Magnetically Separable and Recyclable Fe3O4-Supported Ag Nanocatalysts for Reduction of Nitro Compounds and Selective Hydration of Nitriles to Amides in Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
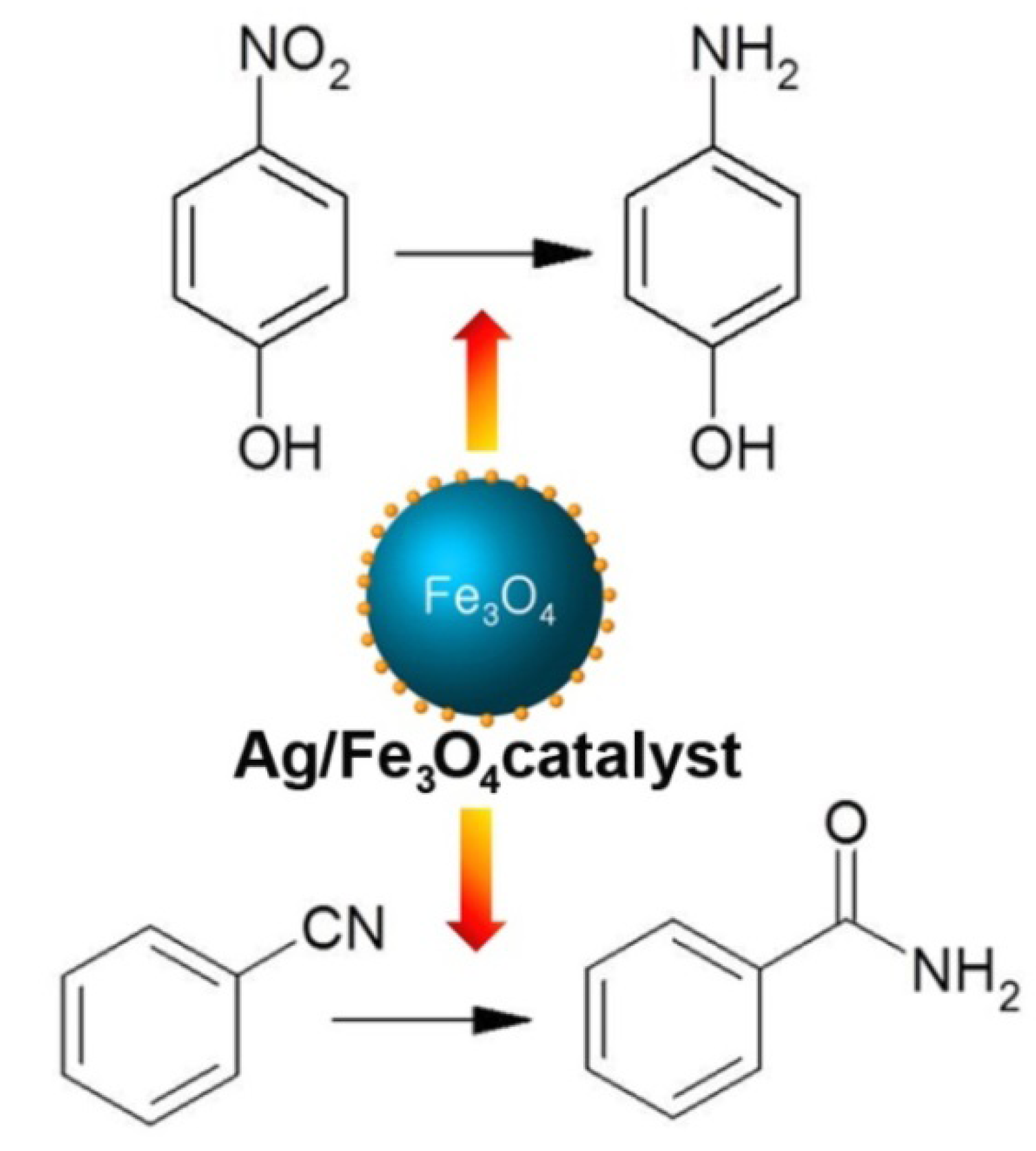
2. Results and Discussion
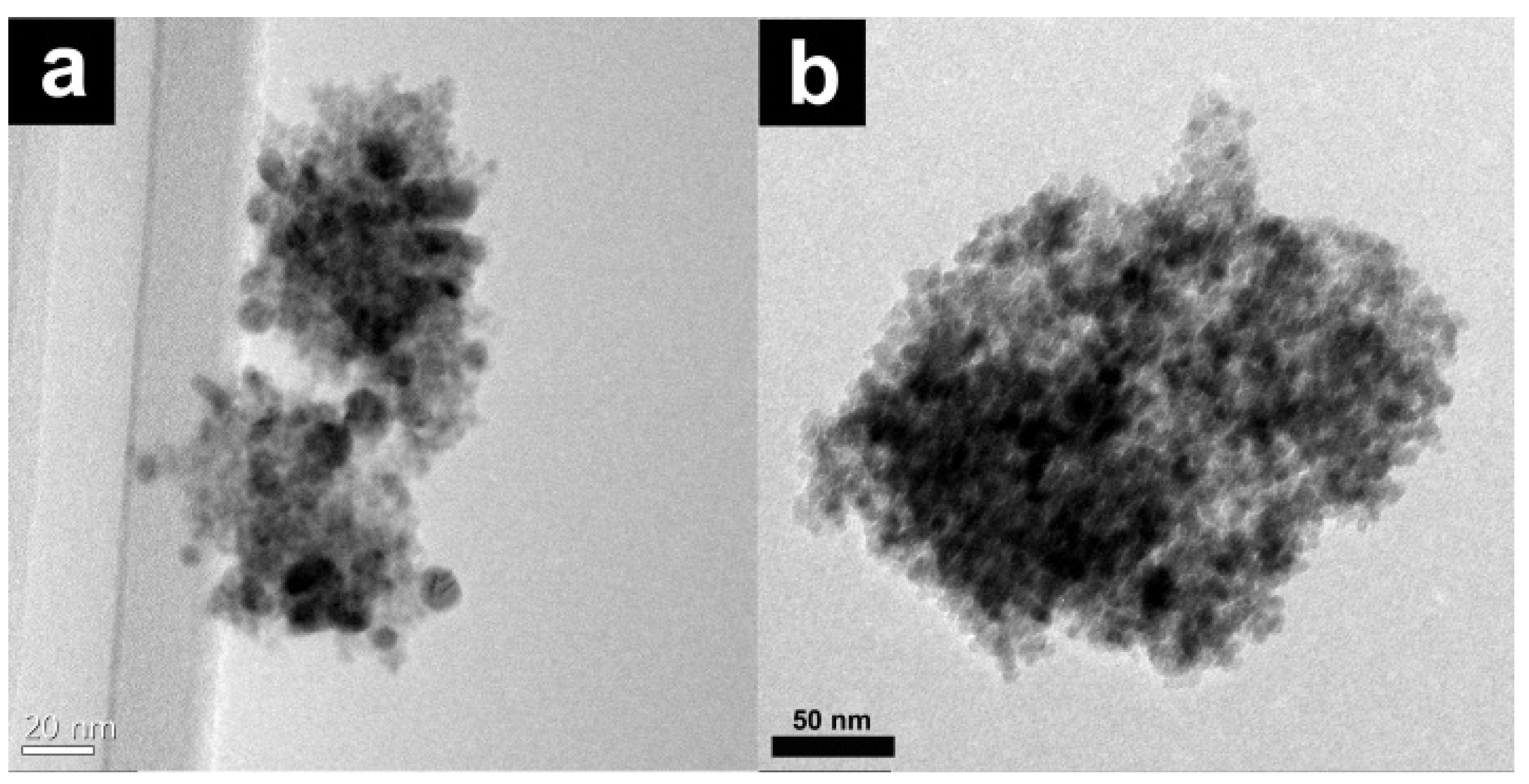
2.1. Catalyst Preparation and Characterization
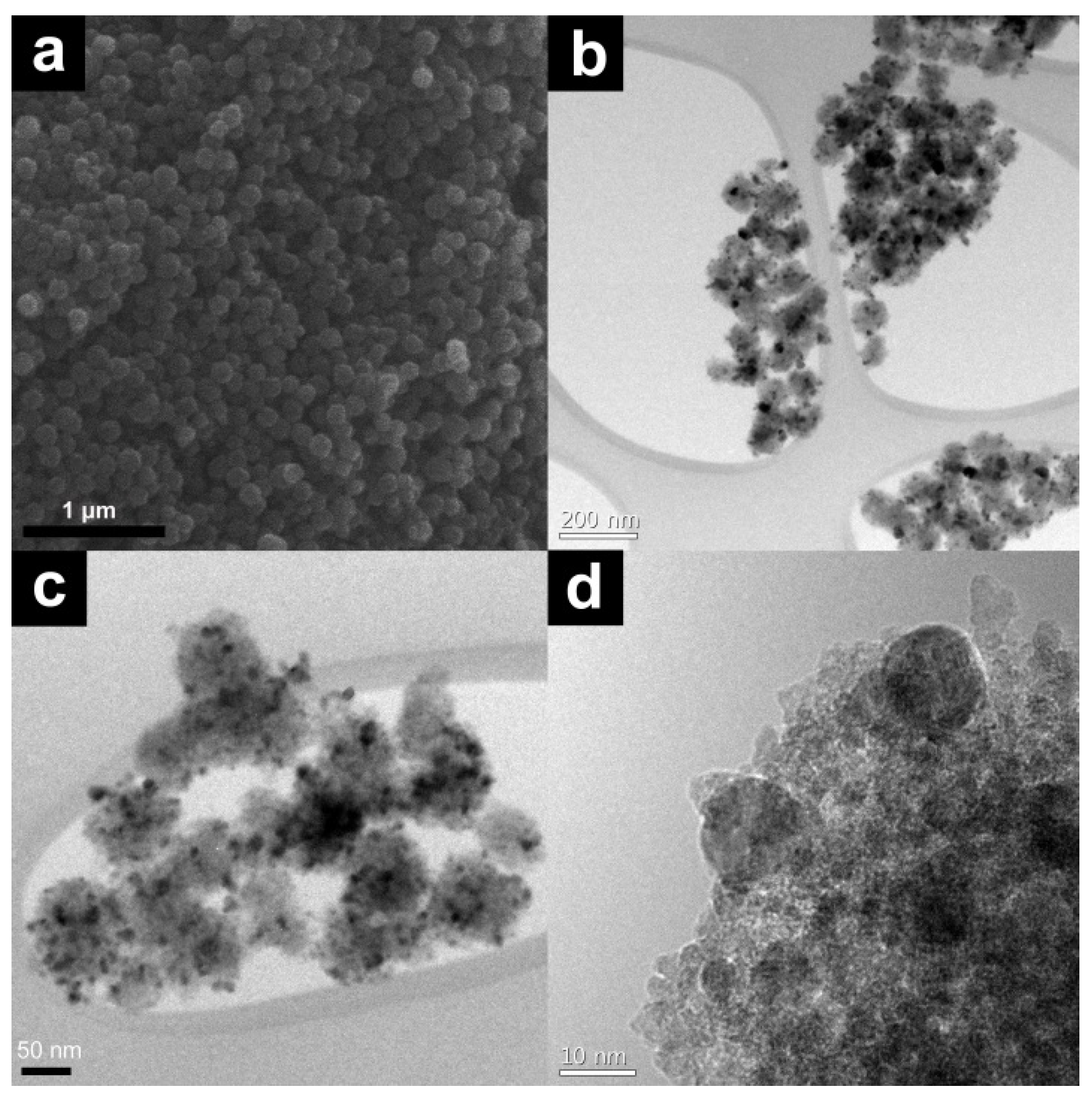
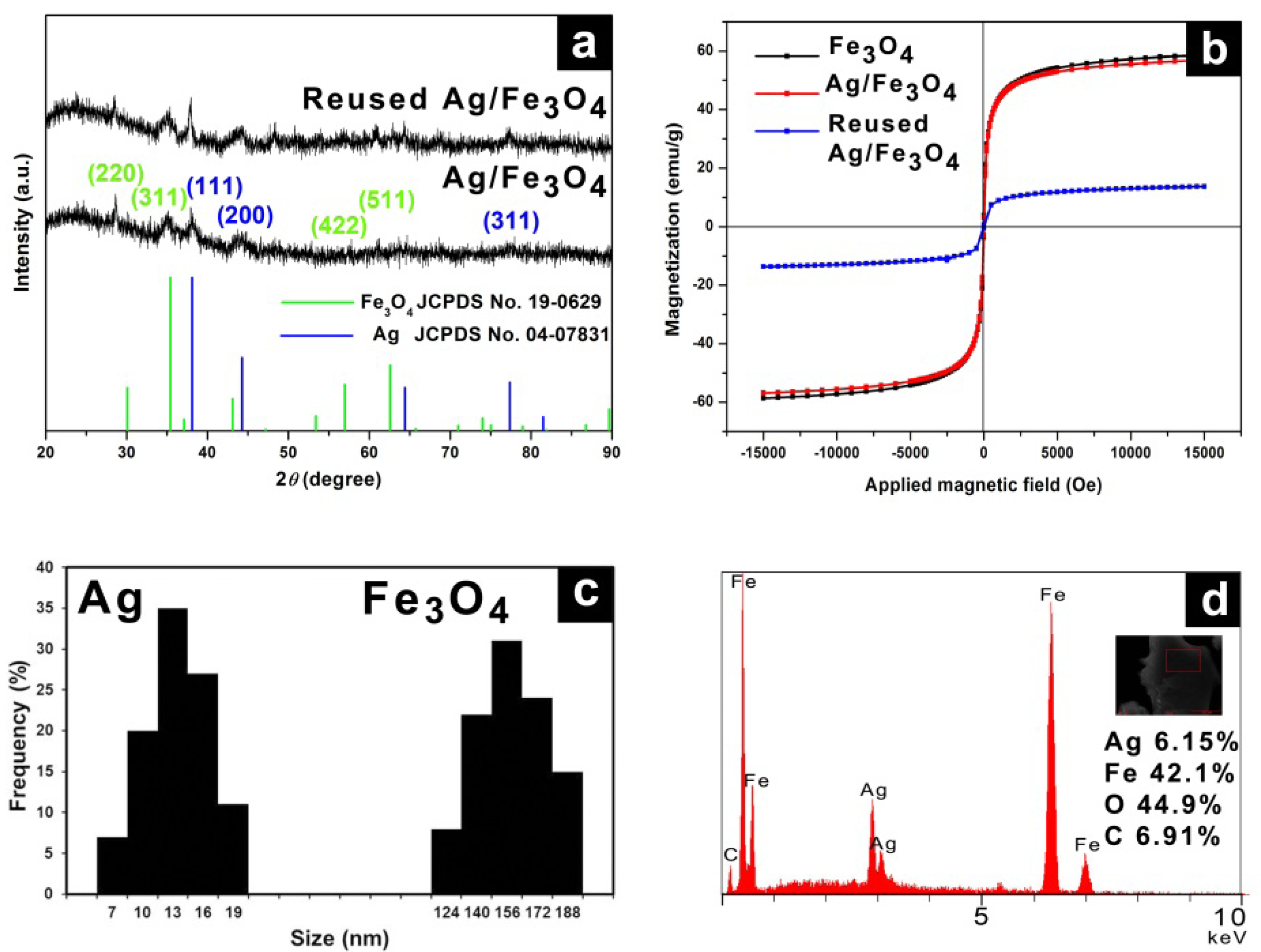
2.2. Reaction Tests
2.2.1. Reduction of Nitro Compounds

| Entry | Catalyst (mol%) | Temp. (°C) | NaBH4 (equiv.) | Time | TOF (h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fe3O4 (2.0) | 25 | 300 | 4 h | No reaction |
| 2 | Ag/Fe3O4 (2.0) | 25 | 0 | 4 h | No reaction |
| 3 | Ag/Fe3O4 (2.0) | 25 | 50 | 20 min | 150 |
| 4 | Ag/Fe3O4 (2.0) | 25 | 200 | 3 min | 1000 |
| 5 | Ag/Fe3O4 (2.0) | 25 | 300 | 4 min 10 s | 1059 |
| 6 | Ag/Fe3O4 (2.0) | 25 | 300 | 2 min 5 s | 1440 |
| Entry | Substrate | Product | Time | TOF (h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  | 2 min 5 s | 1440 |
| 2 |  |  | 1 min 40 s | 1800 |
| 3 |  |  | 6 min 50 s | 439 |
| 4 |  |  | 6 min | 500 |
| 5 |  |  | 5 min 40 s | 529 |
| 6 |  |  | 18 min 20 s | 164 |
2.2.2. Hydration of Nitriles to Amides
| Entry | Catalyst (mol%) | Temp. (°C) | Time (h) | Conversion a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Blank | 150 | 6 | 8 |
| 2 | 1 | 100 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 150 | 2 | 25 |
| 4 | 1 | 150 | 6 | 36 |
| 5 | 3 | 150 | 6 | >99 |
| 6 | 3 | 120 | 6 | 27 |
| 7 | 2 | 150 | 6 | 85 |
| 8 | 3 | 150 | 1 | 31 |
| 9 | Recovered from #5 | 150 | 6 | >99 |
| 10 | Recovered from #9 | 150 | 6 | >99 |
| 11 | Recovered from #10 | 150 | 6 | >99 |
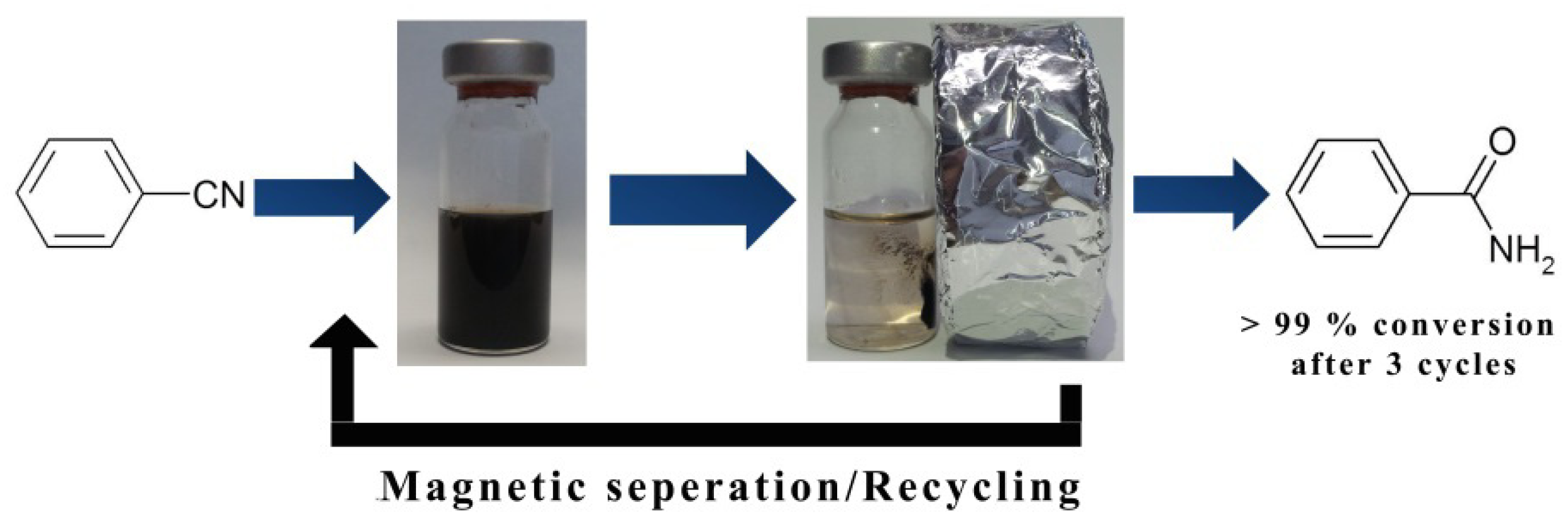

