Abstract
We report the determination of phenolic compounds in olive leaves by reversed-phase HPLC/DAD, and the evaluation of their in vitro activity against several microorganisms that may be causal agents of human intestinal and respiratory tract infections, namely Gram positive (Bacillus cereus, B. subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus), Gram negative bacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae) and fungi (Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans). Seven phenolic compounds were identified and quantified: caffeic acid, verbascoside, oleuropein, luteolin 7-O-glucoside, rutin, apigenin 7-O-glucoside and luteolin 4’-O-glucoside. At low concentrations olive leafs extracts showed an unusual combined antibacterial and antifungal action, which suggest their great potential as nutraceuticals, particulalry as a source of phenolic compounds.
Introduction
Olive tree (Olea europaea L.) is one of the most important fruit trees in Mediterranean countries, where they cover 8 million ha, accounting for almost 98% of the world crop. This demonstrates the great economic and social importance of this crop and the possible benefits to be derived from utilisation of any of its byproducts [1,2]. Olea europaea L. is widely studied for its alimentary use (the fruits and the oil are important components in the daily diet of a large part of the world’s population), whereas the leaves are important for their secondary metabolites such as the secoiridoid compounds oleacein and oleuropein, the former responsible for hypotensive activity [3] and the latter also for hypoglycemic activity [4]. Several reports have shown that olive leaf extract has the capacity to lower blood pressure in animals [5] and increase blood flow in the coronary arteries [6], relieve arrhythmia and prevent intestinal muscle spasms [7]. Also leaves may be used in infusions, allowing a considerable intake/uptake of bioactive compounds.
Papers concerning the analysis of the phenolic components of the olive fruits, olive oil [8,9] and olive leaves [10,11,12,13,14] are can be found in the literature, but the investigation of those volatiles is mostly correlated to their antioxidant properties. The reports describing antimicrobial properties of phenolic compounds in olive products refer to compounds obtained from olive fruit, particularly hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein [15,16]. A study [17] about the in vitro antimicrobial activity of olive leaves was reported, but the minimal inhibitory concentrations for the inhibition of microbial growth obtained were higher than in the present study. Herein, we have analysed the phenolic compounds present in olive leaves by HPLC/DAD and we evaluated the extracts antimicrobial activity against Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria and fungi.
Results and Discussion
Phenolic compounds in olive leaves
The HPLC-DAD analysis of olive leaf aqueous extract allowed the identification of seven phenolic compounds (Figure 1): caffeic acid, verbascoside, oleuropein, luteolin 7-O-glucoside, rutin, apigenin 7-O-glucoside and luteolin 4’-O-glucoside (Figure 2). All these compounds were previously reported to occur in olive leaf [10,11,12,13,14]. The quantification of the phenolics present in the aqueous extract revealed a high amount of these compounds (Table 1), that was considerably superior to the values found before for hydromethanolic extracts of the same and other olive leaf cultivars [14]. Additionally, in opposition to what happened with the hydromethanolic extracts in which flavonoids were the major compounds [14], the aqueous extract exhibited a profile in which oleuropein was the compound present in highest amount, representing ca. 73% of total identified compounds (Table 1). Caffeic acid was the minor compound, corresponding to ca. 1% of total phenolics.
The differences found in the phenolic composition are not surprising, considering that a different extractive method was applied, involving a much higher temperature, and that the present extract (aqueous) is more polar than the hydromethanolic ones analysed before [14]. On the other hand, the influence of the sample origin, in terms of both geographic provenance and year of collection, cannot be excluded.
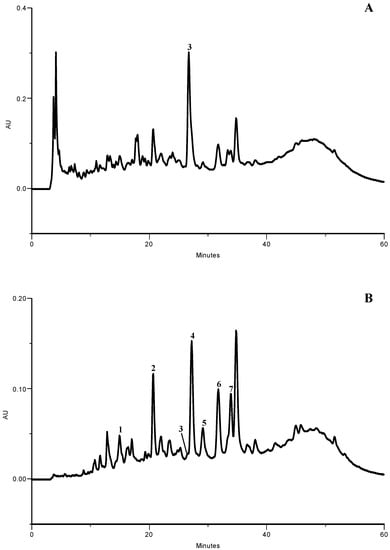
Figure 1.
HPLC phenolic profile of olive leaf lyophilized extract. Detection at (A) 280 and (B) 350 nm. (1) caffeic acid; (2) verbascoside; (3) oleuropein; (4) luteolin 7-O-glucoside; (5) rutin; (6) apigenin 7-O-glucoside; (7) luteolin 4’-O-glucoside.

