4-Amino-substituted Benzenesulfonamides as Inhibitors of Human Carbonic Anhydrases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
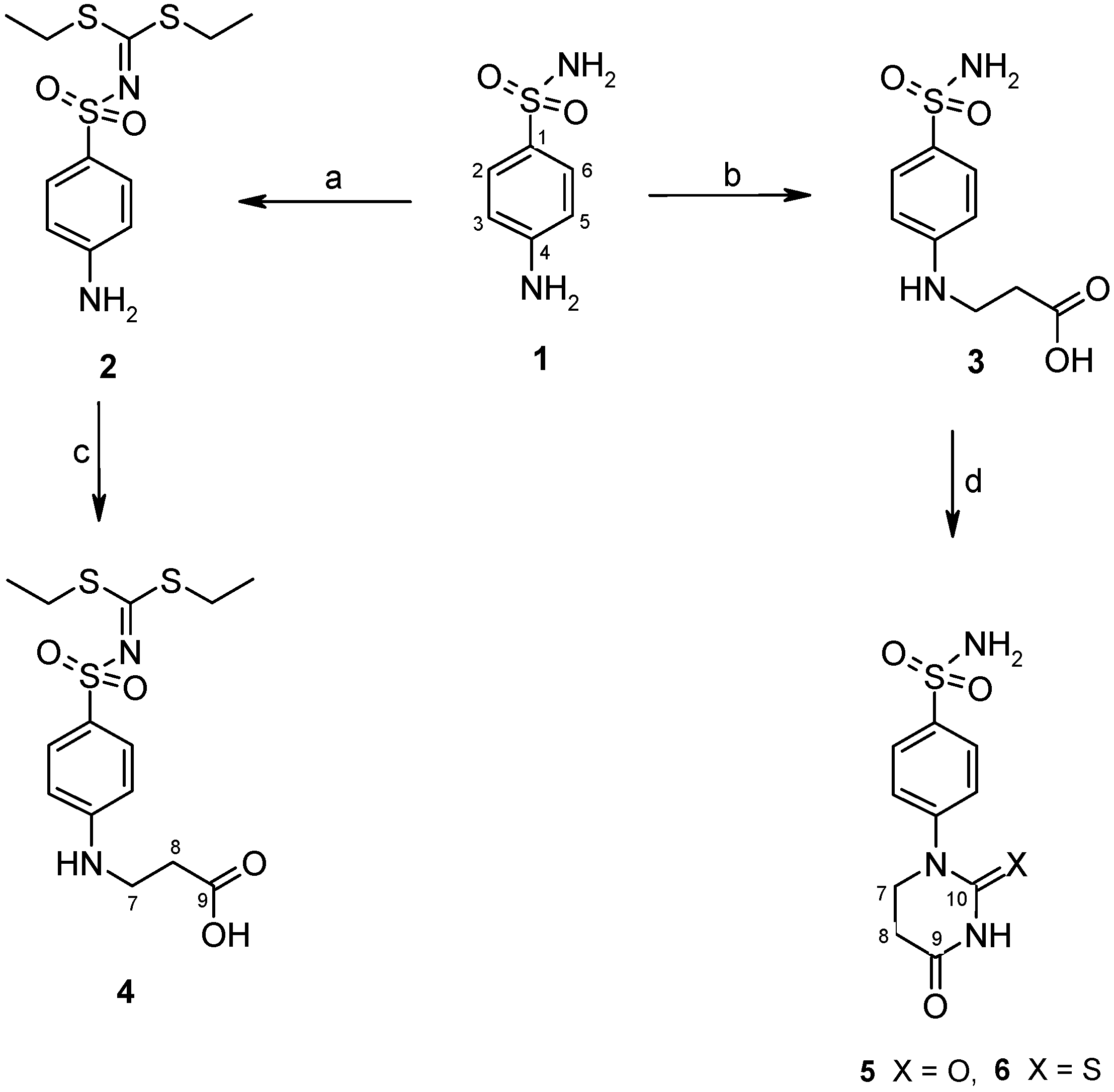
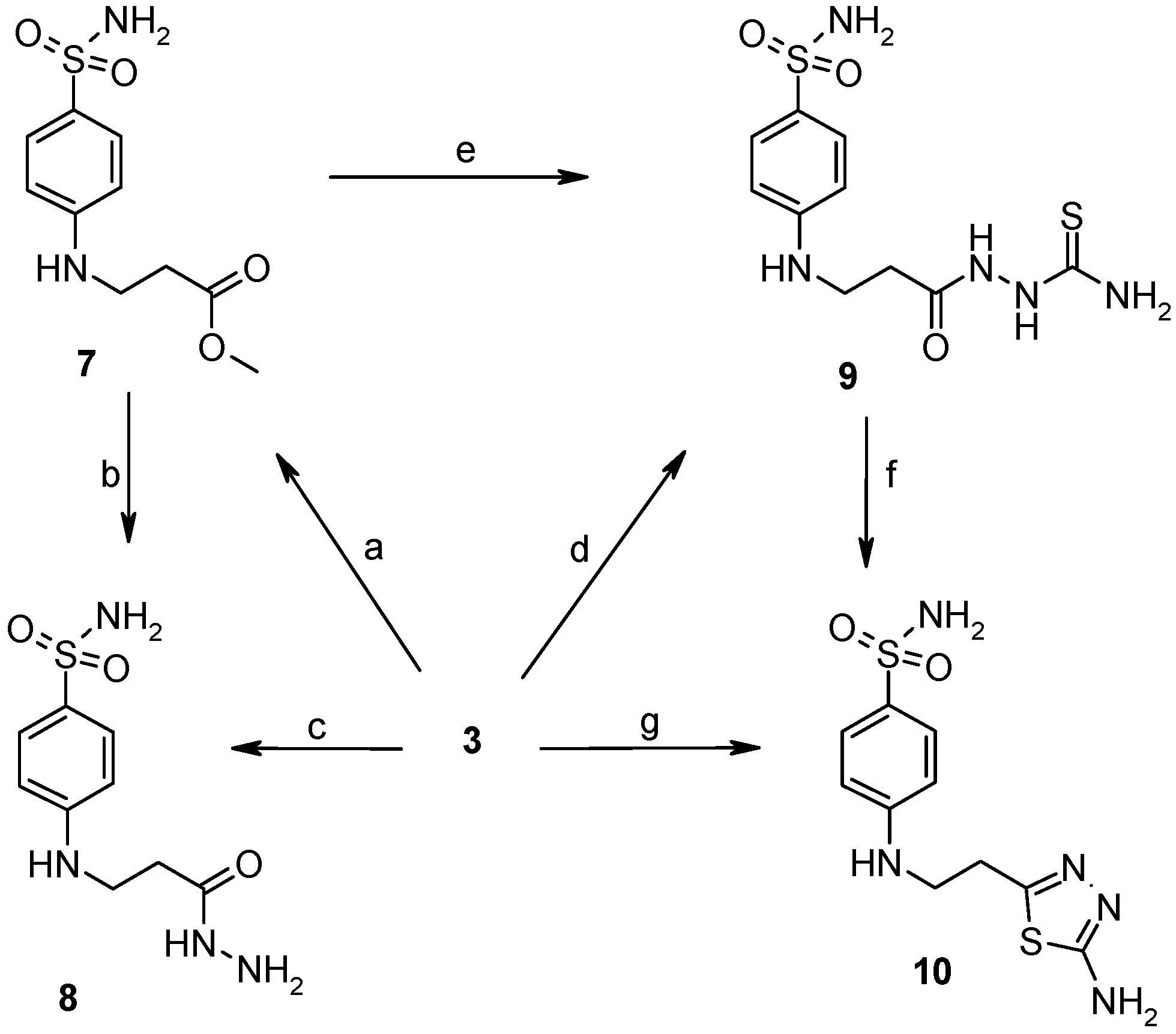
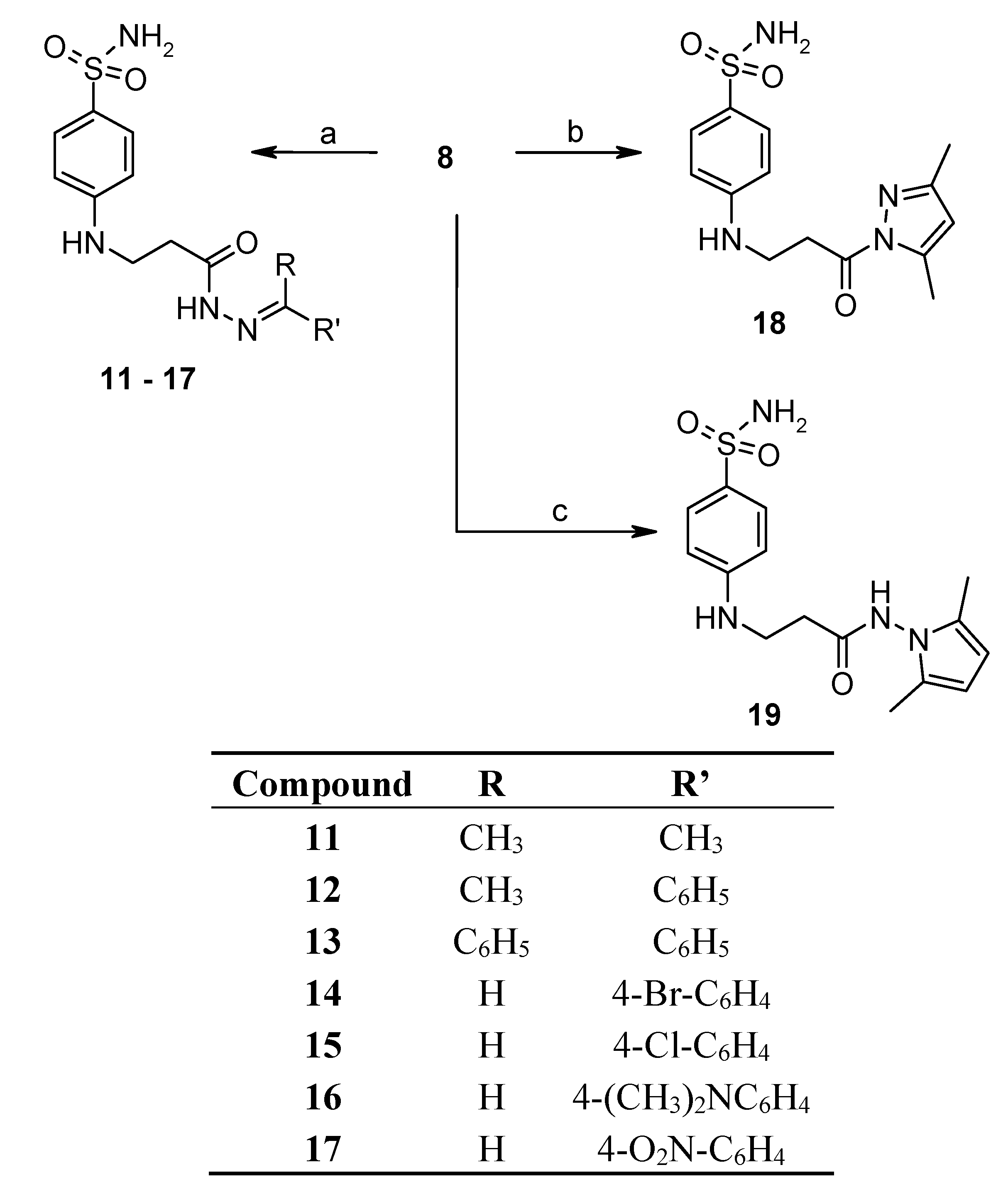
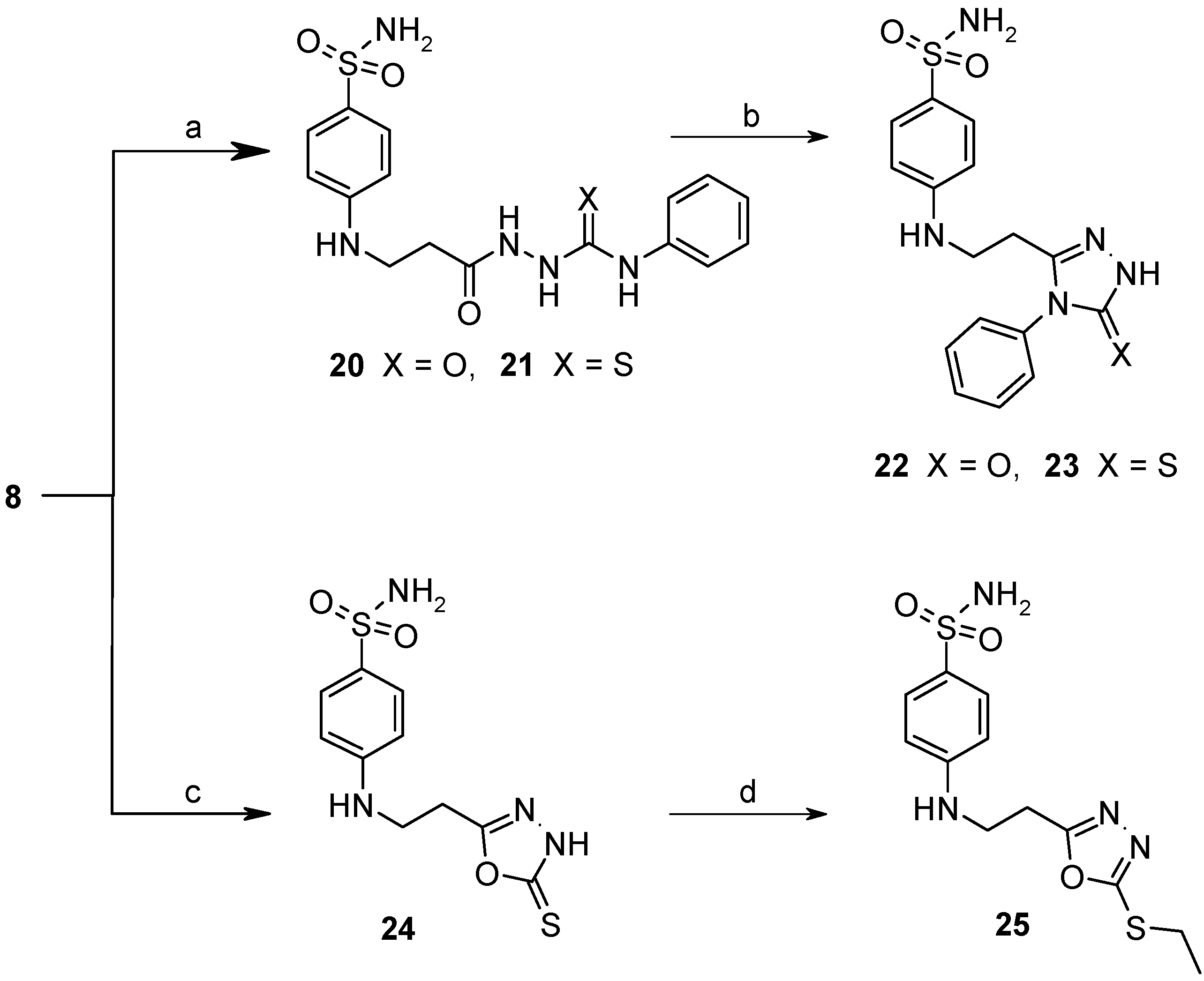
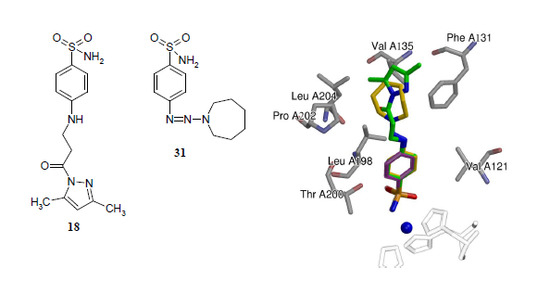
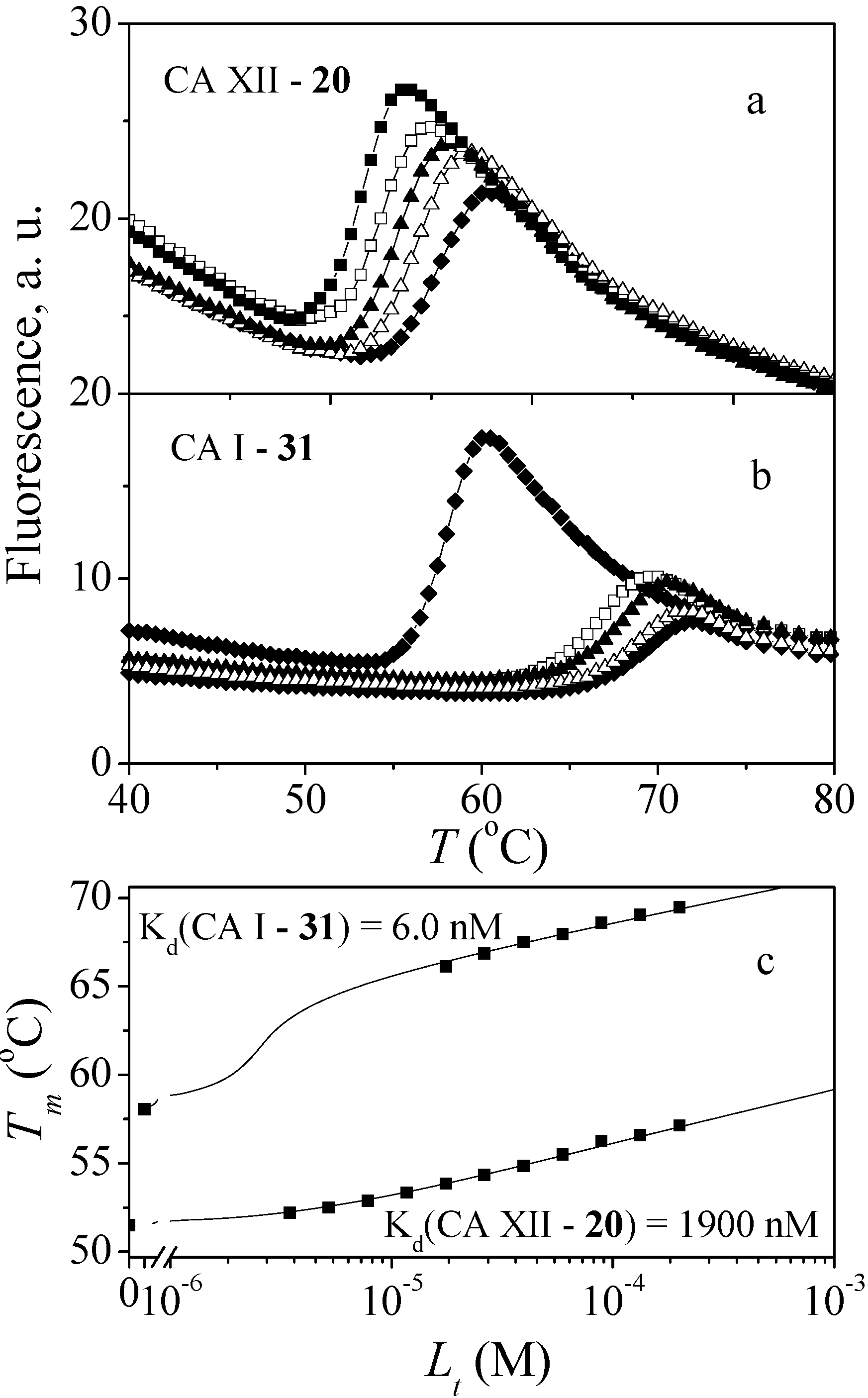
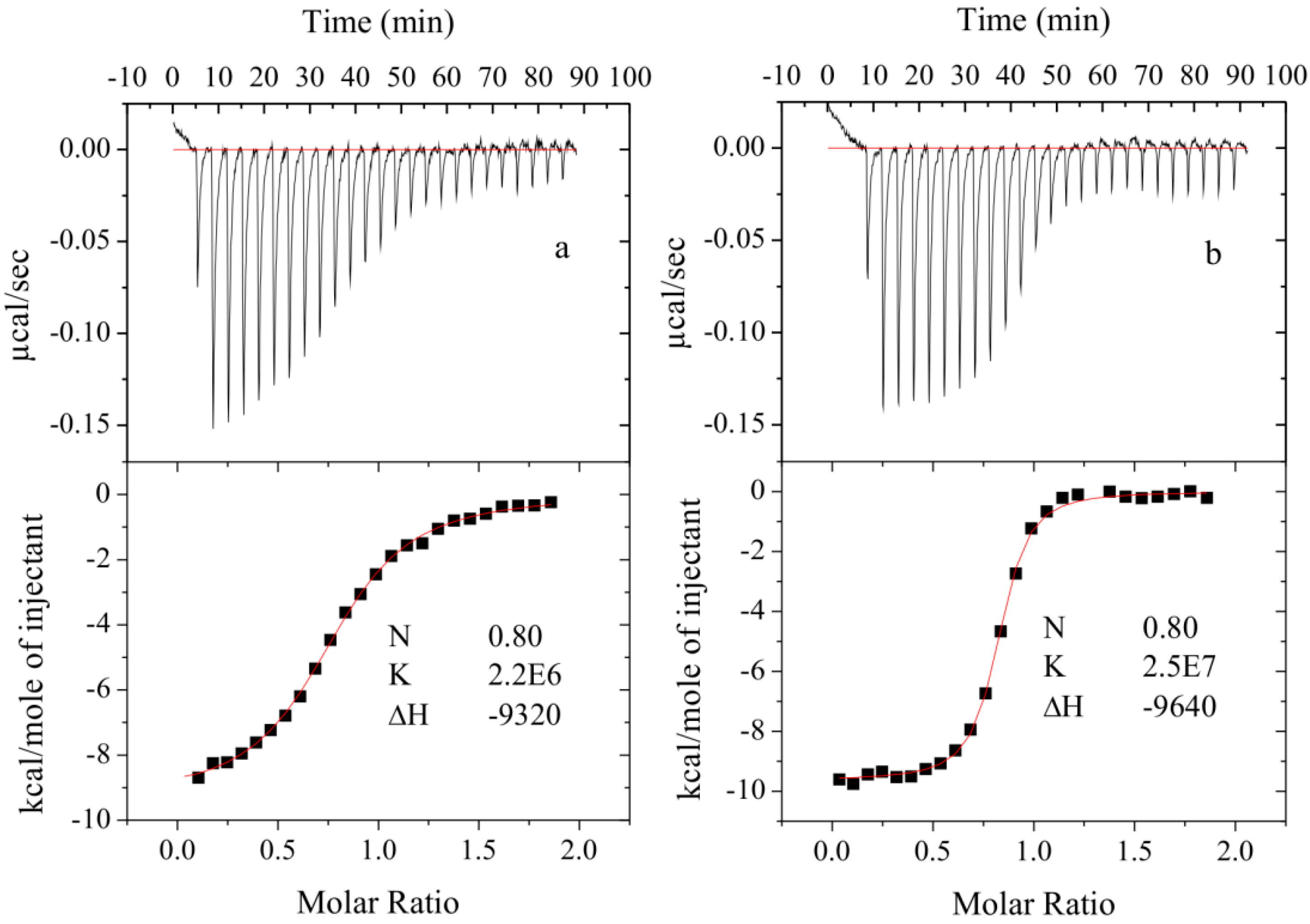
2.2. Binding Studies
| CA I | CA II | CA VI | CA VII | CA XII | CA XIII | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -NH2 | 100 | 13.0 | 56.0 | 50.0 | 67.0 | 100 |
| 3 | 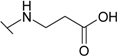 | 40 | 12.5 | 62.5 | 22.2 | 9.5 | 33.3 |
| 4 | 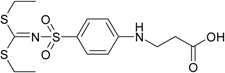 a a | >200 | 40 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 5 | 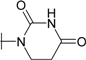 | 3.85 | 0.833 | 12.5 | 1.54 | 5.56 | 8.33 |
| 6 | 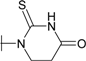 | 1.11 | 0.667 | 8.3 | 1.61 | 5.56 | 2.86 |
| 7 | 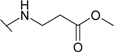 | 35.7 | 9.10 | 71.4 | 35.7 | 33.3 | 58.8 |
| 8 | 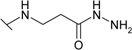 | 55.6 | 10.5 | 62.5 | 28.6 | 33.3 | 76.9 |
| 9 | 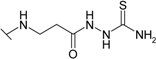 | 58.8 | 10.0 | 50.0 | 28.6 | 33.3 | 76.9 |
| 10 | 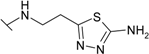 | 170 | 20.0 | 140 | 100 | 130 | 83.0 |
| 11 | 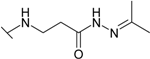 | 45.5 | 7.14 | 71.4 | 28.6 | 33.3 | 50.0 |
| 12 | 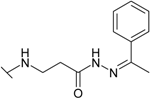 | 15.4 | 1.85 | 25.0 | 12.5 | 33.3 | 5.56 |
| 13 | 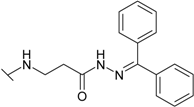 | 11.5 | 1.43 | 25.0 | 16.7 | 50.0 | 4.35 |
| 14 | 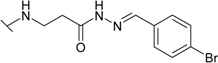 | 12.5 | 1.82 | 7.10 | 5.88 | 31.3 | 7.14 |
| 15 | 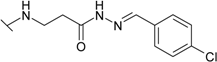 | 12.5 | 2.00 | 6.7 | 12.5 | 33.3 | 8.33 |
| 16 | 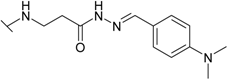 | 37.0 | 8.33 | 50.0 | 25.0 | 33.3 | 55.6 |
| 17 | 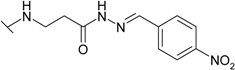 | 20.0 | 3.60 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 67.0 | 50.0 |
| 18 | 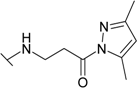 | 1.67 (0.750) | 0.667 (0.454) | 27.0 (ND) | 3.33 (0.90) | 14.3 (ND) | 4.00 (1.00) |
| 19 | 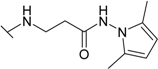 | 16.7 | 2.0 | 25.0 | 11.1 | 28.6 | 6.25 |
| 20 | 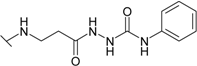 | 28.6 | 4.0 | 7.1 | 12.5 | 1.85 | 18.5 |
| 21 |  | 9.09 | 4.0 | 8.3 | 5.56 | 5.56 | 9.09 |
