TMPRSS6 rs855791 Polymorphism Status in Children with Celiac Disease and Anemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. DNA Analysis
2.5. Serum Biochemical Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
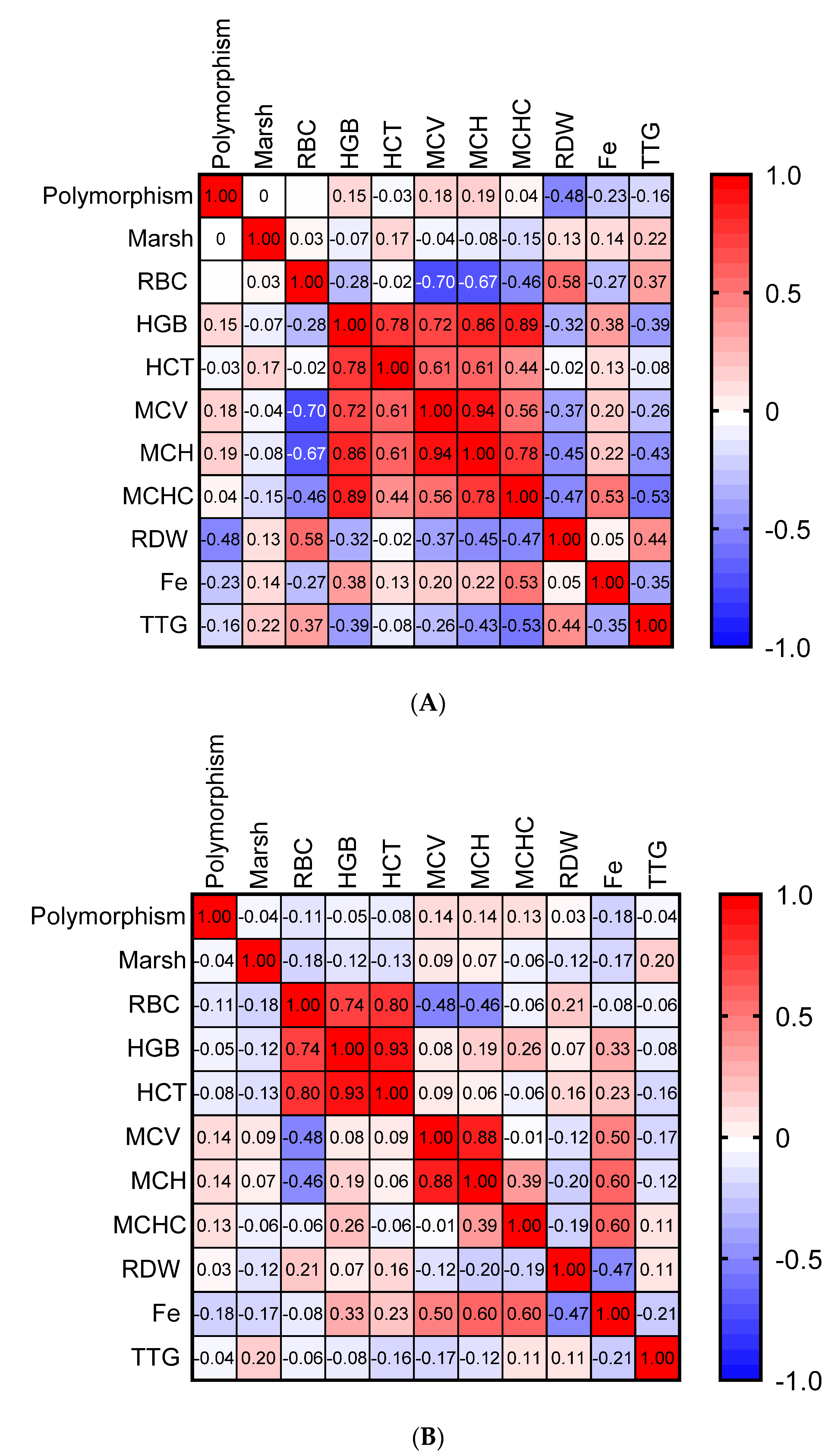
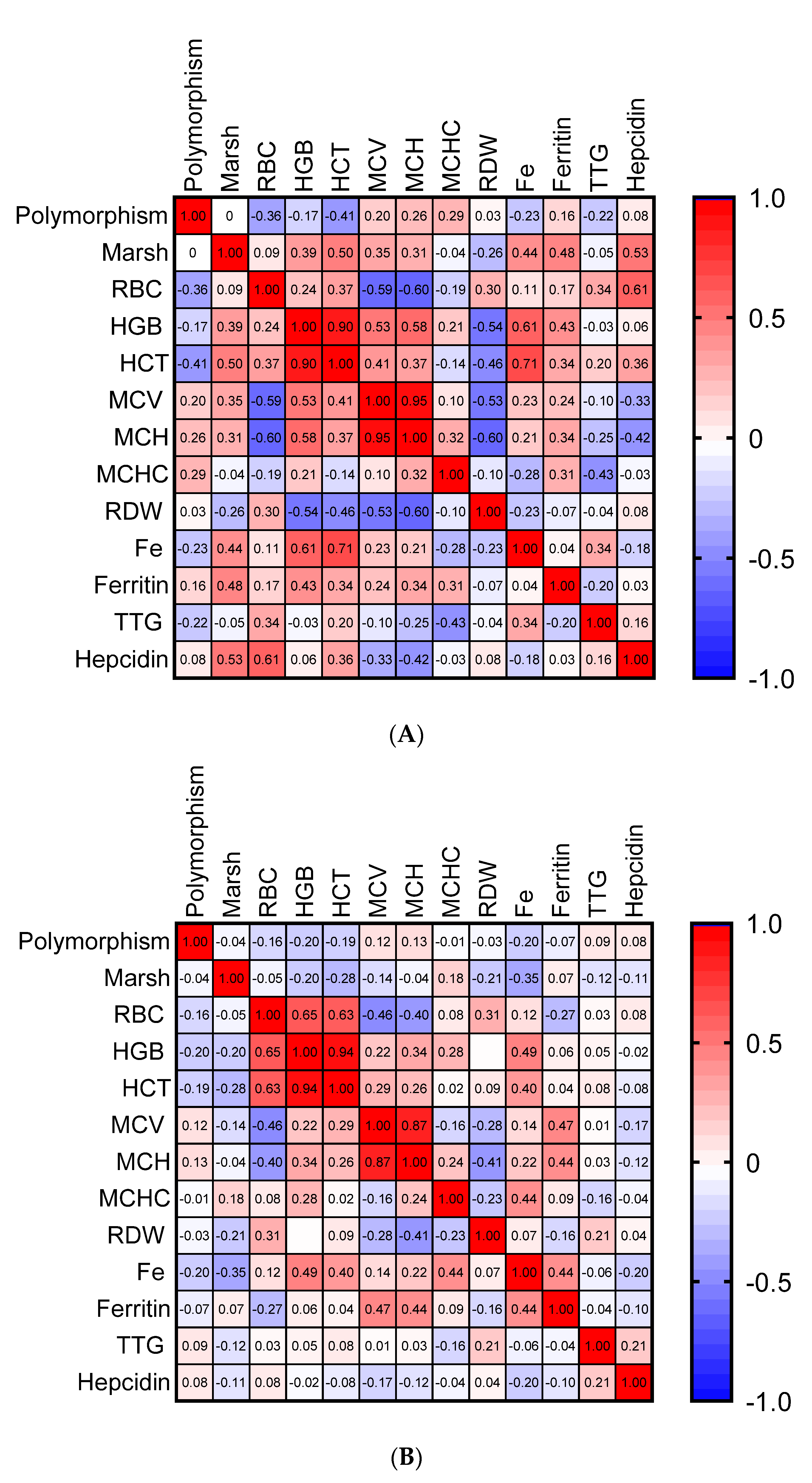
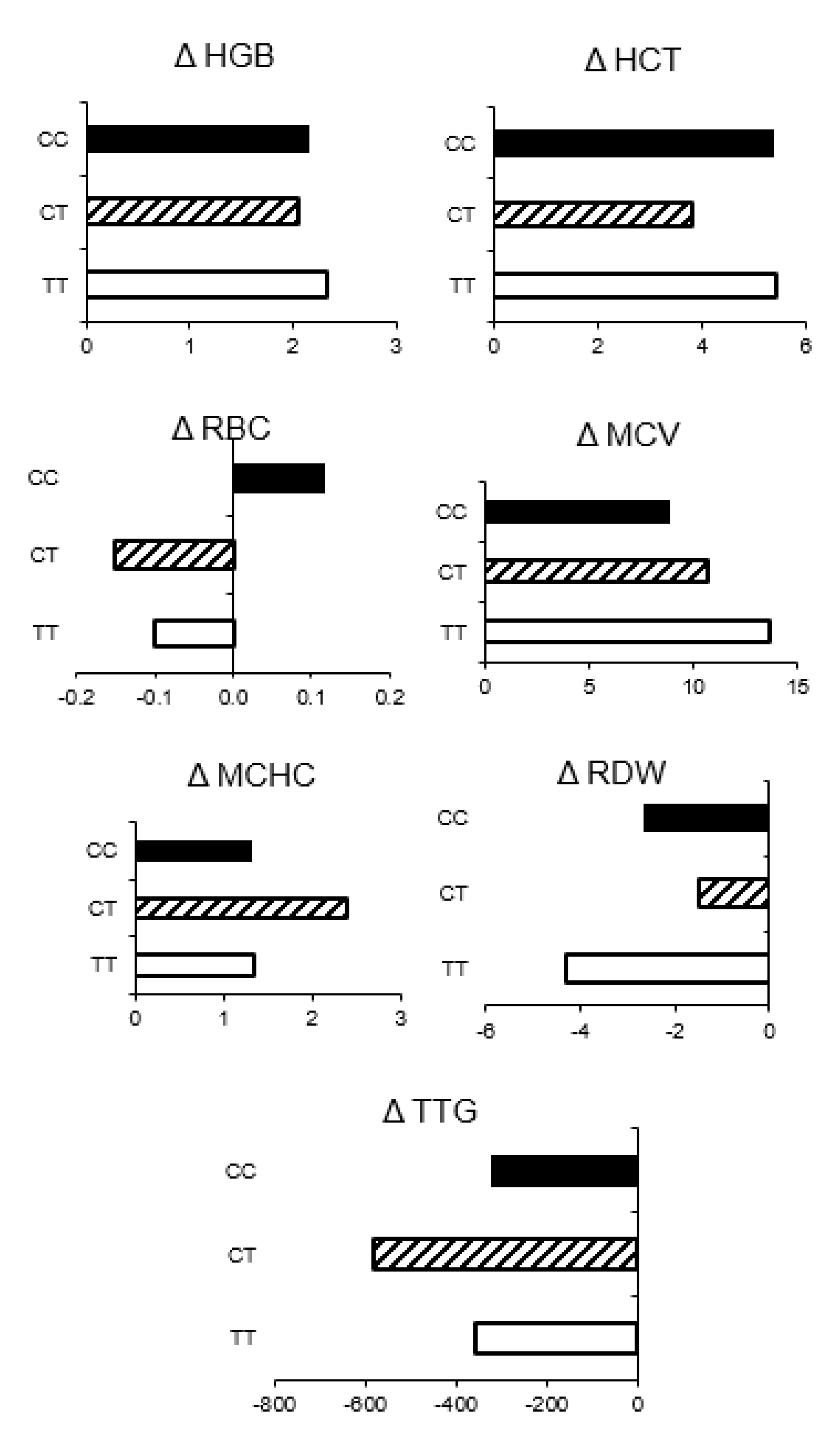
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubio-Tapia, A.; Hill, I.D.; Kelly, C.P.; Calderwood, A.H.; Murray, J.A.; Gastroenterology, A.C. American College of ACG clinical guidelines: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 656–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halfdanarson, T.R.; Litzow, M.R.; Murray, J.A. Hematologic manifestations of celiac disease. Blood 2007, 109, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, W.; Sano, K.; Lebwohl, B.; Diamond, B.; Green, P.H.R. Changing presentation of adult celiac disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2003, 48, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsworth, D.J.; Lock, F.J.; Harvey, R.F. Iron-deficiency anaemia in premenopausal women. Lancet 1999, 353, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadev, S.; Laszkowska, M.; Sundström, J.; Björkholm, M.; Lebwohl, B.; Green, P.H.R.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Prevalence of Celiac Disease in Patients with Iron Deficiency Anemia—A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 374–382.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.A.; Rubio-Tapia, A.; Van Dyke, C.T.; Brogan, D.L.; Knipschield, M.A.; Lahr, B.; Rumalla, A.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Gostout, C.J. Mucosal atrophy in celiac disease: Extent of involvement, correlation with clinical presentation, and response to treatment. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 125–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, G.; Viscido, A.; Longo, S.; Magistroni, M.; Latella, G. Persistent Iron Deficiency Anemia in Patients with Celiac Disease Despite a Gluten-Free Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annibale, B.; Severi, C.; Chistolini, A.; Antonelli, G.; Lahner, E.; Marcheggiano, A.; Iannoni, C.; Monarca, B.; Fave, G.D. Efficacy of Gluten-Free Diet Alone on Recovery From Iron Deficiency Anemia in Adult Celiac Patients. