Abstract
Copaiba oleoresins are exuded from the trunks of trees of the Copaifera species (Leguminosae-Caesalpinoideae). This oleoresin is a solution of diterpenoids, especially, mono- and di-acids, solubilized by sesquiterpene hydrocarbons. The sesquiterpenes and diterpenes (labdane, clerodane and kaurane skeletons) are different for each Copaifera species and have been linked to several reported biological activities, ranging from anti-tumoral to embriotoxic effects. This review presents all the substances already described in this oleoresin, together with structures and activities of its main terpenoids.
1. Introduction
The Copaiba oleoresin is obtained from the trunk of several Copaifera L. species (Leguminosae-Caesalpinoideae). These trees are native to the tropical regions of Latin America and Western Africa. There are more than twenty species occurring in the Brazilian territory, the most abundant being C. officinalis L., C. guianensis Desf., C. reticulata Ducke, C. multijuga Hayne, C. confertiflora Bth., C. langsdorffii Desf., C. coriacea Mart. and C. cearensis Huber ex Ducke [1,2,3].
Copaiba oleoresin is widely used as a popular medicine, through topical and oral administration. It has various ethnopharmacological indications, including: gonorrhea, bronchitis, pains in general, back pain, injury, blennorrhagia, leucorrhea, psoriasis, “catarro da bexiga”, wounds, asthma, as an antiseptic for wounds, skin ulcers, aching joints, ovarian cysts, uterine myoma, weak uterus, vaginal discharge, ovarian problem, ulcers, sore throat, uterine infections, general inflammations, as a tonic and to treat ulcers and other digestive diseases, and cancer, and leishmanioses [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12].
Many studies have been performed in order to confirm these properties scientifically, and validate the widespread use of this oleoresin and its various pharmacological activities. Despite the many published papers, some of the data on the chemical composition and pharmacological activity of copaiba oleoresin remains contradictory. This study aims to expand knowledge about the chemical composition, biological activities and pharmacological actions of copaiba oleoresin and its major constituents.
2. Biological Studies with Crude Copaiba Oleoresins
Athough many species of Copaifera have been decribed, only nine of those have some biological study in the literature that evaluates the traditional uses. In some cases, these studies do not discriminate among the Copaifera species being studied, sometimes using commercial copaiba oleoresins. Table 1 shows all the biological and pharmacological activities that have been already tested for Copaifera oleoresins.

Table 1.
Biological activities tested in different species of Copaifera oleoresins.
| Species | Biological activity evaluated | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| C. cearensis Huber ex Ducke | Antimicrobial | [13] |
| Anti-inflammatory | [14] | |
| Antileishmanial | [15] | |
| C. duckei Dwyer | antiproliferative | [16] |
| Antimutagenic | [17] | |
| Embriotoxicity | [18] | |
| Anti-inflammatory | [19] | |
| Analgesic | [19] | |
| C. langsdorffii Desf. | Antimicrobial | [13,20,21,22,23] |
| Attenuation of ischemia/reperfusion-induced intestinal | [24] | |
| Gastroprotective effect on experimental gastric ulcer models in rats | [25] | |
| C. langsdorffii Desf. | Ischemia-Reperfusion of Randomized Skin Flaps | [26] |
| Antileishmanial | [15] | |
| Wound Healing | [27,28,29] | |
| Antioxidant | [30] | |
| Insecticide | [31] | |
| Anti-inflammatory | [32,33] | |
| Antimutagenic | [34] | |
| C. lucens Dwyer | Antimicrobial | [13] |
| Antileishmanial | [15] | |
| C. martii Hayne | Antimicrobial | [13] |
| Antileishmanial | [15,35] | |
| C. multijuga Hayne | Anti-inflammatory | [14,36,37,38] |
| Antimicrobial | [13,39,40,41,42] | |
| Antitumor | [43,44] | |
| Antinociceptive | [36,45] | |
| Antileishmanial | [15] | |
| Healing | [46] | |
| C. officinalis (Jacq.) L. | Antimicrobial | [13,22,23,47,48] |
| Antischemic | [49] | |
| Anti-inflammatory | [50] | |
| Antileishmanial | [15] | |
| Inhibition of human leukocyte elastase | [51] | |
| Effect Antitumor (Walker 256 carcinoma) | [52] | |
| C. paupera (Herzog) Dwyer | Antimicrobial | [13] |
| Antileishmanial | [15,53] | |
| C. reticulata Ducke | Antiinflammatory | [14] |
| Antimicrobial | [13,54] | |
| Inseticide | [55,56,57,58] | |
| Antinociceptive | [45] | |
| Teratogenicity and embriotoxicity | [59] | |
| Toxicity | [60] | |
| Antileishmanial | [15,61] | |
| Wound Healing | [62,63] | |
| Anxiolytic | [64] | |
| C. sp. (commercial copaiba oleoresins) | Antimicrobial | [40] |
| Anti-inflammatory | [65,66] | |
| Skin perfusion | [67] | |
| Insecticide | [68,69,70,71] |
Of the various ethnopharmacological indications of copaiba oleoresins, some, such as anti-inflammatory, wound healing, antimicrobial, antileishmanial, larvicidal, antineoplasic and antinoceptive activities have been confirmed by pharmacological studies, as will be detailed below.
The very first study aiming to demonstrate the anti-inflammatory activity of copaiba oleoresin was performed by Basile et al. [65]. The activity found was related to the anti-oedematogenic effect observed in carragenin induced rat paw oedema, and was later confirmed by Veiga, Jr. et al. [66]. This later study also showed that the activity varies with copaiba oleoresins from different species, and using different flogistic agents. All these studies were performed with commercial copaiba oleoresins, but without identifying the individual species. Baylac and Racine [50] showed that C. officinalis oleoresin causes in vitro inhibition of 5-lipoxygenases, an important enzyme of the inflammatory cascade. The same authors [51] showed that the copaiba oleoresin obtained from C. officinalis was not capable of causing in vitro inhibition of HLE (Human leukocyte elastase), one of the main proteases in the neutrophils, which play an important role in the pathogenesis of many inflammatory disorders.
Veiga, Jr. et al. [14] evaluated the anti-inflammatory activity of three different copaiba oleoresins (C. multijuga Hayne, C. cearensis Huber ex Ducke and C. reticulata Ducke), and demonstrated that although similar in composition, they showed different activities. The assay was evaluated in vitro by measuring NO production by murine macrophages and in vivo using the zymosan induced pleurisy model in mice. The C. multijuga Hayne oleoresin was the most potent, inhibiting the NO production at a low concentration (5 µg/mL). The oleoresins from C. cearensis and C. reticulata presented similar activities but with less intensity (50 µg/mL and 500 µg/mL, respectively). Veiga, Jr. et al. [37] evaluated and afirmed that the crude C. multijuga Hayne oleoresin and its fractions (hexane, dichloromethane and methanolic) have anti-inflammatory properties against carrageenan- and bradykinin-induced oedema formation in the rat paw. Gomes et al. [36] suggest that C. multijuga Hayne oleoresin has anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting histamine and the serotonine pathways. The C. duckei Dwyer oleoresin demonstrated anti-oedematogenic effect observed on carragenin induced rat paw oedema [19]. Araujo, Jr. et al. [49] studied the anti-inflammatory activity of C. oficinalis oleoresin in aminotransferases in rats submitted to hepatic ischemic and reperfusion, and found that it presented no activity. In a similar study, Brito et al. [38] evaluated the effect of the oleoresin of C. multijuga on urea and creatinine serum levels in rats submitted to ischemia and reperfusion kidney. They observed a decrease in vascular permeability to proinflammatory agents caused by copaiba oleoresin, when in turn, decreased the migration of toxic agents to the renal parenchyma, thereby mitigating the damage of this organ. Nogueira Neto et al. [33] tested the C. langsdorffii oleoresin on endometriosis foci in female rats, and found significant histological changes, with a reduction in volume of the endometrioses.
The strong healing activity of copaiba oleoresins is one of the properties most frequently cited in ethnopharmacological studies. Despite this fact, the pharmacological studies are controversial. Brito et al. [62,63] observed that wounded rats treated with copaiba oleoresin obtained from C. reticulata took longer to heal and showed more inflammation than the control animals (saline). Similar results were obtained by Vieira et al. [28], who found that copaiba oleoresin from C. langsdorffii impairs the normal process of wound repair in the presence of a foreign body. Westphal et al. [46] observed an increase in tissue inflammation in rats treated by intrapleural injection of C. multijuga oleoresin. Also, according to Comelli, Jr et al. [29] the crude C. langsdoffii oleoresin has no effect on wound healing in intestinal mucosa of rats oil-treated orally. On the other hand, Paiva et al. [27] investigated the activity of wound healing in rats treated with copaiba oleoresin from C. langsdorffii, and obtained results that allowed them to affirm the benefits of this copaiba oleoresin, justifying its traditional use. These contradictory results may be due to the fact that oleoresins have different sources, because depending on environmental factors, plants produce different metabolites that can directly influence the activity [72].
