Optimization of Shikonin Homogenate Extraction from Arnebia euchroma Using Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
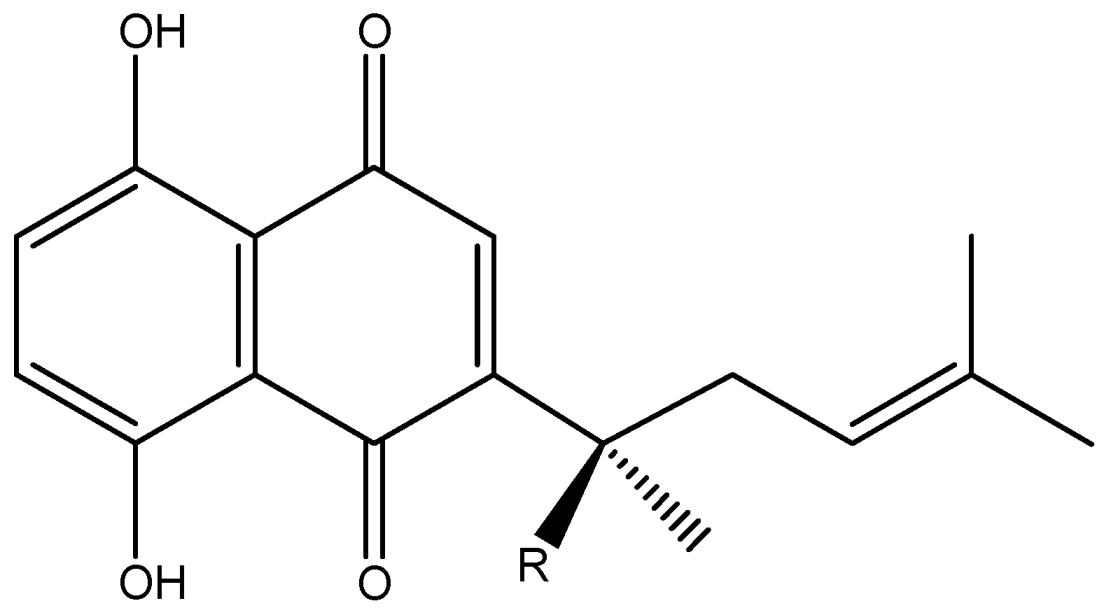
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Single-Factor Shikonin Extraction Experiments
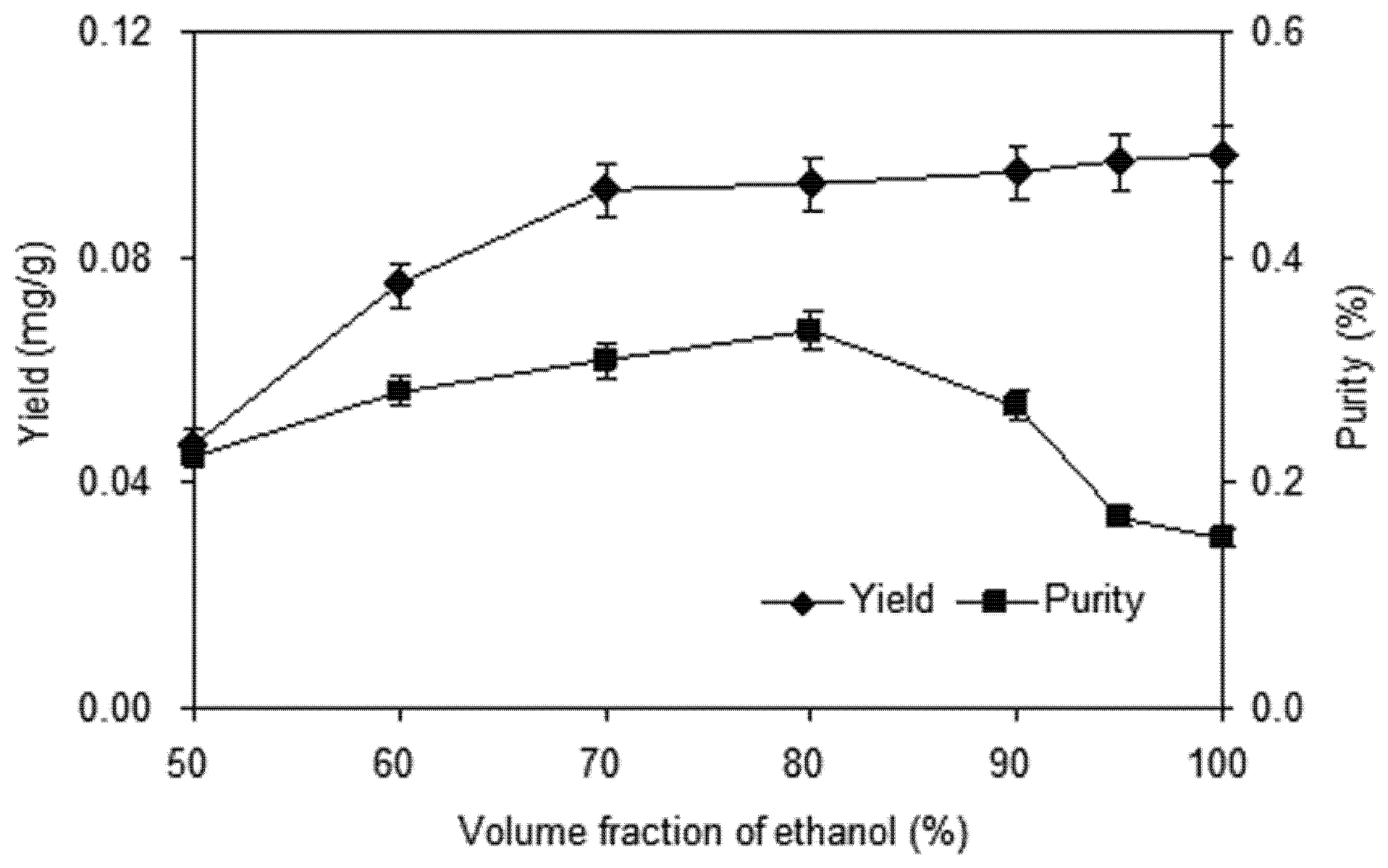
2.1.1. Effect of Volume Fraction of Ethanol
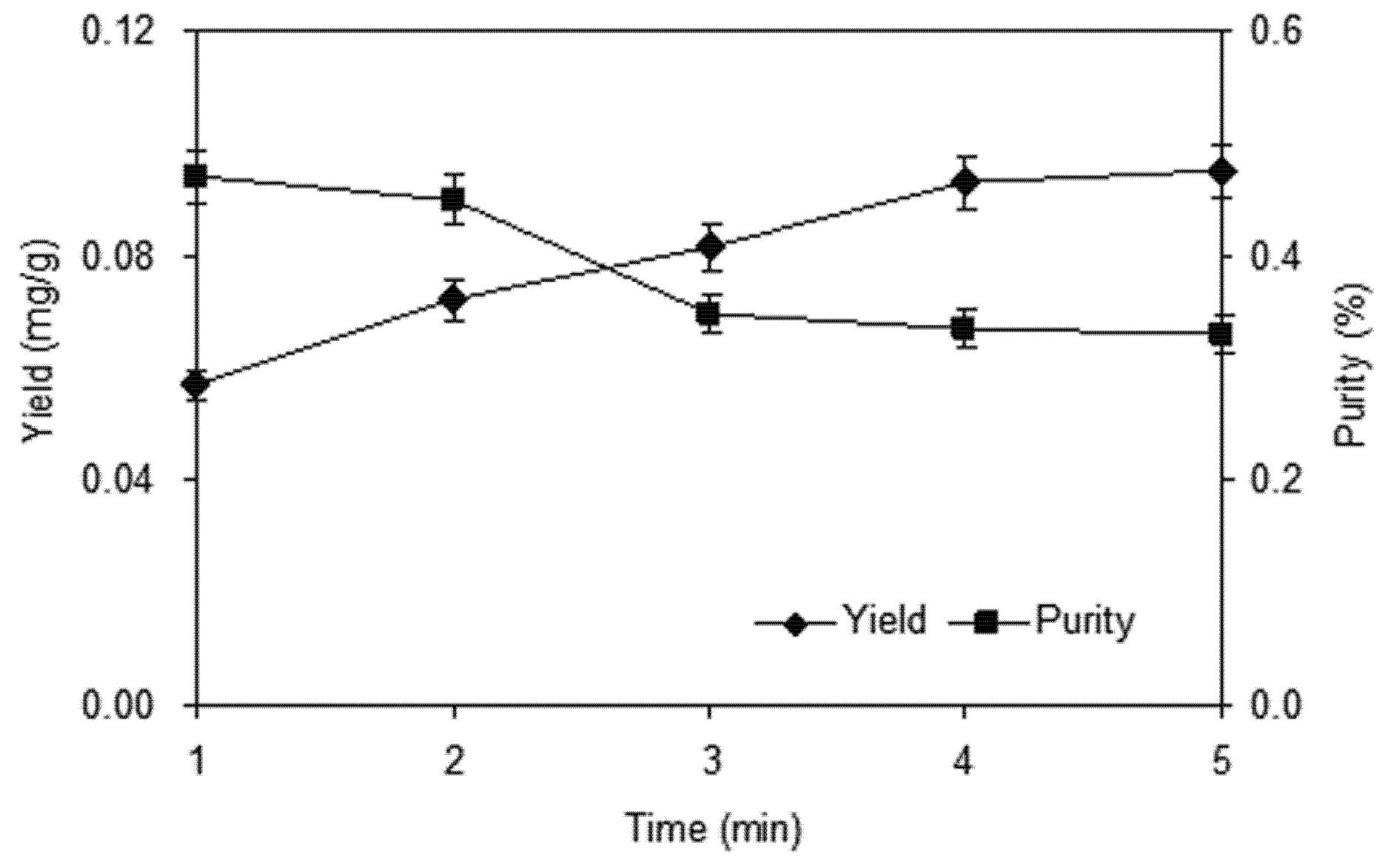
2.1.2. Effect of Homogenate Extraction Time
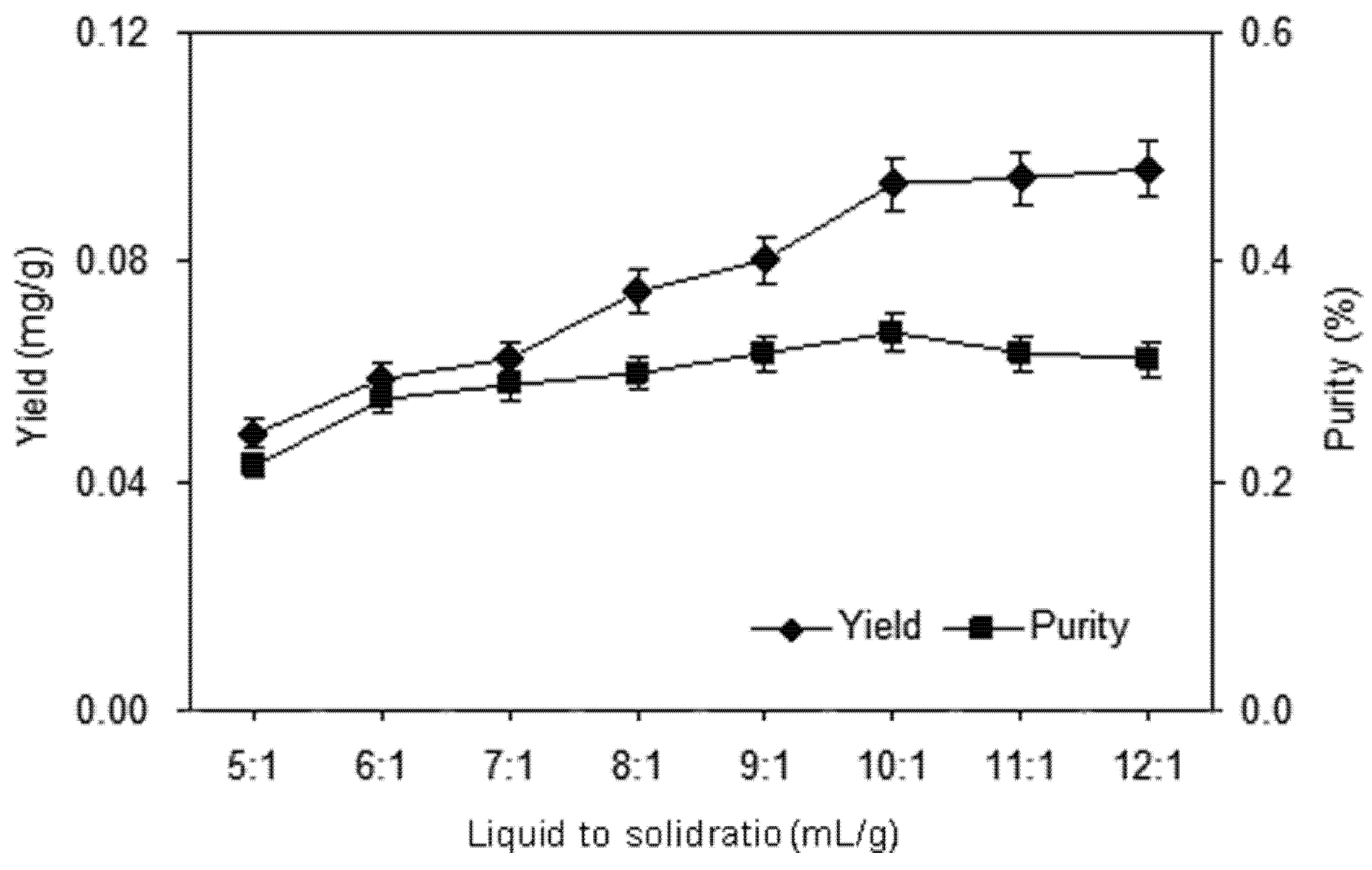
2.1.3. Effect of Liquid to Solid Ratio
2.1.4. Effect of Number of Extraction Cycles
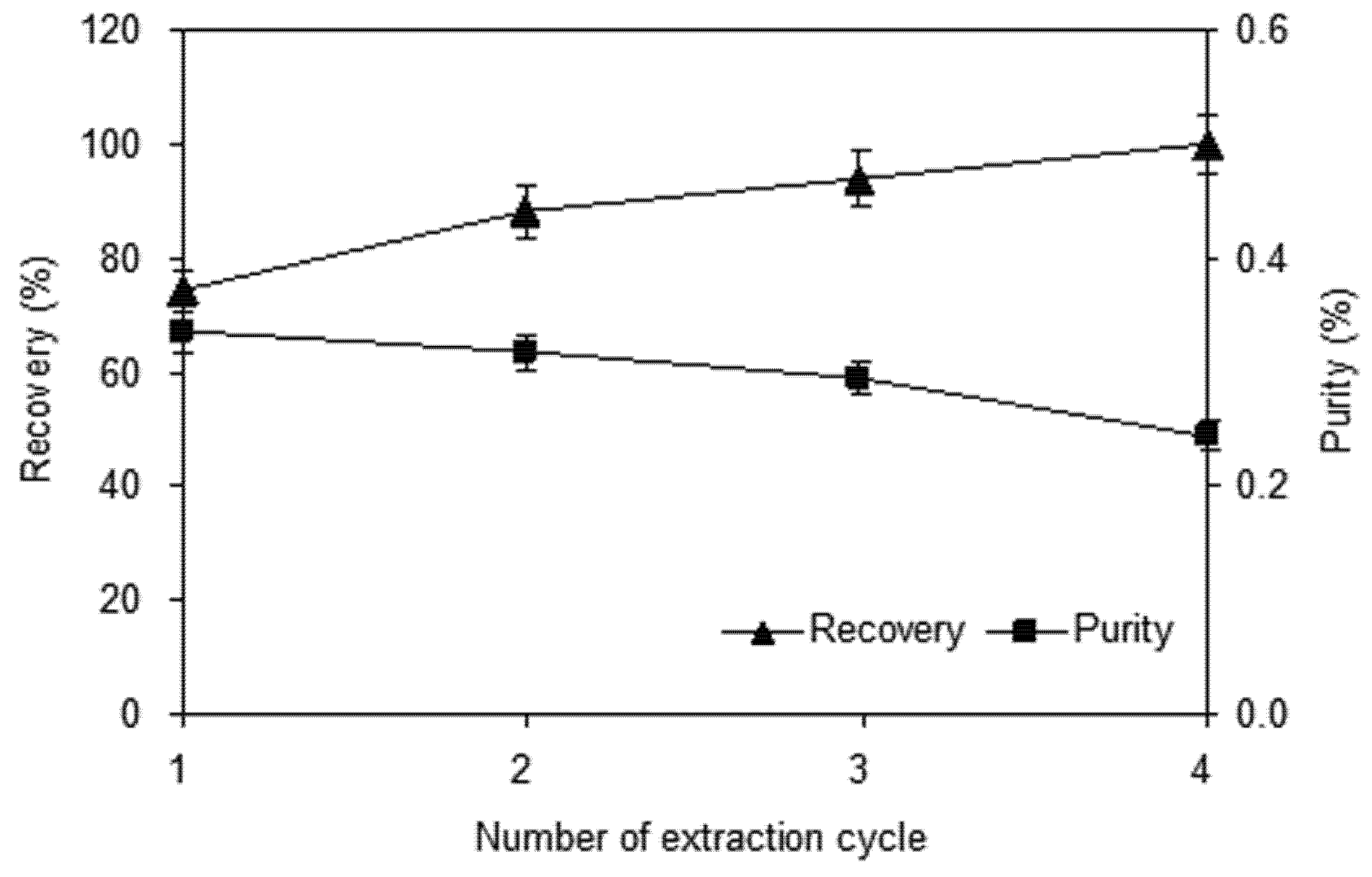
2.2. Parameter Optimization by Response Surface Methodology
2.2.1. Model Building and Statistical Analysis
