Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibiting Activity of Salicylanilide N-Alkylcarbamates and Their Molecular Docking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
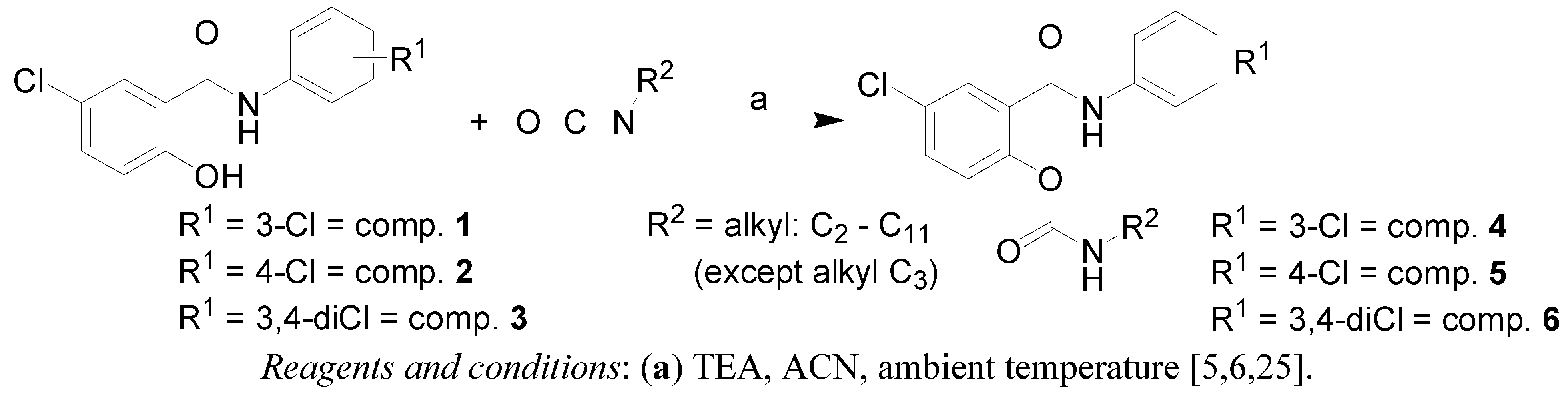
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Lipophilicity
| Comp. | R 1 | R 2 | log k | log P * | AChE IC50 (μmol/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GROUP 1 | 4a | 3-Cl | C2H5 | 0.7523 | 4.02 ± 0.40 | N.D. |
| 4b | 3-Cl | C4H9 | 0.7611 | 5.08 ± 0.40 | N.D. | |
| 4c | 3-Cl | C5H11 | 0.7732 | 5.61 ± 0.40 | 50.4 ± 0.48 | |
| 4d | 3-Cl | C6H13 | 0.7758 | 6.14 ± 0.40 | 35.1 ± 0.31 | |
| 4e | 3-Cl | C7H15 | 0.7772 | 6.67 ± 0.40 | 61.7 ± 0.50 | |
| 4f | 3-Cl | C8H17 | 0.7831 | 7.20 ± 0.40 | 69.9 ± 0.49 | |
| 4g | 3-Cl | C9H19 | 0.7837 | 7.74 ± 0.40 | 34.2 ± 0.26 | |
| 4h | 3-Cl | C10H21 | 0.7873 | 8.27 ± 0.40 | 52.7 ± 0.45 | |
| 4i | 3-Cl | C11H23 | 0.7902 | 8.80 ± 0.40 | 56.9 ± 0.48 | |
| GROUP 2 | 5a | 4-Cl | C2H5 | 0.7695 | 3.98 ± 0.39 | 59.1 ± 0.33 |
| 5b | 4-Cl | C4H9 | 0.7759 | 5.04 ± 0.39 | 48.1 ± 0.31 | |
| 5c | 4-Cl | C5H11 | 0.7838 | 5.57 ± 0.39 | 41.7 ± 0.29 | |
| 5d | 4-Cl | C6H13 | 0.7859 | 6.10 ± 0.39 | 31.0 ± 0.29 | |
| 5e | 4-Cl | C7H15 | 0.7872 | 6.63 ± 0.39 | 49.4 ± 0.31 | |
| 5f | 4-Cl | C8H17 | 0.7899 | 7.16 ± 0.39 | 62.5 ± 0.41 | |
| 5g | 4-Cl | C9H19 | 0.7919 | 7.70 ± 0.39 | 52.2 ± 0.39 | |
| 5h | 4-Cl | C10H21 | 0.7942 | 8.23 ± 0.39 | 64.6 ± 0.41 | |
| 5i | 4-Cl | C11H23 | 0.7947 | 8.76 ± 0.39 | 44.3 ± 0.33 | |
| GROUP 3 | 6a | 3,4-Cl | C2H5 | 1.0234 | 4.88 ± 0.41 | 67.3 ± 0.52 |
| 6b | 3,4-Cl | C4H9 | 1.0457 | 5.94 ± 0.41 | 64.7 ± 0.79 | |
| 6c | 3,4-Cl | C5H11 | 1.0601 | 6.47 ± 0.41 | 56.0 ± 0.42 | |
| 6d | 3,4-Cl | C6H13 | 1.0611 | 7.01 ± 0.41 | 41.2 ± 0.36 | |
| 6e | 3,4-Cl | C7H15 | 1.0667 | 7.54 ± 0.41 | 36.7 ± 0.28 | |
| 6f | 3,4-Cl | C8H17 | 1.0845 | 8.07 ± 0.41 | 32.1 ± 0.29 | |
| 6g | 3,4-Cl | C9H19 | 1.0880 | 8.60 ± 0.41 | 43.9 ± 0.32 | |
| 6h | 3,4-Cl | C10H21 | 1.0894 | 9.13 ± 0.41 | 21.8 ± 0.20 | |
| 6i | 3,4-Cl | C11H23 | 1.0903 | 9.66 ± 0.41 | 29.9 ± 0.22 | |
| RIV | – | – | – | 2.14 ± 0.27 | 501 ± 3.08 | |
| GLT | – | – | – | 1.59 ± 0.45 | 4.0 ± 0.13 | |