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2001, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cau, M.; Melis, M.A.; Congiu, R.; Galanello, R. Iron-deficiency anemia secondary to mutations in genes controlling hepcidin. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2010, 3, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulec, S.; Anderson, G.J.; Collins, J.F. Mechanistic and regulatory aspects of intestinal iron absorption. AJP Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G397–G409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Béliveau, F.; Tarkar, A.; Dion, S.P.; Désilets, A.; Ghinet, M.G.; Boudreault, P.-L.; St-Georges, C.; Marsault, É.; Paone, D.; Collins, J.; et al. Discovery and Development of TMPRSS6 Inhibitors Modulating Hepcidin Levels in Human Hepatocytes. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 1559–1572.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, J.C.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Sehmi, J.; Wass, M.N.; Zabaneh, D.; Hoggart, C.; Bayele, H.; McCarthy, M.I.; Peltonen, L.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants in TMPRSS6 associated with hemoglobin levels. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Falco, L.; Tortora, R.; Imperatore, N.; Bruno, M.; Capasso, M.; Girelli, D.; Castagna, A.; Caporaso, N.; Iolascon, A.; Rispo, A. The role of TMPRSS6 and HFE variants in iron deficiency anemia in celiac disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elli, L.; Poggiali, E.; Tomba, C.; Andreozzi, F.; Nava, I.; Bardella, M.T.; Campostrini, N.; Girelli, D.; Conte, D.; Cappellini, M.D. Does TMPRSS6 RS855791 polymorphism contribute to iron deficiency in treated celiac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Mearin, M.L.; Phillips, A.; Shamir, R.; Troncone, R.; Giersiepen, K.; Branski, D.; Catassi, C.; et al. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Coeliac Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 136–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Haemoglobin Concentrations for the Diagnosis of Anaemia and Assessment of Severity; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Caio, G.; Volta, U.; Sapone, A.; Leffler, D.A.; De Giorgio, R.