| 22 | 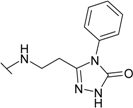 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 23 | 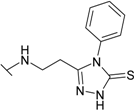 | 10.0 | 2.0 | 11.1 | 6.67 | 6.67 | 10.0 |
| 24 | 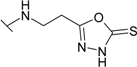 | 12.5 | 4.55 | 33.3 | 4.55 | 5.88 | 26.3 |
| 25 | 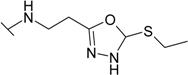 | 5.88 | 1.18 | 28.6 | 5.60 | 10.5 | 3.33 |
| 26 | 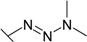 | 0.100 | 0.181 | 13.3 | 0.769 | 2.70 | 0.40 |
| 27 | 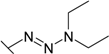 | 0.0133 | 0.0714 | 13.3 | 0.200 | 0.588 | 0.100 |
| 28 | 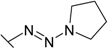 | 0.0333 | 0.133 | 13.3 | 0.454 | 1.81 | 0.167 |
| 29 | 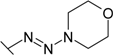 | 0.0290 | 0.100 | 11.8 | 0.400 | 3.30 | 0.222 |
| 30 |  | 0.00667 | 0.0625 | 10.0 | 0.120 | 0.770 | 0.0667 |
| 31 | 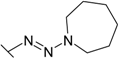 | 0.0060 (0.022) | 0.0435 (0.040) | 14.3 (ND) | 0.125 (0.192) | 0.670 (0.22) | 0.0222 (0.078) |
| 32 | 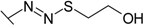 | 0.0333 | 0.0667 | 3.20 | 0.286 | 2.00 | 1.40 |
| 33 | 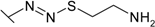 | 0.500 | 0.278 | 8.30 | 1.00 | 6.25 | 2.86 |
| 34 |  b b | 0.200 b | 0.130 b | 4.0 | 0.170 b | 2.50 b | 1.40 b |
| BSA | 7.14 | 1.79 | 14.0 | 6.67 | 12.50 | 10.0 | |
| AZM c | 1.40 | 0.017 | 0.180 | 0.017 | 0.133 | 0.050 |
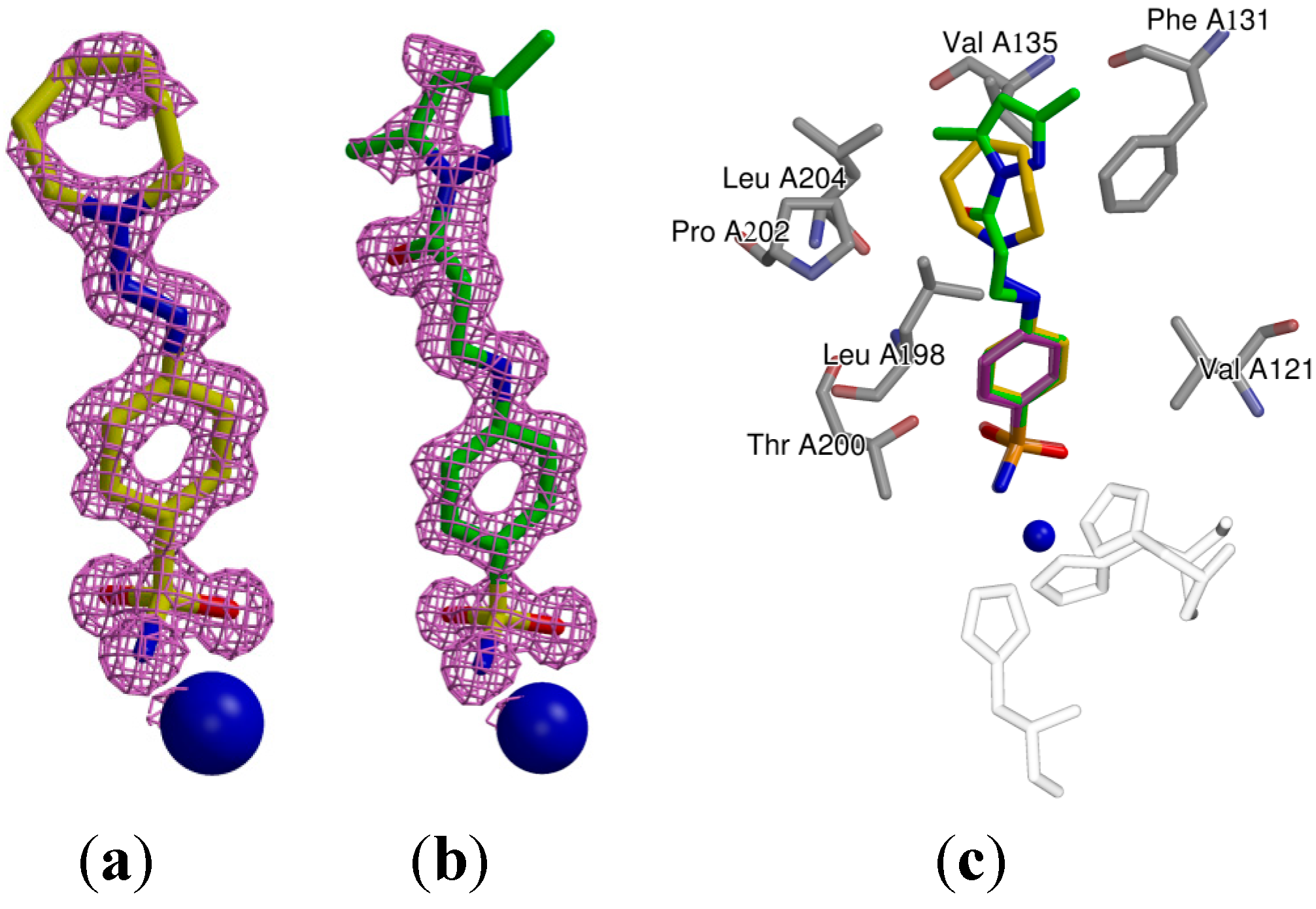
2.3. Crystallography
| Protein-Compound | CA II-31 | CA II-18 |
|---|---|---|
| PDB ID | 4Q6D | 4Q6E |
| Spacegroup | P21 | P21 |
| Unit cell, Å | a = 42.13, b = 41.20, c = 71.81 α = γ = 90°, β = 104.19° | a = 42.24, b = 41.24, c = 72.19 α = γ = 90°, β = 104.30° |
| Number of chains | 1 | 1 |
| Resolution, Å | 39.73–1.12 | 39.88–1.12 |
| Nref (unique) | 87368 | 85569 |
| Rmerge, (outer shell) | 0.076 (0.166) | 0.063 (0.193) |
| I/σ (outer shell) | 13.6 (7.0) | 14.4 (6.4) |
| Multiplicity (outer shell) | 6.5 (5.1) | 6.5 (5.2) |
| Completeness (%) (outer shell) | 95.8 (80.2) | 92.8 (66.7) |
| Number of atoms | 2583 | 2552 |
| Number of solvent molecules | 299 | 321 |
| Rcryst (Rfree) | 0.128 (0.154) | 0.130 (0.158) |
| RMS bonds/angles | 0.025 (2.605) | 0.024 (2.362) |
| Average B-factors (Å2) | 16.370 | 14.630 |
| main chain: | 13.3 | 11.7 |
| side chains: | 17.4 | 15.3 |
| solvent: | 28.6 | 25.2 |
| inhibitor: | 17.4 | 19.0 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
3.2. Chemistry
3.2.1. General Procedure for Synthesis of Hydrazones 11–13
