A Facile Synthesis of Fully Protected meso-Diaminopimelic Acid (DAP) and Its Application to the Preparation of Lipophilic N-Acyl iE-DAP
Abstract
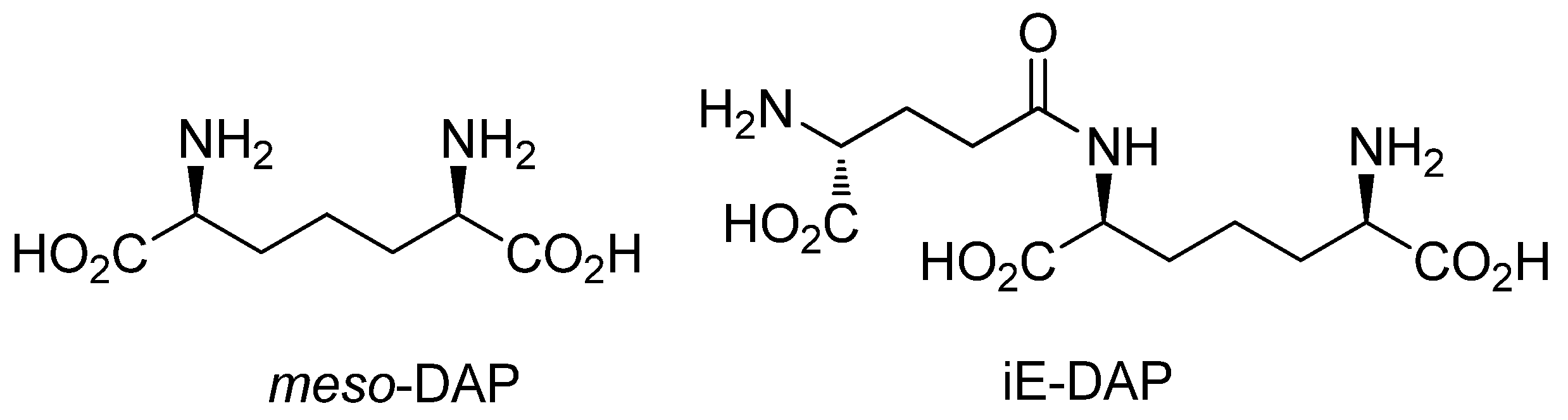
:1. Introduction
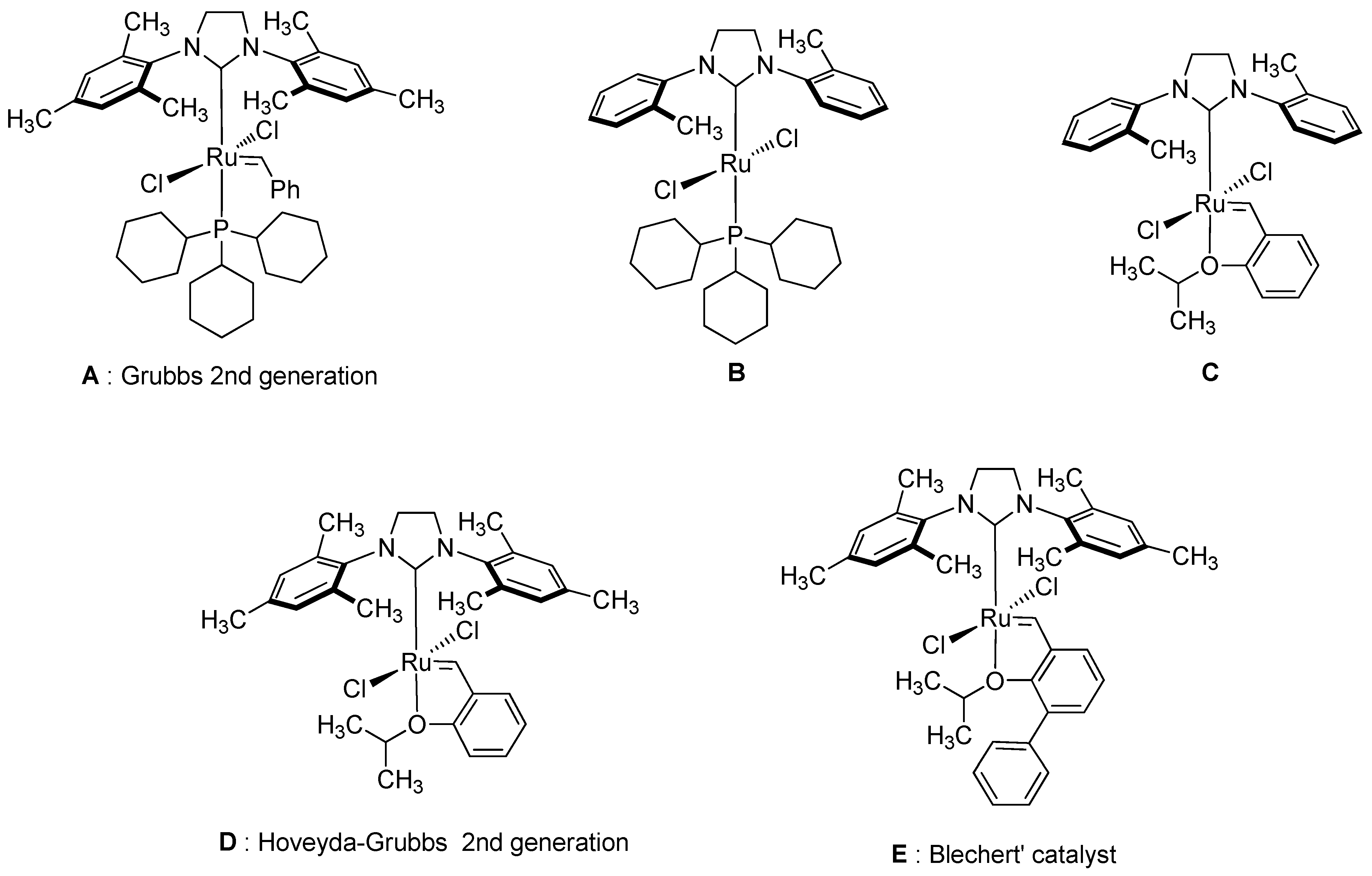
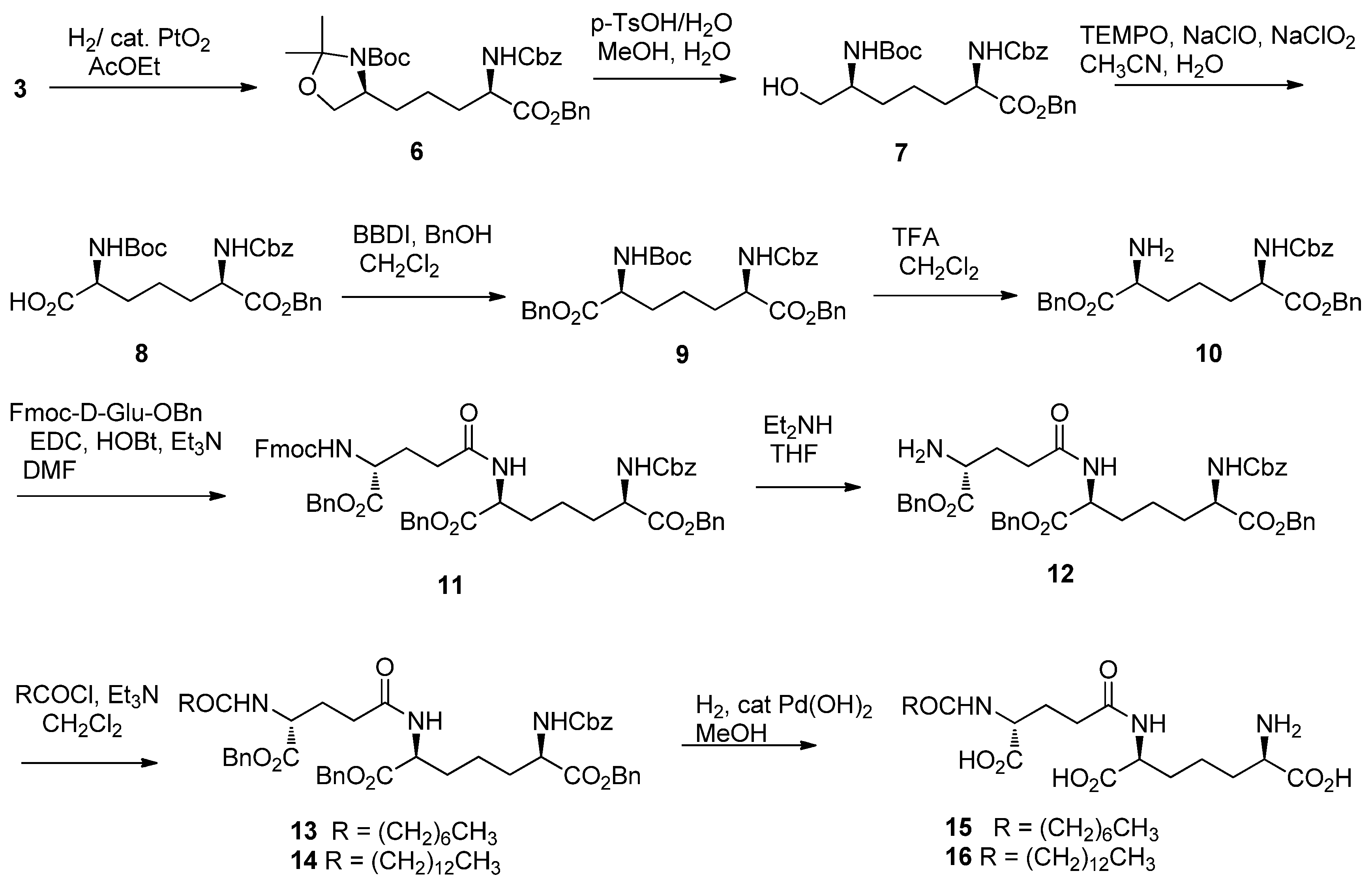
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Rietschel, E.T.; Schletter, J.; Weidemann, B.; El-Samalouti, V.; Mattern, T.; Zahringer, U.; Seydel, U.; Brade, H.; Flad, H.D.; Kusumoto, S.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan: CD14-dependent bacterial inducers of inflammation. J. Microb. Drug Resist. 1998, 4, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Heijenoort, J. Formation of the glycan chains in the synthesis of bacterial peptidoglycan. Glycobiology 2001, 11, 25R–36R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugg, T.D.H.; Braddick, D.; Dowson, C.G.; Roper, D.I. Bacterial cell wall assembly: Still an attractive antibacterial target. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamaillard, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Horie, Y.; Masumoto, J.; Qiu, S.; Saab, L.; Ogura, Y.; Kawasaki, A.; Fukase, K.; Kusumoto, S. An essential role for NOD1 in host recognition of bacterial peptidoglycan containing diaminopimelic acid. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardin, S.E.; Travassos, L.H.; Herve, M.; Blanot, D.; Boneca, I.G.; Philpott, D.J.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Mengin-Lecreulx, D. Peptidoglycan molecular requirements allowing detection by Nod1 and Nod 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41702–41708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masumoto, J.; Yang, K.; Varambally, S.; Hasegawa, M.; Tomlins, S.A.; Qiu, S.; Fujimoto, Y.; Kawasaki, A.; Foster, S.J.; Horie, Y.; et al. Nod1 acts as an intracellular receptor to stimulate chemokine production and neutrophil recruitment in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kawasaki, A.; Yang, K.; Fujimoto, Y.; Masumoto, J.; Breukink, E.; Nunez, G.; Fukase, K.; Inohara, N. A