Epstein-Barr Virus Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis by Activating STIM1-Dependent Ca2+ Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. STIM1 Knockdown
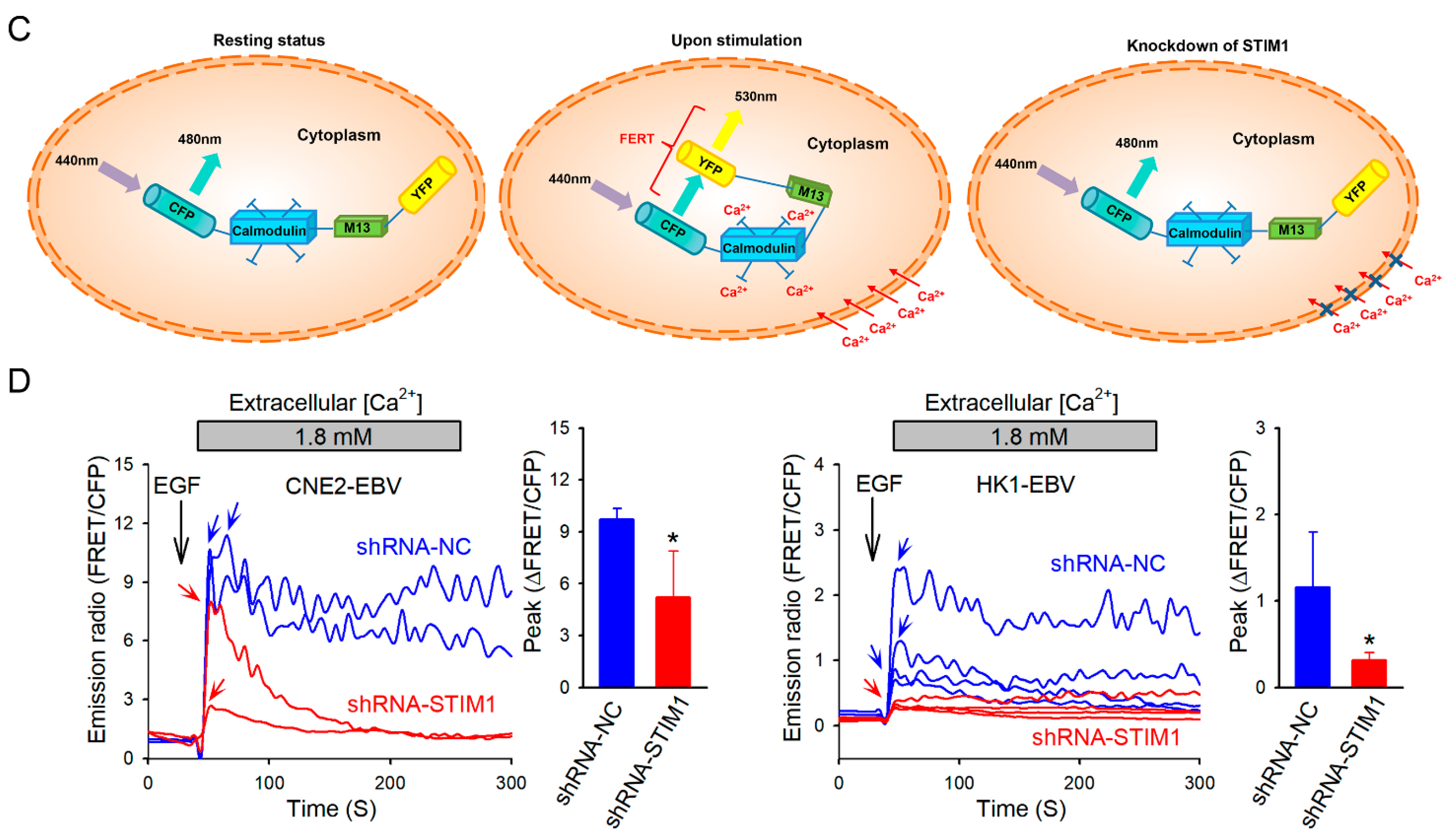
2.3. Cytosolic Ca2+ Measurement
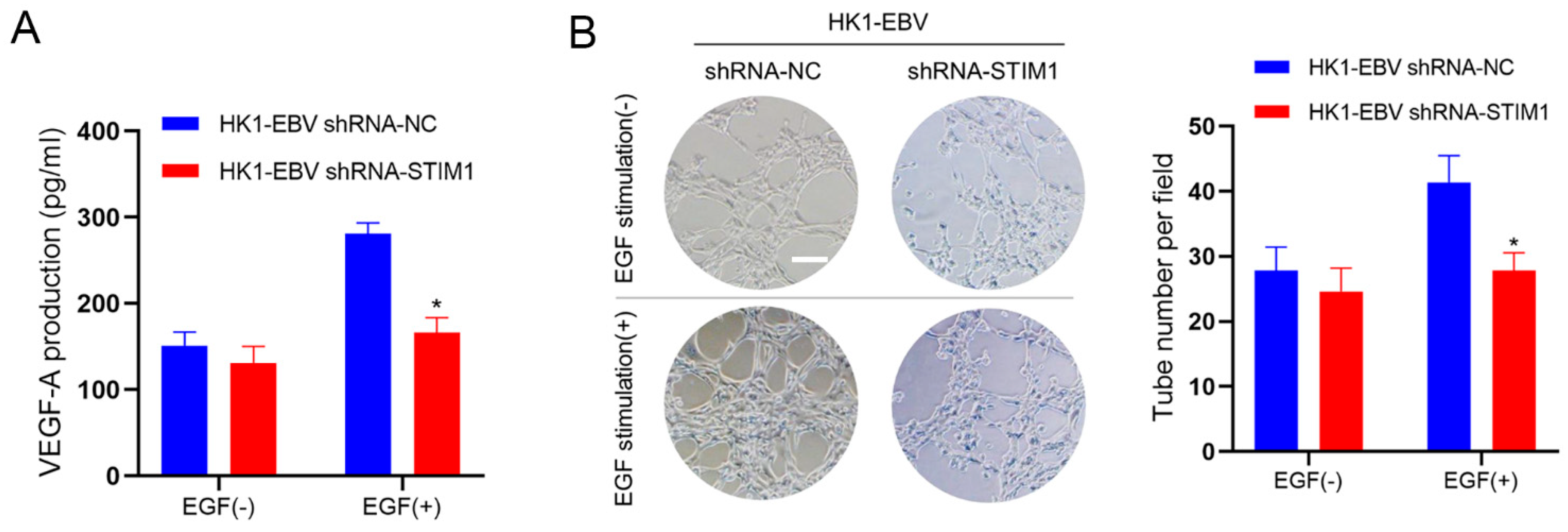
2.4. Assays of VEGF and Tubule Formation
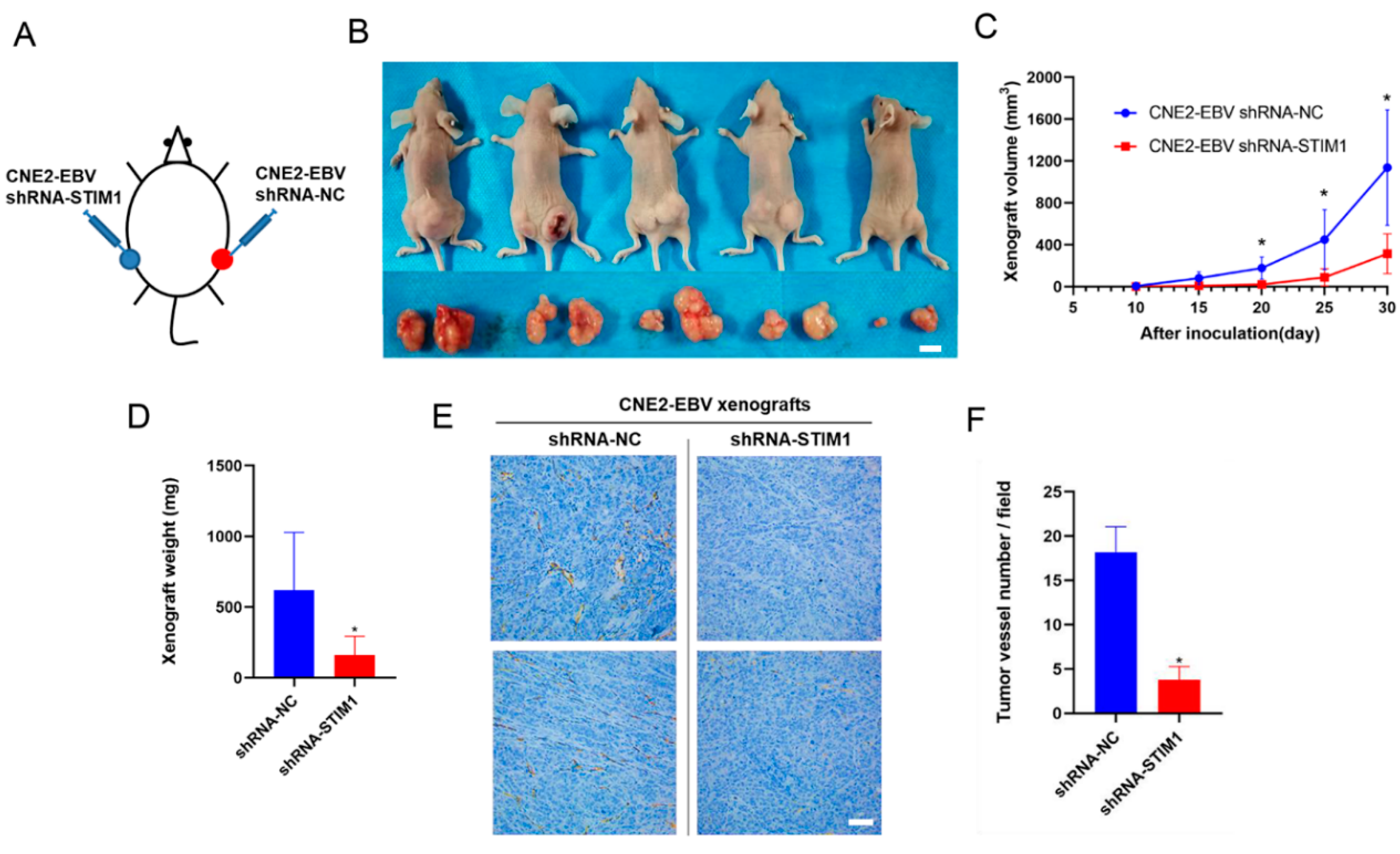
2.5. Xenograft Model in Mice
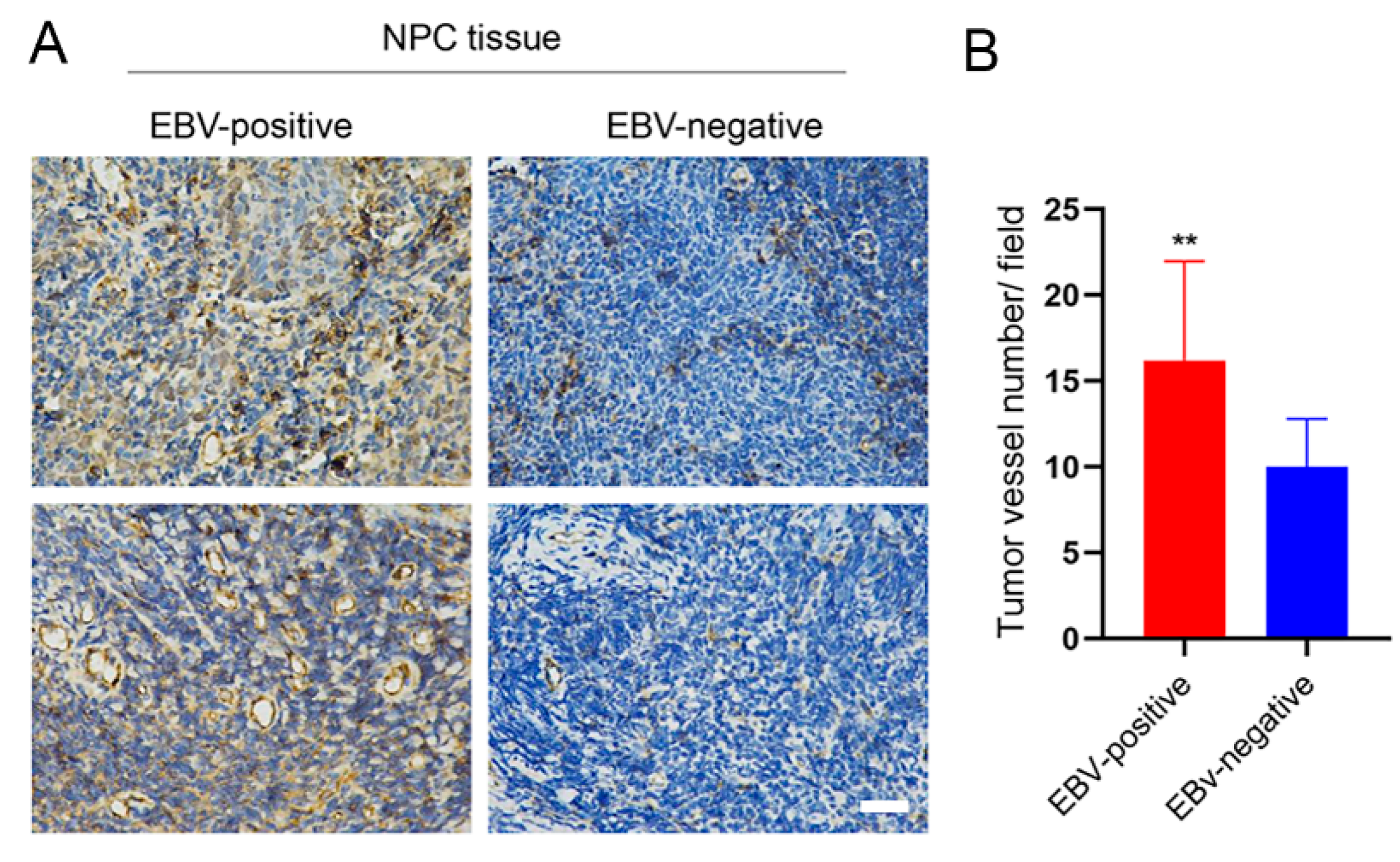
2.6. Clinical NPC Tissues
2.7. Measurement of Ca2+-Related Signaling Pathways in NPC Cells
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
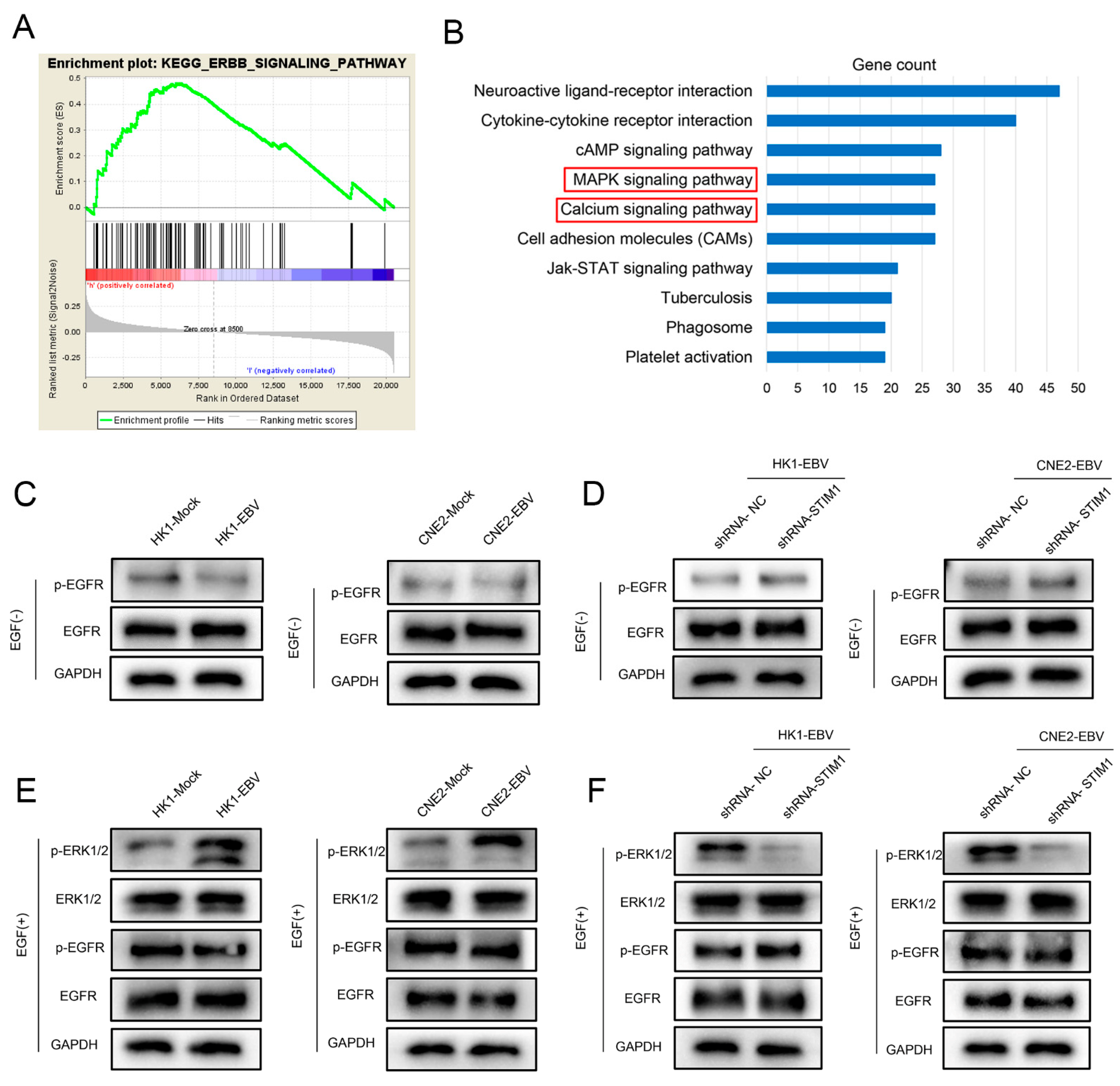
3.1. STIM1 Knockdown Reduces EGF-Induced, SOCE-Mediated Ca2+ Influx in EBV-Positive NPC Cells
3.2. STIM1 Knockdown Decreases EGF-Induced VEGF Production and Endothelial Tube Formation
3.3. STIM1 Knockdown Slows Xenograft Growth and Angiogenesis
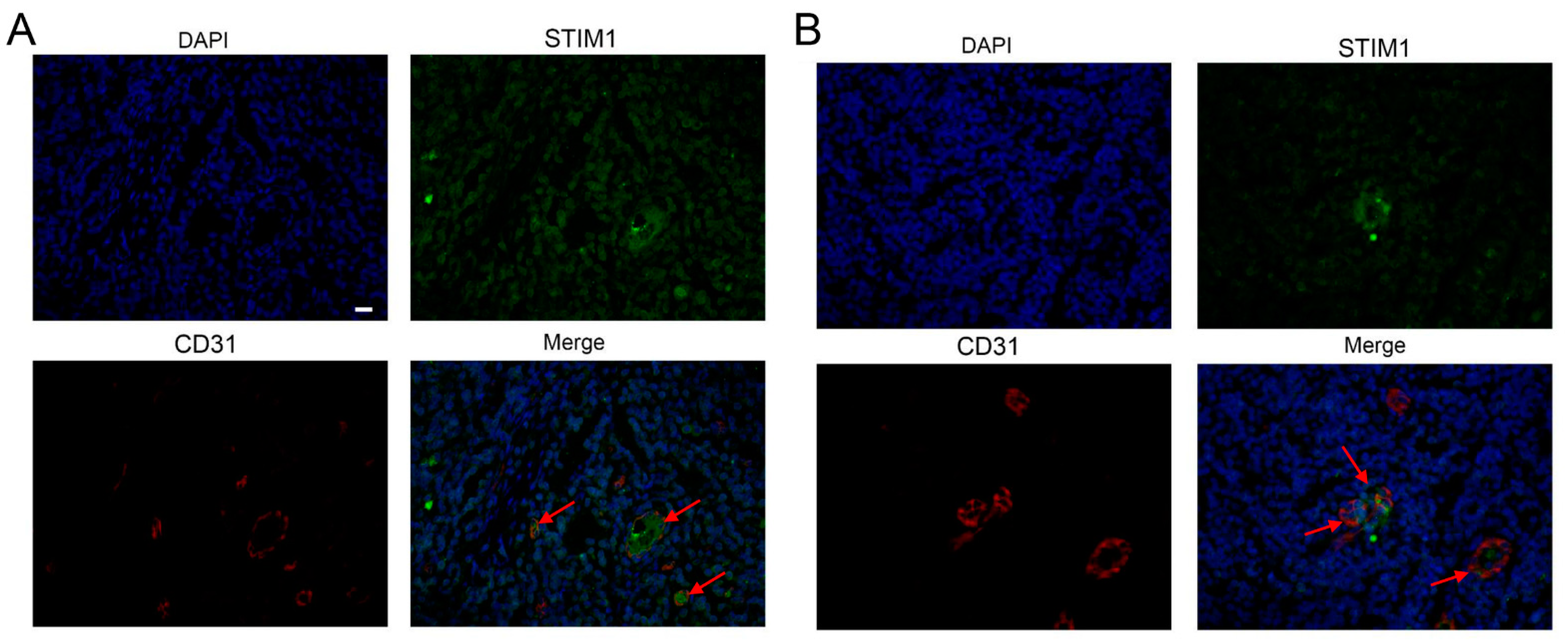
3.4. EBV Infection Promotes Angiogenesis by Upregulating STIM1
3.5. EGF Activates the EGFR/p-EGFR Pathway in NPC Cells
3.6. STIM1 Knockdown Partially Reverses EBV-Promoted Activation of the ERK1/2/p-ERK1/2 Pathway
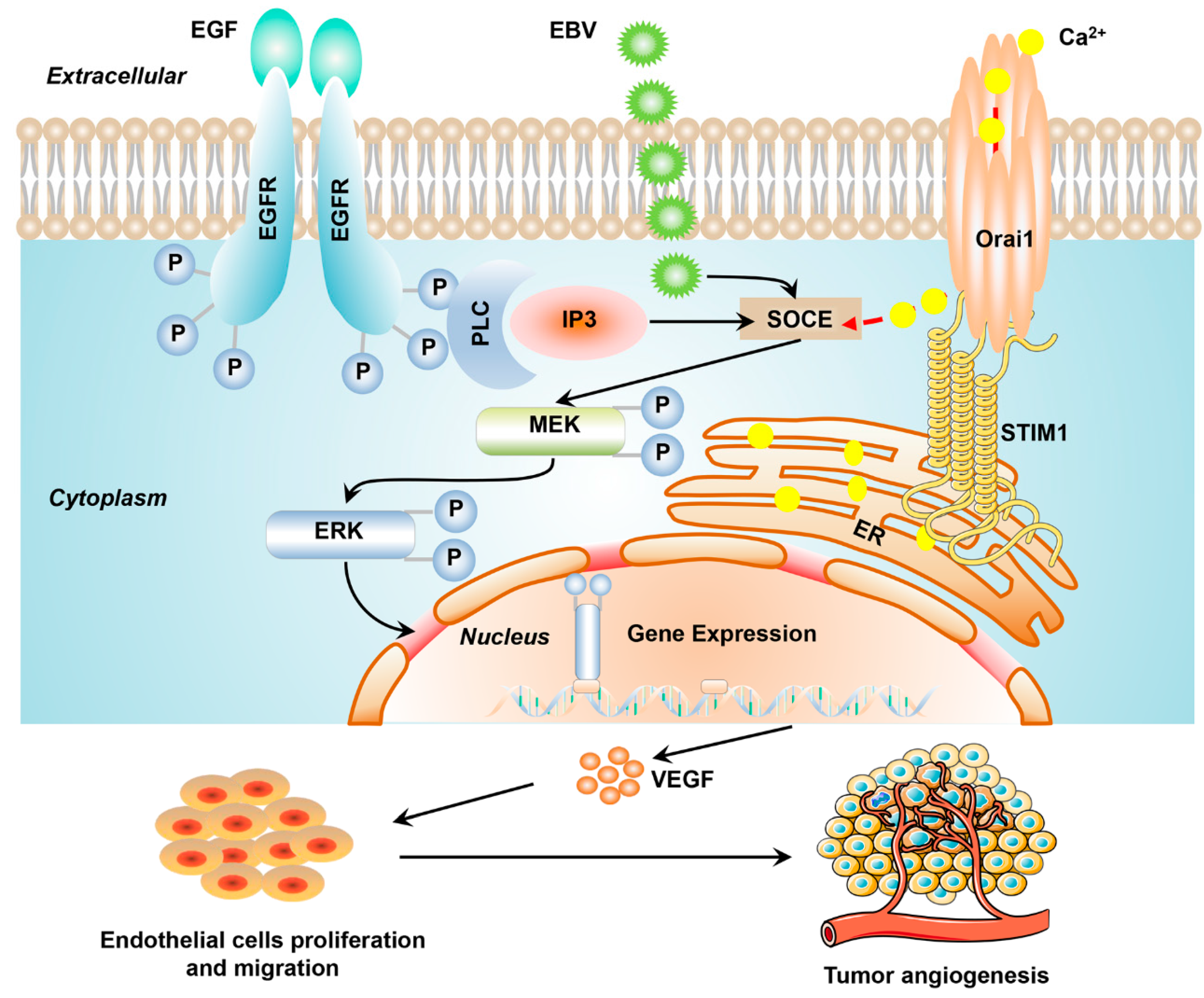