Table 1.
Quantification of the phenolic compounds in olive leaf lyophilized extract.a
| Compound | mg/kg |
|---|---|
| 1 Caffeic acid | 220.5 ± 23.3 |
| 2 Verbascoside | 966.1 ± 18.1 |
| 3 Oleuropein | 26471.4 ± 1760.2 |
| 4 Luteolin 7-O-glucoside | 4208.9 ± 97.8 |
| 5 Rutin | 495.9 ± 12.2 |
| 6 Apigenin 7-O-glucoside | 2333.1 ± 74.7 |
| 7 Luteolin 4’-O-glucoside | 1355.9 ± 75.9 |
| Σ | 36051.8 |
a Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of three determinations. Σ: sum of the determined phenolic compounds. nq: not quantified.
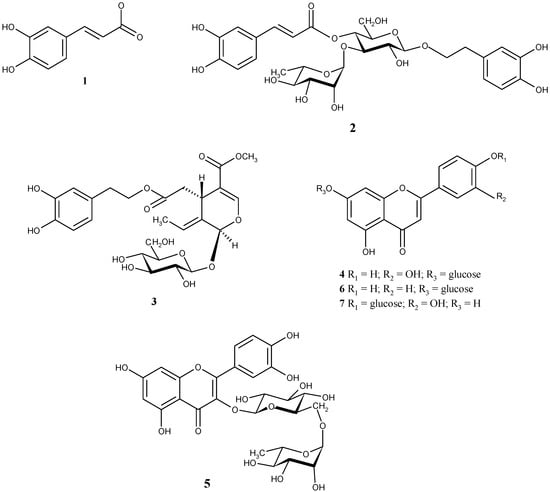
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of identified phenolic compounds. (1) caffeic acid; (2) verbascoside; (3) oleuropein; (4) luteolin 7-O-glucoside; (5) rutin; (6) apigenin 7-O-glucoside; (7) luteolin 4’-O-glucoside.
Antimicrobial activity
As previously described, individual phenolic compounds present in the olive leaves extracts were identified and quantified, but we choose to submit the entire extracts to antimicrobial activity studies for several reasons. First, in a general way, the antimicrobial capacity of phenolic compounds is well-known [18,19,20,21,22]. In addition, extracts may be more beneficial than isolated constituents, since a bioactive individual component can change its properties in the presence of other compounds present in the extracts [23]. According to Liu [24] additive and synergistic effects of phytochemicals in fruits and vegetables are responsible for their potent bioactive properties and the benefit of a diet rich in fruits and vegetables is attributed to the complex mixture of phytochemicals present in whole foods. This explains why no single antimicrobial can replace the combination of natural phytochemicals to achieve the health benefits.
Olive leaf aqueous extracts were screened for their antimicrobial activity against B. cereus, B. subtilis, S. aureus (Gram +), E. coli, P. aeruginosa, K. pneumoniae (Gram -) bacteria, and C. albicans and C. neoformans (fungi). Aside from concerns with food quality degradation, these microorganisms may be causal agents of intestinal infections in humans. The extract inhibited all the tested bacteria and fungi, suggesting a broad antimicrobial activity of olive leaf extracts in a concentration-dependent manner. According to the values of microbial growth rate in the presence of different extract concentrations, olive leaf presented antimicrobial capacity following the order B. cereus ~ C. albicans > E. coli > S. aureus > C. neoformans ~ K. pneumoniae ~ P. aeruginosa > B. subtilis (Table 2). B. cereus (Gram positive) and C. albicans (fungi) were the most sensitive microorganisms, presenting IC25 values lower than 1 mg/mL. These are interesting results since 7-O-methylnaringenin, a known flavonoid isolated from the leaves of Rhus retinorrhoea Steud, Ex Olive, showed weak antimicrobial activity against Candida albicans, C. krusei, Staphylococcus aureus, Mycobacterium smegmatis, M. intracellulare, and M. xenopi [25]. B. subtilis was the most resistant microorganism.

Table 2.