Antimicrobial activity of oleoresin of copaiba is one of the most frequently studied properties, and various works have evaluated its antimicrobial activity against the following bacteria: Escherichia coli [21,39], Staphylococcus aureus [13,20,23,39,40,54], Pseudomonas aeruginosa [23,39], methicillin-resistant S. aureus [13], Listeria monocytogenes [21], Staphylococcus epidermidis [13], Bacillus subtilis [13,20,40], Streptococcus mutans [47], Streptococcus salivarius [47], Streptococcus pyogenes [47], Proteus mirabilis [13,23], Klebsiella pneumoniae [13,23], Shigella flexinerii [13,23], Enterobacter cloacae [13], Enterococcus faecalis [13,47], Citrobacter freundi [23], Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae [23], Haemophilus parasuis [23], Paenibacillus alginolyticus [48], P. pabuli [48], P. azotofixans [48], P. borealis [48], P. gluconolyticus [48], P. validus [48], P. thiaminolyticus [48] and P. larvae [48]; yeasts: Candida albicans [13], C. parapsilosis [13,41,42], C. tropicalis [13,41,42] and C. guilliermondii [41,42]; and fungi: Aspergillus flavus [41,42], A. niger [41,42], A. tamari [41,42], A. terreus [41,42], Trichophyton rubrum [13], T. mentagrophytes [13], Microsporum canis [13] and M. gypseum [13].
Copaiba oleoresin from C. multijuga showed antimicrobial activity against E. coli, S. aureus and P. aeruginosa [39]. However, Pacheco et al. [40] did not observe any activity of the copaiba oleoresin from C. multijuga against S. aureus (or against any other bacteria analyzed). The authors also mention that another copaiba oleoresin (species not identified) showed no activity against B. subtilis and S. aureus. The fungicidal activity fungicida of C. multijuga oleoresin in natura, and a volatile fraction obtained of the hydrodistillation of this oleoresin, were evaluated in vitro against filamentous fungi (Aspergillus) and yeast (Candida). Samples were compared with the antibiotic drug Miconazole nitrate (MIC = 0.1–0.5 µg/mL), the volatile fraction being more active (MIC = 0.08–0.5 µg/mL) [41,42].
Oleoresins obtained from the species C. martii, C. officinalis and C. reticulata showed in vitro bactericidal activity against S. aureus, methicillin-resistant S. aureus, S. epidermidis, B. subtilis, and E. faecalis with minimum inhibitory concentrations ranging from 31.3–62.5 μg/mL [13]. The oleoresin from C. reticulata showed high activity against S. aureus multidrug resistant (MIC = 2.5 µg/mL) and S. aureus ATCC strains (MIC = 5.0 µg/mL) [54]. Pieri et al. [47] showed the ability of the C. officinalis oleoresin to inhibit bacterial adhesion in dog’s teeth by clinical and microbiological trials.
Antimicrobial activity of two solutions containing oleoresins of two different species of Copaifera was tested against 27 strains of Escherichia coli obtained from mastitic milk of animal origin. The solution of C. langsdorffii oleoresin inhibited the growth of eight strains and another solution containing C. officinalis inhibited the growth of seven isolates. The results of this study suggest that the copaiba oleoresin may be a potential source of new and selective antimicrobial agents [22]. Pieri et al. [21] found that C. langsdorffii oleoresin did not alter its antimicrobial activity against bacteria of the Listeria monocytogenes species after exposure to high temperatures in an autoclave. In another study, two copaiba oleoresins were evaluated for antibacterial activity against pathogenic species of interest to animal and human health. The C. langsdorffii and C. officinalis oleoresins showed activities against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. flexneri and S. aureus [23]. Santos et al. [48] demonstrated that the essential oil of C. officinalis presents high activity against Paenibacillus species. These results show that some copaiba oleoresins have antimicrobial activity, confirming the findings of the ethnopharmacological studies.
The studies of Paiva et al. [25] with C. langsdorffii copaiba oleoresin found a reduction in gastric wounds induced by ethanol, and a hypothermic restraint-stress in the indomethacin model mediated through its effect on mucus production and by its antiacid secretory properties. Later, Paiva et al. [24] demonstrated the protector activity of this oleoresin against ischemia/reperfusion-induced intestinal tissue damage.
The anticancer activity of copaiba oleoresins from some species has been studied using diverse models. The C. multijuga oleoresin and its (hexane and chloroform) fractions obtained by fractionation using KOH impregnated gel column chromatography demonstrated significant inhibitory effect on Erlich tumor-bearing mice [44], and found that it reduced the growth of melanoma cells on mice [43], both after oral administration, confirming its use by traditional medicine. However, Brito et al. [52] found that the species C. officinalis stimulated the tumor growth of Walker 256 carcinoma inoculated into the vagina and uterine cervix of rats.
Gomes et al. [45] observed a central and peripheral antinociceptive activity in two copaiba oleoresins (C. multijuga and C. reticulata), and suggest that fractions (hexane, chloroform and methanol) obtained from C. multijuga oleoresin after a KOH impregnated gel column chromatography have antinociceptive effect mediated by the opioid receptors [36]. Carvalho et al. [19] demonstrated the existence of analgesic activity from C. duckei Dwyer oleoresin by intraperitoneal administration of acetic acid solution in mice.
The mutagenic and cytotoxic activity of C. langsdorffii oleoresin were evaluated in erythrocytes of Mus musculos mice treated with crude oleoresin by oral administration, in which dose-dependant toxic capacity was found [34]. The mutagenic and cytotoxic activities of C. duckei oleoresin were evaluated in Wistar rats by dermal application, and was found to have no toxicity to the peripheral blood reticulocytes and bone marrow cells [17]. In another study, the acude toxic and neurotoxic effects of C. reticulata oleoresin administered orally to the Wistar rats species were evaluated, presenting low mortality and a very high toxic dose [60]. The same author evaluated the embriotoxicity of oleoresin from C. reticulata in pregnant rats. The oleoresin was toxic to the mother and embryotoxic, but not letal at any dose level [59].
Lima et al. [18] performed a pre-clinical trial in Wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus) of a vaginal cream containing 2.5% of C. duckei oleoresin. This study demonstrated the absence of maternal toxicity, embryofoetotoxicity and fetotoxicity at the dose administered (10 times that recommended in humans), and it was concluded that the vaginal cream is safe during pregnancy.
The anxiolytic activity was evaluated in an ethological study in rats treated with C. reticulata oleoresin. The studies demonstrated that copaiba oleoresin produced dose-dependent anxiolytic-like effects across all the dose ranges tested, within conventional and ethological parameters, without adversely affecting general activity [64].
Many studies still report insecticidal activity of great interest in popular knowledge, such as C. reticulata oleoresin tested for its insecticidal activities against the Japanese termite (Reticulitermes speratus Kolbe) using a fumigation bioassay, which did not demonstrate insecticidal activity [57].
A study evaluated the use of commercially available insect repellents used by military personnel in a jungle environment in the Amazon region. The repellent DEET (N,N-diethyl-3-methylbenzamide) was compared with natural oil-repellents containing Copaifera spp. oleoresin. The results showed a higher degree of perceived protection against damage caused by insects with the repellant containing copaiba oleoresin [68].
The acaricidal activity of oleoresinous extract from C. reticulata was investigated; larval mortality was tested after treatment with a solution containing the oleoresin, and the concentration was evaluated to determine lethal concentrations [58].
Larvicidal activity of C. reticulata oleoresin was observed for Culex quinquefasciatus, the main transmitter of Bancroftian filariasis [56]. Copaiba oleoresins from C. langsdorffii showed significant activities against Aedes aegypti (LC50 = 41 µg/L) in the larvicidal assay [31]. Another study demonstrated the potential of Copaifera spp. oleoresin to inhibit A. aegypti proliferation, showing larvicidal activity at low concentrations (LC50 = 44–51 mg/mL), and a gradual reduction in activity was observed over several days [69]. Silva et al. [55] showed that the hexanic and methanolic fractions of oleoresin from C. reticulata exhibited high toxicity against A. aegypti larvae. Prophiro et al. [71] investigated the efficiency of solution prepared with Copaifera spp. oleoresin as a larvicide in wild populations of A. aegypti with resistence to organophosphate, showing larvicidal activity in all concentrations tested. The same author studied the start time of larvicidal activity, residual effect, and the effect of very low concentrations of this oleoresin on A. aegypti; the results demonstrated a lethal effect between the first 2 and 3 h of larval development, with the toxic effect remaining totally effective (100% mortality) until the sixth day for Copaifera sp. (90 mg/L) [70].
Santos et al. [15] screened eight different Brazilian copaiba oleoresins for antileishmanial activity, and observed a variable level of activity against Leishmania amazonensis (IC50 = 5.0 to 22 µg/mL), with the oleoresin from C. reticulata showing the strongest antileishmanial activity (IC50 = 5 μg mL−1) for promastigote forms of L. amazonensis after 72 h of incubation. Kvist et al. [53] observed moderate leismanicide activity for C. paupera oleoresin (IC50 = 17 µg/mL), lower than that found by Santos et al. [15], that was IC50 = 11 µg/mL. The oral treatment with C. martii oleoresin showed a significant reduction in the average lesion size (1.1 ± 0.4 mm) caused by L. amazonensis when compared with untreated mice (4.4 ± 1.3 mm), and histopathological evaluation did not reveal any changes in the animals treated with copaiba oleoresin, compared with the control animals. In this study, morphological and ultrastructural analyses demonstrated notable changes in parasite cells treated with this oleoresin [35]. Significant antileishmanial activity of copaiba oleoresin from C. reticulata was demonstrated against axenic amastigote (IC50 = 15.0 μg/mL) and intracellular amastigote (IC50 = 20.0 μg/mL), forms of the parasite L. amazonensis [61].
Copaiba oleoresin is also used by the cosmetics and varnish industries [12]. Oliveira et al. [67] observed that copaiba oleoresin has potential for use in topical formulation, as a stimulant agent for the absorption of hydrofilic bioactive substances. Despite the high volume of published works on copaiba oleoresin and its biological activities, there are few references that identifiy the compounds responsible for its biological activity.
