Eudragit® L100/N-Trimethylchitosan Chloride Microspheres for Oral Insulin Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of TMC
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
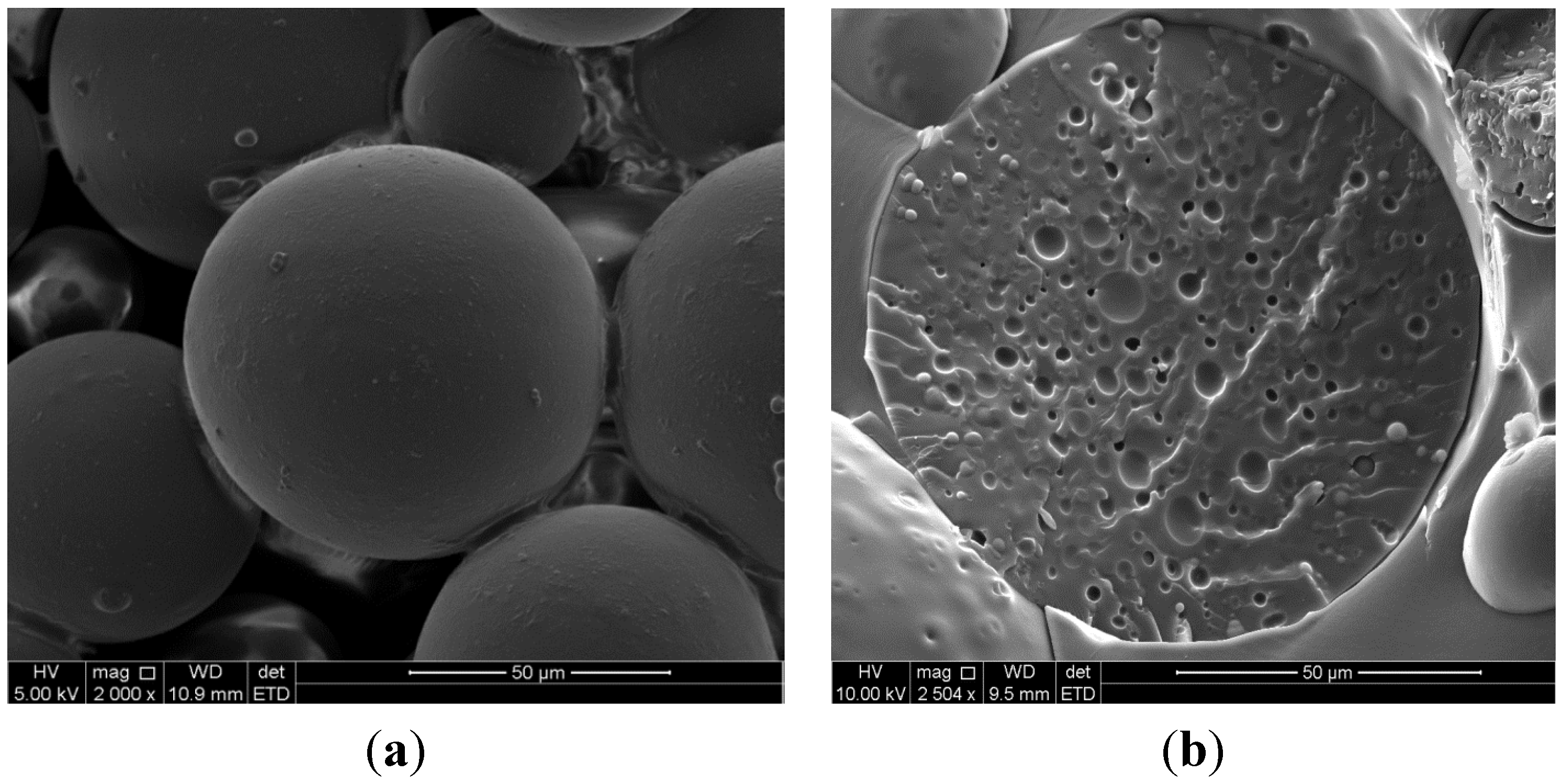
2.3. Insulin and TMC Loading
2.4. Particle Size
| TMC 5% w/w | TMC 10% w/w | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eudragit® L100 (% w/w) | Eudragit® L100 (% w/w) | ||||
| 7.5% | 3.5% | 7.5% | 3.5% | ||
| Insulin | 2 (% w/w) | Formula A | Formula B | Formula E | Formula F |
| 1 (% w/w) | Formula C | Formula D | Formula G | Formula H | |
2.5. Dissolution Behavior
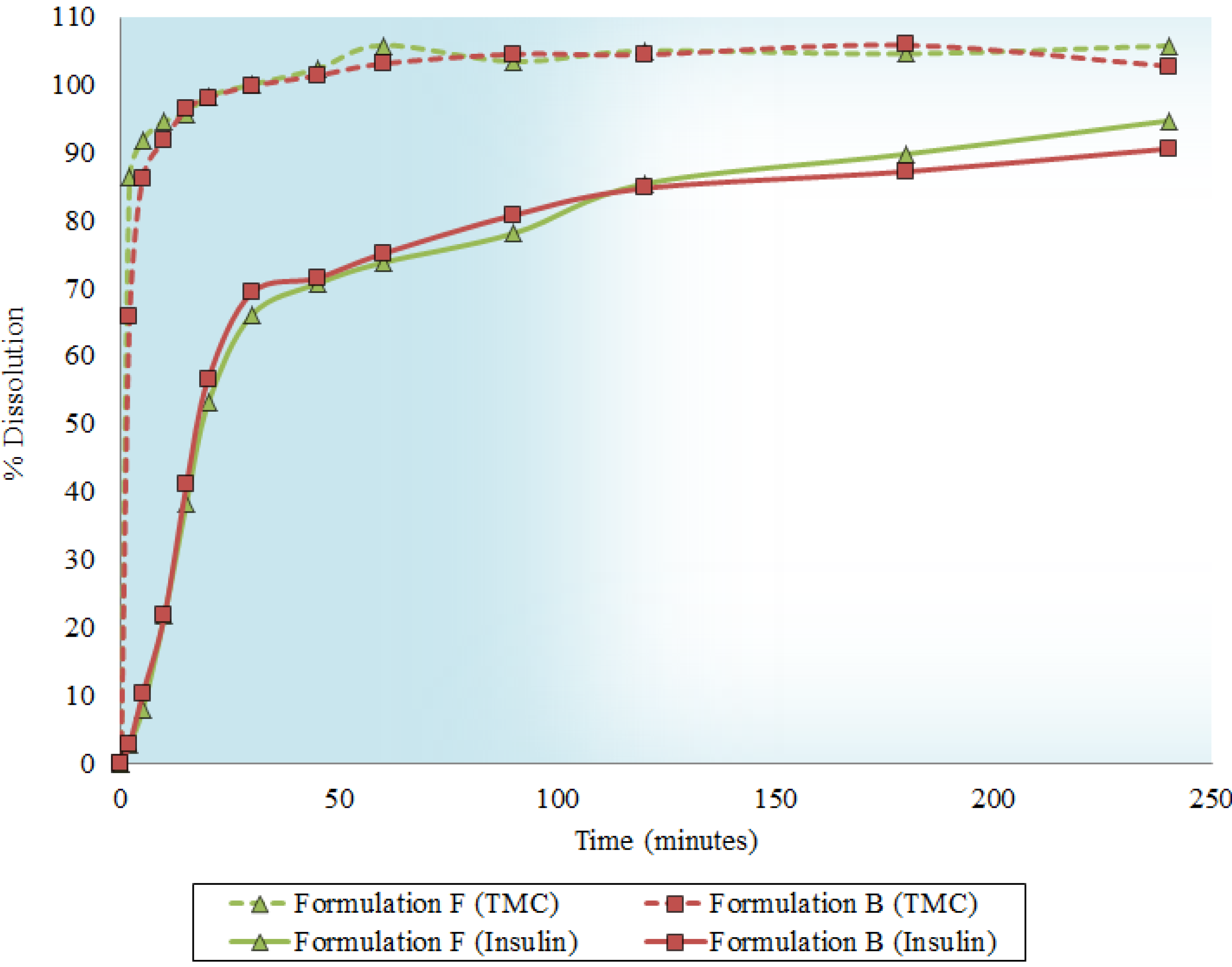
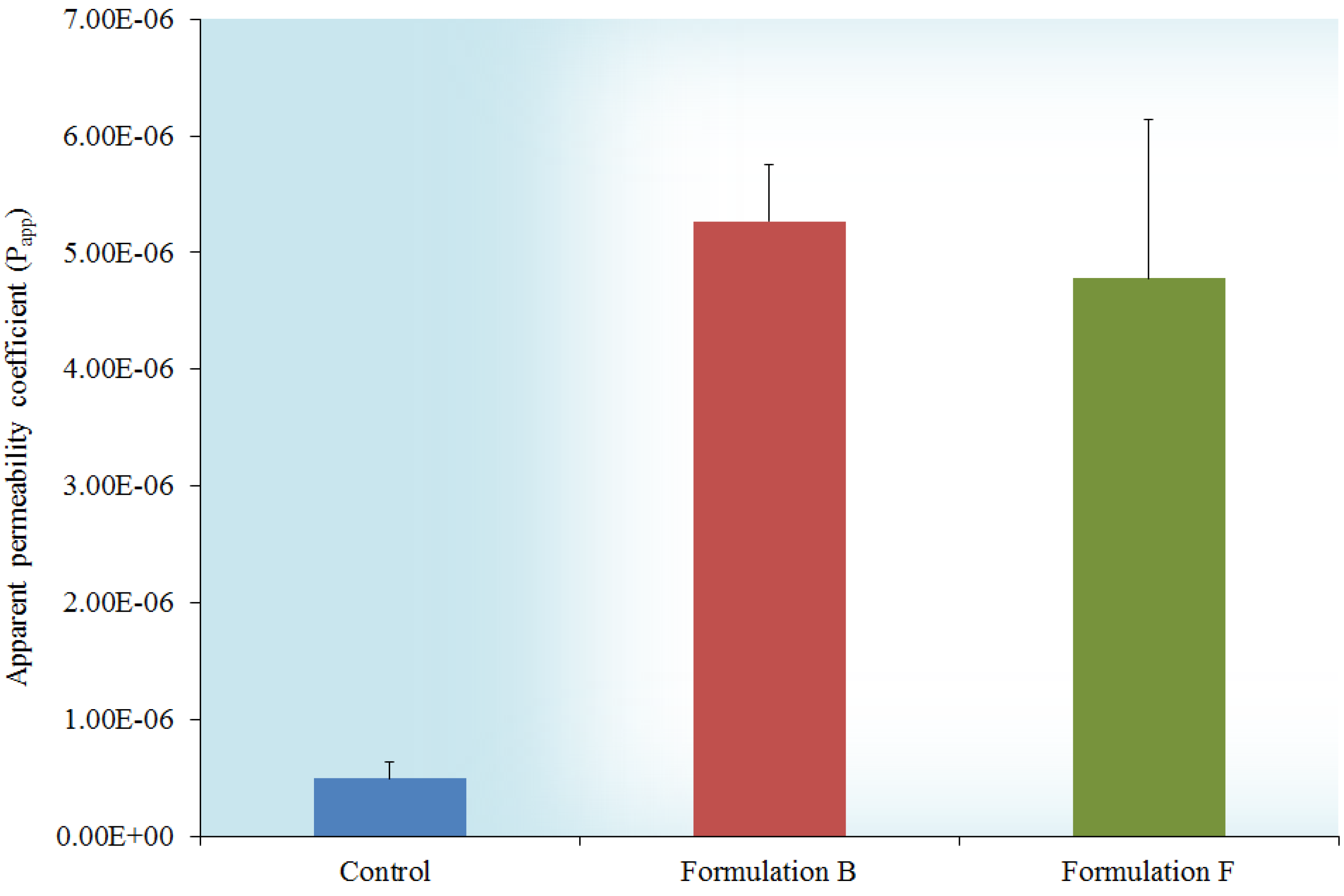
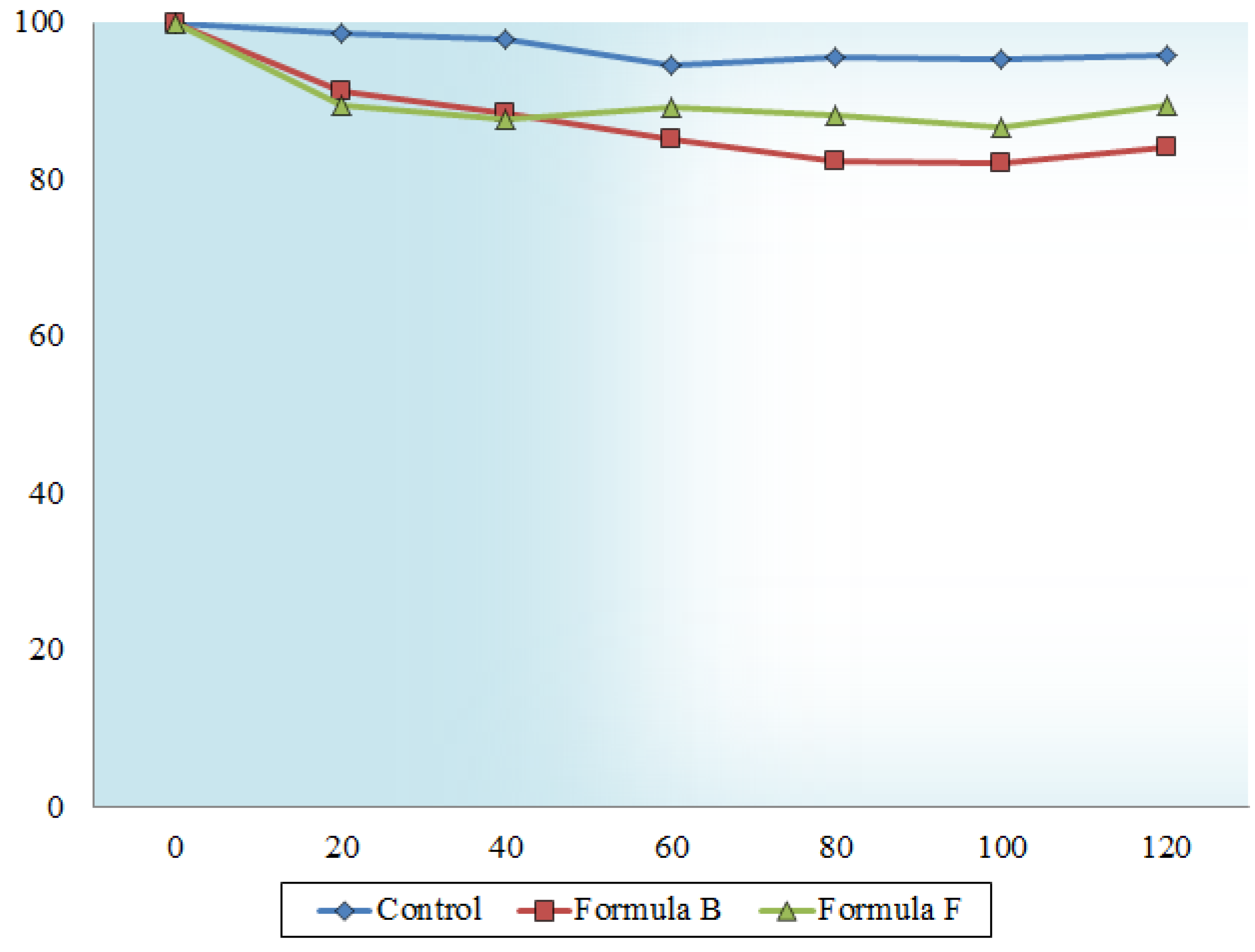
2.6. In Vitro Transport across Excised Intestinal Tissue
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of TMC
3.2.1. First Reaction Step
3.2.2. Second Reaction Step
3.2.3. Additional Step
3.3. Microsphere Preparation
3.3.1. Surface Morphology and Internal Structure
3.3.2. Insulin Loading and TMC Loading
3.3.3. Particle Size Distribution
3.3.4. Dissolution Studies
3.3.5. In Vitro Transport Studies
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pauletti, G.M.; Gangwar, S.; Knipp, G.T.; Nerurkar, M.M.; Okumu, F.W.; Tamura, K.; Siahaan, T.J.; Borchardt, R.T. Structural requirements for intestinal absorption of peptide drugs. J. Controlled Release 1996, 41, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, J.H.; Enslin, G.M.; Kotzé, A.F. Oral delivery of peptide drugs: barriers and developments. Biodrugs 2005, 19, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, M.; Peppas, N.A. Is the oral route possible for peptide and protein drug delivery. Drug Discovery Today 2006, 11, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, A.L.; Mrsny, R.J. Transcellular uptake mechanisms of the intestinal epithelial barrier: part one. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 1999, 2, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Park, P. Oral protein delivery: Current status and future prospect. React. Funct. Polym. 2010, 71, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, E.; Lior, O.; Kidron, M. Absorption of protein via the intestinal wall. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Hosny, E.A.; Al-Shora, H.; Elmazar, M.M.A. Oral delivery of insulin from enteric-coated capsules containing sodium salicylate: Effect on relative hypoglycemia of diabetic beagle dogs. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 237, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilkumhang, S.; Basit, A.W. The robustness and flexibility of an emulsion solvent evaporation method to prepare pH-responsive microparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 377, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.N.; Hemant, K.S.Y.; Ram, M.; Shivakumar, H.G. Microencapsulation: a promising technique for controlled drug delivery. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 5, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Salamat-Miller, N.; Johnston, T.P. Current strategies used to enhance the paracellular transport of therapeutic polypeptides across the intestinal epithelium. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 294, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Merwe, S.M.; Verhoef, J.C.; Verheijden, J.H.M.; Kotzé, A.F.; Junginger, H.E. Trimethylated chitosan as polymeric absorption enhancer for improved peroral delivery of peptide drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanou, M.; Verhoef, J.C.; Junginger, H.E. Oral drug absorption enhancement by chitosan and its derivatives. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2001, 52, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanou, M.; Verhoef, J.C.; Junginger, H.E. Chitosan and its derivatives as intestinal absorption enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2001, 50, S91–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzé, A.F.; Lueßen, H.L.; De Boer, A.G.; Verhoef, J.C.; Junginger, H.E. Chitosan for enhanced intestinal permeability: prospects for derivatives soluble in neutral and basic environments. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 7, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Kotzé, A.F.; Lueßen, H.L.; De Leeuw, B.J.; De Boer, A.G.; Verhoef, J.C.; Junginger, H.E. Comparison of the effect of different chitosan salts and N-trimethyl chitosan chloride in the permeability of intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J. Control. Release 1998, 51, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanou, M.M.; Verhoef, J.C.; Romeijn, S.G.; Nagelkerke, J.F.; Merkus, F.W.H.M.; Junginger, H.E. Effects of N-trimethyl chitosan chloride, a novel absorption enhancer, on Caco-2 intestinal epithelia and the ciliary beat frequency of chicken embryo trachea. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 185, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyman, D.; Hamman, J.H.; Kotzé, A.F. Evaluation of the mucoadhesive properties of N-trimethyl chitosan chloride. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2003, 29, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzé, A.F.; Thanou, M.M.; Lueen, H.L.; de Leeuw, B.J.; de Boer, A.G.; Verhoef, J.C.; Junginger, H.E. Enhancement of paracellular drug transport with highly quaternized N-trimethyl chitosan chloride on the permeability of intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, J.H.; Schultz, C.M.; Kotzé, A.F. N-trimethyl chitosan chloride: optimum degree of quaternization for drug absorption enhancement across epithelial cells. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2003, 2, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieval, A.B.; Thanou, M.; Kotzé, A.F.; Verhoef, J.C.; Brussee, J.; Junginger, H.E. Preparation and NMR characterization of highly substituted N-trimethyl chitosan chloride. Carbohyd. Polym. 1998, 36, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, P.J.; Davies, M.C.; Mella, C.D. Microencapsulation using emulsification/solvent evaporation: An overview of techniques and applications. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 1990, 7, 235–259. [Google Scholar]
- Rosca, I.D.; Watari, F.; Uo, M. Microparticle formation and its mechanism in single and double emulsion solvent evaporation. J. Controlled Release 2004, 99, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A. Colorimetric determination of chitosan. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 260, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.N.; Bustamante, P.; Chun, A.H.C. Physical Pharmacy: Physical Chemical Principles in the Pharmaceutical Sciences, 4th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1993; p. 622. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.W.; Flanner, H.H. Mathematical comparison of dissolution profiles. Pharm. Technol. 1996, 20, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo, P.; Picchini, U.; Beck, B.; Van Gelder, J.; Delbar, N.; Degaetano, A. A general approach to the apparent permeability index. J. Pharmacokinet. Phar. 2008, 35, 235–248. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Marais, E.; Hamman, J.; Plessis, L.D.; Lemmer, R.; Steenekamp, J. Eudragit® L100/N-Trimethylchitosan Chloride Microspheres for Oral Insulin Delivery. Molecules 2013, 18, 6734-6747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066734
Marais E, Hamman J, Plessis LD, Lemmer R, Steenekamp J. Eudragit® L100/N-Trimethylchitosan Chloride Microspheres for Oral Insulin Delivery. Molecules. 2013; 18(6):6734-6747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066734
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarais, Etienne, Josias Hamman, Lissinda Du Plessis, Righard Lemmer, and Jan Steenekamp. 2013. "Eudragit® L100/N-Trimethylchitosan Chloride Microspheres for Oral Insulin Delivery" Molecules 18, no. 6: 6734-6747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066734
APA StyleMarais, E., Hamman, J., Plessis, L. D., Lemmer, R., & Steenekamp, J. (2013). Eudragit® L100/N-Trimethylchitosan Chloride Microspheres for Oral Insulin Delivery. Molecules, 18(6), 6734-6747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066734