| Run No. | Experimental Design | Dependent Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1: Homogenate time (min) | X2: Liquid to solid ratio (mL/g) | X3: Volume fraction of ethanol (%) | Yield of shikonin Y (mg/g) | Purity of shikonin P (%) | |
| 1 | 5 | 10 | 90 | 0.106 | 0.25 |
| 2 | 4 | 10 | 80 | 0.099 | 0.32 |
| 3 | 4 | 10 | 80 | 0.094 | 0.33 |
| 4 | 4 | 11 | 90 | 0.105 | 0.22 |
| 5 | 3 | 10 | 90 | 0.099 | 0.25 |
| 6 | 4 | 9 | 90 | 0.087 | 0.23 |
| 7 | 3 | 11 | 80 | 0.091 | 0.28 |
| 8 | 5 | 10 | 70 | 0.096 | 0.29 |
| 9 | 3 | 9 | 80 | 0.066 | 0.30 |
| 10 | 4 | 10 | 80 | 0.096 | 0.33 |
| 11 | 4 | 10 | 80 | 0.093 | 0.35 |
| 12 | 5 | 11 | 80 | 0.100 | 0.27 |
| 13 | 4 | 11 | 70 | 0.096 | 0.29 |
| 14 | 4 | 9 | 70 | 0.068 | 0.30 |
| 15 | 4 | 10 | 80 | 0.093 | 0.33 |
| 16 | 3 | 10 | 70 | 0.082 | 0.30 |
| 17 | 5 | 9 | 80 | 0.071 | 0.29 |
| Regression coefficients | Value | Sum of Squares | Degree of freedom | Mean Square | F value | Prob > F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (mg/g) | ||||||
| Model | 24.06 | 9 | 2.67 | 51.19 | <0.0001 | |
| β0 | 9.51 | |||||
| β1 | 0.45 | 1.64 | 1 | 1.64 | 31.44 | 0.0008 |
| β2 | 1.27 | 12.84 | 1 | 12.84 | 245.85 | <0.0001 |
| β3 | 0.69 | 3.79 | 1 | 3.79 | 72.57 | <0.0001 |
| β12 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.97 | 0.3569 |
| β13 | −0.18 | 0.13 | 1 | 0.13 | 2.55 | 0.1541 |