3. Chemical Composition of Copaiba Oleoresins
Copaiba oleoresin is a transparent liquid with variable colour and viscosity. It consists of a mixture of sesquiterpenes and diterpenes. The oldest chemical study with copaiba oleoresin dates back to the beginning of the 19th century, when Schweitzer, in 1829, described how copaiba oleoresin, when left standing, turned into a solid substance and crystallized. He called this substance copaivic acid [12]. It is difficult to say precisely what the structure of this substance was, due to the lack of information described, and the unavailability of identification techniques at that time.
A review article from 2002 listed the sesquiterpenes and diterpenes described in the literature on copaiba oleoresins [12]. New substances and other undescribed terpenoids have been published since then. At least 38 other sesquiterpenes were identified. Of these, 35 were found in oleoresins of C. duckei, C. paupera, C. piresii, C. pubiflora and C. reticulata: cyclosativene [73,74,75,76], 7-episesquithujene [76], cyperene [76], cis-α-bergamotene [73,76], trans-α-bergamotene [73,74,75,76], (Z)-β-farnesene [75,76], guaia-6,9-diene [76], epi-β-santalene [73,76], (E)-β-farnesene [73,76], sesquisabinene [76], 4,5-diepiaristolochene [76], germacrene A, [74], trans-cadina-1(6),4-diene [74], β-chamigrene [73,76], cis-β-guaiene [76]; viridiflorene [76], γ-gurjunene [73], γ-curcumene [73], epi-cubebol [74], valencene [73,76], trans-β-guaiene [76], (E,E)-α-farnesene [76], (Z)-α-bisabolene [73,75,76], α-bulnesene [73], β-curcumene [73], (Z)-γ-bisabolene [76], 7-epi-α-selinene, [74,75,76], trans-cadina-1(2),4-diene [74], (E)-γ-bisabolene [73,75,76], globulol [74], humulene epoxide II [75], epi-cubenol [74], cubenol, [74], epi-α-muurolol [74] and epi-β-bisabolol [73]. From hydrodistillation of the C. langsdorffi and C. martii oleoresins, a further identified three sesquiterpenes were identified: seline-3,7(11)-diene [77], α-calacorene [78] and gleenol [78]. Even with the great variation that the chemical composition of these oleoresins usually presents, β-caryophyllene, considered a chemical marker of these oleoresins, is usually the major constituent [79]. However, α-copaene was the major constituent of samples of C. paupera and C. piresii oleoresins collected in Acre and Rondônia, respectively [74], and was also the major constituent in the samples of C. martii oleoresins collected in Pará, subjected to hydrodistillation [78]. Meanwhile, β-bisabolene was the major constituent in several samples of C. duckei and C. reticulata collected in Pará [73,75].
As for the diterpenes, at least 15 other diterpenes not reported in the review article of 2002 were identified, including four with kaurane-type skeletons: ent-kaur-16-ene [80], ent-kaur-16-en-19-al [80], 19-nor-kaur-16-en-4α-ol [80,81] and ent-kaur-16-en-19-ol [80]; three of clerodane-type skeleton: clerodan-15,18-dioic acid [82], 7α-acetoxyhardwickiic acid [83] and 7α-acetoxybacchotricuneatin D [84]; and eight with labdane-type skeletons: ent-4-epi-agathic acid [81], 3-hydroxycopalic acid [85], 3-acetoxy-copalic acid [79], 14, 15-dinorlabd-8(17)-en-13-one [86], (-)-3-β-hydroxy-15,16-dinorlabd-8(17)-ene-13-one [84], (-)-15,16-dinorlabd-8(17)-en-3β,13-diol [87], (-)-13(R)-14,15-dinorlabd-8(17)-ene-3,13-diol [88] and pauperol [86].
There are some doubts as to the exact structures of these two last diterpenes. The ent-dinorlabdane (-)-13(R)-14,15-dinorlabd-8(17)-ene-3,13-diol, was isolated from a commercial copaiba oleoresin [88]. This substance may have been degraded from 3-hydroxycopalic acid, since the oleoresin, without identification, would have been exposed to light and temperature conditions that could lead to loss of part of the side chain. The other is a C35 methyl ester, a substance produced by the coupling of a labdanoic diterpene and a sesquiterpene alcohol, giving the ester pauperol, isolated from C. paupera [86]. Indeed, this substance may not be originally present in the oleoresin, since the authors report that they performed esterification (diazomethane) prior to the isolation.
The perfume and cosmetics industries have shown great interest in the sesquiterpene fraction, which is responsible for the aroma of copaiba oleoresin. The commercial value of concentrates of sesquiterpenes of Copaifera is as much as six hundred times higher than that of the whole copaiba oleoresin. Sant’Anna et al. [89] evaluated the volatile fraction of C. multijuga oleoresin and indicated minor compounds such as δ-cadinene, δ-cadinol, (Z)-α-santalol, caryophyllene oxide, α-cadinol and τ-muurolol as the most intense compounds in the aroma of the copaiba oleoresin studied. Chiral GC-O-MS proved (+)-δ cadinene to be the only enantiomer present in the oleoresin, with a sweet, green, refreshing aroma.
3.1. Pharmacological Activities of the Main Sesquiterpenes from Copaiba Oleoresin
Many studies have shown that sesquiterpenes are the main substances present in copaiba oleoresins. Sometimes, these account for more than 90% of their composition. Because they are the major components, many of the pharmacological activities of copaiba oleoresins are attributed to the main sesquiterpenes from the oleoresin. However, the pharmacological effect of the oleoresin, cannot be attributed to just one constituent, because the constituents present in oleoresin may interact synergistically in the promotion of the activity observed.
The main sesquiterpenes found in copaiba oleoresins are: β-caryophyllene, caryophyllene oxide, α-humulene, δ-cadinene, α-cadinol, α-cubebene, α- and β-selinene, β-elemene, α-copaene, trans-α-bergamotene, and β-bisabolene (Figure 1).
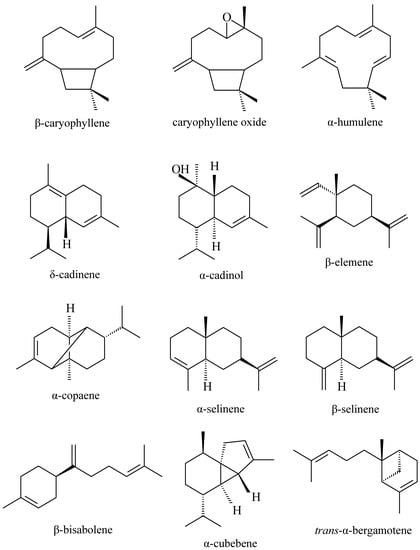
Figure 1.
Main sesquiterpenes detected in copaiba oleoresin.
Some of the sesquiterpenes are major components in the oleoresin and others, although present in minor proportions, are often detected. Some studies of the pharmacological activities of some of the main sesquiterpenes found in the copaiba oleoresin are described below.
The sesquiterpenes β-caryophyllene and its oxide are both commonly found in copaiba oleoresins and in many other plant species [90,91]. Cascon et al. [79] suggested that caryophyllene oxide is possibly an oxidative artefact produced during storage of oleoresin. Several biological activities are attributed to β-caryophyllene, such as insecticidal [92,93], antimicrobial [94,95], local anaesthetic [96], anticarcinogenic [97,98,99,100,101], and anti-inflammatory [90,91] activities.
Rodilla et al. [92] isolated β-caryophyllene and its oxide from Laurus novocanariensis leaves essential oil and they showed that both were strong antifeedants to Leptinotarsa decemlineata and Spodoptera littoralis. Another study demonstrated the repellent effect of caryophyllene oxide against Anopheles gambiae [93]. The sesquiterpenes β-caryophyllene and caryophyllene oxide, isolated from the oil of Calocedrus formosana leaves, presented antitermitic activity and antifungal activity against L. sulphureus [95]. Goren et al. [94] reported that β-caryophyllene presented antimicrobial activity against E. coli, S. aureus, K. pneumonia, P. aeruginosa and C. albicans, and caryophyllene oxide showed activity only for C. albicans. Ghelardini et al. [96] demonstrated that β-caryophyllene has a strong local anaesthetic action.
Many authors have reported the anticarcinogenic properties of β-caryophyllene. According to Silva et al. [97] and Kubo et al. [98], this sesquiterpene exhibits cytotoxic activity against several solid tumor cell lines. A previous study showed that β-caryophyllene exhibited antiproliferative activity in human renal adenocarcinoma and amelanotic melanoma cells [102]. Futhermore, β-caryophyllene has also been reported to increase the anticancer activity of α-humulene, isocaryophyllene and paclitaxel against tumour cell lines [101]. In study by Zheng et al. [99], the compounds: β-caryophyllene, β-caryophyllene oxide, and α-humulene (all present in the copaiba oleoresins) showed significant activity as inducers of the detoxifying enzyme glutathione S-transferase in mouse liver and small intestine. Finally, antimutagenic activity of the β-caryophyllene was observed by Di Sotto et al. [100]. According to the authors, this sesquiterpene was able to protect human lymphocytes cultivated with genotoxic damage induced by ethylic methanesulfonate and colcemid.