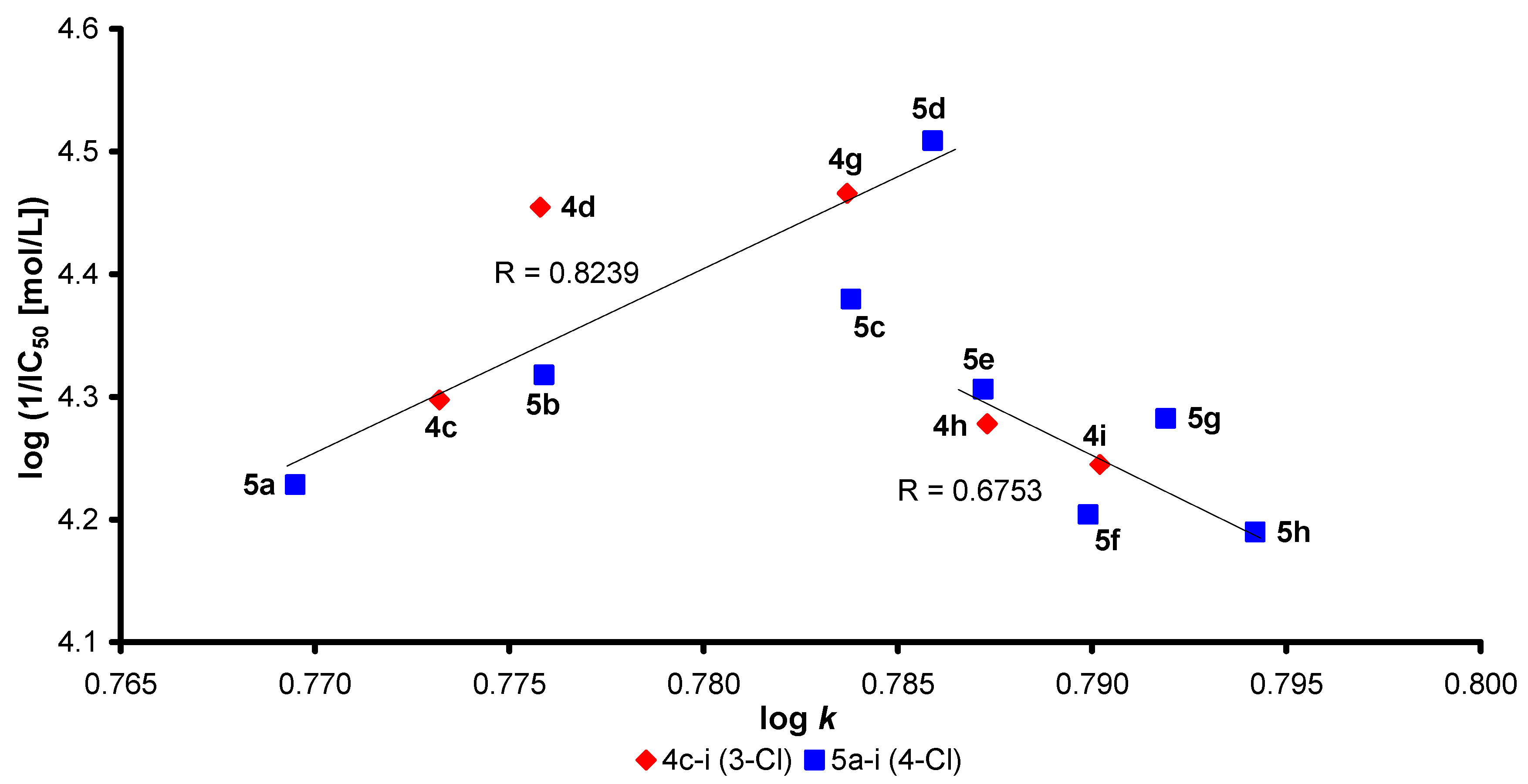
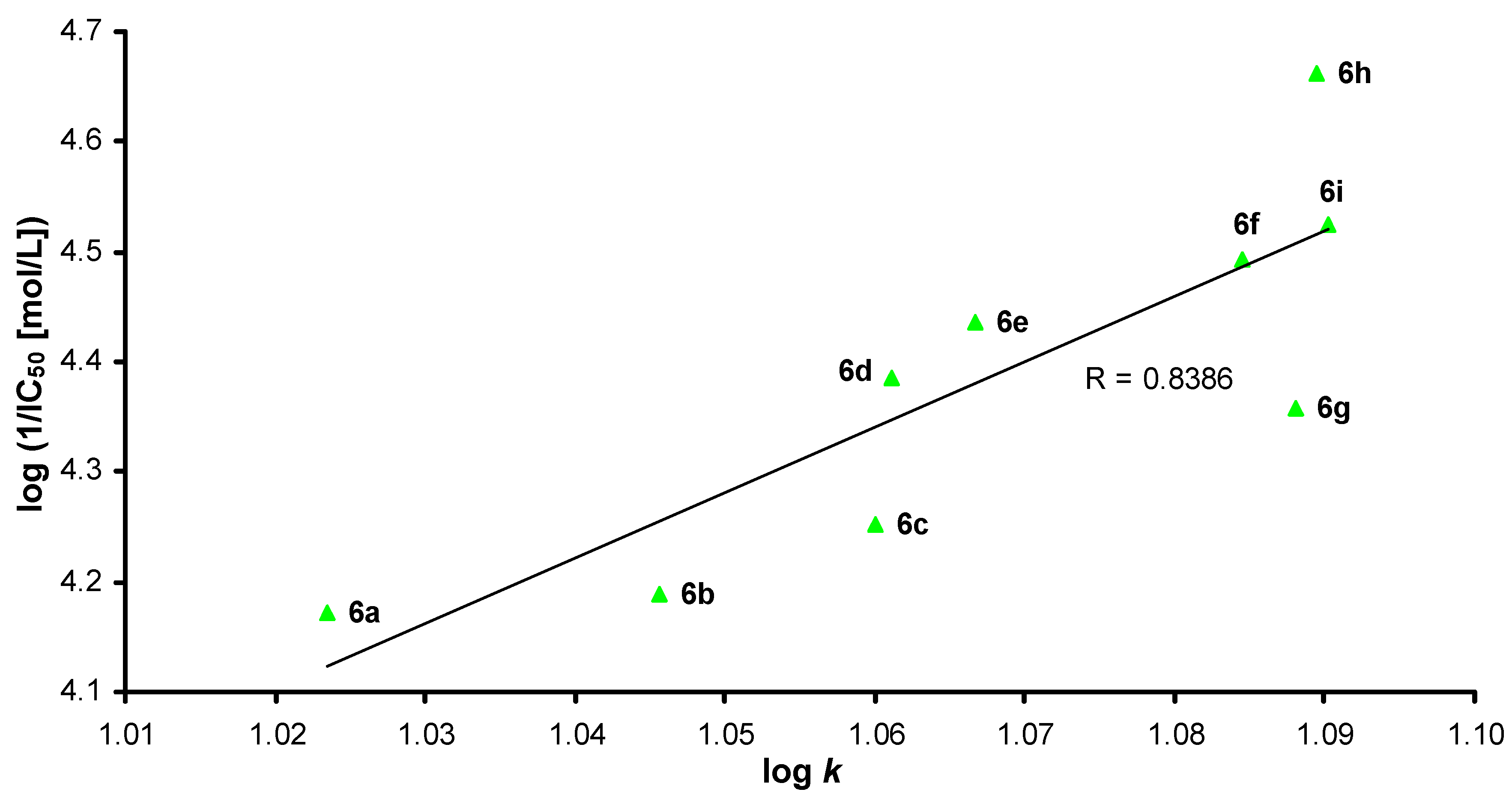
2.3. In Vitro Evaluation of AChE-Inhibiting Activity

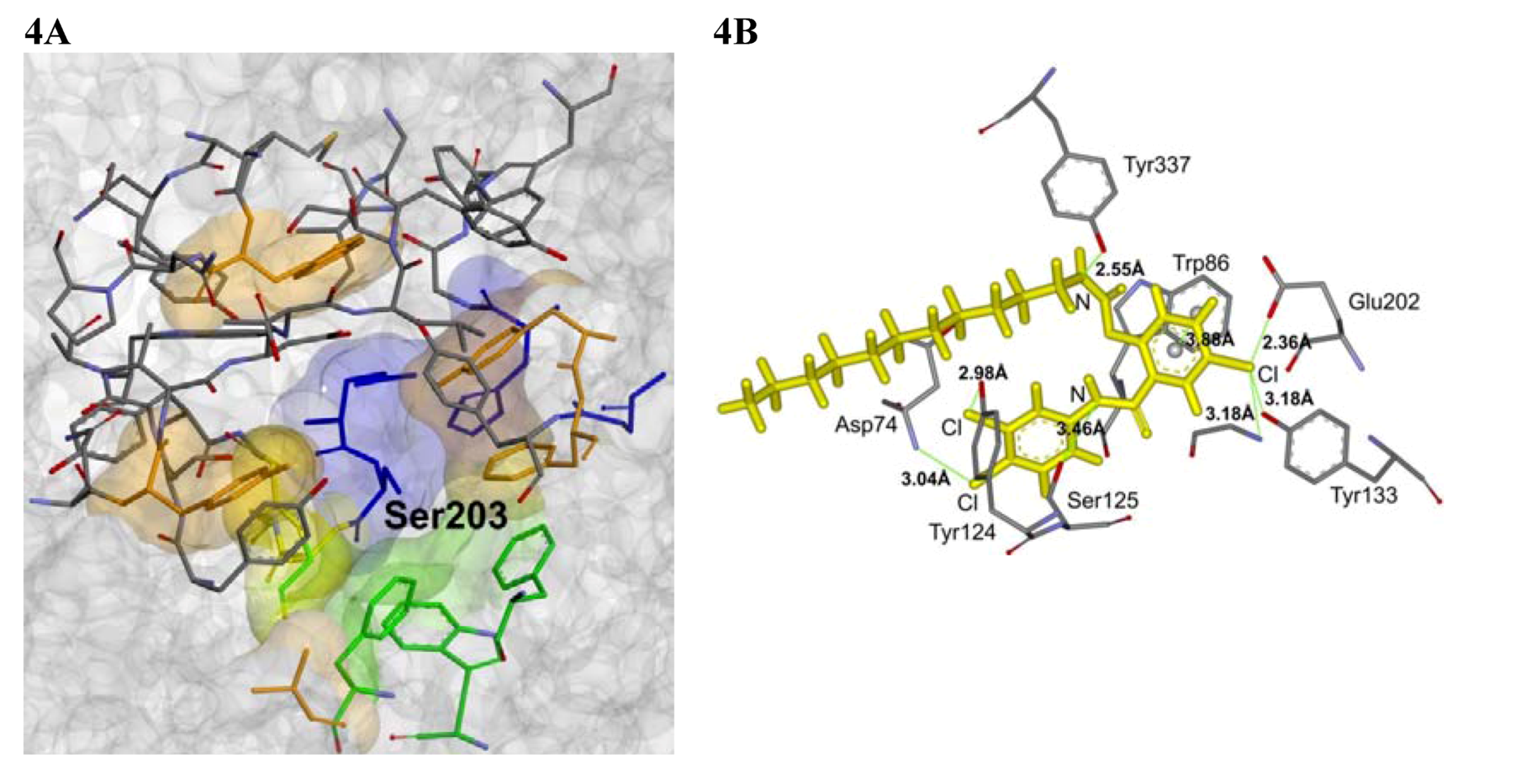
2.4. Molecular Docking
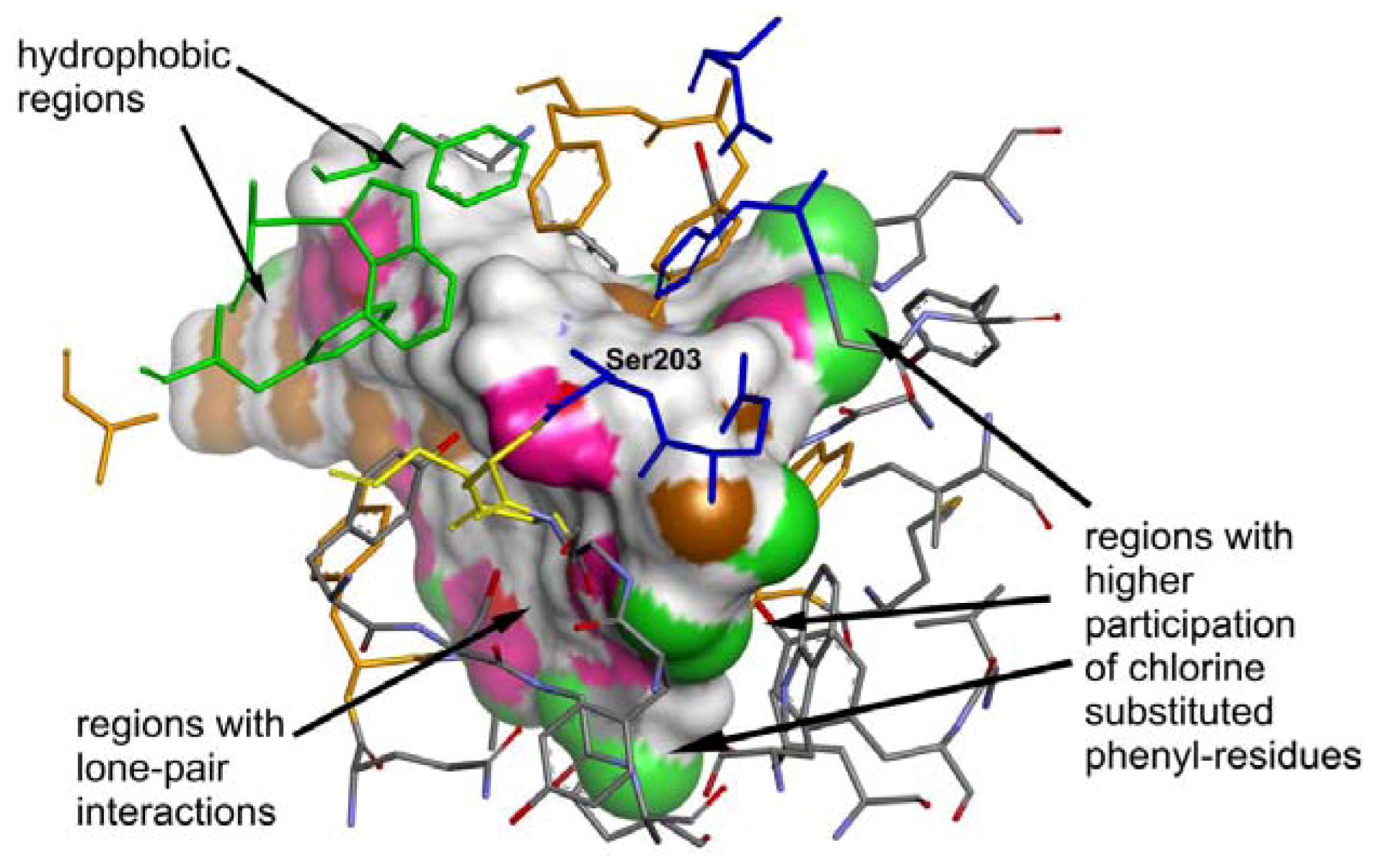
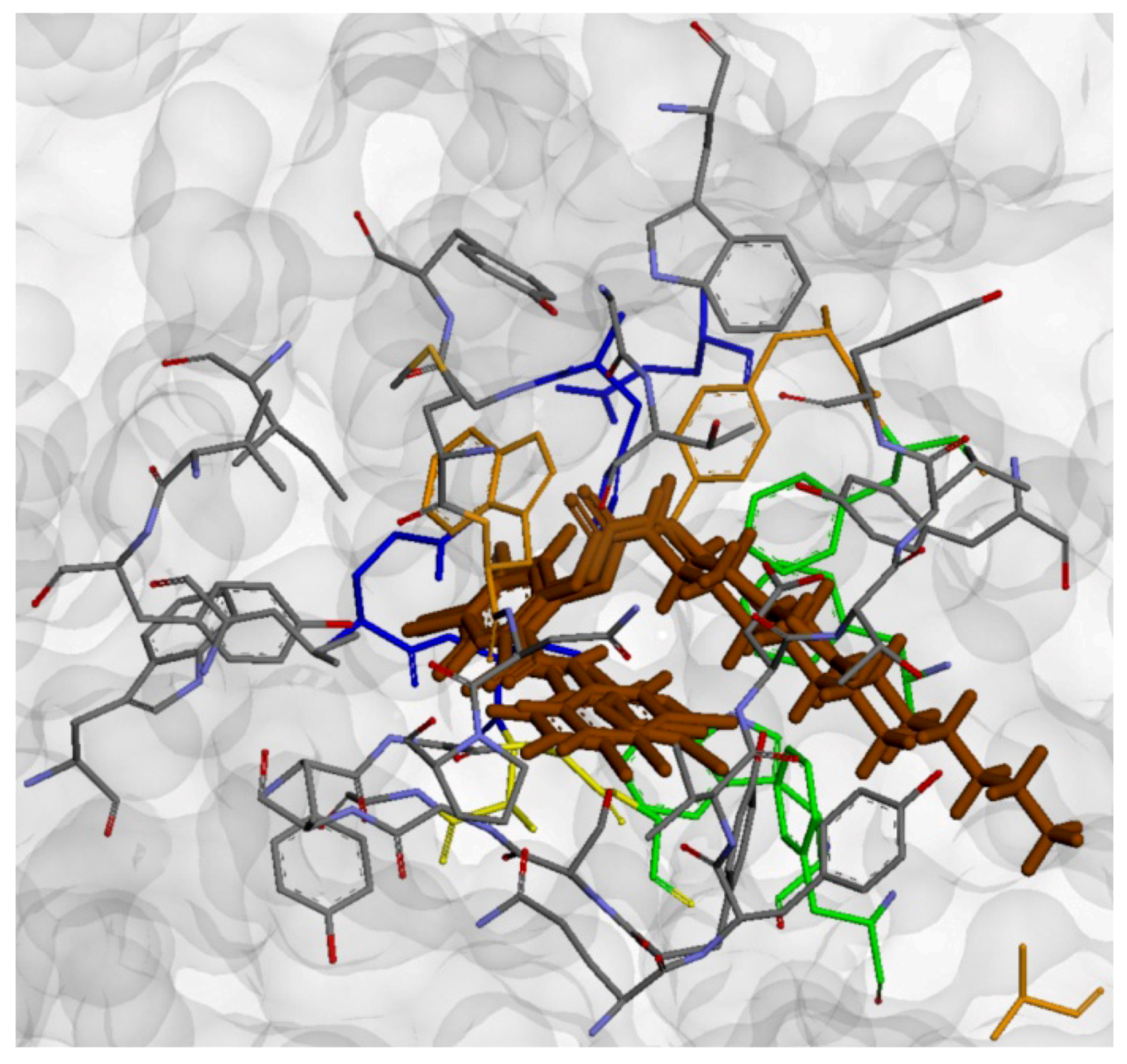
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Lipophilicity Determination by HPLC (Capacity Factor k/Calculated log k)
3.3. Calculation of Lipophilicity
3.4. In Vitro Evaluation of AChE-Inhibiting Activity
3.5. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Roth, H.J.; Fenner, H. Arzneistoffe, 3rd ed; Deutscher Apotheker Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vinsova, J.; Imramovsky, A. Salicylanilides: Still a topical potential antibacterially active group. Ces. Slov. Farm. 2004, 53, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Vinsova, J.; Imramovsky, A.; Buchta, V.; Ceckova, M.; Dolezal, M.; Staud, F.; Jampilek, J.; Kaustova, J. Salicylanilide acetates: Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation. Molecules 2007, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imramovsky, A.; Vinsova, J.; Ferriz, J.M.; Dolezal, R.; Jampilek, J.; Kaustova, J.; Kunc, F. New antituberculotics originated from salicylanilides with promising in vitro activity against atypical mycobacterial strains. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3572–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imramovsky, A.; Vinsova, J.; Ferriz, J.M.; Buchta, V.; Jampilek, J. Salicylanilide esters of N-protected amino acids as novel antimicrobial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 348–351. [Google Scholar]
- Ferriz, J.M.; Vavrova, K.; Kunc, F.; Imramovsky, A.; Stolarikova, J.; Vavrikova, E.; Vinsova, J. Salicylanilide carbamates: Antitubercular agents active against multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Otevrel, J.; Mandelova, Z.; Pesko, M.; Guo, J.; Kralova, K.; Sersen, F.; Vejsova, M.; Kalinowski, D.; Kovacevic, Z.; Coffey, A.; et al. Investigating the spectrum of biological activity of ring-substituted salicylanilides and carbamoylphenylcarbamates. Molecules 2010, 15, 8122–8142. [Google Scholar]
