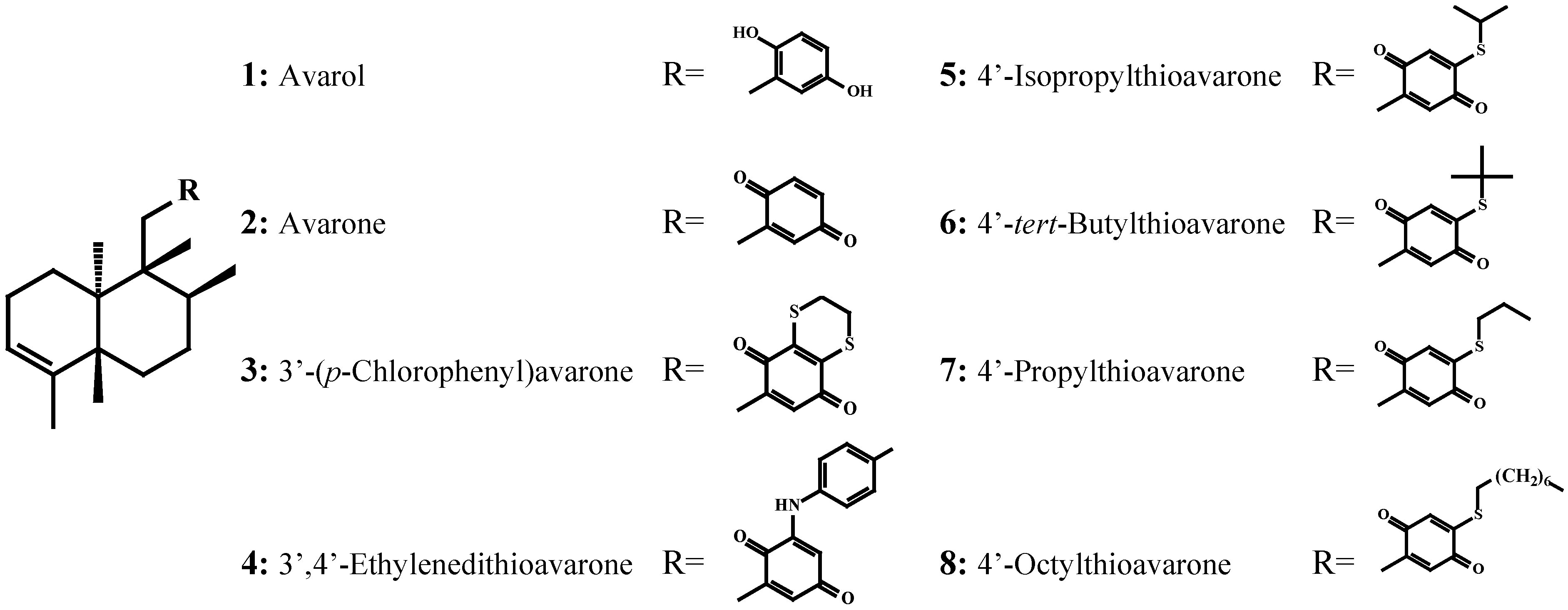
Evaluation of the Activity of the Sponge Metabolites Avarol and Avarone and their Synthetic Derivatives Against Fouling Micro- and Macroorganisms
Abstract
:Introduction
Results and Discussion
Antimicrobial activity against Cobetia marina, Marinobacterium stanieri, Vibrio fischeri and Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis
| No | Compound | Cobetia marina | Marinobacterium stanieri | Vibrio fischeri | Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Avarol | 2.5 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| 2 | Avarone | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 3 | 3’-(p-Chlorophenyl)avarone | 1.0 | 5.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 |
| 4 | 3’,4’-Ethylenedithioavarone | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
| 5 | 4’-Isopropylthioavarone | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 6 | 4’-tert-Butylthioavarone | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 1.0 |
| 7 | 4’-Propylthioavarone | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 8 | 4’-Octylthioavarone | 1.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
Antifungal activity against Halosphaeriopsis mediosetigera, Asteromyces cruciatus, Lulworthia uniseptata and Monodictys pelagica
| No | Compound | Halosphaeriopsis mediosetigera | Asteromyces cruciatus | Lulworthia uniseptata | Monodictys pelagica |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Avarol | 10.0 | 10.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 |
| 2 | Avarone | 1.0 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 3 | 3’-(p-Chlorophenyl)avarone | 25.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 50.0 |
| 4 | 3’,4’-Ethylenedithioavarone | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
| 5 | 4’-Isopropylthioavarone | 5.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 |
| 6 | 4’-tert-Butylthioavarone | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
| 7 | 4’-Propylthioavarone | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 1.0 |
| 8 | 4’-Octylthioavarone | 10.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
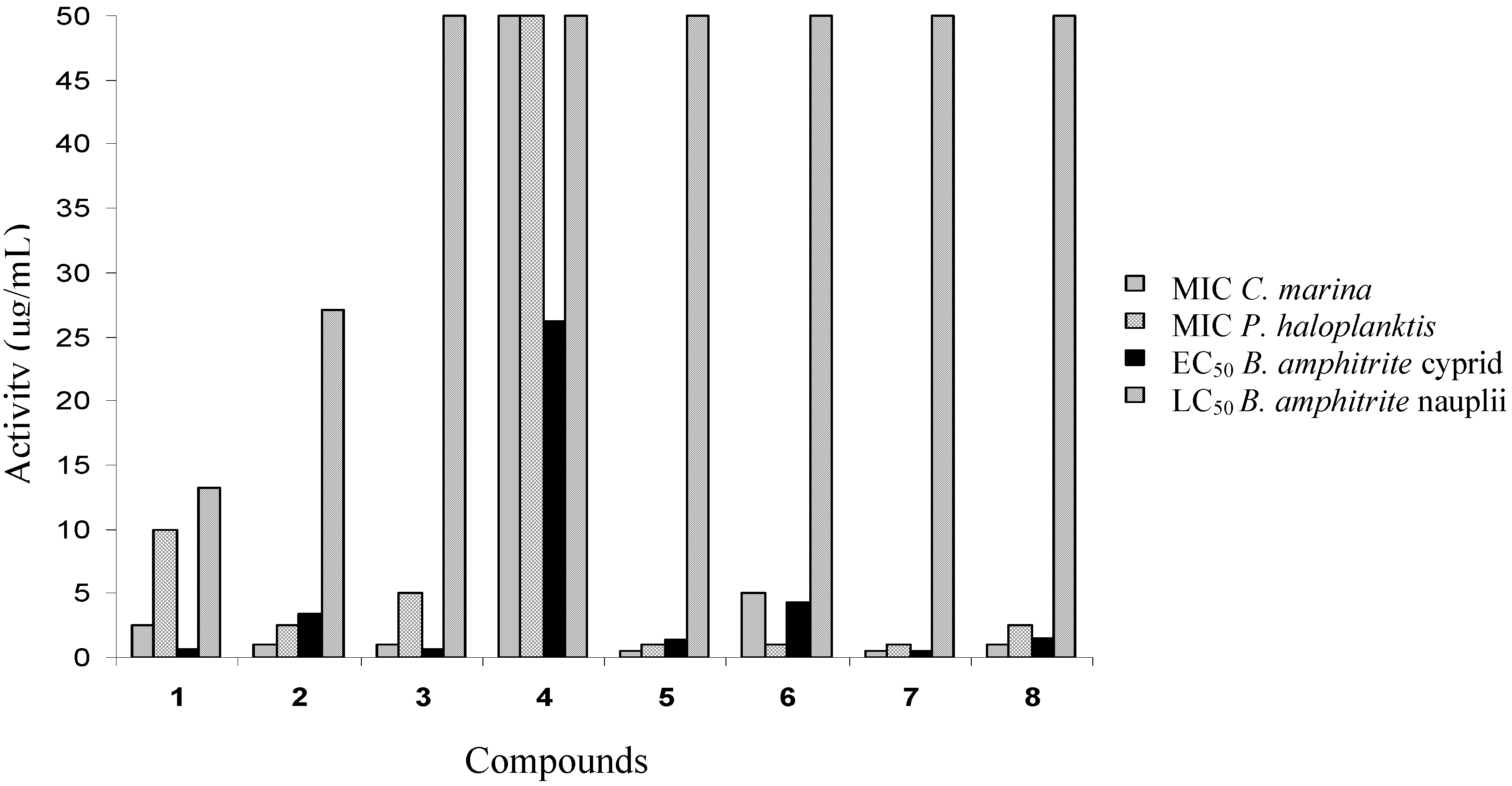
Cyprid settlement and mortality
Toxicity of compounds 1–8 to nauplii
| No | Compound | Balanus amphitrite | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC50 (μg/mL) | Cyprid LC50 (μg/mL) | Nauplii LC50 (μg/mL) | ||
| 1 | Avarol | 0.65 ± 0.03 | 13.28 ± 0.70 | 1.58 ± 0.05 |
| 2 | Avarone | 3.41 ± 0.12 | 27.12 ± 1.51 | 25.12 ± 0.93 |
| 3 | 3’-(p-Chlorophenyl)avarone | 0.65 ± 0.02 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
| 4 | 3’,4’-Ethylenedithioavarone | 26.22 ± 0.27 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
| 5 | 4’-Isopropylthioavarone | 1.33 ± 0.06 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
| 6 | 4’-tert-Butylthioavarone | 4.23 ± 0.12 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
| 7 | 4’-Propylthioavarone | 0.45 ± 0.02 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
| 8 | 4’-Octylthioavarone | 1.46 ± 0.05 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
Conclusions
Experimental
Isolation of avarol (1) and avarone (2)
Preparation of compounds 3-8
Antibacterial assays
Antifungal assays
Balanus amphitrite adult broodstock maintenance
Larval culture
Algal culture
Balanus amphitrite cyprid settlement assay
Toxicity tests on Balanus amphitrite nauplii
Acknowledgments
References
