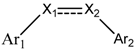3D-QSAR Study of Combretastatin A-4 Analogs Based on Molecular Docking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
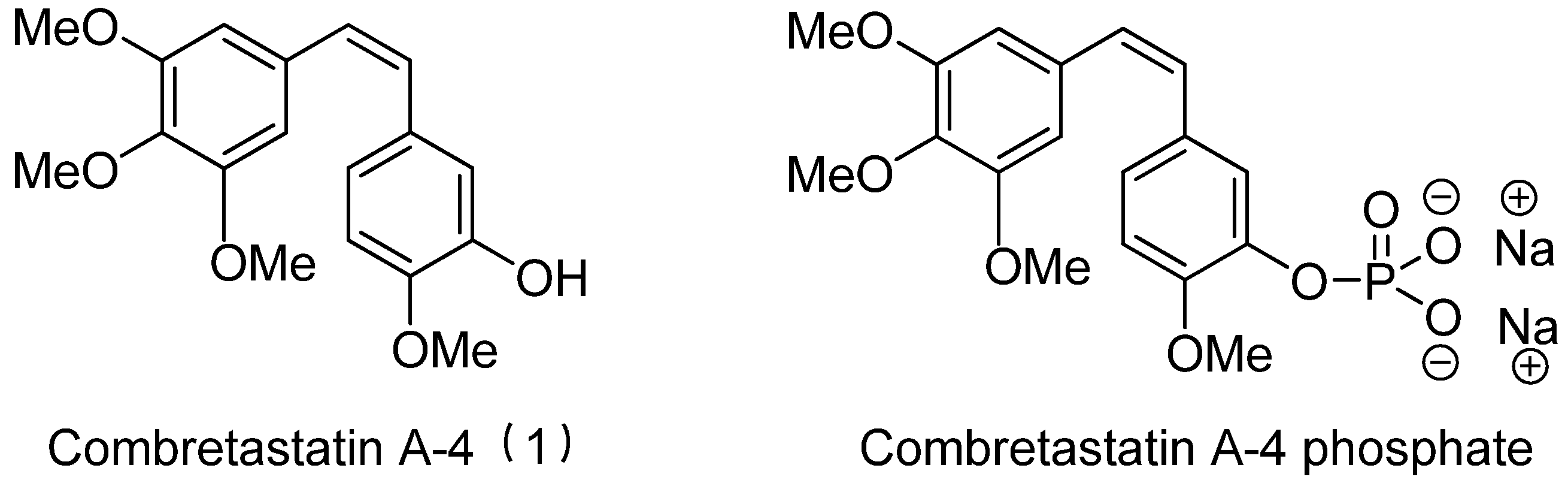
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sets
2.2. Molecular Docking
2.3. Molecular Modeling and Alignment
2.4. CoMFA Descriptors
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation of the Molecular Docking Reliability
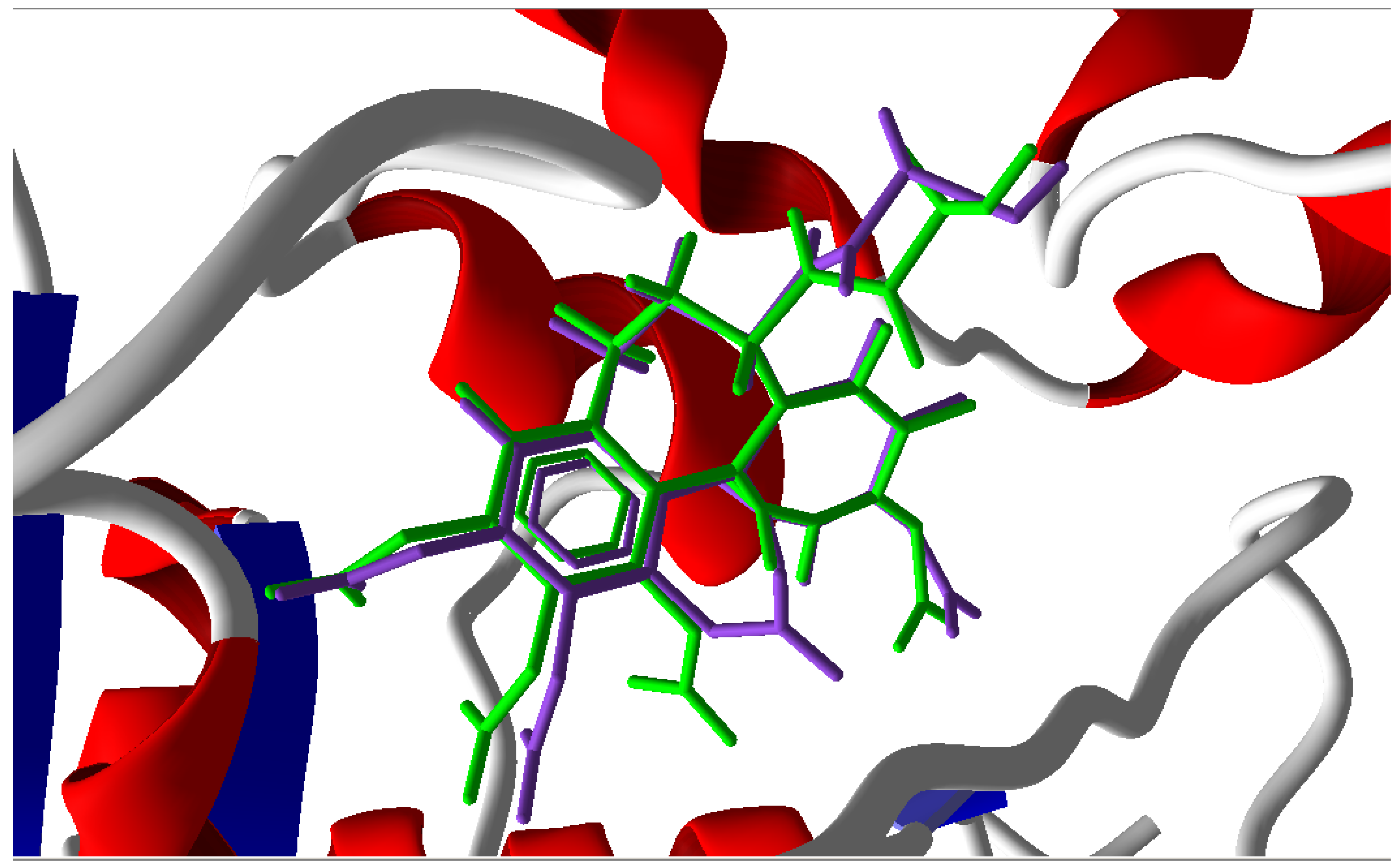
3.2. Molecular Docking Results
| Compounds | Ar1 | X1 | X2 | Ar2 | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | CH | CH | 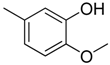 | [8] |
| 2 |  | CO | CO |  | [9] |
| 3 | 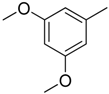 | CH2 | NH | 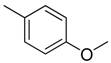 | [10] |
| 4 | 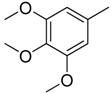 | CH | CH |  | [10] |
| 5 |  | CH | CH | 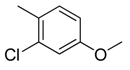 | [10] |
| 6 |  | CH2 | NCH3 |  | [11] |
| 7 |  | CH2 | NCH2CH3 |  | [11] |
| 8 | 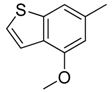 | CH | CH |  | [12] |
| 9 | 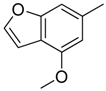 | CH | CH |  | [12] |
| 10 |  | CF | CH | 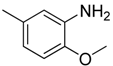 | [13] |
| 11 |  | CF | CF |  | [13] |
| 12 |  | CF | CH |  | [13] |
| 13 |  | CH2 | CH2 | 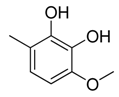 | [14] |
| 14 | 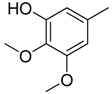 | CH | CH |  | [14] |
| 15 | 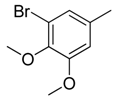 | CH | CH |  | [15] |
| 16 | 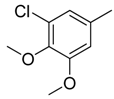 | CH | CH |  | [15] |
| 17 | 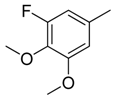 | CH | CH |  | [15] |
| 18 |  | CH | CH | 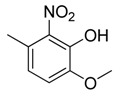 | [16] |
| 19 |  | CCN | CH |  | [17] |
| 20 |  | CH | CCN |  | [17] |
| 21 |  | CCN | CH | 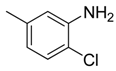 | [17] |
| 22 |  | CH | CH | 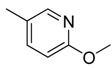 | [18] |
| 23 |  | CH | CH |  | [18] |
| 24 |  | CH | CH | 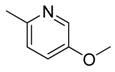 | [18] |
| 25 |  |  |  | [19] | |
| 26 |  | CH | CH |  | [20] |
| 27 |  | CH | CH |  | [22] |
| 28 |  |  | 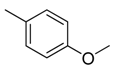 | [21] | |
| 29 | 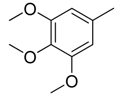 | CH | CH | 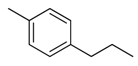 | [22] |
| 30 |  | CHCN | CH2 | 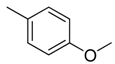 | [22] |