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Celiac disease: A comprehensive current review. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riznik, P.; De Leo, L.; Dolinsek, J.; Gyimesi, J.; Klemenak, M.; Koletzko, B.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Krencnik, T.; Not, T.; et al. Diagnostic Delays in Children With Coeliac Disease in the Central European Region. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurikka, P.; Nurminen, S.; Kivelä, L.; Kurppa, K. Extraintestinal Manifestations of Celiac Disease: Early Detection for Better Long-Term Outcomes. Nutrients. 2018, 10, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talarico, V.; Giancotti, L.; Mazza, G.A.; Miniero, R.; Bertini, M. Iron Deficiency Anemia in Celiac Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurminen, S.; Kivelä, L.; Huhtala, H.; Kaukinen, K.; Kurppa, K. Extraintestinal manifestations were common in children with coeliac disease and were more prevalent in patients with more severe clinical and histological presentation. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansotta, N.; Amirikian, K.; Guandalini, S.; Jericho, H. Celiac Disease Symptom Resolution: Effectiveness of the Gluten-free Diet. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessels, M.M.S.; van Veen, I.I.; Vriezinga, S.L.; Putter, H.; Rings, E.H.H.M.; Mearin, M.L. Complementary Serologic Investigations in Children with Celiac Disease Is Unnecessary during Follow-Up. J. Pediatr. 2016, 169, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kochhar, R.; Jain, K.; Thapa, B.R.; Rawal, P.; Khaliq, A.; Kochhar, R.; Bhadada, S.; Vaiphei, K.; Varma, S.; Dutta, U.; et al. Clinical presentation of celiac disease among pediatric compared to adolescent and adult patients. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 31, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebwohl, B.; Sanders, D.S.; Green, P.H.R. Coeliac disease. Lancet 2018, 391, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jericho, H.; Guandalini, S. Extra-intestinal manifestation of celiac disease in children. Nutrients 2018, 10, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silvestri, L.; Pagani, A.; Nai, A.; De Domenico, I.; Kaplan, J.; Camaschella, C. The serine protease matriptase-2 (TMPRSS6) inhibits hepcidin activation by cleaving membrane hemojuvelin. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finberg, K.E.; Heeney, M.M.; Campagna, D.R.; Aydınok, Y.; Pearson, H.A.; Hartman, K.R.; Mayo, M.M.; Samuel, S.M.; Strouse, J.J.; Markianos, K.; et al. Mutations in TMPRSS6 cause iron-refractory iron deficiency anemia (IRIDA). Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benyamin, B.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Willemsen, G.; Gordon, S.; Middelberg, R.P.S.; McEvoy, B.P.; Hottenga, J.-J.; Henders, A.K.; Campbell, M.J.; Wallace, L.; et al. Common variants in TMPRSS6 are associated with iron status and erythrocyte volume. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, P.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Guan, Y.; Mu, M.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, D.; Song, P.; Wang, C.; Meng, L.; et al. TMPRSS6, but not TF, TFR2 or BMP2 variants are associated with increased risk of iron-deficiency anemia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nai, A.; Pagani, A.; Silvestri, L.; Campostrini, N.; Corbella, M.; Girelli, D.; Traglia, M.; Toniolo, D.; Camaschella, C. TMPRSS6 rs855791 modulates hepcidin transcription in vitro and serum hepcidin levels in normal individuals. Blood 2011, 118, 4459–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ballouz, S.; Dobin, A.; Gillis, J.A. Is it time to change the reference genome? Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tolone, C.; Bellini, G.; Punzo, F.; Papparella, A.; Miele, E.; Vitale, A.; Nobili, B.; Strisciuglio, C.; Rossi, F. The DMT1 IVS4+44C>A polymorphism and the risk of iron deficiency anemia in children with celiac disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Parameter | CD with IDA | CD without IDA |
|---|---|---|
| Number | 25 23.6% | 81 76.4% |
| Gender | ||
| Girls n. | 20 80.0% | 42 51.9% |
| Boys n. | 5 20.0% | 39 48.1% |
| Age [years] | 8.06 ± 4.89 | 8.04 ± 4.12 |
| Height [m] | 1.23 ± 0.29 | 1.28 ± 0.24 |
| Weight [kg] | 28.66 ± 19.43 | 28.10 ± 15.38 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 16.99 ± 3.97 | 16.18 ± 2.82 |
| Main complaints | ||
| Gastrointestinal n. * Classical Non-Classical | 15 60.0% 11 73.3% 4 26.7% | 51 62.9% 29 56.9% 22 43.1% |