Many studies have also confirmed the anti-inflammatory activity of β-caryophyllene and/or caryophyllene oxide. Tung et al. [90] studied anti-inflammatory activities of essential oil from Cinnamomum osmophloeum twigs and its main constituents. In this study, the sesquiterpenes β-caryophyllene and its oxide exhibited excellent anti-inflammatory activities in suppressing nitric oxide production by LPS-stimulated macrophages. In other studies, caryophyllene oxide showed significant central as well as peripheral analgesic, along with anti-inflammatory, activity [91] and showed inhibitory effect on histamine-induced contraction in guinea pig ileum [103]. Cho et al. [104] demonstrated the ameliorative effect of oral administration of β-caryophyllene in mice on experimental colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium.
The sesquiterpenes β-caryophyllene and α-humulene, isolated from Cordia verbenacea leaves essential oil, showed systemic anti-inflammatory activity in rat paw oedema induced by carregeenin, bradykinin, P Substance, histamin and plaquetary activating fator (PAF), and also oedema induced by Apis mellifera venom or ovalbumin in sensitized rats. In the same paper, a decreasing in TNF level was observed, without this affecting the production of interleukin-1 [105]. The link between isolated α-humulene and β-caryophyllene and the release of inflammatory mediators, such as bradykinin, FAP, histamine, interleukin-1β, TNF and prostaglandins, was observed, together with COX-2 inhibition NF-KB [106].
Likewise, a solution of α-humulene and β-caryophyllene showed action against allergy-related inflammation in an experimental model in which this solution was used to treat mice sensitized with oral or nasal administration. α-Humulene showed activity even in therapeutic or preventive treatments, reducing the eotaxin and interleukin-5 levels of the mediastine lymph nodes (in vitro), a result not shown for β-caryophyllene. α-Humulene also reduced the nuclear transcription factor (NF-KB), P-selectin expression in the lung tissue and mucus secretion from the lungs, results that suggest its potential use for the treatment of asthma and allergy-related inflammatory diseases [107]. Furthermore, α-humulene showed cytotoxity activity against several solid tumor cell lines, including breast cancer adenocarcinoma, prostatic adenocarcinoma, lung carcinoma, colon adenocarcinoma lines, and human melanoma cell line, besides mouse colon cell line. The authors suggested that the cytotoxicity of α-humulene resulted in cellular glutathione depletion and reactive oxygen species production [108].
Other common sesquiterpenes in the copaiba oleoresin are δ-cadinene and α-cadinol. δ-Cadinene inhibited the growth of Streptococcus mutans (one of the most important cariogenic bacteria) and Propionibacterium acnes (one of the bacteria responsible for acne) [109]. Pérez-Lopez et al. [110] performed a bioassay-guided fractionation of the essential oil obtained from the fruit of Schinus molle against S. pneumonia resistant to conventional antibiotics, which led to the identification of δ-cadinene as the principal active constituent (MIC of 31.25 μg/mL) from the oil.
Previous studies have reported that α-cadinol showed antitermitic activity [95], insecticidal activity against yellow fever mosquito larvae, and was selectively cytotoxic against human colon adeno-carcinoma [111]. Furthermore, it exhibited antifungal activity against C. versicolor [112] and L. sulphureus [95,112].
Elemene is mainly composed of β- and δ- and γ-elemene, with β-elemene accounting for 60%–72% of all three isoforms [113]. β-Elemene is a broad-spectrum antitumor agent. It has been shown that this sesquiterpene is an effective treatment for various types of cancer, including gastric [114], lung [115], laryngeal [116], ovarian [117], brain [118], prostate [119] cancer, and leukemia [120].
Liu et al. [114] investigated the anti-tumor effect of β-elemene on human gastric cancer cells, and the molecular mechanism involved. The data provides the first evidence that β-elemene induces protective autophagy and prevents human gastric cancer cells from undergoing apoptosis. Wang et al. [115] indicated that human lung carcinoma cells were more sensitive to β-elemene than the others.
The inhibitory effects and mechanism of elemene were also investigated in the growth of laryngeal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo, transplanting cell subcutaneously to BALB/c nude mice to produce solid tumors. Increased apoptosis was observed in elemene administered cells. In vivo, the growth of HEp-2 cell-transplanted tumors in nude mice was inhibited by intraperitoneal injection of elemene [116].
Li et al. [117] showed that β-elemene inhibited the proliferation of cisplatin resistant human ovarian cancer cells and their parental cells, but had only a marginal effect in human ovary cells, indicating differential inhibitory effects on cell growth when comparing ovarian cancer cells with normal ovary cells. It was also demonstrated for the first time that β-elemene markedly enhanced cisplatin induced growth inhibition in resistant cells compared to sensitive cells.
β-Elemene induced the formation of apoptotic bodies and DNA ladder on K562 leukemia cells, an effect that was dose- and time-dependent in β-elemene treated cells as compared with the untreated control cells [120]. Moreover, β-elemene has been shown to antagonize glioblastoma (the most prevalent type of primary brain tumor in adults) cells by inducing apoptosis disrupting the formation of a key step in maintaining the conformation stability of Hsp90/Raf-1 complex [118].
Another study was performed to assess the effect of β-elemene on prostate cancer cells, as well as other types of tumour cells, and to determine whether the effect of β-elemene on prostate cancer cell death was mediated through the induction of apoptosis. It was demonstrated that β-elemene suppresses the growth and proliferation of prostate cancer cells and other types of tumour cells in vitro [119].
Inhibition of cell proliferation [121] and induction of apoptosis [122] have been proposed as the underlying mechanism of the anti-tumor effects of β-elemene. Furthermore, several studies have indicated that β-elemene enhances the cytotoxic effect of radiation in vitro and in vivo. Li et al. [123] suggested that β-elemene can enhance lung (A549) cell radiosensitivity through the enhancement of DNA damage and the suppression of DNA repair.
3.2. Pharmacological Activities of the Main Diterpenes from Copaiba Oleoresin
The diterpenes most commonly found in copaiba oleoresins are copalic, polyalthic, hardwickiic, kaurenoic and ent-kaurenoic acids, together with their derivatives 3-hydroxy-copalic, 3-acetoxy-copalic, and ent-agathic (Figure 2).
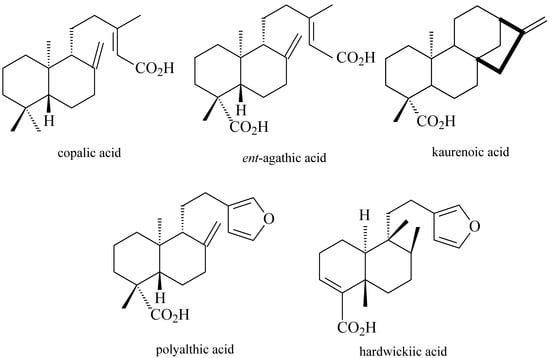
Figure 2.
Main diterpenes detected in copaiba oleoresin.
Copalic acid was first described by Nakano and Djerassi [124], who isolated it from Hymenea courbaril resin samples. This diterpene is considered a biomarker for this genus Copaifera and some studies have been performed to evaluate the antibacterial activities of this substance. It has been demonstrated to have significant antimicrobial activity against B. subtilis, S. aureus, and S. epidermidis [86]. Recently, Souza et al. [125] investigated the antimicrobial activity of four labdane-type diterpenes [(-)-copalic acid, (-)-acetoxycopalic acid, (-)-hydroxycopalic acid and (-)-agathic acid] isolated from the copaiba oleoresin from C. langsdorffii against a representative panel of microorganisms responsible for periodontitis. Copalic acid was the most active diterpene, displaying a very promising MIC value (3.1 μg mL−1) against the key pathogen (Porphyromonas gingivalis) involved in this infectious disease. Moreover, it did not exhibit cytotoxicity when tested in human fibroblasts. In another paper, Souza et al. [126] reported that copalic acid was active against the main microorganisms responsible for dental caries: Streptococcus salivarius, S. sobrinus, S. mutans, S. mitis, S. sanguinis and Lactobacillus casei.
Hardwickiic acid is another diterpene that is very common in copaiba oleoresins, being detected in about 42% of them [127]. Some studies have been performed with this diterpene to determine its antibicrobial activity [128]. It has shown significant qualitative antibacterial activity against B. subtilis, S. aureus and Mycobacterium smegmatis. Moreover, hardwickiic acid, isolated from the stem bark of Irvingia gabonensis, inhibited the growth of several bacteria and fungus species using dilution methods [129]. However, in a recent study, when it was assayed against a collection of Gram-negative multidrug-resistant bacteria, the diterpene was inactive [130].
Kaurenoic acid (ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid) was first described in 1971 by Ferrari et al. [131]. However, this acid was only detected in copaiba oleoresins in 1998 by Braga et al. [132] who isolated it from C. cearensis using ion-exchange chromatography. Although this diterpene is present in about 30% of copaiba oleoresins [124], it sometimes cannot be detected by GC because its retention time is similar to with that of copalic acid, resulting in co-elution. Therefore, it was not possible to distinguish the kaurenoic (or the copalic) acid [133]. Several pharmacological studies were performed with kauran acid, to determine it uterine muscle relaxant [134], anti-inflammatory [135], bactericidal [86], and cytotoxicity [136] effects, activity against Trypanosoma cruzi tripomastigotes [137], genotoxicity induction [138], and vasodilatory effects [139].
The uterine relaxant effects of kaurenoic acid were reported by Cunha et al. [134], who isolated this diterpene from C. langsdorffii oleoresin. Accoding to these authors, kaurenoic acid exerts this relaxant effect principally through calcium blockade and in part, by the opening of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Another study investigated the mechanisms involved in the vasorelaxant action of kaurenoic acid in isolated aortic rings in rats [139].
