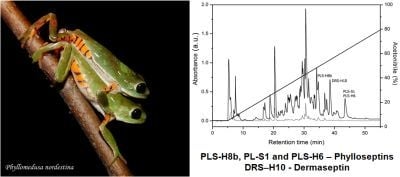
The Skin Secretion of the Amphibian Phyllomedusa nordestina: A Source of Antimicrobial and Antiprotozoal Peptides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
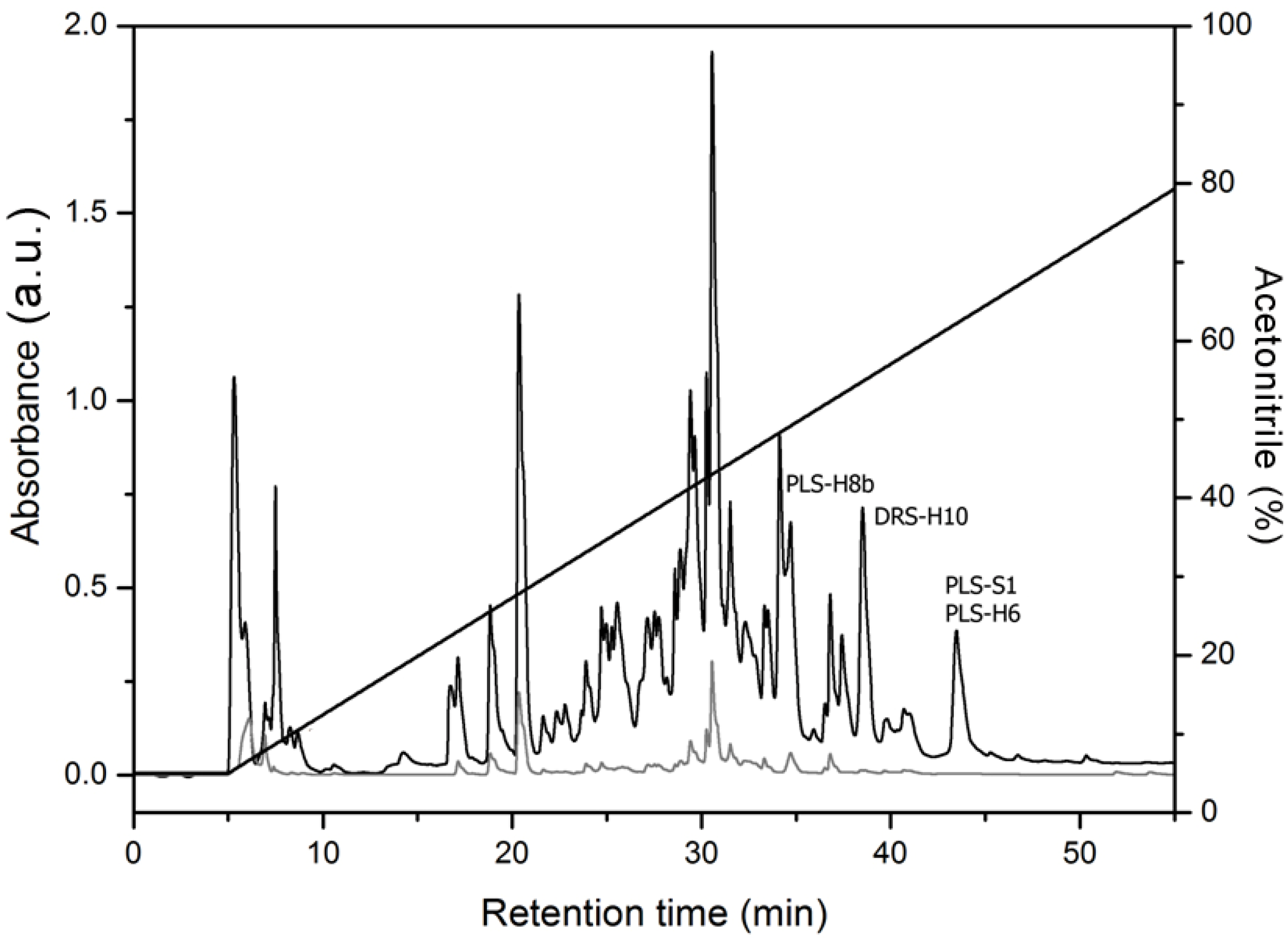
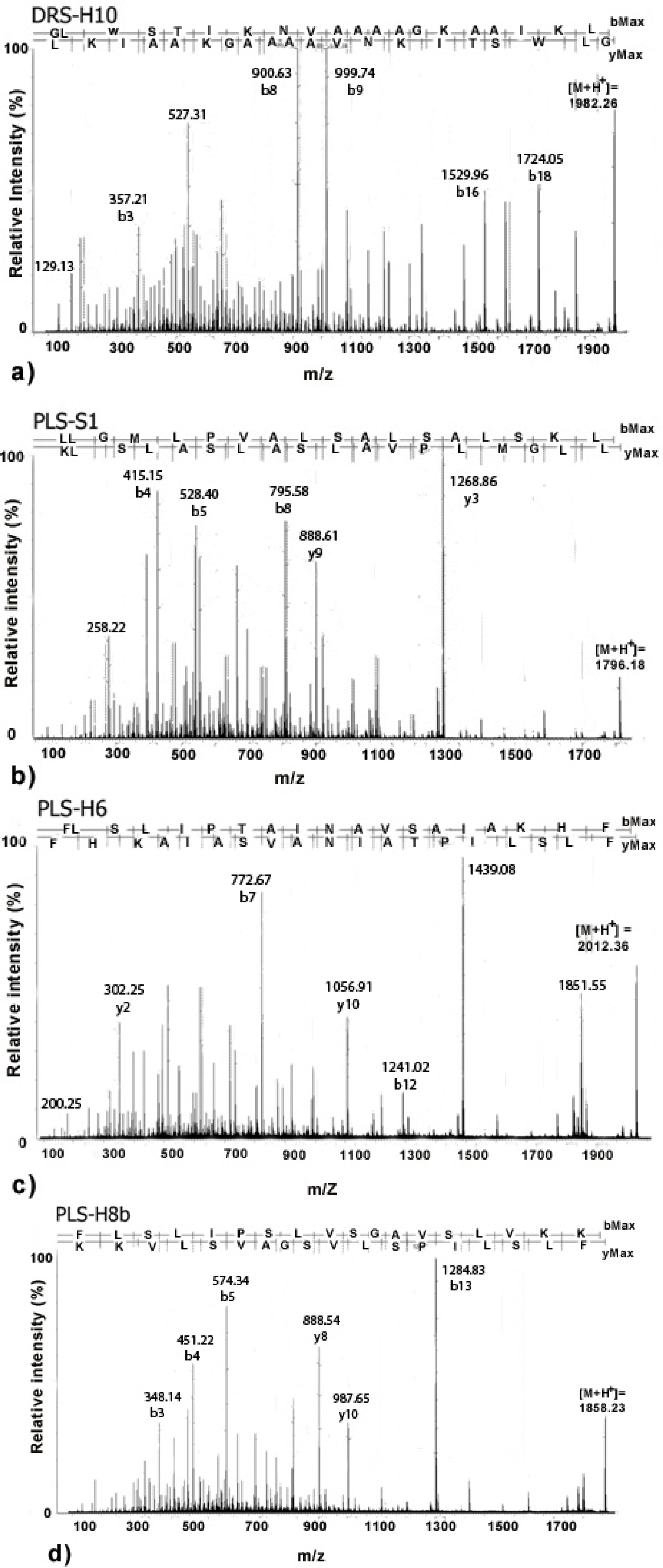
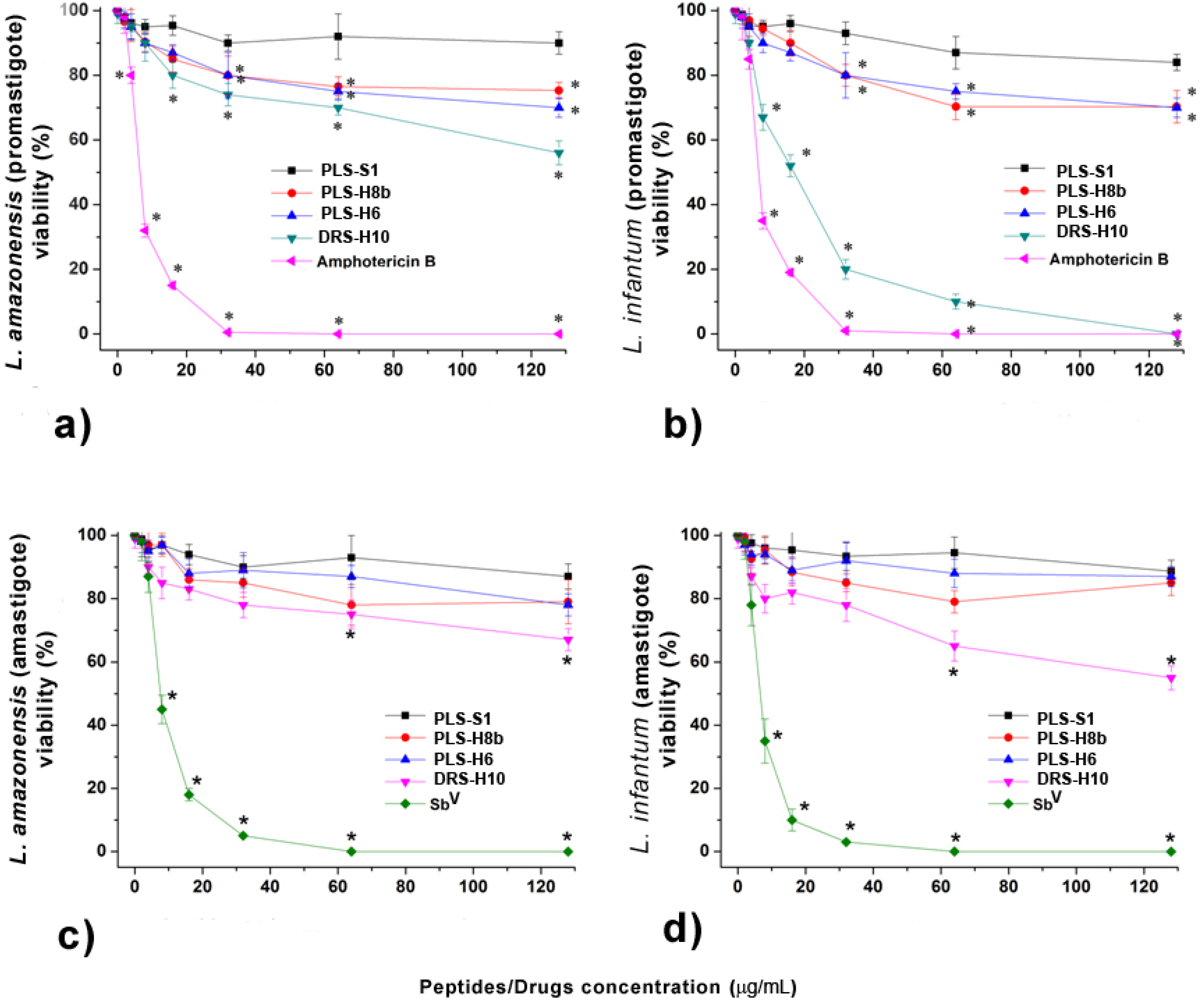
2. Results and Discussion
| Primary structure | Exp. [M+H]+ | Peptide name(s) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dermaseptins | ||||
| 1 | GLWSTIKQKGKEAAIAAAKAAGQAALNAASEAL-NH2 | 3208.63 | DRS-H9 | [6] |
| 2 | GLWSTIKQKGKEAAIAAAKAAGQAALNAASEAL-NH2 | 3208.92 | - | - |
| 3 | WSTIKQKGKEAAIAAAKAAGQAALNAASEAL-NH2 | 3038.70 | ||
| 4 | TIKQKGKEAAIAAAKAAGQAALNAASEAL-NH2 | 2765.52 | ||
| 5 | GLWSTIKQKGKEAAIAAAKAAGQAALGAL-NH2 | 2793.78 | DRS-01, DRS-H7 | [14] |
| 6 | GLWSTIKQKGKEAAIAAAKAAGQAALGAL-NH2 | 2793.75 | - | - |
| 7 | GLWSTIKQKGKEAAIAAAKAAGQAALG-OH | 2610.64 | ||
| 8 | TIKQKGKEAAIAAAKAAGQAALGAL-OH | 2350.40 | ||
| 9 | WSTIKQKGKEAAIAAAKAAGQAALGAL-NH2 | 2623.49 | ||
| 10 | WSTIKQKGKEAAIAAAK-COOH | 1801.18 | ||
| 11 | GLWSKIKDVAAAAGKAALGAVNEAL-NH2 | - | DRS-H15 | [15] |
| 12 | GLWSKIKDVAAAAGKAALNAVNEAL-NH2 | 2480.55 | - | - |
| 13 | WSKIKDVAAAAGKAALNAVNEAL-NH2 | 2310.40 | ||
| 14 | GLWSTIKNVGKEAAIAAGKAALGAL–NH2 | 2409.41 | DRS-H3, DRS-H12 | [6] |
| 15 | GLWSTIKNVGKEAAIAAGKAALGAL-NH2 | 2409.55 | - | - |
| 16 | GLWSTIKNVGKEAAIAAGKAALGAL-OH | 2410.55 | ||
| 17 | WSTIKNVGKEAAIAAGKAALGAL-NH2 | 2238.25 | ||
| 18 | TIKNVGKEAAIAAGKAALGAL-NH2 | 1966.23 | ||
| 19 | GLWSTIKNVAAAAGKAALGAL-NH2 | - | DRS-H10 | [15] |
| 20 | GLWSTIKNVAAAAGKAALGAL-NH2 | 1982.26 | - | - |
| Phylloseptins | ||||