| 31 |  |  |  | [23] | |
| 32 |  |  |  | [23] | |
| 33 |  | 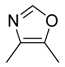 |  | [23] | |
| 34 |  |  |  | [23] | |
| 35 | 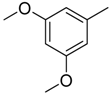 | CH | CH | 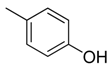 | [24] |
| 36 | 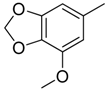 | CH | CH | 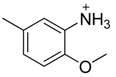 | [25] |
| 37 |  | CH | CH | 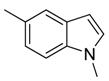 | [26] |
| 38 | 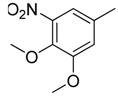 | CH | CH | 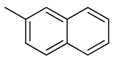 | [26] |
| 39 |  | CH | CH | 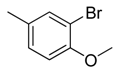 | [27] |
| 40 |  | CH | CH | 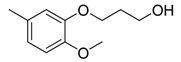 | [27] |
| 41 |  | CH | CH | 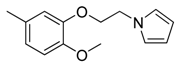 | [27] |
| 42 |  | CH | CH | 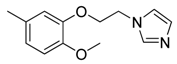 | [27] |
| 43 |  | CH | CH |  | [28] |
| 44 |  | 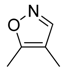 |  | [29] | |
| 45 |  | CH | CH | 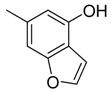 | [30] |
| Compound | Relative | Predicted | Residue | MolDockScore |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00 | 0.03 | −0.03 | −92.11 |
| 2 t | −0.18 | −0.08 | −0.10 | −102.1 |
| 3 | −1.18 | −1.20 | 0.01 | −83.85 |
| 4 | −0.67 | −0.68 | 0.01 | −86.39 |
| 5 | −0.26 | −0.26 | −0.01 | −84.69 |
| 6 | −1.06 | −1.02 | −0.04 | −81.16 |
| 7 | −0.59 | −0.56 | −0.02 | −95.79 |
| 8 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.05 | −84.34 |
| 9 | −0.02 | −0.03 | 0.01 | −80.87 |
| 10 | −0.05 | −0.02 | −0.03 | −117.5 |
| 11 | −0.17 | −0.13 | −0.04 | −105.8 |
| 12 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.08 | −103.8 |
| 13 t | −0.26 | −0.21 | −0.05 | −88.41 |
| 14 t | -0.26 | −0.06 | −0.19 | −90.39 |
| 15 | 0.08 | 0.10 | −0.01 | −85.25 |
| 16 t | 0.05 | −0.12 | 0.17 | −82.73 |
| 17 t | 0.08 | −0.07 | 0.15 | −81.14 |
| 18 | −0.10 | −0.09 | 0.00 | −94.13 |
| 19 | −0.40 | −0.43 | 0.04 | −101.3 |
| 20 t | −0.10 | −0.07 | −0.03 | −108.7 |
| 21 t | −0.18 | −0.44 | 0.27 | −101.9 |
| 22 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −80.97 |
| 23 | −0.18 | −0.15 | −0.03 | −84.11 |
| 24 t | −0.18 | −0.08 | −0.09 | −95.84 |
| 25 | −0.23 | −0.21 | −0.03 | −123.1 |
| 26 t | −0.06 | −0.24 | 0.18 | −101.0 |
| 27 | −0.48 | −0.49 | 0.01 | −105.3 |
| 28 | −0.74 | −0.79 | 0.05 | −117.5 |
