Efficient Indium-Mediated Dehalogenation of Aromatics in Ionic Liquid Media
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
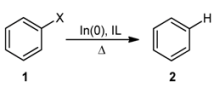 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Solvent | X | Temperature (°C) | Yield b (%) 2 | Recovery b (%) 1 |
| 1 | H2O | Br | rt | - | >99 |
| 2 | H2O | Br | 100 | - | >99 |
| 3 | THF | Br | rt | - | >99 |
| 4 | THF | Br | 65 | - | >99 |
| 5 | THF/H2O | Br | rt | - | >99 |
| 6 | THF/H2O | Br | 65 | - | >99 |
| 7 | TBAF | Br | 95 | - | >99 |
| 8 | [bmim]Cl | Br | 95 | 70 | 30 |
| 9 | [bmim]Cl | Cl | 95 | 60 | 40 |
| 10 | [bmim]Cl | I | 95 | 3 | 97 |
| 11 | [bmim]Br | Br | 95 | >99 | - |
| 12 | [bmim]Br | Cl | 95 | >99 | - |
| 13 | [bmim]Br | I | 95 | >99 | - |
| 14 | [(d3)-bmim]Br | Br | 95 | >99 c | - |
| 15 | [bmim]BF4 | Br | 95 | - | >99 |
| 16 | [bmim]PF6 | Br | 95 | - | >99 |
| 17 | [bmpy]F3CSO3 | Br | 95 | - | >99 |
| Entry | Substrate | Product | Yield b (%) | Recovery b (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 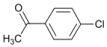 | 3 | 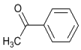 | 20 | 80 |
| 2 |  | 4 |  | >99 | - |
| 3 | 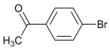 | 3 |  | 80 | 20 |
| 4 | 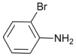 | 5 | 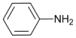 | 76 | 24 |
| 5 | 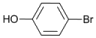 | 6 | 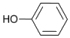 | 10 | 90 |
| 6 | 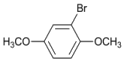 | 7 | 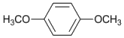 | >99 | - |
| 7 | 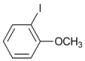 | 8 | 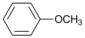 | >99 | - |
| 8 |  | 9 | 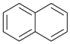 | >99 | - |
| 9 | 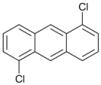 | 10 | 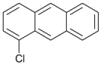 | 11 | 89 |
| 10 c | 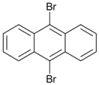 | 11 | 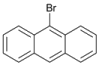 | >99 | - |
| 11 c | 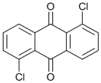 | 12 |  | >99 | - |
| 12 | 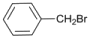 | 13 | 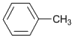 | >99 | - |
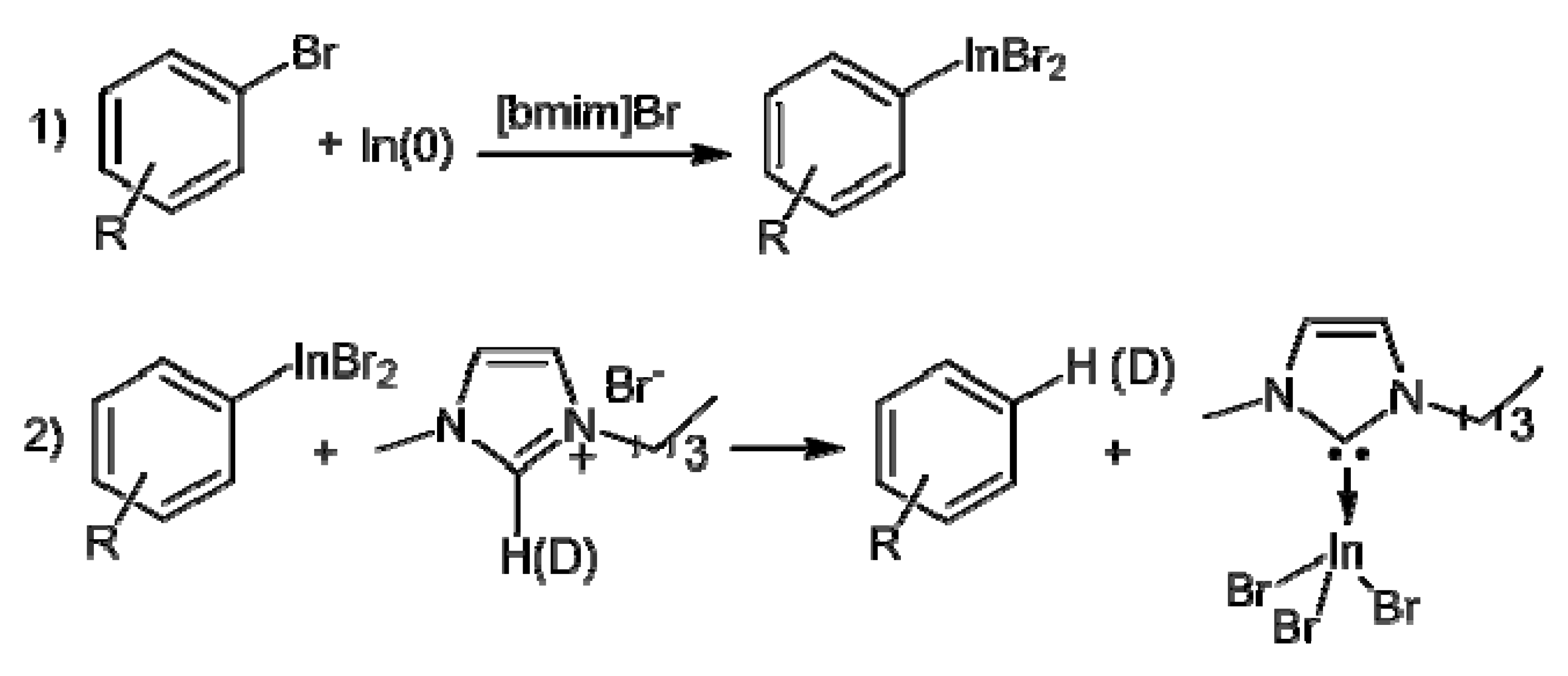
| Entry | Substrate | Product | Yield b (%) | Recovery b (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 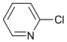 | 14 | 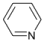 | - | >99 |
| 2 | 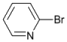 | 14 |  | >99 | - |
| 3 | 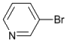 | 14 |  | 60 | 40 |
| 4 | 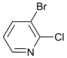 | 15 c 16 d | 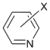 | 20 c 80 d | - |
| 5 | 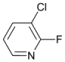 | 17 | 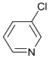 | - | >99 |
| 6 |  | 18 e19 f | 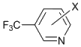 | 60 e30 f | 10 |
| 7 | 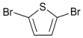 | 20 | 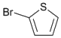 | 90 | 10 |
| 8 | 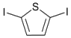 | 21 | 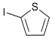 | >99 | - |
3. Experimental
3.1. General Methods
3.2. General Procedure for the Dehalogenation of Haloaromatics
3.3. Characterization Data
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Hennebel, T.; Benner, J.; Clauwaert, P.; Vanhaecke, L.; Aelterman, P.; Callebaut, R.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. Dehalogenation of environmental pollutants in microbial electrolysis cells with biogenic palladium nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, F.; Beletskaya, I.; Yus, M. Metal-mediated reductive hydrodehalogenation of organic halides. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4009–4091. [Google Scholar]
- Trost, B.; Fleming, I. Comprehensive Organic Synthesis; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1991; Volume 8, pp. 794–795. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, A.G. Comprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations; Katritzky, A.R., Meth-Cohn, O., Rees, C.W., Roberts, S.M., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; El-Sheikh, M.I.; Cook, J.M. Synthesis of 1,6-Diazaphenalene, A Vinylogous Imidazole. Heterocycles 1979, 12, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakray, S.; Castle, R.N. The synthesis of dimethoxy[1]benzothieno[2,3-c]quinolines. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1986, 23, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahler, S.E.; Burger, A. Cyclic Aminoalkylamino Derivatives of Lepidine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1941, 63, 2367–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, O.; Marull, M.; Schlosser, M. 4-(Trifluoromethyl)quinoline derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 11, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto, O.; Aoki, K.; Tanji, K. Magnesiation of functionalized iodobenzenes at room temperature: Clarification of the stability of ethoxycarbonylphenylmagnesium iodides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 1915–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Kamei, T.; Okamoto, A. Evaluation of novel one-electron reduction with metal in DNA. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. (Oxf) 2006, 50, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranu, B.C.; Dutta, P.; Sarkar, A. Indium as a reducing agent. Chemoselective reduction of alpha-halocarbonyl compounds and benzyl halides by indium metal in water under sonication. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I 1999, 1139–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Fukuda, E.; Sugimoto, O.; Tanji, K. Indium-mediated dehalogenation of haloheteroaromatics in water. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 1492–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Palou, R. Ionic liquid and microwave-assisted organic synthesis: A “green” and synergic couple. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2007, 51, 252–264. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlinac, J.; Zupan, M.; Laali, K.; Stavber, S. Halogenation of organic compounds in ionic liquids. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 5625–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmiah, S.; Srinivasadesikan, V.; Tseng, M.-C.; Chu, Y.-H. On the Chemical Stabilities of Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2009, 14, 3780–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabe, H.; Naito, T. The utility of indium in aqueous médium radical reactions. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 1267–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Fujii, K.; Nabeshima, S.; Ikeda, R.; Konakahara, T. Highly selective conversión of nitrobenzenes using a simple reducing system combined with a trivalent indium salt and a hydrosilane. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3171–3175. [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke, M.G. Hetarynes. Tetrahedron 1982, 38, 427–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranu, B. Indium metal and its halides in organic synthesis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 55, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C. The Stabilisation and Reactivity of Indium Trihydride Complexes. Chem. Commun. 2001, 2293–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Rubero, S.; Baldelli, S. Influence of water on the surface of the water-miscible ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate: A sum frequency generation analysis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4756–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Sawada, A.; Shibata, I.; Baba, A. Indium(III) chloride-sodium borohydride system: A convenient radical reagent for an alternative to tributyltin hydride system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 906–907. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, K.; Sawada, A.; Shibata, I.; Baba, A. Indium hydride: A novel radical initiator in the reduction of organic halides with tributyltin hydride. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 4661–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 2, 3, 10–12, 18 and 19 are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cañete, Á.F.; Salas, C.O.; Zacconi, F.C. Efficient Indium-Mediated Dehalogenation of Aromatics in Ionic Liquid Media. Molecules 2013, 18, 398-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010398
Cañete ÁF, Salas CO, Zacconi FC. Efficient Indium-Mediated Dehalogenation of Aromatics in Ionic Liquid Media. Molecules. 2013; 18(1):398-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010398
Chicago/Turabian StyleCañete, Álvaro F., Cristian O. Salas, and Flavia C. Zacconi. 2013. "Efficient Indium-Mediated Dehalogenation of Aromatics in Ionic Liquid Media" Molecules 18, no. 1: 398-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010398
APA StyleCañete, Á. F., Salas, C. O., & Zacconi, F. C. (2013). Efficient Indium-Mediated Dehalogenation of Aromatics in Ionic Liquid Media. Molecules, 18(1), 398-407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010398





