Semi-Synthesis of Labeled Proteins for Spectroscopic Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Total Synthesis of Proteins: SPPS and Chemical Ligation
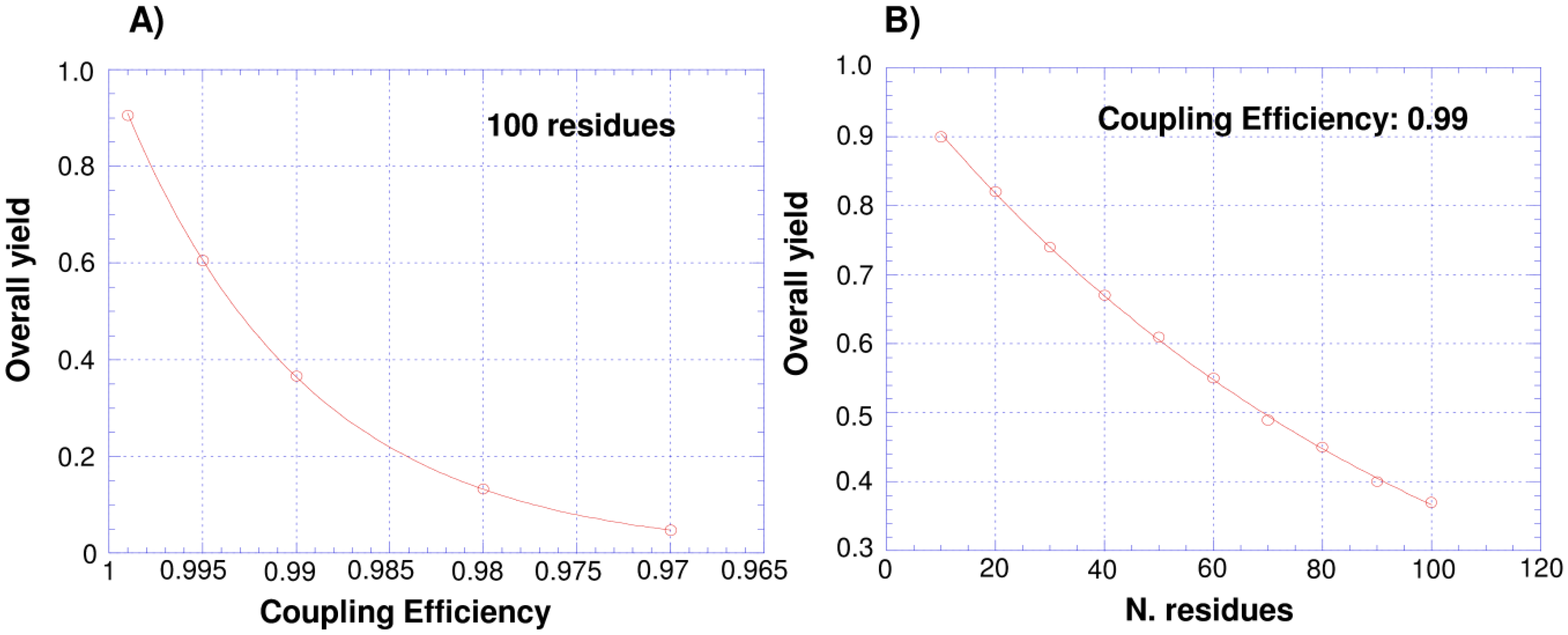

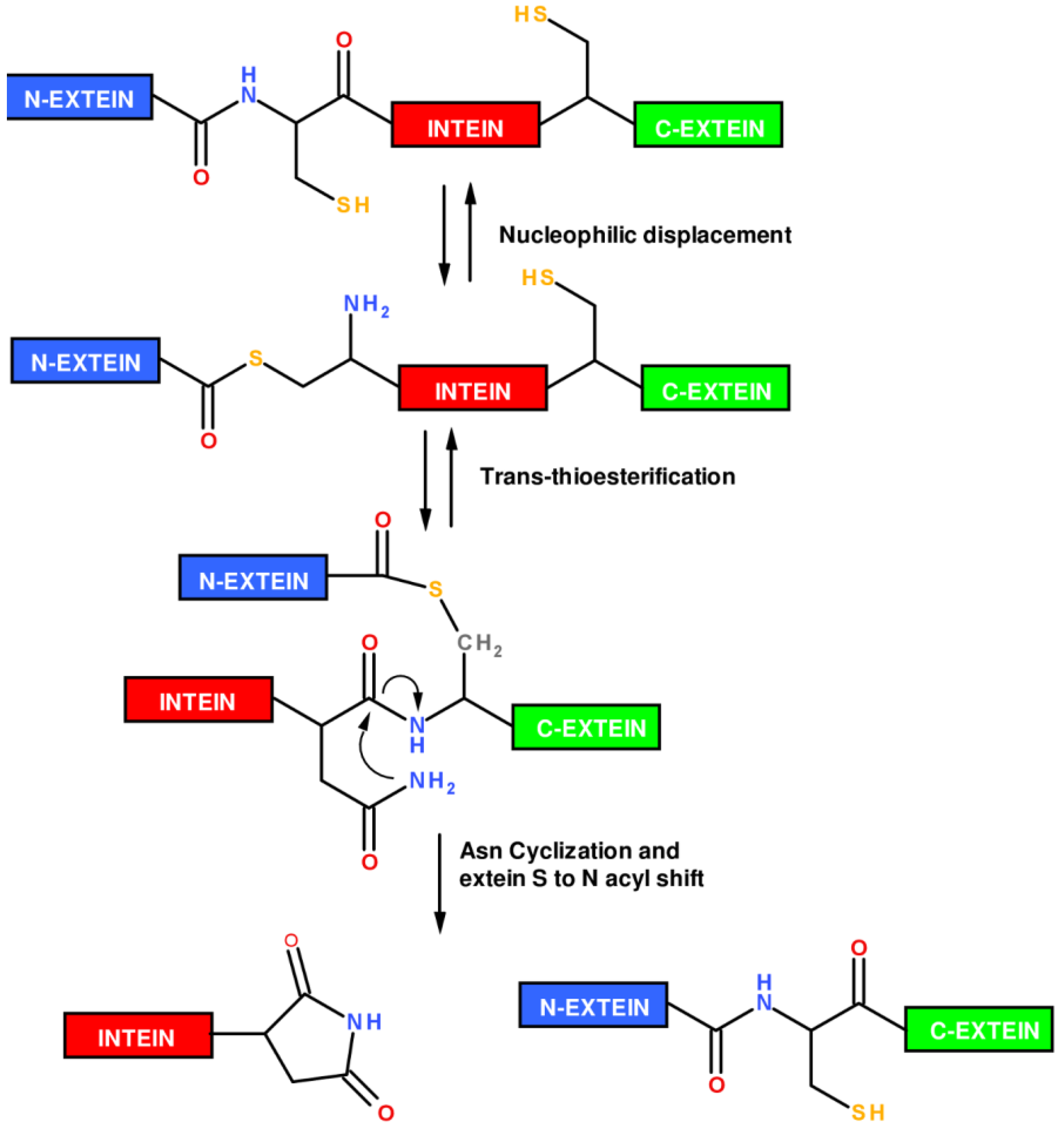
1.2. Protein Synthesis via Intein Chemistry (EPL and PTS)
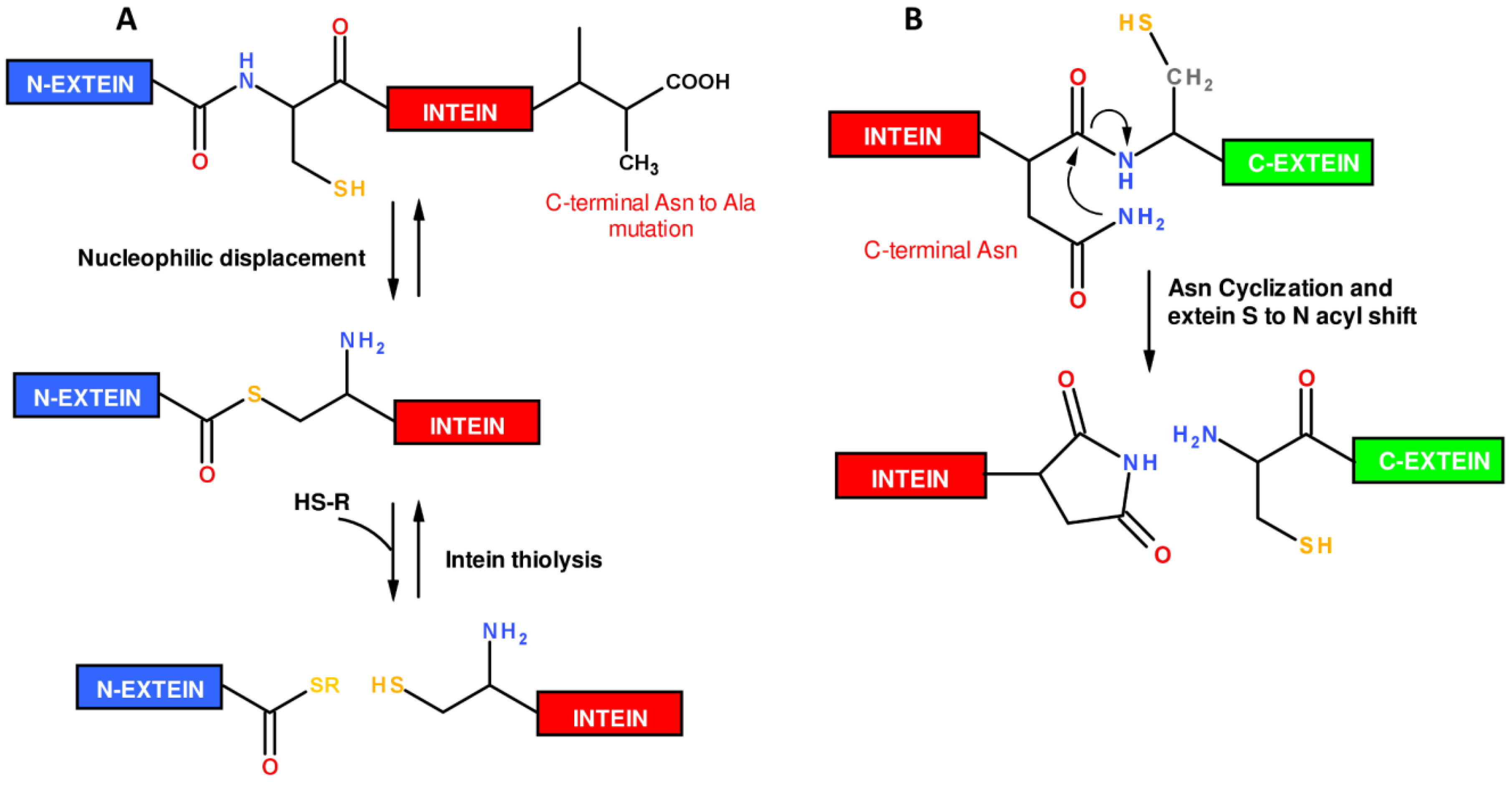
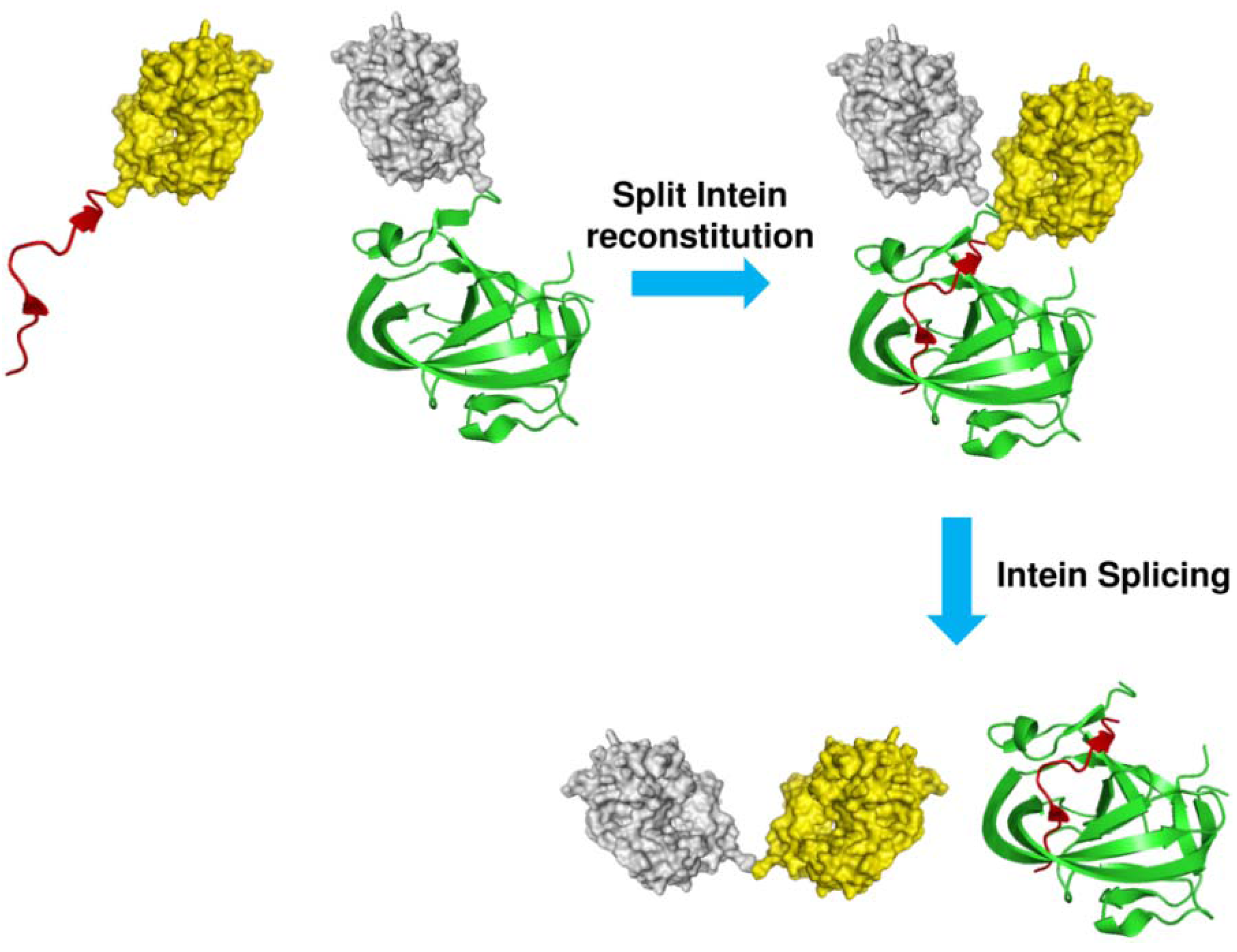
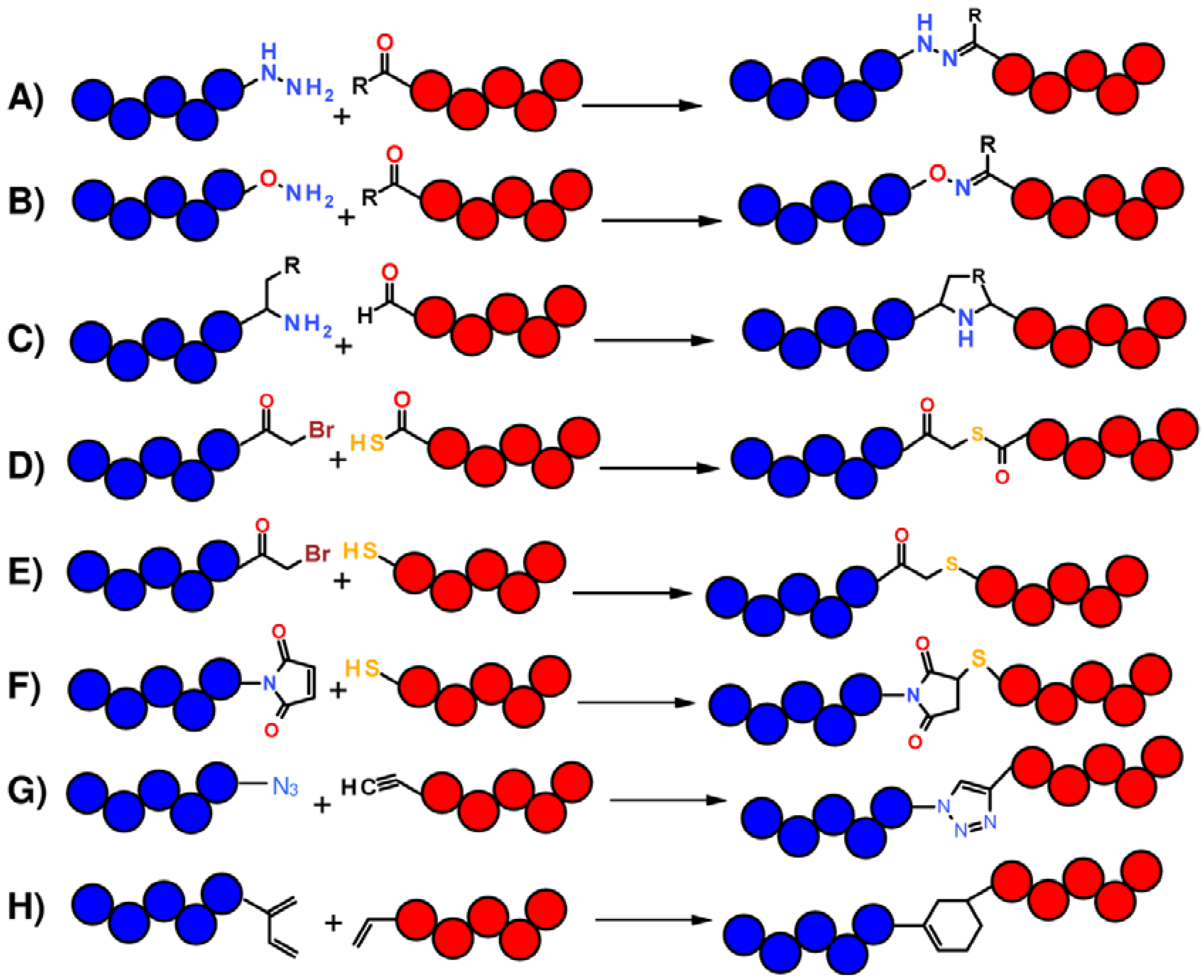
2. Fluorescent Labeling
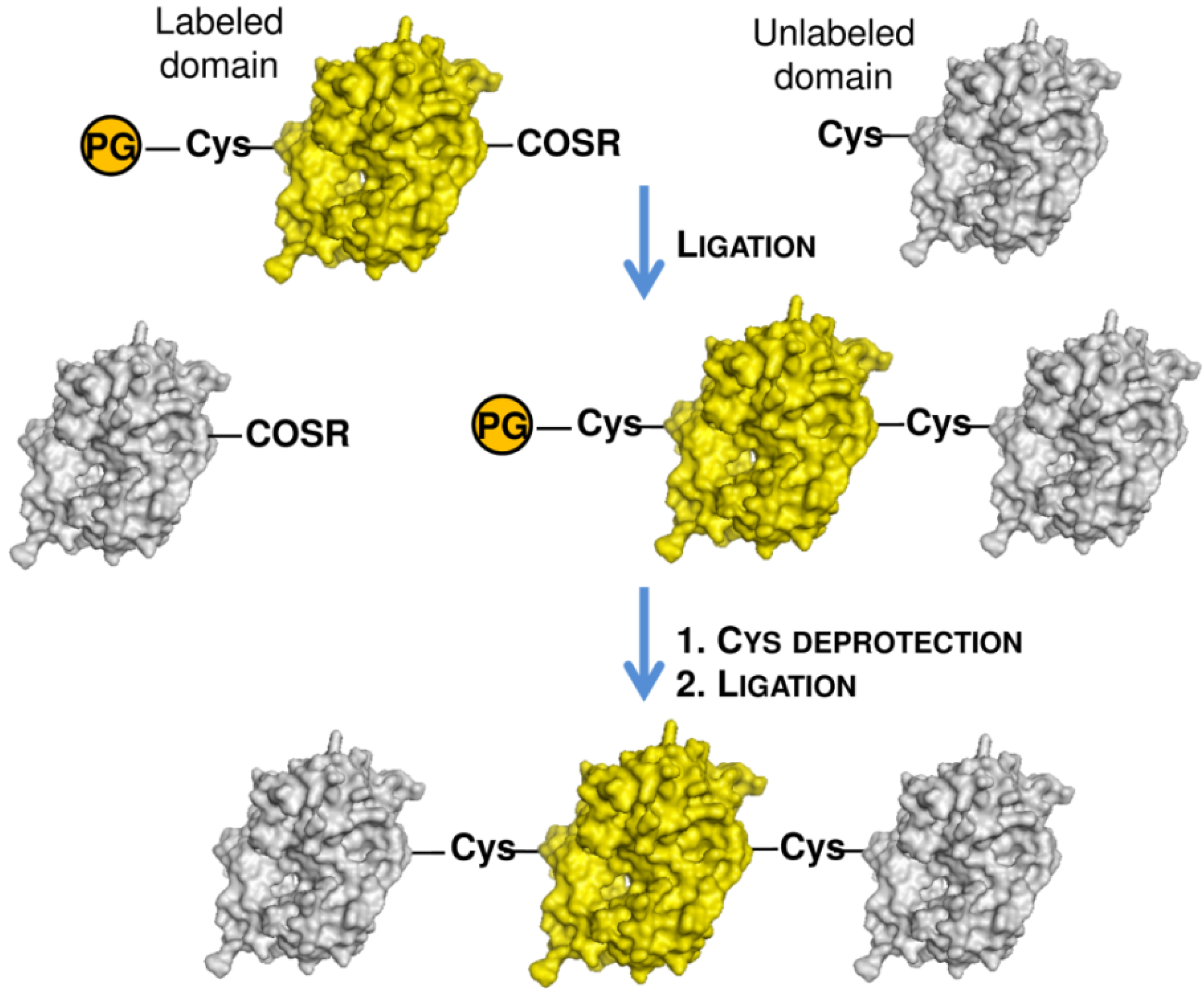
2.1. Protein Labeling with Fluorescent Probes for FRET Studies
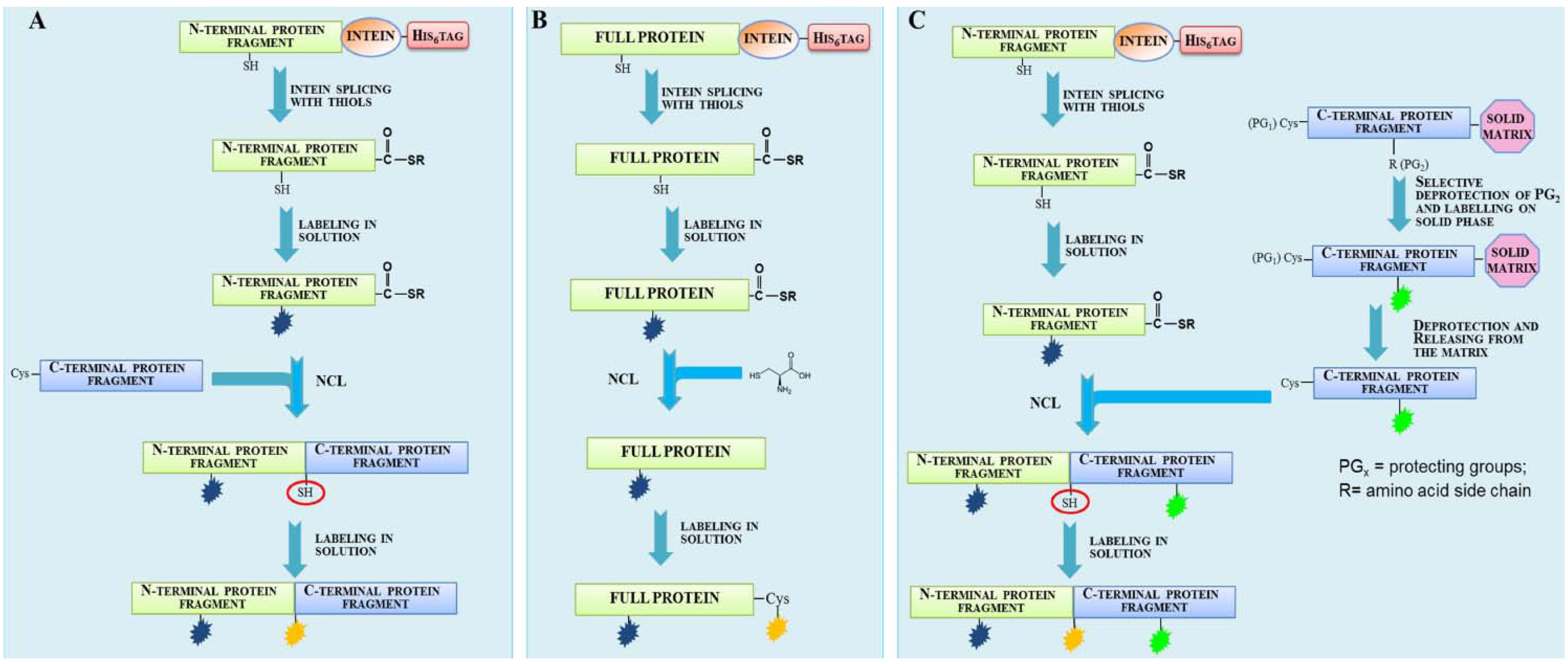
2.2. Protein Labeling with Fluorescent Probes for Fluorescence Microscopy in Living Cells
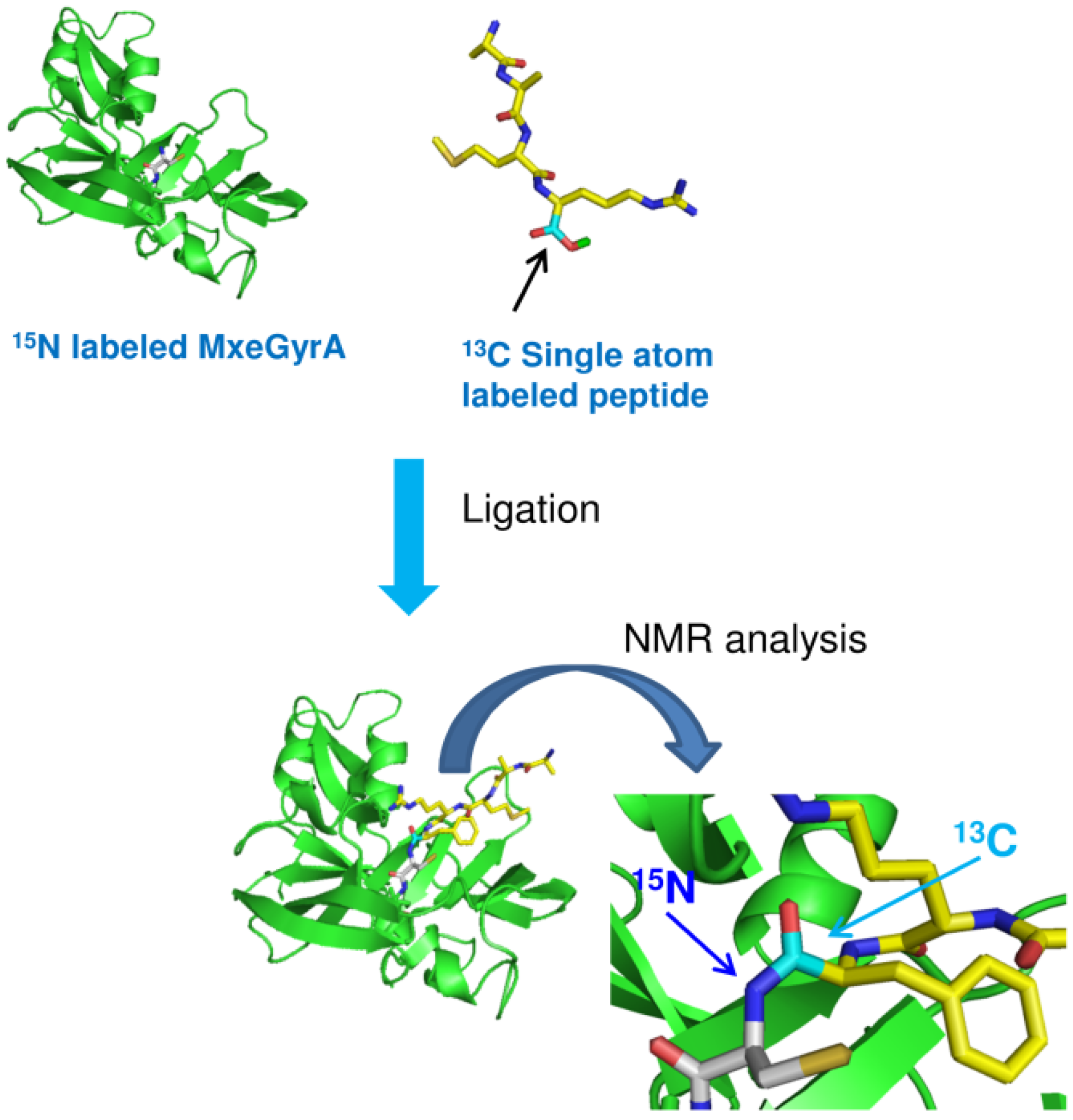
3. Isotopic Labeling
4. Conclusions
References
- Stephanopoulos, N.; Francis, M.B. Choosing an effective protein bioconjugation strategy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basle, E.; Joubert, N.; Pucheault, M. Protein chemical modification on endogenous amino acids. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhaya, S.; Abu Bakar, F.B.; Yao, S.Q. Use of intein-mediated protein ligation strategies for the fabrication of functional protein arrays. Meth. Enzymol. 2009, 462, 195–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinner, M.J.; Johnsson, K. How to obtain labeled proteins and what to do with them. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 766–776. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, S.B. Total chemical synthesis of proteins. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, V.; Muir, T.W. Protein ligation: An enabling technology for the biophysical analysis of proteins. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 429–438. [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield, B.R. Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis. I. The synthesis of a tetrapeptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnolzer, M.; Kent, S.B. Constructing proteins by dovetailing unprotected synthetic peptides: Backbone-engineered HIV protease. Science 1992, 256, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.F.; Tam, J.P. Peptide segment ligation strategy without use of protecting groups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6584–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.F.; Tam, J.P. Chemical ligation approach to form a peptide bond between unprotected peptide segments. Concept and model study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 4149–4153. [Google Scholar]
- Robey, F.A.; Fields, R.L. Automated synthesis of N-bromoacetyl-modified peptides for the preparation of synthetic peptide polymers, peptide-protein conjugates, and cyclic peptides. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 177, 373–377. [Google Scholar]
- Smyth, D.G.; Blumenfeld, O.O.; Konigsberg, W. Reactions of N-Ethylmaleimide with Peptides and Amino Acids. Biochem. J. 1964, 91, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Rostovtsev, V.V.; Green, L.G.; Fokin, V.V.; Sharpless, K.B. A stepwise huisgen cycloaddition process: Copper(I)-catalyzed regioselective “ligation” of azides and terminal alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2002, 41, 2596–2599. [Google Scholar]