| Extraintestinal n. ** | 25/3 1 100.0%/12.0% | 62 76.5% |
| Diabetes type 1 n. | 0.0 0.0% | 17 20.9% |
| Polymorphism of rs855791 | ||
| TT homozygote n. | 3 12.0% | 7 8.6% |
| CT heterozygote n. | 14 56.0% | 42 51.9% |
| CC homozygote n. | 8 32.0% | 32 39.5% |
| Allele frequency | ||
| Allele T n. | 20 40.0% | 56 34.6% |
| Allele C n. | 30 60.0% | 106 65.4% |
| Parameter | TT Homozygote | CC Homozygote | CT Heterozygote | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 10 | 40 | 56 | |||
| RBC [×106/mm3] | 4.75 (4.53–4.95) a 1 | 4.70 (4.43–5.08) a | 4.70 (4.40–4.93) a | |||
| HGB [g/dL] | 11.95 (10.78–13.05) a | 13.10 (11.68–13.63) a | 12.60 (11.30–13.30) a | |||
| HCT [%] | 37.80 (34.40–40.40) a | 38.80 (35.05–40.80) a | 37.30 (34.35–40.10) a | |||
| MCV [µm3] | 79.00 (75.00–82.25) a | 81.00 (77.50–86.00) a | 82.00 (79.00–86.00) a | |||
| MCH [pg] | 26.05 (23.13–26.40) a | 27.40 (25.85–28.70) a | 27.30 (26.15–28.45) a | |||
| MCHC [g/dL] | 32.50 (31.90–32.80) a | 32.90 (32.65–33.80) a | 33.10 (32.30–33.80) a | |||
| RDW [%] | 12.60 (12.50–14.30) a | 13.40 (12.60–15.48) a | 13.20 (12.60–14.20) a | |||
| Fe [µg/dL] | 59.00 (56.00–84.00) a | 41.00 (26.50–107.50) a | 54.00 (41.25–86.00) a | |||
| TTG [U/mL] | 289.5 (112.8–398.5) a | 201.0 (49.40–801.0) a | 191.0 (41.10–539.0) a | |||
| Anemic | Non-anemic | Anemic | Non-anemic | Anemic | Non-anemic | |
| N | 3 | 7 | 8 | 32 | 14 | 42 |
| RBC [× 106/mm3] | 4.70 (4.70–4.70) a | 4.80 (4.45–5.00) a | 4.80 (4.45–4.95) a | 4.70 (4.43–5.08) a | 4.85 (4.45–5.00) a | 4.65 (4.40–4.90) a |
| HGB [g/dL] | 10.10 (9.25–10.35) a | 12.30 (11.95–13.55) b | 10.20 (9.28–10.48) a | 13.30 (12.70–13.75) b | 10.20 (9.60–10.80) a | 13.05 (12.30–13.70) b |
| HCT [%] | 33.90 (33.80–34.00) a,b | 38.40 (37.15–40.50) b | 32.75 (30.43–33.43) a | 40.00 (37.65–41.00) b | 32.75 (32.60–33.55) a | 38.50 (37.00–41.20) b |
| MCV [µm3] | 71.00 (61.00–72.50) a | 80.00 (79.00–84.00) b | 67.00 (62.75–72.00) a | 82.00 (80.00–87.00) b | 69.50 (66.25–77.00) a | 83.50 (81.00–86.75) b |
| MCH [pg] | 21.80 (18.55–22.10) a | 26.40 (26.05–27.00) b | 20.40 (19.68–22.38) a | 27.80 (26.90–28.80) b | 21.75 (20.10–23.30) a | 27.80 (27.10–28.70) b |