| Entry | Substrate | Product | Yield a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  | >99 |
| 2 |  |  | 96 |
| 3 |  |  | 60 |
| 4 |  |  | 40 |
| 5 |  |  | 98 |
| 6 |  |  | 86 |
| 7 |  |  | 13 |
| 8 | H3C—CH |  | >99 |
| 9 |  |  | 87 |
3. Experimental
3.1. General Remarks
3.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Microspheres
3.3. Immobilization of Ag NPs onto Fe3O4 Microspheres
3.4. A Typical Procedure for Reduction of Nitroarenes
3.5. A Typical Procedure for the Hydration of Nitriles
3.5.1. GC-MS Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaneda, K.; Mitsudome, T.; Mizugaki, T.; Jitsukawa, K. Development of heterogeneous olympic medal metal nanoparticle catalysts for environmentally benign molecular transformations based on the surface properties of hydrotalcite. Molecules 2010, 15, 8988–9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, N.; Hou, J.; Hu, F.; Zheng, L.; Ni, M.; Cao, Y. An amperometric immunosensor based on a polyelectrolyte/ gold magnetic nanoparticle supramolecular assembly-modified electrode for the determination of HIV p24 in serum. Molecules 2010, 15, 5053–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.V. Meeting the clean energy demand: Nanostructure architectures for solar energy conversion. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 2834–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D.; Mokari, T.; Banin, U.; Millo, O. Electronic structure of metal-semiconductor nanojunctions in gold CdSe nanodumbbells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 056805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M.; Yamada, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Iijima, S. Gold catalysts prepared by coprecipitation for low-temperature oxidation of hydrogen and of carbon monoxide. J. Catal. 