- Tornoe, C.W.; Christensen, C.; Meldal, M. Peptidotriazoles on solid phase: [1,2,3]-Triazoles by regiospecific copper(i)-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions of terminal alkynes to azides. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araujo, A.D.; Palomo, J.M.; Cramer, J.; Seitz, O.; Alexandrov, K.; Waldmann, H. Diels-Alder ligation of peptides and proteins. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 6095–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, P.E.; Kent, S.B. Synthesis of native proteins by chemical ligation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 923–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirksen, A.; Dawson, P.E. Expanding the scope of chemoselective peptide ligations in chemical biology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, P.E.; Muir, T.W.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Kent, S.B. Synthesis of proteins by native chemical ligation. Science 1994, 266, 776–779. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, B.L.; Kiessling, L.L.; Raines, R.T. Staudinger ligation: A peptide from a thioester and azide. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1939–1941. [Google Scholar]
- Muir, T.W. Semisynthesis of proteins by expressed protein ligation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 249–289. [Google Scholar]
- Muir, T.W.; Sondhi, D.; Cole, P.A. Expressed protein ligation: A general method for protein engineering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6705–6710. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.Q.; Perler, F.B. The mechanism of protein splicing and its modulation by mutation. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 5146–5153. [Google Scholar]
- Flavell, R.R.; Muir, T.W. Expressed protein ligation (EPL) in the study of signal transduction, ion conduction, and chromatin biology. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowburn, D.; Muir, T.W. Segmental isotopic labeling using expressed protein ligation. Meth. Enzymol. 2001, 339, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaco, B.; Pensato, S.; D’Andrea, L.D.; Benedetti, E.; Romanelli, A. Semisynthesis of dimeric proteins by expressed protein ligation. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 1955–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Hamilton, B.S.; Tolbert, T.J. Synthesis of N-terminally linked protein and peptide dimers by native chemical ligation. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southworth, M.W.; Amaya, K.; Evans, T.C.; Xu, M.Q.; Perler, F.B. Purification of proteins fused to either the amino or carboxy terminus of the Mycobacterium xenopi gyrase A intein. Biotechniques 1999, 27, 110–114,116,118–120. [Google Scholar]
- Telenti, A.; Southworth, M.; Alcaide, F.; Daugelat, S.; Jacobs, W.R., Jr.; Perler, F.B. The Mycobacterium xenopi GyrA protein splicing element: Characterization of a minimal intein. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 6378–6382. [Google Scholar]
- Valiyaveetil, F.I.; MacKinnon, R.; Muir, T.W. Semisynthesis and folding of the potassium channel KcsA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9113–9120. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.C.; Kent, S.B. Insights into the mechanism and catalysis of the native chemical ligation reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6640–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathys, S.; Evans, T.C.; Chute, I.C.; Wu, H.; Chong, S.; Benner, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Xu, M.Q. Characterization of a self-splicing mini-intein and its conversion into autocatalytic N- and C-terminal cleavage elements: Facile production of protein building blocks for protein ligation. Gene 1999, 231, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, J.; Yao, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.N. Use of Ssp dnaB derived mini-intein as a fusion partner for production of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 43, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esipov, R.S.; Stepanenko, V.N.; Chupova, L.A.; Boyarskikh, U.A.; Filipenko, M.L.; Miroshnikov, A.I. Production of recombinant human epidermal growth factor using Ssp dnaB mini-intein system. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 61, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.S.; Yan, J.; Shi, G.; Xu, Q.; Chen, S.C.; Tian, Y.W. Production of native protein by using Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 DnaB mini-intein in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 40, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hu, Z.; Liu, X.Q. Protein trans-splicing by a split intein encoded in a split DnaE gene of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9226–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, J.H.; Zhou, K.; Volkmann, G.; Liu, X.Q. Novel split intein for trans-splicing synthetic peptide onto C terminus of protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6194–6199. [Google Scholar]
- Aranko, A.S.; Zuger, S.; Buchinger, E.; Iwai, H. In vivo and in vitro protein ligation by naturally occurring and engineered split DnaE inteins. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5185. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, C.; Pfeiff, M.; Linne, U.; Mootz, H.D. Ligation of a synthetic peptide to the N terminus of a recombinant protein using semisynthetic protein trans-splicing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2006, 45, 5218–5221. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.Q. Synthetic two-piece and three-piece split inteins for protein trans-splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 35281–35286. [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Patterson, G.H. Development and use of fluorescent protein markers in living cells. Science 2003, 300, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, R.Y. The green fluorescent protein. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 509–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaner, N.C.; Steinbach, P.A.; Tsien, R.Y. A guide to choosing fluorescent proteins. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 905–909. [Google Scholar]
- Tsien, R.Y. Imagining imaging’s future. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, SS16–SS21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Campbell, R.E.; Ting, A.Y.; Tsien, R.Y. Creating new fluorescent probes for cell biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, D.S.; Srinivasan, R.; Chen, G.Y.; Yao, S.Q. Expanded utility of the reaction. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 4664–4672. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.; Ting, A.Y. Site-specific labeling of proteins with small molecules in live cells. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.E.; Schumacher, F.F.; Ryan, C.P.; Tedaldi, L.M.; Papaioannou, D.; Waksman, G.; Caddick, S.; Baker, J.R. Protein modification, bioconjugation, and disulfide bridging using bromomaleimides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, M.W.; Yang, L.L.; Lin, J.C.; Lim, T.S.; Fann, W.; Chen, R.P. Strategy for efficient site-specific FRET-dye labeling of ubiquitin. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1124–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.J.; Conrad, D.W.; Cuneo, M.J.; Hellinga, H.W. Orthogonal site-specific protein modification by engineering reversible thiol protection mechanisms. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, B.A.; Adams, S.R.; Tsien, R.Y. Specific covalent labeling of recombinant protein molecules inside live cells. Science 1998, 281, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, S.R.; Campbell, R.E.; Gross, L.A.; Martin, B.R.; Walkup, G.K.; Yao, Y.; Llopis, J.; Tsien, R.Y. New biarsenical ligands and tetracysteine motifs for protein labeling in vitro and in vivo: Synthesis and biological applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6063–6076. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Chen, B.; Squier, T.C.; Mayer, M.U. CrAsH: A biarsenical multi-use affinity probe with low non-specific fluorescence. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2006, 2006, 2601–2603. [Google Scholar]
- Halo, T.L.; Appelbaum, J.; Hobert, E.M.; Balkin, D.M.; Schepartz, A. Selective recognition of protein tetraserine motifs with a cell-permeable, pro-fluorescent bis-boronic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 438–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchinomiya, S.H.; Nonaka, H.; Fujishima, S.H.; Tsukiji, S.; Ojida, A.; Hamachi, I. Site-specific covalent labeling of His-tag fused proteins with a reactive Ni(II)-NTA probe. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2009, 2009, 5880–5882. [Google Scholar]
- Strunk, J.J.; Gregor, I.; Becker, Y.; Lamken, P.; Lata, S.; Reichel, A.; Enderlein, J.; Piehler, J. Probing protein conformations by in situ non-covalent fluorescence labeling. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojida, A.; Honda, K.; Shinmi, D.; Kiyonaka, S.; Mori, Y.; Hamachi, I. Oligo-Asp tag/Zn(II) complex probe as a new pair for labeling and fluorescence imaging of proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 10452–10459. [Google Scholar]
- Keppler, A.; Gendreizig, S.; Gronemeyer, T.; Pick, H.; Vogel, H.; Johnsson, K. A general method for the covalent labeling of fusion proteins with small molecules in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, A.; Juillerat, A.; Heinis, C.; Correa, I.R., Jr.; Kindermann, M.; Beaufils, F.; Johnsson, K. An engineered protein tag for multiprotein labeling in living cells. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, G.V.; Encell, L.P.; McDougall, M.G.; Hartzell, D.D.; Karassina, N.; Zimprich, C.; Wood, M.G.; Learish, R.; Ohana, R.F.; Urh, M.; et al. HaloTag: A novel protein labeling technology for cell imaging and protein analysis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antos, J.M.; Chew, G.L.; Guimaraes, C.P.; Yoder, N.C.; Grotenbreg, G.M.; Popp, M.W.; Ploegh, H.L. Site-specific N- and C-terminal labeling of a single polypeptide using sortases of different specificity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10800–10801. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.W.; Ting, A.Y. Transglutaminase-catalyzed site-specific conjugation of small-molecule probes to proteins in vitro and on the surface of living cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 4542–4543. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.; Howarth, M.; Lin, W.; Ting, A.Y. Site-specific labeling of cell surface proteins with biophysical probes using biotin ligase. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivero-Pol, L.; George, N.; Krumm, H.; Johnsson, K.; Johnsson, N. Multicolor imaging of cell surface proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12770–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heal, W.P.; Jovanovic, B.; Bessin, S.; Wright, M.H.; Magee, A.I.; Tate, E.W. Bioorthogonal chemical tagging of protein cholesterylation in living cells. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2011, 47, 4081–4083. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, G.J.; Muir, T.W. Peptide ligation and its application to protein engineering. Chem. Biol. 1999, 6, R247–R256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, G.J.; Muir, T.W. Generation of a dual-labeled fluorescence biosensor for Crk-II phosphorylation using solid-phase expressed protein ligation. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, R.M.; Cotton, G.J.; Chang, E.J.; Vidal, E.; Veach, D.; Bornmann, W.; Muir, T.W. Fluorescent monitoring of kinase activity in real time: Development of a robust fluorescence-based assay for Abl tyrosine kinase activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 3091–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, V.; Cho, J.; Trester-Zedlitz, M.; Kowalik, L. Domain-specific incorporation of noninvasive optical probes into recombinant proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 14004–14012. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, J.; Kapanidis, A.N.; Mekler, V.; Kortkhonjia, E.; Ebright, Y.W.; Ebright, R.H. Translocation of sigma(70) with RNA polymerase during transcription: Fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay for movement relative to DNA. Cell 2001, 106, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekler, V.; Kortkhonjia, E.; Mukhopadhyay, J.; Knight, J.; Revyakin, A.; Kapanidis, A.N.; Niu, W.; Ebright, Y.W.; Levy, R.; Ebright, R.H. Structural organization of bacterial RNA polymerase holoenzyme and the RNA polymerase-promoter open complex. Cell 2002, 108, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Elangwe, E.N.; Asher, S.; Zheng, Y.G. A dual-mode fluorescence strategy for screening HAT modulators. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibner, K.A.; Zhang, Z.; Cole, P.A. Merging fluorescence resonance energy transfer and expressed protein ligation to analyze protein-protein interactions. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 317, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.F.; Seidel, R.; Jahnz, M.; Bacia, K.; Niederhausen, T.; Alexandrov, K.; Schwille, P.; Goody, R.S.; Engelhard, M. C-terminal fluorescence labeling of proteins for interaction studies on the single-molecule level. Chembiochem 2006, 7, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Sun, H.; Itzen, A.; Triola, G.; Waldmann, H.; Goody, R.S.; Wu, Y.W. One-pot dual-labeling of a protein by two chemoselective reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 8287–8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Sun, H.; Wu, Y.W.; Triola, G.; Waldmann, H.; Goody, R.S. A highly efficient strategy for modification of proteins at the C terminus. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 9417–9421. [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert, T.J.; Wong, C.H. New methods for proteomic research: Preparation of proteins with N-terminal cysteines for labeling and conjugation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2002, 41, 2171–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovenko, A.; Rostkova, E.; Merzlyak, E.; Hillebrand, A.M.; Thomä, N.H.; Goody, R.S.; Alexandrov, K. Semi-synthetic Rab proteins as tools for studying intermolecular interactions. FEBS Lett. 2000, 468, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.W.; Goody, R.S.; Alexandrov, K. Intein-mediated construction of a library of fluorescent Rab GTPase probes. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 2813–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, L.; Cortajarena, A.L.; Romanelli, A.; Regan, L.; D’Andrea, L.D. Site-specific protein double labeling by expressed protein ligation: Applications to repeat proteins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Deniz, A.A.; Laurence, T.A.; Beligere, G.S.; Dahan, M.; Martin, A.B.; Chemla, D.S.; Dawson, P.E.; Schultz, P.G.; Weiss, S. Single-molecule protein folding: Diffusion fluorescence resonance energy transfer studies of the denaturation of chymotrypsin inhibitor 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5179–5184. [Google Scholar]