| 21 | FLSLIPHAINAVSAIAKHF-NH2 | 2048.25 | PLS-H5 | [15] |
| 22 | FLSLIPHAINAVSAIAKHF-NH2 | 2048.38 | - | - |
| 23 | LIPHAINAVSAIAKHF-NH2 | 1701.00 | ||
| 24 | IPHAINAVSAIAKHF-NH2 | 1587.88 | ||
| 25 | FLSLIPHAINA-OH | 1195.71 | ||
| 26 | FLSLIPTAINAVSALAKHF-NH2 | 2012.12 | PLS-H6 | [15,16] |
| 27 | FLSLIPTAINAVSALAKHF-NH2 | 2012.36 | - | - |
| 28 | LSLIPTAINAVSALAKHF-NH2 | 1865.19 | ||
| 29 | SLIPTAINAVSALAKHF-NH2 | 1752.14 | ||
| 30 | LIPTAINAVSALAKHF-NH2 | 1665.17 | ||
| 31 | IPTAINAVSALAKHF-NH2 | 1551.91 | ||
| 32 | FLSLLPSLVSGAVSLVKKL-OH | 1970.43 | PLS-H8 | [16] |
| 33 | FLSLLPSLVSGAVSLVKK-OH | 1858.23 | - | - |
| 34 | SLLPSLVSGAVSLVKKL-NH02 | 1710.19 | ||
| 35 | LLGMIPVAISAISALSKL-NH2 | - | PLS-S1 | [17] |
| 36 | LLGMIPVAISAISALSKL-NH2 | 1796.18 | - | - |
| Hyposins | ||||
| 37 | LRPAFIRPKGK-NH2 | 1280.87 | HPS-H2 | [18] |
| 38 | LRPAFIRPKGR-NH2 | 1309.95 | - | - |
| 39 | RPAFIRPKGR-NH2 | 1196.87 | ||
| 40 | FRPALIVRTKGK-NH2 | 1383.80 | HPS-J1 | [19] |
| 41 | LRPALIVRTKG-OH | 1223.90 | - | - |
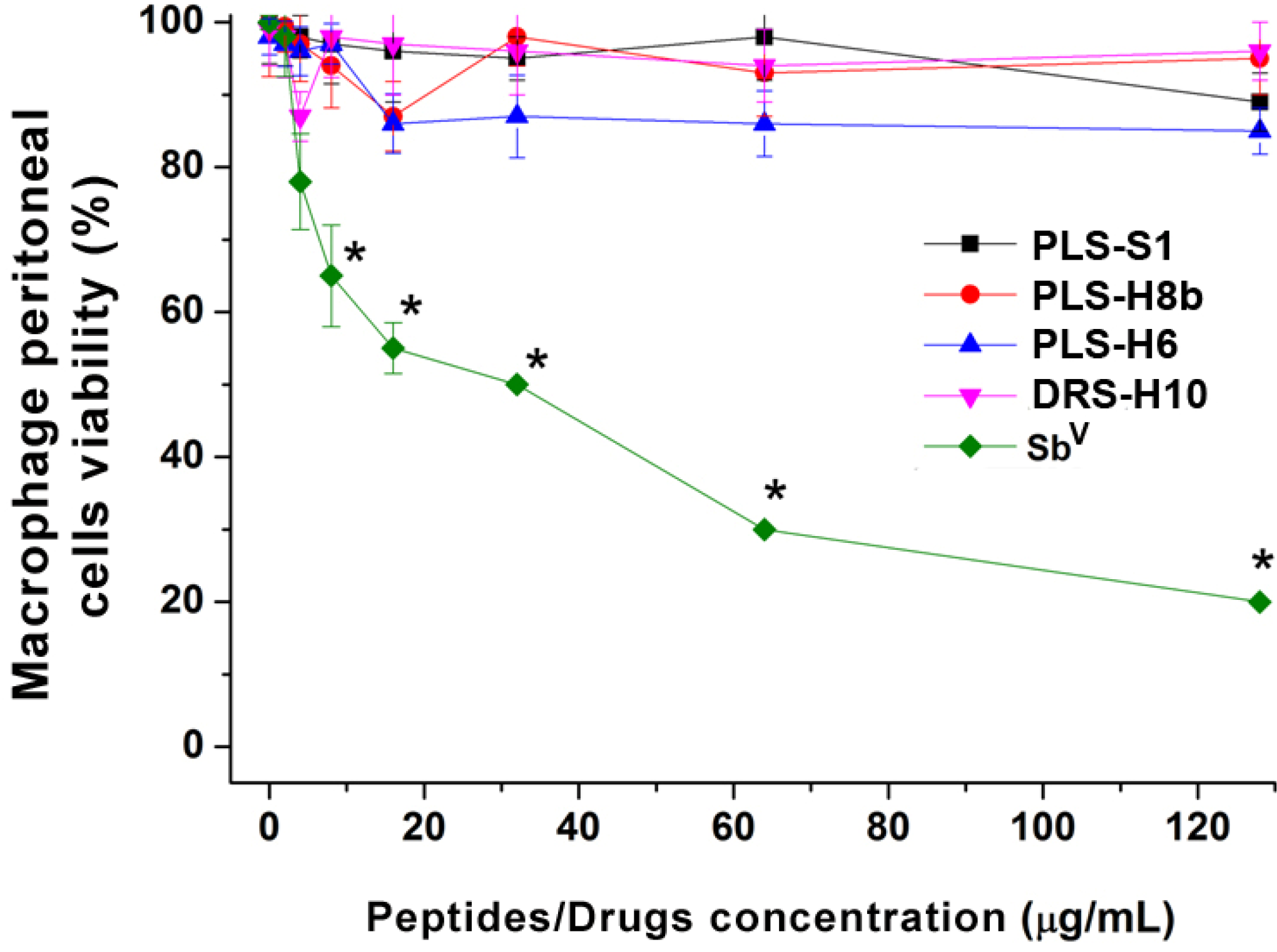
3. Experimental
3.1. Amphibians
3.2. Frog Skin Secretion Fractionation, Peptide Sequencing and Similarity Searches
3.3. Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis
3.4. Leishmania Isolates
3.5. In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of the Antimicrobial Peptides on the L. amazonensis and L. infantum
3.6. Cytotoxic Effects of Antimicrobial Peptides on Peritoneal Cells