1989, 115, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.S.; Goodman, D.W. The structure of catalytically active Au on titania. Science 2004, 306, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; You, T.; Shi, W.; Li, J.; Guo, L. Au/TiO2/Au as a plasmonic coupling photocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 6490–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Si, R.; Taylor, E.; Janzen, J.; Chen, J. Synthesis of Pd/Fe3O4 hybrid nanocatalysts with controllable interface and enhanced catalytic activities for CO oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 12969–12976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Murray, C.B.; Weller, D.; Folks, L.; Moser, A.A. monodisperse FePt nanoparticles and ferromagnetic FePt nanocrystal superlattices. Science 2000, 287, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.M.; Prinz, G.A.; Cheng, S.F.; Bounnak, S. Detection of a micron-sized magnetic sphere using a ring-shaped anisotropic magnetoresistance-based sensor: A model for a magnetoresistance-based biosensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 2211–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.K.; Morales, M.A.; Sahoo, S.K.; Leslie-Pelecky, D.L.; Labhasetwar, V. Iron oxide nanoparticles for sustained delivery of anticancer agents. Mol. Pharm. 2005, 2, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourpa, I.; Douziech-Eyrolles, L.; Ngaboni-Okassa, L.; Fouquenet, J.F.; Cohen-Jonathan, S.; Souce, M.; Marchais, H.; Dubois, P. Molecular composition of iron oxide nanoparticles, precursors for magnetic drug targeting, as characterized by confocal Raman microspectroscopy. Analyst 2005, 130, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Chung, J.; Kim, S.; Jun, S.W.; Kim, B.H.