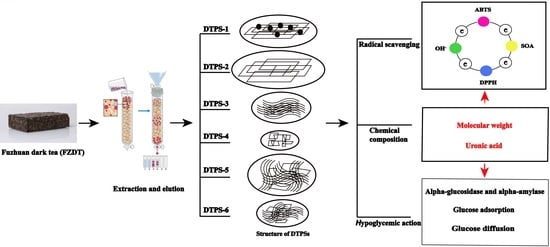
Valorization of Polysaccharides Obtained from Dark Tea: Preparation, Physicochemical, Antioxidant, and Hypoglycemic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Single-Factor and Response Surface Methodologies
2.3. Isolation of Polysaccharides
2.4. Preliminary Chemical Analysis
2.5. Physicochemical Composition and Structural Characterization
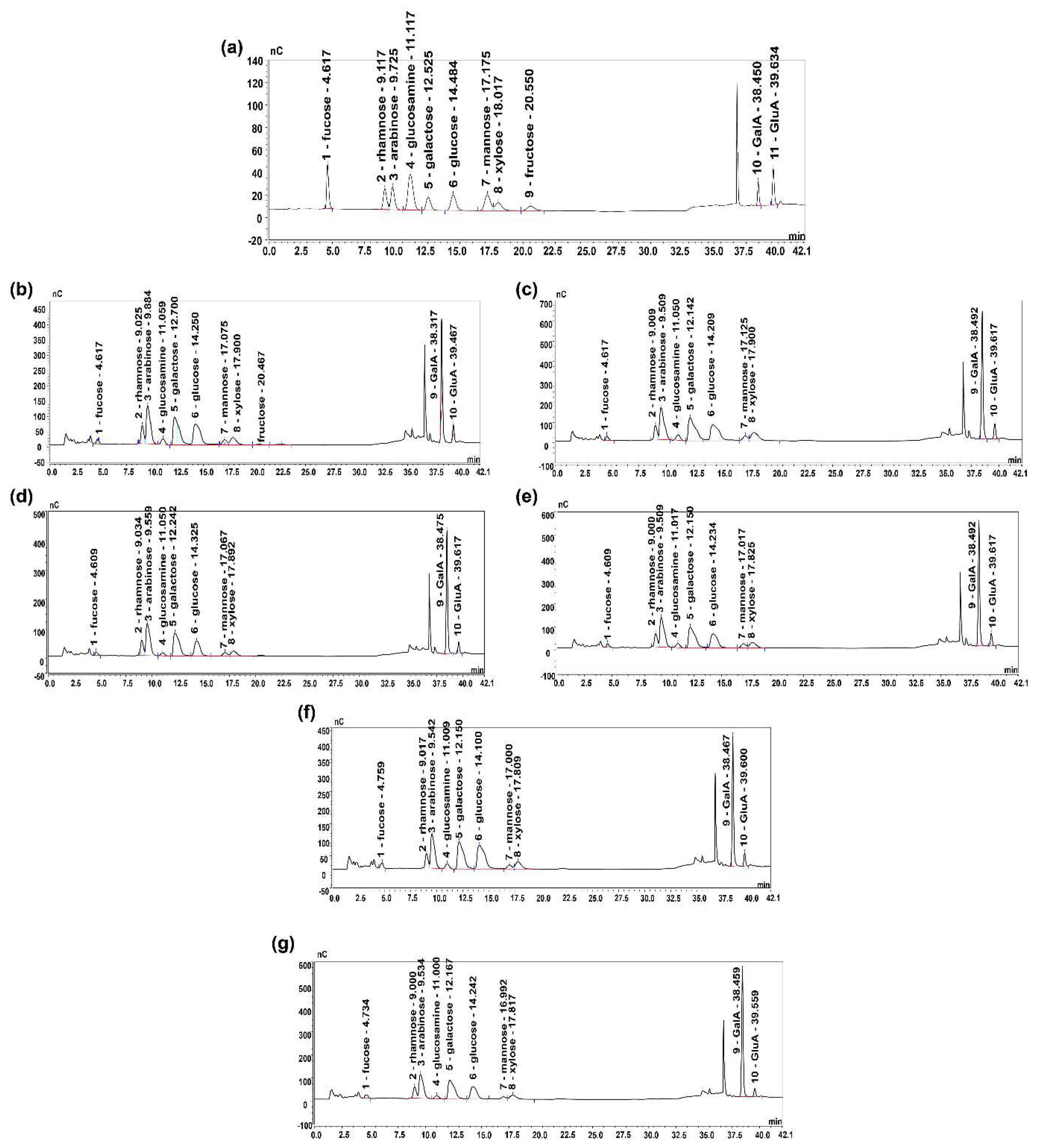
2.5.1. Monosaccharide Composition and Molecular Weight Analysis
2.5.2. Ultraviolet–Visible (UV–Vis) and Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
2.5.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.5.4. Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) Analysis
2.5.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.5.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.5.7. Solubility and pH of DTPSs
2.6. In Vitro Antioxidant Activities
2.6.1. ABTS Radical Scavenging Assay
2.6.2. Superoxide Anion (SOA) Radical Scavenging Assay
2.6.3. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.6.4. Hydroxyl Radical (OH¯) Scavenging Assay
2.7. In Vitro Hypoglycemic Activities
2.7.1. α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibiting Assays
α-Glucosidase Inhibiting Assay
α-Amylase Inhibiting Assay
2.7.2. Glucose Adsorption Capacity (GAC) and Glucose Diffusion and Dialysis Retardation Index (GDRI) Assays
GAC Assay
GDRI Assay
2.7.3. MTT and Glucose Consumption (GC) Assays
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Fitting
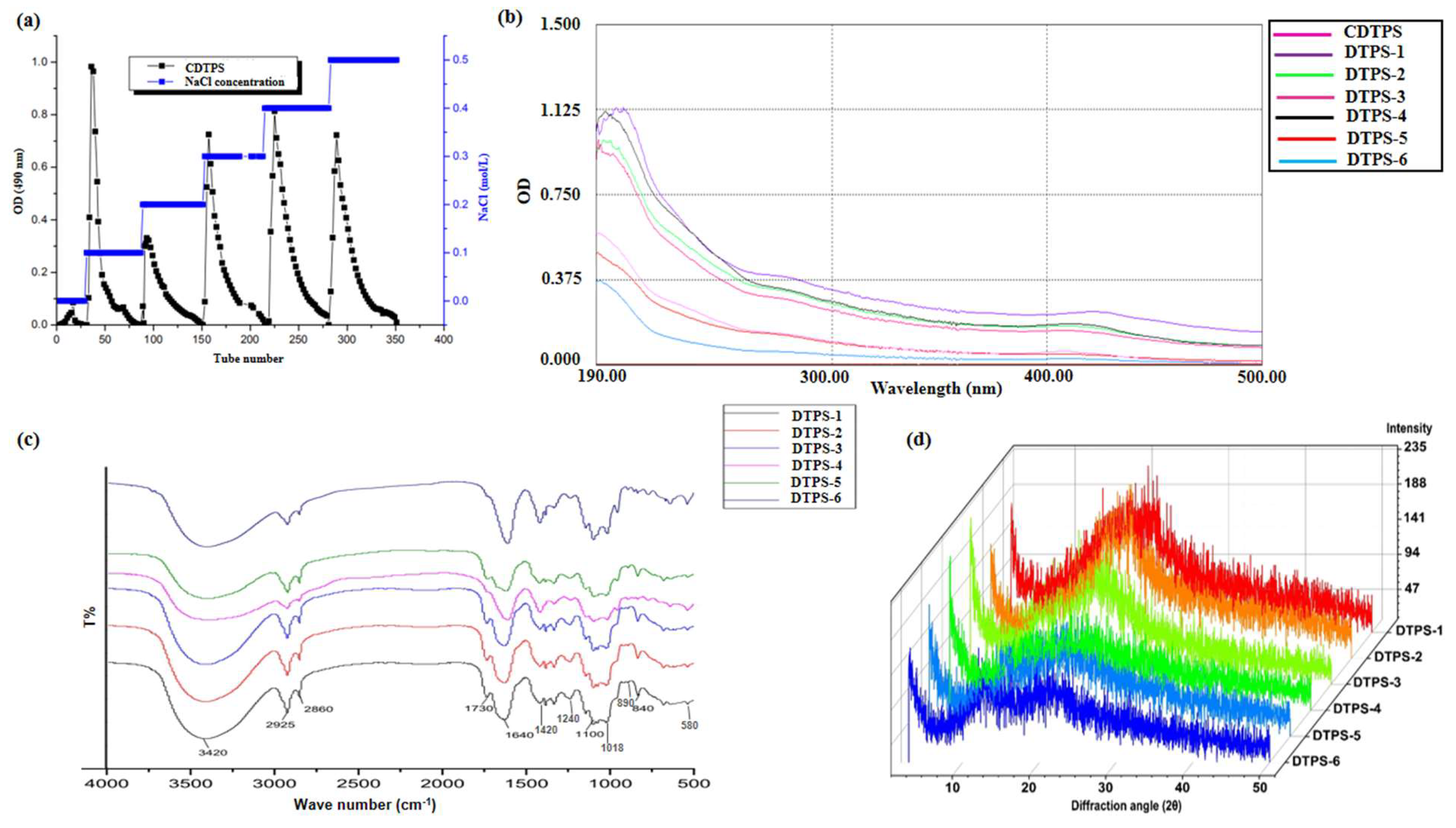
3.2. Separation of CDTPS
3.3. Preliminary Chemical Analysis
3.4. Physicochemical Compositions
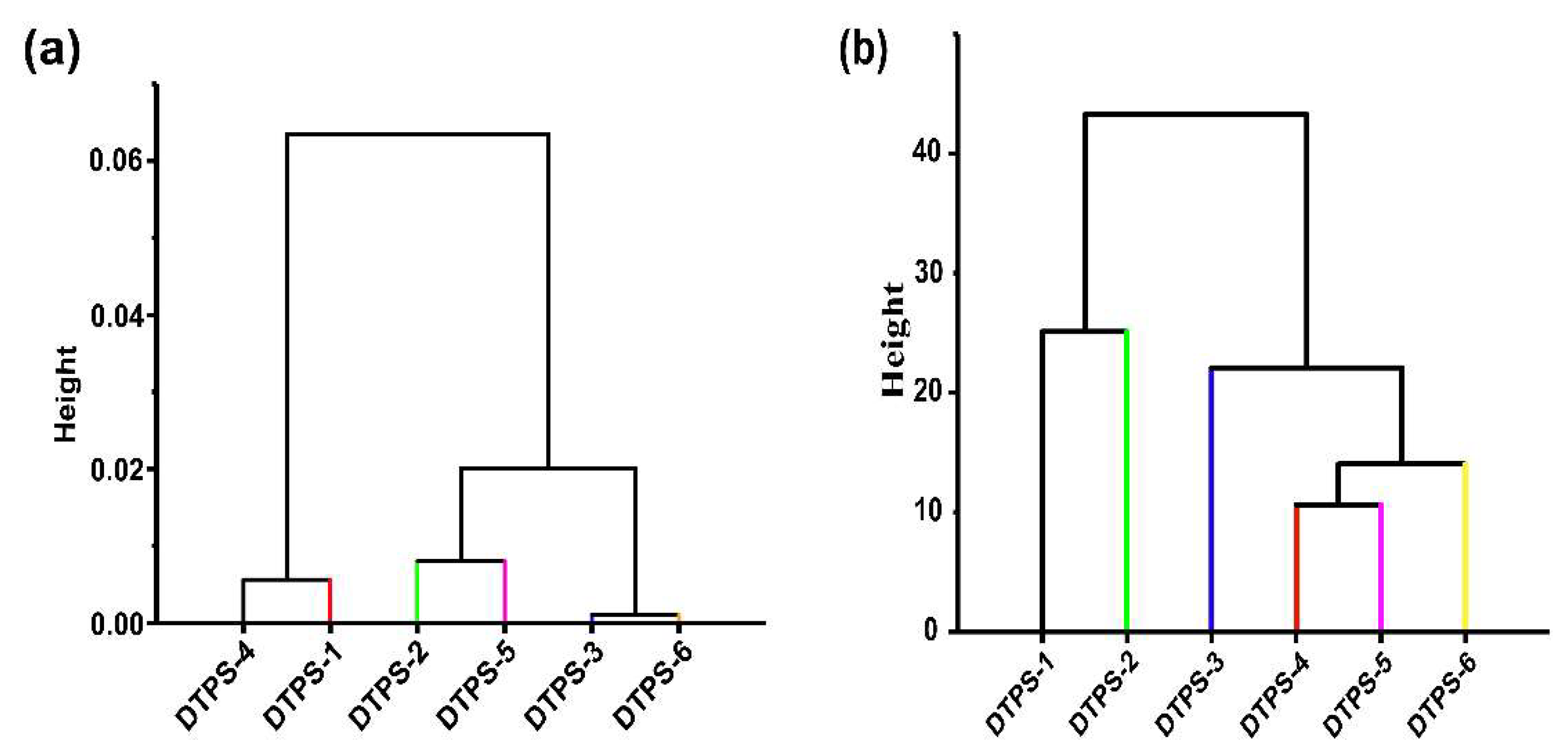
3.5. Structural Characteristics
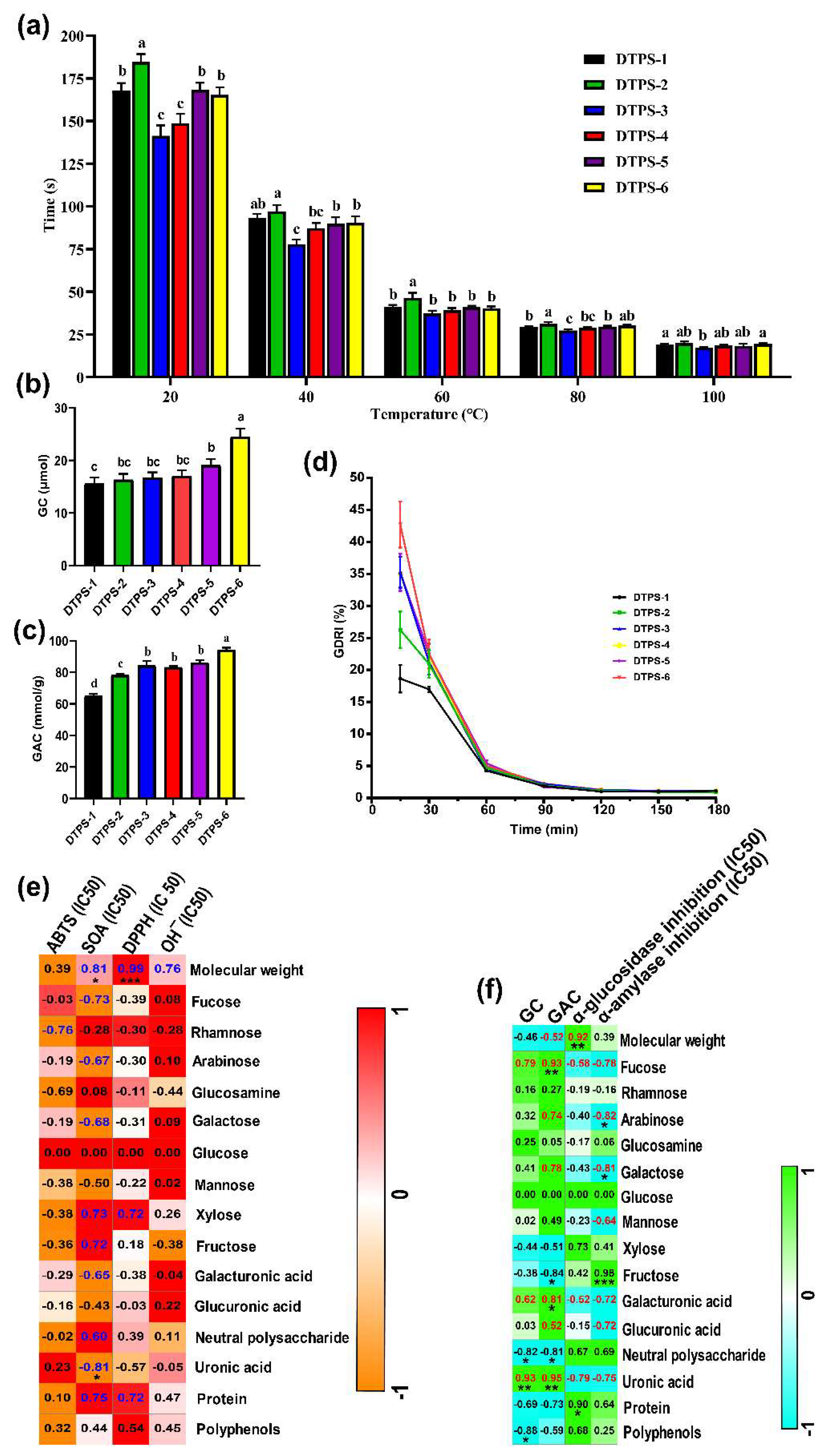
3.6. In Vitro Antioxidant Activities
3.7. In Vitro Hypoglycemic Activities of DTPSs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, G.-Y.; Meng, X.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Liu, Q.; Feng, Y.-B.; Li, S.; Wei, X.-L.; Atanasov, A.G.; Corke, H.; et al. Health Functions and Related Molecular Mechanisms of Tea Components: An Update Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, F.-J.; Wei, X.-L.; Liu, H.-Y.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Wu, D.-T.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Gandhi, G.R.; Li, H.-B.; Gan, R.-Y. State-of-the-art review of dark tea: From chemistry to health benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xie, M.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Dai, Z.; Ye, H.; Hu, B.