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.P.; Chan, A.T.C.; Le, Q.T.; Blanchard, P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2019, 394, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.L.K.; Wee, J.T.S.; Hui, E.P.; Chan, A.T.C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2016, 387, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demircioglu, F.; Hodivala-Dilke, K. alphavbeta3 Integrin and tumour blood vessels-learning from the past to shape the future. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 42, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valastyan, S.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumor metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 2011, 147, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, J.; Si, Y.; Kanada, M.; Zhang, Z.; Terakawa, S.; Watanabe, H. Blockage of LMP1-modulated store-operated Ca(2+) entry reduces metastatic potential in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell. Cancer Lett. 2015, 360, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, D.E. Calcium signaling. Cell 2007, 131, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.M.; Azimi, I.; Faville, R.A.; Peters, A.A.; Jalink, K.; Putney, J.W., Jr.; Goodhill, G.J.; Thompson, E.W.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J.; Monteith, G.R. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in breast cancer cells is calcium signal dependent. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevarskaya, N.; Skryma, R.; Shuba, Y. Calcium in tumour metastasis: New roles for known actors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Huang, J.; He, Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, J. Blockage of store-operated Ca(2+) entry antagonizes Epstein-Barr virus-promoted angiogenesis by inhibiting Ca(2+) signaling-regulated VEGF production in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; He, Q.; Lin, Y.; Liang, R.; Ye, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. SKF95365 induces apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest by disturbing oncogenic Ca(2+) signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 3123–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Yu, Y.; Roos, J.; Kozak, J.A.; Deerinck, T.J.; Ellisman, M.H.; Stauderman, K.A.; Cahalan, M.D. STIM1 is a Ca2+ sensor that activates CRAC channels and migrates from the Ca2+ store to the plasma membrane. Nature 2005, 437, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.F.; Chiu, W.T.; Chen, Y.T.; Lin, P.Y.; Huang, H.J.; Chou, C.Y.; Chang, H.C.; Tang, M.J.; Shen, M.R. Calcium