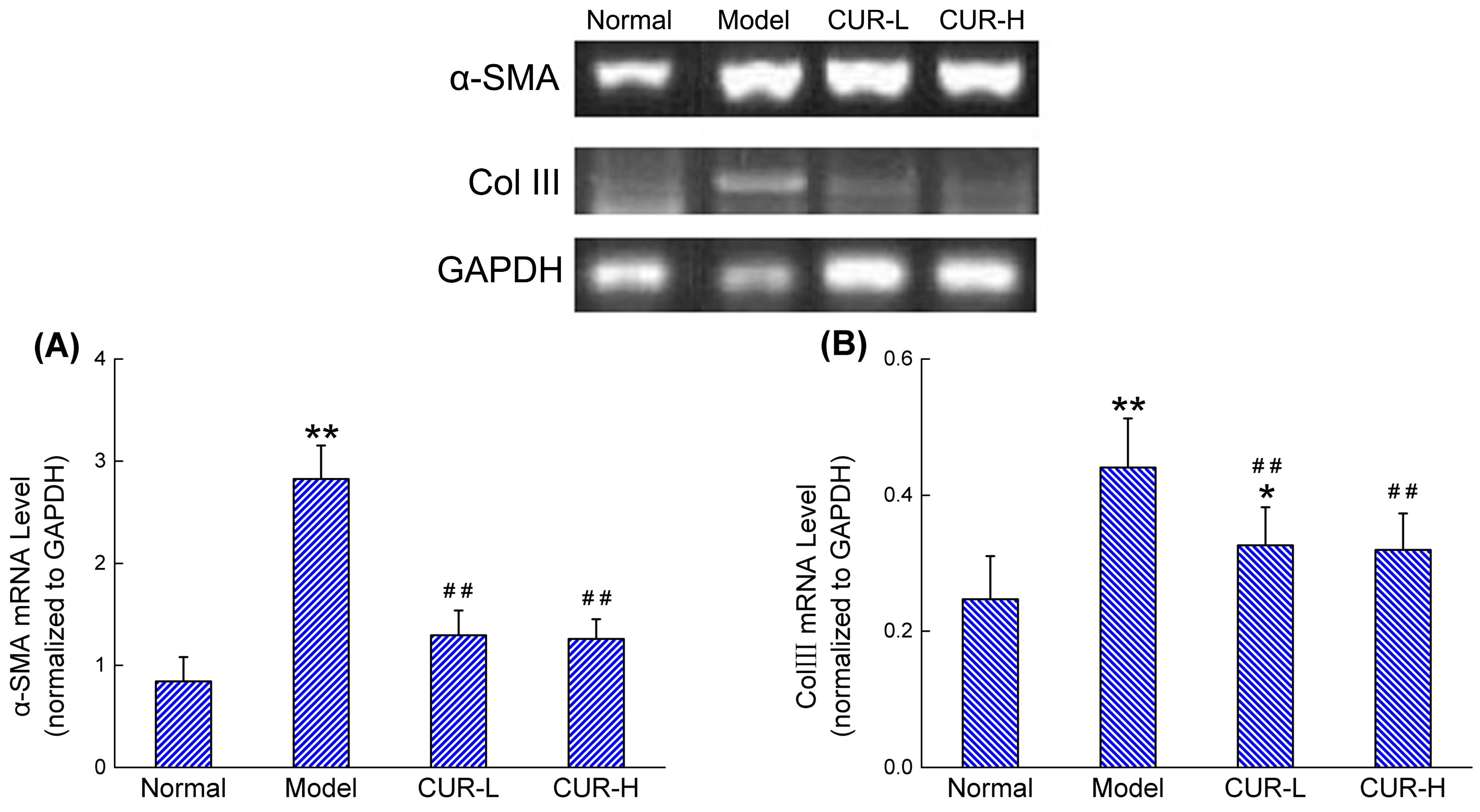
2.4. Effects of Curcumin on Activation of HIF-1α and p-ERK
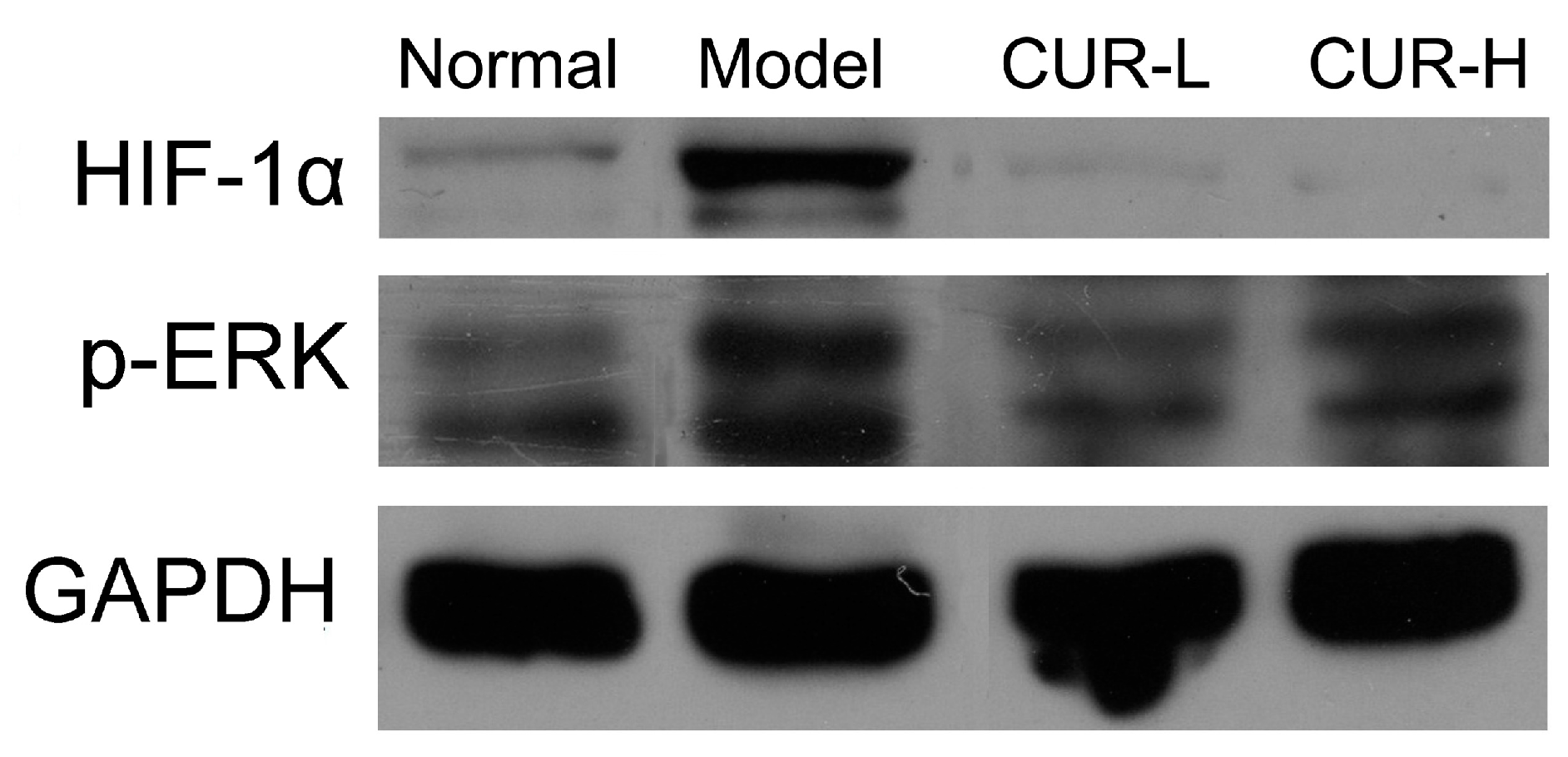

2.5. Cell Viability of Curcumin on HSC-T6 in Vitro
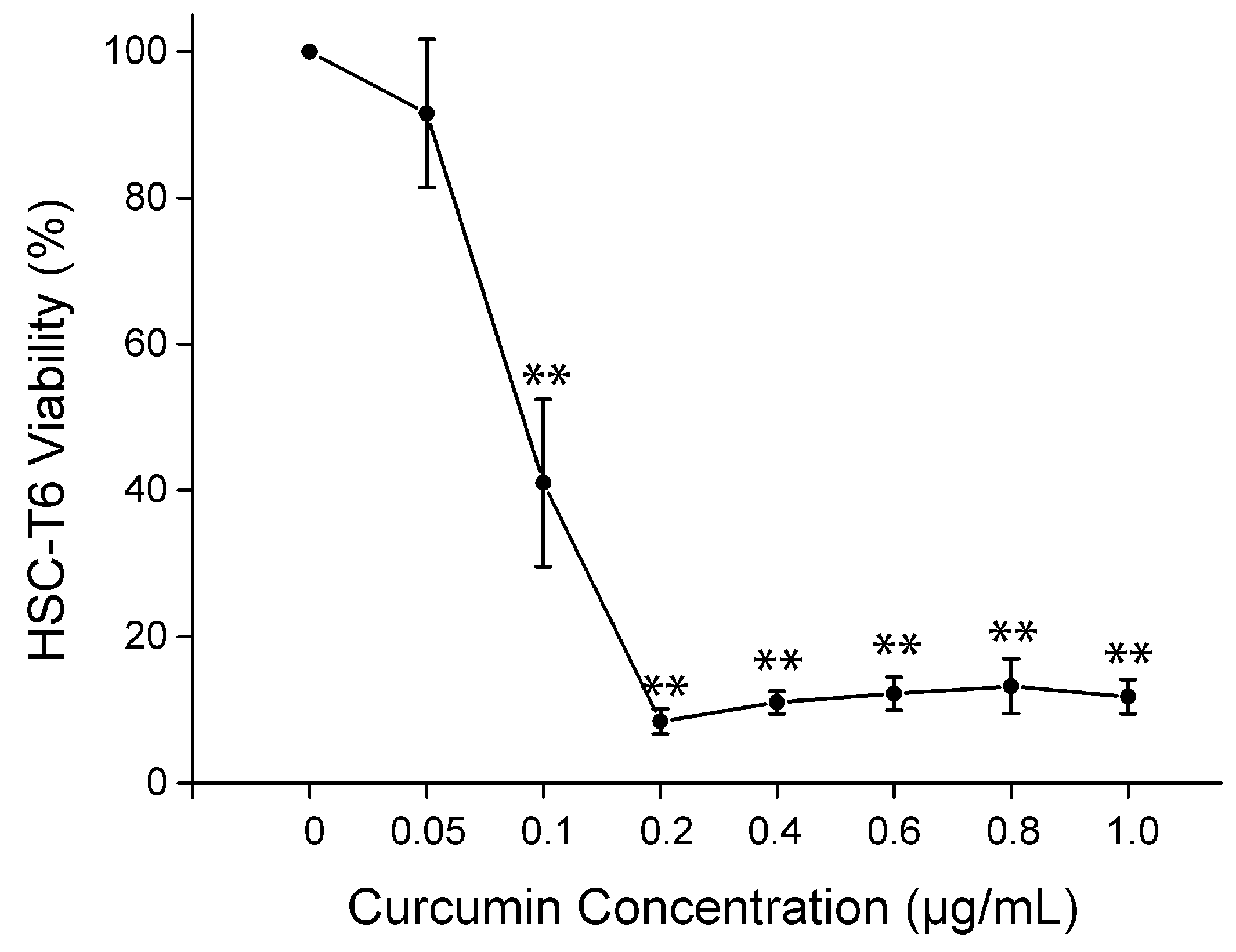
2.6. Discussion
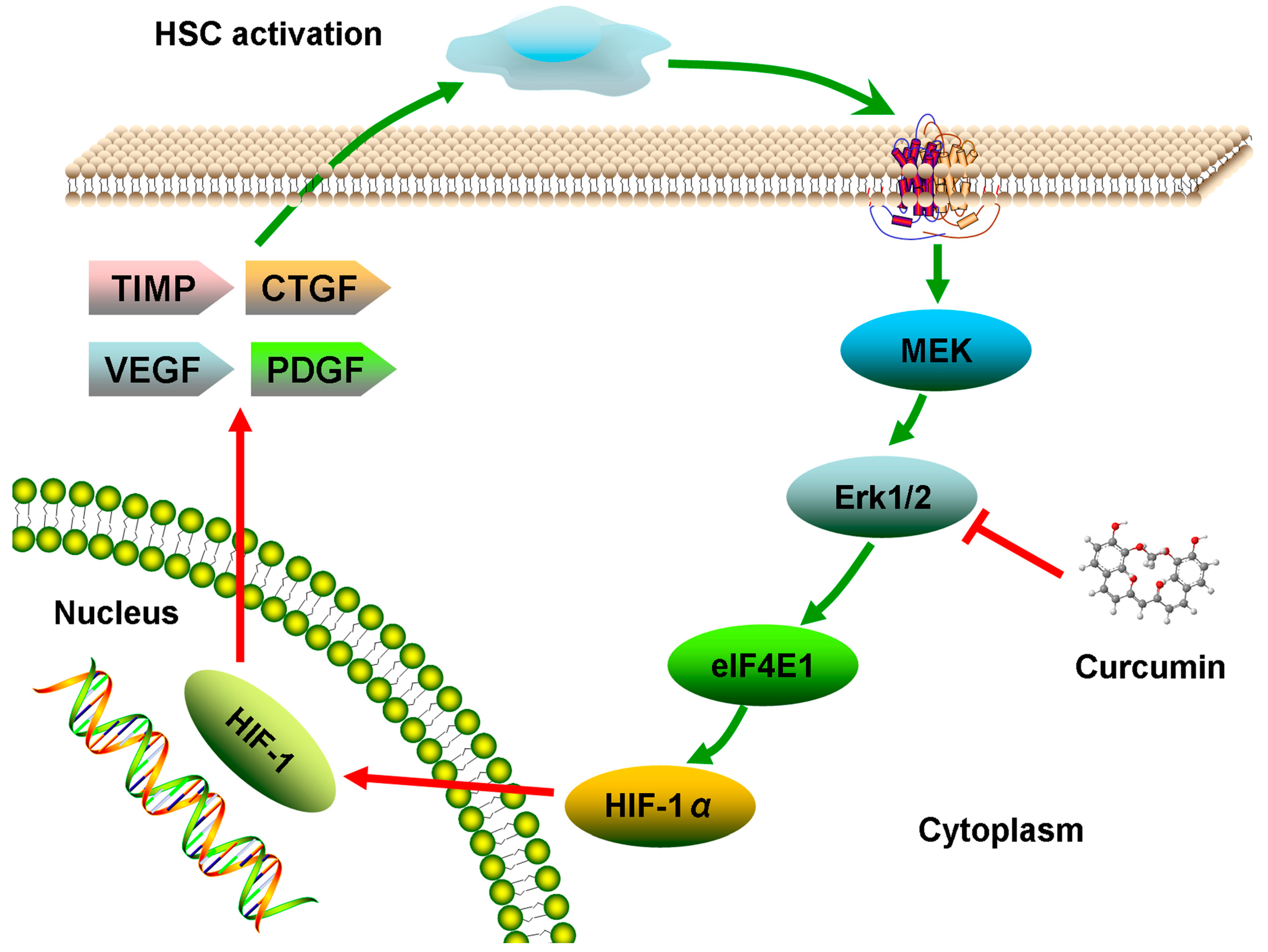
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemical and Reagents
3.2. Animals
3.3. Treatment Regimens/Experiment Protocols
3.4. Measurement of Serum Biomarkers ALT, AST, ALP, ALB and TP
3.5. Histological Assessment
3.6. RT-PCR Analysis for Collagen III and α-SMA
| Gene | Sense Primer (5'–3') | Anti-Sense Primer (5'–3') | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | ACAGCAACAGGGTGGTGGAC | TTTGAGGGTGCAGCGAACTT | 150 |
| α-SMA | CTGCTTCTCTTCTTCCCT | GCCAGCTTCGTCATACTCC | 410 |
| ColIII | GTCCACAGCCTTCTACAC | CATCAAAGCCTCTGTGTC | 540 |
3.7. Western Blot Analysis for ERK and HIF-1α
3.8. Effect of Curcumin on HSC-T6 in Vitro
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Abbreviations
| α-SMA | alpha-smooth muscle actin |
| CUR | curcumin |
| CHM | Chinese herbal medicines |
| Col III | collagen III |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EB | ethidium bromide |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| HIF | hypoxia inducible factor |
| HSC | hepatic stellate cell |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernandez-Gea, V.; Friedman, S.L. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Luan, Y.; Zou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhou, C.; Fu, J.; Gao, B.; et al. Pathological functions of interleukin-22 in chronic liver inflammation and fibrosis with hepatitis B virus infection by promoting T helper 17 cell recruitment. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Iwaisako, K.; Brenner, D.A.; Kisseleva, T. What’s new in liver fibrosis? The origin of myofibroblasts in liver fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A. Hepatic stellate cells and the reversal of fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, S84–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Szabo, G. Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factors: Diverse roles in liver diseases. Hepatology 2012, 55, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, E.; Cannito, S.; Zamara, E.; Valfre di Bonzo, L.; Caligiuri, A.; Cravanzola, C.; Compagnone, A.; Colombatto, S.; Marra, F.; Pinzani, M.; et al. Proangiogenic cytokines as hypoxia-dependent factors stimulating migration of human hepatic stellate cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Schelter, F.; Halbgewachs, B.; Baumler, P.; Neu, C.; Gorlach, A.; Schrotzlmair, F.; Kruger, A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1-induced scattered liver metastasis is mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Unwith, S.; Zhao, H.; Hennah, L.; Ma, D. The potential role of HIF on tumour progression and dissemination. Int. J. Cancer 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Guan, F.; Xiao, Y.; Deng, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Shi, C. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and MAPK co-regulate activation of hepatic stellate cells upon hypoxia stimulation. PLoS One 2013, 8, e74051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, K.M.; Hayat, S.; Chau, N.M.; Cook, S.; Pouyssegur, J.; Ahmed, A.; Perusinghe, N.; le Floch, R.; Yang, J.; Ashcroft, M. Selective inhibition of MEK1/2 reveals a differential requirement for ERK1/2 signalling in the regulation of HIF-1 in response to hypoxia and IGF-1. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3920–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.T.; Yao, Q.Y.; Xu, B.