- Armstrong, E.; Boyd, K.; Burgess, J. Prevention of marine biofouling using natural compounds from marine organisms. Biotech. Ann. Rev. 2000, 6, 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- Rittschof, D. Natural product antifoulants: one perspective on the challenges related to coatings developments. Biofouling 2000, 15, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellas, J. Comparative toxicity of alternative antifouling biocides on embryos and larvae of marine invertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, R.A.; Fletcher, R.L. The toxicity of Irgarol 1051 and Sea-Nine 211 to the non-target macroalga Fucus serratus with the aid of an image capture and analysis system. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 322, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Alba, A.R.; Hernando, M.D.; Piedra, L.; Chisti, Y. Toxicity evaluation of single and mixed antifouling biocides measured with acute toxicity bioassays. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 456, 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, N.; Okamura, H. Effects of new antifouling compounds on the development of sea urchin. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, K.W.H.; Leung, K.M.H. Toxicity of antifouling biocides to the intertidal harpacticoid copepod Trigriopus japonicus (Crustacea, Copepoda): effects of temperature and salinity. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- i>Myers, J.H.; Gunthorpe, L.; Allinson, G.; Duda, S. Effects of antifouling biocides to the germination and growth of the marine macroalga, Hormosira banksii (Turner) Desicaine. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coehlo, M.R.; Bebianno, M.J.; Langston, W.J. Routes of TBT uptake in the clam Rudiatpes decussates. II. Food as a vector of TBT uptake. Mar. Environ. Res. 2002, 54, 193–207. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, S.; Batley, G.; Scammell, M. Tetracycline in antifouling paints. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1993, 26, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Landa, G.; Ansanelli, G.; Ciccoli, R.; Cremisini, C. Occurrence of antifouling paint booster biocides in selected harbors and marinas inside the Gulf of Napoli: a preliminary survey. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlström, M.; Martensson, L.; Jonsson, P.; Amebrant, T.; Elwing, H. Surface active adrenoreceptor compounds prevent the settlement of cyprid larvae of Balanus improvisus. Biofouling 2000, 16, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Clare, A.S. Towards non-toxic antifouling. J. Mar. Biotechnol. 1998, 6, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hellio, C.; Tsoukatou, M.; Maréchal, J.P.; Aldred, N.; Beaupoil, C.; Clare, A.S.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V. Inhibitory effects of Mediterranean sponge extracts and metabolites on larval settlement of the barnacle, Balanus amphitrite. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukatou, M.; Hellio, C.; Vagias, C.; Harvala, C.; Roussis, V. Chemical defense and antifouling activity of three Mediterranean sponges of the genus Ircinia. Z. Naturforsch. C 2002, 57, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.J.; Cooney, J.J. Effects of marine paints on microbial biofilm development on three materials. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 20, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Sladić, D.; Gašić, M.J. Reactivity and biological activity of the marine sesquiterpene hydroquinone avarol and related compounds from sponges of the order Dictyoceratida. Molecules 2006, 11, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2000: Marine compounds with antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiplatelet, antituberculosis and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Mar. Biotechnol. 