Astragalus membranaceus Extract Activates Immune Response in Macrophages via Heparanase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
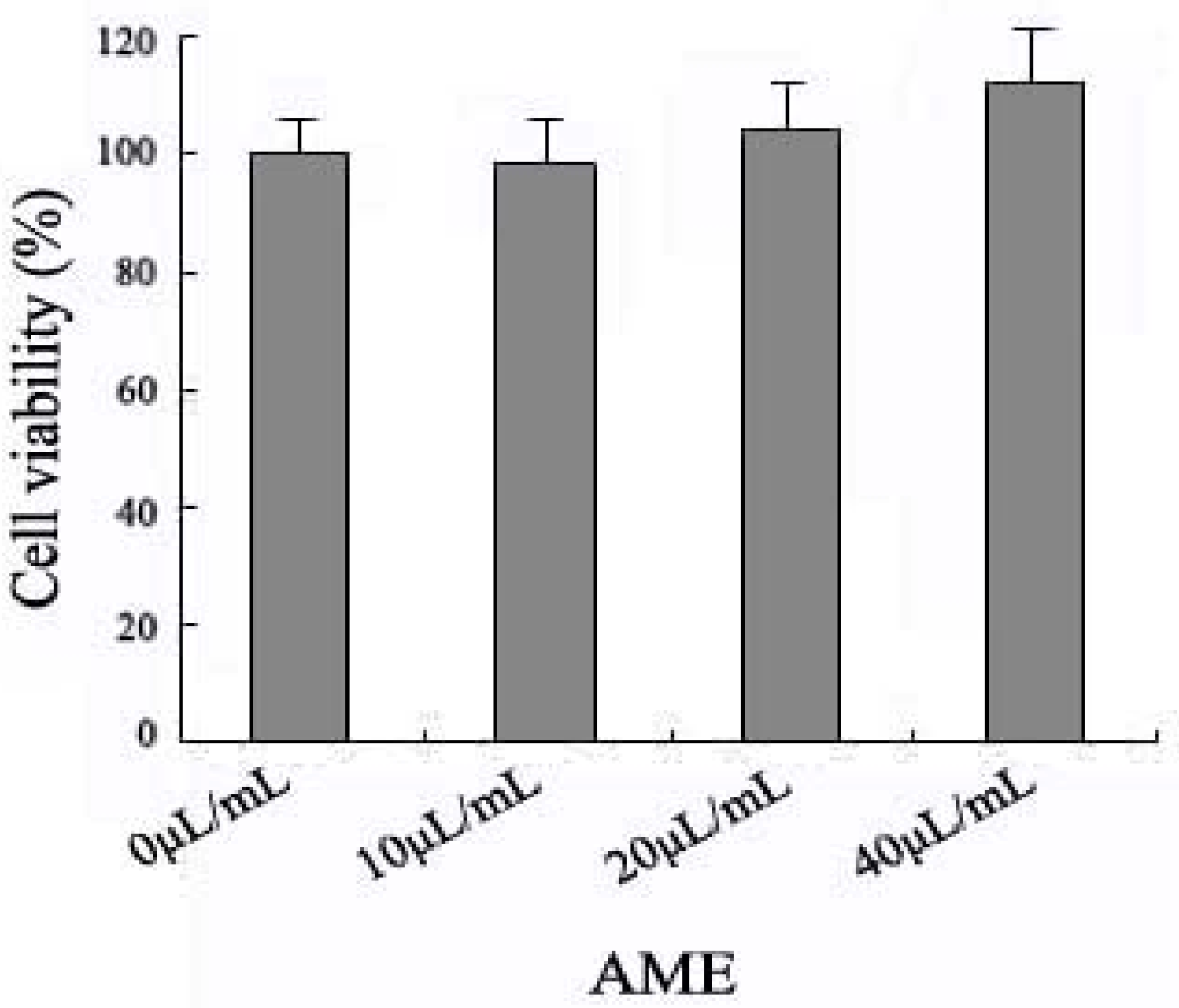
2.1. Effects of AME on Cell Viability
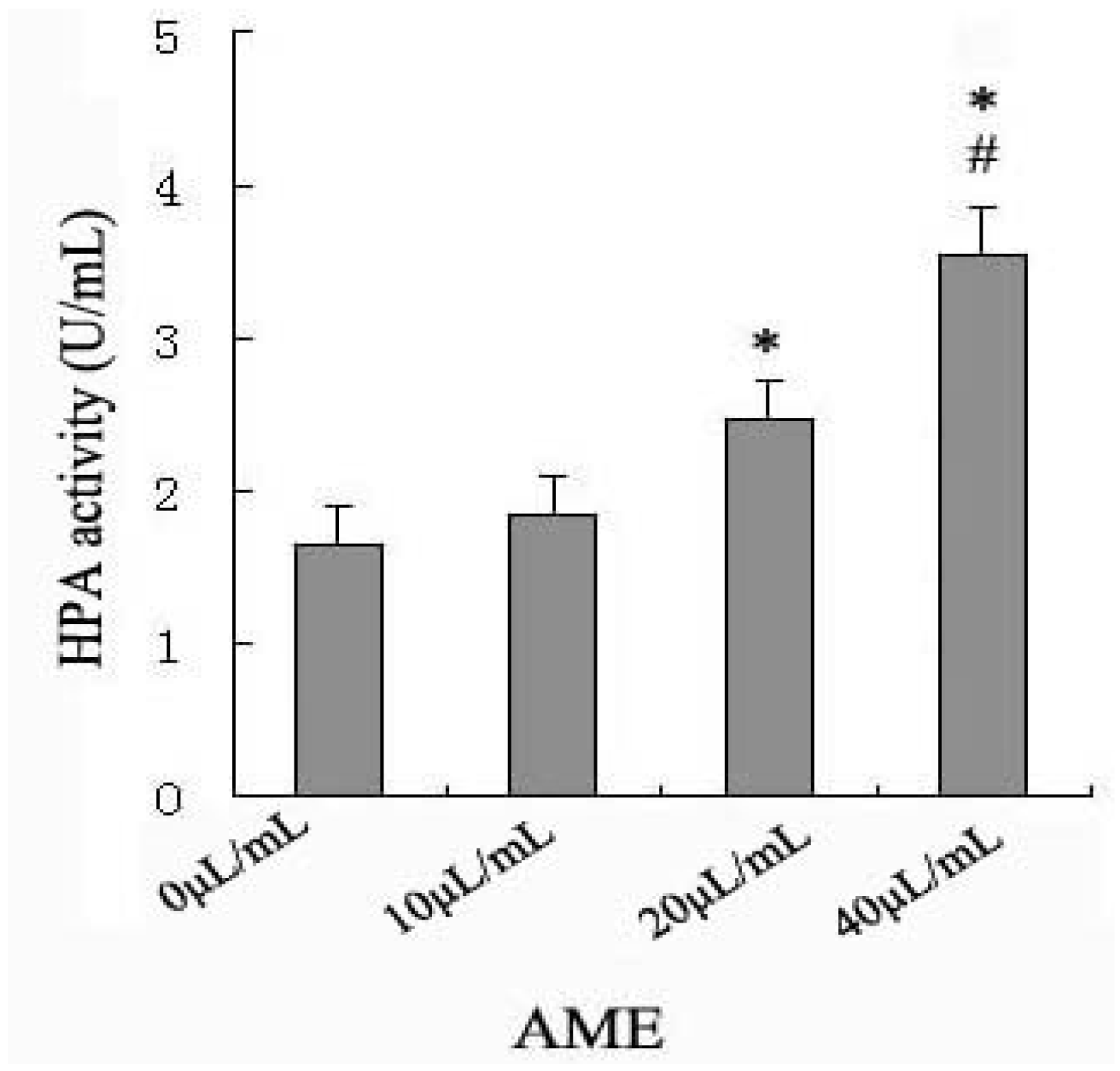
2.2. Effects of AME on HPA Enzymatic Activity
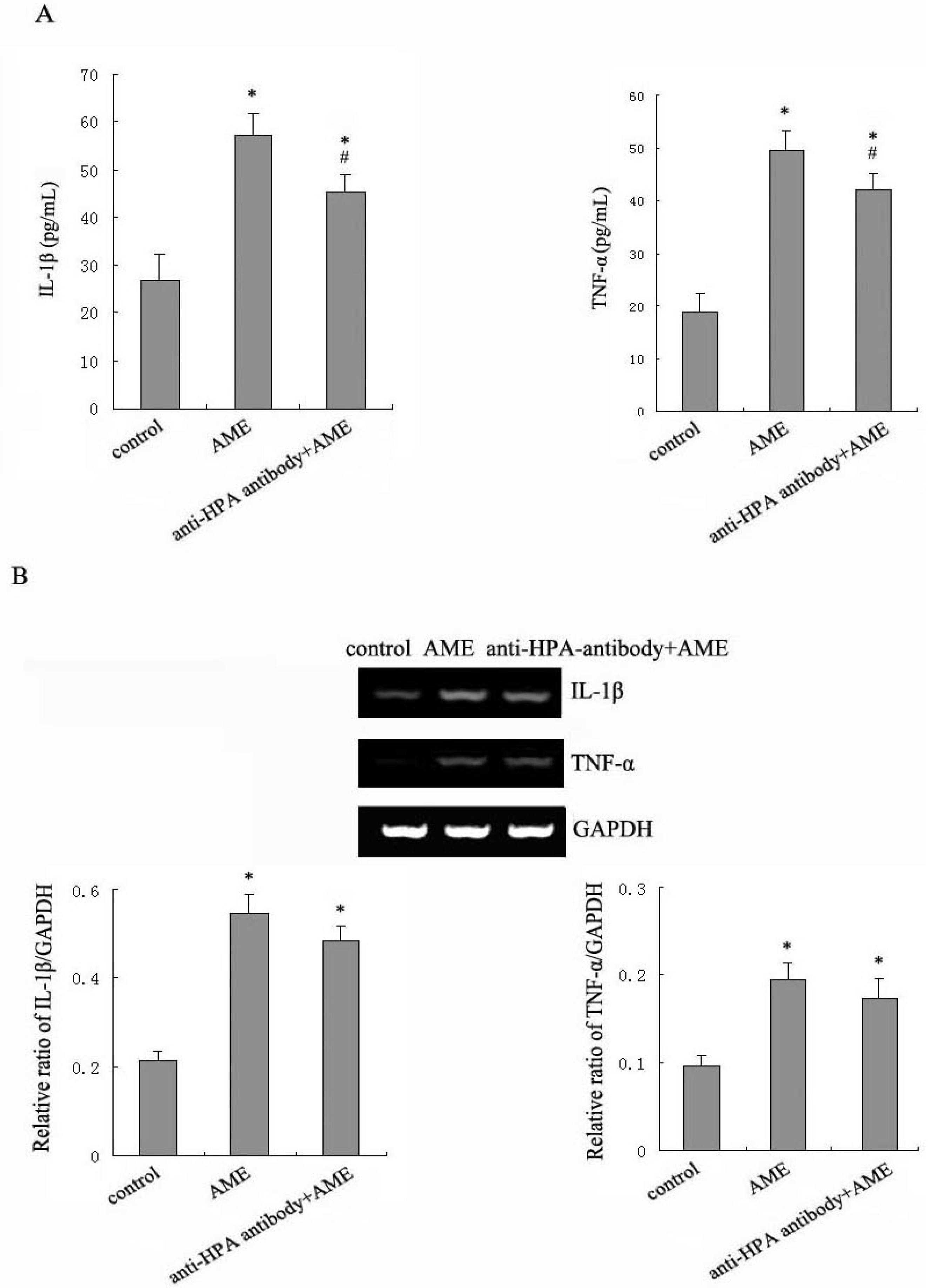
2.3. Effects of Anti-HPA Antibody on AME-Induced Secretion and mRNA levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in Macrophages
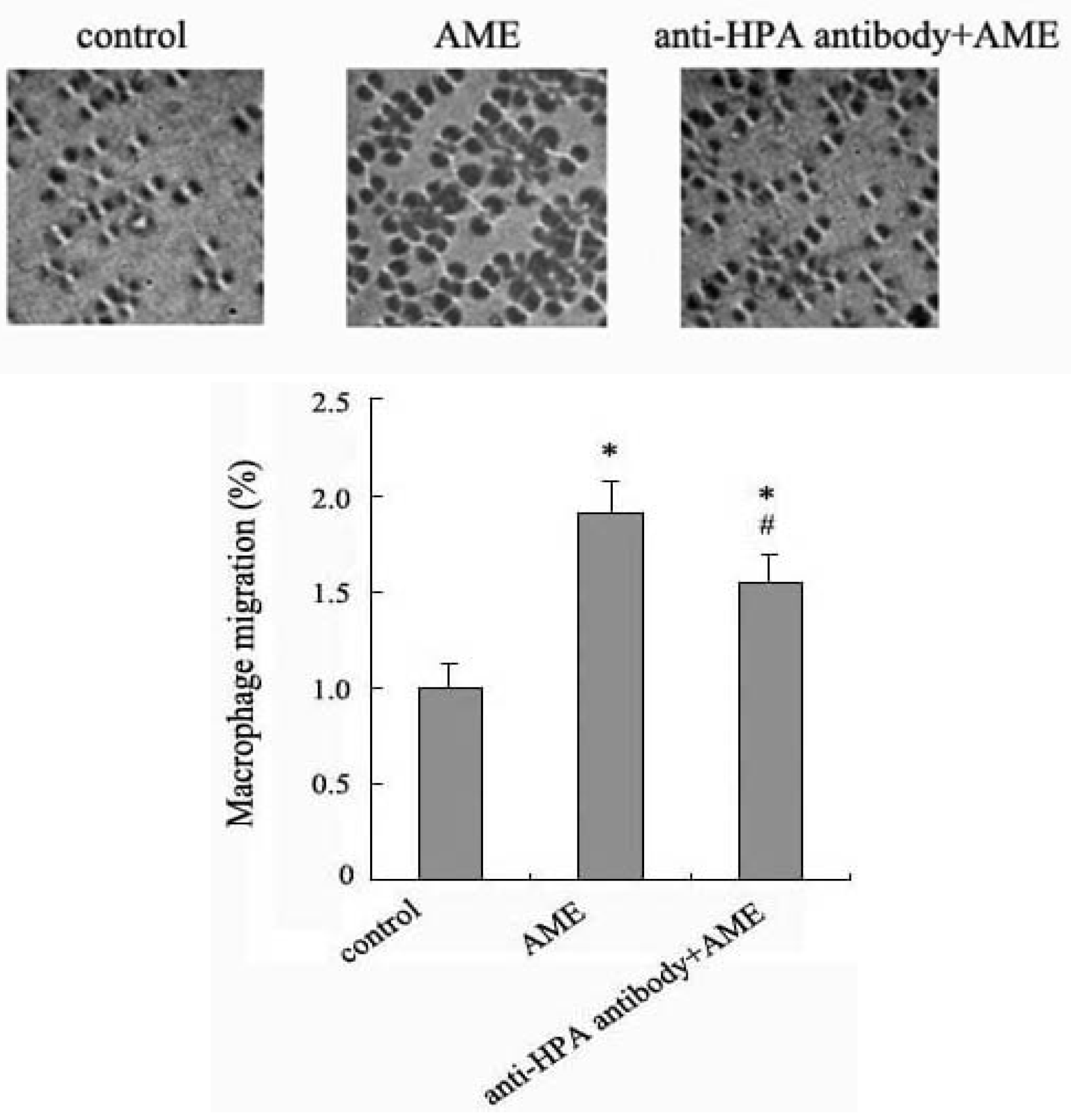
2.4. Effects of Anti-HPA Antibody on Macrophage Migration in AME-Induced Macrophages
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of AME
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Assessment of Cell Viability
3.5. Assessment of HPA Activity
3.6. Assessment of TNF-α and IL-1β Release
3.7. Detection of mRNAs by RT-PCR
3.8. Migration Assay
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References and Notes
- Zhao, L.H.; Ma, Z.X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, X.H.; Weng, D.P. Characterization of polysaccharide from Astragalus radix as the macrophage stimulator. Cell Immunol. 