3.7. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mor, A.; Nicolas, P. Isolation and structure of novel defensive peptides from frog skin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 219, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, S.R.; Wallace, J.; Harris, F.; Phoenix, D.A. Amphiphilic alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides and their structure/function relationships. Protein Pept. Lett. 2005, 12, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes, J.; Nascimento, C.; Miura, L.M.; Leite, J.R.; Nakano, E.; Kawano, T. Evaluation of the in vitro activity of dermaseptin 01, a cationic antimicrobial peptide, against Schistosoma mansoni. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, L.; Luque-Ortega, J.R.; Andreu, D. Amphibian antimicrobial peptides and Protozoa: lessons from parasites. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 1570–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, G.D.; Leite, J.R.; de Sa Mandel, S.M.; Mesquita, D.A.; Silva, L.P.; Prates, M.V.; Barbosa, E.A.; Vinecky, F.; Martins, G.R.; Galasso, J.H.; et al. Novel dermaseptins from Phyllomedusa hypochondrialis (Amphibia). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, V.; Feio, M.J.; Bastos, M. Role of lipids in the interaction of antimicrobial peptides with membranes. Prog. Lipid Res. 2012, 51, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogden, N.K.; Brogden, K.A. Will new generations of modified antimicrobial peptides improve their potential as pharmaceuticals? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Zampa, M.F.; Araujo, I.M.; Costa, V.; Nery Costa, C.H.; Santos, J.R., Jr.; Zucolotto, V.; Eiras, C.; Leite, J. R. Leishmanicidal activity and immobilization of dermaseptin 01 antimicrobial peptides in ultrathin films for nanomedicine