store sensor stromal-interaction molecule 1-dependent signaling plays an important role in cervical cancer growth, migration, and angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15225–15230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, J.J.; Huang, X.Y. Orai1 and STIM1 are critical for breast tumor cell migration and metastasis. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, A.K.; Lo, K.W.; Tsao, S.W.; Wong, H.L.; Hui, J.W.; To, K.F.; Hayward, D.S.; Chui, Y.L.; Lau, Y.L.; Takada, K.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus infection alters cellular signal cascades in human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maruo, S.; Yang, L.; Takada, K. Roles of Epstein-Barr virus glycoproteins gp350 and gp25 in the infection of human epithelial cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.Y.; Choy, K.W.; Tsao, S.W.; Tao, Q.; Tang, T.; Chung, G.T.; Lo, K.W. Authentication of nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumor lines. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2169–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, M.J.; Baddoo, M.; Nanbo, A.; Xu, M.; Puetter, A.; Lin, Z. Comprehensive high-throughput RNA sequencing analysis reveals contamination of multiple nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines with HeLa cell genomes. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10696–10704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgui de Oliveira, D.; Marques, C.S.; Losi, V.C. “Cell identity” crisis: Another call for immediate action. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nagai, T.; Yamada, S.; Tominaga, T.; Ichikawa, M.; Miyawaki, A. Expanded dynamic range of fluorescent indicators for Ca(2+) by circularly permuted yellow fluorescent proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10554–10559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Ye, J.; Luo, Y.; Weng, J.; He, Q.; Liu, F.; Li, M.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. EB virus promotes metastatic potential by boosting STIM1-dependent Ca(2+) signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2020, 478, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, N.; Folkman, J.; Pozza, F.; Bevilacqua, P.; Allred, E.N.; Moore, D.H.; Meli, S.; Gasparini, G. Tumor angiogenesis: A new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1992, 84, 1875–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moccia, F.; Negri, S.; Shekha, M.; Faris, P.; Guerra, G. Endothelial