- Imramovsky, A.; Pesko, M.; Ferriz, J.M.; Kralova, K.; Vinsova, J.; Jampilek, J. Photosynthesis-Inhibiting efficiency of 4-chloro-2-(chlorophenylcarbamoyl)phenyl alkylcarbamates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4564–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.S. Principles of Weed Science, 2nd ed; Science Publishers: Enfield, New Hampshire, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf, R.L. Structure-Activity relationships for insecticidal carbamates. Bull. World Health Org. 1971, 44, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, G.; Mei, X.; Yuan, H.; Ning, J. Design of novel carbamate acetylcholinesterase inhibitors based on the multiple binding sites of acetylcholinesterase. J. Pestic. Sci. 2008, 34, 371–375. [Google Scholar]
- Pejchal, V.; Stepankova, S.; Drabina, P. Synthesis of 1-[(1R)-1-(6-fluoro-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)ethyl]-3-substituted phenyl ureas and their inhibition activity to acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. J. Het. Chem. 2011, 48, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Pejchal, V.; Stepankova, S.; Padelkova, Z.; Imramovsky, A.; Jampilek, J. 1,3-Substituted imidazolidine-2,4,5-triones: Synthesis and inhibition of cholinergic enzymes. Molecules 2011, 16, 7565–7582. [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg, R.J.; Dalvie, D.; Cordero, J.; Sabat, M.; Musallam, H.A. Carbamates of (hydroxyphenoxy)methyl heteroaromatic salts as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and protective agents against organophosphorus compounds. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1993, 6, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Liao, W.C.; Chan, C.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Tsai, H.J.; Hsieh, C.W. Quantitative structure-activity relationships for the pre-steady state acetylcholinesterase inhibition by carbamates. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxic. 2004, 18, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Groner, E.; Ashani, Y.; Schorer-Apelbaum, D.; Sterling, J.; Herzig, Y.; Weinstock, M. The kinetics of inhibition of human acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase by two series of novel carbamates. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1610–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.K.; Dixit, A.; Saxena, A.K. An investigation of structurally diverse carbamates for acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition using 3D-QSAR analysis. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2008, 27, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, S.Y.; Huang, C.F.; Hwang, M.T.; Lin, G. Comparison of active sites of butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase based on inhibition by geometric isomers of benzene-di-N-substituted carbamates. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxic. 2009, 23, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhaery, S.S.; Roy, K.K.; Shakya, N.; Saxena, G.; Sammi, S.R.; Nazir, A.; Nath, C.; Saxena, A.K. Novel carbamates as orally active acetylcholinesterase inhibitors found to improve scopolamine-induced cognition impairment: pharmacophore-based virtual screening, synthesis, and pharmacology. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6490–6505. [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt, H.M.; Dvir, H.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Acetylcholinesterase: A multifaceted target for structure-based drug design of anticholinesterase agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2003, 20, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukup, J.E. Alzheimer’s Disease: A Guide to Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management; Greenwood Publishing Group: Westport, CT, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.C.; Bludau, J. Alzheimer’s Disease; Greenwood Publishing Group: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Contestabile, A. The history of the cholinergic hypothesis. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 221, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.T.; Palmer, A.M.; Snape, M.; Wilcock, G.K. The cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: A review of progress. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 66, 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Imramovsky, A.; Vinsova, J.; Ferriz, J.M.; Kunes, J.; Pour, M.; Dolezal, M. Salicylanilide esterification: Unexpected formation of novel seven-membered rings. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 5007–5011. [Google Scholar]
- Erkell, L.; Walum, E. Differentiation of cultured neuro-blastoma cells by urea derivates. FEBS Lett. 1979, 104, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellgehausen, H.; D’Hondt, C.; Fuerer, R. Reversed-phase chromatography as a general-method for determing octanol-water partition-coefficients. Pestic. Sci. 1981, 12, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, G.J. Theoretical and experimental relationships between soil adsorption, octanol-water partition-coefficients, water solubilities, bioconcentartion factors, and the parachor. Agric. Food Chem. 1981, 29, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Crippen, G.M. Atomic physicochemical parameters for 3-dimensional-structure-directed quantitative structure-activity-relationships. 2. Modelling dispersive and hydrophobic interactions. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1987, 27, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanadhan, V.N.; Ghose, A.K.; Revankar, G.R.; Robins, R.K. Atomic physicochemical parameters for 3-dimensional-structure-directed quantitative structure-activity-relationships. 2. Additional parameters for hydrophobic and dispersive interactions and their application for an automated superposition of certain naturely-occuring nucleoside antibiotics. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1989, 29, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broto, P.; Moreau, G.; Vandycke, C. Molecular structures–Perception, auto-correlation descriptor and SAR studies–System of atomic contributions for the calculation of the normal-octanol water partition-coefficients. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Chim. Theor. 