applications. Nanomedicine 2009, 5, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo Calderon, L.D.; Silva, A.D.; Ciancaglini, P.; Stábeli, R. Antimicrobial peptides from Phyllomedusa frogs: From biomolecular diversity to potential nanotechnologic medical applications. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas, P.; El Amri, C. The dermaseptin superfamily: A gene-based combinatorial library of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 1537–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Caramaschi, U. Redefinição do grupo de Phyllomedusa hypochondrialis, com redescrição de P. megacephala (Miranda-Ribeiro, 1926), revalidação de P. azurea cope, 1862 e descrição de uma nova espécie (Amphibia, Anura, Hylidae). Arquivos do Museu Nacional, Rio de Janeiro 2006, 64, 159–179. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, G.D.; Leite, J.R.; Silva, L.P.; Albuquerque, S.; Prates, M.V.; Azevedo, R.B.; Carregaro, V.; Silva, J.S.; Sa, V.C.; Brandao, R.A.; Bloch, C., Jr. Dermaseptins from Phyllomedusa oreades and Phyllomedusa distincta. Anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity without cytotoxicity to mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49332–49340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.H.; Bjourson, A.J.; Orr, D.F.; Shaw, C.; McClean, S. A combined mass spectrometric and cDNA sequencing approach to the isolation and characterization of novel antimicrobial peptides from the skin secretions of Phyllomedusa hypochondrialis azurea. Peptides 2007, 28, 1331–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhou, M.; Gagliardo, R.; Walker, B.; Shaw, C. Elements