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, B.M.; Hyeon, T. Simple synthesis of Pd–Fe3O4 heterodimer nanocrystals and their application as a magnetically recyclable catalyst for Suzuki cross-coupling reactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 2512–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.-G.; Hu, M.-C.; Li, S.-N.; Jiang, Y.-C. Synthesis, structure and blue luminescent properties of a new silver(I) triazolate coordination polymer with 8210-a topology. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2009, 362, 1355–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Cohen, R.E.; Rubner, M.F. Antibacterial properties of Ag nanoparticle loaded multilayers and formation of magnetically directed antibacterial microparticles. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9651–9659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Morrin, A.; Killard, A.J.; Smyth, M.R. Application of nanoparticles in electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudome, T.; Mikami, Y.; Funai, H.; Mizugaki, T.; Jitsukawa, K.; Kaneda, K. Oxidant-free alcohol dehydrogenation using a reusable hydrotalcite-supported silver nanoparticle catalyst. Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Li, Y.; van Santen, R.A.; Hensen, E.J.M.; Li, C. Controlling reaction pathways for alcohol dehydration and dehydrogenation over FeSBA-15 catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2007, 117, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, N.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Silver nanoparticle catalyzed reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. Colloid. Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 196, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.; Becker, C.F.; Elliott, S.J.; Grinstaff, M.W.; Porco, J.A., Jr. Silver nanoparticle-catalyzed Diels-Alder cycloadditions of 2'-hydroxychalcones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7514–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, R.; El-Sayed, M.A. Catalysis with transition metal nanoparticles in colloidal solution: Nanoparticle shape dependence and stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 12663–12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motokura, K.; Fujita, N.; Mori, K.; Mizugaki, T.; Ebitani, K.; Kaneda, K. One-pot synthesis of α-alkylated nitriles with carbonyl compounds through consecutive aldol reaction/hydrogenation using a hydrotalcite-supported palladium nanoparticle as a multifunctional heterogeneous catalyst. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 5507–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Watanuki, T.; Kashiwaguru, T. Diesel exhaust particles disturb gene expression in mouse testis. Environ. Toxicol. 2007, 22, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Taneda, S.; Suzuki, A.K.; Furuta, C.; Watanabe, G.; Taya, K. Estrogenic and anti-androgenic activities of 4-nitrophenol in diesel exhaust particles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 217, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, N.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Catalytic reduction of aromatic nitro compounds by coinage metal nanoparticles. Langmuir 2001, 17, 1800–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esumi, K.; Isono, R.; Yoshimura, T. Preparation of PAMAM- and PPI-metal (silver, platinum, and palladium) nanocomposites