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z. Fuzhuan Brick Tea Polysaccharides Attenuate Metabolic Syndrome in High-Fat Diet Induced Mice in Association with Modulation in the Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Jin, S.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Su, C.; Shi, Q.; Chen, C.; Yu, Q.; Song, C. The hypoglycemic effect of extract/fractions from Fuzhuan Brick-Tea in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice and their active components characterized by LC-QTOF-MS/MS. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.M.; Battson, M.L.; Jarrell, D.K.; Cox-York, K.; Foster, M.T.; Weir, T.L.; Gentile, C.L. Fuzhuan tea reverses arterial stiffening after modest weight gain in mice. Nutrition 2017, 33, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, S.; Bao, B.; Li, X.; Wang, S. Structure characterization of an arabinogalactan from green tea and its anti-diabetic effect. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 124, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y. Protective Effects of Tea Polysaccharides and Polyphenols on Skin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7757–7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Gao, Z.-Y.; Li, T.-Q.; Song, W.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, G.-H.; Zou, H.-Y. Anti-tumor activity and the mechanism of a green tea (Camellia sinensis) polysaccharide on prostate cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Li, Z.; Peng, F.; Xiao, F.; Ren, D.; Xue, H.; Chen, T.; Mushtaq, G.; Kamal, M.A. Combination of selenium-enriched green tea polysaccharides and Huo-ji polysaccharides synergistically enhances antioxidant and immune activity in mice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 3211–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Yuan, Q.; Saeeduddin, M.; Ou, S.; Zeng, X.; Ye, H. Recent advances in tea polysaccharides: Extraction, purification, physicochemical characterization and bioactivities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Jia, L.-Y.; Tu, Y.-Y. Structural analysis of an acidic polysaccharide isolated from white tea. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Fu, S.; Wu, R.; Wei, S.; Yi, J.; Zhang, L.-M.; Yang, L. Chain conformation of an acidic polysaccharide from green tea and related mechanism of α-amylase inhibitory activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.-L.; Fu, Q.-Y.; Xiang, L.-P.; Zheng, X.-Q.; Lu, J.-L.; Ye, J.-H.; Li, Q.-S.; Polito, C.A.; Liang, Y.