Values for microbial growth rate in the presence of different olive leaf extract concentrations and IC25 values.
| [Extract](mg/mL) | B. cereus | B. subtilis | S. aureus | E. coli | K. pneumoniae | P. aeruginosa | C. albicans | C. neoformans |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.66 | 0.57 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.40 | 0.18 |
| 0.05 | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.56 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.35 | 0.17 |
| 0.10 | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.73 | 0.56 | 0.60 | 0.63 | 0.36 | 0.16 |
| 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 0.52 | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.39 | 0.16 |
| 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.60 | 0.46 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 0.26 | 0.15 |
| 5.00 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| IC25 | 0.63 | 4.12 | 2.68 | 1.81 | 3.13 | 3.22 | 0.85 | 3.00 |
The extract decreased the absorbance values at 540 nm at a concentration of 5 mg/mL, indicating inhibition of bacterial (Figure 3) and fungal growth (Figure 4), relative to the control (without extract) after 24h and 48 h of incubation, respectively. Certainly the chemical composition of olive leaf extracts conditioned the antimicrobial effects observed. The high content of oleuropein and the other phenolic compounds identified in the extract might contribute for its antimicrobial properties.
Hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein are other phenolic compounds that have been proven to inhibit or delay the rate of growth of several human intestinal or respiratory tract pathogens, namely Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Salmonella typhi, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio alginolyticus [15].
The unusual combined antibacterial and antifungal action obtained in this study for olive leaf extracts is in agreement with that reported by Markin et al. [17]. Nevertheless, we obtained lower IC25 values than the 0.6% described by them. Olive leaves may be useful in cases where prolonged use of antibiotics encourage development of opportunistic infections [26], being especially effective against Klebsiella and Pseudomonas, two bacterial genera which pose a major resistance problem [27].
In conclusion, the data obtained in this study demonstrate that the use of olive leaves as nutraceuticals may lower the risk of microbial infections, particularly in the intestinal and respiratory tract, mainly due to the protective action provided by its phenolic compounds. The use of extracts is recommended to achieve health benefits due to the additive and synergistic effects of phytochemicals present in whole extract.
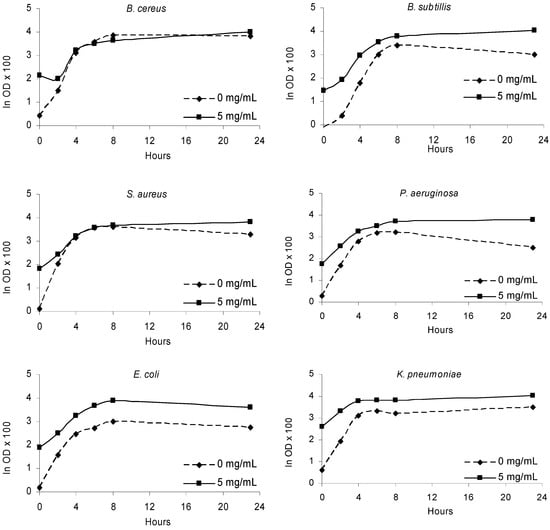
Figure 3.
Bacterial growth in the presence of olive leaves extract (5 mg/mL) and in the absence of extract (0 mg/mL) along the incubation period (24 h).
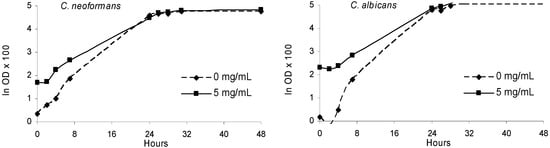
Figure 4.
Fungal growth in the presence of olive leaves extract (5 mg/mL) and in the absence of extract (0 mg/mL) along the incubation period (48 h).
Experimental
Samples
Olive leaves samples of Cv. Cobrançosa were collected in November 2004 in an olive grove located in Trás-os-Montes, Northeast Portugal. The orchard has a planting density of 7 × 7 m. The trees have twelve years old, being pruned when necessary, not irrigated and no phytosanitary treatments had been applied in the last year. The leaves were collected at the operator height around the whole perimeter of each tree. The collected samples were put in plastic bags and immediately frozen at -20°C. The plant material was then freeze dried and powdered (20 mesh).
Identification and quantification of phenolic compounds
Standards and reagents. The standards used were from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA) or Extrasynthèse (Genay, France). Methanol and formic acid were obtained from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). The water was treated in a Milli-Q water purification system (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA) before use.
Extraction of phenolic compounds. An aqueous extract of olive leaves was prepared by putting dried material (ca. 5.0 g) in boiling water (150 mL). The mixture was boiled for 30 min and then filtered over a Büchner funnel. The obtained extract was then lyophilised. The lyophilised extract was kept in an exsicator, in the dark. For phenolic compounds analysis it was redissolved in water.