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhou, C.H.; Zhang, S.C. Protective effects of curcumin against hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride: Modulation of high-mobility group box 1, Toll-like receptor 4 and 2 expression. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3343–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.Y.; Xu, B.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Liu, H.C.; Zhang, S.C.; Tu, C.T. Inhibition by curcumin of multiple sites of the transforming growth factor-beta1 signalling pathway ameliorates the progression of liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, X.; Wang, J.; Tu, C. Curcumin ameliorates intrahepatic angiogenesis and capillarization of the sinusoids in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver fibrosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 222, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Kong, D.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, S. Curcumin attenuates angiogenesis in liver fibrosis and inhibits angiogenic properties of hepatic stellate cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 1392–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Chen, A. Activation of PPARgamma is required for curcumin to induce apoptosis and to inhibit the expression of extracellular matrix genes in hepatic stellate cells in vitro. Biochem. J. 2004, 384, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, N.L.; Fu, Q.; Shi, H.; Cai, C.H.; Wan, J.; Xu, S.P.; Wu, B.Y. Oxymatrine liposome attenuates hepatic fibrosis via targeting hepatic stellate cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 4199–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, J.P.; Liu, F.T.; Zhou, B.; Xie, W.F.; Guo, C. Antifibrotic effects of matrine on in vitro and in vivo models of liver fibrosis in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2001, 22, 183–186. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, M.F.; Lian, L.H.; Piao, D.M.; Nan, J.X. Tetrandrine stimulates the apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells and ameliorates development of fibrosis in a thioacetamide rat model. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhilarasan, D.; Karthikeyan, S.; Vivekanandan, P. Ameliorative effect of silibinin against N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xu, L.; Liang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Duan, X. Puerarin mediates hepatoprotection against CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis rats through attenuation of inflammation response and amelioration of metabolic function. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 52, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.C.; Lu, I.W.; Chung, C.F.; Wu, H.Y.; Liu, Y.T. Antiproliferative mechanisms of quercetin in rat activated hepatic stellate cells. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Yan, X.; Wang, Q.; Tao, Y.; Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Liu, P.; Liu, C. Salvianolic Acid B Attenuates Rat Hepatic Fibrosis via Downregulating Angiotensin II Signaling. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 160726. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lv, Z.; Xu, Q.; Pan, Q.; Lu, L. Paeoniflorin regulates macrophage activation in dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.L.; Viswanathan, P.; Anuradha, C.V. Taurine enhances the metabolism and detoxification of ethanol and prevents hepatic fibrosis in rats treated with iron and alcohol. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 27, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, R.; Munday, M.R.; York, M.J.; Clarke, C.J.; Dare, T.; Turton, J.A. Comprehensive characterization of serum clinical chemistry parameters and the identification of urinary superoxide dismutase in a carbon tetrachloride-induced model of hepatic fibrosis in the female Hanover Wistar rat. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2007, 88, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, B.; Nie, F.; Jiang, H. Dietary supplementation of blueberry juice enhances hepatic expression of metallothionein and attenuates liver fibrosis in rats. PLoS One 2013, 8, e58659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Noh, S.M.; Kang, D.Y.; Lee, B.S. Inhibitory effects of rapamycin on the different stages of hepatic fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7452–7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozova, S.; Elpek, G.O. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression in experimental cirrhosis: Correlation with vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis. APMIS 2007, 115, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.; Goehring, A.S.; Kapiloff, M.S.; Langeberg, L.K.; Scott, J.D. mAKAP compartmentalizes oxygen-dependent control of HIF-1alpha. Sci. Signal. 2008, 1, ra18. [Google Scholar]
- Copple, B.L.; Kaska, S.; Wentling, C. Hypoxia-inducible factor activation in myeloid cells contributes to the development of liver fibrosis in cholestatic mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweppe, R.E.; Cheung, T.H.; Ahn, N.G. Global gene expression analysis of ERK5 and ERK1/2 signaling reveals a role for HIF-1 in ERK5-mediated responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 20993–21003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, T.M.; Watkins, P.B. The application of metabonomics to predict drug-induced liver injury. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 88, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; McLeod, H.L.; Weinshilboum, R.M. Genomics and Drug Response. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B. Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: Theory, methodology and application. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wu, L.J.; Zhang, X.G.; Li, Y.D.; Wang, Y.Y. Understanding ZHENG in traditional Chinese medicine in the context of neuro-endocrine-immune network. IET Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.R.; Fang, B.W.; Lou, S.J. Effects of Haobie Yangyin Ruanjian Decoction on hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the curcumin are availablefrom the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, R.; Li, R.; Gong, M.; Luo, S.; et al. Curcumin Protects against CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats by Inhibiting HIF-1α Through an ERK-Dependent Pathway. Molecules 2014, 19, 18767-18780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191118767
Zhao Y, Ma X, Wang J, He X, Hu Y, Zhang P, Wang R, Li R, Gong M, Luo S, et al. Curcumin Protects against CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats by Inhibiting HIF-1α Through an ERK-Dependent Pathway. Molecules. 2014; 19(11):18767-18780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191118767
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yanling, Xiao Ma, Jiabo Wang, Xuan He, Yan Hu, Ping Zhang, Ruilin Wang, Ruisheng Li, Man Gong, Shengqiang Luo, and et al. 2014. "Curcumin Protects against CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats by Inhibiting HIF-1α Through an ERK-Dependent Pathway" Molecules 19, no. 11: 18767-18780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191118767
APA StyleZhao, Y., Ma, X., Wang, J., He, X., Hu, Y., Zhang, P., Wang, R., Li, R., Gong, M., Luo, S., & Xiao, X. (2014). Curcumin Protects against CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats by Inhibiting HIF-1α Through an ERK-Dependent Pathway. Molecules, 19(11), 18767-18780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191118767