2011, 271, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Shu, J.; Xu, L.; Lu, C.; Lu, A. Inhibitory effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α and IL-1β production in THP-1 cells. Molecules 2012, 17, 3155–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement-Kruzel, S.; Hwang, S.A.; Kruzel, M.C.; Dasgupta, A.; Actor, J.K. Immune modulation of macrophage pro-inflammatory response by goldenseal and Astragalus extracts. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinfeld, H.; Cohen-Kaplan, V.; Nass, D.; Ilan, N, Meisel; Cohen, Z.R.; Hadani, M.; Vlodavsky, I.; Shimon, I. Heparanase is highly expressed and regulates proliferation in GH-secreting pituitary tumor cells. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 4562–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerner, I.; Hermano, E.; Zcharia, E.; Rodkin, D.; Bulvik, R.; Doviner, V.; Rubinstein, A.M.; Ishai-Michaeli, R.; Atzmon, R.; Sherman, Y.; et al. Heparanase powers a chronic inflammatory circuit that promotes colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermano, E.; Lerner, I.; Elkin, M. Heparanase enzyme in chronic inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Vlodavsky, I. Heparin, heparan sulfate and heparanase in inflammatory reactions. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 823–828. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, W.C.; Leung, K.N. In vitro and in vivo immunomodulating and immunorestorative effects of Astragalus membranaceus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 113, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Xue, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, D.; Kong, X.; Li, P.; Xu, W. Compound Chinese herbal medicinal ingredients can enhance immune response and efficacy of RHD vaccine in rabbit. Vaccine 2008, 26, 4451–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilada, E.; Bedir, E.; Caliş, I.; Takaishi, Y.; Ohmoto, Y. Effects of triterpene saponins from Astragalus species on in vitro cytokine release. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barash, U.; Cohen-Kaplan, V.; Dowek, I.; Sanderson, R.D.; Ilan, N.; Vlodavsky, I. Proteoglycans in health and disease: New concepts for heparanase function in tumor progression and metastasis. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3890–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreys, V.; Delande, N.; Zhang, Z.; Coomans, C.; Roebroek, A.; Dürr, J.; David, G. Cellular uptake of mammalian heparanase precursor involves low density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins, mannose 6-phosphate receptors, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33141–33148. [Google Scholar]