- Appleby-Tagoe, J.H.; Thiel, I.V.; Wang, Y.; Mootz, H.D.; Liu, X.Q. Highly efficient and more general cis- and trans-splicing inteins through sequential directed evolution. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 34440–34447. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.Y.; Yang, W.Y. Site-specific two-color protein labeling for FRET studies using split inteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11644–11645. [Google Scholar]
- Zettler, J.; Schütz, V.; Mootz, H.D. The naturally split Npu DnaE intein exhibits an extraordinarily high rate in the protein trans-splicing reaction. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.H.; Dann, G.P.; Vila-Perelló, M.; Liu, Z.; Muir, T.W. Ultrafast protein splicing is common among cyanobacterial split inteins: Implications for protein engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11338–11341. [Google Scholar]
- Bellmann-Sickert, K.; Baumann, L.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Selective labelling of stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha with carboxyfluorescein to study receptor internalisation. J. Pept. Sci. 2010, 16, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellois, J.P.; Hahn, M.E.; Muir, T.W. Simultaneous triggering of protein activity and fluorescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7170–7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.E.; Pellois, J.P.; Vila-Perello, M.; Muir, T.W. Tunable photoactivation of a post-translationally modified signaling protein and its unmodified counterpart in live cells. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 2100–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisemartin, L.; Chinestra, P.; Favre, G.; Blonski, C.; Faye, J.C. Synthesis and application of a N-1' fluorescent biotinyl derivative inducing the specific carboxy-terminal dual labeling of a novel RhoB-selective scFv. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 847–855. [Google Scholar]
- Schuler, B.; Pannell, L.K. Specific labeling of polypeptides at amino-terminal cysteine residues using Cy5-benzyl thioester. Bioconjug. Chem. 2002, 13, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, D.S.; Srinivasan, R.; Uttamchandani, M.; Chen, G.Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yao, S.Q. Cell-permeable small molecule probes for site-specific labeling of proteins. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2003, 2003, 2870–2871. [Google Scholar]
- Gentle, I.E.; de Souza, D.P.; Baca, M. Direct production of proteins with N-terminal cysteine for site-specific conjugation. Bioconjug. Chem. 2004, 15, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giriat, I.; Muir, T.W. Protein semi-synthesis in living cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7180–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, T.; Mootz, H.D. Modification of transmembrane and GPI-anchored proteins on living cells by efficient protein trans-splicing using the Npu DnaE intein. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2011, 47, 3063–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Ayers, B.; Cowburn, D.; Muir, T.W. Chemical ligation of folded recombinant proteins: Segmental isotopic labeling of domains for NMR studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 388–393. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Liu, D.; Cowburn, D. Abl kinase constructs expressed in bacteria: Facilitation of structural and functional studies including segmental labeling by expressed protein ligation. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 1878–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarero, J.A.; Shekhtman, A.; Campbell, E.A.; Chlenov, M.; Gruber, T.M.; Bryant, D.A.; Darst, S.A.; Cowburn, D.; Muir, T.W. Autoregulation of a bacterial sigma factor explored by using segmental isotopic labeling and NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8536–8541. [Google Scholar]
- Clerico, E.M.; Zhuravleva, A.; Smock, R.G.; Gierasch, L.M. Segmental isotopic labeling of the Hsp70 molecular chaperone DnaK using expressed protein ligation. Biopolymers 2010, 94, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, F.; Henning, A.; Oberstrass, F.C.; Hargous, Y.; Auweter, S.D.; Erat, M.; Allain, F.H. Structure of the two most C-terminal RNA recognition motifs of PTB using segmental isotope labeling. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Skrisovska, L.; Allain, F.H. Improved segmental isotope labeling methods for the NMR study of multidomain or large proteins: Application to the RRMs of Npl3p and hnRNP L. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 375, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J. A segmental labeling strategy for unambiguous determination of domain-domain interactions of large multi-domain proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 2011, 50, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. An efficient on-column expressed protein ligation strategy: Application to segmental triple labeling of human apolipoprotein E3. Protein Sci. 2008, 17, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, C.A.; Spasser, L.; Bavikar, S.N.; Brik, A.; Fushman, D. Segmental isotopic labeling of ubiquitin chains to unravel monomer-specific molecular behavior. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 11210–11214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanelli, A.; Shekhtman, A.; Cowburn, D.; Muir, T.W. Semisynthesis of a segmental isotopically labeled protein splicing precursor: NMR evidence for an unusual peptide bond at the N-extein-intein junction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6397–6402. [Google Scholar]
- Frutos, S.; Goger, M.; Giovani, B.; Cowburn, D.; Muir, T.W. Branched intermediate formation stimulates peptide bond cleavage in protein splicing. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 527–533. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, L.L.; Marshall, G.R.; Crocker, E.; Smith, S.O.; Baranski, T.J. Motion of carboxyl terminus of Galpha is restricted upon G protein activation. A solution NMR study using semisynthetic Galpha subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31019–31026. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschke, U.K.; Silberstein, J.; Muir, T.W. Protein engineering by expressed protein ligation. Meth. Enzymol. 2000, 328, 478–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagöz, G.E; Sinnige, T.; Hsieh, O.; Rüdiger, S.G.D. Expressed protein ligation for a large dimeric protein. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2011, 24, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, S.D.; Woys, A.M.; Buchanan, L.E.; Bixby, E.; Decatur, S.M.; Zanni, M.T. Two-dimensional IR spectroscopy and segmental 13C labeling reveals the domain structure of human γD-crystallin amyloid fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 128, 3329–3334. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, S.D.; Decatur, S.M.; Zanni, M.T. Structural and Sequence Analysis of the Human γD-Crystallin Amyloid Fibril Core Using 2D IR Spectroscopy, Segmental (13)C Labeling, and Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18410–18416. [Google Scholar]