| 29 | −0.78 | −0.80 | 0.02 | −110.2 |
| 30 | −0.74 | −0.74 | 0.00 | −80.49 |
| 31 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.05 | −120.4 |
| 32 t | −0.37 | −0.59 | 0.23 | −126.9 |
| 33 | 0.18 | 0.20 | −0.02 | −125.1 |
| 34 | 0.11 | 0.16 | −0.04 | −118.4 |
| 35 | −1.16 | −1.15 | −0.01 | −89.72 |
| 36 | −0.14 | −0.14 | 0.00 | −83.71 |
| 37 | 0.17 | 0.19 | −0.01 | −95.28 |
| 38 | −0.92 | −0.95 | 0.03 | −88.45 |
| 39 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.03 | −89.74 |
| 40 | −0.73 | −0.72 | −0.01 | −113.6 |
| 41 | −1.22 | −1.21 | −0.01 | −130.7 |
| 42 t | −0.80 | −1.15 | 0.35 | −117.9 |
| 43 | 0.00 | 0.04 | −0.04 | −90.15 |
| 44 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.00 | −118.4 |
| 45 | −0.32 | −0.33 | 0.00 | −91.68 |

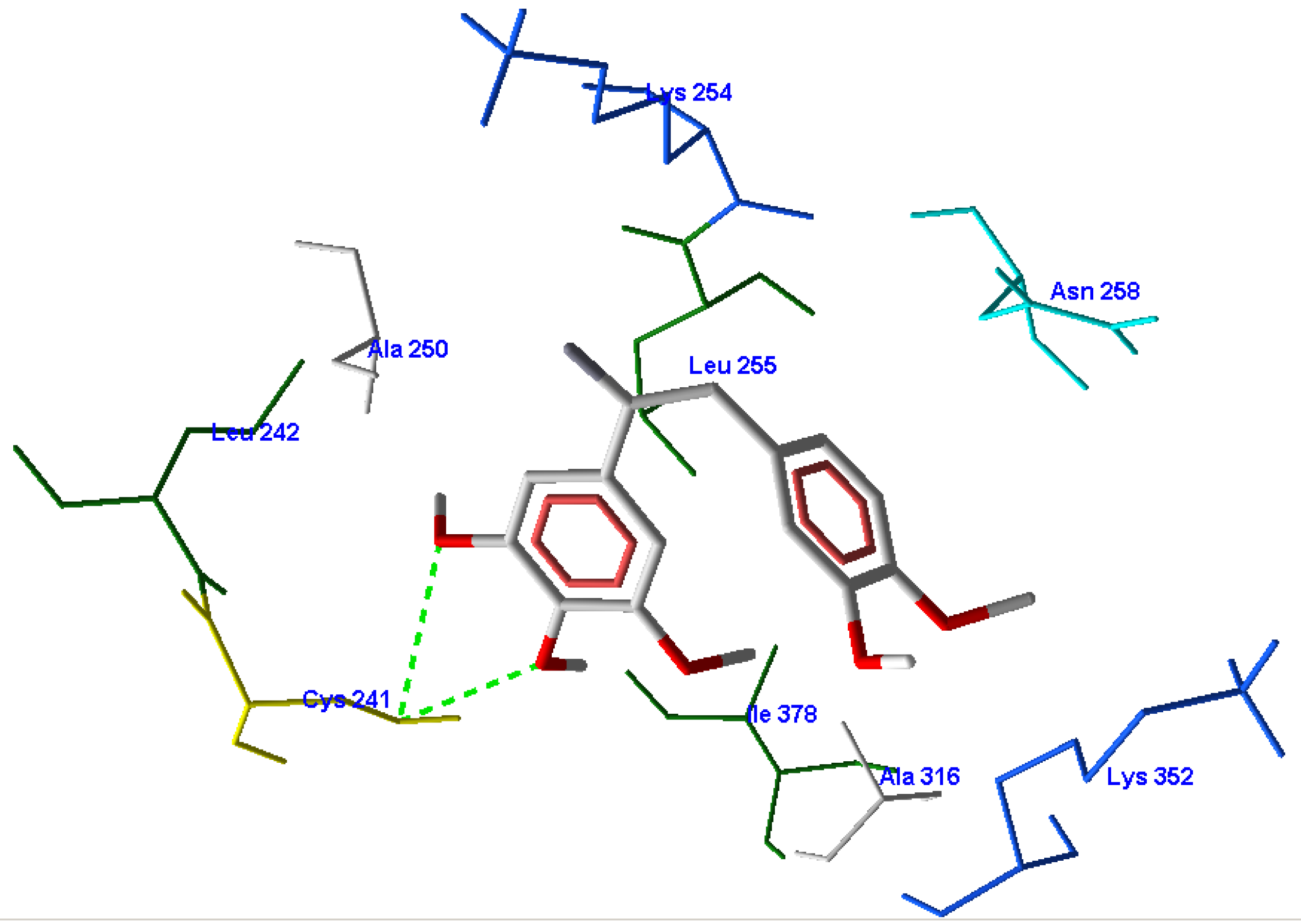
3.3. CoMFA Results
| Statistical parameters CoMFA | CoMFA |
|---|---|
| the number of training set compounds | 34 |
| Components | 5 |
| q2 | 0.786 |
| Convention r2 | 0.988 |
| Standard error of estimated | 0.055 |
| F values | 472.301 |
| Predictive r2 | 0.7412 |
| Fraction | |
| Steric | 79.7% |
| Electrostatic | 20.3% |
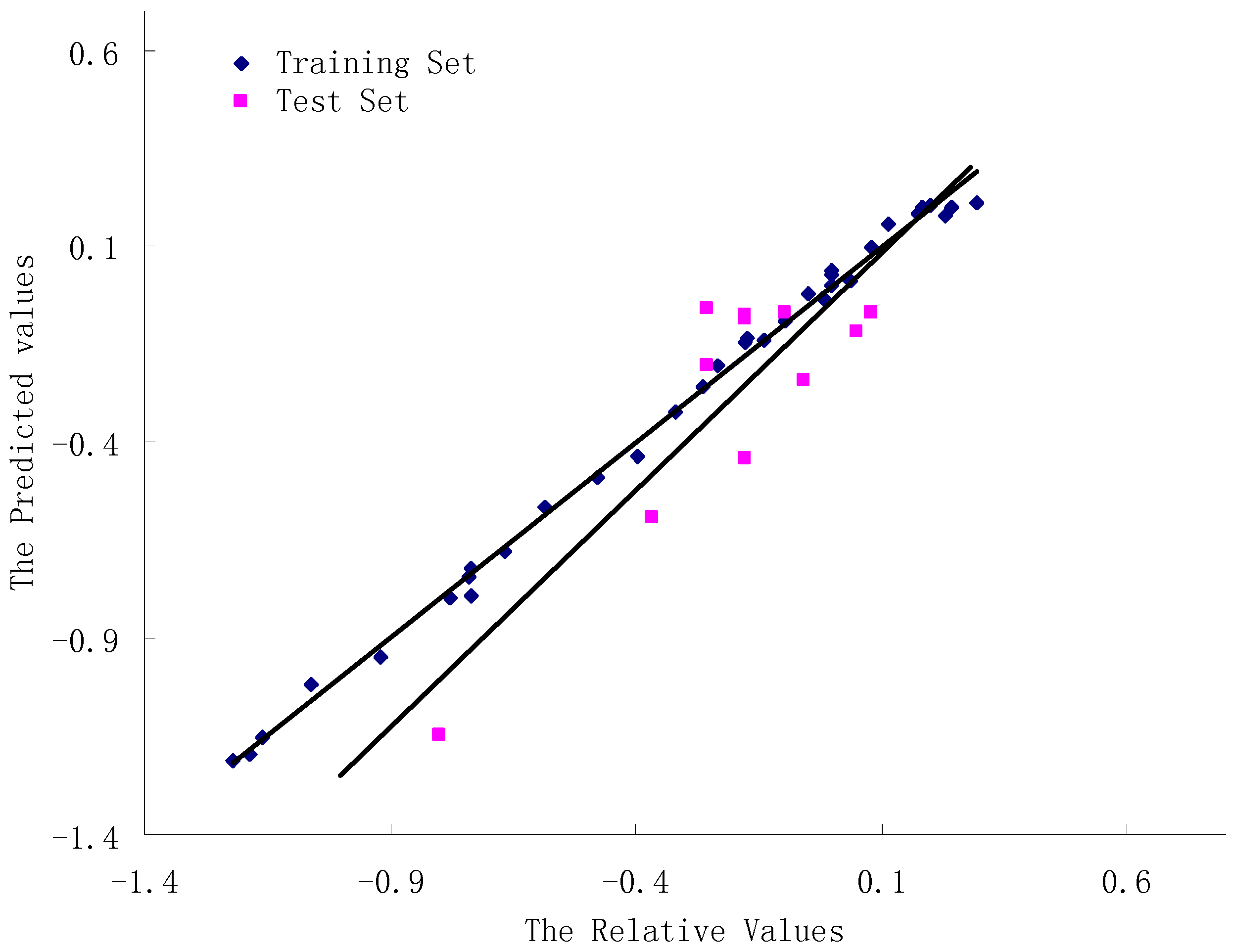
3.4. Validation of the 3D-QSAR Models
3.5. 3D-QSAR Contour Analysis
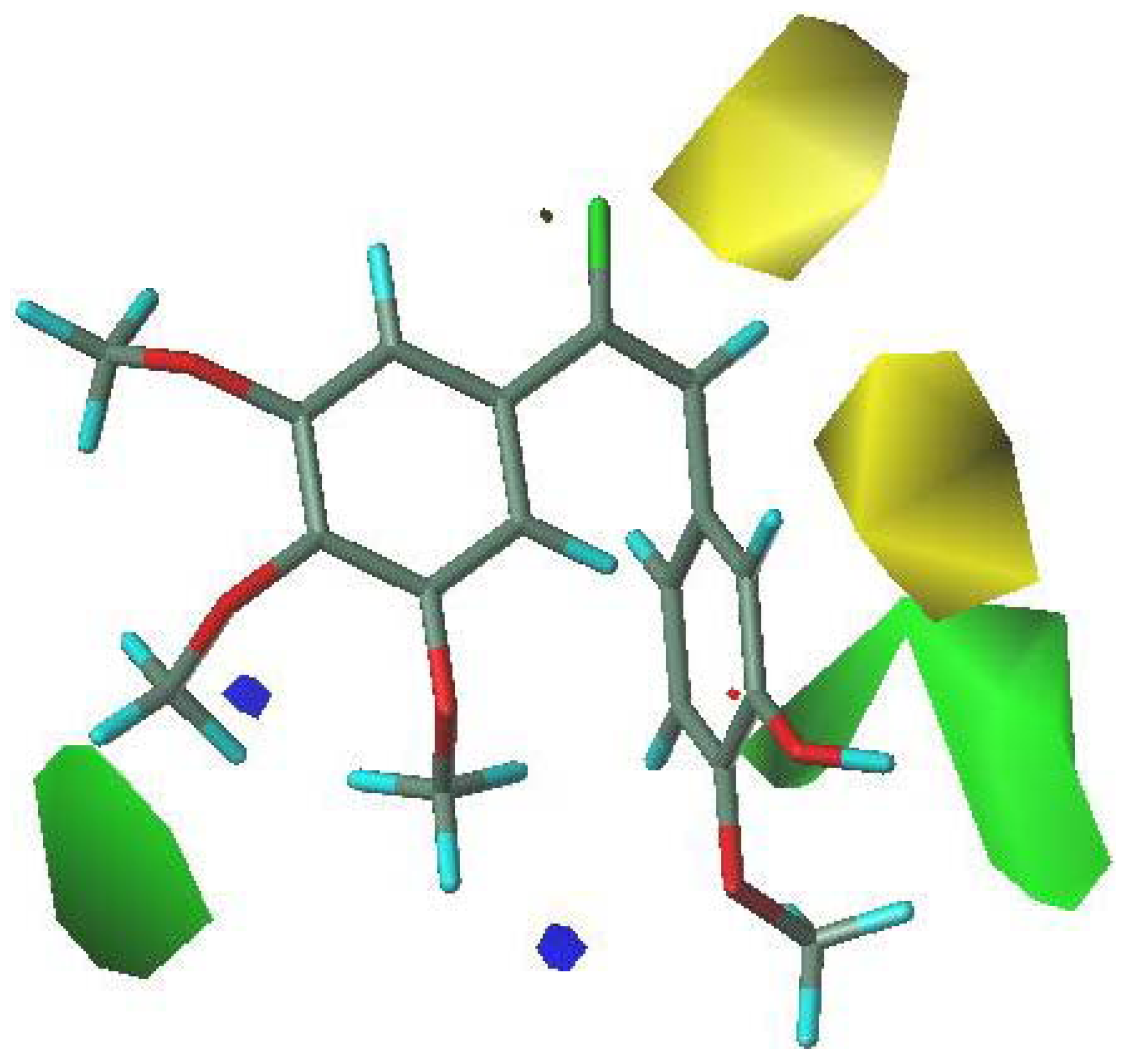
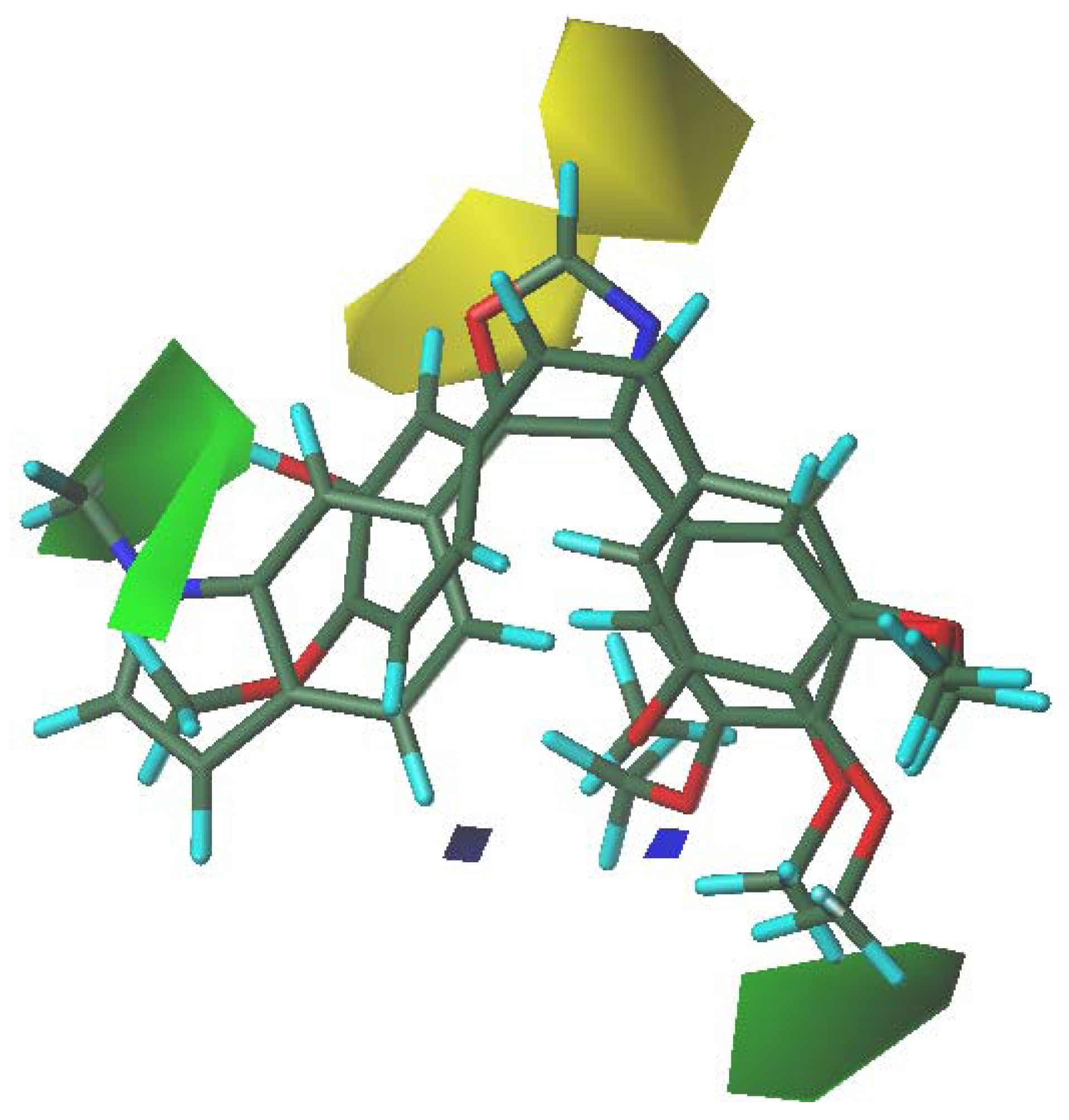
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Pettit, G.R.; Singh, S.B.; Hamel, E.; Lin, C.M.; Alberts, D.S.; Garcia-Kendall, D. Isolation and structure of the strong cell growth and tubulin inhibitor combretastatin A-4. Experientia 1989, 45, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Singh, S.R.; Chu, P.S.; Dempcy, R.O.; Schmidt, J.M.; Pettit, G.R.; Hamel, E. Interactions of tubulin with potent natural and synthetic analogs of the antimitotic agent combretastatin: A structure-activity study. Mol.Phamacol. 1988, 34, 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- Pettit, G.R.; Singh, S.G.; Boyd, M.R.; Hamel, E.; Pettit, R.K.; Schmidt, J.M.; Hogan, F. Antineoplastic agents. 291. Isolation and synthesis of combretastatins A-4, A-5, and A-6. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, D.M.; Rustin, G.J.S. Combretastatin A-4 phosphate. Drugs Future 2007, 32, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, J.W. Vascular disrupting agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.Y.; Chen, J.C.; Miao, T.F.