Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution Based on N-APSK Modulation over Seawater Channel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CVQKD Based on N-APSK Modulation
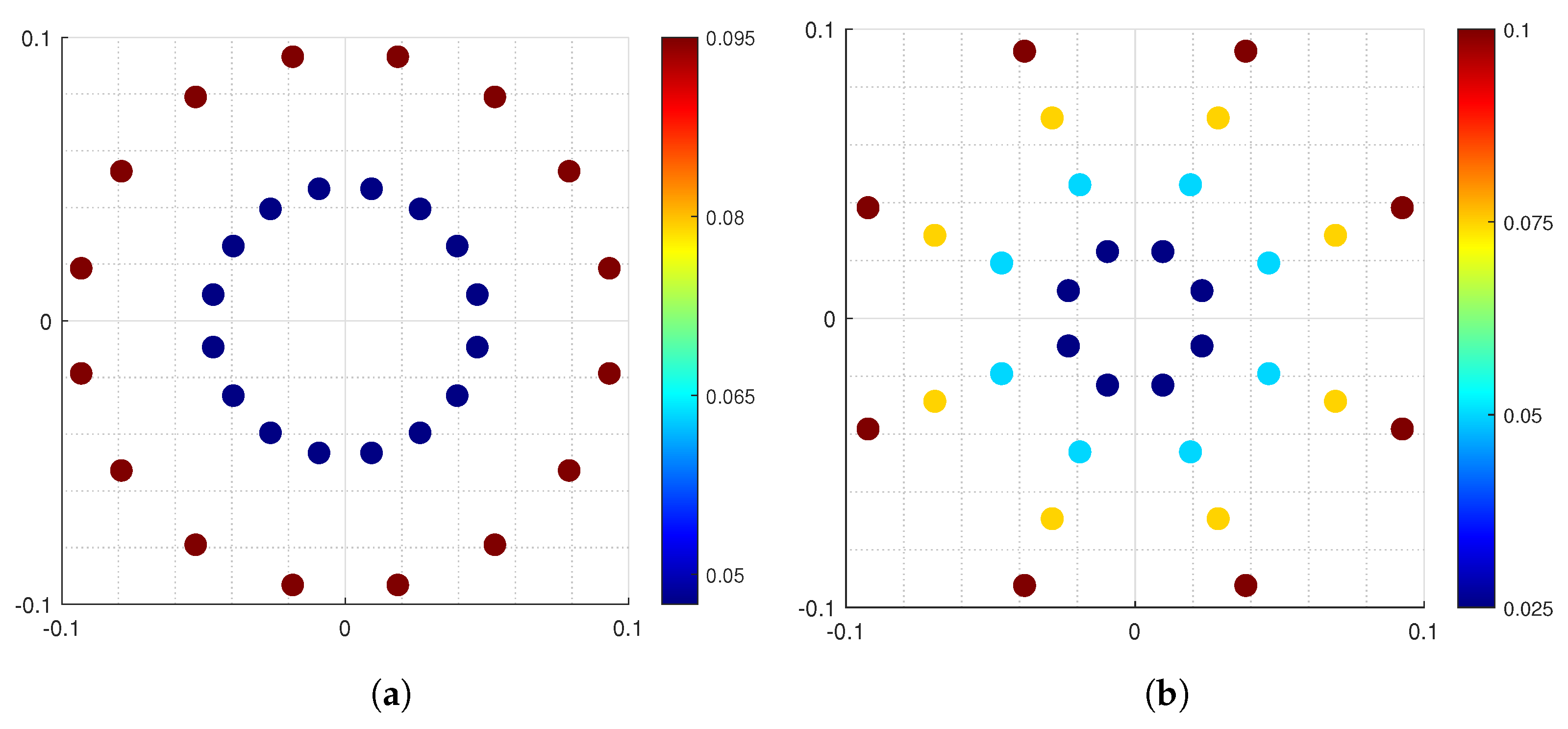
2.1. N-APSK Modulation
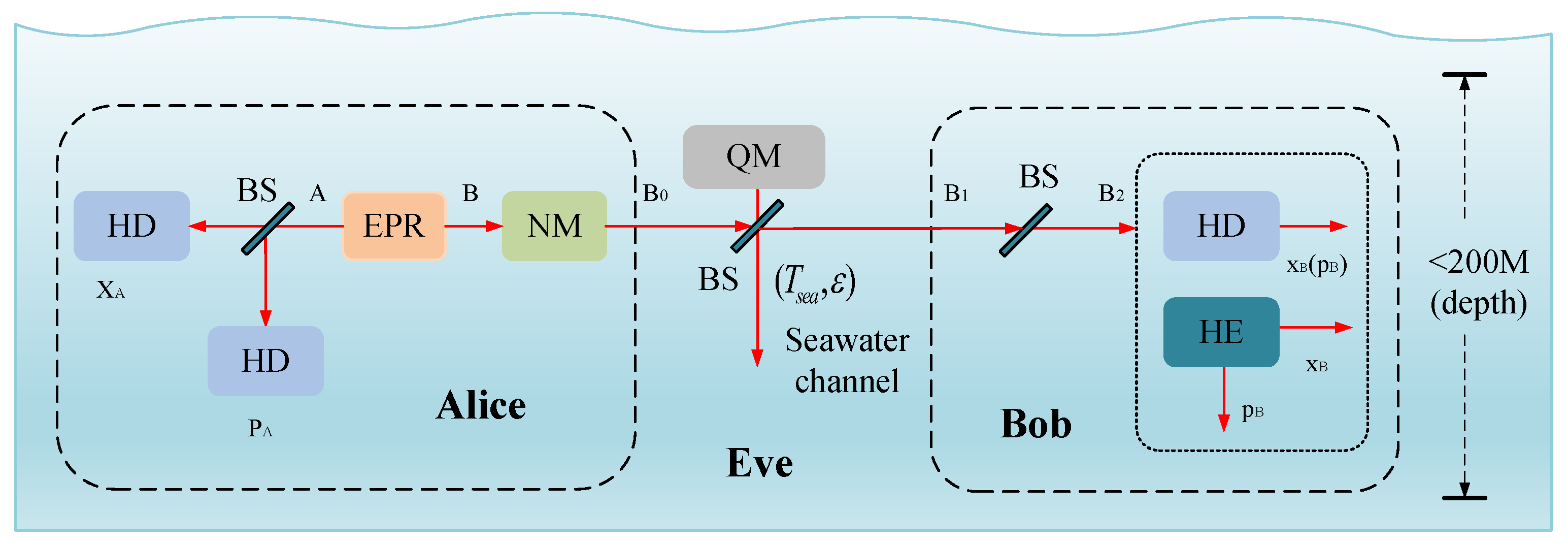
2.2. The Proposal of CVQKD Based on N-APSK Modulation over Seawater Channel
- Step 1: Alice generates a Gaussian random number sequence S based on the probability distribution of the N-APSK constellation points, then encodes the information to be transmitted onto the sequence S. Alice modulates the regular components and of the quantum state using the Gaussian random number sequence S to obtain the corresponding quantum state , which is then sent to the seawater channel. Since the modulation of the regular position and regular momentum of the quantum state corresponds to the amplitude and phase modulation of the constellation points in N-APSK modulation, a correspondence is established between the quantum state and the Gaussian random number interval;
- Step 2: The optical properties (absorption and scattering) of the seawater channel cause significant attenuation of the transmitted quantum signal, with a transmittance of . Based on the above analysis, in short-distance transmission scenarios, this channel also introduces excess noise , which is mainly caused by environmental disturbances. Therefore, relative to the noise level at the channel input end, the total noise generated by the seawater channel can be expressed by the formula ;
- Step 3: At Bob’s side, an imperfect detector with efficiency and electrical noise rate is used to measure the received quantum state. The noise introduced by the detector corresponding to Bob’s input end can be expressed as (in shot noise units) and satisfied asfor homodyne detection andfor hetrodyne detection. The total noise referred to the channel input can be expressed as .