2004, 6, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.G.H.; Northcote, T.P.; Princep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihopoulos, N.; Vagias, C.; Chinou, I.; Roussakis, C.; Scoullos, M.; Harvala, C.; Roussis, V. Antibacterial and cytotoxic natural and synthesized hydroquinones from the sponge Ircinia spinosula. Z. Naturforsch. C 1999, 54, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sera, Y.; Adachi, K.; Fujii, K.; Shizuri, Y. A new antifouling hexapeptide from a Palauan sponge, Haliclona sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- i>Hirota, H.; Okino, T.; Yoshimura, E.; Fusetani, N. Five new antifouling sesquiterpenes from two marine sponges of the genus Axinyssa and the nudibranch Phyllidia pustulosa. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 13791–13980. [Google Scholar]
- Okino, T.; Yoshimura, E.; Hirota, H.; Fusetani, N. Antifouling kalihinenes from the marine sponge Acanthella cavernosa. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 8637–8640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemsen, P. The screening of sponge extract for antifouling activity using a bioassay with laboratory reared cyprid larvae of the barnacle Balanus amphitrite. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 1994, 10, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Sodano, G. Avarol, a novel sesquiterpenoid hydroquinone with a rearranged drimane skeleton from the sponge Dysidea avara. Tetrahedron Lett. 1974, 38, 3401–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Zahn, R.K.; Gašić, M.J.; Dogović, N.; Maidhof, A.; Becker, C.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Eich, E. Avarol, a cytostatically active compound from the marine sponge Dysidea avara. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 1985, 80, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Maidhof, A.; Zahn, R.K.; Schröder, H.C.; Gašić, M.J.; Heidemann, D.; Bernd, A.; Kurelec, B.; Eich, E.; Seibert, G. Potent antileukemic activity of the novel cytostatic agent avarone and its analogues in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 4822–4826. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Sladić, D.; Zahn, R.K.; Bässler, K-H.; Dogović, N.; Gerner, H.; Gašić, M.J.; Schröder, H.C. Avarol-induced DNA strand breakage in vitro and in Friend erythroleukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 6565–6571. [Google Scholar]
- De Giulio, A.; De Rosa, S.; Strazzullo, G.; Diliberto, L.; Obino, P.; Marongiu, M.E.; Pani, A.; La Colla, P. Synthesis and evaluation of cytostatic and antiviral activities of 3' and 4'-avarone derivatives. Antivir. Chem. Chemoth. 1991, 2, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Sarin, P.S.; Sun, D.; Thornton, A.; Müller, W.E.G. Inhibition of replication of the etiological agent of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (human T-lymphotropic retrovirus/lymphadenopathy-associated virus) by avarol and avarone. J. Nat. Cancer Inst. 1987, 78, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loya, S.; Hizi, A. The inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase by avarol and avarone derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1990, 269, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrá, M.L.; Sanz, M.J.; Bustos, G.; Payá, M.; Alcaraz, M.J.; De Rosa, S. Avarol and avarone, two new anti-inflammatory agents of marine origin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 253, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Amigó, M.; Terencio, M.C.; Mitova, M.; Iodice, C.; Payá, M.; De Rosa, S. Potential antipsoriatic avarol derivatives as antioxidants and inhibitors of PGE2 generation and proliferation in the HaCaT cell line. J. Nat. Prod 2004, 67, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Seibert, G.; Raether, W.; Dogović, N.; Gašić, M.J.; Zahn, R.K.; Müller, W.E.G. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of avarone and avarol. ZBL Bakt. Hyg. A 1985, 260, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, B.; De Giulio, A.; De Rosa, S.; Strazzullo, G.; Gašić, M.J.; Sladić, D.; Zlatović, M. Biological activities of avarol derivatives, 1. amino derivatives. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriz, M.J.; Turon, X.; Galera, J.; Tur, J.M. New light on the cell location of avarol within the sponge Dysidea avara (Dendroceratida). Cell Tissue Res. 1996, 285, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadury, P.; Wright, P.C. Exploitation of marine algae: biogenic compounds for potential antifouling applications. Planta 2004, 219, 561–578. [Google Scholar]
- Costerton, J.W.; Lewandowski, Z.; Caldwell, D.; Korber, D.; Lappin-Scott, H.M. Microbial biofilms. Ann. Rev. Microbiol 1995, 49, 711–745. [Google Scholar]
- Abarzua, S.; Jakubowski, S. Biotechnological investigation for the prevention of biofouling. I. Biological and biochemical principles for the prevention of biofouling. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. II 1995, 123, 301–312. [Google Scholar]
- Clare, A.S. Marine natural product antifoulants: status and potential. Biofouling 1996, 9, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, P.D.; de Nys, R. Chemical mediation of colonization of seaweed surfaces. J. Phycol. 2002, 38, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, M.E. Marine chemical ecology: what is known and what is next. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 200, 103–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, A.S.; Chattopadhyay, P. Synthetic studies of trans-clerodane diterponoids and congeners: stereocontrolled total synthesis of (±)-avarol. J. Org. Chem. 1982, 47, 1727–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittschof, D.; Ali, C.-H.; Kok, L.-M.; Teo, S.L.-M. Pharmaceuticals as antifoulants: concept and principles. Biofouling 2003, 19, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Božić, T.; Sladić, D.; Zlatović, M.; Novaković, I.; Trifunović, S.; Gašić, M.J. Regioselectivity of conjugate additions to monoalkyl-1,4-benzoquinones. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2002, 67, 547–551. [Google Scholar]
- Maréchal, J-P.; Culioli, G.; Hellio, C.; Thomas-Guyon, H.; Callow, M.E.; Clare, A.S.; Ortalo-Magne, A. Seasonal variations in antifouling activity of crude extracts of the brown alga Bifurcaria bifurcata (Cystoseiraceae) against cyprids of Balanus amphitrite and the marine bacteria Cobetia marina and Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 313, 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- Amsterdam, D. Antibiotics in laboratory medicineLoman, V., Ed.; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, 1996, 4th ed.; pp. 52–111. [Google Scholar]