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, K.C. Binding conformations and QSAR of CA-4 analogs as tubulin inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010, 25, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.B.; Tian, R.; Lin, W.H. QSAR and molecular docking study of a series of combretastatin analogues tubulin inhibitors. Lect. Notes. Comput. Sci. 2007, 4689, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, B.L.; Flynn, G.P.; Hamel, E.; Jung, M.K. The synthesis and tubulin binding activity of thiophene-based analogues of combretastatin A-4. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 2341–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousset, C.; Giraud, A.; Provot, O.; Hamzé, A.; Bignon, J.; Jian, M.L.; Thoret, S.; Dubois, J.; Brion, J.D.; Alami, M. Synthesis and antitumor activity of benzils related to combretastatin A-4. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 3266–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, M.; Nagarathnam, D.; Gopal, D.; Chakraborti, A.K.; Lin, C.M.; Hamel, E. Synthesis and evaluation of stilbene and dihydrostilbene derivatives as potential anticancer agents that inhibit tubulin polymerization. J. Med. Chem. 1991, 34, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, R.; Tokuda, K.; Koiso, Y.; Iwasaki, S. Synthesis and anti-tubulin activity of Aza-combretastatins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1994, 4, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, D.; Romagnoli, R.; Baruchello, R.; Rondanin, R.; Grisolia, G.; Eleopra, M.; Rizzi, M.; Tolomeo, M.; Giannini, G.; Alloatti, D.; et al. Novel A-ring and B-ring modified combretastatin A-4 (CA-4) analogues endowed with interesting cytotoxic activity. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 6211–6215. [Google Scholar]
- Alloatti, D.; Giannini, G.; Cabri, W.; Lustrati, I.; Marzi, M.; Ciacci, A.; Gallo, G.; Tinti, M.O.; Marcellini, M.; Riccioni, T.; et al. Synthesis and biological activity of fluorinated combretastatin analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2708–2721. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.M.; Singh, S.B.; Chu, P.S.; Dempcy, R.O.; Schmidt, J.M.; Pettit, G.R.; Hamel, E. Interactions of tubulin with potent natural and synthetic analogs of the antimitotic agent combretastatin: A structure-activity study. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988, 34, 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- Pettit, G.R.; Minardi, M.D.; Rosenberg, H.J.; Hamel, E.; Bibby, M.C.; Martin, S.W.; Jung, M.K.; Pettit, R.K.; Cuthbertson, T.J.; Chapuis, J.C. Antineoplastic agents. 509. Synthesis of fluorcombstatin phosphate and related 3-Halostilbenes. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, K.A.; Siles, R.; Hadimani, M.B.; Mugabe, B.E.; Freeland, A.J.; Studerus, S.W.; Edvardsen, K.; Trawick, M.L.; Garner, C.M.; Rhodes, M.R.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of combretastatin nitrogen-containing derivatives as inhibitors of tubulin assembly and vascular disrupting agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 3231–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsumi, K.; Nakagawa, R.; Fukuda, Y.; Hatanaka, T.; Morinaga, Y.; Nihei, Y.; Ohishi, K.; Suga, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Tsuji, T. Novel combretastatin analogues effective against murine solid tumors: Design and structure-activity relationships. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 3022–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, T.; Fujita, K.; Ohsumi, K.; Nakagawa, R.; Fukuda, Y.; Nihei, Y.; Suga, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Tsuji, T. Novel B-ring modifield combretastatin analogues: Synthesis and antineoplastic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 3371–3374. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, B.L.; Flynn, G.P.; Hamelb, E.; Jungc, M.K. The synthesis and tubulin binding activity of thiophene-based analogues of combretastatin A-4. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 2341–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Yang, M.F.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, C.M.; Kuo, C.C.; Liou, J.P. 2-amino and 2'-aminocombretastatin derivatives as potent antimitotic agents. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6412–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurjar, M.K.; Wakharkar, R.D.; Singh, A.T.; Jaggi, M.; Borate, H.B.; Shinde, P.D.; Verma, R.; Rajendran, P.; Dutt, S.; Singh, G.