According to Cavalcanti et al. [138], kaurenoic acid has DNA damaging activity in cultured Chinese hamster fibroblasts (V79 cells) under the conditions of the Comet assays. Costa-Lotufo et al. [136] indicated the potential cytotoxicity of kaurenoic acid by the destruction of sea urchin embryos, the inhibition of tumor cell growth and the hemolysis of mouse and human erythrocytes.
Anti-inflammatory activity was reported by Paiva et al. [135] who isolated the kaurenoic acid from oleoresin of C. langsdorffii Desf. In this study, it was observed that kaurenoic acid prevented tissue damage in the rat model of acetic acid colitis, an effect which the authors verified through macroscopic, histological and biochemical changes.
It has been reported also that kaurenoic acid, isolated from C. paupera oleoresin, showed antibacterial activity against B. subtilis, S. aureus, S. epidermidis [86]. In other study, kaurenoic acid, and some of its derivatives, showed in vitro activity against trypomastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi [137], with kaurenoic acid derivatives presenting less side effects than the acid.
Souza et al. [140] showed that kaurenoic and polyalthic acids (the latter less active) were capable of promoting inhibition of rhodamine 6G efflux in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with Pdr5p enzyme (protein that confers multiple drug resistance).
Another diterpene detected in copaiba oleoresin, 3α-hydroxy-kaurenoic acid presented higher fungitoxic activity against Botrytis cinerea (a phytopathogenic fungus that attacks the flowers, fruits, leaves, and stems of several plants). The authors suggest that the diterpene probably acts by inhibiting germination and mycelium growth this fungus [141].
Larvicidal activity has also been reported against A. aegypti larvae, of two labdane diterpenes isolated from C. reticulata oleoresin: (-)-3β-hydroxilabd-8(17)-13-dien-15-oic acid and 3-β-acetoxy-labd-8(17)-13-dien-15-oic acid [142]. In another study, this latter diterpene was reported to cause death of the A. aegypti larvae by cell destruction in the midgut [143]. Also, another diterpene present in copaiba oleoresin, kovalenol, showed potent antitumor activity against IMC carcinoma (murine tumor) in mice [144].
4. Conclusions
Although many papers have been published on the chemical composition of copaiba oleoresins, several questions remain unsolved, such as the fingerprint of the chemical composition of the different species and the presence of biomarkers, probably a combination of sesquiterpenes and diterpernic acids. Ethnopharmacological studies indicate many activities that are still not fully understood through pharmacological experiments. Also, the activities of the isolated compounds do not explain the strong activities of crude oleoresins. Indeed, several substances have being described, and new biological studies have been published that go some way to unraveling the action mechanism of the isolated sesquiterpenes and diterpenes. All these topics still require further investigation, as copaiba oil is a resource on which there is still much work to be done.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), FAPEAM, FACEPE and CAPES.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dwyer, J.D. The Central American, West Indian and South American species of Copaifera (Caesalpinaceae). Brittonia 1951, 7, 143–172. [Google Scholar]
- Martins-da-Silva, R.C.V.; Pereira, J.F.; Lima, H.C. O gênero Copaifera (Leguminosae-Caesalpinioideae) na Amazônia Brasileira. Rodriguesia 2008, 455–476. [Google Scholar]
- Pio Corrêa, M. Dicionário das Plantas Úteis do Brasil; Ministério da Agricultura: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1931; p. 370. [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque, U.P.; Medeiros, P.M.; Almeida, A.L.S.; Monteiro, J.M.; Lins Neto, E.M.F.; Melo, J.G.; Santos, J.P. Medicinal plants of the caatinga (semi-arid) vegetation of NE Brazil: A quantitative approach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 114, 325–354. [Google Scholar]
- Brandão, M.G.L.; Zanetti, N.N.S.; Oliveira, P.; Grael, C.F.F.; Santos, A.C.P.; Monte-Mór, R.L.M. Brazilian medicinal plants described by 19th century European naturalists and in the Official Pharmacopoeia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz-Biset, J.; Campos-de-la-Cruz, J.; Epiquién-Rivera, M.A.; Canigueral, S. A first survey on the medicinal plants of the Chazuta valley (Peruvian Amazon). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 333–362. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho-Ferreira, M. Medicinal knowledge and plant utilization in an Amazonian coastal community of Marudá, Pará State (Brazil). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- Desmarchelier, C.; Gurni, A.; Ciccia, G.; Giulietti, A.M. Ritual and medicinal plants of the Ese’ejas of the Amazonian rainforest (Madre de Dios, Perú). J. Ethnopharmacol. 1996, 52, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz-Biset, J.; Canigueral, S. Plant use in the medicinal practices known as “strict diets” in Chazuta valley (Peruvian Amazon). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 271–288. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, J.F. Plants in traditional medicine en Brazil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1980, 2, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Calderon, L.A.; Silva-Jardim, I.; Zuliani, J.P.; Silva, A.A.; Ciancaglini, P.; Silva, L.H.P.; Stábeli, R.G. Amazonian biodiversity: A view of drug development for Leishmaniasis and malaria. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Pinto, A.C. O Gênero Copaifera L. Quim. Nova 2002, 25, 273–286. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.O.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Dias Filho, B.P.; Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Pinto, A.C.; Nakamura, C.V. Antimicrobial activity of Brazilian copaiba oils obtained from different species of the Copaifera genus. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2008, 103, 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Rosas, E.C.; Carvalho, M.V.; Henriques, M.G.M.O.; Pinto, A.C. Chemical composition and anti-inflammatory activity of copaiba oils from Copaifera cearensis Huber ex Ducke, Copaifera reticulata Ducke and Copaifera multijuga Hayne-A comparative study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.O.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Dias Filho, B.P.; Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Pinto, A.C.; Nakamura, C.V. Effect of Brazilian copaiba oils on Leishmania amazonensis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 204–208. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-e-Silva, O., Jr.; Zucoloto, S.; Ramalho, F.S.; Ramalho, L.N.Z.; Reis, J.M.C.; Bastos, A.A.C.; Brito, M.V.H. Antiproliferative activity of Copaifera duckei oleoresin on liver regeneration in rats. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- Maistro, E.L.; Carvalho, J.C.T.; Cascon, V.; Kaplan, M.A.C. In vivo evaluation of the mutagenic potential and phytochemical characterization of oleoresin from Copaifera duckei Dwyer. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2005, 28, 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, C.S.; Medeiros, B.J.L.; Favacho, H.A.S.; Santos, K.C.; Oliveira, B.R.; Taglialegna, J.C.; Costa, E.V.M.; Campos, K.J.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Pré-clinical validation of a vaginal cream containing copaiba oil (reproductive toxicology study). Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, J.C.T.; Cascon, V.; Possebon, L.S.; Morimoto, M.S.S.; Cardoso, L.G.V.; Kaplan, M.A.C.; Gilbert, B. Topical antiinflammatory and analgesic activities of Copaifera duckei Dwyer. Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 946–950. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, D.F.; Pereira, A.C.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Carvalho, D.A.; Silva, G.; Nunes, A.S.; Alves, D.S.; Carvalho, H.W.P. Antibacterial activity of plant extracts from Brazilian southeast region. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Pieri, F.A.; José, R.M.; Galvão, N.N.; Nero, L.A.; Moreira, M.A.S. Antimicrobial activity of autoclaved and non autoclaved copaiba oil on Listeria monocytogenes. Cienc. Rural 2010, 40, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar]
- Pieri, F.A.; Souza, C.F.; Costa, J.C.M.; Barrero, M.A.O.; Espeschit, I.F.; Silva, V.O.; Moreira, M.A.S. Inhibition of Escherichia coli from mastitic milk by copaiba oil. Semin. Ciências Agrárias 2011, 32, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Pieri, F.A.; Costa, J.C.M.; Souza, C.F.; Santos, L.; Moreira, M.A.S. Antimicrobial Profile Screening of Two Oils of Copaifera Genus. In Proceeding of the 37th CONBRAVET, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, July 2010; Brazilian Congress of Veterinary Medicine (CONBRAVET).