3.2.2. General Procedure for Synthesis of Hydrazones 14–17
3.3. Protein Preparation
3.4. Determination of Compound Binding
3.4.1. Fluorescent Thermal Shift Assay
3.4.2. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
3.5. Crystallography
3.5.1. Crystallization
3.5.2. Data Collection and Structure Determination
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bentley, R. Different roads to discovery; prontosil (hence sulfa drugs) and penicillin (hence β-lactams). J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, R.; Zareef, M.; Ahmed, S.; Zaidi, J.H.; Arfan, M.; Shafique, M.; Al-Masoudi, N.A. Synthesis, antimicrobial and anti-hiv activity of some novel benzenesulfonamides bearing 2,5-disubstituted-1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2006, 53, 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Saingar, S.; Kumar, R.; Joshi, Y. Synthesis and biological activity of novel 1H-1,4-diazepines containing benzene sulfonylpiperazine moiety. Med. Chem. Res. 2011, 20, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, K.J.; Austin, R.S.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fung, P.; Wang, P.W.; Guttman, D.S.; Desveaux, D. Forward chemical genetic screens in arabidopsisidentify genes that influence sensitivity to the phytotoxic compound sulfamethoxazole. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.S.; Rivera, G.; Ashfaq, M. Recent advances in medicinal chemistry of sulfonamides. Rational design as anti-tumoral, anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Inhibition of bacterial carbonic anhydrases and zinc proteases: From orphan targets to innovative new antibiotic drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulf, N.R.; Matuszewski, K.A. Sulfonamide cross-reactivity: Is there evidence to support broad cross-allergenicity? Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2013, 70, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, F.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Sulfonamides: A patent review (2008–2012). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, E.; Carta, F.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Antiglaucoma carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases—An overview. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3467–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, M.; Boone, C.D.; Kondeti, B.; McKenna, R. Structural annotation of human carbonic anhydrases. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2013, 28, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, M.; Kondeti, B.; McKenna, R. Insights towards sulfonamide drug specificity in α-carbonic anhydrases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.I.; Shajee, B.; Waheed, A.; Ahmad, F.; Sly, W.S. Structure, function and applications of carbonic anhydrase isozymes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 1570–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterio, V.; Fiore, A.D.; D’Ambrosio, K.; Supuran, C.T.; Simone, G.D. Multiple binding modes of inhibitors to carbonic anhydrases: How to design specific drugs targeting 15 different isoforms? Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4421–4468. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, V.M.; Kaufman, G.K.; Urbach, A.R.; Gitlin, I.; Gudiksen, K.L.; Weibel, D.B.; Whitesides, G.M. Carbonic anhydrase as a model for biophysical and physical-organic studies of proteins and protein-ligand binding. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 946–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Scozzafava, A.; Casini, A. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Med. Res. Rev. 2003, 23, 146–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, K.K.; Kalyan, K.; Verma, S.M.; Tanç, M.; Purper, G.; Calafato, G.; Carta, F.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Synthesis and inhibition of the human carbonic anhydrase isoforms I, II, IX and XII with benzene sulfonamides incorporating 4- and 3-nitrophthalimide moieties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güzel-Akdemir, O.; Biswas, S.; Lastra, K.; McKenna, R.; Supuran, C.T. Structural study of the location of the phenyl tail of benzene sulfonamides and the effect on human carbonic anhydrase inhibition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6674–6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congiu, C.; Onnis, V.; Balboni, G.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis and carbonic anhydrase I, II, IX and XII inhibition studies of 4-N,N-disubstituted sulfanilamides incorporating 4,4,4-trifluoro-3-oxo-but-1-enyl, phenacylthiourea and imidazol-2(3H)-one/thione moieties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1776–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchenal, J.H.; Dagg, M.K.; Beyer, M.; Stock, C.C. Chemotherapy of leukemia.VII. Effect of substituted triazenes on transplanted mouse leukemia. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1956, 398, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spassova, M.K.; Golovinsky, E.V. Pharmacobiochemistry of arylalkyltriazenes and their application in cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 1985, 27, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalezari, I.; Afghahi, F. Synthesis and evaluation of antitumor activity of 1-[N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)sulfamoylphenyl]-3,3-dialkyltriazenes. J. Pharm. Sci. 1975, 64, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, H.A.; Teimouri, A.; Shiasi, R.; Chermahini, A.N. DFT, ab initio and FTIR studies of the structure of sulfonamide triazenes. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2008, 5, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Ueda, H.; Ogata, K.; Kohra, S. N-bis(methylthio)methylene derivatives. 5. New synthesis of 2-aminoindolizine and related compounds via a formal [3 + 3] cycloaddition reaction using n-bis(ethoxycarbonylmethylthio)methylenephenylsulfonamides. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1992, 29, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurd, C.D.; Hayao, S. Reaction of propiolactone with aniline derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 5889–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusevičius, K.; Jonuškienė, I.; Mickevičius, V. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of N-(4-chlorophenyl)-β-alanine derivatives with an azole moiety. Monatch. Chem. 2013, 144, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaickelionienė, R.; Mickevičius, V.; Mikulskienė, G. Synthesis and characterization of 4-substituted 1-(4-halogenophenyl)pyrrolidin-2-ones with azole and azine moieties. Heterocycles 2013, 87, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikovaitė, V.; Beresnevičius, Z.J. Synthesis of azoles based on N,N'-bis(hydrazinocarbonyl-ethyl)-1,4-phenylenediamine. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2009, 45, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumosienė, I.; Beresnevičius, Z.J. Synthesis of azoles from 3,3'-[(4-alkoxyphenyl)imino]bis(propanoic acid hydrazides). Monatsh. Chem. 2009, 140, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumosienė, I.; Jonuškienė, I.; Kantminienė, K.; Beresnevičius, Z.J. The