Highly Efficient Procedure for the Synthesis of Fructone Fragrance Using a Novel Carbon based Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
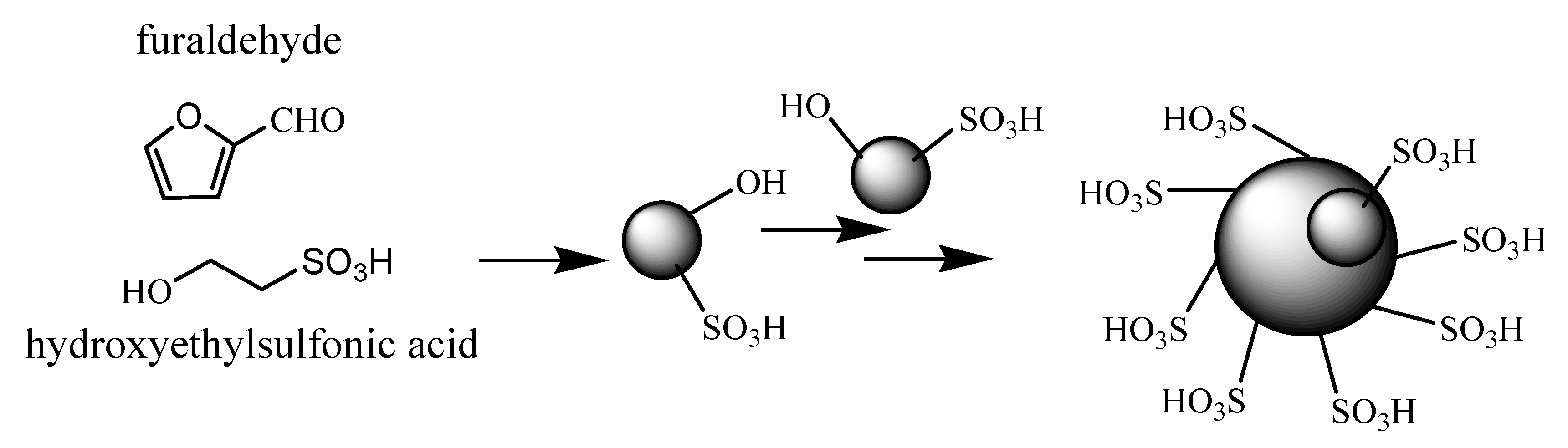
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Novel Carbon Based Acid
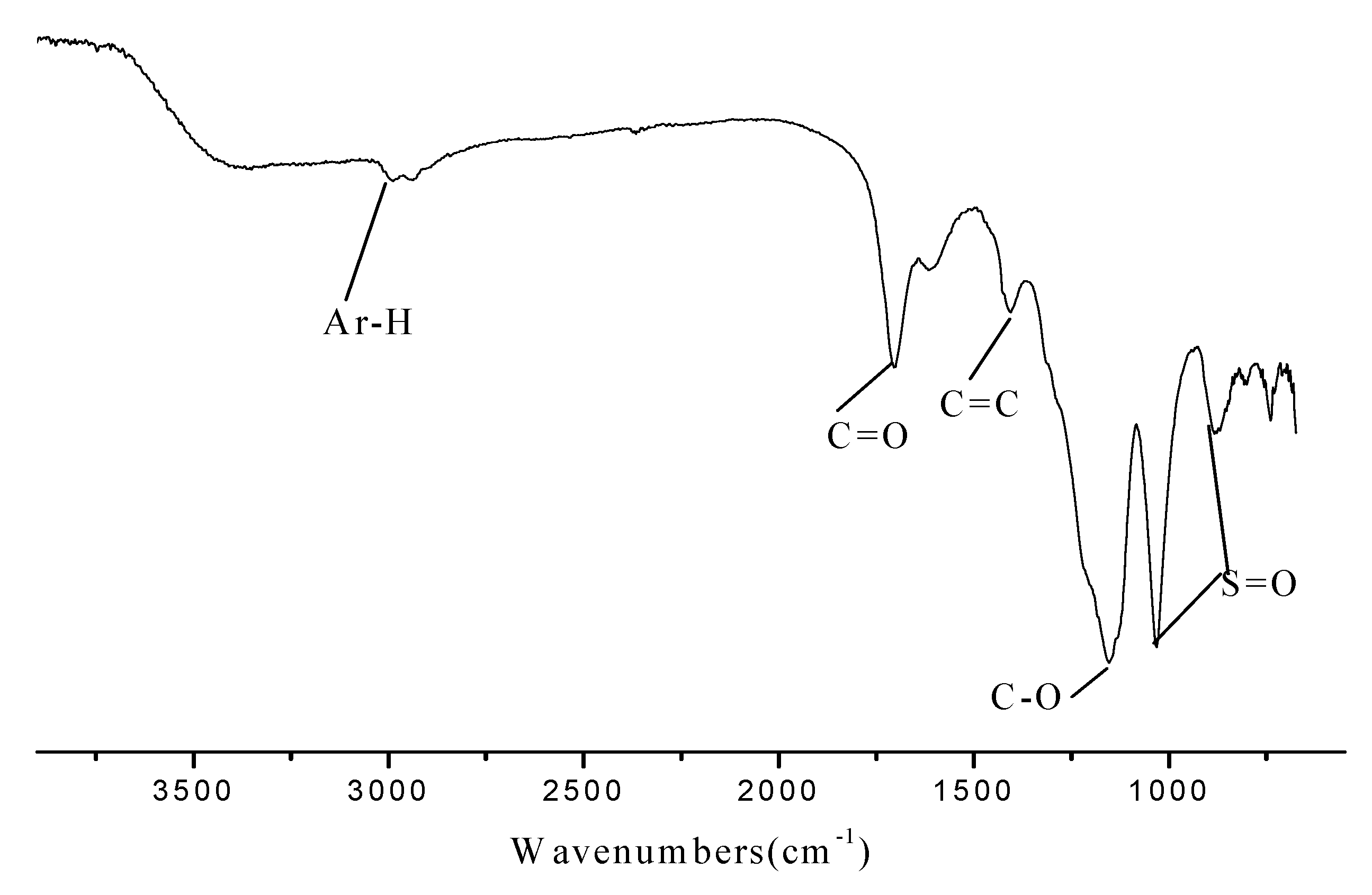

2.2. The Catalytic Activities for the Synthesis of Fructone
2.2.1. The Effect of the Reaction Time on the Yield

2.2.2. The Effect of the Molar Ratio of the Reactants on the Yield
| n(ethyl acetoacetate)/n(ethylene glycol) | 1:1.0 | 1:1.2 | 1:1.5 | 1:2.0 |
| Conversion/% | 85.6 | 91.4 | 98.7 | 99.3 |
| Selectivity/% | 98.3 | 98.6 | 99.3 | 98.7 |
2.2.3. The Effect of the Catalyst Amount on the Yield
| Catalyst usage/g | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| Conversion/% | 97.0 | 97.4 | 98.7 | 98.7 |
| Selectivity/% | 98.3 | 98.6 | 99.3 | 98.7 |
2.2.4. The Effect of the Solvents on the Yield
| Solvent | cyclohexane | toluene | isooctane |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conversion/% | 98.7 | 95.3 | 96.4 |
| Selectivity/% | 99.3 | 85.1 | 93.0 |
2.2.5. The Results with Different Diols
| Diols | 1,2-ethanediol | 1,2-propandeniol | 1,4-butanediol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conversion/% | 98.7 | 95.4 | 93.7 |
| Selectivity/% | 99.3 | 99.2 | 98.9 |
2.2.6. The Results of Different β-keto Esters
| β-keto esters | Conversion/% | Selectivity/% |
|---|---|---|
 | 99.1 | 99.3 |
 | 98.5 | 99.2 |
 | 97.8 | 99.3 |
 | 97.2 | 99.1 |
 | 96.5 | 99.3 |
2.2.7. A Comparative Study of Different Catalysts
| Catalyst | Acid carbon | H2SO4 | PTSA | Hβ | Nafion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalyst amount/g | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Reaction time/h | 2.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 |
| Conversion/% | 97.4 | 98.5 | 97.3 | 92.1 | 94.2 |
| Selectivity/% | 99.3 | 62.3 | 67.3 | 98.9 | 98.7 |
2.3. The Reuse of the Novel Catalyst

3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis of the Carbonaceous Material
3.3. Typical Procedure for Synthesis of Fructone (Scheme 2)
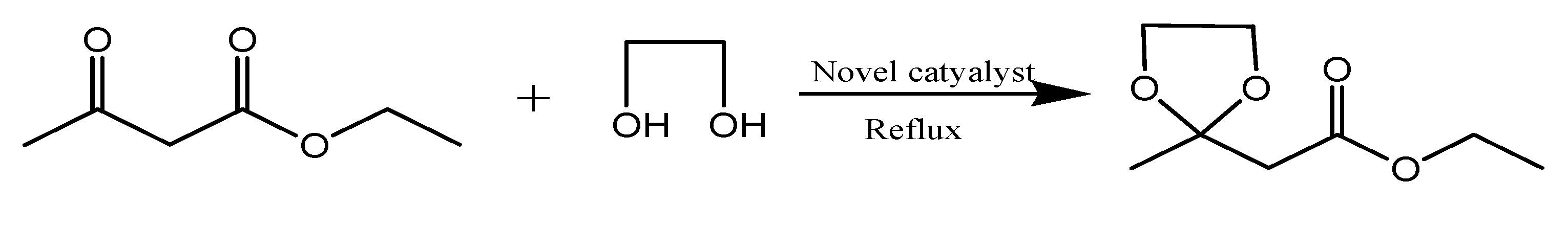