- Busche, A.E.; Aranko, A.S.; Talebzadeh-Farooji, M.; Bernhard, F.; Dotsch, V.; Iwai, H. Segmental isotopic labeling of a central domain in a multidomain protein by protein trans-splicing using only one robust DnaE intein. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 6128–6131. [Google Scholar]
- Minato, Y.; Ueda, T.; Machiyama, A.; Shimada, I.; Iwai, H. Segmental isotopic labeling of a 140 kDa dimeric multi-domain protein CheA from Escherichia coli by expressed protein ligation and protein trans-splicing. J. Biomol. NMR 2012, 53, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, H.; Tsujimoto, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Yoshida, M.; Akutsu, H. Conformational change of H+-ATPase beta monomer revealed on segmental isotope labeling NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 16632–16638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, H.; Kajiwara, N.; Iwabuchi, T.; Izumi, K.; Yoshida, M.; Akutsu, H. Stepwise propagation of the ATP-induced conformational change of the F1-ATPase beta subunit revealed by NMR. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 2374–2382. [Google Scholar]
- Muona, M.; Aranko, A.S.; Iwai, H. Segmental isotopic labelling of a multidomain protein by protein ligation by protein trans-splicing. Chembiochem 2008, 9, 2958–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muona, M.; Aranko, A.S.; Raulinaitis, V.; Iwai, H. Segmental isotopic labeling of multi-domain and fusion proteins by protein trans-splicing in vivo and in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 574–587. [Google Scholar]
- Zuger, S.; Iwai, H. Intein-based biosynthetic incorporation of unlabeled protein tags into isotopically labeled proteins for NMR studies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Yoshida, T.; Inouye, M. Significant enhanced expression and solubility of human proteins in Escherichia coli by fusion with protein S from Myxococcus xanthus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5356–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Swapna, G.V.; Wu, K.P.; Afinogenova, Y.; Conover, K.; Mao, B.; Montelione, G.T.; Inouye, M. Segmental isotope labeling of proteins for NMR structural study using a protein S tag for higher expression and solubility. J. Biomol. NMR 2012, 52, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
De Rosa, L.; Russomanno, A.; Romanelli, A.; D'Andrea, L.D. Semi-Synthesis of Labeled Proteins for Spectroscopic Applications. Molecules 2013, 18, 440-465. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010440
De Rosa L, Russomanno A, Romanelli A, D'Andrea LD. Semi-Synthesis of Labeled Proteins for Spectroscopic Applications. Molecules. 2013; 18(1):440-465. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010440
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Rosa, Lucia, Anna Russomanno, Alessandra Romanelli, and Luca Domenico D'Andrea. 2013. "Semi-Synthesis of Labeled Proteins for Spectroscopic Applications" Molecules 18, no. 1: 440-465. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010440
APA StyleDe Rosa, L., Russomanno, A., Romanelli, A., & D'Andrea, L. D. (2013). Semi-Synthesis of Labeled Proteins for Spectroscopic Applications. Molecules, 18(1), 440-465. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010440