| β23 | −0.25 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.25 | 4.84 | 0.0638 |
| β11 | −0.33 | 0.46 | 1 | 0.46 | 8.72 | 0.0213 |
| β22 | −1.01 | 4.28 | 1 | 4.28 | 82.02 | <0.0001 |
| β33 | 0.40 | 0.68 | 1 | 0.68 | 13.02 | 0.0086 |
| Lack of Fit | 0.14 | 3 | 0.05 | 0.86 | 0.5294 | |
| Purity (%) | ||||||
| Model | 201.15 | 9 | 22.35 | 20.20 | 0.0003 | |
| β0 | 33.09 | |||||
| β1 | −0.54 | 2.30 | 1 | 2.30 | 2.08 | 0.1927 |
| β2 | −0.75 | 4.45 | 1 | 4.45 | 4.02 | 0.0849 |
| β3 | −2.89 | 66.75 | 1 | 66.75 | 60.31 | 0.0001 |
| β12 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.9700 |
| β13 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 1 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.6177 |
| β23 | −0.16 | 0.10 | 1 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.7750 |
| β11 | −1.80 | 13.65 | 1 | 13.65 | 12.33 | 0.0098 |
| β22 | −2.92 | 35.96 | 1 | 35.96 | 32.49 | 0.0007 |
| β33 | −3.95 | 65.72 | 1 | 65.72 | 59.38 | 0.0001 |
| Lack of Fit | 3.79 | 3 | 1.26 | 1.27 | 0.3963 | |
2.2.2. Interpretation of Response Surface Models
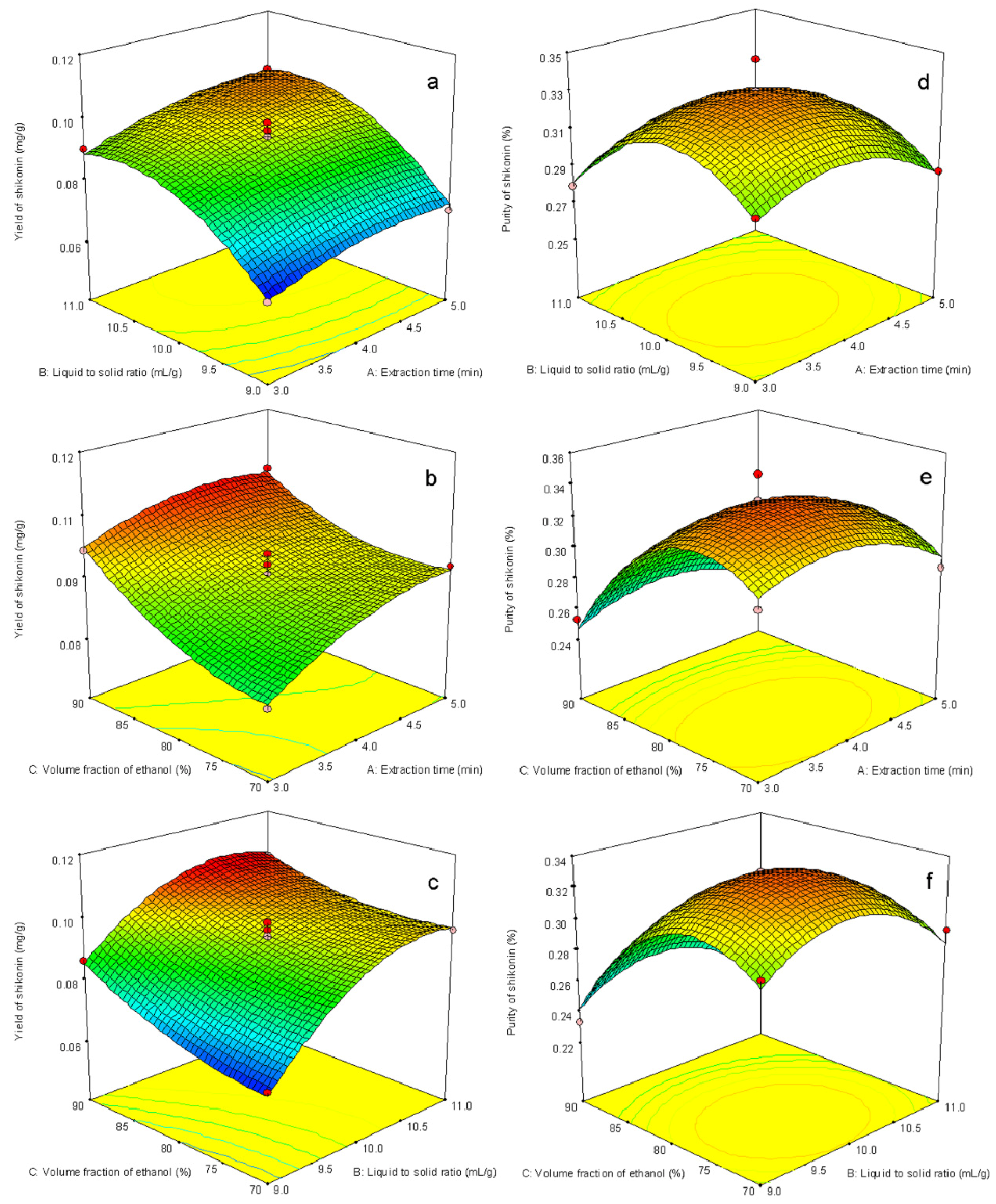
2.2.3. Verification Tests
2.3. Method Validation
2.3.1. Stability
| Concentration level | Initial concentration (μg/mL) | Recovered concentration after extraction (μg/mL) | RSD% (n = 3) | Average recovery (%) | Recovered concentration after 7 day (μg/mL) | RSD% (n = 3) | Average recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.37 | 99.51 | 0.07 | 0.64 | 87.77 |