-R. Tea Polysaccharides and Their Bioactivities. Molecules 2016, 21, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Sun, J.; Dong, W.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Z. Effects of polysaccharides and polyphenolics fractions of Zijuan tea (Camellia sinensis var. kitamura) on α-glucosidase activity and blood glucose level and glucose tolerance of hyperglycaemic mice. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-T.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y.; Shyur, L.-F.; Lin, J.-K. Pu-erh tea polysaccharides decrease blood sugar by inhibition of α-glucosidase activity in vitro and in mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Iglesia, R.; Loria-Kohen, V.; Zulet, M.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Reglero, G.; De Molina, A.R. Dietary Strategies Implicated in the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Wang, M.; Xie, M.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Hu, B.; Ye, H.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z. Evaluation of chemical property, cytotoxicity and antioxidant activity in vitro and in vivo of polysaccharides from Fuzhuan brick teas. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.H.; Huang, M.J.; Qin, C.Q.; Lv, B.Y.; Mao, Q.L.; Liu, Z.H. Structural characterization and evaluation of the an-tioxidant activities of polysaccharides extracted from Qingzhuan brick tea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yu, C.; Han, Z.; Shao, S.; Hu, X.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y. Effects of extraction methods on physicochemical properties and hypoglycemic activities of polysaccharides from coarse green tea. Glycoconj. J. 2020, 37, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenkrantz, N.; Asboe-Hansen, G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 54, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Yue, P.; Tang, D.; Wei, X. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of a new polysaccharide from Bletilla striata fibrous roots. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yu, C.; Han, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y. Comparative analysis of existence form for selenium and structural characteristics in artificial selenium-enriched and synthetic selenized green tea polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.C.; Huang, X.D. Determination the removing rate of superoxide anion radical by traditional Chinese medicine. Guangzhou Chem. 2012, 37, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.; Tang, H.L.; Luo, Z.Y.; Luo, H.Y.; Li, M. Primary structure analysis and antioxidant activity in vitro of crude poly-saccharide from Chuanminshen violaceum. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 21, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Liu, S.; Sun, N.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q. Modification of tea residue dietary fiber by high-temperature cooking assisted enzymatic method: Structural, physicochemical and functional properties. LWT 2021, 145, 111314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Qiu, S.; Gao, Z.; Liu, R.; Yu, Y.; et al. Selenylation modification can enhance immune-enhancing activity of Chinese angelica polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.K.; Ke, Y.Y.; Feng, A.Z.; Yuan, P.P.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Feng, W.S. The mechanism by which amen-toflavone improves insulin resistance in HepG2 cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Xie, J.; Liu, S.; Shen, M.; Tang, W.; Xie, M. Polysaccharide from Mesona chinensis: Extraction optimization, physicochemical characterizations and antioxidant activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B. Structural characterization of a novel neutral polysaccharide from Lentinus giganteus and its antitumor activity through inducing apoptosis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; He, N.; Ling, X.; Ye, M.; Zhang, C.; Shao, W.; Yao, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q. The isolation and characterization of poly-saccharides from longan pulp. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, F.H.; Wang, M.C.; Ma, L.P.; Ye, H.; Zeng, X.X. A comparative study of the neutral and acidic poly-saccharides from Allium macrostemon Bunge. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffall, K.H.; Mohnen, D. The structure, function, and biosynthesis of plant cell wall pectic polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 1879–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.X.; Zhang, M.; Qu, Z.S.; Xie, B.J. Compositional analysis and preliminary toxicological evaluation of a tea poly-saccharide conjugate. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2007, 55, 2256–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colodel, C.; Vriesmann, L.C.; Petkowicz, C.L.D.O. Cell wall polysaccharides from Ponkan mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco cv. Ponkan) peel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, D.; Xing, X.; Cheng, T.-J.R.; Liang, P.