HPLC-DAD system for analysis of phenolic compounds. Chromatographic separation was achieved as previously reported [14] with an analytical HPLC unit (Gilson) coupled to a diode array detector (DAD) (Gilson), using a reversed-phase Spherisorb ODS2 (250 x 4.6 mm, 5 μm particle size, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) column. The solvent system used was a gradient of water/formic acid (19:1) (A) and methanol (B), starting with 15% methanol and installing a gradient to obtain 18%B at 3 min, 25%B at 6 min, 39%B at 19 min, 39%B at 22 min, 50%B at 36 min, 79%B at 59 min and 100%B at 60 min. The flow rate was 0.9 ml/min, and the injection volume was 20 μl. Chromatograms were recorded at 280, 320 and 350 nm. Spectral data from all peaks were accumulated in the 200–400 nm range. Data were processed on a Unipoint system software (Gilson Medical Electronics, Villiers le Bel, France). Phenolic compound quantification was achieved by the absorbance recorded in the chromatograms relative to external standards, with detection at 280 nm for oleuropein, at 320 nm for caffeic acid and verbascoside and at 350 nm for flavonoids. Luteolin derivatives were quantified as luteolin 7-O-glucoside. The other compounds were quantified as themselves.
Antimicrobial Activity
Extract preparation. Powdered sample (5 g) was extracted with boiling water (250 mL) for 45 min and filtered through Whatman n°4 paper. The aqueous extract was frozen, lyophilized and redissolved in water at a concentration of 50 mg/mL, and analysed for their antimicrobial activity.
Microorganisms and culture conditions. The bacterial strains used were Bacillus cereus CECT 148, B. subtilis CECT 498, Staphylococus aureus ESA 7, Escherichia coli CECT 101, Pseudomonas aeruginosa CECT 108, and Klebsiella pneumoniae ESA 8. The fungi strains used were Candida albicans CECT 1394 and Cryptococcus neoformans ESA 3. Microorganisms CECT were obtained from the Spanish type culture collection (CECT) of Valencia University, while microorganisms ESA were clinically isolated strains identified in Microbiology Laboratory of Escola Superior Agrária de Bragança. Microorganisms were cultured aerobically at 37 °C in nutrient agar medium for bacteria, and at 30 °C (Scientific 222 oven model, 2003) in Sabouraud dextrose agar medium for fungi. Before experimental use, cultures from solid medium were subcultivated in liquid media, incubated and used as the source of inoculums for each experiment.
Test assays for antibacterial activity. A macro-broth-dilution technique [38] was used to determine the growth inhibition of the susceptible Gram + (B. subtilis, B. cereus, S. aureus) and Gram – (E. coli, K. pneumoniae) bacteria, and fungi (C. albicans, C. neoformans) to olive leaves. A nutrient medium (10 g tryptone, 5 g meat extract, water to 1 L) was used to prepare the inocula after being sterilized in an autoclave (P Selecta model, 2002) at 121 °C for 20 min). Erlenmeyer flasks (50 mL) containing the liquid culture medium (10 mL) were inoculated with the bacteria suspension (108 cfu/mL) and each extract concentration to be tested (0.05-5 mg/mL) was added. Incubation was carried out for 24 hours at 37 °C in a rotary shaker (Stuart Scientific SI50 model, 2001) at 150 rpm. The growth of bacteria cultures was monitored by measuring optical density at 540 nm in a UV–visible spectrophotometer (Varian Cary 50 Scan model, 1998). Controls were carried out in the same conditions but in the absence of sample extract. All assays were carried out under aseptic conditions. Values for bacteria growth rate were obtained by linear regression analysis in the exponential growth range in the graphs of optical density at 540 nm versus incubation time. The equation curve slope was considered the rate of microbial growth. IC25 values (extract concentration which inhibits 25% of microbial growth) were also determinate.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to INTERREG III A Program, Project MOABEPE for financial support of this work.