- Paiva, L.A.F.; Gurgel, L.A.; Campos, A.R.; Silveira, E.R.; Rao, V.S.N. Attenuation of ischemia/reperfusion-induced intestinal injury by oleo-resin from Copaifera langsdorffii in rats. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Paiva, L.A.F.; Rao, V.S.N.; Gramosa, N.V.; Silveira, E.R. Gastroprotective effect of Copaifera langsdorffii oleo- resin on experimetal gastric ulcer models in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1998, 62, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.J.L.; Guimarães, S.B.; Silveira, E.R.; Vasconcelos, P.R.L.; Lima, G.G.; Torres, S.M.; Vasconcelos, R.C. Effects of Copaifera langsdorffii Desf. on ischemia-reperfusionof randomized skin flaps in rats. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2009, 33, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, L.A.F.; Cunha, K.M.A.; Santos, F.A.; Gramosa, N.V.; Silveira, E.R.; Rao, V.S.N. Investigation on the wound healing activity of oleo-resin from Copaifera langsdorffii in rats. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 737–739. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, R.C.; Bombardiere, E.; Oliveira, J.J.; Lino-Júnior, R.S.; Brito, L.A.B.; Junqueira-Kipnis, A.P. Influência do óleo de Copaifera langsdorffii no reparo de ferida cirúrgica em presença de corpo estranho. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2008, 28, 358–366. [Google Scholar]
- Comelli-Júnior, E.; Skinovski, J.; Sigwalt, M.F.; Branco, A.B.; Luz, S.R.; Baulé, C.P. Rupture point analysis of intestinal anastomotic healing in rats under the action of pure Copaíba (Copaifera langsdorfii) oil. Acta Cir. Bras. 2010, 25, 362–367. [Google Scholar]
- Maciel, H.P.F.; Gouvêa, C.M.C.P.; Toyama, M.; Smolka, M.; Marangoni, S.; Pastore, G.M. Extraction, purification and biochemical characterization of a peroxidase from Copaifera langsdorffii leaves. Quim. Nova 2007, 30, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, F.A.C.; Silva, K.F.S.; Santos, K.K.; Ribeiro, K.A.L., Jr.; Sant’Ana, A.E.G. Activities of some Brazilian plants against larvae of the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 629–636. [Google Scholar]
- Paiva, L.A.F.; Gurgel, L.A.; Sousa, E.T.; Silveira, E.R.; Silva, R.M.; Santos, F.A.; Rao, V.S.N. Protective effect of Copaifera langsdorffii oleo-resin against acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 93, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira-Neto, J.; Lindoso, M.J.S.; Coelho, L.F.; Carvalho, R.A.F.; Rodrigues, T.G.P.M.; Araújo, A.G.P.; Girão, M.J.B.C.; Schor, E. Changes in the volume and histology of endometriosis foci in rats treated with copaiba oil (Copaifera langsdorffii). Acta Cir. Bras. 2011, 26, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen-Chen, L.; Sena, M.A. Atividade toxica e mutagênica do óleo de copaiba (Copaifera langsdorffii Desfon) em camundongos. Rev. Bras. Plant Med. 2002, 5, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.O.; Costa, M.A.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Dias-Filho, B.P.; Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Lima, M.M.S.; Nakamura, C.V. Leishmania amazonensis: Effects of oral treatment with copaiba oil in mice. Experim. Parasitol. 2011, 129, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, N.M.; Rezende, C.M.; Fontes, S.P.; Matheus, M.E.; Pinto, A.C.; Fernandes, P.D. Characterization of the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of fractions obtained from Copaifera multijuga Hayne. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Zunino, L.; Patitucci, M.L.; Pinto, A.C.; Calixto, J.B. The inhibition of paw oedema formation caused by the oil of Copaifera multijuga Hayne and its fractions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, M.V.H.; Moreira, R.J.; Tavares, M.L.C.; Carballo, M.C.S.; Carneiro, T.X.; Santos, A.A.S. Efeito do óleo de copaíba nos níveis séricos de uréia e creatinina em ratos submetidos à síndrome de isquemia e reperfusão renal. Acta Cir. Bras. 2005, 20, 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, D.E.; Onofre, S.B. Atividade antimicrobiana do óleo-resina produzido pela copaiba – Copaifera multijuga Hayne (Leguminosae). Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2009, 19, 577–581. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, T.A.R.C.; Barata, L.E.S.; Duarte, M.C.T. Antimicrobial activity of copaiba (Copaifera spp.) balsams. Rev. Bras. Pl. Med. 2006, 8, 123–124. [Google Scholar]
- Deus, R.J.A.; Carvalho, A.S.C.; Banna, D.A.D.S.; Arruda, M.S.P.; Alves, C.N.; Santos, A.S. Efeito fungitóxico in vitro do óleo resina e do óleo essencial de copaíba (Copaifera multijuga Hayne). Rev. Bras. Pl. Med. 2009, 11, 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- Deus, R.J.A.; Alves, C.N.; Arruda, M.S.P. Avaliação do efeito antifúngico do óleo resina e do óleo essencial de copaíba (Copaifera multijuga Hayne). Rev. Bras. Pl. Med. 2011, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, S.R.M.; Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Christo, H.B.; Pinto, A.C.; Fernandes, P.D. In vivo and in vitro studies on the anticancer activity of Copaifera multijuga Hayne and its fractions. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, N.M.; Rezende, C.M.; Fontes, S.P.; Hovell, A.M.C.; Landgraf, R.G.; Matheus, M.E.; Pinto, A.C.; Fernandes, P.D. Antineoplasic activity of Copaifera multijuga oil and fractions against ascitic and solid ehrlich tumor. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, N.M.; Rezende, C.M.; Fontes, S.P.; Matheus, M.E.; Fernandes, P.D. Antinociceptive activity of Amazonian copaiba oils. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 109, 486–492. [Google Scholar]
- Westphal, F.L.; Lima, L.C.; Guimarães, R.A.; Souza, R.F.S.; Couto, S.B.; Nakajima, S.R. Avaliação das alterações pleuropulmonares após a injeção de óleo de resina de copaíba, extrato aquoso de crajiru e polivinilpirrolidona iodado (PVPI) na pleura e parênquima pulmonar de ratos. Rev. Col. Bras. Cir. 2007, 34, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Pieri, F.A.; Mussi, M.C.; Fiorini, J.E.; Schneedorf, J.M. Efeitos clínicos e microbiológicos do óleo de copaiba (Copaifera officinalis) sobre bactérias formadoras de placa dental em cães. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2010, 62, 578–585. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, R.C.V.; Alves, C.F.S.; Schneider, T.; Lopes, L.Q.S.; Aurich, C.; Giongo, J.L.; Brandelli, A.; Vaucher, R.A. Antimicrobial activity of Amazonian oils against paenibacillus species. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 109, 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, F.A., Jr.; Braz, M.N.; Rocha Neto, O.G.; Costa, F.D.; Brito, M.V.H. Efeito do óleo de copaíba nas aminotransferases de ratos submetidos à isquemia e reperfusão hepática com e sem pré-condicionamento isquêmico. Acta Cir. Bras. 2005, 20, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Baylac, S.; Racine, P. Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase by essential oils and other natural fragrant extracts. Int. J. Aromather. 2003, 13, 138–142. [Google Scholar]
- Baylac, S.; Racine, P. Inhibition of human leukocyte elastase by natural fragrant extracts of aromatic plants. Int. J. Aromather. 2004, 14, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, N.M.B.; Brito, M.V.H.; Carvalho, R.K.V.; Matos, L.T.M.B.; Lobato, R.C.; Correa, S.C.; Brito, R.B. The effect of copaiba balsam on Walker 256 carcinoma inoculated into the vagina and uterine cervix of female rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2010, 25, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Kvist, L.P.; Christensen, S.B.; Rasmussen, H.B.; Mejia, K.; Gonzalez, A. Identification and evaluation of Peruvian plants used to treat malaria and leishmaniasis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 390–402. [Google Scholar]
- Correia, A.F.; Segovia, J.F.O.; Gonçalves, M.C.A.; Oliveira, V.L.; Silveira, D.; Carvalho, J.C.T.; Kanzaki, L.I.B. Amazonian plant crude extract screening for activity against multidrug-resistant bactéria. Eur.Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 12, 369–380. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, H.H.G.; Geris, R.; Rodrigues-Filho, E.; Rocha, C.; Silva, I.G. Larvicidal activity of oil-resin fractions from the Brazilian medicinal plant Copaifera reticulata Ducke (Leguminosae-Caesalpinoideae) against Aedes aegypti (Diptera, Culicidae). Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2007, 40, 264–267. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, I.G.; Zanon, V.O.M.; Silva, H.H.G. Larvicidal activity of Copaifera reticulata Ducke oil-resin against Culex quinquefasciatus say (Diptera: Culicidae). Neotrop. Entomol. 2003, 32, 729–732. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.G.; Hoonshin, C.H.; Shin, S.C.; Park, I.K. Fumigant antitermitic activity of plant essential oils and components from ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi), allspice (Pimenta dioica), caraway (Carum carvi), dill (Anethum graveolens), geranium (Pelargonium graveolens), and litsea (Litsea cubeba) oils against Japanese termite (Reticulitermes speratus Kolbe). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6596–6602. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, F.F.; Freitas, E.P.S. Acaricidal activity of an oleoresinous extract from Copaifera reticulata (Leguminosae: Caesalpinioideae) against larvae of the southern cattle tick, rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 147, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Sachetti, C.G.; Carvalho, R.R.; Paumgartten, F.J.R.; Lameira, O.A.; Caldas, E.D. Developmental toxicity of copaiba tree (Copaifera reticulata Ducke, Fabaceae) oleoresin in rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Sachetti, C.G.; Fascineli, M.L.; Sampaio, J.A.; Lameira, O.A.; Caldas, E.D. Avaliação da toxicidade aguda e potencial neurotóxico do óleo-resina de copaíba (Copaifera reticulata Ducke, Fabaceae). Braz. J. Pharmacog. 2009, 19, 937–941. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.O.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Dias Filho, B.P.; Veiga-Junior, V.F.; Nakamura, C.V. Copaiba oil: An alternative to development of new drugs against leishmaniasis. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, N.M.B.; Simões, M.J.; Pessoa, A.F.; Melo, M.C.F. Efeitos do óleo de copaíba na cicatrização de feridas cutâneas abertas de ratos. Rev. Para. Med. 1998, 12, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, N.M.B.; Simões, M.J.; Gomes, P.O.; Pessoa, A.F.; Melo, M.C.F. Aspecto microscópicos da cicatrização de feridas cutâneas abertas tratadas com óleo de copaíba em ratos. Rev. Para. Med. 1999, 13, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Curio, M.; Jacone, H.; Perrut, J.; Pinto, A.C.; Veiga-Filho, V.F.; Silva, R.C.B. Acute effect of Copaifera reticulata Ducke copaiba oil in rats tested in the elevated plus-maze: An ethological analysis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Basile, A.C.; Sertie, J.A.A.; Freitas, P.C.D.; Zanini, A.C. Anti-inflammatory activity of oleoresin from Brazilian copaifera. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1988, 22, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Zunino, L.; Calixto, J.B.; Patitucci, M.L.; Pinto, A.C. Phytochemical and antioedematogenic studies of commercial copaiba oils available in Brazil. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, R.V.M.; Ohara, M.T.; Vila, M.M.D.C.; Gonçalves, M.M. In vitro evaluation of copaiba oil as a kojic acid skin enhancer. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 46, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Ribas, J.; Carreño, A.M. Avaliação do uso de repelentes contra picada de mosquitos em militares na Bacia Amazônica. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2010, 85, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kanis, L.A.; Prophiro, J.S.; Vieira, E.S.; Nascimento, M.P.; Zepon, K.M.; Kulkamp-Guerreiro, I.C.; Silva, O.S. Larvicida activity of Copaifera spp. (Leguminosae) oleoresin microcapsules against Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Prophiro, J.S.; Silva, M.A.N.; Kanis, L.; Silva, B.M.; Duque-Luna, J.E.; Silva, O.S. Evaluation of time toxicity, residual effect, and growth-inhibiting property of Carapa guianensis and Copaifera sp. in Aedes aegypti. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 713–719. [Google Scholar]
- Prophiro, J.S.; Silva, M.A.N.; Kanis, L.; Rocha, L.C.B.P.; Duque-Luna, J.E.; Silva, O.S. First report on susceptibility of wild Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) using Carapa guianensis (Meliaceae) and Copaifera spp. (Leguminosae). Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 699–705. [Google Scholar]
- Gobbo-Neto, L.; Lopes, N.P. Plantas medicinais: Fatores de influência no conteúdo de metabólitos secundários. Quim. Nova 2007, 30, 374–381. [Google Scholar]
- Lameira, O.S.; Martins-da-Silva, R.C.V.; Zoghbi, M.G.B.; Oliveira, E.C.P. Seasonal variation in the volatiles of Copaifera duckei Dwyer growing wild in the state of Pará – Brazil. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2009, 21, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zoghbi, M.G.B.; Martins-da-Silva, R.C.V.; Trigo, J.R. Volatiles of oleoresins of Copaifera paupera (Herzog) Dwyer, C. piresii Dwyer and C. pubiflora Benth. (Leguminosae). J. Essent. Oil Res. 2009, 21, 403–404. [Google Scholar]
- Zoghbi, M.G.B.; Andrade, E.H.A.; Martins-da-Silva, R.C.V.; Trigo, J.R. Chemical variation in the volatiles of Copaifera reticulata Ducke (Leguminosae) growing wild in the states of Pará and Amapá, Brazil. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2009, 21, 501–503. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero-Jáuregui, C.; Casado, M.A.; Zoghbi, M.G.B.; Martins-da-Silva, R.C.V. Chemical variability of Copaifera reticulata Ducke oleoresin. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 674–685. [Google Scholar]
- Gramosa, N.V.; Silveira, E.R. Volatiles constituents of Copaifera langsdorffii from the Brazilian Northeast. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2005, 17, 130–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zoghbi, M.G.B.; Lameira, O.S.; Oliveira, E.C.P. Seasonal variation of oleoresin and volatiles from Copaifera martii Hayne growing wild in the state of Pará, Brazil. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2007, 19, 504–506. [Google Scholar]
- Cascon, V.; Gilbert, B. Characterization of the chemical composition of oleoresins of Copaifera guianensis Desf., Copaifera duckei Dwyer and Copaifera multijuga Hayne. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 773–778. [Google Scholar]
- Gramosa, N.V. Estudo Químico-Farmacológico de Copaifera langsdorffii Desf. Doctoral Thesis in Chemistry, Federal University of Ceará, Ceará, Brasil, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gramosa, N.V.; Silveira, E.R.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; Ferreira, J.R.O.; Almeida, F.S.; Rao, V.S.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; Odorico-de-Moraes, M.; Pessoa, C. Chemistry and pharmacology of Copaifera langsdorffii Desf.: An overview. Rec. Prog. Med. Plants 2010, 27, 235–260. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, A.C.; Braga, W.F.; Rezende, C.M.; Garrido, F.M.S.; Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Bergter, L.; Patitucci, M.L.; Antunes, O.A.C. Separation of Acid Diterpenes of Copaifera cearensis Huber ex ducke by flash chromatography using potassium hydroxide impregnated silica gel. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2000, 11, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Spanevello, R.O.; Vila, A.J. 7-α-acetoxyhardwickiic acid: A furanoid clerodane. Phytochemistry 1994, 35, 537–538. [Google Scholar]
- Monti, H.; Tiliacos, N.; Faure, R. Two diterpenoids from copaiba oil. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 1653–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan, J.R.; Ferreira, G.A.L. New diterpenoids from copaiba oil. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1971, 43, 611–613. [Google Scholar]
- Tincusi, B.M.; Jiménez, I.A.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Moujir, L.M.; Mamani, Z.A.; Barroso, J.P.; Ravelo, A.G.; Hernández, B.V. Antimicrobial terpenoids from the oleoresin of the peruvian medicinal plant Copaifera paupera. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 808–812. [Google Scholar]
- Monti, H.; Tiliacos, N.; Faure, R. Copaiba oil: Isolation and charaterization of a new diterpenoid with the dinorlabdane skeleton. Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 1013–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, A.L.; Baptistella, L.H.B.; Imamura, P.M. Absolute configuration of some dinorlabdanes from the copaiba oil. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Sant’Anna, B.M.P.; Fontes, S.P.; Pinto, A.C.; Rezende, C.M. Characterization of woody odorant contributors in copaiba oil (Copaifera multijuga Hayne). J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2007, 18, 984–989. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, Y.T.; Chua, M.T.; Wang, S.Y.; Chang, S.T. Anti-inflammation activities of essential oil and its constituentes from indigenous Cinnamon (Cinnamomun osmophloeum) twigs. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3908–3913. [Google Scholar]
- Chavan, M.J.; Wakte, P.S.; Shinde, D.B. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of caryophyllene oxide from Annona squamosa L. bark. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 149–151. [Google Scholar]
- Rodilla, J.M.; Tinoco, M.T.; Morais, J.C.; Gimenez, C.; Cabrera, R.; Martín-Benito, D.; Castillo, L.; Gonzalez-Coloma, A. Laurus novocanariensis essential oil: Seasonal variation and valorization. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2008, 36, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Omolo, M.O.; Okinyo, D.; Ndiege, I.O.; Lwande, W.L.; Hassanali, A. Repellency of essential oils of some Kenyan plants against Anopheles gambiae. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 2797–2802. [Google Scholar]
- Goren, A.C.; Piozzi, F.; Akcicek, E.; Kılıç, T.; ÇarıkçI, S.; Mozioglu, E.; Setzer, W.N. Essential oil composition of twenty-two Stachys species (mountain tea) and their biological activities. Phytochem. Lett. 2011, 4, 448–453. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.S.; Wu, C.L.; Chang, H.T.; Kao, Y.T.; Chang, S.T. Antitermitic and antifungal activities of essential oil of Calocedrus formosana leaf and its composition. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar]
- Ghelardini, C.; Galeotti, N.; Mannelli, L.D.C.; Mazzanti, G.; Bartolini, A. Local anaesthetic activity of β-caryophyllene. Il Farmaco 2001, 56, 387–389. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.L.; Figueiredo, P.M.S.; Yano, T. Chemotherapeutic potential of the volatile oils from Zanthoxylum rhoifolium Lam leaves. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 576, 180–188. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, I.; Chaudhuri, S.K.; Kubo, Y.; Sanchez, Y.; Ogura, T.; Saito, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Haraguchi, H. Cytotoxic and antioxidative sesquiterpenoids from Heterotheca inuloides. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 427–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.Q.; Kenney, P.M.; Lam, L.K.T. Sesquiterpenes from clove (Eugenia caryophyllata) as potential anticarcinogenic agents. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 999–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Di Sotto, A.; Mazzanti, G.; Carbone, F.; Hrelia, P.; Maffei, F. Inhibition by β-caryophyllene of ethyl methanesulfonate-induced clastogenicity in cultured human lymphocytes. Mutat. Res. 2010, 699, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Legault, J.; Pichette, A. Potentiating effect of β-caryophyllene on anticancer activity of α-humulene, isocaryophyllene and paclitaxel. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 1643–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Loizzo, M.R.; Tundis, R.; Menichini, F.; Saab, A.M.; Statti, G.A.; Menichini, F. Antiproliferative effects of essential oils and their major constituents in human renal adenocarcinoma and amelanotic melanoma cells. Cell Prolif. 2008, 41, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, M.; Shogawa, H.; Matsuzawa, T.; Yonezawa, S.; Hayashi, T.; Arisawa, M.; Suzuki, S.; Yoshizaki, M.; Morita, N.; Ferro, E.; et al. Anti-inflamamatory effects of paraguayan crude drug “Alhucema” (Lavandula latifolia Vill). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 2283–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.Y.; Chang, H.J.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, J.K.; Chun, H.S. Amelioration of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by oral administration of β-caryophyllene, a sesquiterpene. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 932–939. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, E.S.; Passos, G.F.; Medeiros, R.; Cunha, F.M.; Ferreira, J.; Campos, M.M.; Pianowski, L.F.; Calixto, J.B. Anti-inflammatory effects of compounds alpha-humulene and (-)-trans-caryophyllene isolated from the essential oil of Cordia verbenacea. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 569, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Passos, G.F.; Fernandes, E.S.; Cunha, F.M.; Ferreira, J.; Pianowski, L.F.; Camposa, M.M.; Calixto, J.B. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties of the essential oil and active compounds from Cordia verbenacea. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 110, 323–333. [Google Scholar]