Role of Lipophilic Peptidoglycan-related Molecules in Induction of Nod1-mediated Immune Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11757–11764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Shinkai, T.; Yoshimura, Y.; Takahata, H. A straightforward stereoselective synthesis of meso-, (S,S)- and (R,R)-2,6-diaminopimelic acids from cis-1,4-diacetoxycyclohept-2-ene. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 5894–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, T.; Nakahara, K.; Iwami, M.; Aoki, H.; Imanaka, H. Studies on a new immunoactive peptide, FK-156. I. Taxonomy of the producing strains. J. Antibiot. 1982, 35, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, T.; Nakahara, K.; Nishiura, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Kino, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Okuhara, M.; Kohsaka, M.; Aoki, H.; Imanaka, H. Studies on a new immunoactive I peptide, FK-156 II. Fermentation, extraction and chemical and biological characterization. J. Antibiot. 1982, 35, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurgens, A.R. Asymmetric synthesis of differentially protected meso-2,6-diaminopimelic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 4727–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.M.; Yuan, C. Asymmetric synthesis of 2,6-diaminopimelic acids. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 6519–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, R.C.; Schow, S.; Ayral-Kaloustian, S.; Powell, D. An asymmetric synthesis of differentially protected meso-2,6-diaminopimelic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 7005–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lane-Bell, P.; Vederas, J.C. Stereoselective Synthesis of meso-2,6-Diaminopimelic Acid and Its Selectively Protected Derivatives. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.A.; Srirajan, V. Asymmetric Synthesis of (2S,6S)- and meso-(2S,6R)-Diaminopimelic Acids from Enantiopure Bis(sulfinimines). J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 3248–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradisi, F.; Porzi, G.; Rinaldi, S.; Sandri, S. A simple asymmetric synthesis of (+)- and (−)-2,6-diaminopimelic acids. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2000, 11, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, P.N.; Patel, I.; Taylor, R.J.K. A concise, stereoselective synthesis of meso-2,6-diaminopimelic acid (DAP). Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 5953–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, P.N.; Campbell, A.D.; Patel, I.; Raynham, T.M.; Taylor, R.J.K. Enantiomerically Pure α-Amino Acid Synthesis via Hydroboration-Suzuki Cross-Coupling. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 1802–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.L.; Chan, C. Asymmetric synthesis of differentially protected meso-2,6-diaminopimelic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 7679–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, A.; Vederas, J.C. Conjugate addition of radicals generated from diacyloxyiodobenzenesto dehydroamino acid derivatives; a synthesis of diaminopimelic acid analogues. Chem. Commun. 2002, 224–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeazzi, R.; Garavelli, M.; Grandi, A.; Monari, M.; Porzi, G.; Sandri, S. Unusual peptides containing the 2,6-diaminopimelic acid framework: Stereocontrolled synthesis, X-ray analysis, and computational modelling. Part 2. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2003, 14, 2639–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spantulescu, M.D.; Jain, R.P.; Derksen, D.J.; Vederas, J.C. Photolysis of Diacyl Peroxides: A Radical-Based Approach for the Synthesis of Functionalized Amino Acids. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2963–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del, J.R.; Goodman, M. An Efficient RCM-Based Synthesis of Orthogonally Protected meso-DAP and FK565. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 8946–8948. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, A.R.; Boons, G. The synthesis of diaminopimelic acid containing peptidoglycan fragments using metathesis cross coupling. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 1675–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, A.; Karasudani, Y.; Otsuka, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Inohara, N.; Fujimoto, Y.; Fukase, K. Synthesis of Diaminopimelic Acid Containing Peptidoglycan Fragments and Tracheal Cytotoxin (TCT) and Investigation of Their Biological Functions. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 10318–10330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xiong, C.; Yang, J.; Hruby, V.J. An efficient synthesis of (2S,6S)- and meso-diaminopimelic acids via asymmetric hydrogenation. Synthesis 2002, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Banba, Y.; Abe, C.; Nemoto, H.; Kato, A.; Adachi, I.; Takahata, H. Asymmetric synthesis of fagomine and its congeners. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2001, 12, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, I.; Pedregal, C.; Mazon, A.; Espinosa, J.F.; Blanco-Urgoiti, J.; Schoepp, D.D.; Wright, R.A.; Johnson, B.G.; Kingston, A.E. (2S,1′S,2′S,3′R)-2-(2′-Carboxy-3′-methylcyclopropyl) Glycine Is a Potent and Selective Metabotropic Group 2 Receptor Agonist with Anxiolytic Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 3619–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fa Liu, F.; Hu, T.-S.; Yao, Z.-J. Stereoselective synthesis of new modified conformationally constrained L-tyrosine analogue with potential applications to SH2 domain ligands. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 4971–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devel, L.; Hamon, L.; Becker, H.; Thellend, A.; Vidal-Crosa, A. Synthesis of protected 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-xylothionolactam derivatives and some aspects of their reactivity. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtmann, F.W.; Benedum, T.E.; McGarvey, G.J. First Total Synthesis of 1-O-β-d-Glucopyranosyl-5-deoxyadenophorine and Its Aglycon Congener: Determination of the Absolute Configuration. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Robl, J.A. Heterocyclo-fused [1,3]oxazepines and –thiazepines and analogs as inhibitors of neutral endopeptiadase and angiotensin converting enzyme. U.S. Patent US 5508272 A, 16 April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Robl, J.A.; Kronenthal, D.R.; Goderey, J.D., Jr. Bicyclic carboxylic acids as inhibitors of neutral endopeptidase and angiotensin-converting enzyme. Eur. Patent EP 629627A2, 21 December 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Schrodi, Y.; Pederson, R.L. Evolution and Applications of Second-Generation Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts. Aldrichimica Acta 2007, 40, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wakamatsu, H.; Blechert, S. A Highly Active and Air-Stable Ruthenium Complex for Olefin Metathesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Takahata, H. A novel 1-tert-butoxy-2-tert-butoxycarbonyl-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline (BBDI)-catalyzed esterification of N-protected amino acids with nearly equimolar amounts of alcohols in the presence of Boc2O. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 3099–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conversion of 10 to meso-DAP has been accomplished by hydrogenlysis and the spectral data of hydrochloride salt of prepared meso-DAP was accordance with those of our reported values (ref. [8]).
- Demaria, S.; Metafora, V.; Metafora, S.; Ravagnan, G.; Carteni, M.; Pontoni, G.; Facchiano, A.; Lepretti, M.; Severino, B.; Caliendo, G.; et al. Effect of positive charge in VIP 16γ-glutamyl diamino derivatives on hVPAC1 and hVPAC2 receptor function. J. Pept. Sci. 2008, 14, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hard, I.; Torres, J.L.; Valencia, G.; Garcia-Anton, J.M.; Reig, F. Synthesis and biological activity of substance P analogues. Int. J. Peptide Protein Res. 1989, 33, 335–339. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Contact the authors. |