and their catalytic activities for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Langmuir 2004, 20, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Mu, J.; Guoab, Z.; Liua, Y. In situ assembly of well-dispersed Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) on electrospun carbon nanofibers (CNFs) for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3357–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizua, K.; Imaiidab, N.; Sawabeb, K.; Satsuma, A. Hydration of nitriles to amides in water by SiO2-supported Ag catalysts promoted by adsorbed oxygen atoms. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2012, 421–422, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsudome, T.; Mikami, Y.; Mori, H.; Arita, S.; Mizugaki, T.; Jitsukawa, K.; Kaneda, K. Supported silver nanoparticle catalyst for selective hydration of nitriles to amides in water. Chem. Commun. 2009, 3258–3260. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.Y.; Bae, H.S.; Park, S.; Park, S.; Park, K.H. Silver nanoparticle catalyzed selective hydration of nitriles to amides in water under neutral conditions. Catal. Lett. 2011, 141, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Yang, F.; Feng, H.; Yang, X. Facile method for synthesis of Fe3O4@Polymer microspheres and their application as magnetic support for loading metal nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 15875–15884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, Z.; Pan, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, S. Ag-coated Fe3O4@SiO2 three-ply composite microspheres: Synthesis, characterization, and application in detecting melamine with their surface-enhanced raman scattering. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 7738–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, M. Silver nanoparticle supported on halloysite nanotubes catalyzed reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3989–3993. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Nath, S.; Pande, S.; Praharaj, S.; Panigrahi, S.; Basu, S.; Endo, T.; Pal, T. Synthesis of silver nanoshell-coated cationic polystyrene beads: A solid phase catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2006, 313, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, H.; Lee, K.; Park, S.; Park, K.H. Magnetically Separable and Recyclable Fe3O4-Supported Ag Nanocatalysts for Reduction of Nitro Compounds and Selective Hydration of Nitriles to Amides in Water. Molecules 2014, 19, 699-712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19010699
Woo H, Lee K, Park S, Park KH. Magnetically Separable and Recyclable Fe3O4-Supported Ag Nanocatalysts for Reduction of Nitro Compounds and Selective Hydration of Nitriles to Amides in Water. Molecules. 2014; 19(1):699-712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19010699
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Hyunje, Kyoungho Lee, Sungkyun Park, and Kang Hyun Park. 2014. "Magnetically Separable and Recyclable Fe3O4-Supported Ag Nanocatalysts for Reduction of Nitro Compounds and Selective Hydration of Nitriles to Amides in Water" Molecules 19, no. 1: 699-712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19010699
APA StyleWoo, H., Lee, K., Park, S., & Park, K. H. (2014). Magnetically Separable and Recyclable Fe3O4-Supported Ag Nanocatalysts for Reduction of Nitro Compounds and Selective Hydration of Nitriles to Amides in Water. Molecules, 19(1), 699-712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19010699