- i>Hellio, C.; Bremer, G.; Pons, A.M.; Le Gal, Y.; Bourgougnon, N. Inhibition of the development of microorganims (bacteria and fungi) by extracts of marine alga from Brittany, France. Appl. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellio, C.; Maréchal, J.P.; Véron, B.; Bremer, G.; Clare, A.S.; Le Gal, Y. Seasonal variation of antifouling activities of marine algae from the Brittany coast (France). Mar. Biotechnol. 2004, 6, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billinghurst, Z.; Clare, A.S.; Fileman, T.; McEvoy, J.; Readman, J.; Depledge, M.H. Inhibition of barnacle settlement by the environmental oestrogen 4-nonylphenol and the natural oestrogen 17β oestradiol. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1998, 36, 833–839. [Google Scholar]
- Hellio, C.; Simon-Colin, C.; Clare, A.S.; Deslandes, E. Isethionic acid and floridoside, isolated from the red alga, Grateloupia turuturu, inhibit settlement of Balanus amphitrite cyprid larvae. Biofouling 2004, 20, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maréchal, J-P.; Hellio, C.; Sebire, M.; Clare, A.S. Settlement behaviour of marine invertebrate larvae measured by Ethovision 3.0. Biofouling 2004, 20, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard, R.; Ryther, J. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms, I: Cyclotella nana (Hustedt) and Detonula confervacea (Cleve). Can. J. Microbiol. 1972, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.; Qian, P.Y. Inhibitory effect of phenolic compounds and marine bacteria on larval settlement of the barnacle Balanus amphitrite Darwin. Biofouling 2000, 16, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.S.S.; Lam, P.K.S.; Zhou, B.S. A settlement inhibition assay with cyprid larvae of the barnacle Balanus amphitrite. Chemosphere 1997, 35, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1-8 are available from the authors.
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Tsoukatou, M.; Maréchal, J.P.; Hellio, C.; Novaković, I.; Tufegdzic, S.; Sladić, D.; Gašić, M.J.; Clare, A.S.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V. Evaluation of the Activity of the Sponge Metabolites Avarol and Avarone and their Synthetic Derivatives Against Fouling Micro- and Macroorganisms. Molecules 2007, 12, 1022-1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/12051022
Tsoukatou M, Maréchal JP, Hellio C, Novaković I, Tufegdzic S, Sladić D, Gašić MJ, Clare AS, Vagias C, Roussis V. Evaluation of the Activity of the Sponge Metabolites Avarol and Avarone and their Synthetic Derivatives Against Fouling Micro- and Macroorganisms. Molecules. 2007; 12(5):1022-1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/12051022
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsoukatou, Maria, Jean Philippe Maréchal, Claire Hellio, Irena Novaković, Srdan Tufegdzic, Dusan Sladić, Miroslav J Gašić, Anthony S Clare, Constantinos Vagias, and Vassilios Roussis. 2007. "Evaluation of the Activity of the Sponge Metabolites Avarol and Avarone and their Synthetic Derivatives Against Fouling Micro- and Macroorganisms" Molecules 12, no. 5: 1022-1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/12051022
APA StyleTsoukatou, M., Maréchal, J. P., Hellio, C., Novaković, I., Tufegdzic, S., Sladić, D., Gašić, M. J., Clare, A. S., Vagias, C., & Roussis, V. (2007). Evaluation of the Activity of the Sponge Metabolites Avarol and Avarone and their Synthetic Derivatives Against Fouling Micro- and Macroorganisms. Molecules, 12(5), 1022-1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/12051022