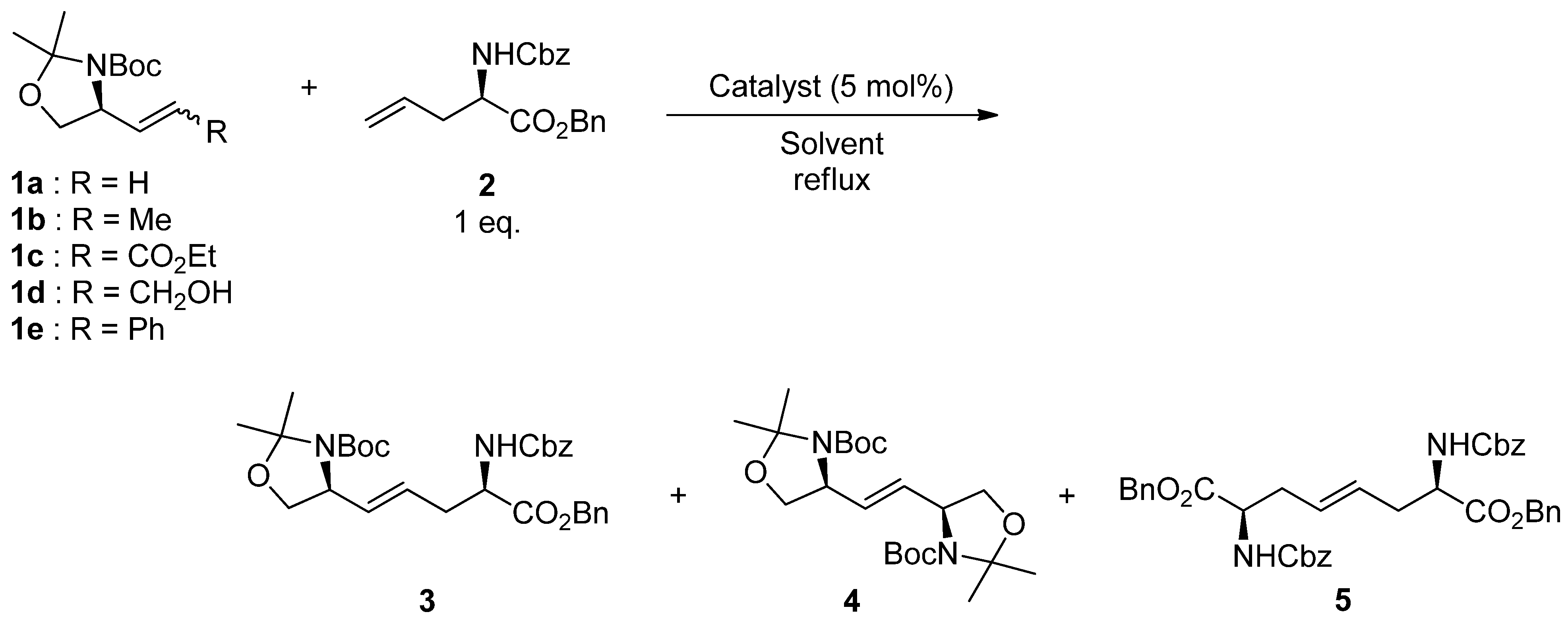
| Entry | 1 | Catalyst | Solvent | Time (h) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1a | A | CH2Cl2 | 7 | 56 |
| 2 | 1a | B | CH2Cl2 | 4.5 | 28 |
| 3 | 1a | C | CH2Cl2 | 36 | 33 |
| 4 | 1a | A | Toluene | 3 | 64 |
| Entry | 1 | Catalyst | Time (h) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1b | A | 4 | 76 |
| 2 | 1b | D | 3 | 56 |
| 3 | 1b | E | 4 | 9 |
| 4 | 1c | A | 4 | trace |
| 5 | 1d | A | 3 | 9 |
| 6 | 1e | A | 3 | 10 |
| 7 | 1b (E:Z = 10:1) | A | 4 | 75 |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Saito, Y.; Yoshimura, Y.; Wakamatsu, H.; Takahata, H. A Facile Synthesis of Fully Protected meso-Diaminopimelic Acid (DAP) and Its Application to the Preparation of Lipophilic N-Acyl iE-DAP. Molecules 2013, 18, 1162-1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18011162
Saito Y, Yoshimura Y, Wakamatsu H, Takahata H. A Facile Synthesis of Fully Protected meso-Diaminopimelic Acid (DAP) and Its Application to the Preparation of Lipophilic N-Acyl iE-DAP. Molecules. 2013; 18(1):1162-1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18011162
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaito, Yukako, Yuichi Yoshimura, Hideaki Wakamatsu, and Hiroki Takahata. 2013. "A Facile Synthesis of Fully Protected meso-Diaminopimelic Acid (DAP) and Its Application to the Preparation of Lipophilic N-Acyl iE-DAP" Molecules 18, no. 1: 1162-1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18011162
APA StyleSaito, Y., Yoshimura, Y., Wakamatsu, H., & Takahata, H. (2013). A Facile Synthesis of Fully Protected meso-Diaminopimelic Acid (DAP) and Its Application to the Preparation of Lipophilic N-Acyl iE-DAP. Molecules, 18(1), 1162-1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18011162