References
- Guinda, A.; Albi, T.; Camino, M. C. P.; Lanzón, A. Supplementation of oils with oleanolic acid from the olive leaf (Olea europaea). Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2004, 106, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabera, J.; Guinda, A.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, A.; Senorans, J. F.; Ibanez, E.; Albi, T.; Reglero, G. Countercurrent supercritical fluid extraction and fractionation of high-added-value compounds from a hexane extract of olive leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4774–4779. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, K.; Adsersen, A.; Christensen, B. S.; Brooegger, S.; Rosendal, J. S.; Nyman, U.; Wagner Smitt, U. Isolation of an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor from Olea europaea and Olea lancea. Phytomedicine 1996, 2, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.; Zarzuelo, A.; Gamez, M. J.; Utrilla, M. P.; Jimenez, J.; Osuna, I. Hypoglycemic activity of olive leaf. Planta Med. 1992, 58, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelsson, G. The blood pressure lowering factor in leaves of Olea europaea. Farmacevtisk Revy 1951, 15, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Zarzuelo, A.; Duarte, J.; Jimenez, J.; Gonzales, M. Utrilla Vasodilator effect of olive leaf. Planta Med. 1991, 57, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, O.B.; Castillo, J.; Lorente, J.; Ortuno, A.; Del-Rio, J.A. Antioxidant activity of phenolics extracted from Olea europaea L. leaves. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.H.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Almeida, M. Antioxidant activity of hydroxytyrosol acetate compared with that of other olive oil polyphenols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2480–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva-Martins, F.; Gordon, M.H.; Gameiro, P. Activity and location of olive oil phenolic antioxidants in liposomes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2003, 124, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Benavente-García, O.; Castillo, J.; Lorente, J.; Ortuño, A.; Del Rio, J.A. Antioxidant activity of phenolics from Olea europaea L. leaves. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 457–462. [Google Scholar]
- Bouaziz, M.; Sayadi, S. Isolation and evaluation of antioxidants from leaves of a Tunisian cultivar olive tree. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2005, 107, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briante, R.; Patumi, M.; Terenziani, S.; Bismuto, E.; Febbraio, F.; Nucci, R. Olea europaea L. leaf extract and derivatives: antioxidant properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4934–4940. [Google Scholar]
- Paiva-Martins, F.; Gordon, M.H. Isolation and characterization of the antioxidant component 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethyl-4-formyl-3-formylmethyl-4-hexenoate from olive (Olea europaea) leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4214–4219. [Google Scholar]
- Meirinhos, J.; Silva, B.; Valentão, P.; Seabra, R.M.; Pereira, J. A.; Dias, A.; Andrade, P.B.; Ferreres, F. Analysis and quantification of flavonoidic compounds from Portuguese olive (Oleae europeae L.) leaf cultivars. Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 19, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Bisignano, G.; Tomaino, A.; Lo Cascio, R.; Crisafi, G.; Uccella, N.; Saija, A. On the in vitro antimicrobial activity of oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1999, 51, 971–974. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, M.G.; Burdock, G.A.; Christian, M.S.; Bitler, C.M.; Crea, R. Safety assessment of aqueous olive pulp extract as an antioxidant or antimicrobial agent in foods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markin, D.; Duek, L.; Berdicevsky, I. In vitro antimicrobial activity of olive leaves. Mycoses 2003, 46, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.A.; Pereira, A.P.G.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Seabra, R.; Estevinho, L.; Bento, A. Table olives from Portugal: phenolic compounds, antioxidant potential and antimicrobial activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8425–8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proestos, C.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Nychas, G.-J. E.; Komaitis, M. RP-HPLC analysis of the phenolic compounds of plant extracts. Investigation of their antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Rauha, J.-P.; Remes, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hopia, A.; Kähkönen, M.; Kujala, T.; Pihlaja, K.; Vuorela, H.; Vuorela, P. Antimicrobial effects of Finnish plant extracts containing flavonoids and other phenolic compounds. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 56, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Lo, R. Phenolic compounds from the leaf extracto f artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and their antimicrobial activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7272–7278. [Google Scholar]
- Puupponen-Pimiä, R.; Nohynek, L.; Meier, C.; Kähkönen, M.; Heinonen, M.; Hopia, A.; Oksman-Caldentey, K.-M. Antimicrobial properties of phenolic compounds from berries. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 494–507. [Google Scholar]
- Borchers, A.T.; Keen, C.L.; Gerstiwin, M.E. Mushrooms, tumors, and immunity: an update. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 393–406. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.H. Health benefits of fruits and vegetables are from additive and synergistic combination of phytochemicals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 517S–520S-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmeda, M.S.; Galalb, A.M.; Rossb, S.A; Ferreira, D.; El Sohlyb, M.A.; Ibrahime, A.S.; Mossa, J.S.; El-Feralya, F.S. A weakly antimalarial biflavanone from Rhus retinorrhoea. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 599–602. [Google Scholar]
- Verduyn-Lunel, F.M.; Meis, J.F.; Voss, A. Nosocomial fungal infections: candidaemia. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1999, 34, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Neu, H.C. The crisis in antibiotic resistance. Science 1992, 257, 1064–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, A.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Calhelha, R.; Andrade, P.B.; Valentão, P.; Seabra, R.; Estevinho, L.; Bento, A.; Pereira, J.A. Phenolics and antimicrobial activity of traditional stoned table olives “alcaparra”. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 8533–8538. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples are not available.
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.