| MCHC [g/dL] | 30.55 (30.08–31.03) a | 32.80 (32.25–33.20) a | 31.30 (30.20–31.65) a | 33.20 (32.80–33.90) b | 30.95 (30.10–31.83) a | 33.30 (32.70–34.00) b |
| RDW [%] | 17.95 (17.83–18.08) b | 12.50 (12.40–12.90) a,b | 16.60 (15.98–16.85) b | 13.10 (12.53–13.65) a,b | 15.30 (13.78–15.80) b | 13.00 (12.40–13.55) a |
| Fe [µg/dL] | 56.00 (40.00–75.50) b | 71.50 (65.25–77.75) b | 23.00 (20.50–27.75) a | 105.00 (52.00–114.00) b | 36.00 (15.75–75.00) b | 56.50 (51.75–91.25) b |
| TTG [U/mL] | 405.6 (331.8–479.3) a | 321.0 (135.9–396.0) a | 301.0 (143.7–801.0) a | 194.5 (34.50–801.0) a | 240.5 (104.5–456.5) a | 161.0 (39.15–733.5) a |
| Parameter | TT Homozygote | CC Homozygote | CT Heterozygote | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 10 | 40 | 56 | |||
| RBC [×106/mm3] | 4.65 (4.60–4.93) a 1 | 4.70 (4.50–5.00) a | 4.60 (4.35–4.80) a | |||
| HGB [g/dL] | 12.80 (11.90–13.20) a,b | 13.30 (12.63–14.13) b ** | 12.60 (12.00–13.45) a ** | |||
| HCT [%] | 38.60 (37.20–39.53) a,b | 40.15 (37.88–41.35) b ** | 37.80 (36.40–40.55) a | |||
| MCV [µm3] | 82.00 (75.00–84.00) a * | 84.00 (80.75–87.00) a ** | 84.00 (80.75–86.25) a | |||
| MCH [pg] | 27.00 (26.10–27.60) a | 27.85 (27.15–29.38) a *** | 28.30 (26.85–29.07) a ** | |||
| MCHC [g/dL] | 33.40 (32.53–34.00) a * | 33.35 (32.60–33.75) a | 33.40 (33.00–33.60) a ** | |||
| RDW [%] | 13.20 (12.30–14.80) a | 12.90 (12.38–13.65) a | 12.90 (12.55–13.75) a | |||
| Fe [µg/dL] | 75.00 (57.75–107.8) a | 98.50 (63.00–118.5) a | 69.00 (45.25–96.75) a | |||
| Ferritin [ng/mL] | 16.60 (13.00–33.40) a | 18.00 (8.10–29.25) a | 17.95 (10.23–38.70) a | |||
| TTG [U/mL] | 3.00 (0.75–33.00) a ** | 5.60 (1.33–14.70) a ** | 4.75 (1.48–18.28) a *** | |||
| Hepcidin [ng/dL] | 219.7 (210.1–275.5) a | 219.6 (208.7–293.5) a | 234.6 (208.4–285.7) a | |||
| Anemic 2 | Non-anemic 2 | Anemic | Non-anemic | Anemic | Non-anemic | |
| N | 3 | 7 | 8 | 32 | 14 | 42 |
| RBC [× 106/mm3] | 4.70 (4.60–4.80) a | 4.60 (4.605–5.00) a | 4.70 (4.58–5.10) a | 4.80 (4.58–5.03) a | 4.50 (4.28–4.80 a | 4.60 (4.40–4.90) a |
| HGB [g/dL] | 12.40 (11.00–12.70) a,b ** | 12.80 (11.90–13.40) a,b | 12.50 (12.08–13.20) a,b ** | 13.65 (12.98–14.30) b ** | 12.05 (11.78–12.73) a *** | 13.10 (12.45–13.60) a,b |
| HCT [%] | 39.35 (38.80–39.90) a,b * | 38.40 (36.00–39.40) a,b | 37.95 (37.08–40.13) a,b *** | 41.20 (39.20–42.43) b * | 36.55 (35.63–38.08) a *** | 38.70 (37.00–41.10) a,b |