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of 4/5-Hydroxy-2,3-diaryl(substituted)-cyclopent-2-en-1-ones as cis-restricted analogues of combretastatin A-4 as novel anticancer agents. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, M.; Nagarathnam, D.; Gopal, D.; He, H.M.; Lin, C.M.; Hamel, E. Synthesis and evaluation of analogs of (Z)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)ethene as potential cytotoxic and antimitotic agents. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 2293–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Woods, K.W.; Li, Q.; Barr, K.J.; McCroskey, R.W.; Hannick, S.M.; Gherke, L.; Credo, R.B.; Hui, Y.H.; Marsh, K.; et al. Potent, orally active heterocycle-based combretastatin A-4 analogues: Synthesis, structure-activity relationship, pharmacokinetics, and in vivo antitumor activity evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 1697–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Grealish, M.P.; Jung, M.K.; Hamel, E.; Pettit, R.K.; Chapuis, J.C.; Schmidt, J.M. Antineoplastic agents. 465. Structural modification of resveratrol: Sodium resverastatin phosphate. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2534–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Anderson, C.R.; Herald, D.L.; Jung, M.K.; Lee, D.J.; Hamel, E.; Pettit, R.K. Antineoplastic agents. 487. Synthesis and biological evaluation of the antineoplastic agent 3,4-methylenedioxy-5,4'-dimethoxy-3'-amino-Z-stilbene and derived amino acid amides. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, A.B.S.; Pérez-Melero, C.; Mateo, C.; Alonso, D.; Fernndez, J.L.; Gajate, C.; Mollinedo, F.; Peláez, R.; Caballero, E.; Medarde, M. Further naphthyl combretastatins. An investigation on the role of the naphthalene moiety. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 556–568. [Google Scholar]
- Pettit, G.R.; Rhodes, M.R.; Herald, D.L.; Hamel, E.; Schmidt, J.M.; Pettit, R.K. Antineoplastic Agents. 445. Synthesis and Evaluation of Structural Modifications of (Z)-and (E)-Combretastatin A-4. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4087–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsumi, K.; Nakagawa, R.; Fukuda, Y.; Hatanaka, T.; Morinaga, Y.; Nihei, Y.; Ohishi, K.; Suga, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Tsuji, T. Novel combretastatin analogues effective against murine solid tumors: Design and structure-activity relationships. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 3022–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaffy, J.; Pontikis, R.; Carrez, D.; Croisy, A.; Monneret, C.; Florent, J.C. Isoxazole-type derivatives related to combretastatin A-4, synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 4067–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, D.; Romagnoli, R.; Baruchello, R.; Rondanin, R.; Rizzi, M.; Pavani, M.G.; Alloatti, D.; Giannini, G.; Marcellini, M.; Riccioni, T.; et al. Novel combretastatin analogues endowed with antitumor activity. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, R.; Christensen, M.H. MolDock: A new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SYBYL, Molecular Modelling System, version 6.9.1; Tripos Inc.: Saint-Louis, MS, USA, 2003.
- Teixeira, C.; Serradji, N.; Maurel, F.; Barbault, F. Docking and 3D-QSAR studies of BMS-806 analogs as HIV-1 gp120 entry inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3524–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Xia, W.; Zhang, R. CoMFA and CoMSIA 3D-QSAR Studies on quionolonecaroxylic acid derivatives inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gao, Y.; Liu, L.; Lai, L. All-orientation search and all-placement search in comparative molecular field analysis. J. Mol. Model. 1998, 4, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelli, R.B.G.; Gigant, B.; Curmi, P.A.; Jourdain, I.; Lachkar, S.; Sobel, A.; Knossow, M. Insight into tubulin regulation from a complex with colchicine and a stathmin-like domain. Nature 2004, 428, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Z.; Li, Y.X.; Zhu, X.L.; Zhen, X.; Niu, C.W.; Wan, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G.F. Rational design based on bioactive conformation analysis of pyrimidinyl benzoates as acetohydroxy acid synthase inhibitors by integrating molecular docking, CoMFA, CoMSIA, and DFT calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 2335–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, H.J.; Stahl, M. Reviews in Computational Chemistry; Lipkowsky, K.B., Boyd, D.B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 41–87. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.Y.; Chen, J.C.; Miao, T.F.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, K.C. Binding conformations and QSAR of CA-4 analogs as tubulin inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010, 25, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Barbault, F.; Delamar, M.; Zhang, R. Receptor- and ligand-based 3D-QSAR study for a series of non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2400–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.J.; Barbault, F.; Maurel, F.; Delamar, M.; Zhang, R.S. Molecular dynamics simulations of 2-Amino-6-arylsulphonylbenzonitriles analogues as HIV inhibitors: Interaction modes and binding free energies. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2010, 76, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiong, X.X.; Mei, D.Z.; Fei, P.B.; Yang, L.; Hong, J.R.; Jian, W.; Sheng, M.C. CoMFA, CoMSIA and eigenvalue analysis on dibenzodioxepinone and dibenzodioxocinone derivatives as cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors. Molecules 2008, 13, 1822–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbraikh, A.; Tropsha, A. Beware of q2. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2002, 20, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Qi, P.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, H. 3D-QSAR Study of Combretastatin A-4 Analogs Based on Molecular Docking. Molecules 2011, 16, 6684-6700. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16086684
Jin Y, Qi P, Wang Z, Shen Q, Wang J, Zhang W, Song H. 3D-QSAR Study of Combretastatin A-4 Analogs Based on Molecular Docking. Molecules. 2011; 16(8):6684-6700. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16086684
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yinghua, Ping Qi, Zhiwei Wang, Qirong Shen, Jian Wang, Weige Zhang, and Hongrui Song. 2011. "3D-QSAR Study of Combretastatin A-4 Analogs Based on Molecular Docking" Molecules 16, no. 8: 6684-6700. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16086684
APA StyleJin, Y., Qi, P., Wang, Z., Shen, Q., Wang, J., Zhang, W., & Song, H. (2011). 3D-QSAR Study of Combretastatin A-4 Analogs Based on Molecular Docking. Molecules, 16(8), 6684-6700. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16086684