-H.; Bulone, V.; Park, J.H.; Hsieh, Y.S. Structural analysis and biological activity of cell wall polysaccharides extracted from Panax ginseng marc. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L. Effect of extraction method on structure and antioxidant activity of Hohenbuehelia serotina polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 83, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, J.; Shen, M.; Nie, S.; Xie, M. Sulfated modification of polysaccharides: Synthesis, characterization and bioactivities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 74, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.T.; Gu, D.H.; Wang, X.F.; Shen, X.J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, W.J.; Pu, Y.H.; Ge, C.R.; Fan, J.P. Purification, character-ization and immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides from Leccinum crocipodium (Letellier.) Watliag. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiercigroch, E.; Szafraniec, E.; Czamara, K.; Pacia, M.Z.; Majzner, K.; Kochan, K.; Kaczor, A.; Baranska, M.; Malek, K. Raman and infrared spectroscopy of carbohydrates: A review. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 185, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.-Q.; Nie, S.-P.; Wang, Y.-X.; Cui, S.W.; Xie, M.-Y. Sulfated modification, characterization and property of a water-insoluble polysaccharide from Ganoderma atrum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, H. In vitro antioxidative and immunological activities of polysaccharides from Zizyphus Jujuba cv. Muzao. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y. Comparison and structural characterization of polysaccharides from natural and artificial Se-enriched green tea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Peng, P.; Chen, L.; Xiao, B. Hydrothermal extraction, structural characterization, and inhibition HeLa cells proliferation of functional polysaccharides from Chinese tea Zhongcha 108. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.; Souza, B.W.; Simões, J.; Teixeira, J.; Domingues, M.R.; Coimbra, M.A.; Vicente, A.A. Structural and thermal characterization of galactomannans from non-conventional sources. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: Curiosity, cause, or consequence? Lancet 1994, 344, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knag, C.C.; Hao, L.M.; Zhhang, L.M.; Zheng, Z.Q.; Yongwu, Y.W. Isolation, purification and antioxidant activity of pol-ysaccharides from the leaves of maca (Lepidium Meyenii). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2611–2619. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.M.; Cheng, C.L.; Zhao, H.T.; Jing, J.; Gong, N.; Lu, W.H. In vivo anti-radiation activities of the Ulva pertusa poly-saccharides and polysaccharide-iron (III) complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 60, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-Q.; Ding, S.; Fan, L. Antioxidant activities of five polysaccharides from Inonotus obliquus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, Y.S.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, S.M.; Park, J.K.; Lee, S.M.; Synytsya, A.; Park, Y.I. Purification, characterization and immunostimulating activity of water-soluble polysaccharide isolated from Capsosiphon fulvescens. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Min, T.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Lai, F.; Tang, Y.; Yang, X. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of acidic polysaccharides from wampee seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wei, X. Antioxidant activities potential of tea polysaccharide fractions obtained by ultra filtration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camer, D.; Yu, Y.; Szabo, A.; Huang, X.-F. The molecular mechanisms underpinning the therapeutic properties of oleanolic acid, its isomer and derivatives for type 2 diabetes and associated complications. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, T.A.; Singer, D.S.; Thompson, J.W. Purification and analysis of protamine. Process. Biochem. 2006, 41, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Miao, J.; Jing, S.; Li, X.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. The effect of different extraction techniques on property and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Dioscorea hemsleyi. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Qu, Z.; Fu, L.; Dong, P.; Zhang, X. Physicochemical characterization and antioxidant activity of a polysaccharide isolated from oolong tea. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Chen, H. Ultrafiltration isolation, physicochemical characterization, and antidiabetic activities analysis of polysaccharides from green tea, oolong tea, and black tea. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 4025–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Xue, P.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ren, G. Antioxidant and immunoregulatory activity of polysaccharides from adzuki beans (Vigna angularis). Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Liu, J. Purification, characterization and biological activity of a novel polysaccharide from Inonotus obliquus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.; Freitas, A.C.; Sousa, S.; Amorim, M.; Vasconcelos, M.W.; da Costa, J.P.; Silva, A.M.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.; Duarte, A.C.; Gomes, A.M. Chemical and structural characterization of Pholiota nameko extracts with biological properties. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Q.; Fu, X.; Li, C. Structural characterization of a novel acidic polysaccharide from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit and its α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3974–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H. Review: An overview about the structure-function relationship of marine sulfated homopolysaccharides with regular chemical structures. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Total Sugar (%) | Uronic Acid (%) | Protein (%) | Polyphenols (%) | pH | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDTPS | 71.20 ± 0.19 f | 41.41 ± 0.10 c | 0.13 ± 0.02 a | 2.69 ± 0.02 a | 4.64 ± 0.01 bc | 6.07 |
| DTPS-1 | 80.17 ± 0.14 e | 33.06 ± 0.12 g | 0.12 ± 0.02 a | 1.64 ± 0.01 c | 4.77 ± 0.01 a | 1.07 |
| DTPS-2 | 80.53 ± 0.21 e | 36.88 ± 0.17 f | 0.11 ± 0.03 a | 1.94 ± 0.04 b | 4.65 ± 0.01 b | 3.25 |
| DTPS-3 | 85.26 ± 0.17 c | 39.70 ± 0.12 e | 0.11 ± 0.02 a | 1.83 ± 0.05 bc | 4.62 ± 0.01 cd | 2.44 |
| DTPS-4 | 82.33 ± 0.29 d | 40.36 ± 0.22 d | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 1.33 ± 0.03 d | 4.60 ± 0.01 de | 6.27 |
| DTPS-5 | 88.03 ± 0.28 b | 44.12 ± 0.21 b | 0.08 ± 0.02 ab | 1.73 ± 0.04 c | 4.59 ± 0.01 ef | 5.03 |
| DTPS-6 | 88.89 ± 0.17 a | 49.53 ± 0.13 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 0.32 ± 0.02 e | 4.57 ± 0.01f | 5.12 |
| Samples | DTPS-1 | DTPS-2 | DTPS-3 | DTPS-4 | DTPS-5 | DTPS-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fucose | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.18 |
| Rhamnose | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 0.36 | 0.69 |
| Arabinose | 0.29 | 1.16 | 1.65 | 1.48 | 0.84 | 1.44 |
| Glucosamine | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.09 |
| Galactose | 0.74 | 1.90 | 2.57 | 2.29 | 1.47 | 2.47 |
| Glucose | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Mannose | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.15 |
| Xylose | 0.82 | 0.95 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.51 | 0.70 |
| Fructose | 0.10 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Galacturonic acid | 1.13 | 2.92 | 4.06 | 3.84 | 2.05 | 5.07 |