| MCV [µm3] | 83.00 (70.00–84.00) a * | 82.00 (79.00–84.00) a | 79.00 (75.00–83.00) a * | 84.00 (82.00–87.25) a * | 81.50 (78.00–85.00) a ** | 85.00 (81.00–87.00) a |
| MCH [pg] | 25.80 (23.00–27.60) a | 27.20 (26.40–28.30) a | 26.25 (24.88–27.55) a * | 28.00 (27.40–29.63) a ** | 26.92 (25.50–28.38) a ** | 28.45 (27.48–29.18) a |
| MCHC [g/dL] | 31.90 (31.10–32.70) a | 33.50 (33.00–34.00) a * | 33.00 (32.38–33.63) a | 33.50 (32.75–34.13) a | 33.20 (32.98–33.35) a ** | 33.40 (33.20–33.60) a |
| RDW [%] | 13.65 (11.90–15.40) a | 13.20 (12.60–14.20) a | 13.30 (12.28–14.83) a * | 12.85 (12.40–13.65) a * | 13.50 (12.68–14.43) a | 12.90 (12.40–13.50) a |
| Fe [µg/dL] | 68.00 (65.00–71.00) a | 106.0 (36.00–113.0) a | 64.00 (55.50–71.00) a | 105.0 (58.00–123.0) a | 63.00 (36.75–77.50) a | 69.50 (53.00–103.3) a |
| Ferritin [ng/mL] | 13.60 (10.90–16.60) a | 21.20 (13.00–33.40) a | 17.25 (16.50–18.00) a | 23.75 (7.95–30.18) a | 29.70 (2.60–39.80) a | 17.50 (12.00–37.90) a |
| TTG [U/mL] | 46.50 (9.30–83.70) a * | 2.90 (0.8–16.10) a * | 11.85 (1.98–14.70) a * | 3.10 (1.0–11.90) a *** | 5.20 (1.05–33.05) a ** | 3.60 (1.57–19.15) a *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urbaszek, K.; Drabińska, N.; Szaflarska-Popławska, A.; Jarocka-Cyrta, E. TMPRSS6 rs855791 Polymorphism Status in Children with Celiac Disease and Anemia. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082782
Urbaszek K, Drabińska N, Szaflarska-Popławska A, Jarocka-Cyrta E. TMPRSS6 rs855791 Polymorphism Status in Children with Celiac Disease and Anemia. Nutrients. 2021; 13(8):2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082782
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrbaszek, Klaudia, Natalia Drabińska, Anna Szaflarska-Popławska, and Elżbieta Jarocka-Cyrta. 2021. "TMPRSS6 rs855791 Polymorphism Status in Children with Celiac Disease and Anemia" Nutrients 13, no. 8: 2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082782
APA StyleUrbaszek, K., Drabińska, N., Szaflarska-Popławska, A., & Jarocka-Cyrta, E. (2021). TMPRSS6 rs855791 Polymorphism Status in Children with Celiac Disease and Anemia. Nutrients, 13(8), 2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082782