3. Performance Analysis
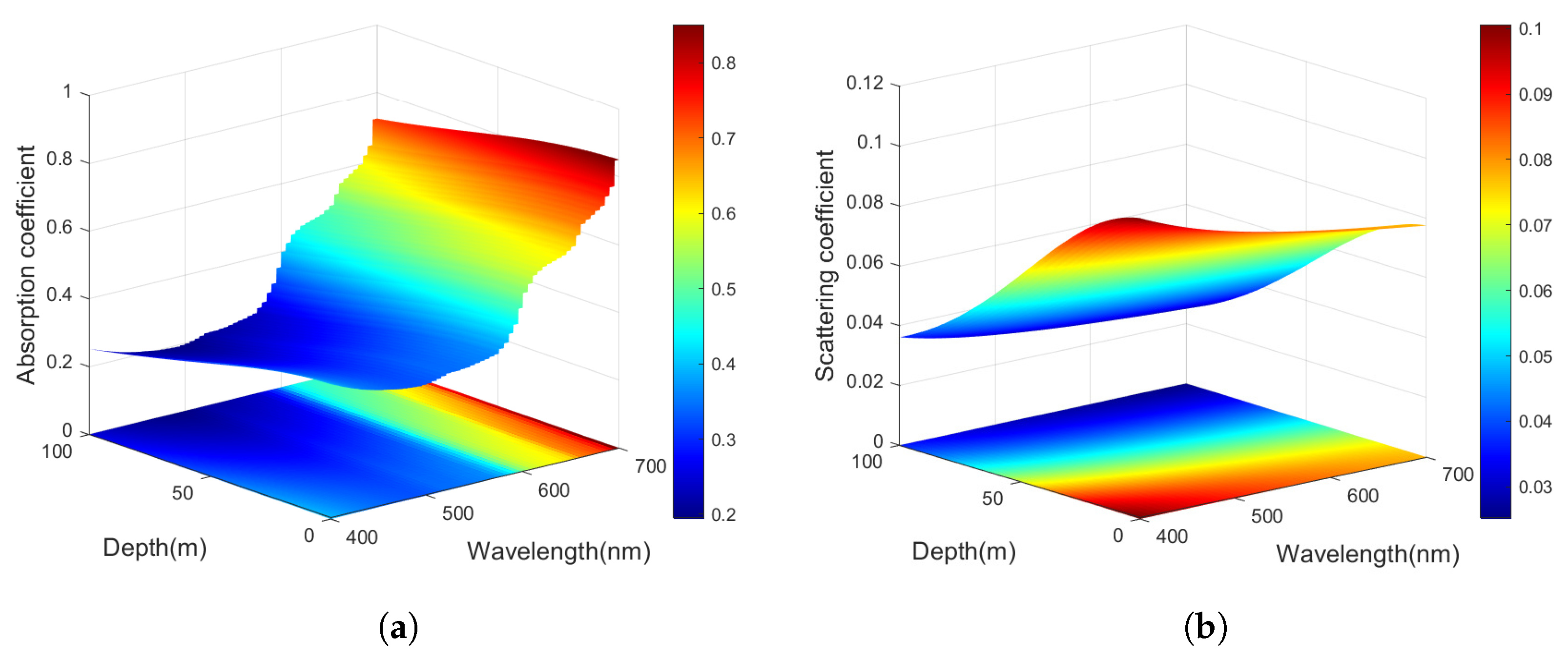
3.1. Parameter Evaluation of Seawater Channel
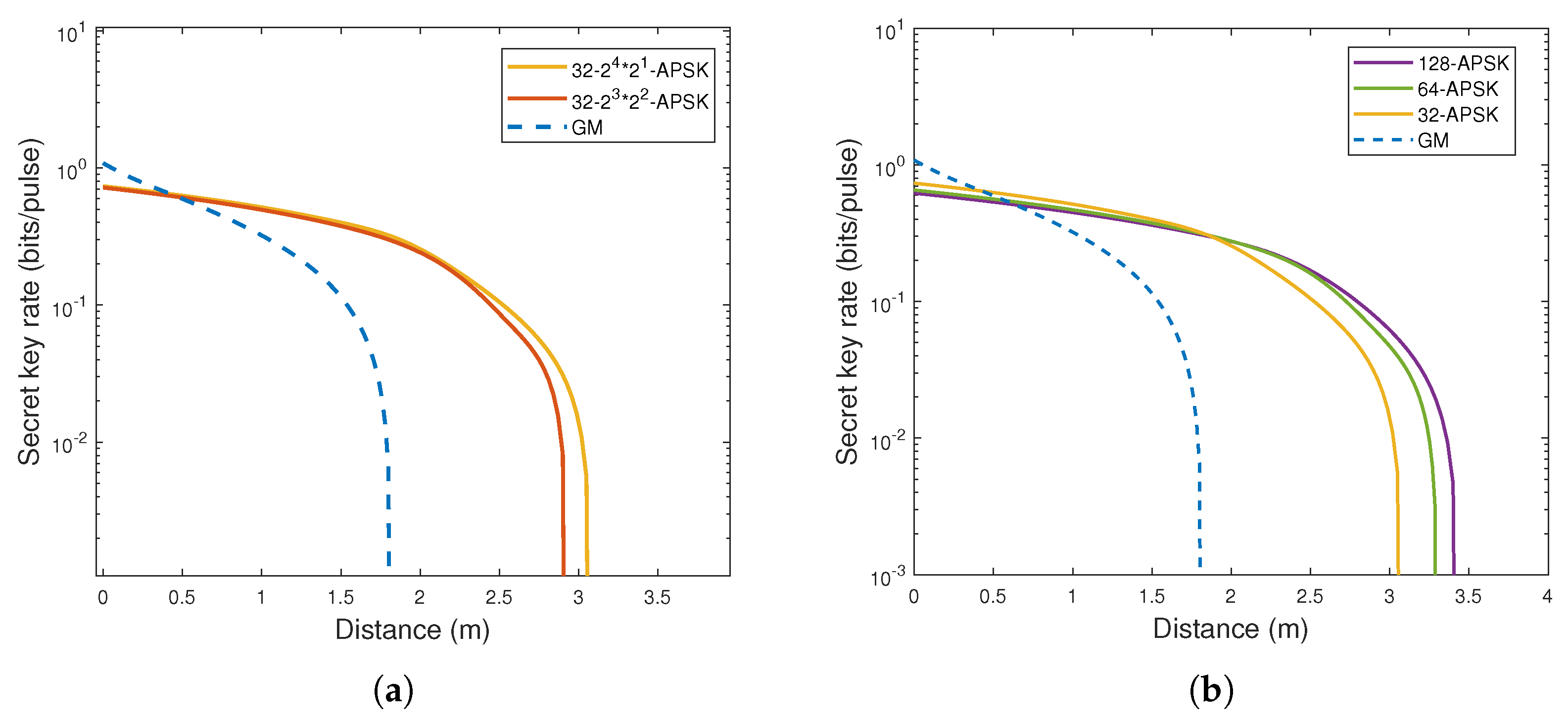
3.2. Performance Analysis of CVQKD Based on N-APSK Modulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Continuous Variable Quantum Cryptography Using Coherent States. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 057902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Mancini, S.; Lloyd, S.; Braunstein, S.L. Continuous-variable quantum cryptography using two-way quantum communication. Nat. Phys. 2008, 4, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usenko, V.C.; Grosshans, F. Unidimensional continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 92, 062337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Pirandola, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Chu, B.; Guo, H. Long-distance continuous-variable quantum keydistribution over 202.81 km of fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 010502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, J. Experimental demonstration of continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution over optical fiber. Optica 2022, 9, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Du, S.; Liu, W.; Lu, Z.; Li, Y. High-performance long-distance discrete-modulation continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 2953–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Huang, P.; Liu, M.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Zeng, G. Phase compensation for free-space continuous-variablequantum key distribution. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 10737–10745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Ruan, X.; Guo, Y. Noiseless attenuation for continuous-variable quantum key distribution over ground-satellite uplink. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, P.; Wang, P.; Wei, S.; Zeng, G. Experimental free-space continuous-variable quantum key distribution with thermal source. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, D.; Guo, Y. Atmospheric effects on satellite-mediated continuous-variable quantum key distribution. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2020, 53, 465302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, J. Wavelength attack on atmospheric continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 012417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, W.; Liao, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Monte Carlo-based performance analysis for underwater continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Guo, Y. Underwater wavelength attack on discrete modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Entropy 2024, 26, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, S.; Zeng, G. High key rate continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a real local oscillator. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 2794–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pi, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, B. High-speed Gaussian-modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a local local oscillator based on pilot-tone-assisted phase compensation. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 32882–32893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Yang, S.; Wonfor, A.; White, I.; Penty, R. Demonstration of high-speed and low-complexity continuous variable quantum key distribution system with local local oscillator. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleis, S.; Rueckmann, M.; Schaeffer, C.G. Continuous variable quantum key distribution with a real local oscillator using simultaneous pilot signals. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 1588–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Pi, Y.; Pan, Y.; Shao, Y.; Ma, L.; Xu, B. Sub-Gbps key rate four-state continuous-variable quantum key distribution within metropolitan area. Commun. Phys. 2022, 5, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitschar, F.; George, I.; Lin, J.; Upadhyaya, T.; Lütkenhaus, N. Finite-size security for discrete-modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution protocols. PRX Quantum 2023, 4, 040306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Pereira, D.; Muga, N.J.; Facão, M.; Pinto, A.N.; Silva, N.A. Secret key rate of multi-ring M-APSK continuous variable quantum key distribution. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 38669–38682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Almeida, M.; Facão, M.; Pinto, A.N.; Silva, N.A. Probabilistic shaped 128-APSK CV-QKD transmission system over optical fibres. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 3948–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Almeida, M.; Pinto, A.N.; Silva, N.A. Impact of transmitter imbalances on the security of continuous variables quantum key distribution. EPJ Quantum Technol. 2023, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Pereira, D.; Facão, M.; Pinto, A.N.; Silva, N.A. Reconciliation efficiency impact on discrete modulated CV-QKD systems key rates. J. Light. Technol. 