| Glucuronic acid | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.15 | 0.21 |
| Sample | Mw | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| DTPS-1 | 24,860,000 | 8 |
| 989,300 | 92 | |
| DTPS-2 | 31,400,000 | 10.5 |
| 1,622,000 | 89.5 | |
| DTPS-3 | 28,200,000 | 17.9 |
| 685,200 | 82.1 | |
| DTPS-4 | 15,670,000 | 8.5 |
| 318,900 | 91.5 | |
| DTPS-5 | 26,450,000 | 12.4 |
| 688,300 | 87.6 | |
| DTPS-6 | 17,490,000 | 10.3 |
| 464,400 | 89.7 |
| Sample | α-Glucosidase | α-Amylase | ABTS | SOA | DPPH | OH¯ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μg/mL) | ||||||
| DTPS-1 | 91.42 ± 0.54 b | 21.45 ± 0.08 a | 570.01 ± 12.18 e | 438.54 ± 9.75 a | 112.13 ± 4.33 b | 52.19 ± 2.92 cd |
| DTPS-2 | 102.23 ± 0.87 a | 4.45 ± 0.56 b | 1063.38 ± 15.67 b | 421.90 ± 6.78 a | 163.90 ± 13.42 a | 92.85 ± 3.52 a |
| DTPS-3 | 79.69 ± 2.91 c | 1.62 ± 0.24 c | 665.61 ± 11.34 d | 351.46 ± 6.44 a | 93.89 ± 2.07 c | 71.59 ± 5.30 b |
| DTPS-4 | 57.50 ± 2.76 e | 0.06 ± 0.01 d | 506.04 ± 13.28 f | 342.09 ± 3.57 a | 64.37 ± 0.08 e | 44.32 ± 0.95 d |
| DTPS-5 | 64.12 ± 0.80 d | 0.04 ± 0.01 d | 1354.71 ± 12.69 a | 341.79 ± 4.53 a | 84.50 ± 2.02 cd | 71.61 ± 3.67 b |
| DTPS-6 | 56.08 ± 0.31 e | 0.02 ± 0.01 d | 721.36 ± 13.21 c | 341.34 ± 3.55 a | 76.60 ± 3.25 de | 60.37 ± 4.58 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Wei, K.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y. Valorization of Polysaccharides Obtained from Dark Tea: Preparation, Physicochemical, Antioxidant, and Hypoglycemic Properties. Foods 2021, 10, 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102276
Zhu J, Zhou H, Zhang J, Li F, Wei K, Wei X, Wang Y. Valorization of Polysaccharides Obtained from Dark Tea: Preparation, Physicochemical, Antioxidant, and Hypoglycemic Properties. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102276
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jiangxiong, Hui Zhou, Junyao Zhang, Fanglan Li, Kang Wei, Xinlin Wei, and Yuanfeng Wang. 2021. "Valorization of Polysaccharides Obtained from Dark Tea: Preparation, Physicochemical, Antioxidant, and Hypoglycemic Properties" Foods 10, no. 10: 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102276
APA StyleZhu, J., Zhou, H., Zhang, J., Li, F., Wei, K., Wei, X., & Wang, Y. (2021). Valorization of Polysaccharides Obtained from Dark Tea: Preparation, Physicochemical, Antioxidant, and Hypoglycemic Properties. Foods, 10(10), 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102276