| 2 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.33 | 98.18 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 90.91 |
2.3.2. Recovery
2.3.3. Repeatability
| Sample | Shikonin content of the sample determined (μg) | Amount of added shikonin standard (μg) | Amount of the sample determined with added shikonin standard (μg ) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 97 | 100 | 195 | 98.98 |
| 2 | 97 | 300 | 390 | 98.23 |
| 3 | 97 | 450 | 531 | 98.88 |
| Average | 98.67 |
2.4. Comparison of Different Extraction Method
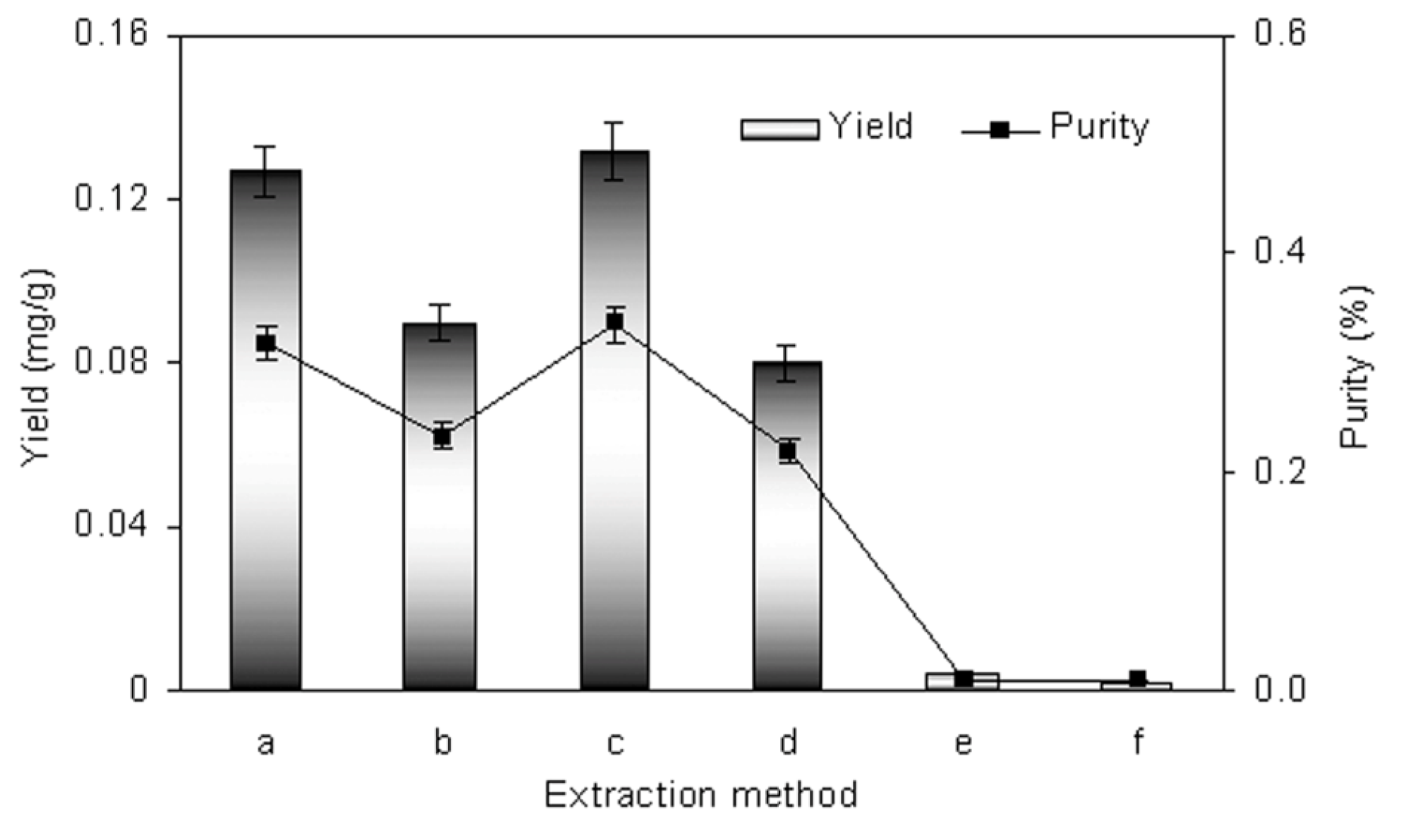