- Rogério, A.P.; Andrade, E.L.; Leite, D.F.P.; Figueiredo, C.P.; Calixto, J.B. Preventive and therapeutic anti-inflammatory properties of the sesquiterpene α-humulene in experimental airways allergic inflammation. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Legault, J.; Dahl, W.; Debiton, E.; Pichette, A.; Madelmont, J.-C. Antitumor activity of balsam fir oil: Production of reactive oxygen species induced by α-humulene as possible mechanism of action. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 402–407. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, I.; Muroi, H.; Himejima, M. Antimicrobial activity of green tea flavor components and their combination effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-López, A.; Cirio, A.T.; Rivas-Galindo, V.M.; Aranda, R.S.; Torres, N.W. Activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae of the essential oil and δ-cadinene isolated from Schinus molle fruit. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2011, 23, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zeng, L.; Shi, G.; Zhao, G.X.; Kozlowski, J.F.; McLaughlin, J.L. Bioactive compounds from Taiwania cryptomerioides. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.T.; Wang, S.Y.; Wu, C.L.; Chen, P.F.; Kuo, Y.H. Comparison of the antifungal activity of cadinane skeletal sesquiterpenoids from Taiwania (Taiwania cryptomerioides Hayata) heartwood. Holzforschung 2000, 54, 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.; Lu, J.J.; Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, G.; Gon, J.; Zhong, Z.G.; Xu, Z.; Dang, Y.; et al. Anti-cancer natural products isolated from chinese medicinal herbs. Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 27:1–27:15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, J.; Xu, L.; Hou, K.; Zhang, J.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y. β-Elemene-induced autophagy protects human gastric cancer cells from undergoing apoptosis. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 183:1–183:10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Huang, F.; Zhao, J.; Ding, H.; Cunningham, C.; Coad, J.E.; Flynn, D.C.; Reed, E.; Li, Q.Q. Antitumor effect of β-Elemene in non-small-cell lung cancer cells is mediated via induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 881–893. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, L.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, L.; Yao, M. Elemene displays anti-cancer ability on laryngeal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Ding, H.; Cunningham, C.; Chen, F.; Flynn, D.C.; Reed, E.; Li, Q.Q. Antiproliferative effect of β-elemene in chemoresistant ovarian carcinoma cells is mediated through arrest of the cell cycle at the G2-M phase. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 894–904. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Zhu, T.Z.; Chen, Y.W.; Yao, Y.Q.; Wu, C.M.; Wei, Z.Q.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.H. β-Elemene inhibits Hsp90/Raf-1 molecular complex inducing apoptosis of glioblastoma cells. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 107, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.Q.; Wang, G.; Huang, F.; Banda, M.; Reed, E. Antineoplastic effect of β-elemene on prostate cancer cells and other types of solid tumour cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.; Liu, W.; Yu, L. β-Elemene induces apoptosis of K562 leukemia cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2001, 23, 196–198. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ren, Y.; Shen, Y.M. Synthesis and in vitro anti-proliferative activity of β-elemene monosubstituted derivatives in HeLa cells mediated through arrest of cell cycle at the G1 phase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, R.; Xu, L.; Dong, J.; Jing, Y. N-(β-Elemene-13-yl)tryptophan methyl ester induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells and synergizes with arsenic trioxide through a hydrogen peroxide dependent pathway. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.J.; Zhong, L.F.; Jiang, L.P.; Geng, C.Y.; Zou, L.J. β-Elemene radiosensitizes lung cancer A549 cells by enhancing DNA damage and inhibiting DNA repair. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1095–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, T.; Djerassi, C. Terpenoids. XLVI. Copalic Acid. J. Org. Chem. 1961, 26, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.B.; Souza, M.G.M.; Moreira, M.A.; Moreira, M.R.; Furtado, N.A.J.C.; Martins, C.H.G.; Bastos, J.K.; Santos, R.A.; Heleno, V.C.G.; Ambrosio, S.R.; et al. Antimicrobial evaluation of diterpenes from Copaifera langsdorffii Oleoresin against periodontal anaerobic bacteria. Molecules 2011, 16, 9611–9619. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.B.; Martins, C.H.G.; Souza, M.G.M.; Furtado, N.A.J.C.; Heleno, V.C.G.; Sousa, J.P.B.; Rocha, E.M.P.; Bastos, J.K.; Cunha, W.R.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of terpenoids from Copaifera langsdorffii Desf. against cariogenic bacteria. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Patitucci, M.L.; Pinto, A.C. Controle de autenticidade de óleos de copaíba comerciais por cromatografia gasosa de alta resolução. Quim. Nova 1997, 20, 612–615. [Google Scholar]
- Mcchesneya, J.D.; Clark, A.M.; Silveira, E.R. Antimicrobial diterpenes of Croton sonderzanus, 1-Hardwickic and 3,4-secotrachylobanoic acids. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Kuete, V.; Wabo, G.F.; Ngameni, B.; Mbaveng, A.T.; Metuno, R.; Etoa, F.X.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Benga, V.P.; Meyer, J.J.M.; Lall, N. Antimicrobial activity of the methanolic extract, fractions and compounds from the stem bark of Irvingia gabonensis (Ixonanthaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 114, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kuete, V.; Franco, S.A.; Eyong, K.O.; Ngameni, B.; Folefoc, G.N.; Nguemeving, J.R.; Tangmouo, J.G.; Fotso, G.W.; Komguem, J.; Ouahouo, B.M.W.; et al. Antibacterial activity of some natural products against bacteria expressing a multidrug-resistant phenotype. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 37, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Pagnoni, U.M.; Pelizzoni, F.; Ferreri, V.L.G. Leguminosae. Terpenoids from copaifera langsdorfii. Phytochemistry 1971, 10, 905–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, W.F.; Rezende, C.M.; Antunes, O.A.C.; Pinto, A.C. Terpenoids from Copaifera cearensis. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 263–264. [Google Scholar]
- Veiga, V.F., Jr.; Pinto, A.C. A utilização do monitoramento seletivo de íons como ferramenta para a detecção de adulterações em óleos de copaíba. Rev. Fitos 2005, 1, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, K.M.A.; Paiva, L.A.; Santos, F.A.; Gramosa, N.V.; Silveira, E.R.; Rao, V.S. Smooth muscle relaxant effect of kaurenoic acid, a diterpene from Copaifera langsdorffii on rat uterus in vitro. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, L.A.F.; Gurgel, L.A.; Silva, R.M.; Tomé, A.R.; Gramosa, N.V.; Silveira, E.R.; Santos, F.A.; Rao, V.S.N. Anti-inflammatory effect of kaurenoic acid, a diterpene from Copaifera langsdorffii on acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2003, 39, 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; Cunha, G.M.A.; Farias, P.A.M.; Viana, G.S.B.; Cunha, K.M.A.; Pessoa, C.; Moraes, M.O.; Silveira, E.R.; Gramosa, N.V.; Rao, V.S.N. The cytotoxic and embryotoxic effects of kaurenoic acid, a diterpene isolated from Copaifera langsdorffii oleo-resin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, H.S.; Takahashi, J.A.; Oliveira, A.B.; Chiari, E.; Boaventura, M.A.D. Novel derivatives of kaurenoic acid: Preparation and evaluation of their trypanocidal activity. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2002, 13, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcanti, B.C.; Costa-lotufo, L.V.; Moraes, M.O.; Burbano, R.R.; Silveira, E.R.; Cunha, K.M.A.; Rao, V.S.N.; Moura, D.J.; Rosa, R.M.; Henriques, J.A.P.; et al. Genotoxicity evaluation of kaurenoic acid, a bioactive diterpenoid present in Copaiba oil. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirapelli, C.R.; Ambrosio, S.R.; Costa, F.B.; Coutinho, S.T.; Oliveira, D.C.R.; Oliveira, A.M. Analysis of the mechanisms underlying the vasorelaxant action of kaurenoic acid in the isolated rat aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 492, 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, P.A.; Rangel, L.P.; Oigman, S.S.; Elias, M.M.; Ferreira-Pereira, A.; Lucasa, N.C.; Leitão, G.G. Isolation of two bioactive diterpenic acids from Copaifera glycycarpa oleoresin by high-speed counter-current chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 539–543. [Google Scholar]
- Cotoras, M.; Folch, C.; Mendoza, L. Characterization of the antifungal activity on Botrytis cinerea of the natural diterpenoids kaurenoic acid and 3β-hydroxy-kaurenoic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2821–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Geris, R.; Silva, I.G.; Silva, H.H.G.; Barison, A.; Rodrigues-Filho, E.; Ferreira, A.G. Diterpenoids from Copaifera reticulata Ducke with larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti (L.) (Diptera, Culicidae). Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. S. Paulo 2008, 50, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Valotto, C.F.B.; Silva, H.H.G.; Cavasin, G.; Geris, R.; Rodrigues-Filho, E.; Silva, I.G. Alterações ultraestruturais em larvas de Aedes aegypti submetidas ao diterpeno labdano, isolado de Copaifera reticulata (Leguminosae), e à uma fração rica em taninos de Magonia pubescens (Sapindaceae). Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2011, 44, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsaki, A.; Lu, T.Y.; Ito, S.; Edatsugi, H.; Iwata, D.; Kmoda, Y. The isolation and in vivo potent antitumor activity of clerodane diterpenoid from the oleoresin of the Brazilian medicinal plant, Copaifera langsdorffii Desf. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1994, 4, 2889–2892. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