Ca(2+) Signaling, Angiogenesis and Vasculogenesis: Just What It Takes to Make a Blood Vessel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, A.H.L.; Monteith, G.R. Calcium signaling and the therapeutic targeting of cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Res. 2018, 1865, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréchard, S.; Tschirhart, E.J. Regulation of superoxide production in neutrophils: Role of calcium influx. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.L.; Cheng, K.T.; Liu, X.; Bandyopadhyay, B.C.; Paria, B.C.; Soboloff, J.; Pani, B.; Gwack, Y.; Srikanth, S.; Singh, B.B.; et al. Dynamic assembly of TRPC1-STIM1-Orai1 ternary complex is involved in store-operated calcium influx. Evidence for similarities in store-operated and calcium release-activated calcium channel components. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9105–9116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P. VEGF as a key mediator of angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology 2005, 69 (Suppl. S3), 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.P.; Raab-Traub, N. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor through effects on Bcl-3 and STAT3. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5486–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, N.J.; Raab-Traub, N. Induction of epidermal growth factor receptor expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 C-terminal-activating region 1 is mediated by NF-kappaB p50 homodimer/Bcl-3 complexes. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12954–12961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, F.; Li, L.; Yang, L.; Hu, D.; Ma, X.; Lu, Z.; Sun, L.; Cao, Y. STAT3 activation induced by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein1 causes vascular endothelial growth factor expression and cellular invasiveness via JAK3 And ERK signaling. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2996–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wei, W.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wu, W.X. Inducing effects of hepatocyte growth factor on the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human colorectal carcinoma cells through MEK and PI3K signaling pathways. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2007, 120, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, C.X.; Shi, Z.; Meng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.Z.; Jiang, B.H. P70S6K 1 regulation of angiogenesis through VEGF and HIF-1alpha expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Wei, J.; Luo, Y.; Deng, Y.; Que, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Luo, X. Epstein-Barr Virus Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis by Activating STIM1-Dependent Ca2+ Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101275
Ye J, Wei J, Luo Y, Deng Y, Que T, Zhang X, Liu F, Zhang J, Luo X. Epstein-Barr Virus Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis by Activating STIM1-Dependent Ca2+ Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101275
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Jiaxiang, Jiazhang Wei, Yue Luo, Yayan Deng, Ting Que, Xiaojian Zhang, Fei Liu, Jinyan Zhang, and Xiaoling Luo. 2021. "Epstein-Barr Virus Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis by Activating STIM1-Dependent Ca2+ Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101275
APA StyleYe, J., Wei, J., Luo, Y., Deng, Y., Que, T., Zhang, X., Liu, F., Zhang, J., & Luo, X. (2021). Epstein-Barr Virus Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis by Activating STIM1-Dependent Ca2+ Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Pathogens, 10(10), 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101275