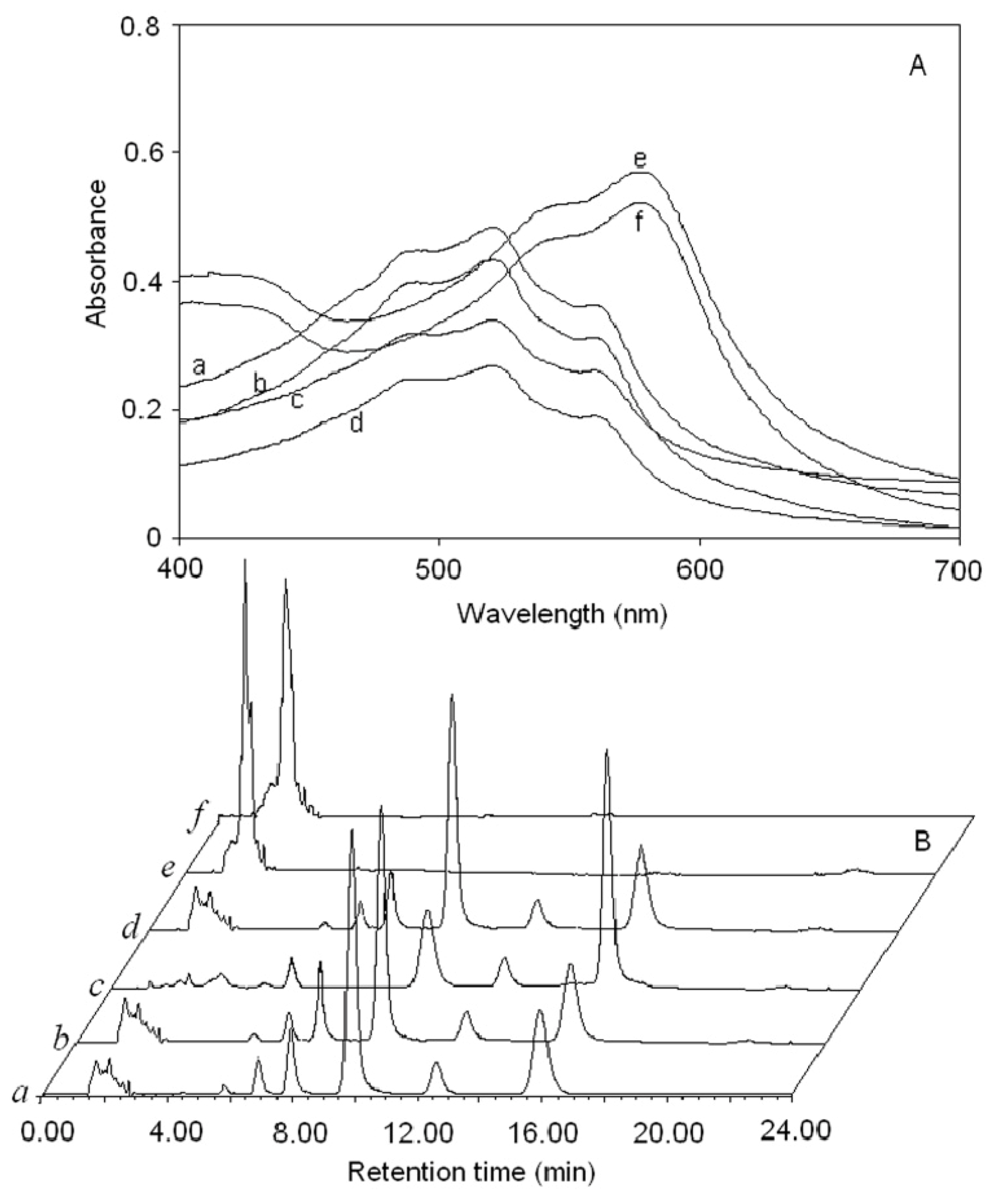
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. HPLC Quantitative Analysis
3.4. Spectrophotometric Qualitative Analysis
3.5. Extraction Efficiency of Shikonin Evaluation
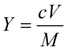
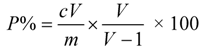
3.6. Homogenate Extraction Process
3.7. Optimization Homogenate Extraction by Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
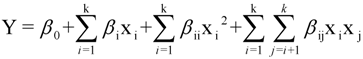
3.8. Stability, Recovery and Repeatability of Homogenate Extraction
3.9. Reference Extraction Procedure
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Sample Availability: Samples of the shikonin are available from the authors.