of the granular gland peptidome and transcriptome persist in air-dried skin of the South American orange-legged leaf frog, Phyllomedusa hypocondrialis. Peptides 2006, 27, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, J.M.; Woodhams, D.C.; Raza, H.; Coquet, L.; Leprince, J.; Jouenne, T.; Vaudry, H.; Rollins-Smith, L.A. Peptides with differential cytolytic activity from skin secretions of the lemur leaf frog Hylomantis lemur (Hylidae: Phyllomedusinae). Toxicon 2007, 50, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.H.; Bjourson, A.J.; Orr, D.F.; Shaw, C.; McClean, S. Amphibian skin secretomics: application of parallel quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and peptide precursor cDNA cloning to rapidly characterize the skin secretory peptidome of Phyllomedusa hypochondrialis azurea: discovery of a novel peptide family, the hyposins. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 3604–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rates, B.; Silva, L.P.; Ireno, I.C.; Leite, F.S.; Borges, M.H.; Bloch, C., Jr.; de Lima, M.E.; Pimenta, A.M. Peptidomic dissection of the skin secretion of Phasmahyla jandaia (Bokermann and Sazima, 1978) (Anura, Hylidae, Phyllomedusinae). Toxicon 2011, 57, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauricio, I.L.; Stothard, J.R.; Miles, M.A. The strange case of Leishmania chagasi. Parasitol. Today 2000, 16, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiche, M.; Ladram, A.; Nicolas, P. A consistent nomenclature of antimicrobial peptides isolated from frogs of the subfamily Phyllomedusinae. Peptides 2008, 29, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, F.S.; Leite, J.R.; Silva, L.P.; Melo, J.A.; Bloch, C., Jr.; Schwartz, E.F. Antimicrobial peptide from the skin secretion of the frog Leptodactylus syphax. Toxicon 2007, 50, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, B.S.; Melo, J.A.; Leite, J.R.; Silva, L.P.; Prates, M.V.; Vinecky, F.; Barbosa, E.A.; Verly, R.M.; Mehta, A.; Nicoli, J.R.; et al. Post-secretory events alter the peptide content of the skin secretion of Hypsiboas raniceps. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuckelhaus, S.A.; Leite, J.R.; Muniz-Junqueira, M.I.; Sampaio, R.N.; Bloch, C., Jr.; Tosta, C.E. Antiplasmodial and antileishmanial activities of phylloseptin-1, an antimicrobial peptide from the skin secretion of Phyllomedusa azurea (Amphibia). Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 123, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, G.D.; Krause, F.C.; Silva, L.P.; Leite, J.R.; Melo, J.A.; Prates, M.V.; Pesquero, J.B.; Santos, E.L.; Nakaie, C.R.; Costa-Neto, C.M.; Bloch, C., Jr. Bradykinin-related peptides from Phyllomedusa hypochondrialis. Peptides 2006, 27, 2137–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Furnham, N.; Garavelli, J.S.; Thornton, J.M. Protein Data Resources. Encyclopedia Biol. Chem. 2013, 3, 611–617. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.E. Methods for studying cell death and viability in primary neuronal cultures. Methods Cell Biol. 1995, 46, 243–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically: Approved Standard, 8th ed.; CLSI document M07-A8 (ISBN 1-56238-689-1); Wayne, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the