- Gingis-Velitski, S.V.; Zetser, A.; Kaplan, V.; Ben-Zaken, O.; Cohen, E.; Levy-Adam, F.; Bashenko, Y.; Flugelman, M.Y.; Vlodavsky, I.; Ilan, N. Heparanase uptake is mediated by cell membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44084–44092. [Google Scholar]
- Bitan, M.; Weiss, L.; Reibstein, I.; Zeira, M.; Fellig, Y.; Slavin, S.; Zcharia, E.; Nagler, A.; Vlodavsky, I. Heparanase upregulates Th2 cytokines, ameliorating experimental autoimmune encephalitis. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Marchetti, D. Cell surface heparan sulfate released by heparanase promotes melanoma cell migration and angiogenesis. J. Cell Biochem. 2009, 106, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, F.; Fujiwara, T.; Takata, Y.; Ohtani, S.; Katsuda, K.; Takaoka, M.; Ohkawa, T.; Naomoto, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Tanaka, N. Antisense-mediated suppression of human heparanase gene expression inhibits pleural dissemination of human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7855–7860. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, C.; Ke, Z.; Luo, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L. Heparanase participates in the growth and invasion of human U-2OS osteosarcoma cells and its close relationship with hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in osteosarcoma. Neoplasma 2010, 57, 562–571. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the Astragalus membranaceus extract are commercially available.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Q.; Niu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, W.; Qiao, Z.; Gu, Y. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Activates Immune Response in Macrophages via Heparanase. Molecules 2012, 17, 7232-7240. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17067232
Qin Q, Niu J, Wang Z, Xu W, Qiao Z, Gu Y. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Activates Immune Response in Macrophages via Heparanase. Molecules. 2012; 17(6):7232-7240. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17067232
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Qiaojing, Jianying Niu, Zhaoxia Wang, Wangjie Xu, Zhongdong Qiao, and Yong Gu. 2012. "Astragalus membranaceus Extract Activates Immune Response in Macrophages via Heparanase" Molecules 17, no. 6: 7232-7240. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17067232
APA StyleQin, Q., Niu, J., Wang, Z., Xu, W., Qiao, Z., & Gu, Y. (2012). Astragalus membranaceus Extract Activates Immune Response in Macrophages via Heparanase. Molecules, 17(6), 7232-7240. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17067232