synthesis of azole derivatives from 3-[(4-methylphenyl)amino]propanehydrazide and its N'-phenylcarbamoyl derivatives, and their antibacterial activity. Monatsh. Chem. 2012, 143, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumosienė, I.; Jonuškienė, I.; Kantminienė, K.; Beresnevičius, Z.J. The synthesis of S-substituted derivatives of 3-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)amino]ethyl]-4-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5-thiones and their antioxidative activity. Monatsh. Chem. 2014, 145, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdag, M.; Ferraroni, M.; Nuti, E.; Vullo, D.; Rossello, A.; Carta, F.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Combining the tail and the ring approaches for obtaining potent and isoform-selective carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Solution and X-ray crystallographic studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimori, I.; Minakuchi, T.; Onishi, S.; Vullo, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. DNA cloning, characterization, and inhibition studies of the human secretory isoform VI, a new target for sulfonamide and sulfamate inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Sly, W.S. Purification and characterization of human salivary carbonic anhydrase. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Čapkauskaitė, E.; Zubrienė, A.; Baranauskienė, L.; Tamulaitienė, G.; Manakova, E.; Kairys, V.; Gražulis, S.; Tumkevičius, S.; Matulis, D. Design of [(2-pyrimidinylthio)acetyl]benzenesulfonamides as inhibitors of human carbonic anhydrases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 51, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudutienė, V.; Zubrienė, A.; Smirnov, A.; Gylytė, J.; Timm, D.; Manakova, E.; Gražulis, S.; Matulis, D. 4-Substituted-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzenesulfonamides as inhibitors of carbonic anhydrases I, II, VII, XII, and XIII. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmperman, P.; Baranauskienė, L.; Jachimovičiūtė, S.; Jachno, J.; Torresan, J.; Michailovienė, V.; Matulienė, J.; Sereikaitė, J.; Bumelis, V.; Matulis, D. A quantitative model of thermal stabilization and destabilization of proteins by ligands. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 3222–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.D.; Phillips, C.; Alex, A.; Flocco, M.; Bent, A.; Randall, A.; O’Brien, R.; Damian, L.; Jones, L.H. Thermodynamic optimisation in drug discovery: A case study using carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Chem. Med. Chem. 2009, 4, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čapkauskaitė, E.; Zubrienė, A.; Smirnov, A.; Torresan, J.; Kišonaitė, M.; Kazokaitė, J.; Gylytė, J.; Michailovienė, V.; Jogaitė, V.; Manakova, E.; et al. Benzenesulfonamides with pyrimidine moiety as inhibitors of human carbonic anhydrases I, II, VI, VII, XII, and XIII. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6937–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sūdžius, J.; Baranauskienė, L.; Golovenko, D.; Matulienė, J.; Michailovienė, V.; Torresan, J.; Jachno, J.; Sukackaitė, R.; Manakova, E.; Gražulis, S.; et al. 4-[N-(Substituted 4-pyrimidinyl)amino]benzenesulfonamides as inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase isozymes I, II, VII, and XIII. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7413–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogaitė, V.; Zubrienė, A.; Michailovienė, V.; Gylytė, J.; Morkūnaitė, V.; Matulis, D. Characterization of human carbonic anhydrase XII stability and inhibitor binding. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranauskienė, L.; Hilvo, M.; Matulienė, J.; Golovenko, D.; Manakova, E.; Dudutienė, V.; Michailovienė, V.; Torresan, J.; Jachno, J.; Parkkila, S.; et al. Inhibition and binding studies of carbonic anhydrase isozymes I, II and IX with benzimidazo[1,2-c][1,2,3]thiadiazole-7-sulphonamides. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010, 25, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W. Integration, scaling, space-group assignment and post-refinement. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, S.; Wilson, K. On the treatment of negative intensity observations. Acta Cryst. A 1978, 34, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborative Computational Project N. The ccp4 suite: Programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1994, 50, 760–763. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, P. Scaling and assessment of data quality. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2006, 62, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagin, A.A.; Teplyakov, A. Molrep: An automated program for molecular replacement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1997, 30, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshudov, G.N.; Vagin, A.A.; Dodson, E.J. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1997, 53, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagin, A.A.; Steiner, R.A.; Lebedev, A.A.; Potterton, L.; McNicholas, S.; Long, F.; Murshudov, G.N. Refmac5 dictionary: Organization of prior chemical knowledge and guidelines for its use. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraulis, P.J. Molscript: A program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1991, 24, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, E.A.; Bacon, D.J. Raster3D: Photorealistic molecular graphics. Methods Enzymol. 1997, 277, 505–524. [Google Scholar]
- Esnouf, R.M. Further additions to Molscript version 1.4, including reading and contouring of electron-density maps. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1999, 55, 938–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rutkauskas, K.; Zubrienė, A.; Tumosienė, I.; Kantminienė, K.; Kažemėkaitė, M.; Smirnov, A.; Kazokaitė, J.; Morkūnaitė, V.; Čapkauskaitė, E.; Manakova, E.; et al. 4-Amino-substituted Benzenesulfonamides as Inhibitors of Human Carbonic Anhydrases. Molecules 2014, 19, 17356-17380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117356
Rutkauskas K, Zubrienė A, Tumosienė I, Kantminienė K, Kažemėkaitė M, Smirnov A, Kazokaitė J, Morkūnaitė V, Čapkauskaitė E, Manakova E, et al. 4-Amino-substituted Benzenesulfonamides as Inhibitors of Human Carbonic Anhydrases. Molecules. 2014; 19(11):17356-17380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117356
Chicago/Turabian StyleRutkauskas, Kęstutis, Asta Zubrienė, Ingrida Tumosienė, Kristina Kantminienė, Marytė Kažemėkaitė, Alexey Smirnov, Justina Kazokaitė, Vaida Morkūnaitė, Edita Čapkauskaitė, Elena Manakova, and et al. 2014. "4-Amino-substituted Benzenesulfonamides as Inhibitors of Human Carbonic Anhydrases" Molecules 19, no. 11: 17356-17380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117356
APA StyleRutkauskas, K., Zubrienė, A., Tumosienė, I., Kantminienė, K., Kažemėkaitė, M., Smirnov, A., Kazokaitė, J., Morkūnaitė, V., Čapkauskaitė, E., Manakova, E., Gražulis, S., Beresnevičius, Z. J., & Matulis, D. (2014). 4-Amino-substituted Benzenesulfonamides as Inhibitors of Human Carbonic Anhydrases. Molecules, 19(11), 17356-17380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191117356