References
- Huang, Z.S.; Zhang, M.; Ma, L.; Gu, L.Q. A survey of chemical and pharmacologic studies on Zicao. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 1999, 12, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, T.; Gan, L.; Wang, T.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Q. Shikonin protects mouse brain against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through its antioxidant activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 643, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.C.; Syu, W.J.; Li, S.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, G.H.; Sun, C.M. Antimicrobial activities of naphthazarins from Arnebia euchroma. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, V.; Assimopoulou, A.; Couladouros, E.; Hepworth, D.; Nicolaou, K. The chemistry and biology of alkannin, shikonin, and related naphthazarin natural product. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 270–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, V.P.; Assimopoulou, A.N.; Samanidou, V.F.; Papadoyannis, I.N. Recent advances in chemistry, biology and biotechnology of alkannins and shikonins. Curr. Org. Chem. 2006, 10, 2123–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Qin, A.; Huang, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, N.; Li, S.; Wen, G.; Zhang, C.; Dong, W.; et al. Shikonin extracted from medicinal Chinese herbs exerts anti-inflammatory effect via proteasome inhibition. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 658, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Wang, C.N.; Lai, Y.T.; Kang, J.J.; Liao, J.W.; Chiang, B.L.; Chen, H.C.; Cheng, Y.W. Shikonin inhibits maturation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells and suppresses allergic airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 1496–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhou, Q. A novel antiestrogen agent shikonin inhibits estrogen-dependent gene transcription in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 121, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Li, W. Shikonin, a Chinese plant-derived naphthoquinone, induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through reactive oxygen species: A potential new treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Separation and preparation of shikonin from Lithospermum erythrorhizon. Nat. Prod. Res. Develop. 2004, 16, 239–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Xing, C.; Wang, C.; Li, C. Study on the supercritical CO2 extraction of alkannin from Alkanna tinctroia. Spec. Petrochem. 2000, 17, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, R.; Xie, M.; Liu, W. Response surface analysis study on naphthaquinonic compounds yield by supercritical CO2 extraction of Arnebia euchroma (Royle) John. Food Sci. 2004, 25, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F. Study on extracting technigue of shikonin from Arnebia euchroma Johnst optimized by orthogonal design. Med. World 2006, 8, 61–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. Optimization on extraction technology of shikonin from Arnebia euchroma by orthogonal design. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2005, 27, 351–353. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Qiao, X.; Zeng, X.; Du, Z. Optimization on microwave extraction technology of shikonin from Arnebia euchroma. Li Shizhen Med. Materia Medica Res. 2007, 18, 148–149. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Xu, W.; Cao, G. Optimization on microwave extraction technology of shikonin from Arnebia euchroma by orthogonal design. Her. Med. 2005, 24, 327–328. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.; Gao, X.; Lan, W.; Liu, L. Study on microwave extraction technology of shikonin. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2007, 29, 899–900. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Ge, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Effect of ultrasonic wave on the extraction of shikonin and its derivatives from Arnebia euchroma roots. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2005, 5, 680–683. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Song, F.; Wu, F.; Chen, H.; Li, S. Optimization of extraction process of Aruebia euchroma (Royle) Johnst. by orthogonal design. Tradit. Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 17, 289–291. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Qiu, M. Study on the extracting procedures of radix Arnebiaeseu Lithospermi in different preparations. Chin. Pharm. 1997, 8, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Ma, C.; Sui, X.; Yang, L.; Zu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, L. Preparation of shikonin by hydrolyzing ester derivatives using basic anion ion exchange resin as solid catalyst. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 36, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Manjkhola, S.; Dhar, U.; Joshi, M. Organogenesis embryogenesis, and synthetic seed production in Arnebia euchroma-a critically endangered medicinal plant of the Himalaya. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Plant 2005, 41, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yang, L. Homogenate extraction technology of camptothecine and hydroxycamptothecin from Camptotheca acuminata leaves. J. For. Res. 2009, 20, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Jia, J.; Zu, Y.; Niu, H.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y. Homogenate extraction of vinblastine, vindoline and catharanthine from fresh Catharanthus roseus. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 2008, 22, 768–773. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, C.; Shi, Q.; Jiao, Y. Homogenate extraction of solanesol from fresh tobacco leaves. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 2005, 19, 757–761. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Zu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Hou, C. Homogenated extraction of total flavonoids from fruits of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.). Chem. Ind. Forest Prod. 2006, 26, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Lin, H.; Xie, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, P. Homogenate extraction of isoflavones from soybean meal by orthogonal design. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2011, 70, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Mang, Y.; Shen, F.; Xie, J.; Su, W. Homogenate extraction of gardenia yellow pigment from Gardenia Jasminoides Ellis fruit using response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, K.; Ramalingam, S.; Krishnan, S.; Balu, K. Application of response surface methodology to optimize the process variables for Reactive Red and Acid Brown dye removal using a novel adsorbent. Dyes Pigments 2006, 70, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Ma, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Sui, X.; Zhao, C.; Zu, Y. Optimization of Shikonin Homogenate Extraction from Arnebia euchroma Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules 2013, 18, 466-481. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010466
Liu T, Ma C, Yang L, Wang W, Sui X, Zhao C, Zu Y. Optimization of Shikonin Homogenate Extraction from Arnebia euchroma Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules. 2013; 18(1):466-481. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010466
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tingting, Chunhui Ma, Lei Yang, Wenjie Wang, Xiaoyu Sui, Chunjian Zhao, and Yuangang Zu. 2013. "Optimization of Shikonin Homogenate Extraction from Arnebia euchroma Using Response Surface Methodology" Molecules 18, no. 1: 466-481. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010466
APA StyleLiu, T., Ma, C., Yang, L., Wang, W., Sui, X., Zhao, C., & Zu, Y. (2013). Optimization of Shikonin Homogenate Extraction from Arnebia euchroma Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules, 18(1), 466-481. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010466