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Anastas, P.T.; Kirchhoff, M.M. Origins, current status, and future challenges of green chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 686–694. [Google Scholar]
- DeSimone, J.M. Practical Approaches to Green Solvents. Science 2002, 297, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harton, B. Green Chemistry Puts Down Roots. Nature 1999, 400, 797–799. [Google Scholar]
- Anastas, P.T.; Zimmermann, J.B. Design through the 12 principles of green engineering. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 94A–101A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.H. Solid Acids for Green Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 791–797. [Google Scholar]
- Misono, M.; Acad, C.R. Heterogeneous catalysis. Sci. Ser. Iic. 2000, 3, 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, K.; Okamura, M.; Kondo, J.N.; Domen, K.; Tatsumi, T.; Hayashi, S.; Hara, M. Amorphous Carbon Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups in Mesoporous Silica as a Selective Catalyst. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Comerford, J.W.; Clark, J.H.; Macquarrie, D.J.; Breeden, S.W. Amidation of Carboxylic Acid with Amines by K60 Silica. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2562–2564. [Google Scholar]
- Toda, M.; Takagaki, A.; Okamura, M.; Kondo, J.N.; Domen, K.; Hayashi, S.; Domen, K.; Hara, M. Biodiesel made with sugar catalyst. Nature 2005, 438, 178. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, M.; Yoshida, T.; Takagaki, A.; Takata, T.; Kondo, J.N.; Domen, K.; Hayashi, S. Carbon material as a strong protonic acid. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2955–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.-M.; Thomas, A.; Antonietti, M. Replication and Coating of Silica Templates by Hydrothermal Carbonization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.Z.; Yang, J.G. Synthesis of a Novel Carbon Based Strong Acid Catalyst Through Hydrothermal Carbonization. Catal. Lett. 2009, 132, 460–463. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.Z.; Xiao, H.Q.; Shen, Y.M.; Qi, C.Z. One-step synthesis of novel sulfuric acid groups functionalized carbon via hydrothermal carbonization. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 953–955. [Google Scholar]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A.B. Chemical and structural properties of carbonaceous products obtained by hydrothermal carbonization of saccharides. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, H.; Yu, S.-H.; Wang, K.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.-W. Functional carbonaceous materials from hydrothermal carbonization of biomass: an effective chemical process. Dalton. Trans. 2008, 40, 5414–5423. [Google Scholar]
- Demir-Cakan, R.; Baccile, N.; Antonietti, M.; Titirici, M.M. Carboxylate-Rich Carbonaceous Materials via One-Step Hydrothermal Carbonization of Glucose in the Presence of Acrylic Acid. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 484–490. [Google Scholar]
- Wadlinger, R.L.; Kerr, G.T.; Rosinski, E. Catalytic composition of a crystalline zeolite. U.S. Patent 3,308,069, 7 March 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples are available from the authors.
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an Open Access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, B.; Li, C.; Zhao, S.-X.; Rong, L.-M.; Lv, S.-Q.; Liang, X.; Qi, C. Highly Efficient Procedure for the Synthesis of Fructone Fragrance Using a Novel Carbon based Acid. Molecules 2010, 15, 5369-5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15085369
Hu B, Li C, Zhao S-X, Rong L-M, Lv S-Q, Liang X, Qi C. Highly Efficient Procedure for the Synthesis of Fructone Fragrance Using a Novel Carbon based Acid. Molecules. 2010; 15(8):5369-5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15085369
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Baowei, Chunqing Li, Sheng-Xian Zhao, Lin-Mei Rong, Shao-Qin Lv, Xuezheng Liang, and Chenze Qi. 2010. "Highly Efficient Procedure for the Synthesis of Fructone Fragrance Using a Novel Carbon based Acid" Molecules 15, no. 8: 5369-5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15085369
APA StyleHu, B., Li, C., Zhao, S.-X., Rong, L.-M., Lv, S.-Q., Liang, X., & Qi, C. (2010). Highly Efficient Procedure for the Synthesis of Fructone Fragrance Using a Novel Carbon based Acid. Molecules, 15(8), 5369-5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15085369