all compounds are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Brand, G.D.; Santos, R.C.; Arake, L.M.; Silva, V.G.; Veras, L.M.C.; Costa, V.; Costa, C.H.N.; Kuckelhaus, S.S.; Alexandre, J.G.; Feio, M.J.; et al. The Skin Secretion of the Amphibian Phyllomedusa nordestina: A Source of Antimicrobial and Antiprotozoal Peptides. Molecules 2013, 18, 7058-7070. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18067058
Brand GD, Santos RC, Arake LM, Silva VG, Veras LMC, Costa V, Costa CHN, Kuckelhaus SS, Alexandre JG, Feio MJ, et al. The Skin Secretion of the Amphibian Phyllomedusa nordestina: A Source of Antimicrobial and Antiprotozoal Peptides. Molecules. 2013; 18(6):7058-7070. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18067058
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrand, Guilherme D., Raimunda C. Santos, Luisa Mayumi Arake, Valdelânia G. Silva, Leiz M. C. Veras, Vladimir Costa, Carlos Henrique N. Costa, Selma S. Kuckelhaus, José Guilherme Alexandre, Maria J. Feio, and et al. 2013. "The Skin Secretion of the Amphibian Phyllomedusa nordestina: A Source of Antimicrobial and Antiprotozoal Peptides" Molecules 18, no. 6: 7058-7070. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18067058
APA StyleBrand, G. D., Santos, R. C., Arake, L. M., Silva, V. G., Veras, L. M. C., Costa, V., Costa, C. H. N., Kuckelhaus, S. S., Alexandre, J. G., Feio, M. J., & Leite, J. R. S. A. (2013). The Skin Secretion of the Amphibian Phyllomedusa nordestina: A Source of Antimicrobial and Antiprotozoal Peptides. Molecules, 18(6), 7058-7070. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18067058