1984, 19, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A.J. Substituent Constants for Correlation Analysis in Chemistry and Biology; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, J.H.; Campbell, W.R.; Kearns, C.W. Inhibition of fly head acetylcholinesterase by bis-(meta-hydroxphenyl)-trimethylammonium iodide! Esters of polymethylenedicarbamic acid. Biochem. J. 1970, 117, 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, G. Effect of N-alkyl Groups of substituted phenyl-N-alkyl carbamates on inhibition of human-plasma cholinesterase. Arch. Toxicol. 1976, 36, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Norrington, F.E.; Hyde, R.M.; Williams, S.G.; Wotton, R. Physicochemical-activity relations in practice. 1. Rational and self-consistent data bank. J. Med. Chem. 1975, 18, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.C.; Lin, G.Z.; Shen, Y.F.; Jian, S.Y.; Hsieh, D.K.; Lin, J.; Lin, G. Synthesis and evaluation of a new series of tri-, di-, and mono-N-alkylcarbamylphloroglucinols as bulky inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Sussman, J.L.; Harel, M.; Frolow, F.; Oefner, C.; Goldman, A.; Toker, L.; Silman, I. Atomic-structure of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo california: A prototypic acetylcholine-binding protein. Science 1991, 253, 872–879. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Liu, Y.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Wu, Y.G. Ortho effects in quantitative structure-activity relationships for acetylcholinesterase inhibition by aryl carbamates. J. Enzym. Inh. Med. Chem. 2004, 19, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Lee, Y.R.; Liu, Y.C.; Wu, Y.G. Ortho effects for inhibition mechanisms of butyrylcholinesterase by o-substituted phenyl N-butyl carbamates and comparison with acetylcholinesterase, cholesterol esterase, and lipase. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryger, G.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J. Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with E2020 (Aricept®): Implications for the design of new anti-Alzheimer drugs. Structure 1999, 7, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, I.; Dorronsoro, L.; Rubio, P.; Munoz, E.; Garcia-Palomero, M.; del Monte, A.; Bidon-Chanal, M.; Orozco, F.J.; Luque, A.; Castro, M.; et al. Donepezil-tacrine hybrid related derivatives as new dual binding site inhibitors of AChE. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 6588–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Chen, G.H.; Lu, C.P.; Yeh, S.C. QSARs for peripheral anionic site of butyrylcholinesterasewith inhibitions by 4-acyloxy-biphenyl-4′-N-butylcarbamates. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2005, 24, 943–952. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Chen, G.H.; Yeh, S.C.; Lu, C.P. Probing the peripheral anionic site of acetylcholinesterase with quantitative structure activity relationships for inhibition by biphenyl-4-acyoxylate-4′-N-butylcarbamates. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2005, 19, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampa, A.; Bisi, A.; Valenti, P.; Recanatini, M.; Cavalli, A.; Andrisano, V.; Cavrini, V.; Fin, L.; Buriani, A.; Giusti, P. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of omega-[N-methyl-N-(3-alkylcarbamoyloxyphenyl)methyl]aminoalkoxyhetero aryl derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 3976–3986. [Google Scholar]
- Rampa, A.; Piazzi, L.; Belluti, F.; Gobbi, S.; Bisi, A.; Bartolini, M.; Andrisano, V.; Cavrini, V.; Cavalli, A.; Recanatini, M.; et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: SAR and kinetic studies on omega-[N-methyl-N-(3-alkylcarbamoyloxyphenyl)methyl]aminoalkoxyaryl derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 3810–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, A.; Xie, Q.; Greenblatt, H.M.; Fu, W.; Tang, Y.; Silman, I.; Qiu, Z.; Sussman, J.L. Crystallographic snapshots of nonaged and aged conjugates of soman with acetylcholinesterase, and of a ternary complex of the aged conjugate with pralidoxime. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7593–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.O.; Wang, K.C.; Kwok, H.B. An improved method to determine SH and -S-S- group content in soymilk protein. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinko, G.; Calic, M.; Bosak, A.; Kovarik, Z. Limitation of the Ellman method: Cholinesterase activity measurement in the presence of oximes. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 370, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Zdrazilova, P.; Stepankova, S.; Komers, K.; Ventura, K.; Cegan, A. Half-inhibition concentrations of new cholinesterase inhibitors. Z. Naturforsch. 2004, 59, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Ekstrom, F.; Hornberg, A.; Artursson, E.; Hammarstrom, L.G.; Schneider, G.; Pang, Y.P. Structure of HI-6 center dot sarin-acetylcholinesterase determined by X-ray crystallography and molecular dynamics simulation: Reactivator mechanism and design. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5957. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Imramovsky, A.; Stepankova, S.; Vanco, J.; Pauk, K.; Monreal-Ferriz, J.; Vinsova, J.; Jampilek, J. Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibiting Activity of Salicylanilide N-Alkylcarbamates and Their Molecular Docking. Molecules 2012, 17, 10142-10158. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910142
Imramovsky A, Stepankova S, Vanco J, Pauk K, Monreal-Ferriz J, Vinsova J, Jampilek J. Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibiting Activity of Salicylanilide N-Alkylcarbamates and Their Molecular Docking. Molecules. 2012; 17(9):10142-10158. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910142
Chicago/Turabian StyleImramovsky, Ales, Sarka Stepankova, Jan Vanco, Karel Pauk, Juana Monreal-Ferriz, Jarmila Vinsova, and Josef Jampilek. 2012. "Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibiting Activity of Salicylanilide N-Alkylcarbamates and Their Molecular Docking" Molecules 17, no. 9: 10142-10158. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910142
APA StyleImramovsky, A., Stepankova, S., Vanco, J., Pauk, K., Monreal-Ferriz, J., Vinsova, J., & Jampilek, J. (2012). Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibiting Activity of Salicylanilide N-Alkylcarbamates and Their Molecular Docking. Molecules, 17(9), 10142-10158. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910142