2023, 41, 6134–6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gaudenzi, R.; Guillén i Fàbregas, A.; Martinez, A. Turbo-coded APSK modulations design for satellite broadband communications. Int. J. Satell. Commun. Netw. 2006, 24, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, Q.; Peng, K.; Yang, Z. APSK constellation with Gray mapping. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2011, 15, 1271–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Ali, T.; Sarwar, R.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, J. Security weaknesses of underwater wireless optical communication. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 21509–21518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilerson, A.; Zhou, J.; Hlaing, S.; Ioannou, I.; Schalles, J.; Gross, B.; Ahmed, S. Fluorescence component in the reflectance spectra from coastal waters. Dependence on water composition. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15702–15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieur, L.; Sathyendranath, S. An optical classification of coastal and oceanic waters based on the specific spectral absorption curves of phytoplankton pigments, dissolved organic matter, and other particulate materials 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 671–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitz, J.; Claustre, H.; Morel, A.; Hooker, S.B. Vertical distribution of phytoplankton communities in open ocean: An assessment based on surface chlorophyll. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111, C8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 32-APSK | MED | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0438 | 1.0666 | |
| 0.0782 | 0.6846 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, L.; Liang, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution Based on N-APSK Modulation over Seawater Channel. Entropy 2025, 27, 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090990
Mao L, Liang Z, Zuo Z, Zhang H, Wang Y. Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution Based on N-APSK Modulation over Seawater Channel. Entropy. 2025; 27(9):990. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090990
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Lei, Zhangtao Liang, Zhiyue Zuo, Hang Zhang, and Yijun Wang. 2025. "Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution Based on N-APSK Modulation over Seawater Channel" Entropy 27, no. 9: 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090990
APA StyleMao, L., Liang, Z., Zuo, Z., Zhang, H., & Wang, Y. (2025). Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution Based on N-APSK Modulation over Seawater Channel. Entropy, 27(9), 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090990






